EES 152: Ecology Exam 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
blue
Within PAR. what color light is used most by photosynthesis?
45%
What percentage does PAR make up of all solar radiation?
photon flux density
What is PAR measured in?
ATP and NADPH
energy from these two molecules is used to build organic molecules, using CO2 as a carbon source
carbon fixation
the process in which inorganic carbon, usually in the form of CO2, is converted into organic molecules, including carbohydrates
C3, C4, and CAM
What are the three ways photosynthesis is done?
mesophyll cells
Where do all C3 reactions take place?
rubisco
In C3 plants, what enzyme is used to initially fix CO2?
open; large
Do C3 plants need to keep their stomata open or closed? Do they have a small or large amount of stomata?
mesophyll and bundle sheath cells
What two different cells are involved or related to C4 plants?
pepco
In C4 plants, what enzyme is used to initially fix CO2?
less
Compared to C3 plants, do more or less stomata need to be open to bring in the same number of CO2 molecules in C4 plants?
lacking in C3 plants; present in C4 plants
Do the bundle sheath cells in C3 plants have chloroplasts? What about in C4 plants?
CAM plants
plants where stomata close during the day and open at night
lower temperatures reduce the vapor pressure deficit
Why do CAM plants fix carbon at night?
mesophyll, PEP
All reactions in CAM plants occur in ______ cells, like C3 plants, but CO2 is combined initially with _______, like C4.
large vacuoles in mesophyll cells
CAM plant leaves have what?
pepco
In CAM plants, what enzyme is used to initially fix CO2?
C3 plants are more competitive; C4 inefficient at low light intensities, ineffective as shade plants, takes more energy
Why aren’t C4 plants more abundant than C3 plants?
shaded regions: C4 does poorly (less light); C3 does well; opposite for sunny habitats
Plants that occur in shaded habitats versus a plant that occurs in open, sunny habitats. Difference between a C4 and C3 species in these conditions?
the rate is limited
The rate at which photosynthetic organisms can take in energy always levels off with increasing light. What does this mean?
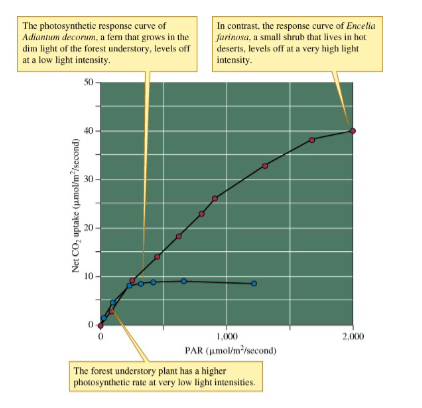
true
TRUE OR FALSE: The current rise in CO2 has potential direct effects on energy acquisition and nutrients
heterotrophs
organisms that obtain their energy by capturing organic molecules manufactured by other organisms
93-97%
How much of biomass is made up of CHONP?
nitrogen
Which nutrient is particularly limiting?
carbon
What other element do ecologists use in ratio with nitrogen?
food
C:N ratio describes the quality of what to consumers?
describes quality of food (plants have high C:N; animals, fungi, bacteria have low C:N)
herbivores need to eat more plants to get enough N and energy; N is used to make DNA, RNA, proteins
Why does the C:N ratio of a food source matter?
toxins and chemical defenses (in tropical plants: mustard oil, capsaicin), symbiosis with ants and trees
What adaptaions have plants developed in response to herbivory?
cellulose; it is not digestible by any animal
What defense do ALL plants have against herbivores, and why?
nitrification
the oxidation of ammonia (NH4) to nitrite (NO2-) to nitrate (NO3-)
camouflage, spines and shells, repellents and poisons, behavior
What defenses have prey evolved in response to predation?
Mullerian mimicry
two or more toxic or harmful species evolve to resemble each other’s warning signals, such as the same pattern or bright colors
Batesian mimicry
a harmless species resembles a harmful one
type I functional response
feeding increases linearly with food supply up to a point and then levels off abruptly; only animals that need little to no time to process food
type II functional response
feeding increases linearly at low densities, rises more slowly at intermediate densities, and then levels off at high densities
time spent finding food
At low food density, feeding rate is limited by what?
time spent finding and handling food
At mid-food-density, feeding rate is limited by what?
time spent handling food
At high food denisty, feeding rate is limited by what?
type III functional response
S-shaped curve; low densities may afford prey more protected hiding spaces
type II
What type functional response is most common?
optimal foraging theory
an ecological concept that predicts animals will evolve behaviors to maximize their fitness by optimizing their foraging decisions, such as maximizing net energy gain or efficiency
principle of allocation
a principle that states an organism has a limited quantity of resources that it can use for life processes
greater energy expenditure
High mortality rate; reproduction at earlier age. What does this mean in terms of energy expenditure?
polygamy
meaning having many mates
polyandry
one female to several mates
polygyny
one male to several females
fecundity
the number of eggs produced per female (physical ability)
distinct differences that results due to competition for mates
Define sexual selection.
intrasexual selection
individuals of one sex compete among themselves for mates (larger size, teeth, antlers)
intersexual selection
members of one sex consistently choose mates on the basis of a particular trait
elaborate, sexually selected displays or adornments act as handicaps that demonstrate high fitness of the individual (a sign of health that is difficult for a male to fake)
Define the handicap hypothesis
individuals in a group usually spend less time looking for predators, but more time moving to find food
What are the advantages of group living and cooperation? Disadvantages?
inclusive fitness
an organism’s overall fitness determined by its own reproductive success PLUS the reproduction of the individuals which it shares genes with
kin selection
under certain conditions, an organism can increase its inclusive fitness by helping its relatives, which it shares its genes with
age at maturity
age at first reproduction
parity
number of reproductive events
principle of allocation
if organisms use energy for one function such as growth, the amount of energy available for other functions is reduced
trade-offs between functions such as number and size of offspring
What does the principle of allocation lead to?
areas of high disturbance
Small plants producing large number of small seeds appear to have an advantage in what areas?
surviving environmental hazards
Plants producing large seeds are constrained to producing fewer seedlings, but are more capable of what?
semelparous
organisms that breed only once during their lifetime; allocate stored resources to reproduction, then die
iteroparous
organisms that breed multiple times during their lfiespan
r-selection
rapid development, early reproduction; semelparity, small body size, many small offspring
k-selection
slow development, late reproduction; iteroparity, large body size; few, large offspring
intensity of disturbance (process limiting plants by destroying biomass); intensity of stress (external constraints limiting rate of growth
What variables are important in Grime’s life history classification of plants?
low disturbance; high stress
stress tolerators
deserts, tundra, alpine meadows, bogs; grow slowly
Where do stress tolerators grow? How do they grow?
low disturbance; low stress
competitors
rapidly; compete with others for resources
How do competitors grow?
high disturbance; low stress
ruderals
colonize disturbed habitats; rapid growth; early maturation and easily dispersed seeds
How do ruderals grow?
metapopulation
a group of subpopulations living on separate patches connected by the exchange of individuals or genetic flow
N=nM/x (where M is individuals in the initial sample, n is the individuals in the second sample, and x is the number of MARKED individuals in the second sample)
What is the formula for population size given the mark and recapture method?
declines
Population density (declines or increases) with increasing organisms size?
type I survivorship curve
low mortality among young but high mortality among older individuals
type II survivorship curve
fairly constant probability of mortality throughout life
type III survivorship curve
high mortality among young but low mortality among older individuals
dispersion
describes the spacing of individuals within a population with respect to one another
even spacing
type of spacing that may arise from direct interactions among individuals; direct competition
clumped distribution
type of spacing that may arise from tendency of progeny to remain near parents or clumped distribution of resources; individuals in discrete groups
random distribution
type of spacing that may arise from neutral interactions between individuals and the local environment
males are subject to sexual selection and they aim for those traits to evolve
Why do males tend to get colorful or extravagant in their morphology?