UNIT 6 (Part 2) -Motor Units, Recruitment, Fatigue, Aging
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Motor Units, Recruitment, Fatigue, Aging
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
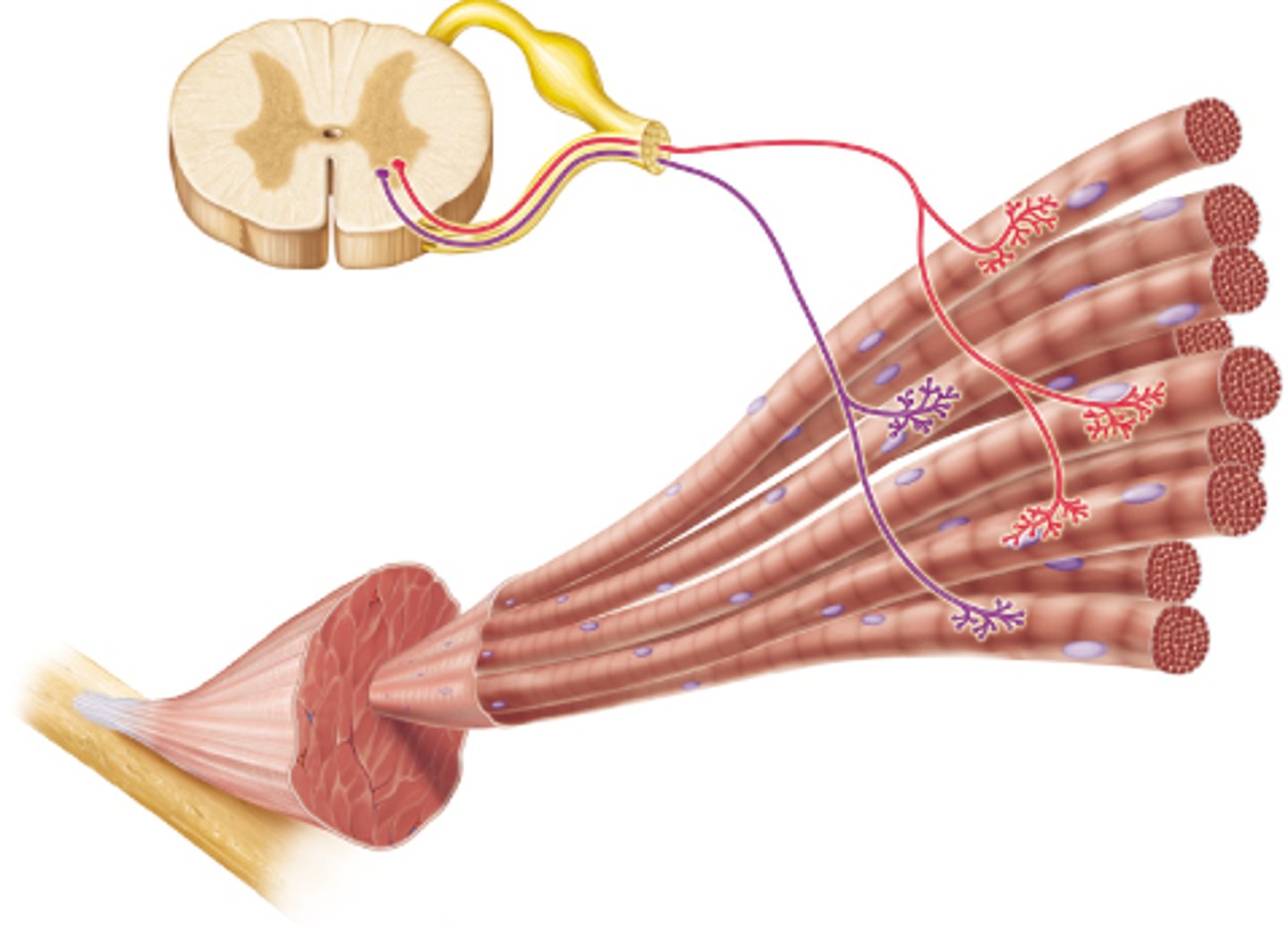
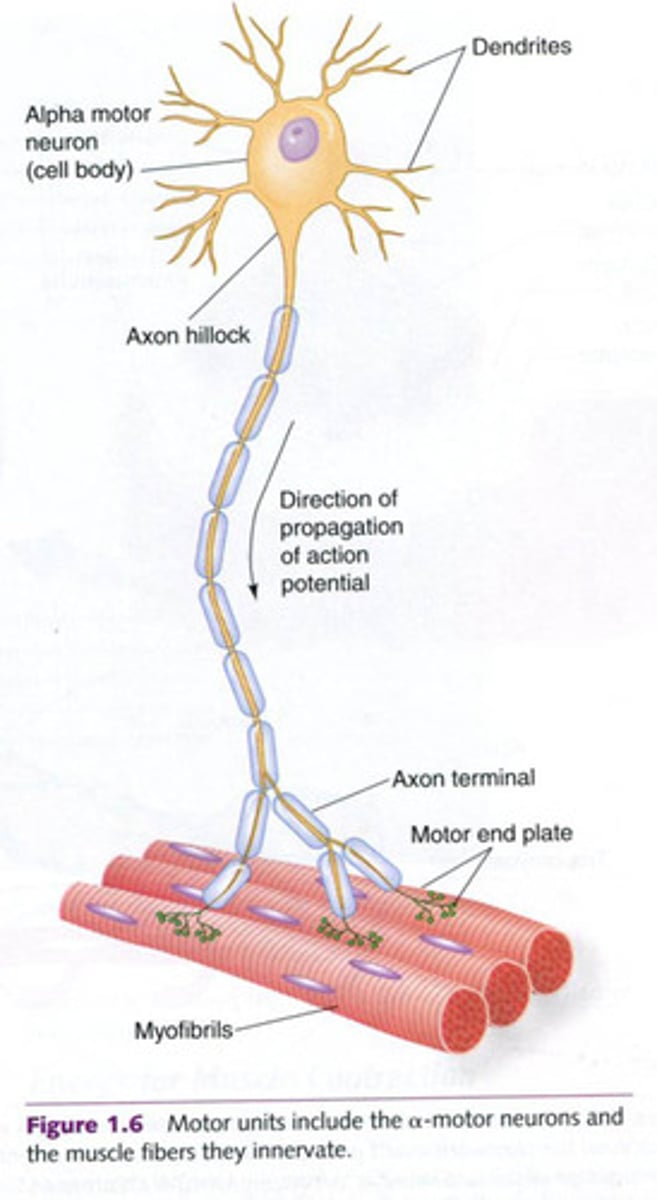
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
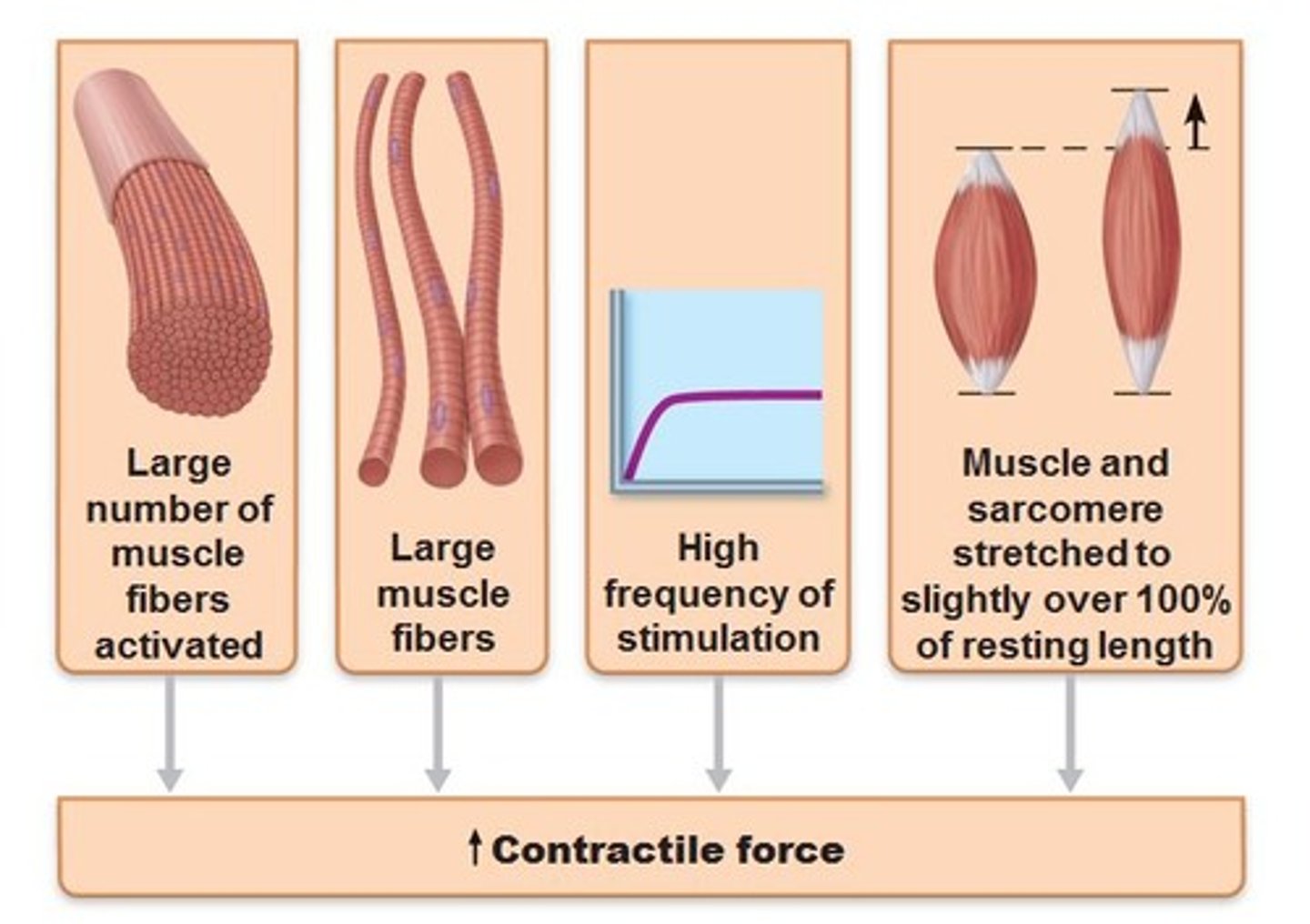
What can affect the strength of a muscle contraction?
Frequency of stimulation, length of sarcomere, size of motor units, recruitment of more motor units
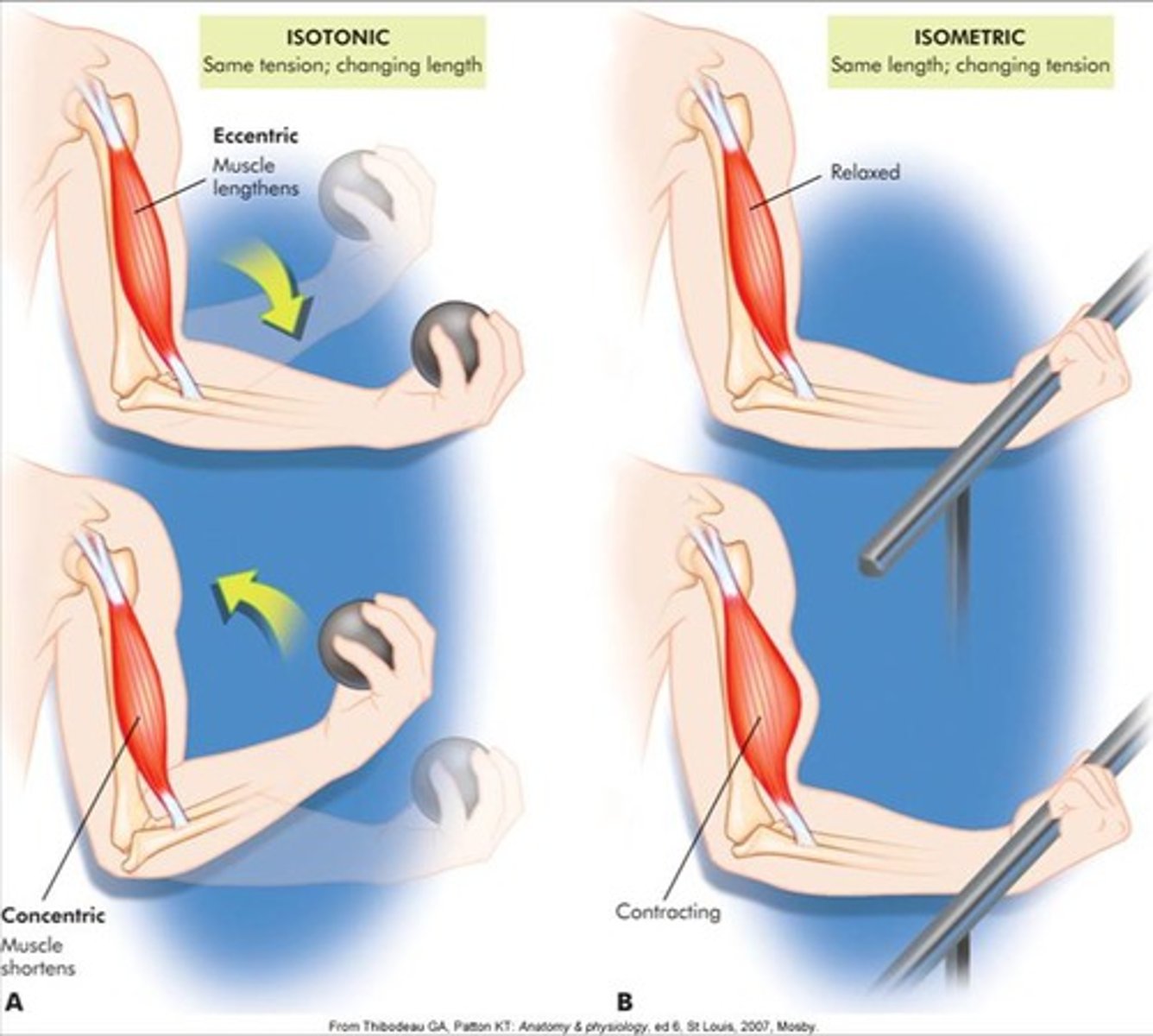
isotonic contraction
[iso = same, tonic = tension, but the muscle changes length] muscles contract and shorten, or maintain tension tension and lengthen to produce body movement
![<p><span class="bgY">[iso = same, tonic = tension, but the muscle changes length]</span> muscles contract and shorten, or maintain tension tension and lengthen to produce body movement</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2849146b-66a9-4e0d-85b9-cd166042cfcd.jpg)
isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length

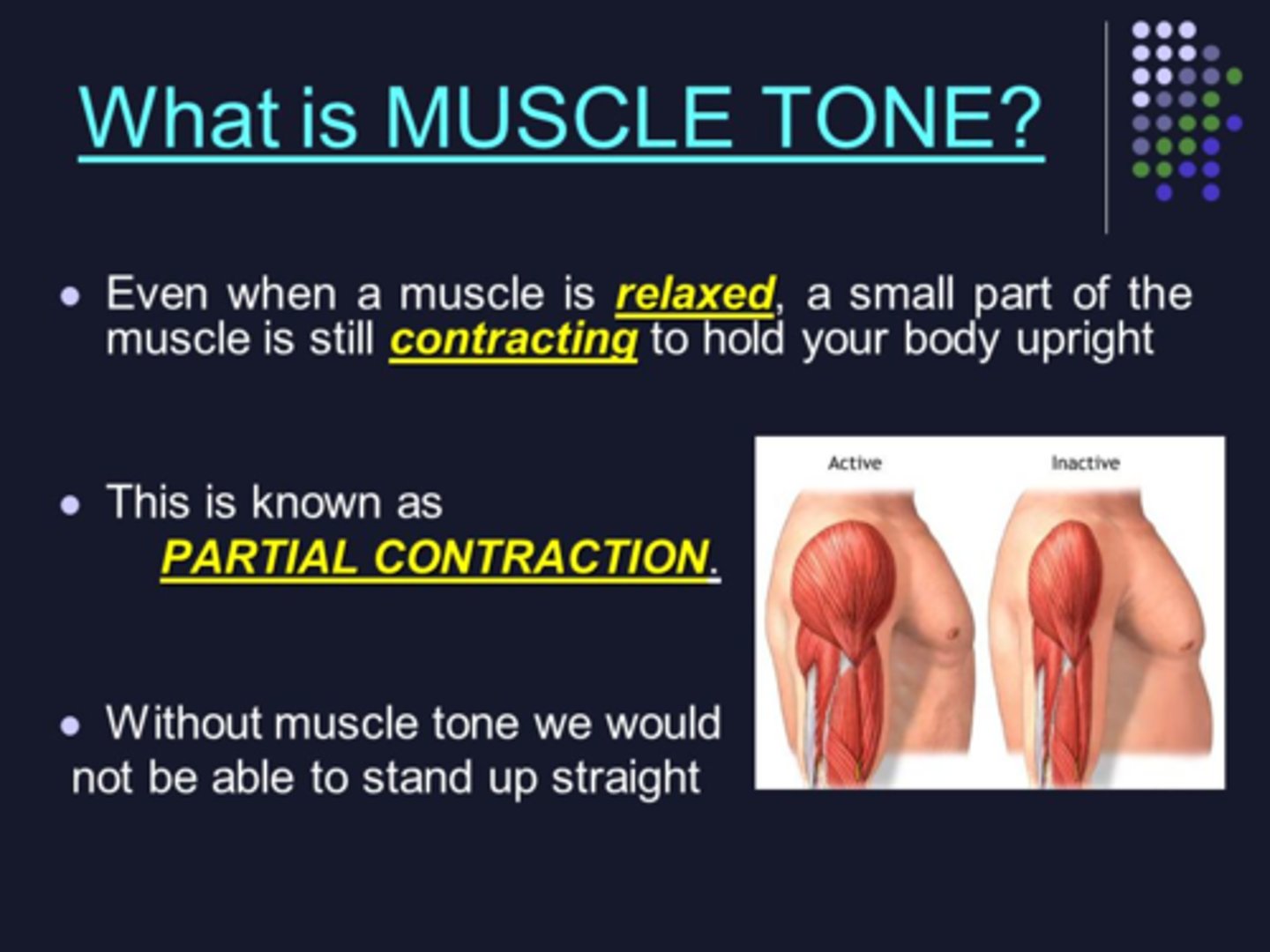
muscle tone
state of partial contraction, no movement produced
aerobic exercise benefits
increases muscle endurance, benefits heart, also helps with attention, memory, goal-directed thinking and behavior, creativity

resistance training
lifting weights to increase strength, power, and muscular endurance

The method that regenerates the most ATP during muscle activity is ________.
aerobic pathway
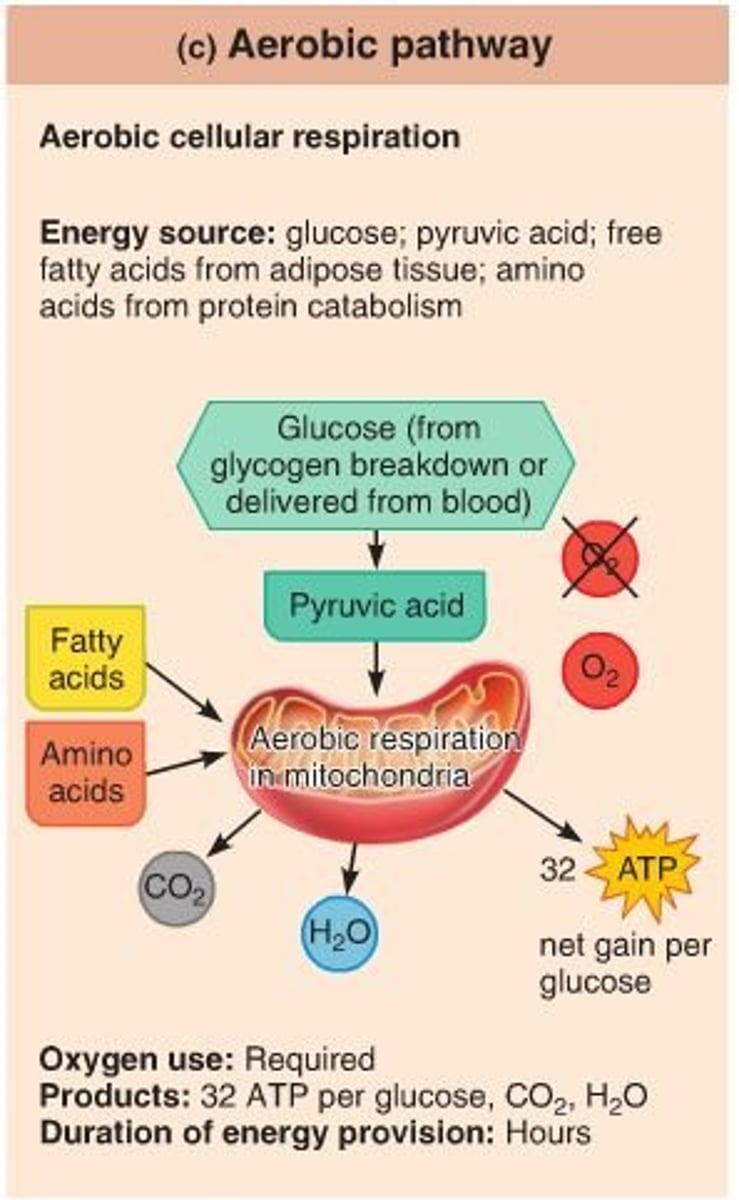
What condition results if muscles are not used, such as when immobilized in a cast for healing a broken bone?
atrophy
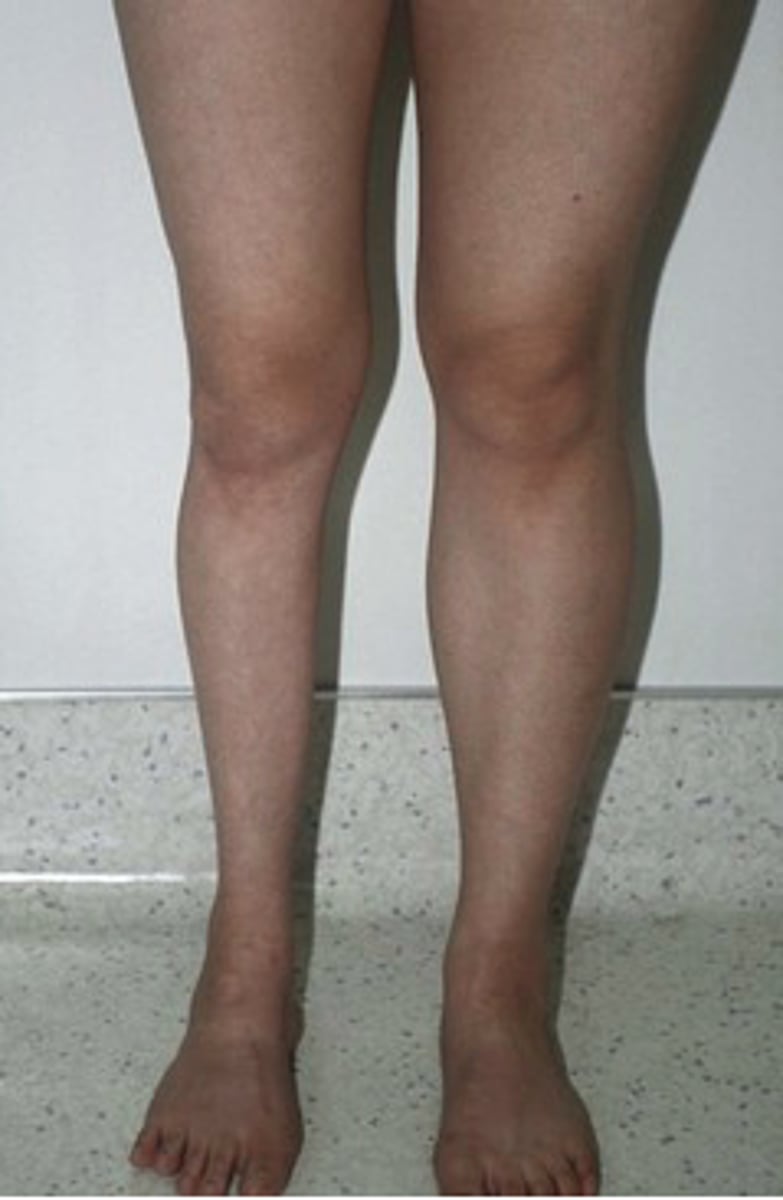
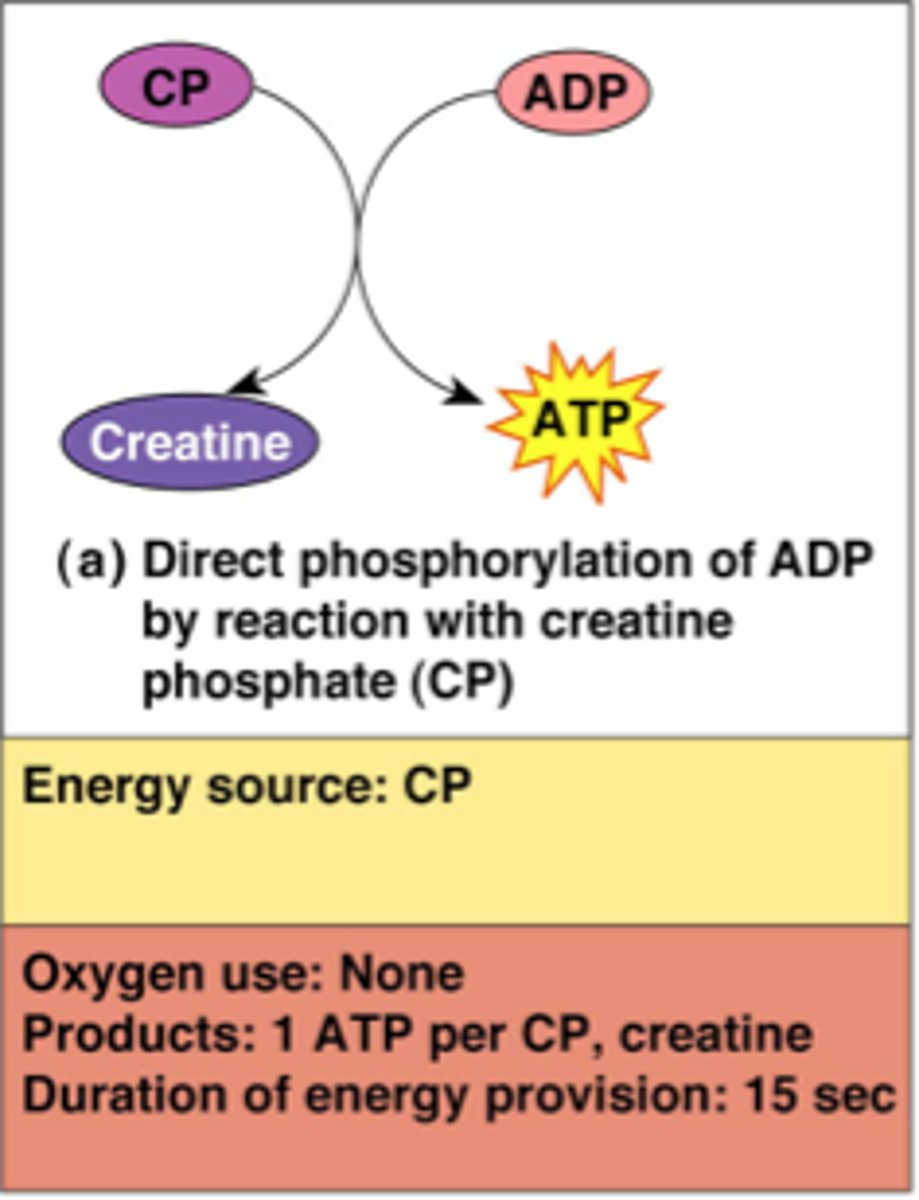
creatine phophate
During rest stores phosphate to generate ATP before aerobic respiration revs up. Can supply energy needs of at a very high rate, but only for about 8-10 seconds. Can give a phosphate to ADP to form ATP.
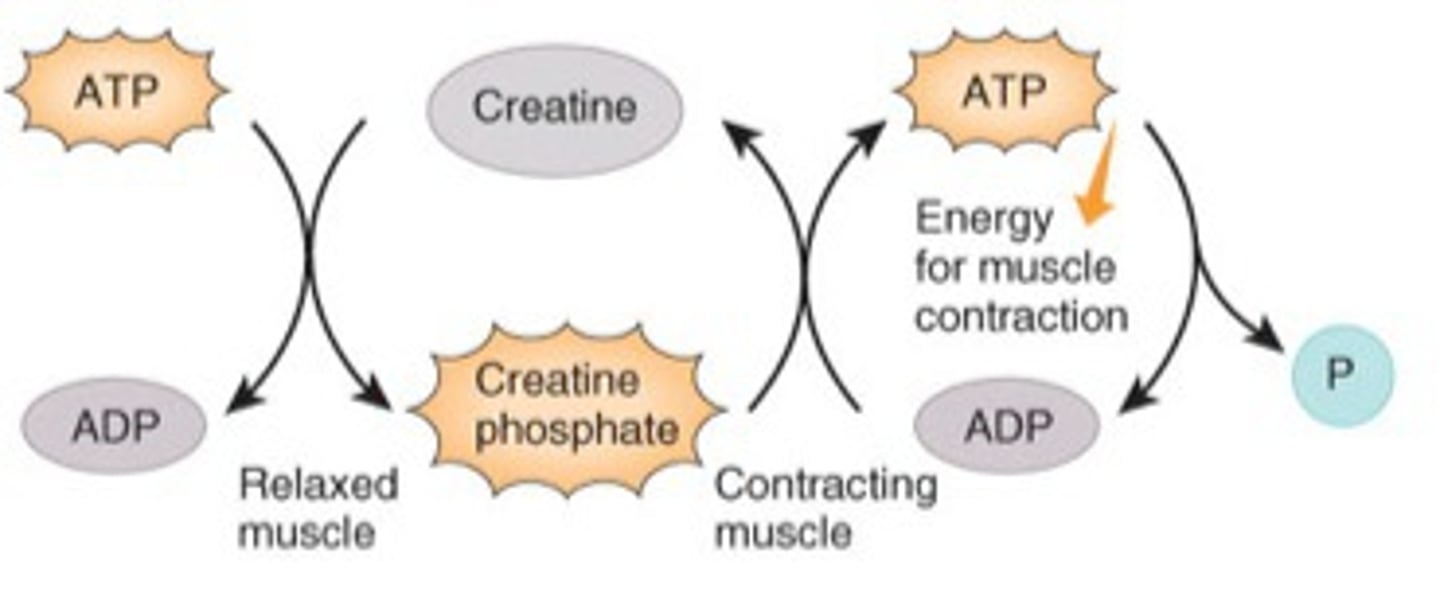
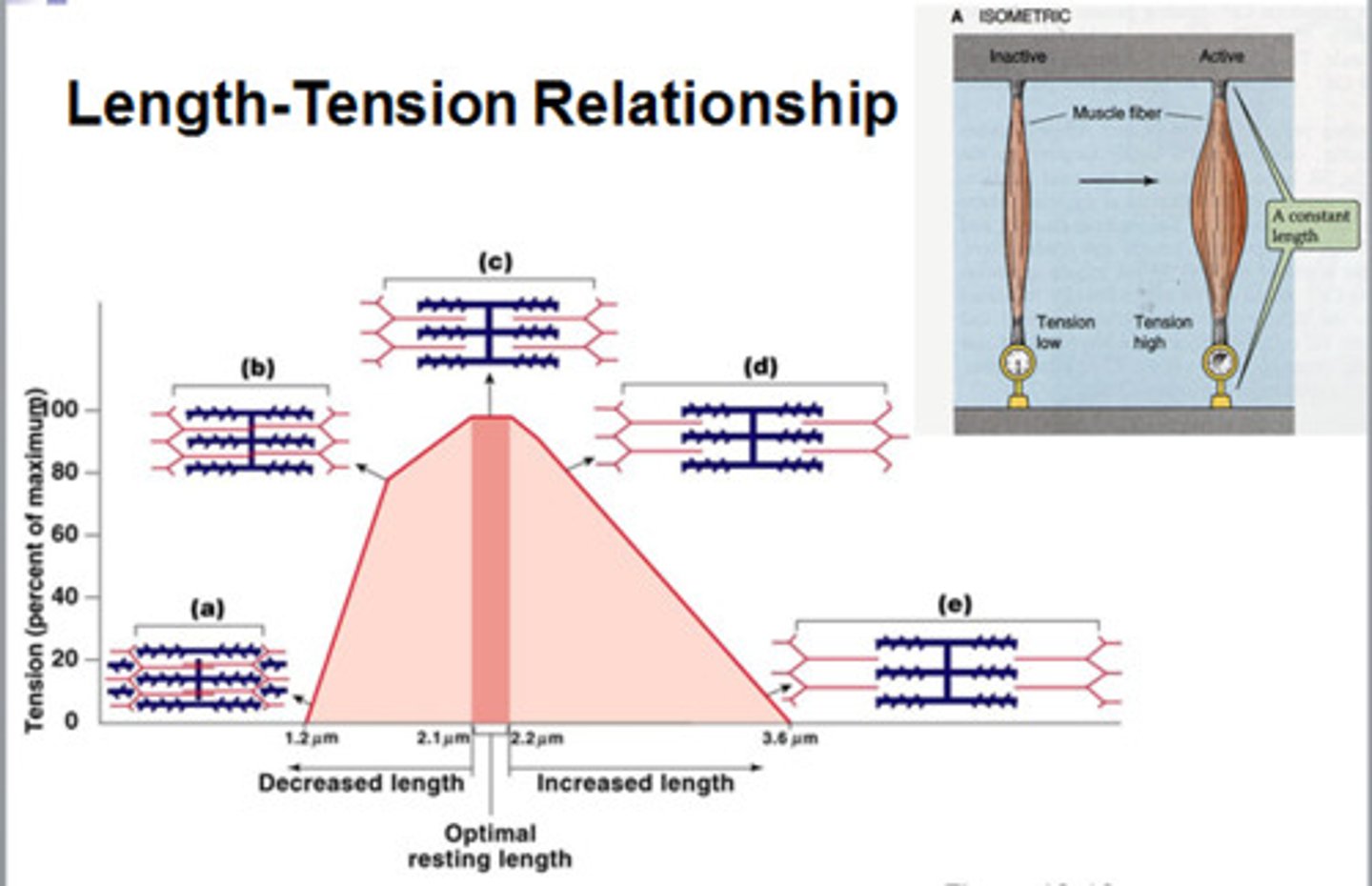
What is the optimal resting length of a sarcomere?
When the zone of overlap is large, but thin filaments to not extend to center of sarcomere
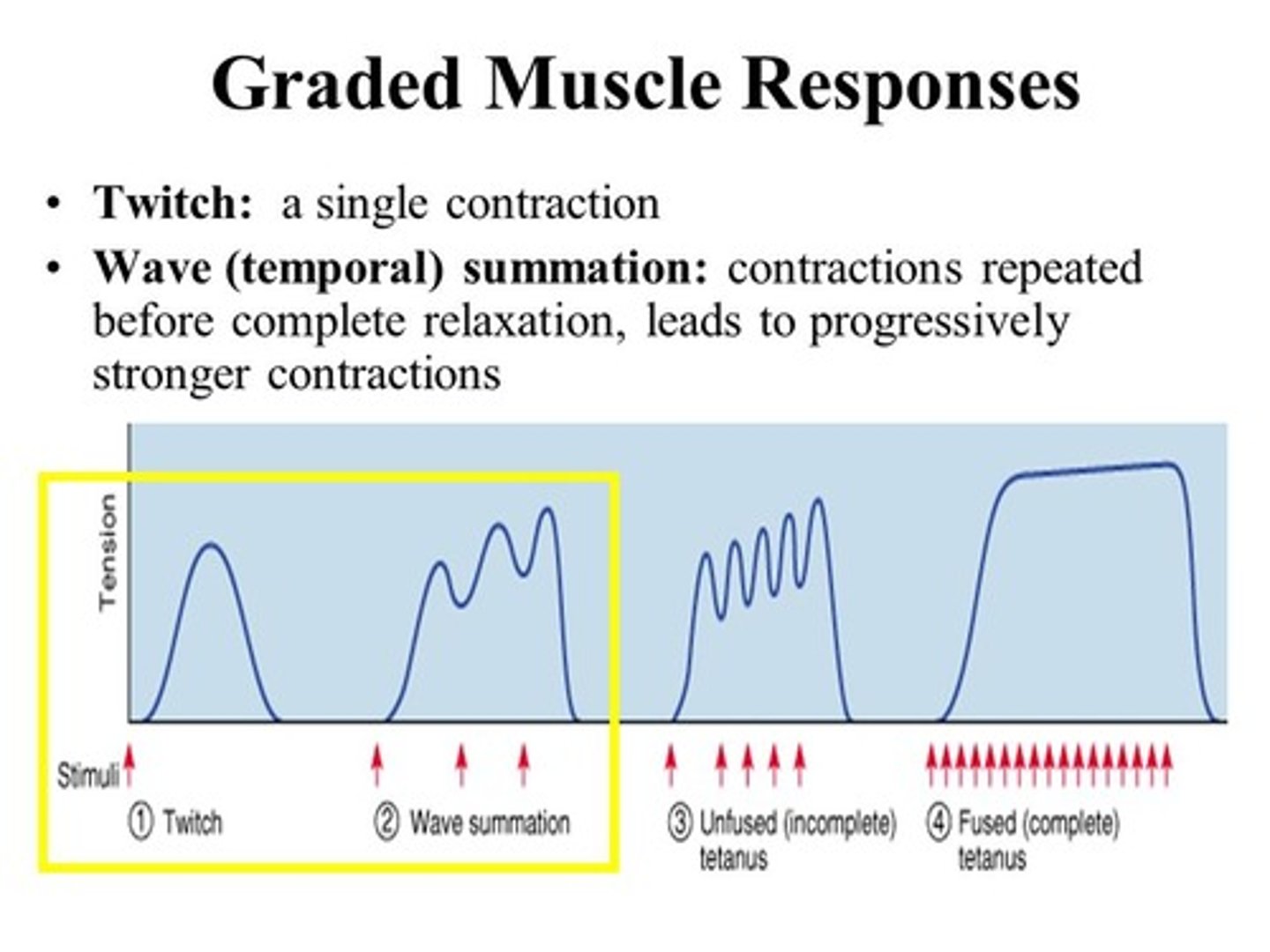
muscle twitch
the response of a muscle to a single brief threshold stimulus
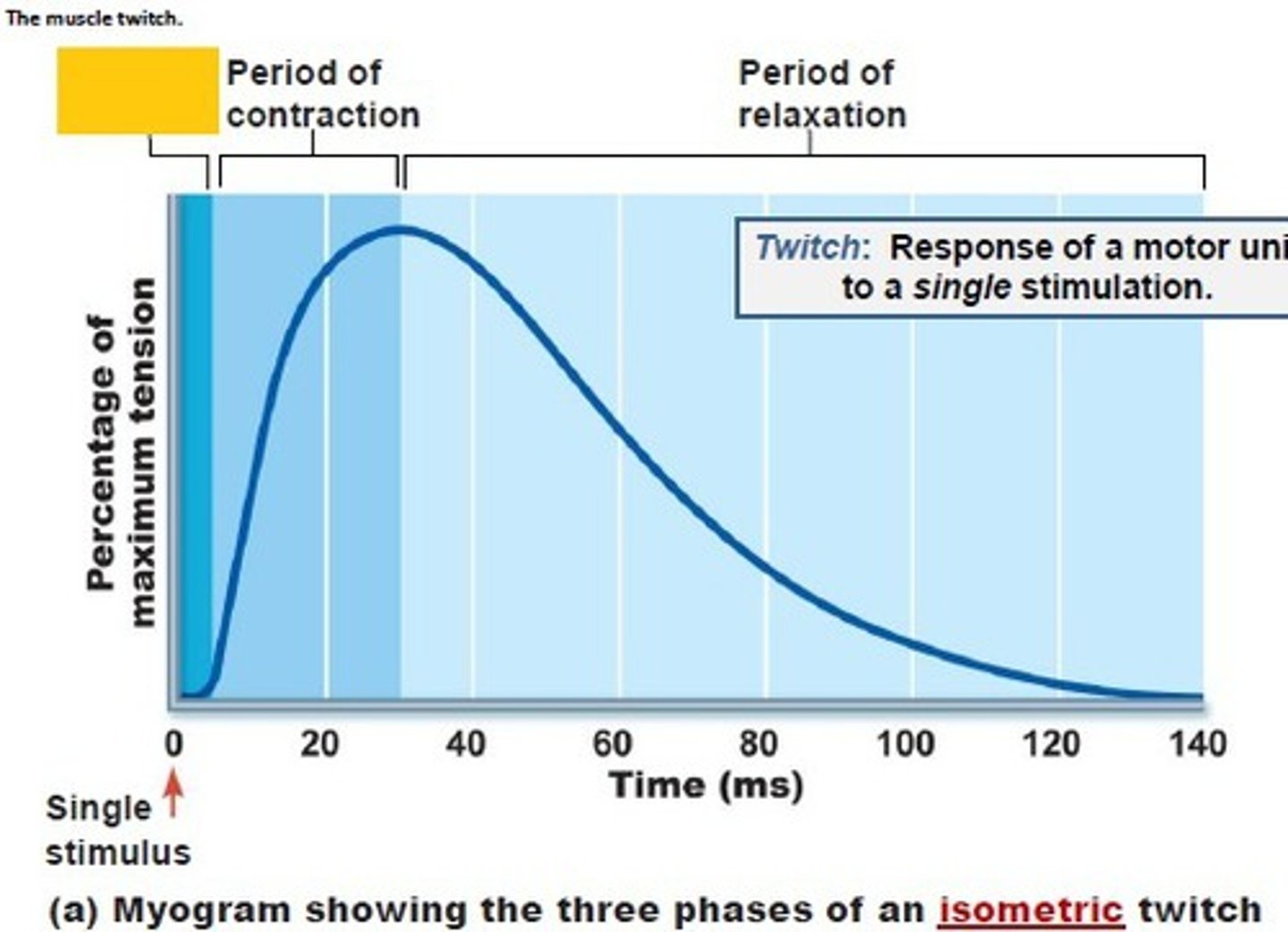
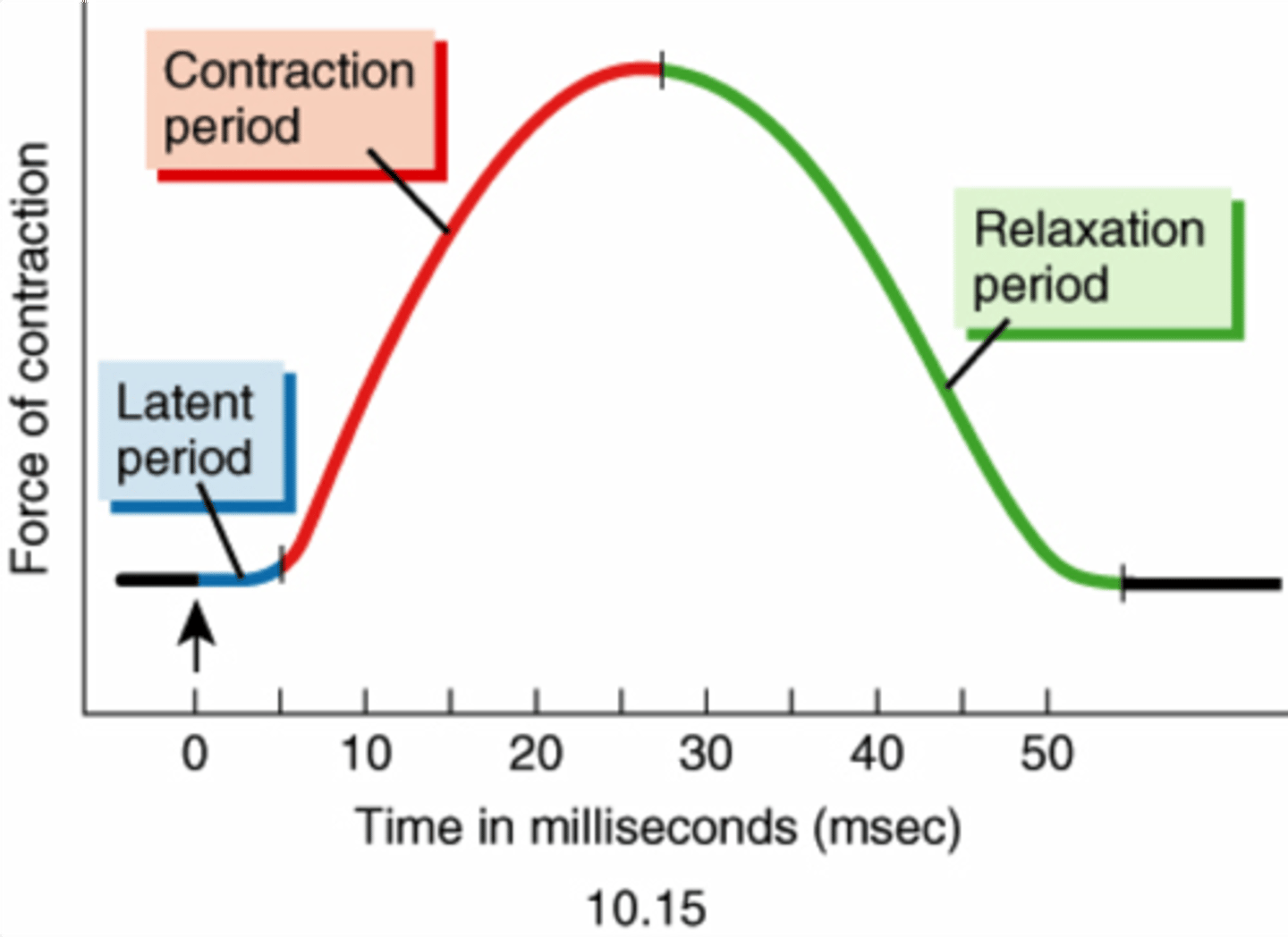
phases of muscle twitch
latent period, period of contraction, period of relaxation
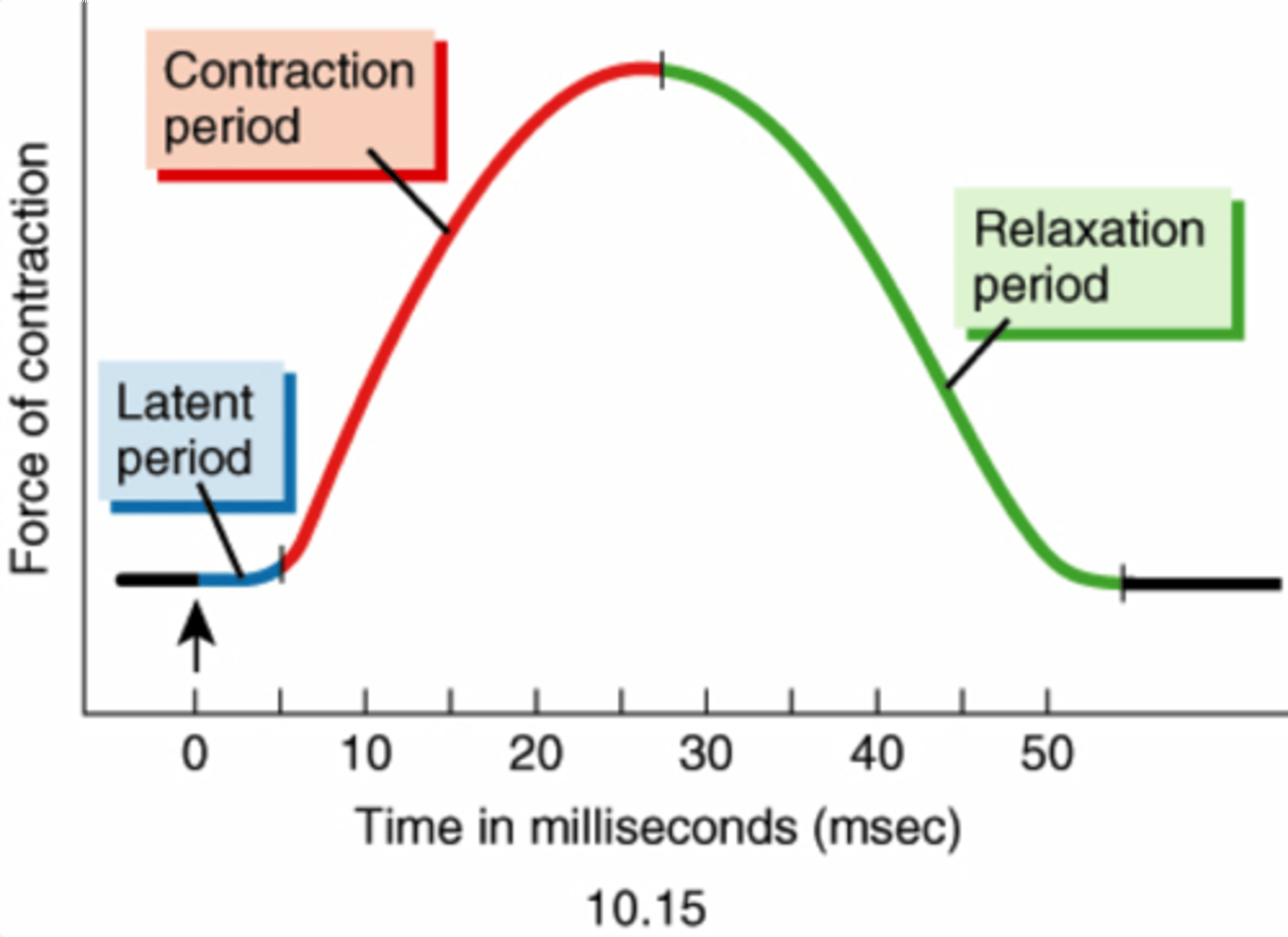
How long can a muscle hold a contraction for?
Durations of contractions are vary for different types of skeletal muscles
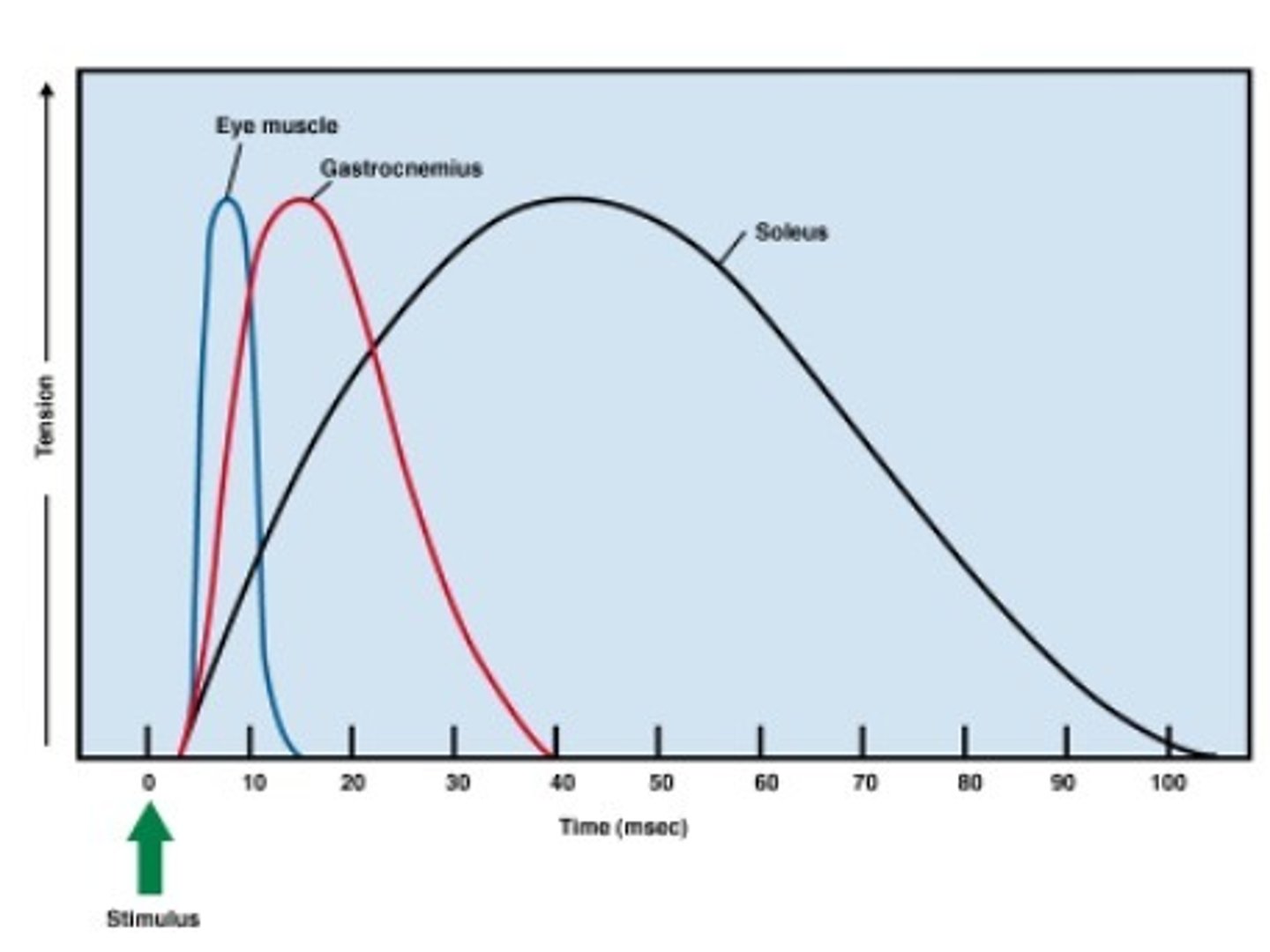
What is a graded response in terms of muscle contraction?
graded means "varied" as in the muscle can produce different amounts of tension. Example: you will use less tension/ force to pick up your keys versus a large suitcase
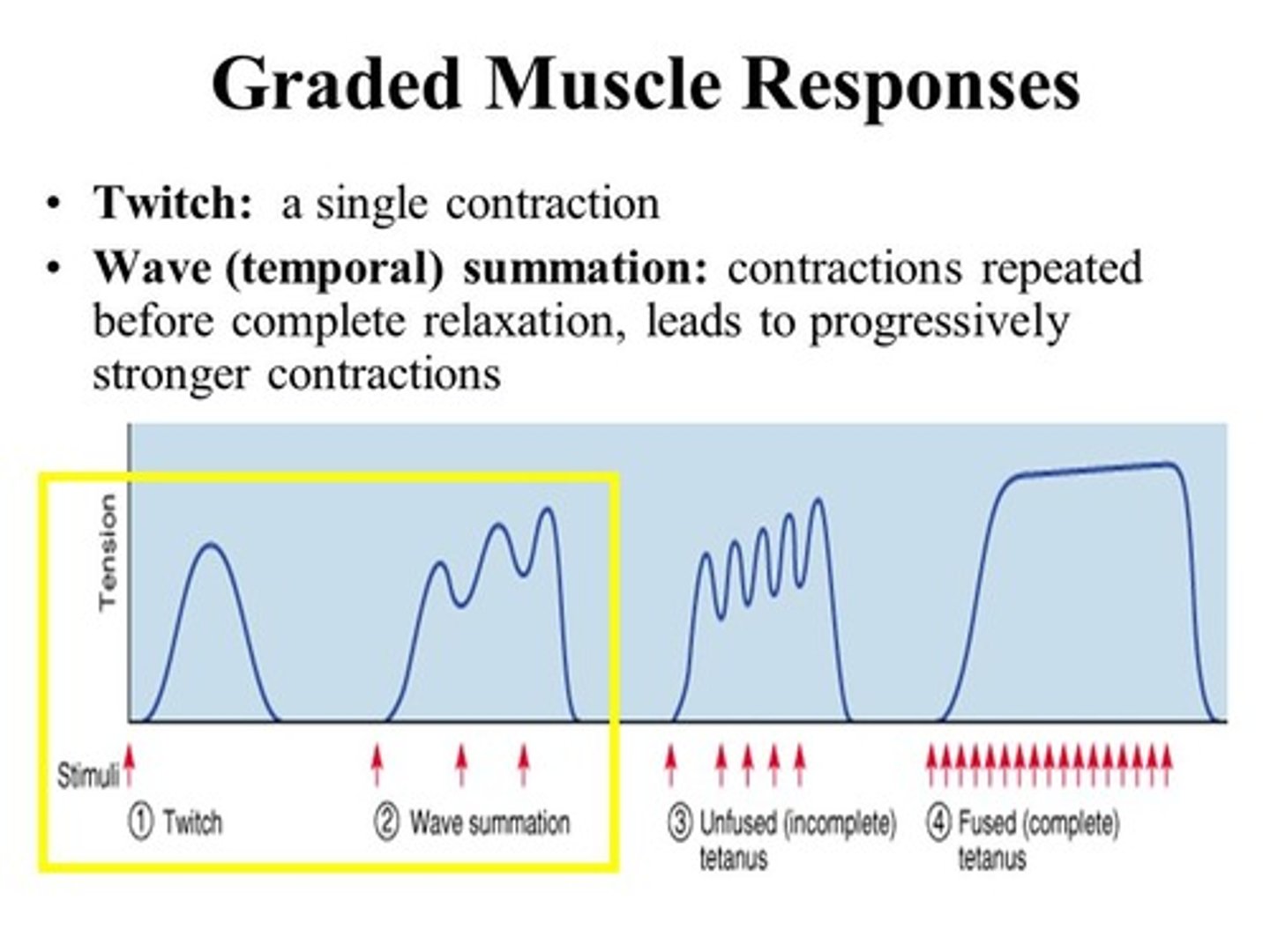
How can muscle contractions be graded/ varied?
1) Frequency of stimulation
2) Number of motor units recruited/ stimulated
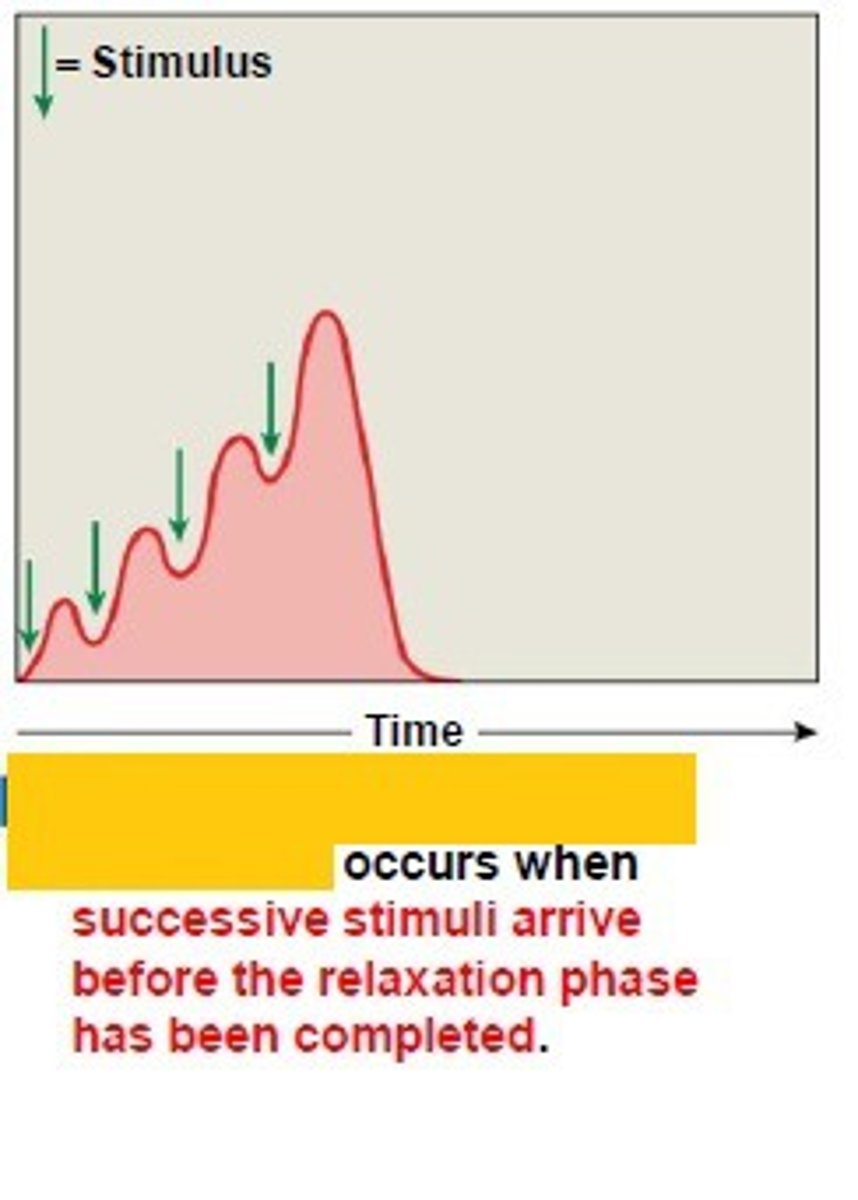
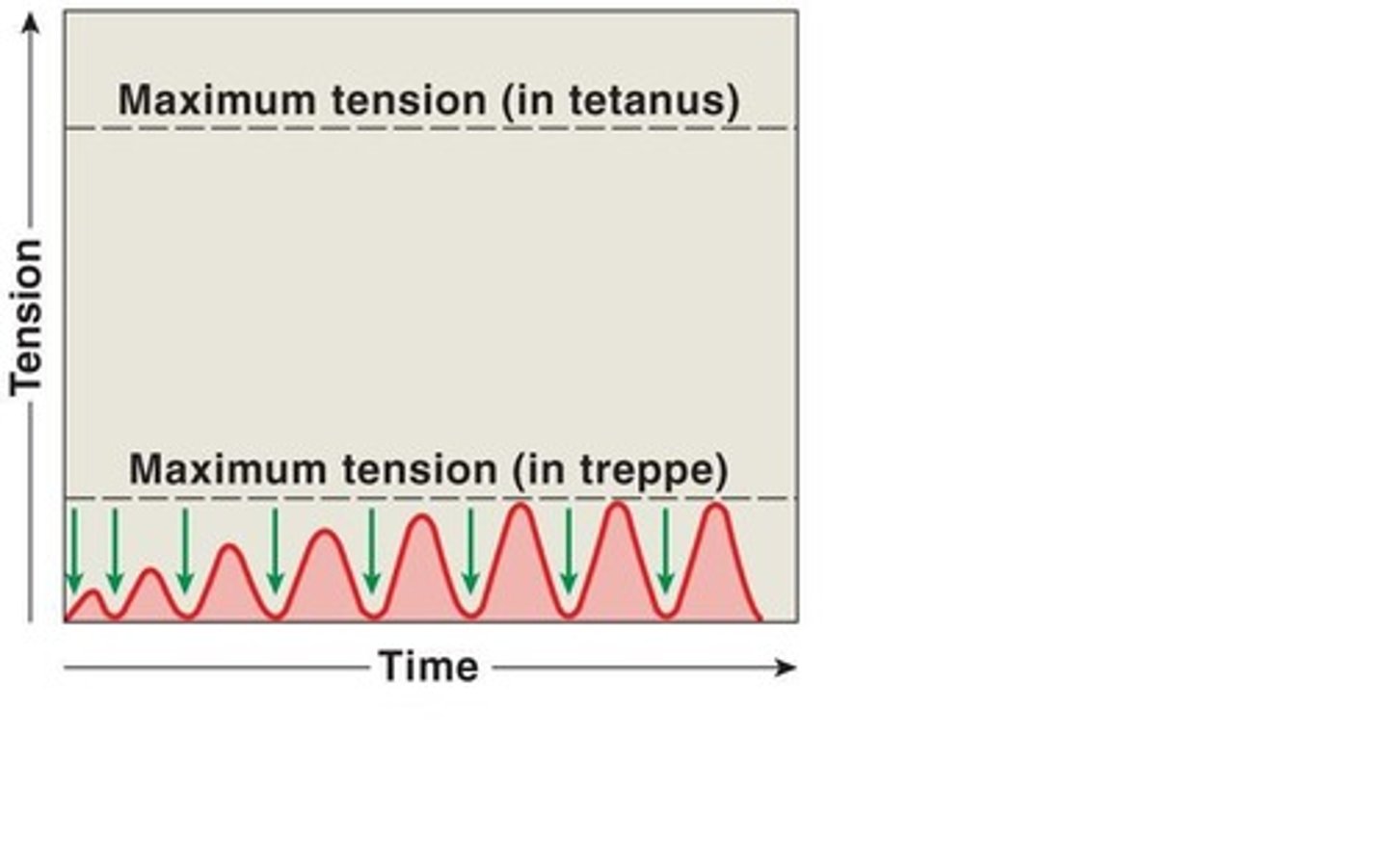
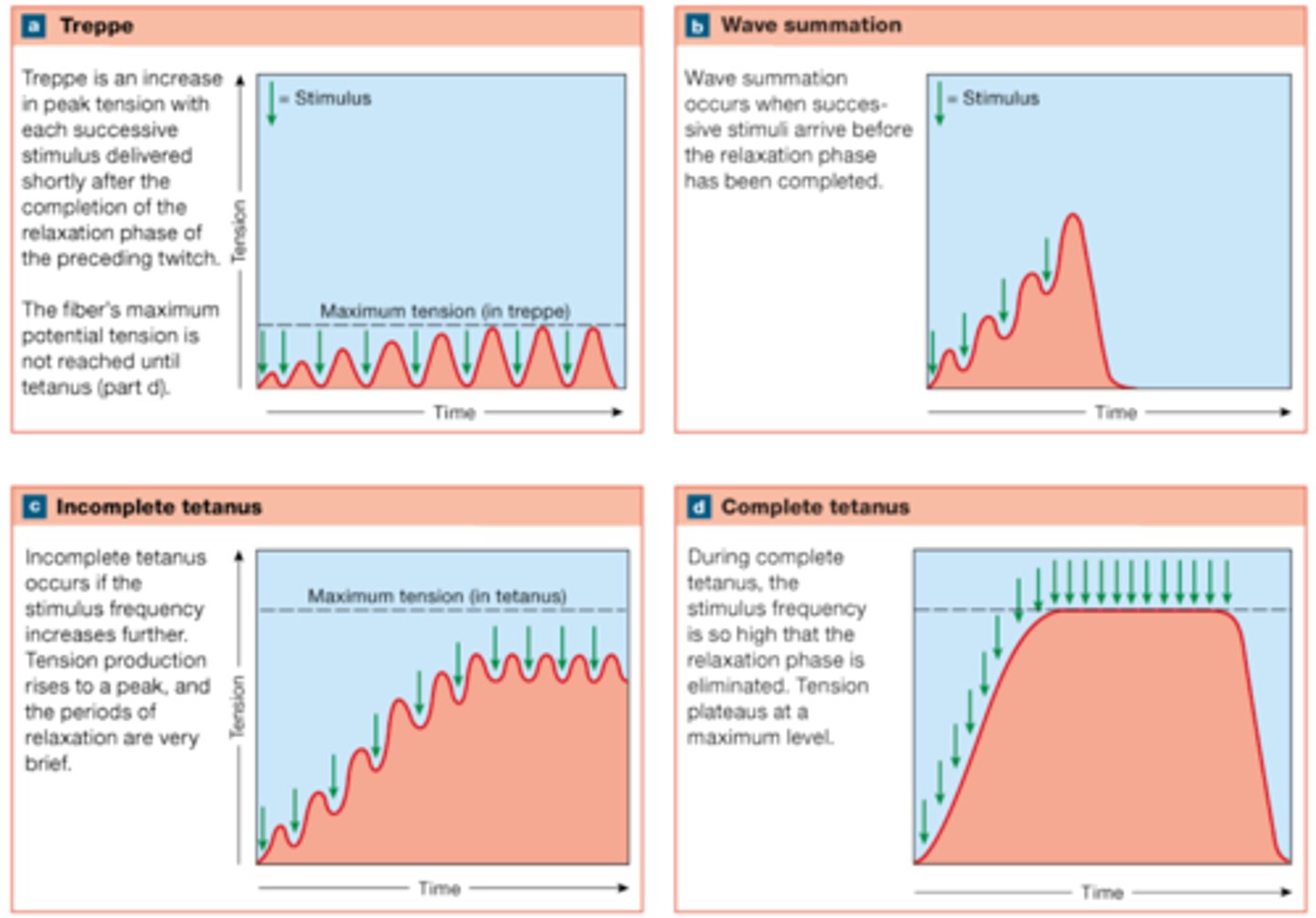
treppe
Muscle stimulated frequently, but the muscle is allowed to fully relax before the next stimulus arrives. Results in greater tension, but not dramatic increase.
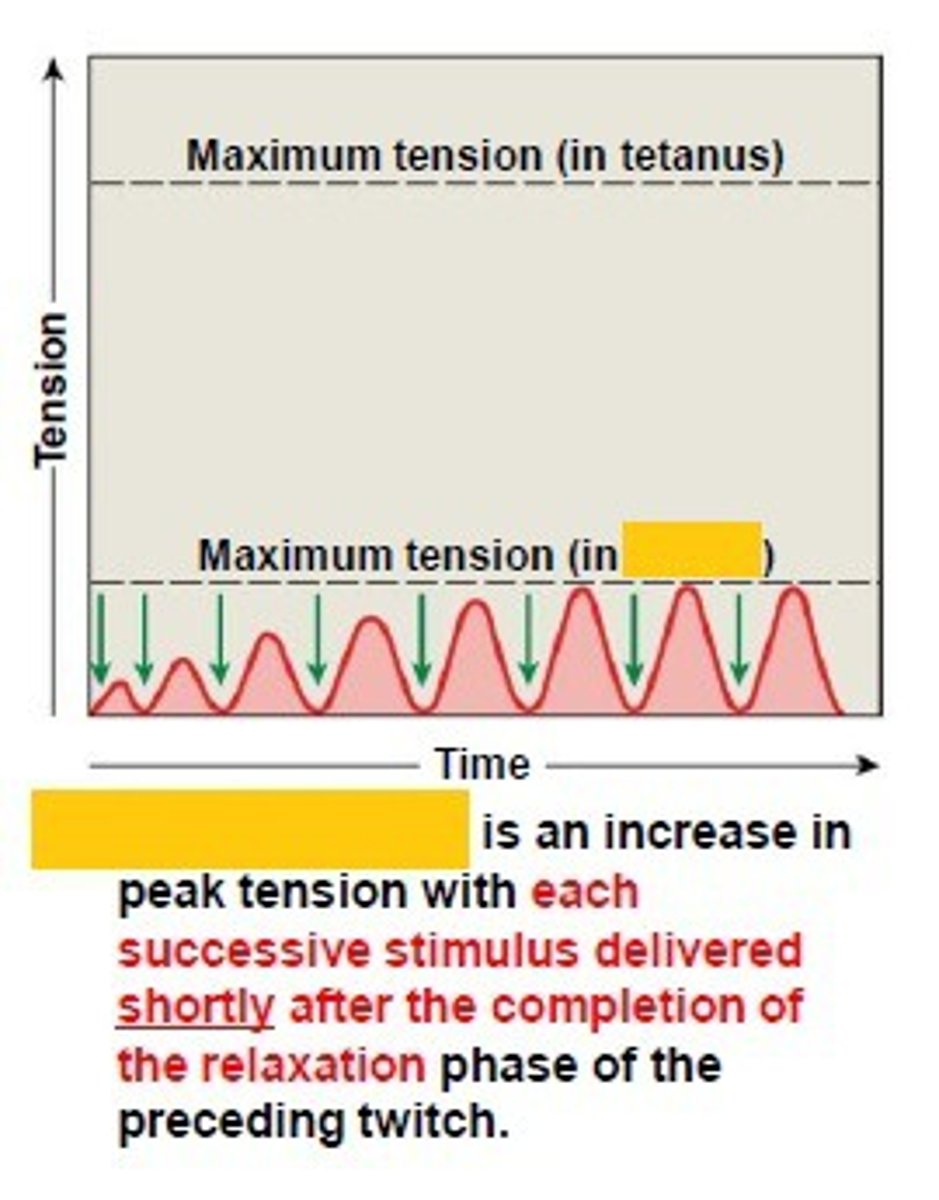
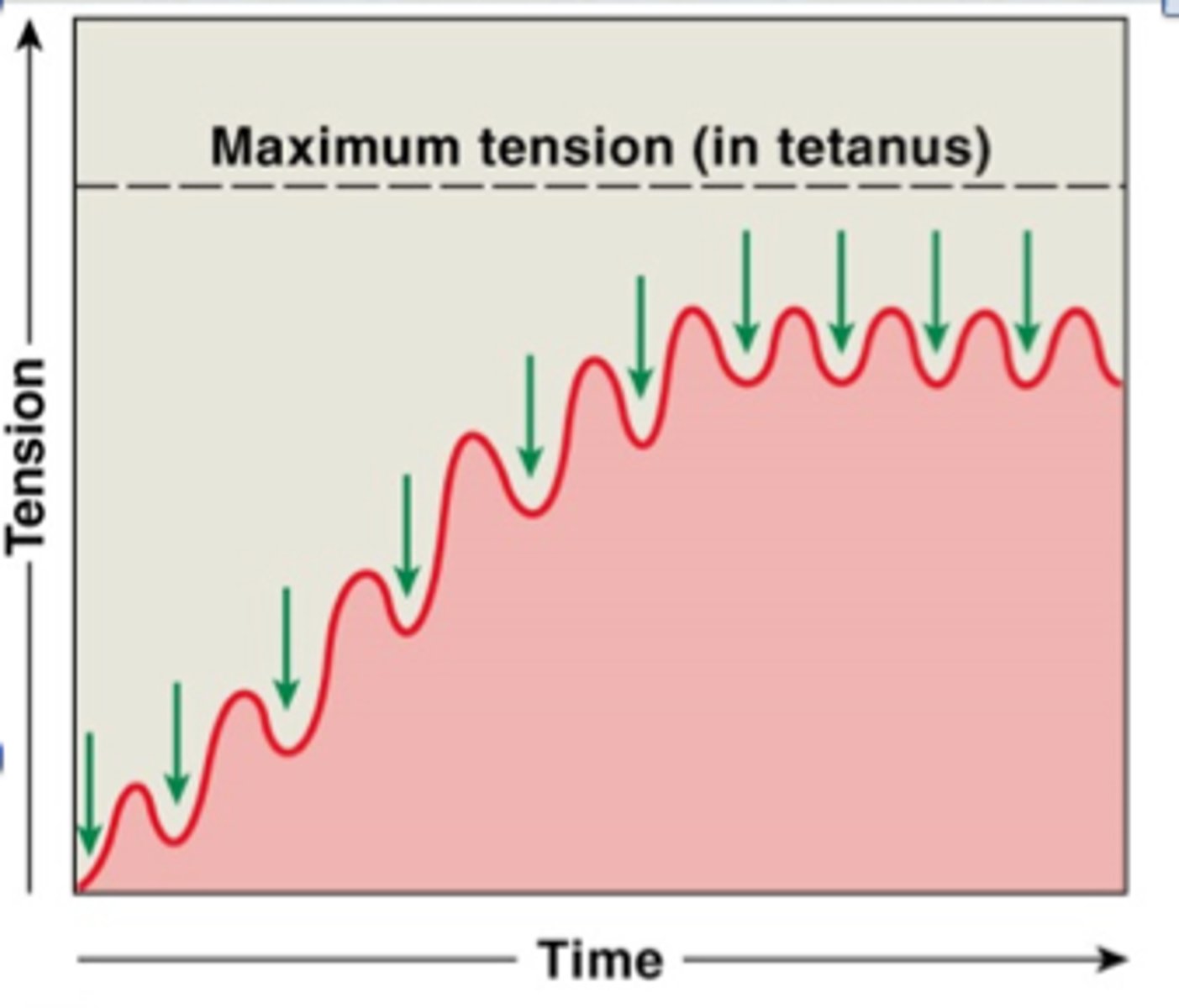
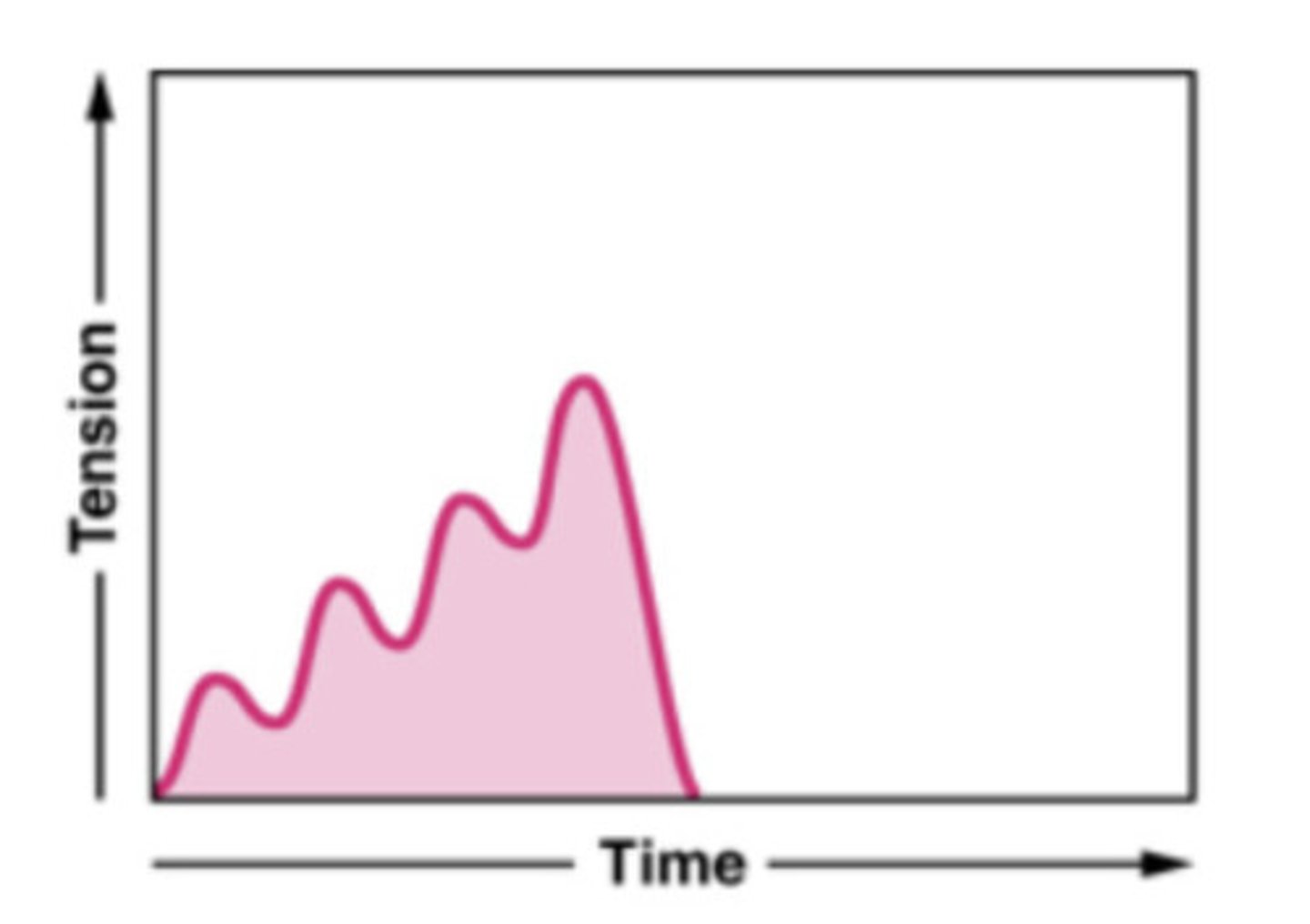
wave summation
this occurs when a second stimulus is received before the muscle fiber has relaxed, creating a second contraction that is stronger than the first
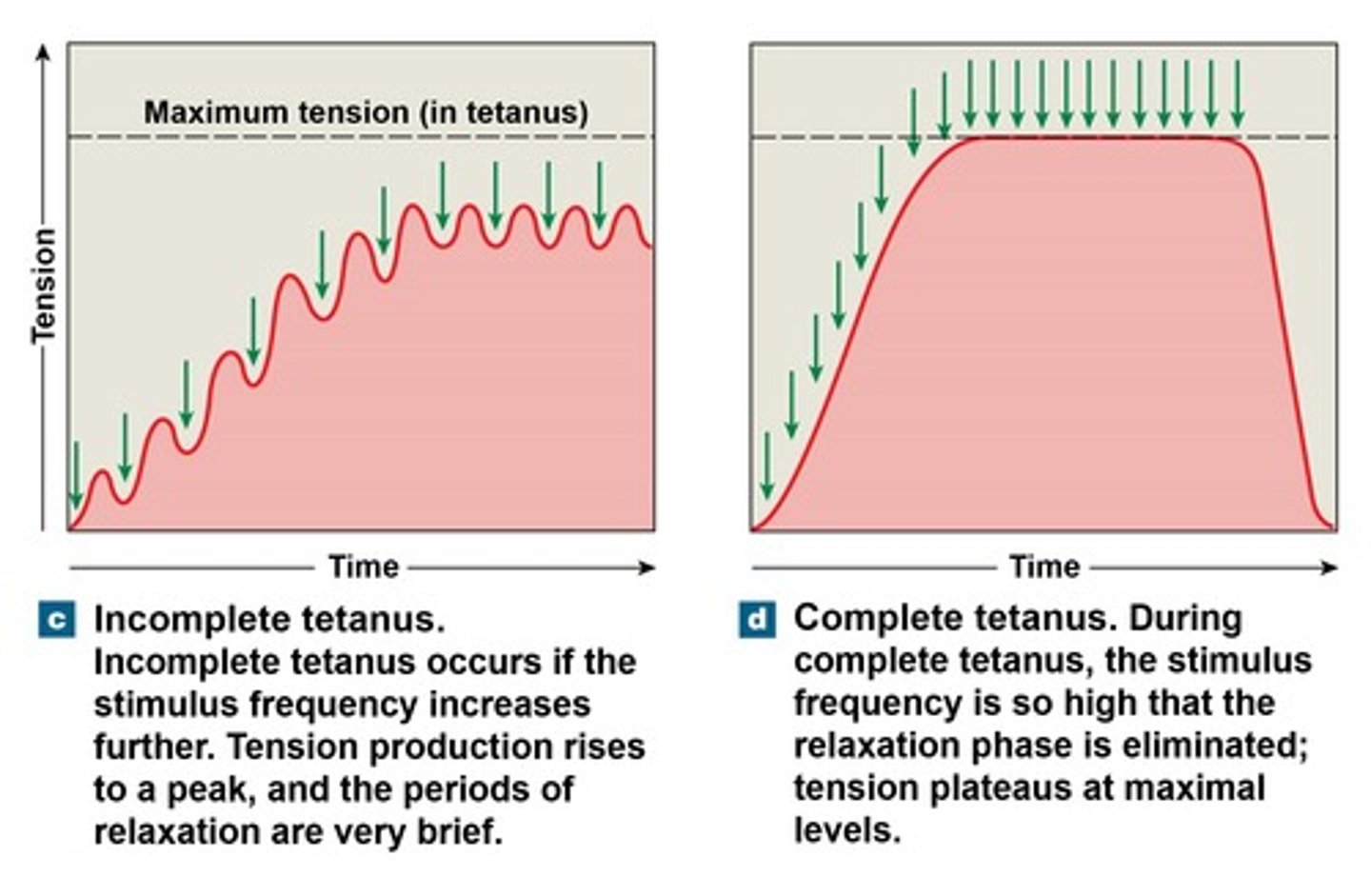
incomplete tetanus (unfused tetanus)
A muscle producing almost peak tension during rapid cycles of contraction and relaxation
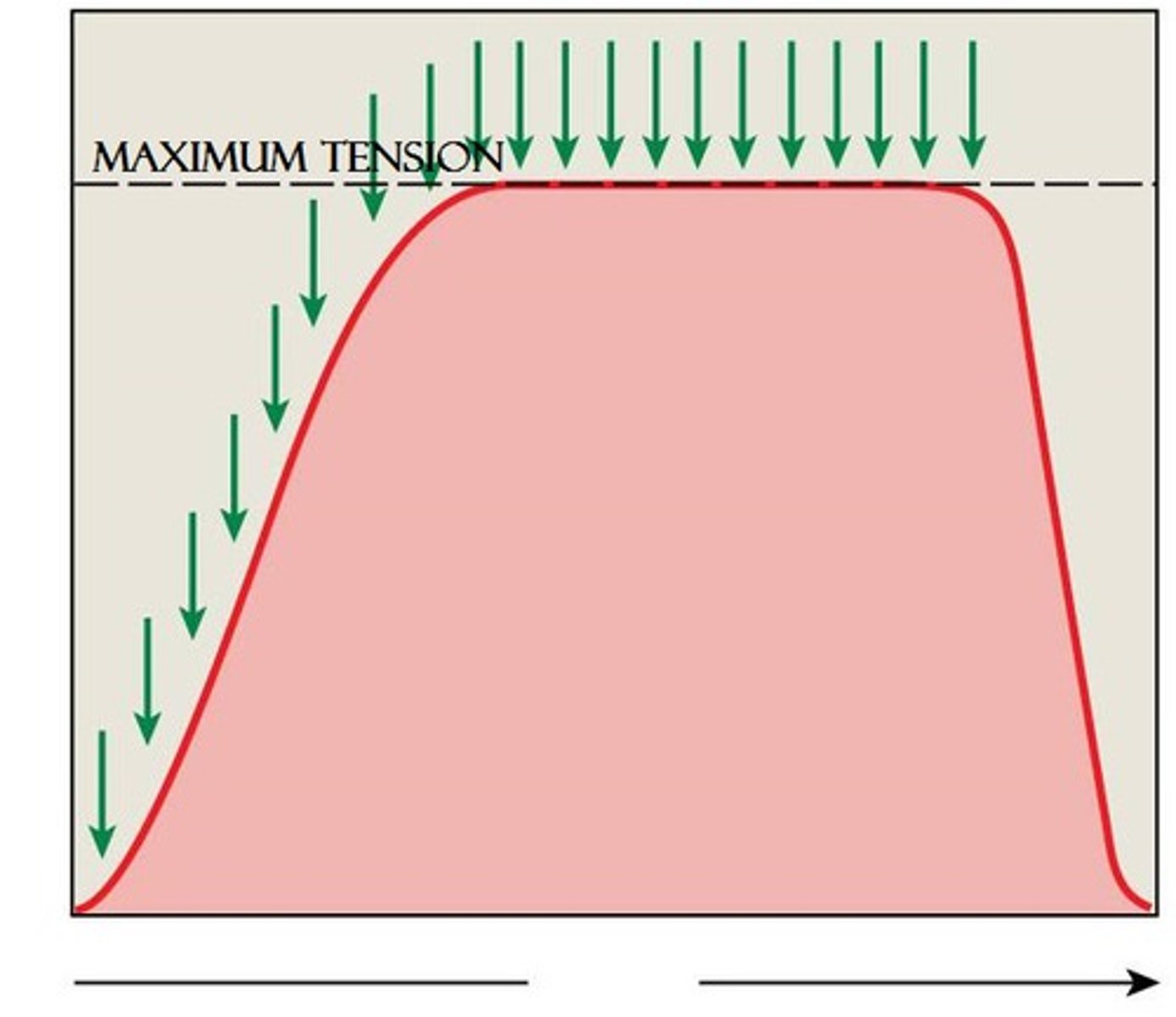
complete tetanus (fused tetanus)
a muscle that is stimulated so frequently that the relaxation phase is completely eliminated
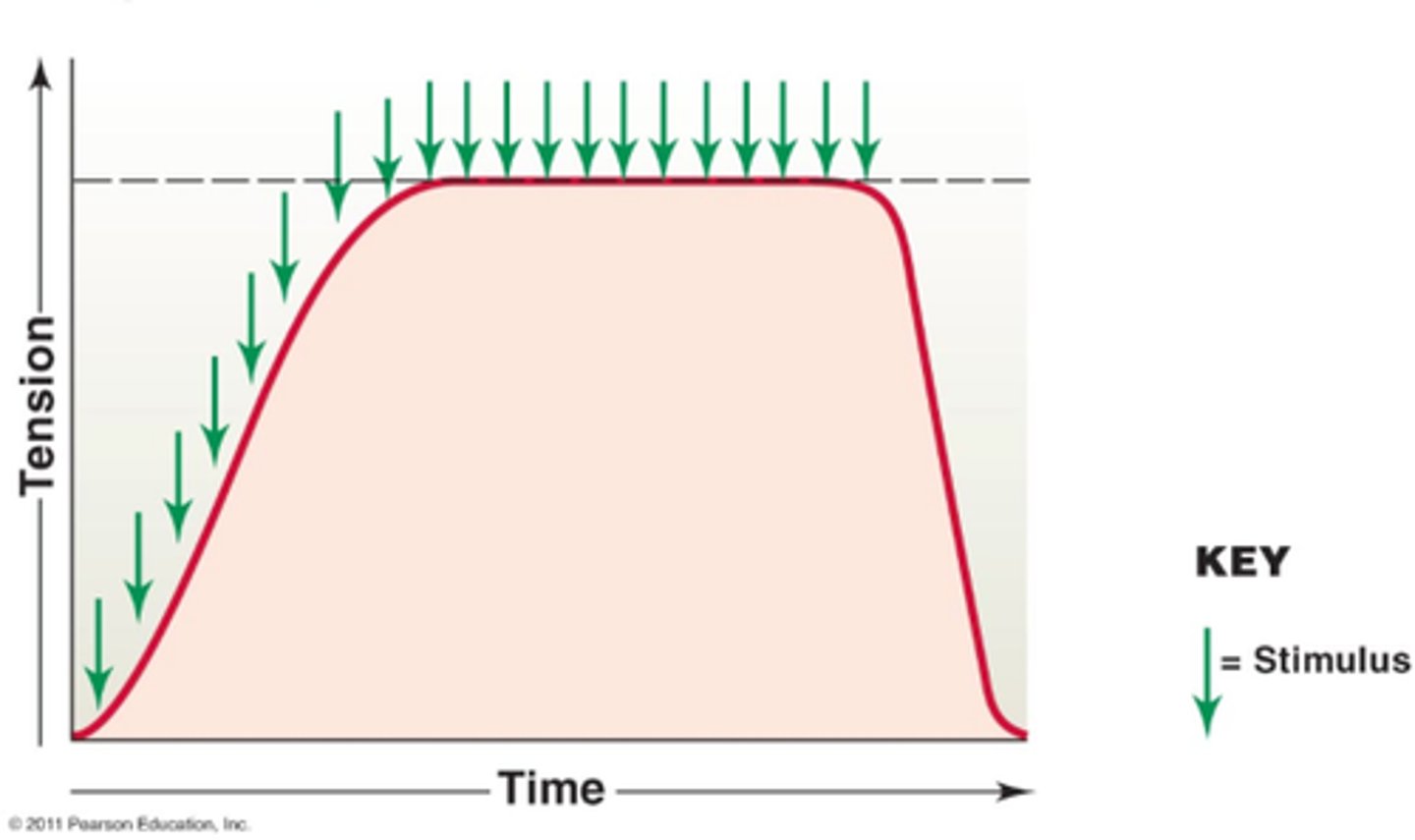
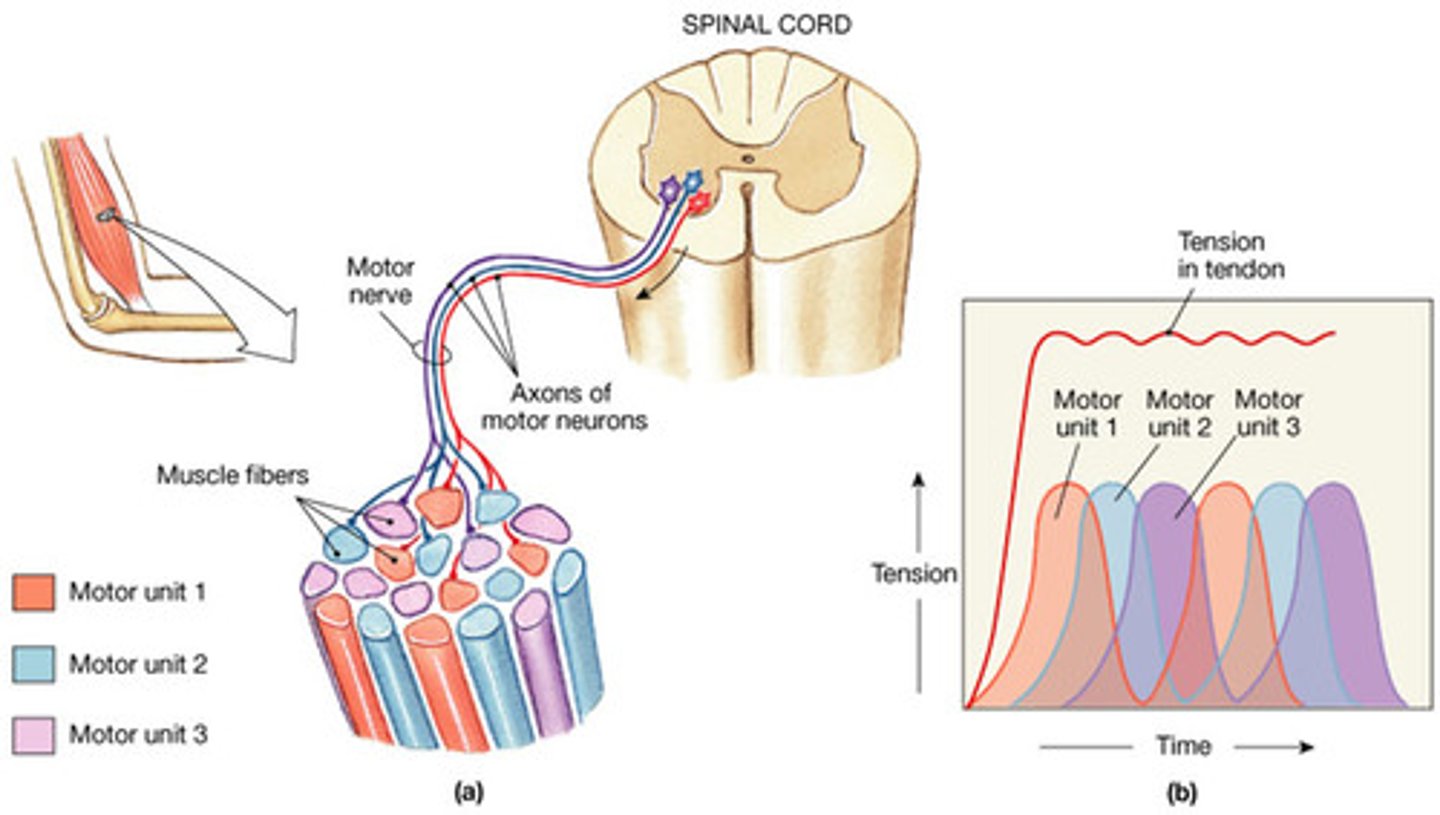
Muscle tension depends on what 4 things?
1) Number of motor units recruited
2) the size of the motor units
3) The length of the resting sarcomere
4) the specific type of muscle (some muscle fibers are larger than others)
Skeletal muscled produce increased tension by __________.
recruiting additional motor units
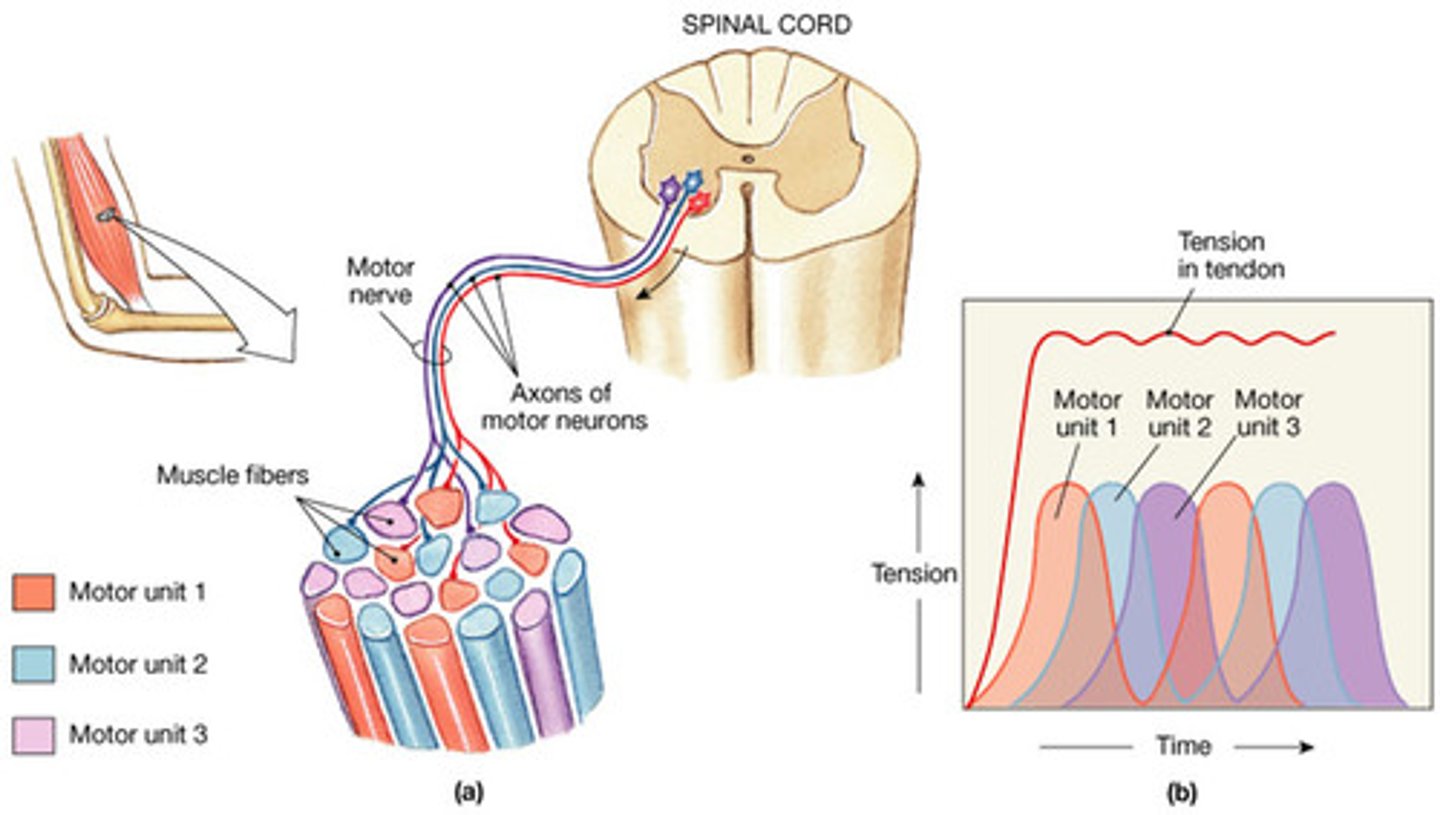
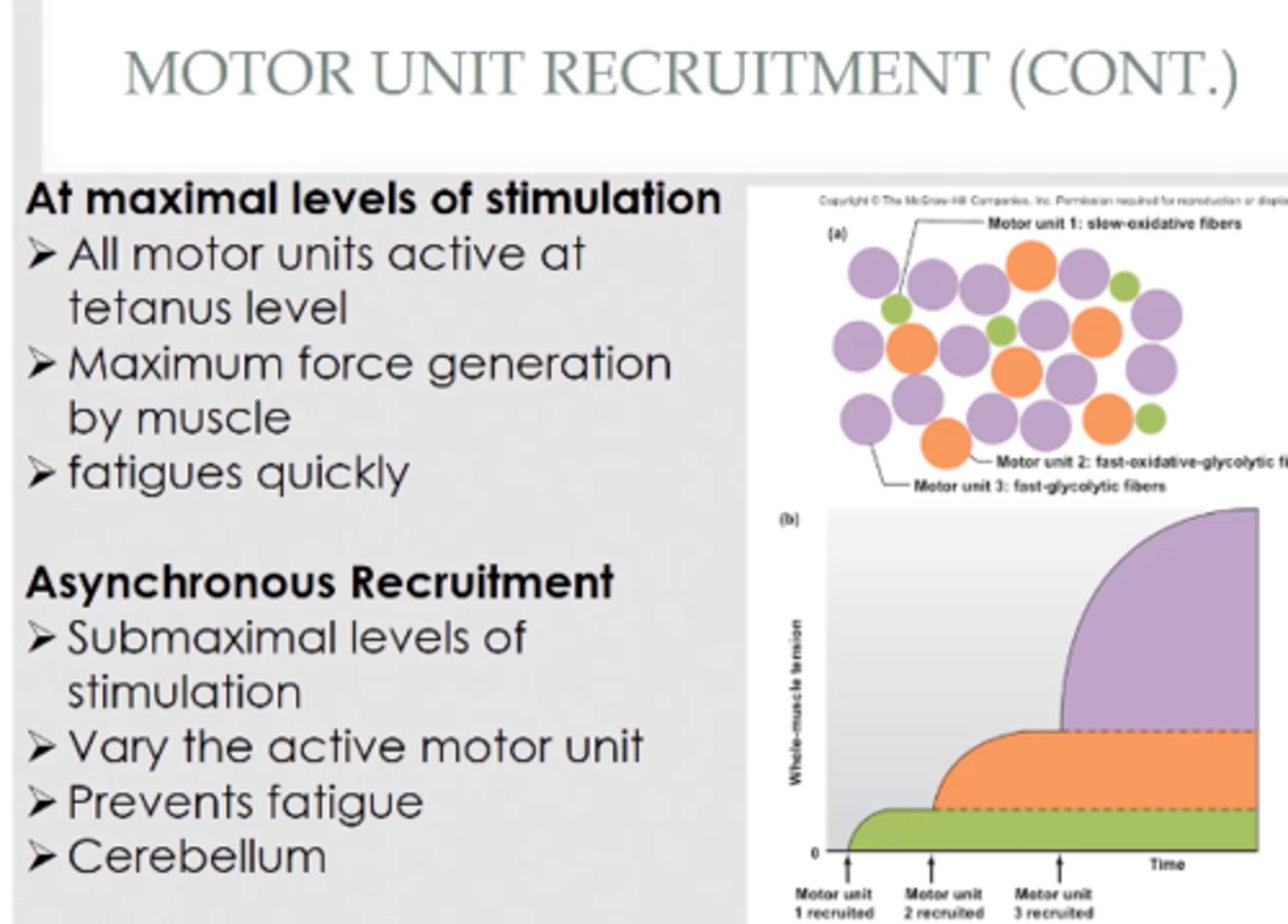
asynchronous recruitment (3 things about)
1) helps avoid fatigue during sustained muscle contractions, 2) different motor units take turns maintaining muscle tension,
3) makes an entire muscle seem to contract smoothly.
muscle tone versus muscle strength
tone is tension in muscle at rest--strength is tension that generates force to move or lift something (such as your arm, or a bok)

How does muscle tone benefit joints?
Muscle tone stabilizes joints.
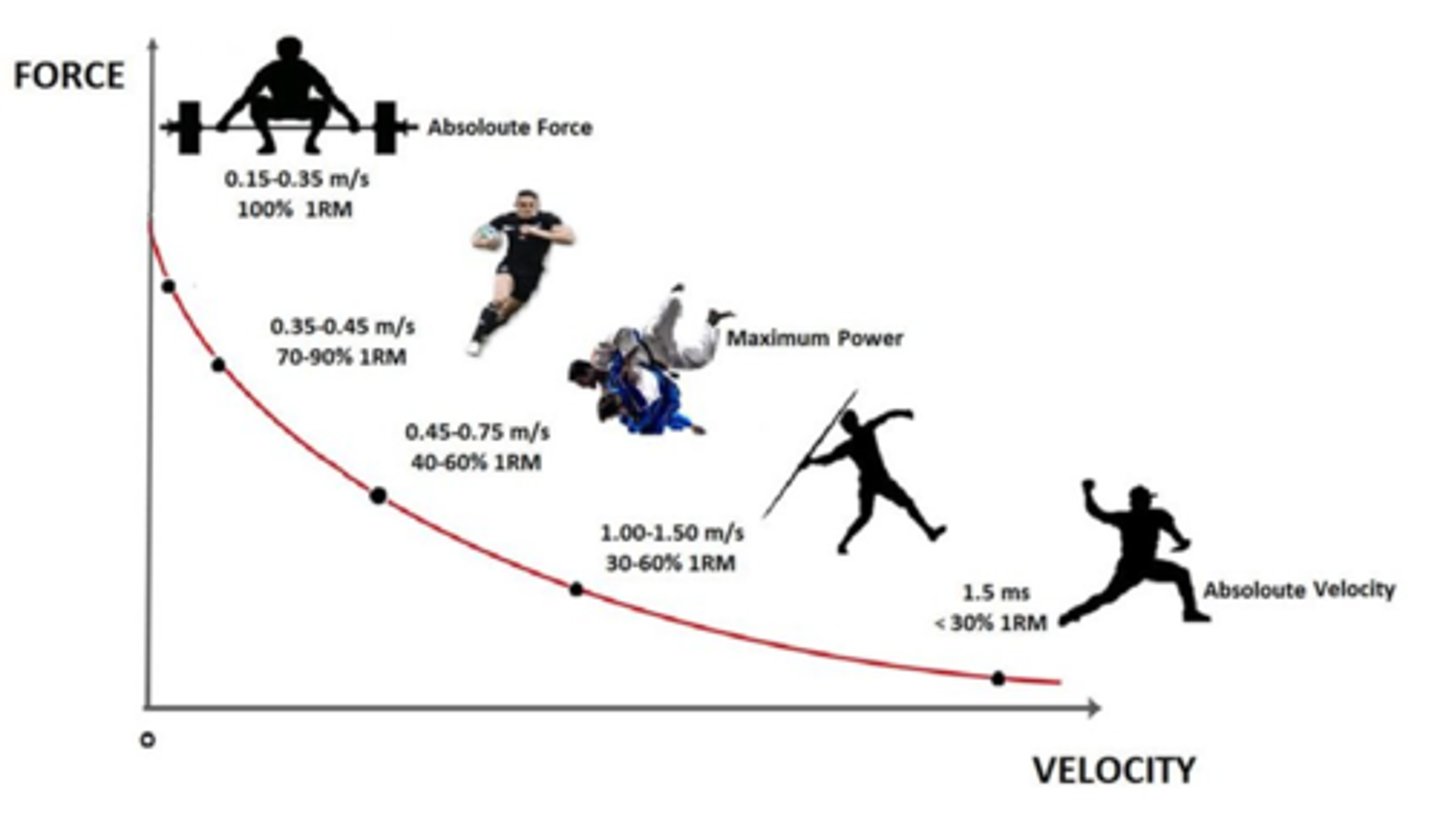
Load and speed of contraction are ________ related
inversely
3 energy sources used in muscle contraction
1) Anaerobic Creatine Phosphate (ATP-CP) System (High Intensity – Short Duration/Bursts)
2) Anaerobic Lactic Acid Fermentation (Glycolytic) Energy System (High to Medium Intensity – Uptempo)
3) Aerobic Energy System in Mitochondria (Low Intensity – Long Duration – Endurance)
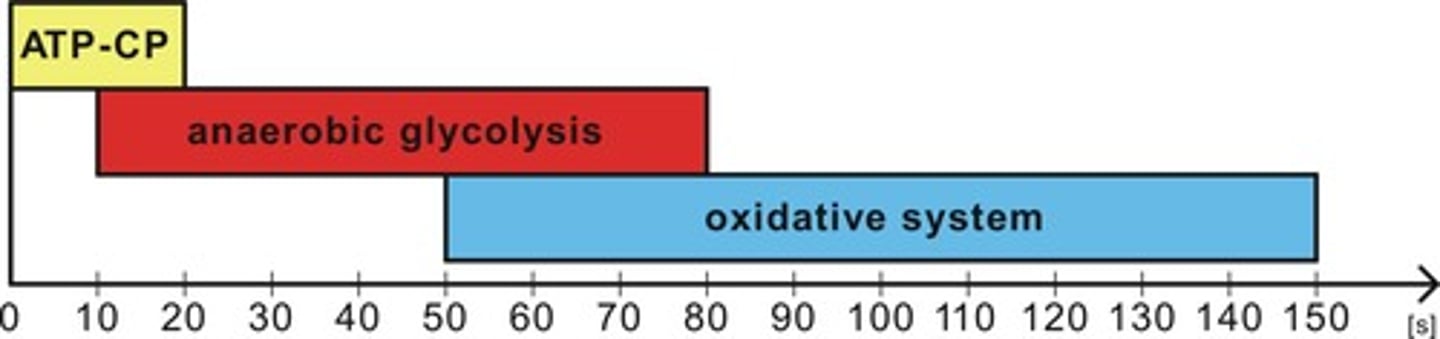
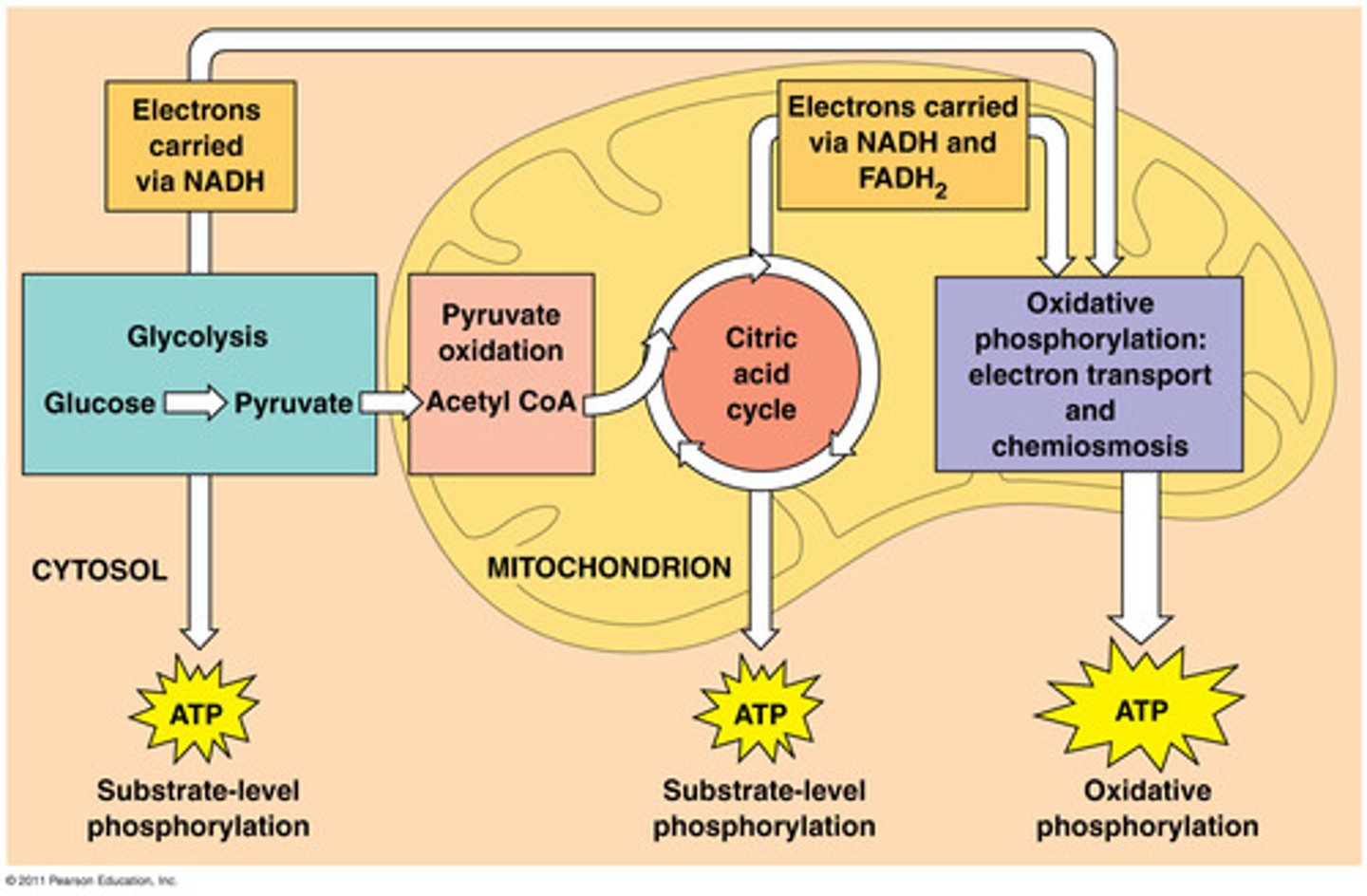
which energy is used most often for muscle contractions
aerobic respiration in mitochondria
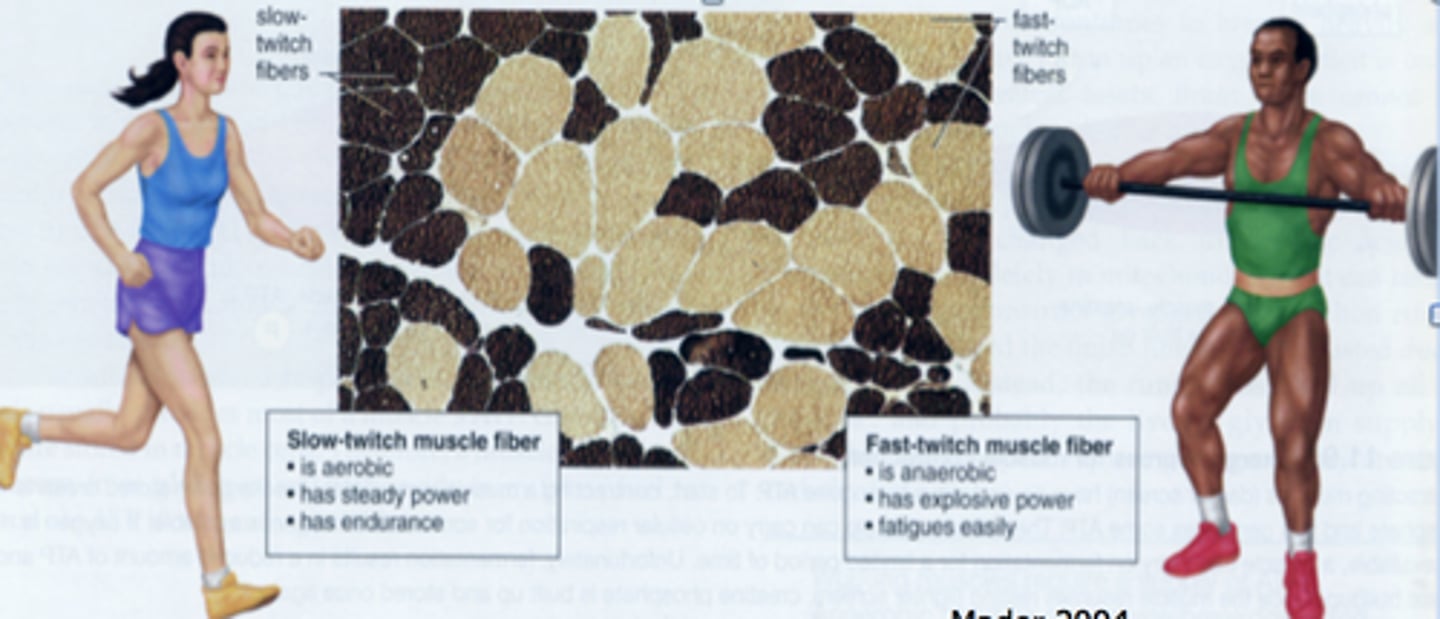
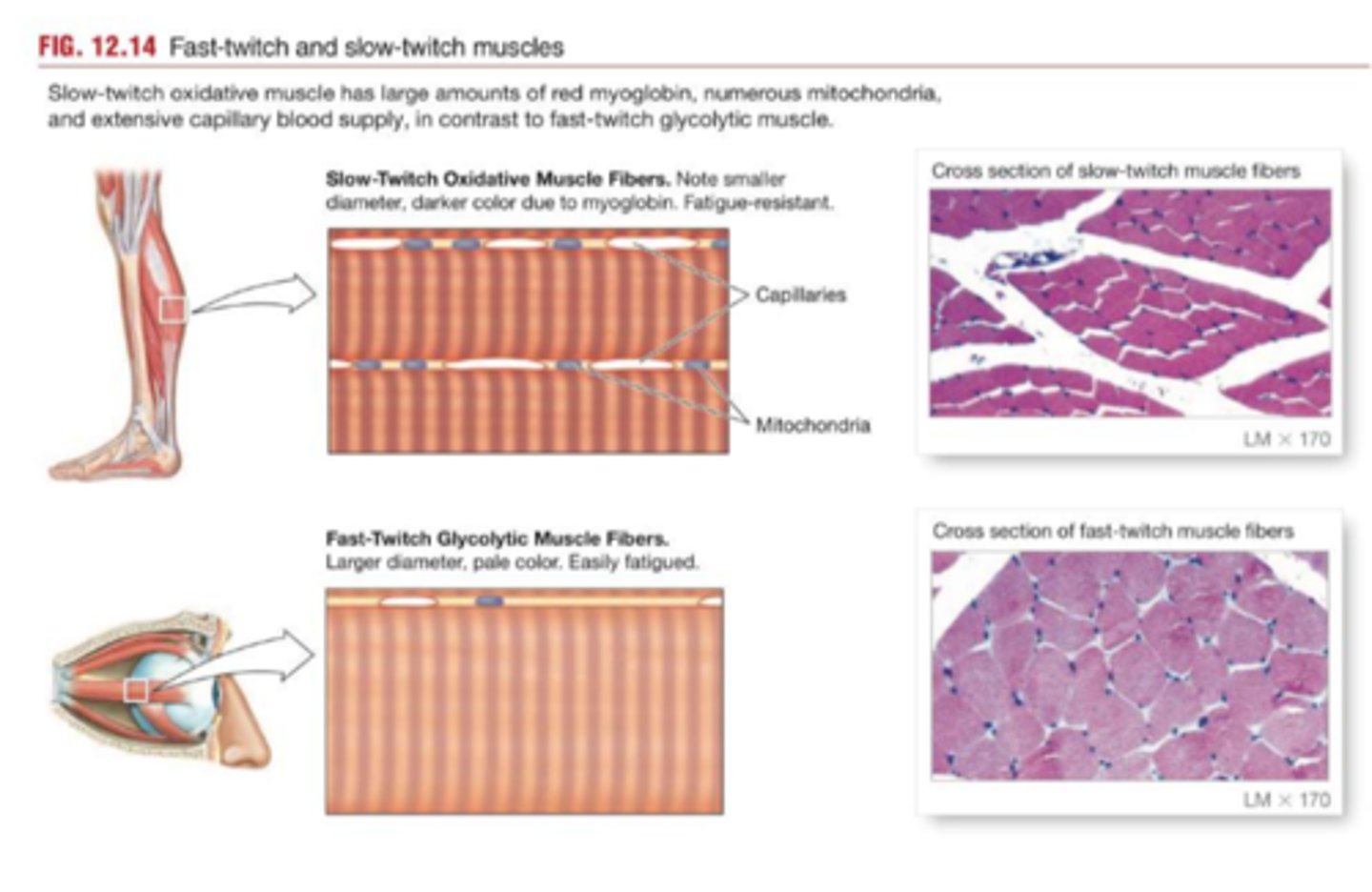
Fast-twitch muscle fibers (low oxidative)
produce powerful bursts of speed but fatigues quickly, uses anaerobic metabolism, white fibers
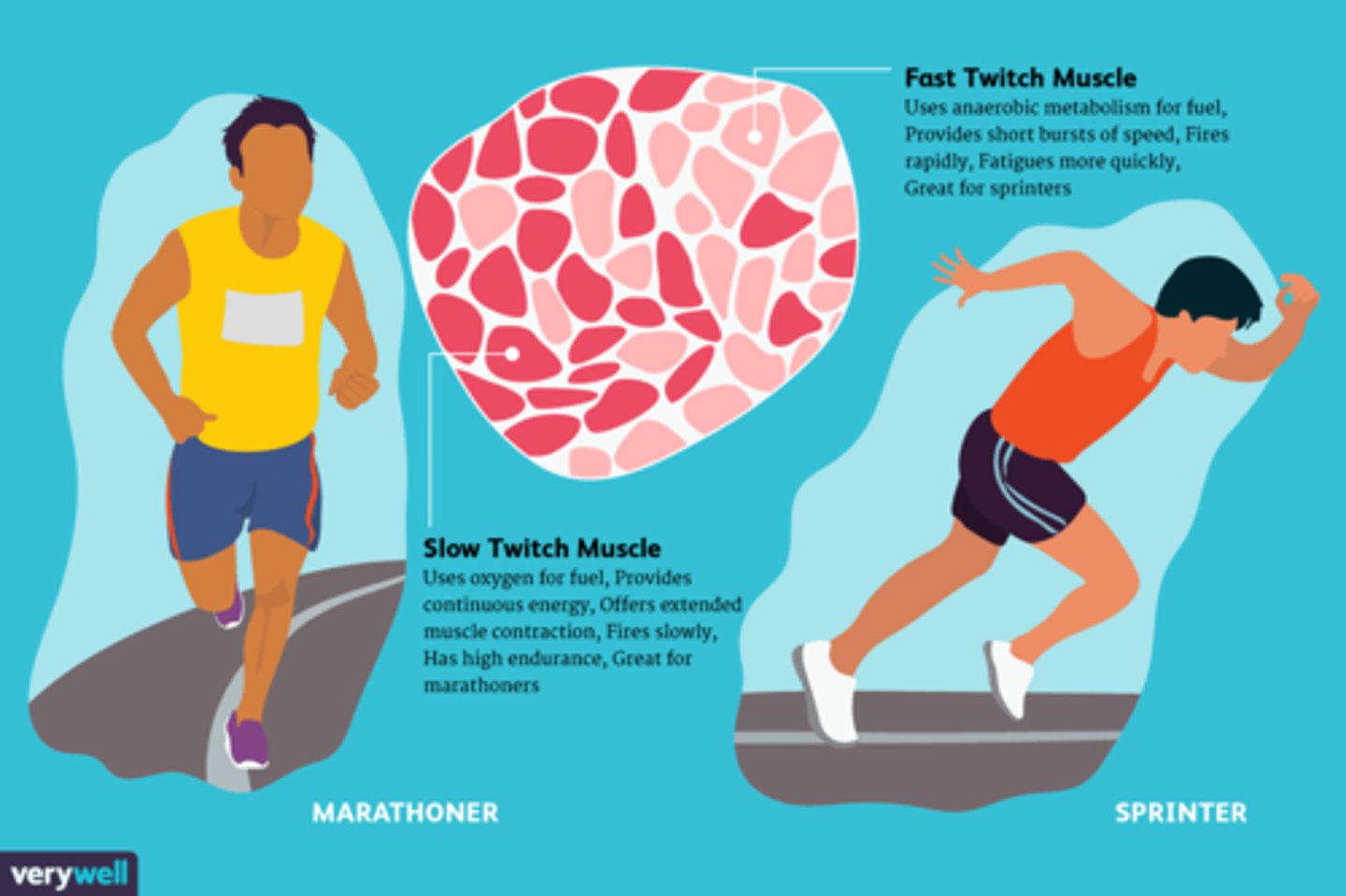
slow twitch muscle fibers
produce sustained continued contractions, do not fatigue easily, relies on aerobic metabolism, 'red' fibers, more myoglobin
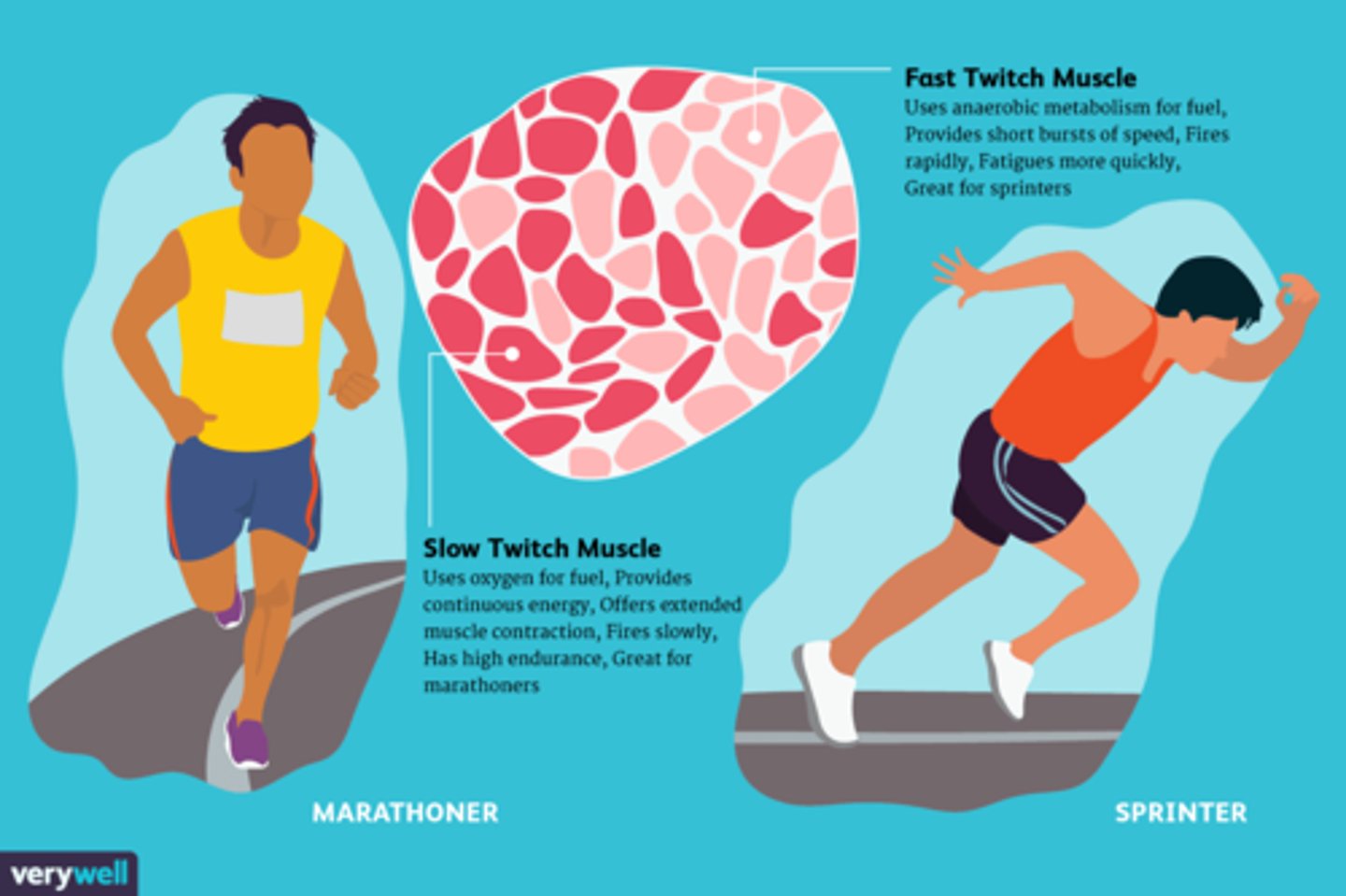
Someone who runs marathons at a moderate pace probably has a large number of __________ muscle fibers.
slow twitch- they have a lot of endurance--more myoglobin

someone who wins a bicycle race by pedaling fast and breaking the world record probably has a large number of ___________ muscle fibers.
fast twitch- produce bursts of speed but muscle fatigue more quickly

What are three types of muscle fatigue?
1) psychological - lacks motivation or confidence
2) muscular- ATP depletion and/or muscle damage
3) synaptic - not enough ACh
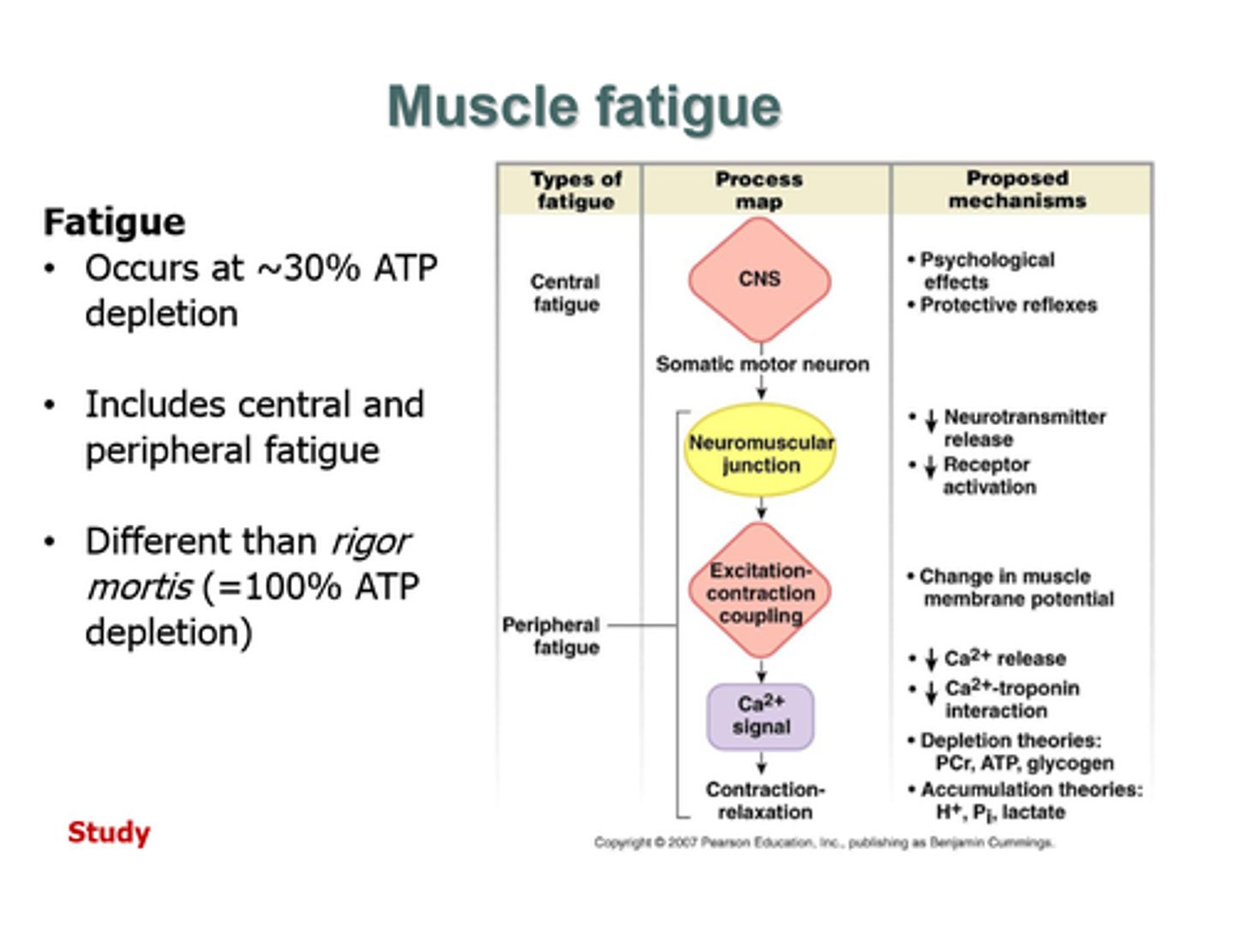
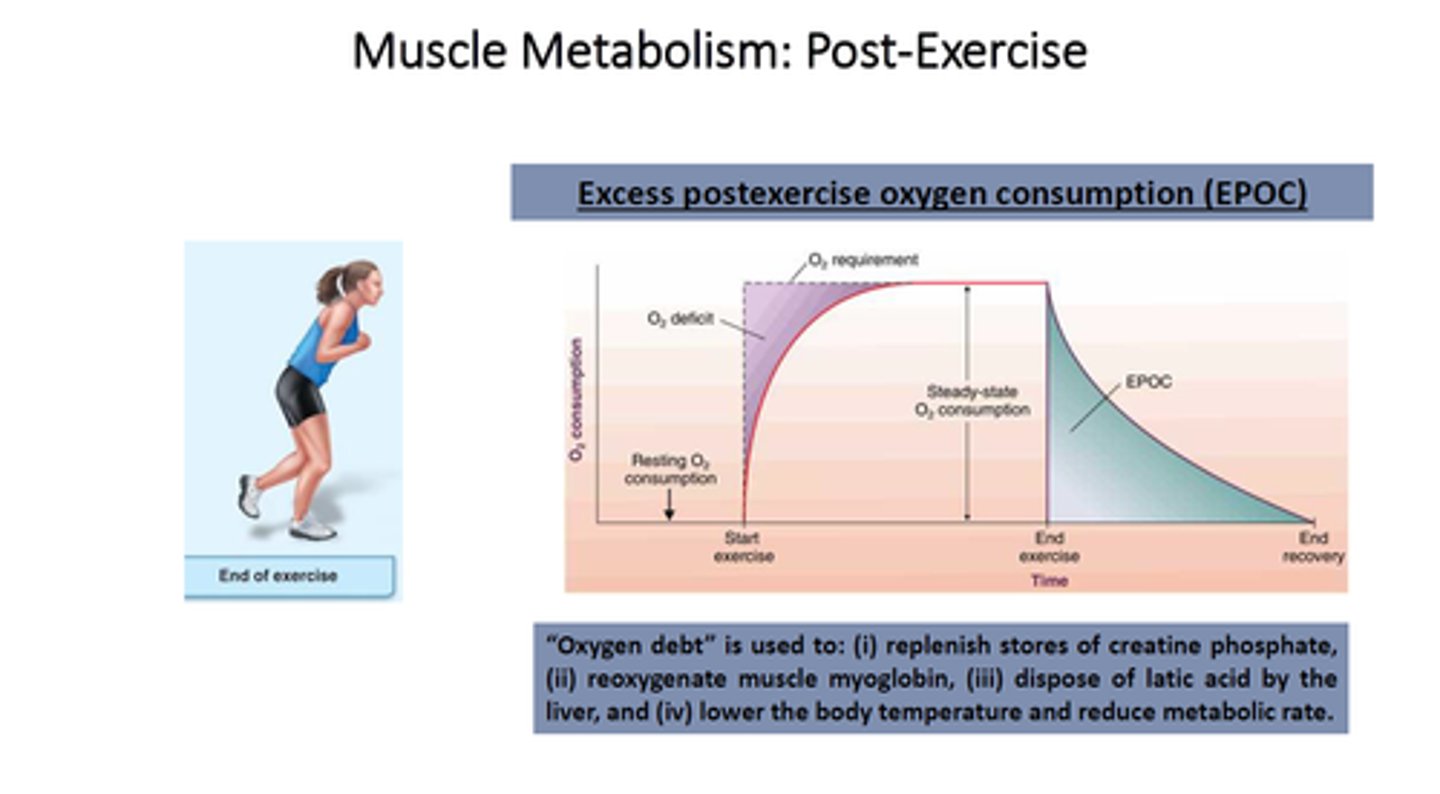
muscle recovery (2 ways)
1) Lactic Acid removal
2) EPOC due to oxygen debt (Excess Post Exercise Oxygen Consumption)
What are the effects of aging on skeletal muscles?
1) Decreased muscle mass
2) Delayed reaction/ response times
3) Reduced stamina
4) Increase needed recovery time
5) Loss of muscle fibers
6) Decreased density of capillaries supplying muscles

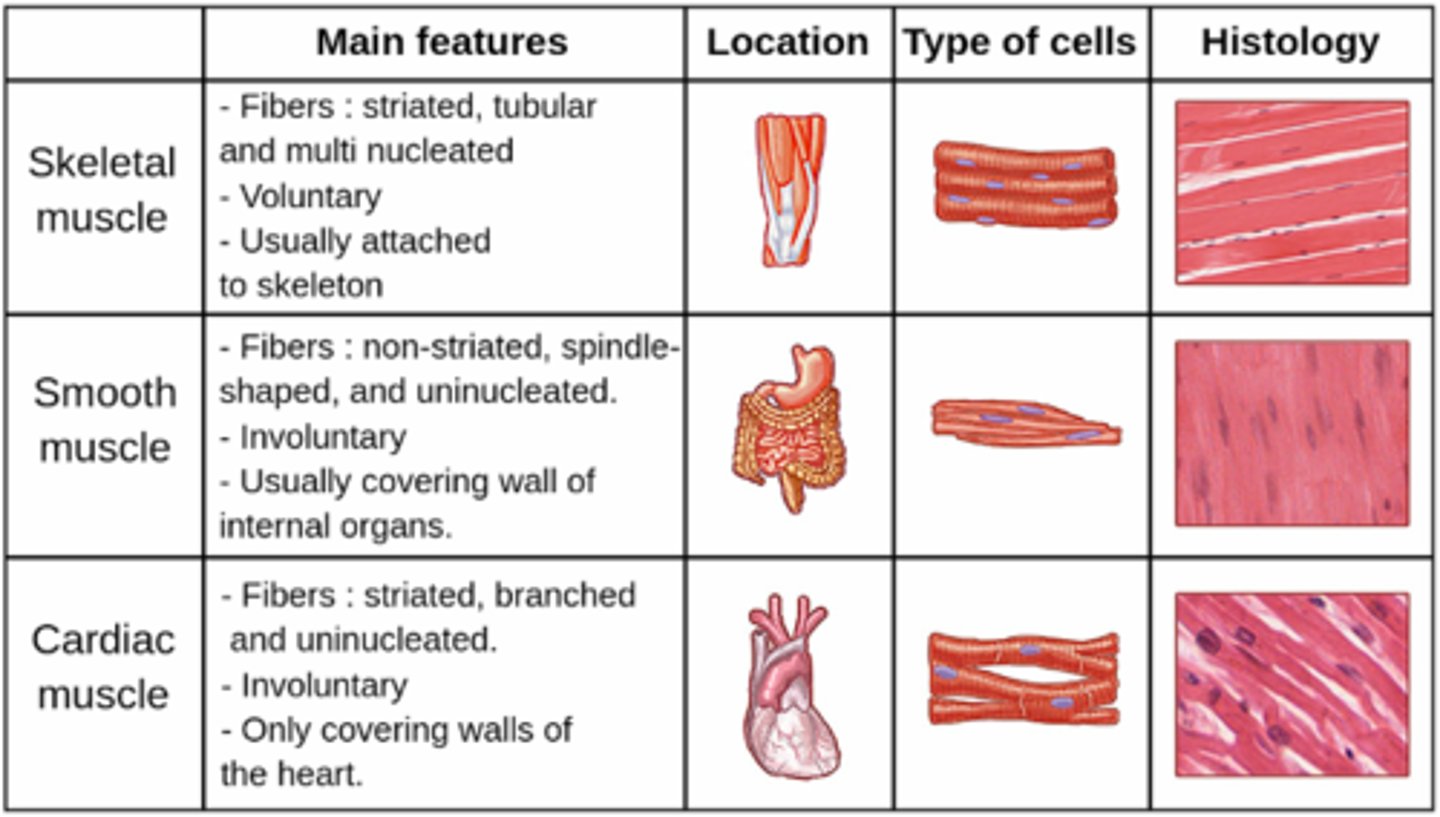
Compare the 3 types of muscle tissue
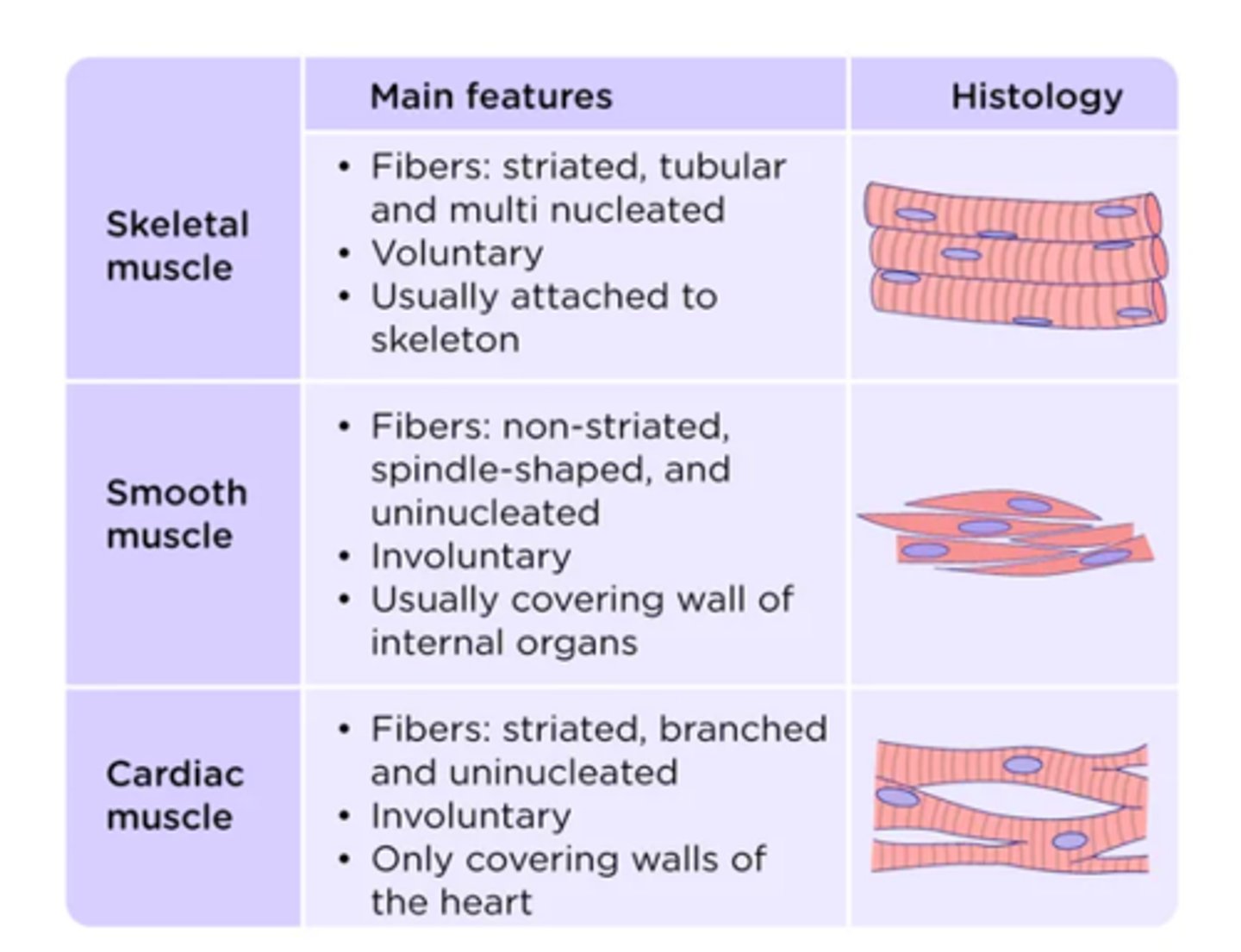
3 types muscle tissue - histology
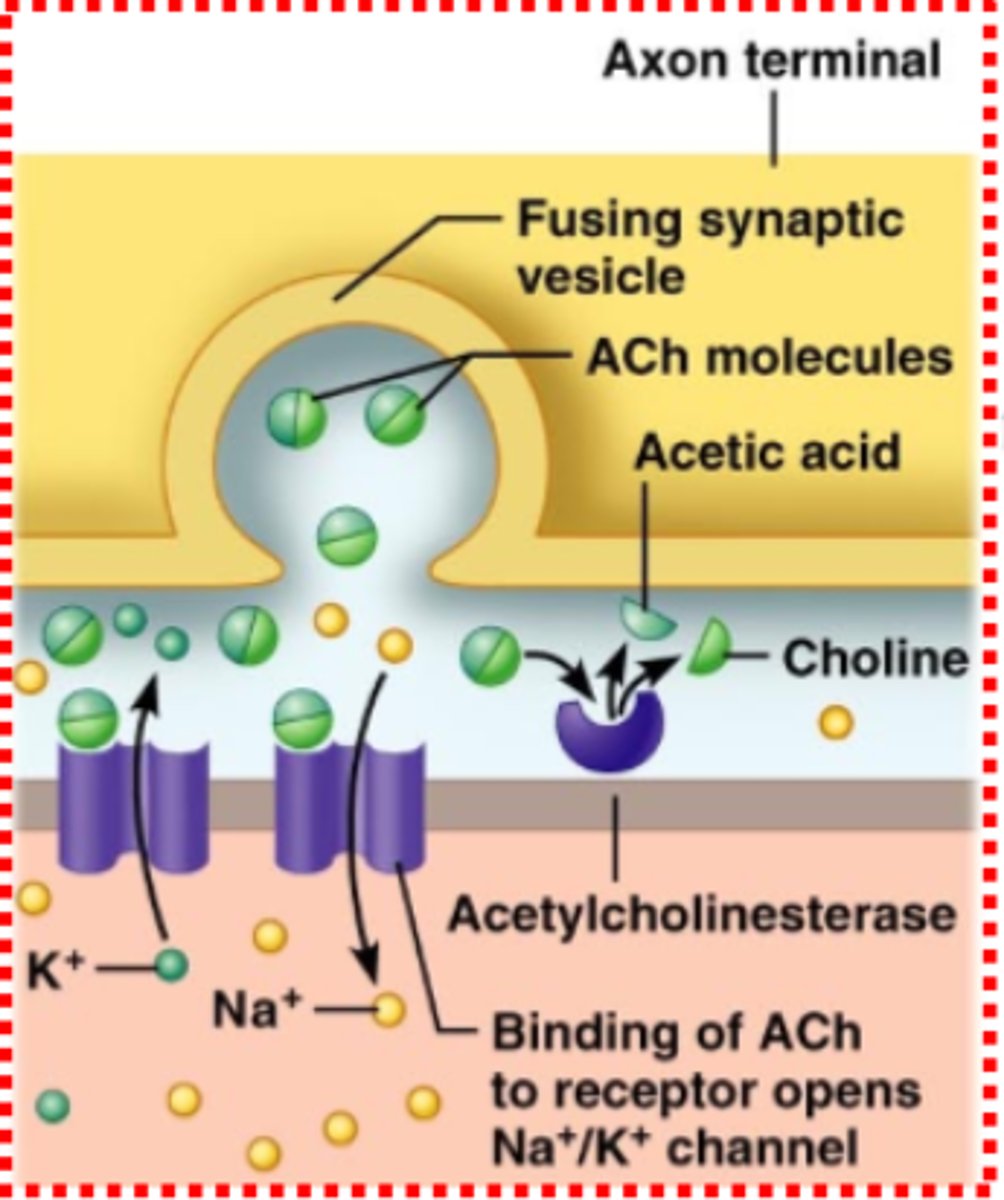
3 ways that acetylcholine is removed from synaptic cleft
1) Broken down by enzyme acetylcholinesterase
2) re-uptake by nerve cell via neurotransmitter surface proteins
3) Diffusion away from the synaptic cleft

How would the loss of acetylcholinesterase from the motor end plate affect skeletal muscle?
It would cause muscles to stay contracted. Sodium channels would stay open.
How does creatine phosphate play a role in providing energy to muscle cells?
It can transfer its phosphate group to ADP. Only for a short time, and only anaerobically.
Which of the following would the motor units have the fewest muscle fibers?
a. muscles that control the eyes
b. postural muscles of the back
c. calf muscles
d. thigh muscles
a. muscles that control the eyes (it is a much smaller muscle)

The type of contraction where the muscle shortens is called ________.
concentric isotonic contraction
Which skeletal muscle fiber type contains the most myoglobin (blood supply)?
slow-twitch muscle fibers
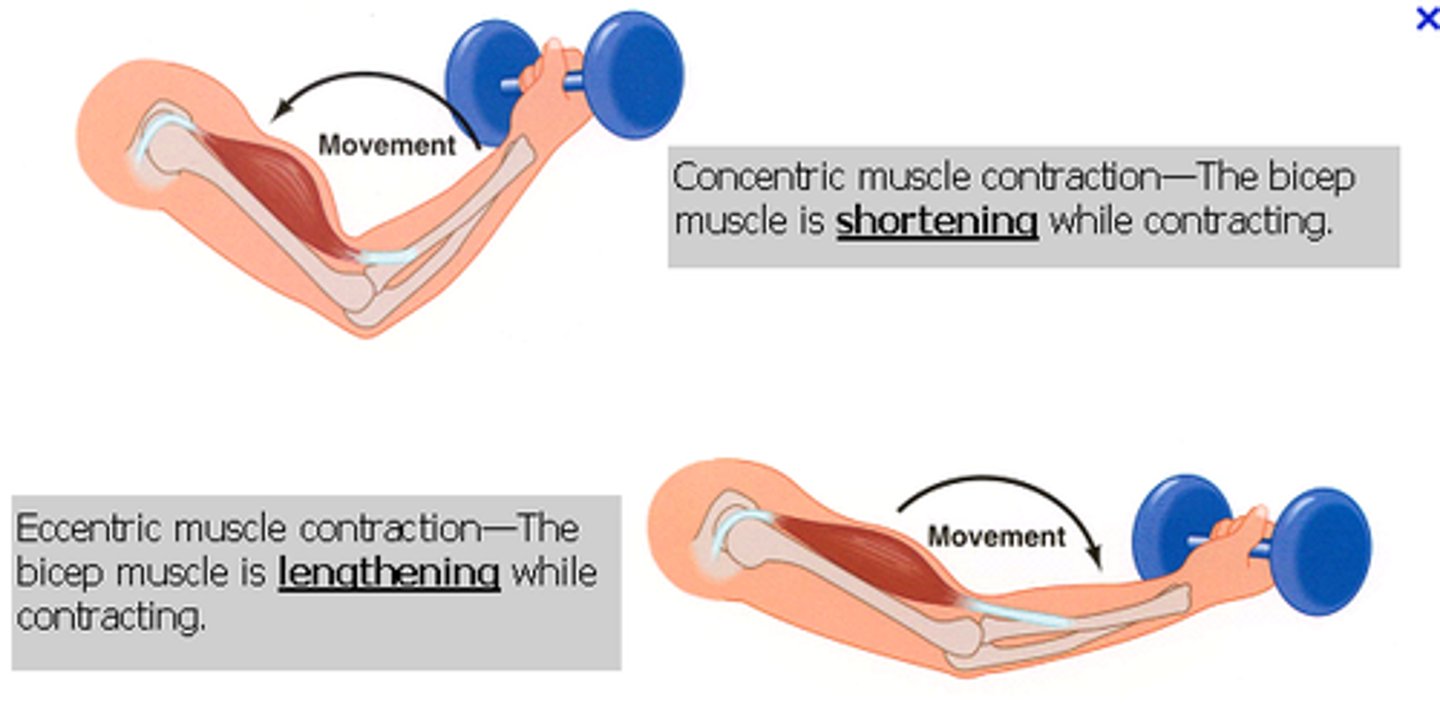
Describe an isotonic eccentric contraction for the biceps brachii.
extending your elbow (lengthening the muscle) and maintaining tension while holding a 5 pound weight
During vigorous exercise, there may be insufficient oxygen available to completely break down pyruvic acid for energy. As a result, the pyruvic acid is converted to ________, causing muscle cramps.
lactic acid
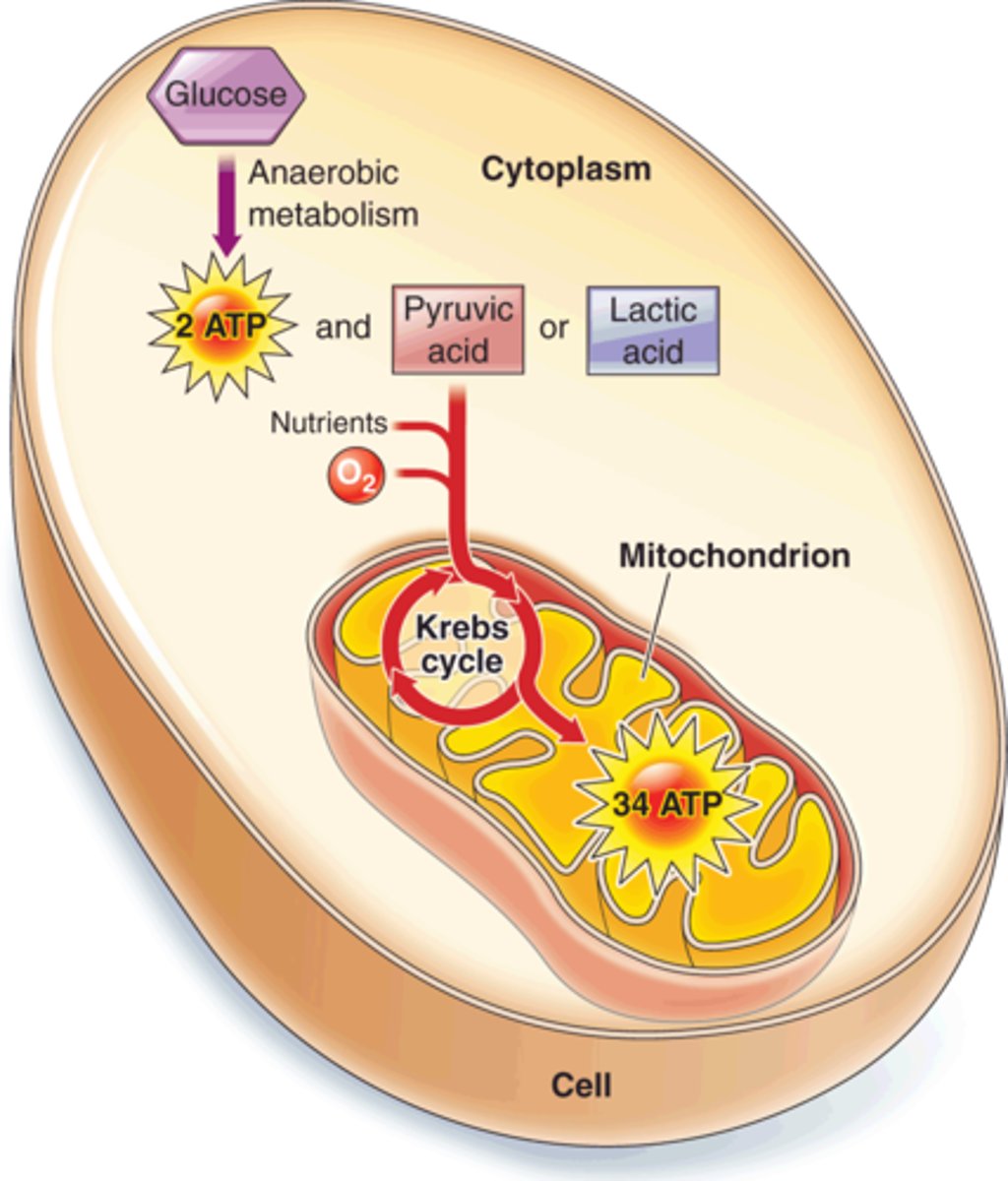
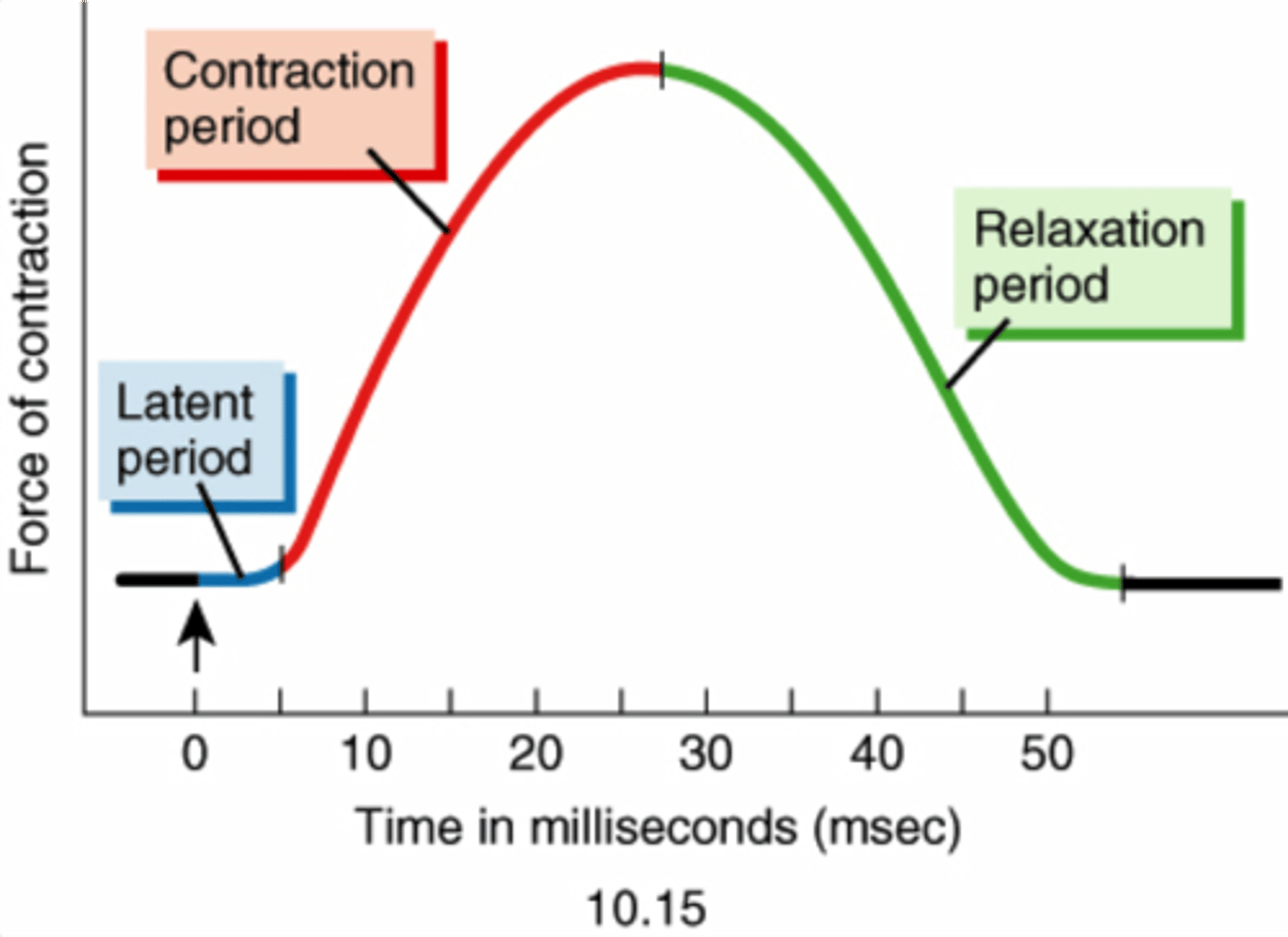
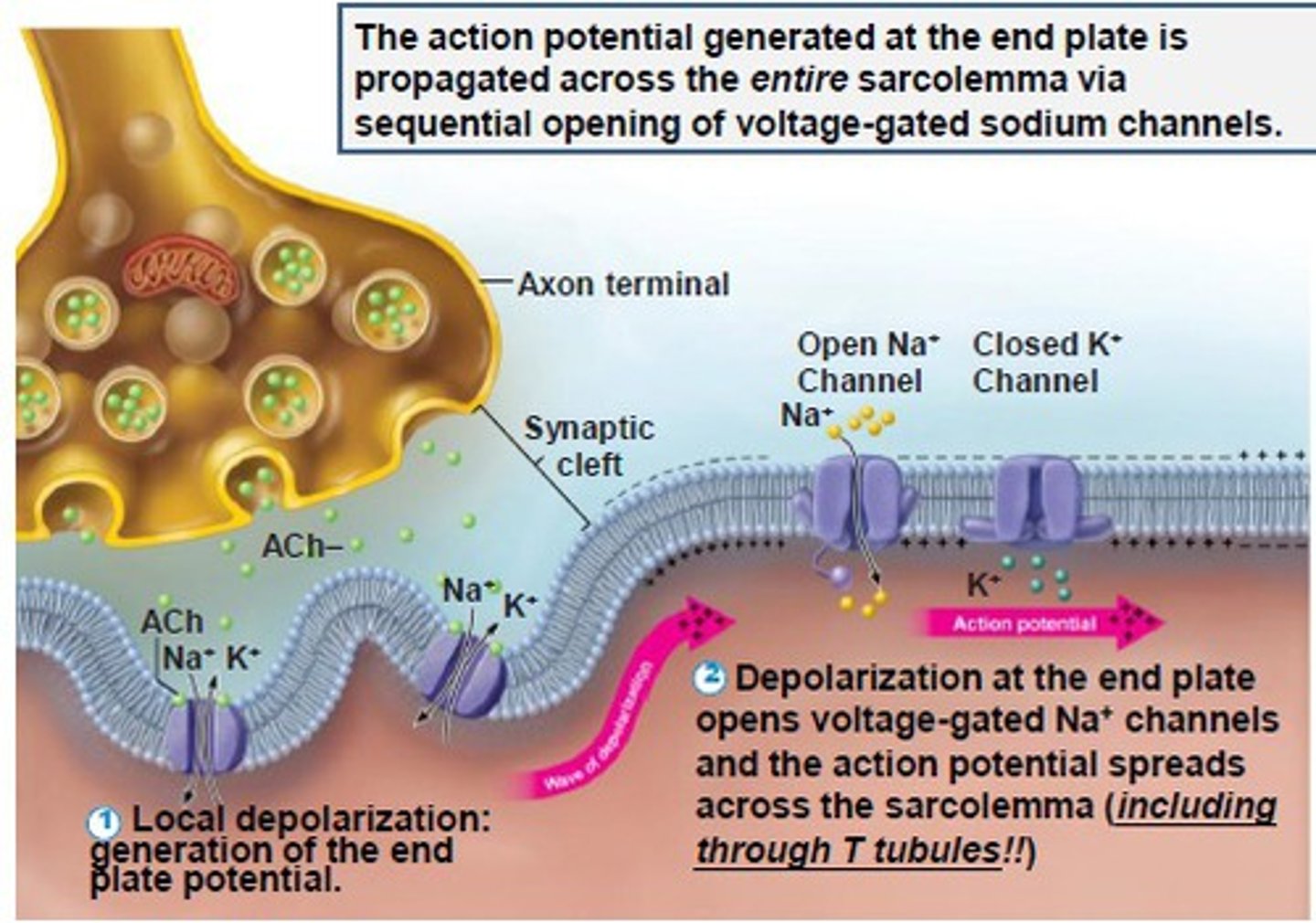
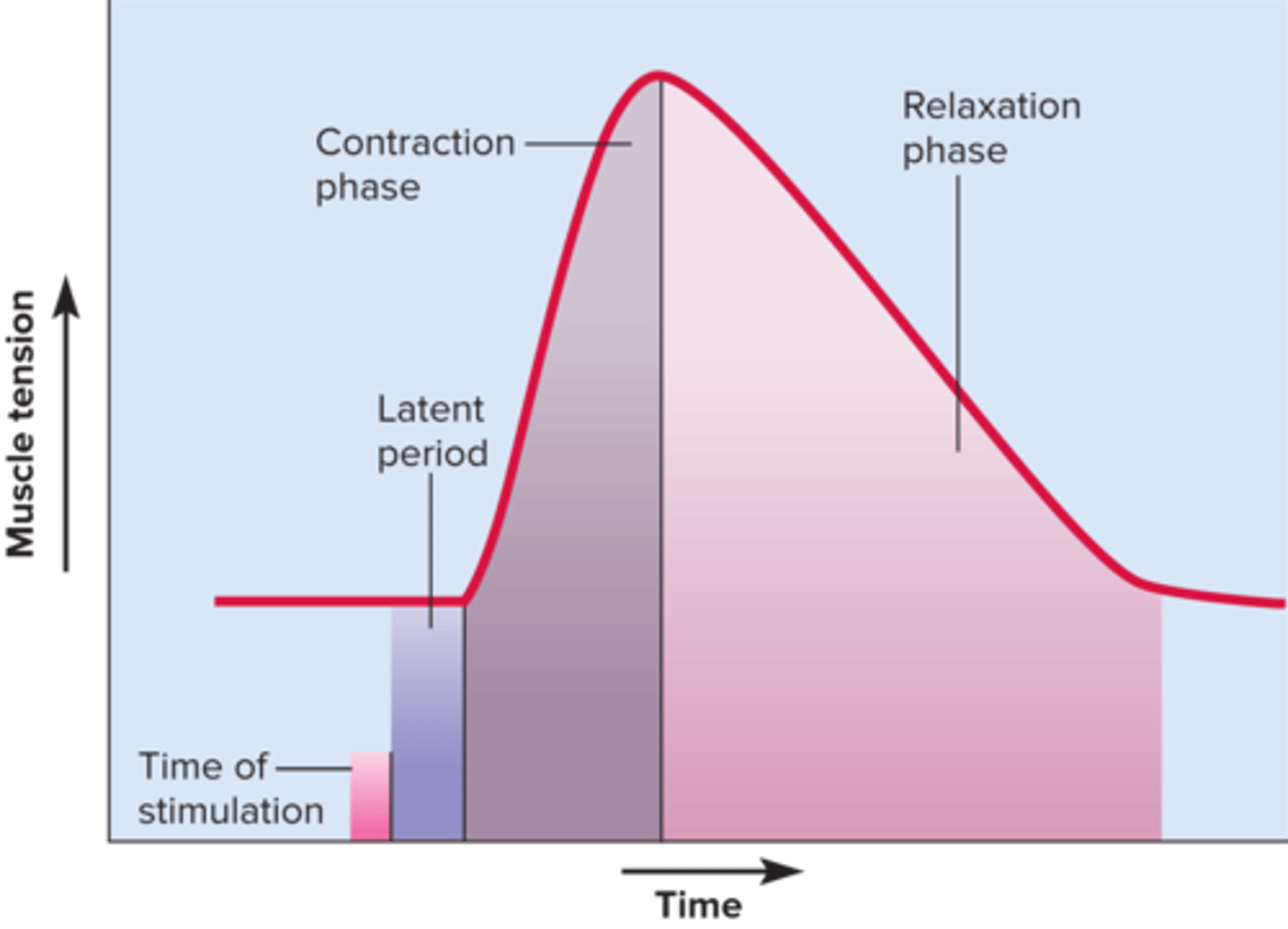
What causes there to be a delay (latent period) in a muscle twitch?
Latent period. Nerve stimulus arrives at NMJ, ACh is released and travels across cleft and binds to receptors on sarcolemma, action potential travels down T-tubules and stimulates release of CA++. That accounts for the brief delay before contraction. Basically everything that happens BEFORE Ca++ binds to troponin
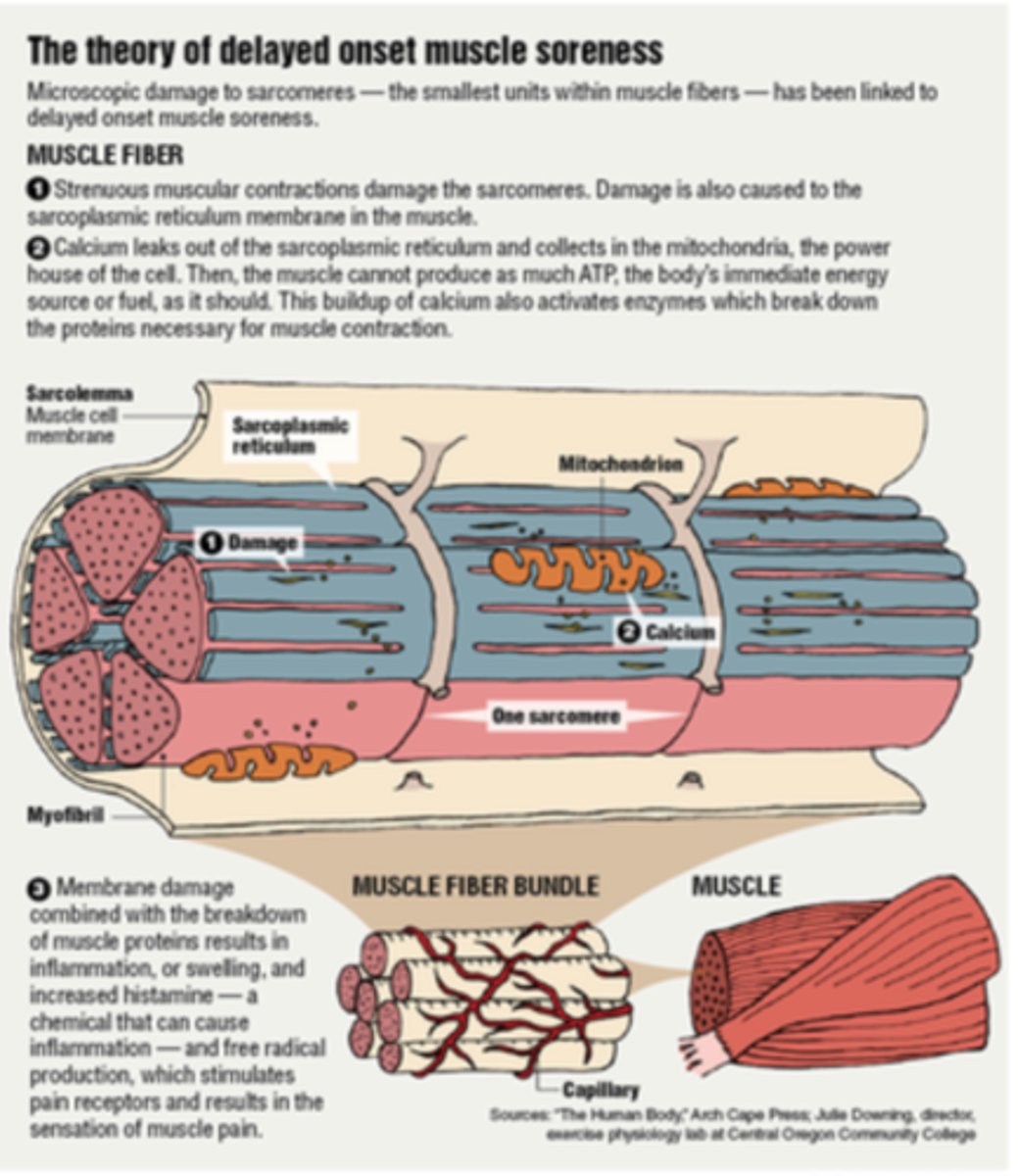
why do we often feel sore a day or two after our workouts?
DOMS (delayed onset muscle soreness)
Oxygen Debt (EPOC)
we breathe hard after exercise due to this --we need to take in the amount of oxygen that we consumed during the anaerobic phase of our exercise (remember, all exercise starts out anaerobically with the Creatine Phosphate pathway)
motor unit
A single motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
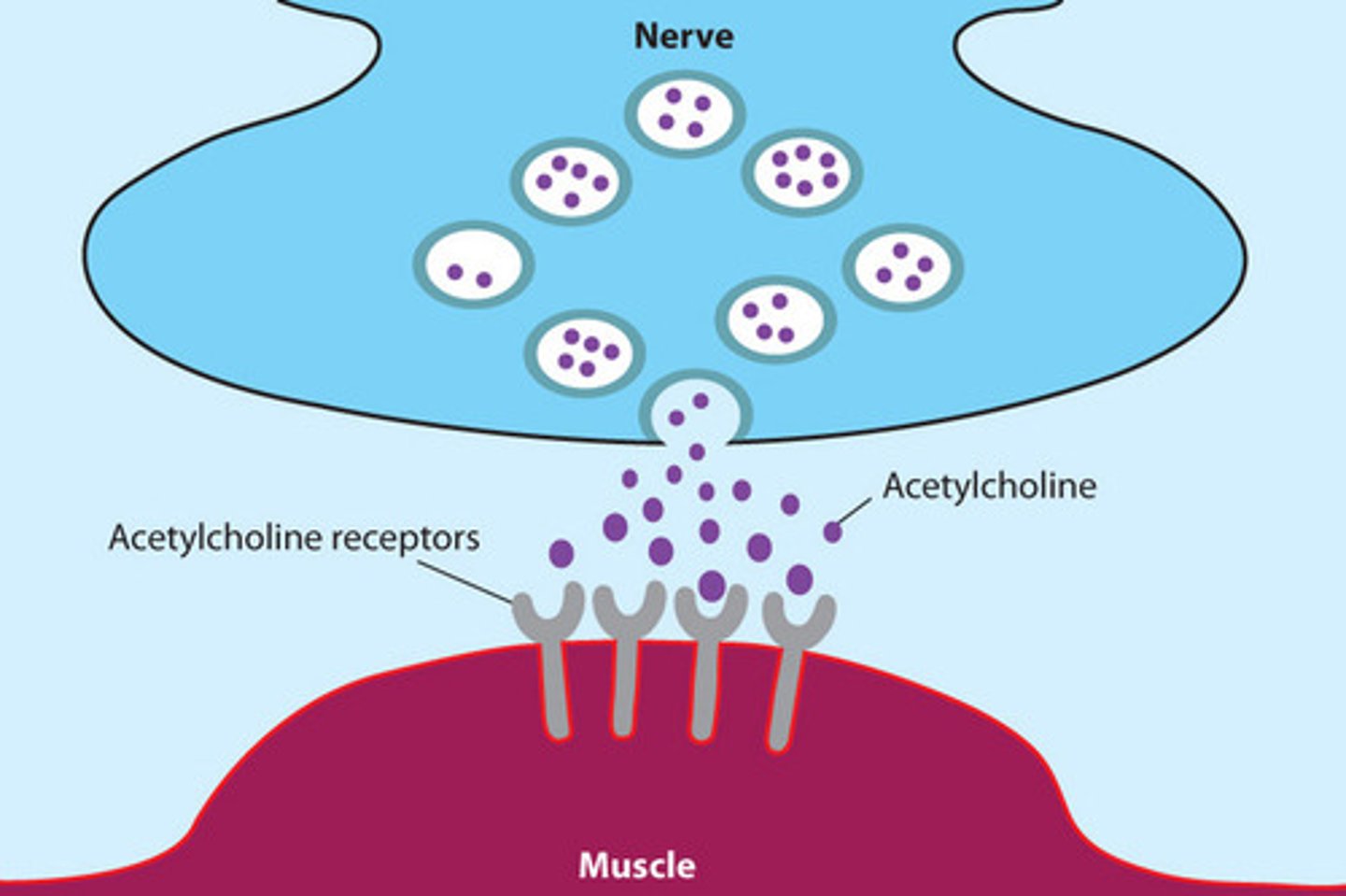
the neurotransmitter that binds to receptors on the motor end plate is _____
ACh (acetylcholine)
When the neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the motor end plate ______ channels open
Na+ (sodium)
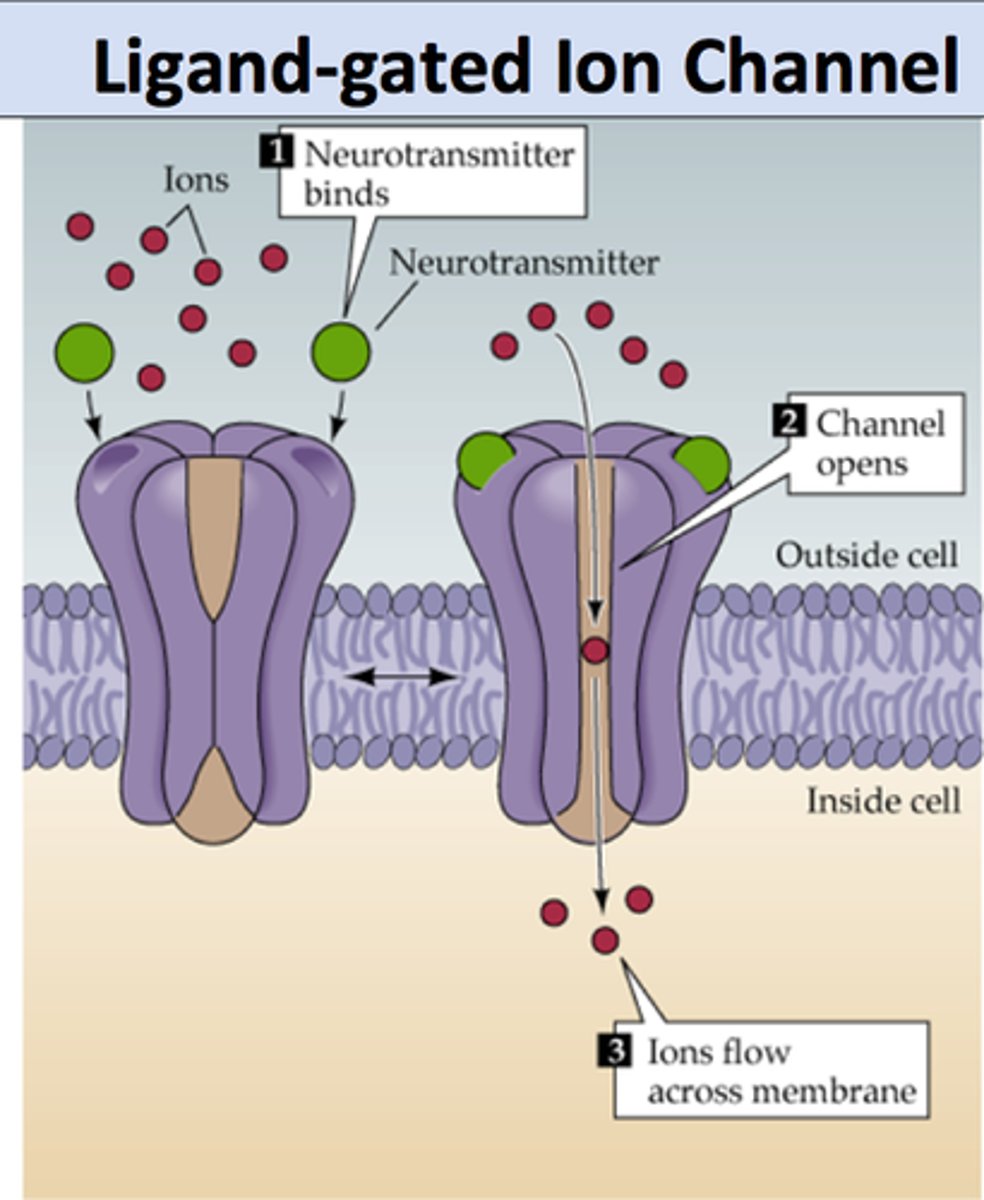
ligand-gated channels
channel that opens when a CHEMICAL (neurotransmitter) attaches
voltage gated channels
open and close in response to changes in membrane potential (electrical impulse)
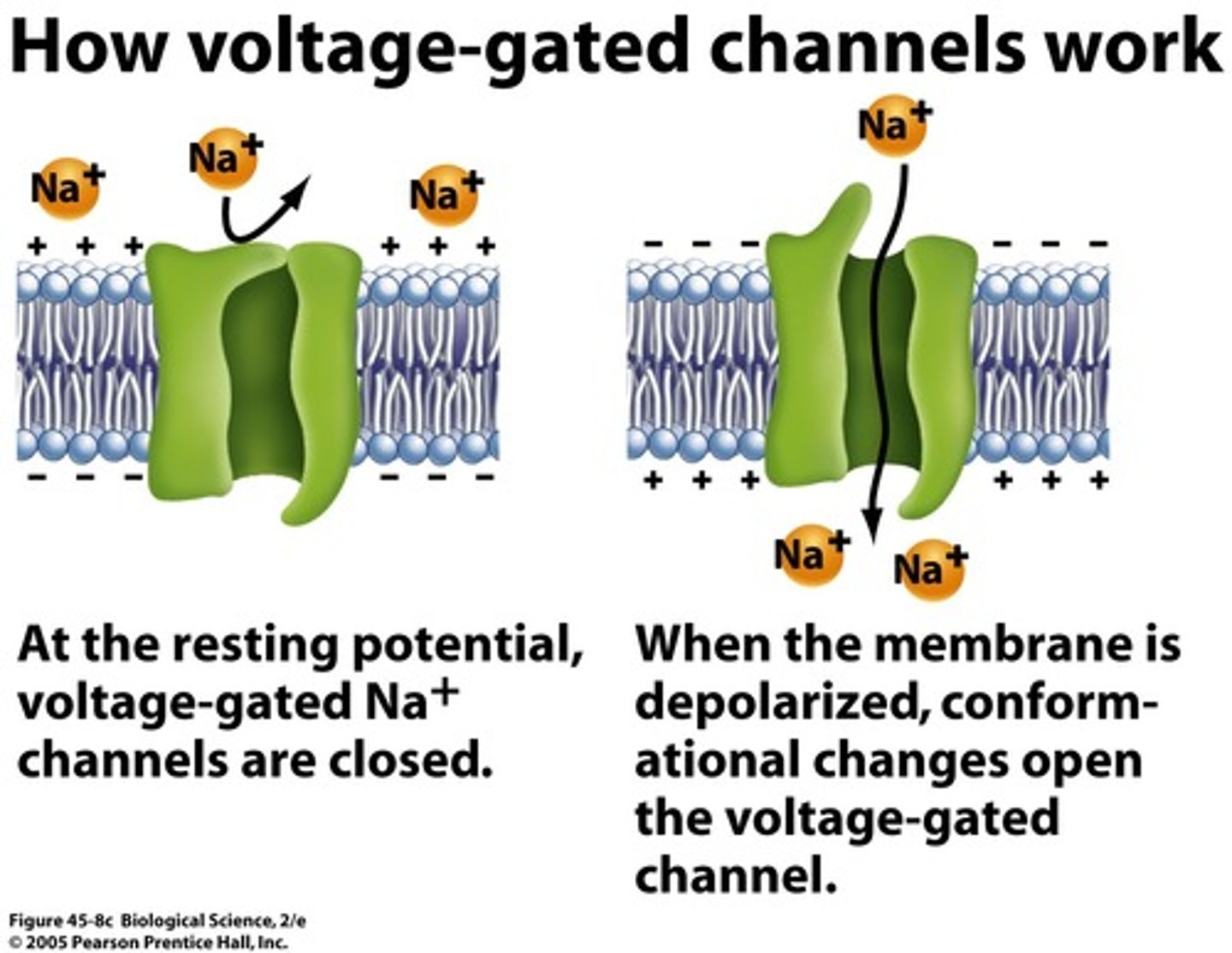
Are the calcium channels in the NERVE terminal boutons voltage-gated or ligand (chemical) -gated?
voltage-gated--they respond to an electrical stimulus (depolarization)
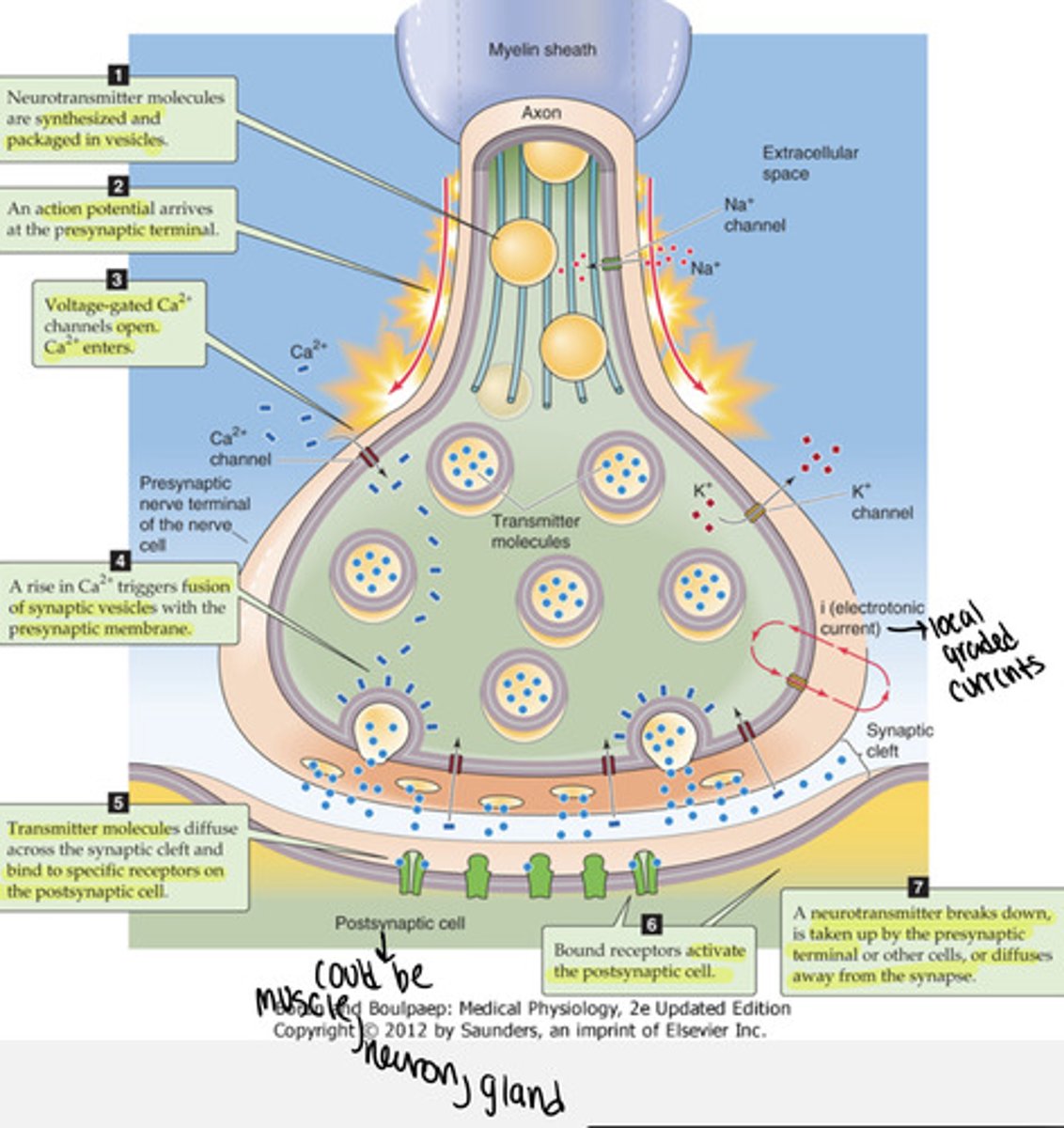
The layer of connective tissue that surrounds an entire muscle is termed _____.
epimysium
How would the loss of acetylcholinesterase from the motor end plate affect skeletal muscle?
the muscle would stay excited because ACh would remain in the cleft and keep binding to ACh receptors
Which of the following are stored in the sarcoplasm as an available store of energy?
glycogen crystals
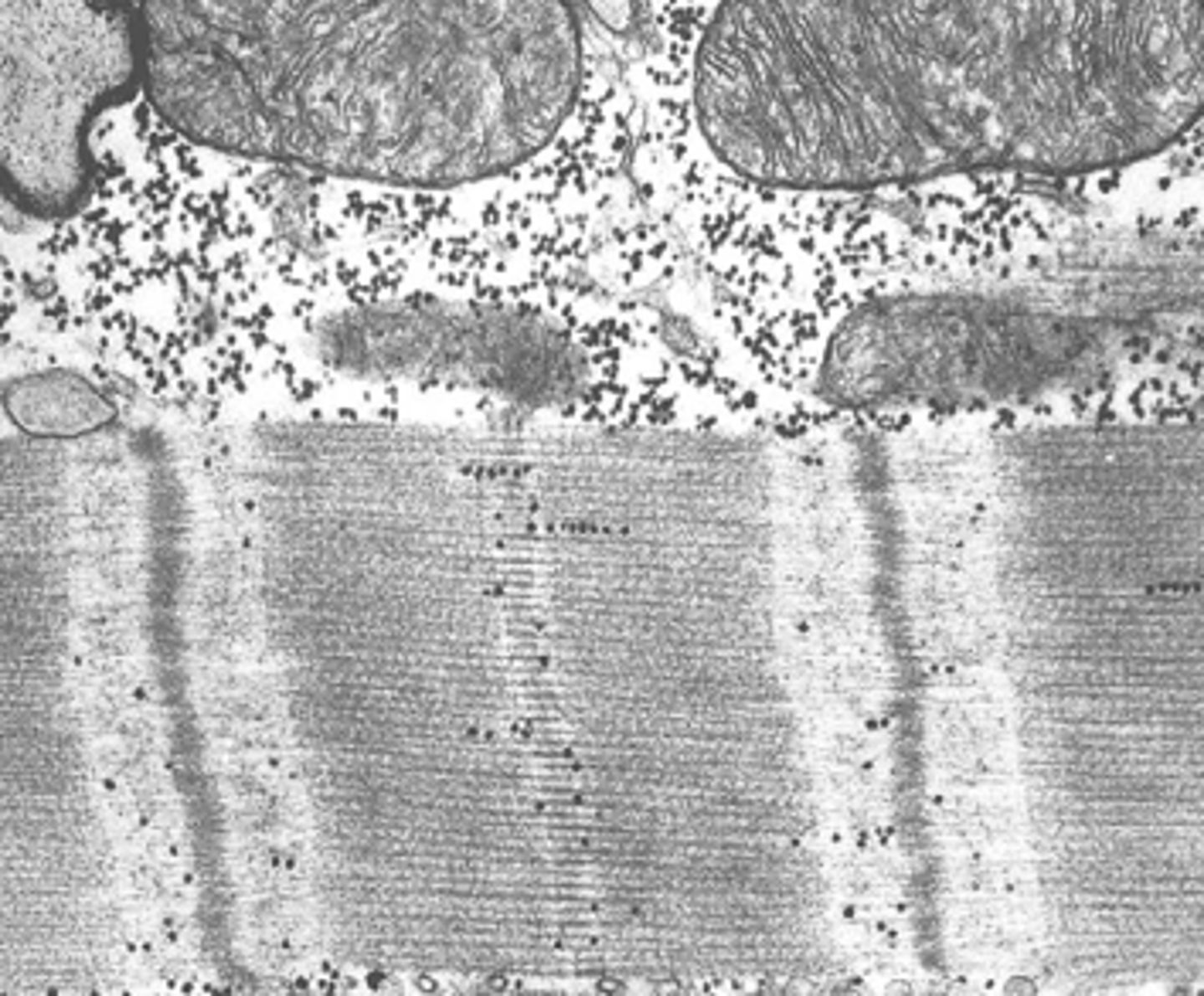

recruitment
the activation of additional motor units to increase muscle strength and force of contraction
Which skeletal muscle fiber type contains the most myoglobin (blood supply)?
slow-twitch muscle fibers
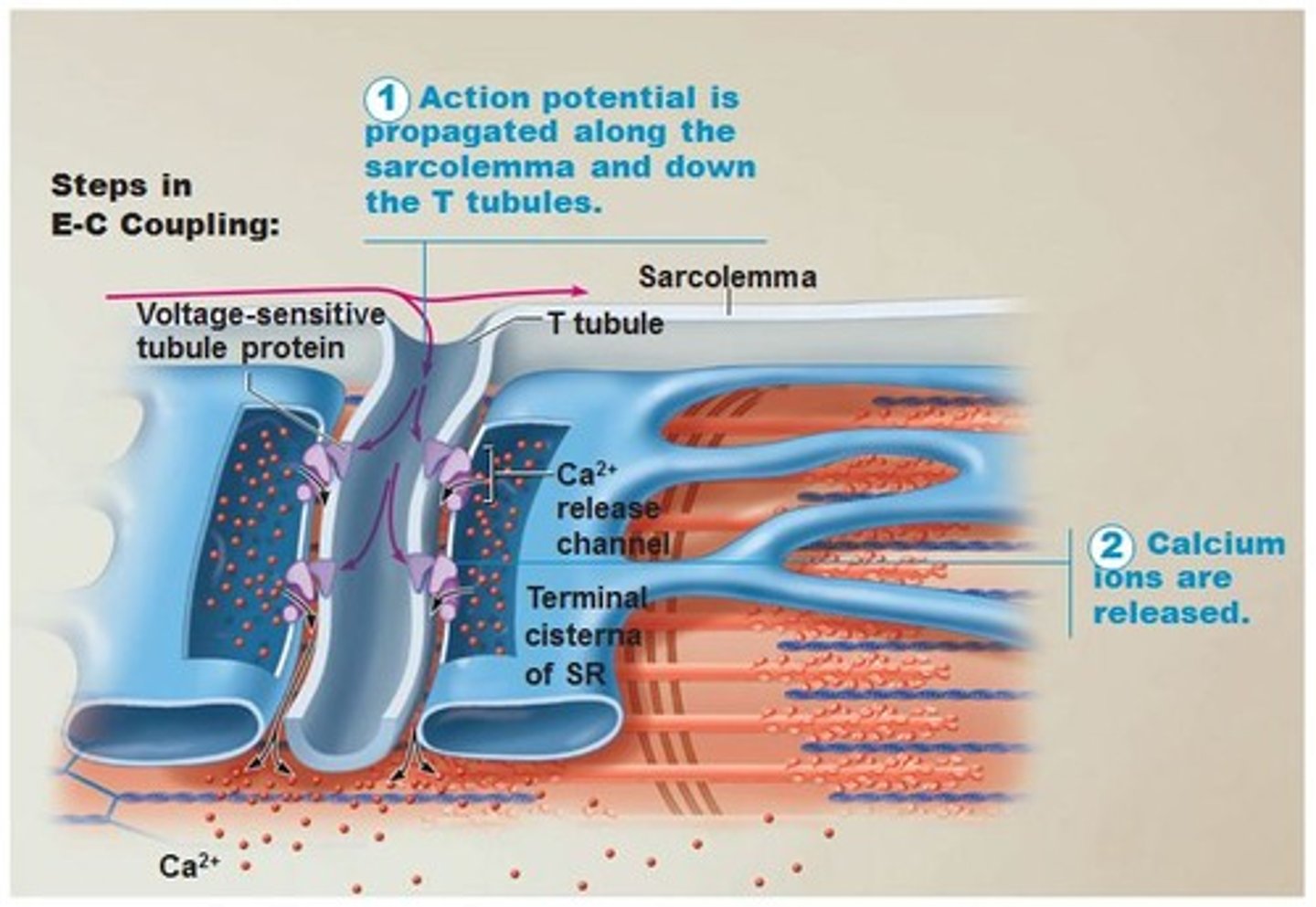
Where does excitation-contraction coupling occur?
triads -- when the action potential travels down the T-tubules and stimulates the terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
myogram
a chart of the timing and strength of a muscle's contraction
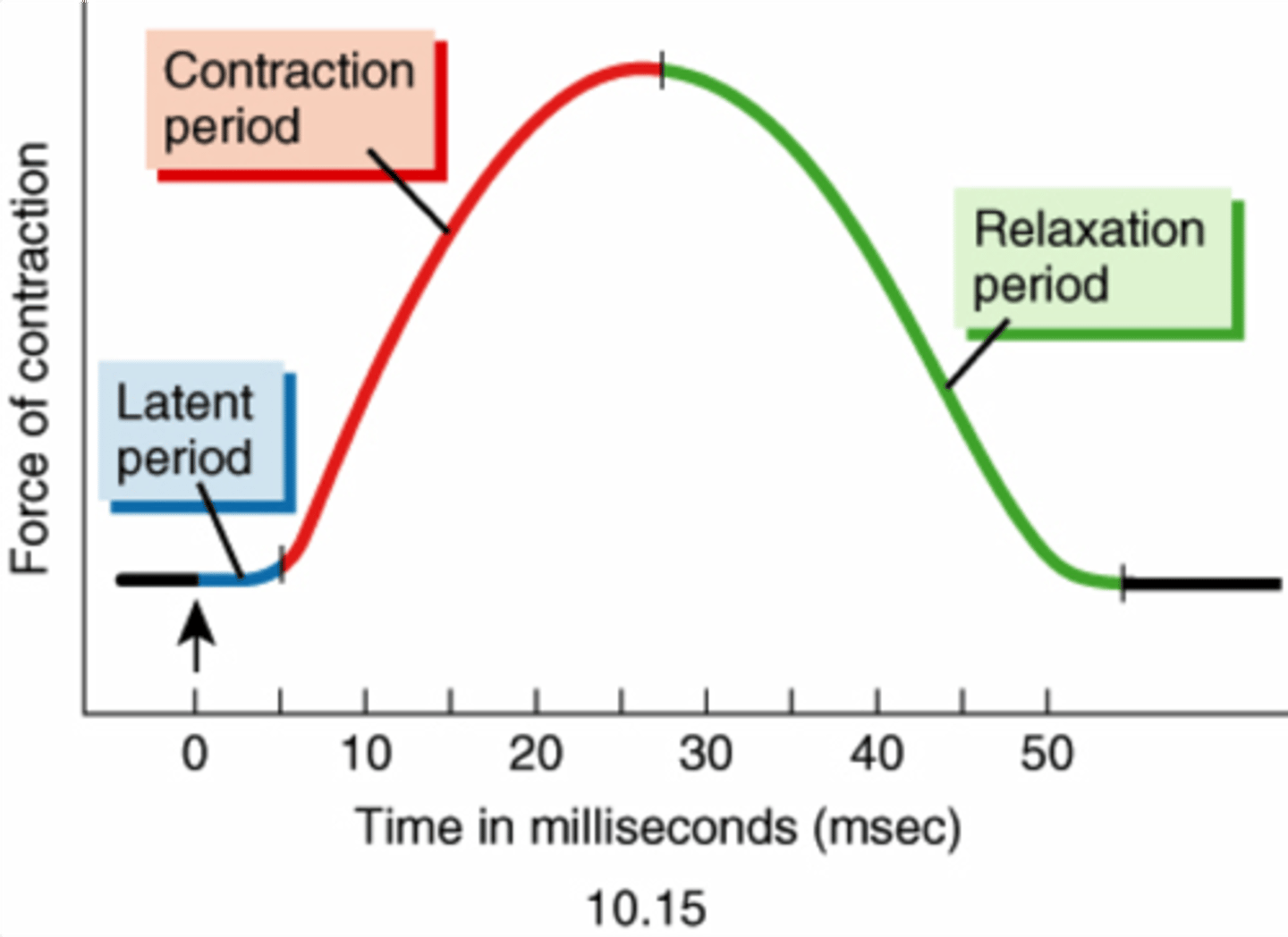
myogram - read and explain the various parts of the graph
What is happening during each phase in terms of the 10 steps?
What does wave summation look like on a graph?
What does treppe look like on a graph?
What does complete tetanus look like on a graph?
What does incomplete tetanus look like on a graph?
What is the difference between wave summation and treppe?
Treppe has complete relaxation between contractions; wave summation does not (the muscle is stimulated again before relaxation can occur).
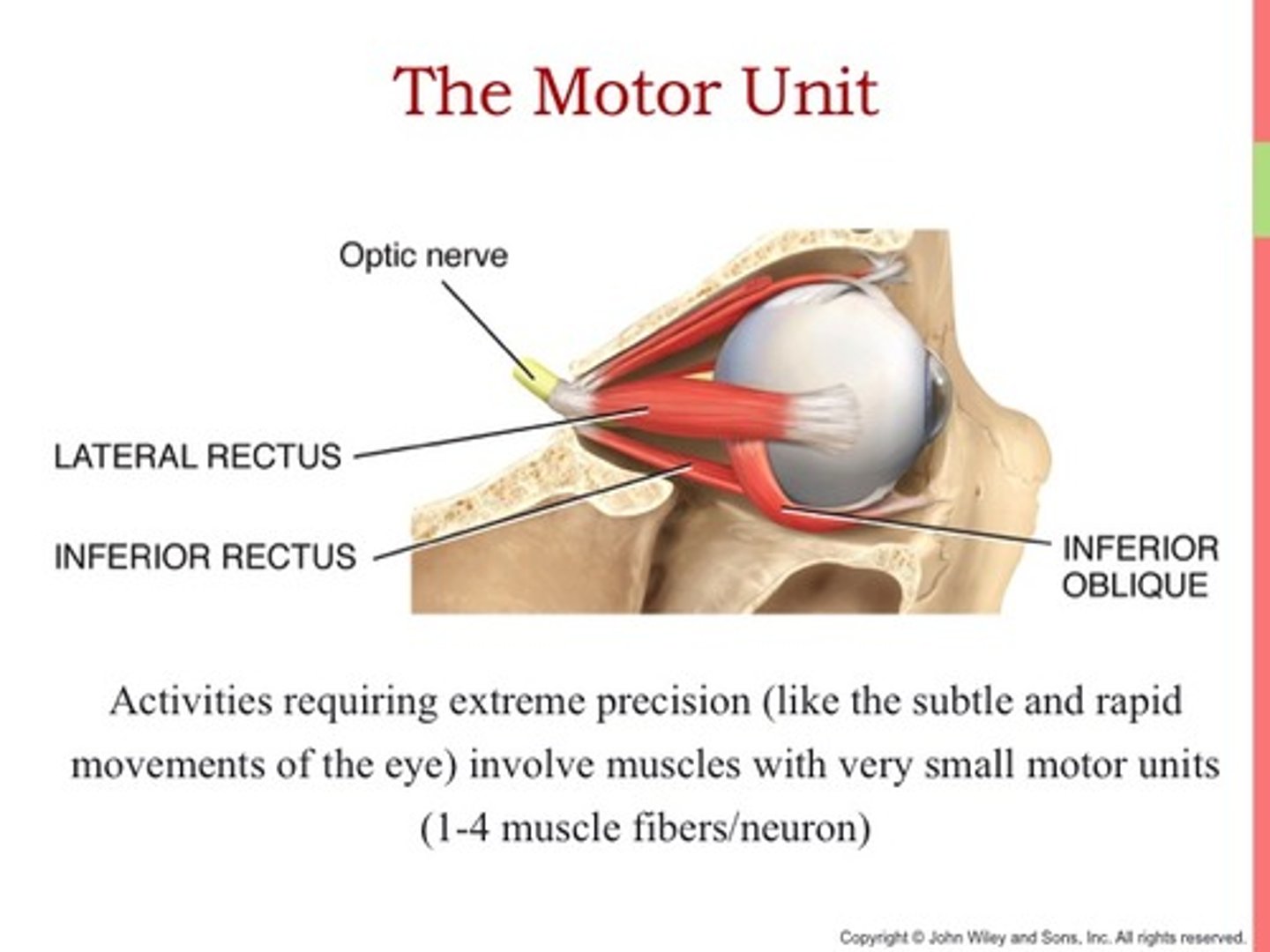
Which area of the body might have very small motor units consisting of only a few muscle fibers?
eye, middle ear
Why is the tension at the end of the myogram zero (0)?
Most calcium has been taken up into the sarcoplasmic reticulum via active transport with SERCA (ATPase).
sarcomere length-tension relationship
The optimum length for producing maximum tension when the muscle contracts- be able to read the graph and answer questions (as you did in your assignment)