Comprehensive MKT 100 Final Road Map: Segmentation, Positioning, and Strategies
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is Needs-Based Segmentation?
Grouping customers by what they need or the benefits they care about.
What does Segment Identification involve?
Adding descriptive characteristics to each segment to understand who they are.
What are the bases for Segment Identification?
Behavior, demographics, geography, and psychographics.
What is Segment Attractiveness?
Evaluating if a segment is worth targeting based on criteria like size and competition.
How does Segment Profitability differ from Attractiveness?
Profitability determines how much money can realistically be made from a segment.
What is Segment Positioning?
Creating a value proposition and brand image tailored to a specific segment.
What is the Marketing Mix Strategy?
Building the Product, Price, Promotion, Place strategy based on chosen positioning.
What is Concentrated Targeting?
Focusing all resources on one narrowly defined segment.
What is Mass Marketing?
Treating the market as one big group with no customization.
What is Micromarketing?
Marketing at the individual level with data-driven personalization.
What is Multi-Segment Marketing?
Targeting multiple segments, each with its own branding or marketing mix.
What is Niche Marketing?
Targeting an extremely specific subset within a segment.
What is Behavioral Segmentation?
Focusing on how customers behave toward the product.
What is Demographic Segmentation?
Focusing on measurable descriptors like age, income, and gender.
What is Geographic Segmentation?
Focusing on where customers live, such as region or climate.
What is Psychographic Segmentation?
Focusing on internal factors like values, lifestyles, and attitudes.
What is Value-Based Positioning?
Defining the brand around the benefits customers receive for what they give up.
What is Attribute Positioning?
Focusing on a specific feature or function of a product.
What is Lifestyle Positioning?
Aligning the brand with a way of living or identity.
What is Emotional Positioning?
Using feelings instead of features to define a brand.
What is Repositioning?
Changing how a brand wants to be perceived due to competition or cultural shifts.
What is the purpose of Segment Profitability?
To determine if a segment will generate profit.
What are common criteria for Segment Attractiveness?
Size, growth potential, accessibility, competition, and profitability.
What is an example of Behavioral Segmentation?
Customers who only buy coffee on weekends.
What is an example of Demographic Segmentation?
A campaign targeting seniors living on a fixed income.
What is an example of Geographic Segmentation?
A winter clothing brand targeting customers in cold climates.
What is an example of Psychographic Segmentation?
Marketing yoga equipment to wellness-focused consumers.
What are the five types of positioning?
Attribute, Value-based, Lifestyle, Emotional, Repositioning
What percentage of users are classified as Innovators in the Adoption Curve?
2.5%
What characterizes Early Adopters in the Adoption Curve?
Influencers who adopt early after some proof of concept and are looked to for guidance.
What is the main goal during the Introduction Stage of the Product Life Cycle?
Build awareness.
What happens during the Growth Stage of the Product Life Cycle?
Rapid sales increase and many new competitors enter the market.
What is the goal during the Maturity Stage of the Product Life Cycle?
Defend your position.
What characterizes the Decline Stage of the Product Life Cycle?
Falling sales and outdated technology.
What are Convenience Products?
Products bought frequently with little effort, such as gum and soda.
What defines Shopping Products?
Products that require comparison based on price, features, and style.
What are Specialty Products?
Products with strong preference for one brand or model, like luxury watches.
What are Unsought Products?
Products that consumers don't normally think of or actively avoid, like life insurance.
What does Product Line Depth refer to?
The number of versions or variations within one product line.
What does Product Line Breadth refer to?
The number of different product lines a company offers.
What is Intangibility in services?
You can't touch or physically examine a service before buying it.
What does Variability in services mean?
Service quality changes depending on who, when, where, and how busy the provider is.
What is Inseparability in services?
Services are produced and consumed at the same time.
What does Perishability in services indicate?
Services cannot be stored, saved, or inventoried.
What is the Knowledge Gap in the Service Gap Model?
The company doesn't correctly understand what customers expect.
What is the Standards Gap in the Service Gap Model?
The company understands customer expectations but sets poor service standards.
What is the Delivery Gap in the Service Gap Model?
Employees fail to meet the company's service standards.
What is the Communication Gap in the Service Gap Model?
The company's external promises don't match the actual service delivered.
What is Elastic Demand?
Demand changes a lot when price changes, typical for non-essential products.
What is Inelastic Demand?
Demand changes very little when price changes, typical for necessities.
What is Perfectly Elastic Demand?
If price increases slightly, demand drops to zero.
What is Perfectly Inelastic Demand?
Demand does not change at all regardless of price.
What is Sales Orientation in pricing objectives?
Prioritizes increasing sales or market share, often using low prices.
What is Profit Maximization in pricing objectives?
Sets prices to earn the maximum profit possible, often means premium pricing.
What is Loss Leader Pricing?
Pricing one or a few items very low to attract customers into the store.
What does Price Bundling mean?
Selling several products together at one combined price that is cheaper than buying separately.
What is dynamic pricing?
Prices change frequently based on demand, time, customer, or algorithm.
Give an example of dynamic pricing.
Uber surge pricing or airline ticket pricing.
What is prestige pricing?
Setting a higher price to signal luxury, quality, or status.
Provide an example of prestige pricing.
Designer handbags or high-end cosmetics.
What is price lining?
Offering a limited number of price points for a product line (good/better/best).
Give an example of price lining.
Fast food combo meals or phone + data + streaming bundles.
What is demand backward pricing?
Starting with what consumers are willing to pay and designing the product and cost structure from there.
Provide an example of demand backward pricing.
Holiday gift tables where all items are priced at $10.
What is captive pricing?
Low price for the main product with high margins on required complements.
Give examples of captive pricing.
Printers and ink, razors and blades, game consoles and games.
What is product mix pricing?
Setting prices for a group of related products to maximize profit across the whole mix.
Provide an example of product mix pricing.
Cheap printer with expensive cartridges or cheaper base phone with pricey accessories.
What is two-part pricing?
A fixed fee plus a variable usage fee.
Give examples of two-part pricing.
Gym membership plus per class fee or theme park entry plus pay per ride.
What is payment pricing (installment pricing)?
Breaking the total price into smaller payments over time to make big purchases feel affordable.
Provide an example of payment pricing.
$99/month for 24 months for furniture or phones.
What is subscription-based pricing?
A recurring fee for ongoing access or delivery.
Give examples of subscription-based pricing.
Netflix, Microsoft 365, subscription boxes.
What is price differentiation (price discrimination)?
Charging different prices to different customer groups for the same product.
Provide examples of price differentiation.
Student/senior discounts, matinee movie tickets.
What is sealed-bid pricing?
Sellers submit one confidential bid, and the buyer chooses.
In what contexts is sealed-bid pricing common?
Government contracts and big construction projects.
What is the push strategy in marketing?
Pushing the product onto retailers to ensure they carry it.
What tactics are used in a push strategy?
Retailer discounts, buying allowances, bonus incentives.
What is the pull strategy in marketing?
Creating demand at the consumer level so stores must stock the product.
What tactics are used in a pull strategy?
Mass advertising, influencer marketing, viral campaigns.
What is intensive distribution?
Getting the product everywhere, typically for convenience products.
What is selective distribution?
Being in some retailers but not all, balancing coverage and control.
What is exclusive distribution?
Having a rare presence, protecting prestige and pricing.
What is advertising?
Paid, non-personal, mass communication aimed at building awareness and shaping perceptions.
Give an example of advertising.
TV ads, YouTube ads, billboards, digital banners.
What is the purpose of Public Relations (PR)?
To build a positive brand image through earned coverage, enhancing credibility and trust.
What is a key memory trick for PR?
PR = others say it for you.
What are sales promotions?
Short-term incentives designed to trigger immediate action, such as coupons and discounts.
What is the purpose of personal selling?
To engage in face-to-face selling and relationship building.
What is direct marketing?
Personalized, direct-to-consumer communication aimed at precise targeting and measurable responses.
What is the ultimate one-liner to summarize the Promotion Mix?
Advertising = paid mass reach; PR = earned reputation; Sales promotion = fast boost; Personal selling = relationships; Direct marketing = personalized targeting.
Who is the sender in the communication process?
The marketer who initiates the message.
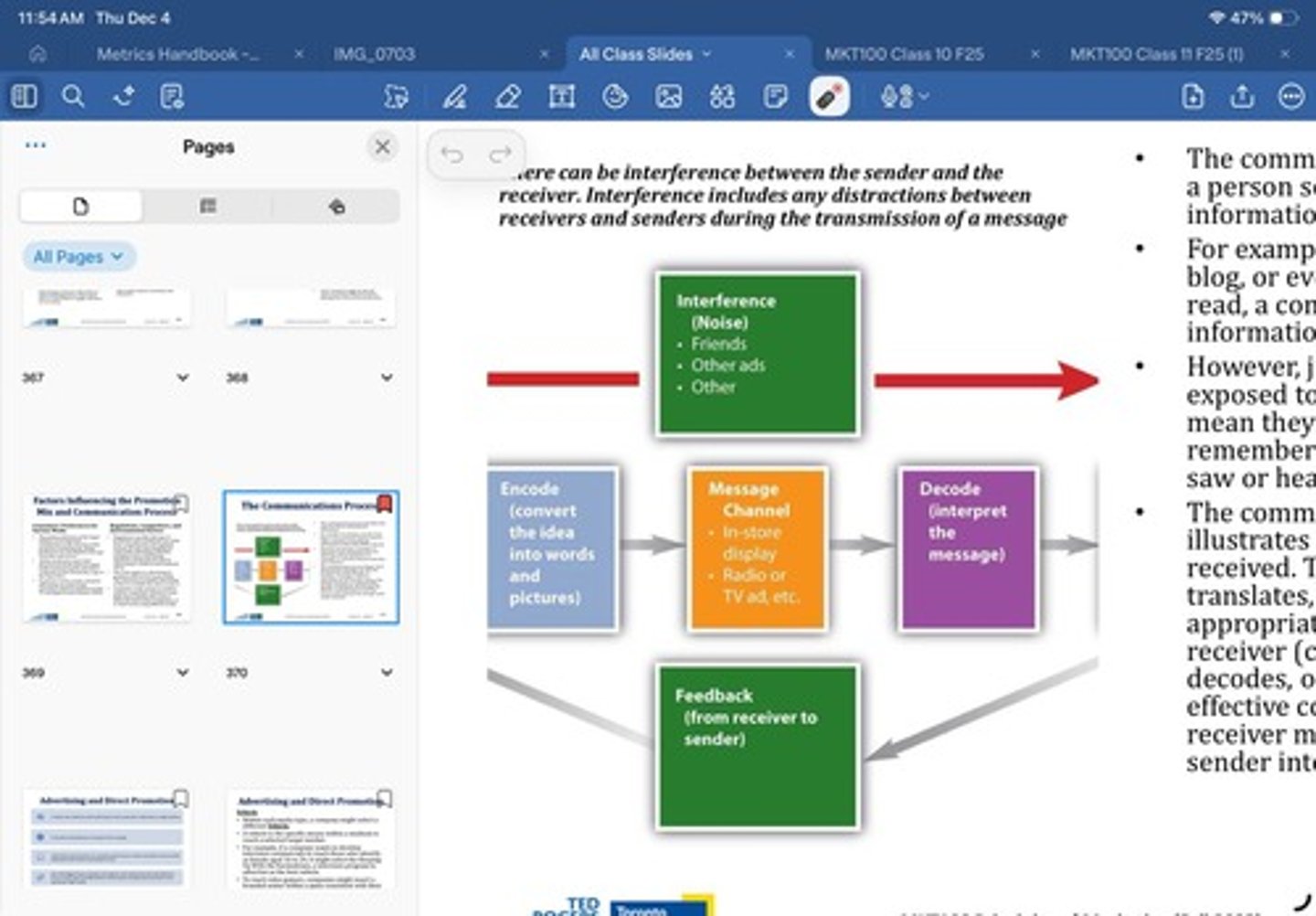
What does encoding refer to in the communication process?
Turning ideas into words, images, symbols, or sounds.
What is the message in the communication process?
The actual content being communicated, including slogans, visuals, and tone.
What is the medium in the communication process?
The channel through which the message travels, such as social media or television.
What does decoding mean in the communication process?
The consumer's interpretation of how they understand the message.
What is noise in the communication process?
Anything that blocks or distorts the message, such as distractions or poor design.
What is feedback in the communication process?
The response from the receiver, such as comments or purchases.