Final Exam Genetics
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
The observable characteristics of organisms are referred to as an organism's ________.
Phenotype
How many spermatids are expected in the end of spermatogenesis of one spermatogonium in
human?
4
Which part of interphase does DNA duplication take place?
S
The disjunction of sister chromatids during ________ in mitosis.
Anaphase
A variant form of a gene is a(n) ________.
Allele
What best describes “the intertwined strands of non-sister chromatids seen in meiosis I”?
Chiasma
Which is the first substage in prophase I of meiosis?
Leptonema
In a female human (2n = 46), what chromosomes should be found in a secondary oocyte?
23 dyads
In spermatogenesis, a(n) _________ contains duplicated DNA and is in the middle of meiosis I
(but not finished yet).
Primary Spermatocyte
Which describes the approach of studying the function of a gene by generating targeted
mutations first?
Reverse Genetics
We perform testcross to decide the genotype of a dominant phenotype by a cross with a
________ individual.
Homozygous Recessive
What part of meiosis provides the most critical mechanism for Mendel’s law of independent
assortment?
How the tetrads align differently at metaphase I.
In oogenesis, a(n) _________ is generated after the cytokinesis of meiosis II but becomes
degenerated eventually.
Second Polar Body
Which of the following three cell division processes halve the ploidy of the mother cell, mitosis,
meiosis I, or meiosis II?
Meiosis 1
Which best describe the focus in Transmission Genetics?
how traits and genes are passed generation by generation
In the early 20th century, Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri noted that the chromosomal
behavior during meiosis is identical to the behavior of genes during gamete formation, which led
to the ________.
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Which of the following statements about rolling normal dice is correct?
Statement #1: The sample space for one die is {1,2,3,4,5,6}.
Statement #2: The event of “getting 1 in a die” and the event of “getting 2 in a die” are mutually
exclusive, so the sum rule can be applied to calculate the probability of the event of “getting 1 or
2 in a die”.
Statement #3: The event of “getting 1 in the first die” and the event of “getting 2 in the second
die” are independent, so the multiplicative rule can be applied to calculate the probability of the
event of “getting 1 in the first die and then getting 2 in the second die”.
#1, #2, and #3
How many different genotypes of gametes can be formed by a genotype AaBBDd?
4
A diploid cell contains three pairs of homologous chromosomes designated as C1/C2; M1/M2;
Q1/Q2. Which of the following combinations of chromosomes is possible for a daughter cell at
the end of normal mitosis?
Combination #1: C1/C2; M1/M2; Q1/Q2
Combination #2: C1/C1; M1/M1; Q1/Q1
Combination #3: C1; M1; Q1
#1 only
A diploid cell contains two pairs of homologous chromosomes designated as C1/C2; M1/M2.
Which of the following combinations of chromosomes is possible for a daughter cell at the end
of normal meiosis? Assumes no crossing overs.
Combination #1: C1/C2; M1/M2
Combination #2: C1/C1; M1/M1
Combination #3: C1; M2
Combination #4: C1; C2
#3 only
Consider a one-gene trait with two alleles: dominant A and recessive a. What kind of parental
cross can generate offspring with a phenotype not belonging to any parent?
Aa x Aa
Consider a cross A/A;B/B;D/d x A/a;b/b;d/d. What is the expected proportion of progeny will
be genotypically AABbdd?
1/4
Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait. The dominant allele is annotated as
A; the recessive allele is annotated as a. A non-affected male and an albino female have six
children, and they are all non-affected. Which of the following options are the most likely
genotypes of parents?
male: AA ; female: aa
In fruit flies, gray body color is dominant to ebony body color, while long wings are dominant to
vestigial wings. One crossed true-breeding fruit flies with gray body and vestigial wings and
true-breeding flies with ebony body and long wings. Then, a female F1 individual and a male F1
individual was crossed for the F2 generation. What would be the predicted phenotypic ratios for
F2 generation?
9/16 gray, long; 3/16 gray, vestigial; 3/16 ebony, long; 1/16 ebony, vestigial
A man and a woman are each heterozygous carriers of an autosomal recessive mutation of a
disorder. We would like to use the equation below to calculate the probability that one out of
their four children are affected by the disease. What is a correct combination of x, n, and p?
x = 1, n = 4, and p = 1/4
Assume the probability that a new birth is a boy or a girl is one half each. What is the probability
that four out of five children are girls?
5/32 ~ 0.156
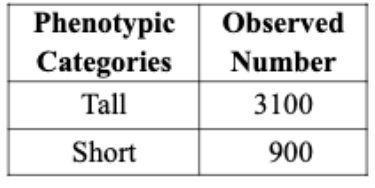
To assess Mendel’s law of segregation by chi-squared test, we crossed a true-breeding tall variety
of tomato with a true-breeding short variety of tomato. All of the heterozygous F1 plants show
tall phenotype. We then intercrossed F1 plants to produce F2 and the data of F2 phenotypes are
shown in the table below. In the chi-squared test, what would be the expected number for F2 short individuals?
1000
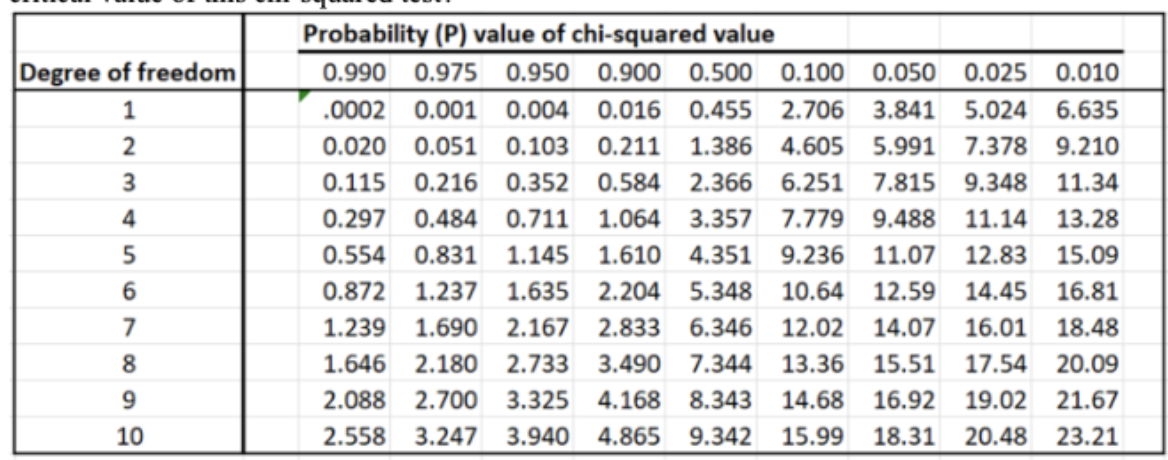
Following the question above, using the conventional cutoff and the table below, what is the
critical value of this chi-squared test?
3.841
Following the question above, which correctly describes the total sum of calculated chi-squared
value?
Between 10.0 and 20.0
Following the question above, what is the conclusion of the chi-squared test?
P-value < 0.05; we reject the null hypothesis.
How many Barr bodies are expected to be found in an XXY, and XYY individual, respectively?
1,0
When its centromere locates at the middle, such that its p arm and q arm show similar sizes, we
classify this kind of chromosome to be ________.
metacentric
In a typically diploid cell, genes with only one copy are ______.
hemizygous
Resulted from the hybridization of two closely related but different species, P. floribunda
(2n=18) and P. verticillata (2n=18), the primrose Primula kewensis (2n=36) is a ________
allopolyploidy
The situation of chromosome number "2n-1" is called ______.
Monosomy
In human, because the egg contributes all of the cytoplasm, and the sperm contributes primarily
only the nucleus, the inheritance mode of mitochondrial DNA is ______ inheritance.
Maternal
Which of the following statements is true?
If two gene loci are on two different pairs of homologous chromosomes, genes at these loci
are generally expected to assort independently.
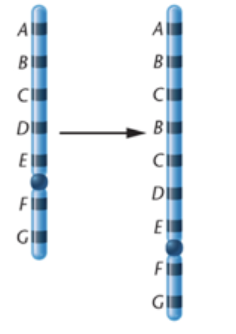
What kind of chromosomal mutation is shown below?
Duplication
What does 1 map unit mean?
1% recombination frequency
Which of the situations below should have less dosage imbalance problems than the others?
Inversion
What is defined by "the formation of new allele combinations on chromosomes"?
Recombination
Based on the below data of sex-chromosomal genotype and sex, what is the most reasonable
hypothesis on the sex determination factor? Assume no differences in their autosomes and
environments.
XY: Male
XX: Female
XO: Female
XXY: Male
XXX: Female
The number of Y chromosomes
In which of the following individual, there is formation of loop during synapsis?
deletion heterozygote
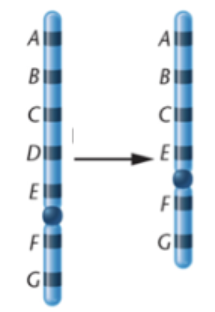
What kind of chromosomal mutation is shown below?
deletion
What is "a chromosomal aberration created by breaks in the short arms of two nonhomologous
chromosomes followed by fusion of the long arms of these chromosomes at the centromere"?
Robertsonian translocation
The phenomenon in which one crossover decreases the likelihood of crossovers in nearby
regions is called ________.
Positive Interference
Which of the following statement is normally correct for the ZZ/ZW mode of sex determination?
Statement #1: The total number of chromosomes in females is one more than the total number of
chromosomes in males.
Statement #2: The gametes generate from females have the same number and the same type of
sex chromosome.
Statement #3: The gametes generate from males have the same number and the same type of sex
chromosome.
#3 only
The region of human Y chromosomes sharing the homology with X chromosomes and synapsing
with X chromosomes during meiosis is called ______.
pseudoautosomal regions (PARs)
What is the explanation to cats showing tortoiseshell phenotype (e.g., black and orange skin
colors) in genetics?
Inactivation of random X chromosome in heterozygous females
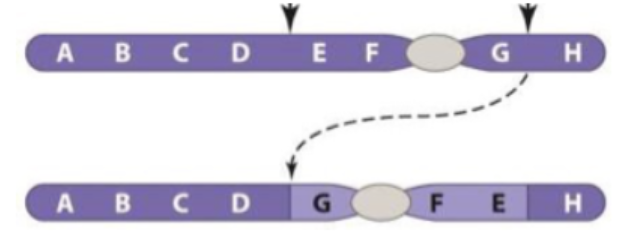
What kind of chromosomal mutation is shown below?
Pericentric inversion
What term is applied when two genes tend to segregate together during gamete formation?
linkage
In fruit flies, the gene white affects the eye color and is on X chromosome. Its mutant allele is
recessive to the wild-type allele. A cross is made between a wild-type pure-line female and a
mutant male pure-line. What is the expected offspring's phenotype and sex?
1/2 wild-type females; 1/2 wild-type males
In a series of two-point map crosses involving three genes (adp, b, c) located on the same
chromosome in fruit flies, the following recombination frequencies were observed. Based on the
data, which gene is in the middle?
adp−b: 35.1%
adp−c: 8.2%
c−b: 27.0%
c
In fruit flies, three genes sc, ec, and cv are on the same chromosome and arranged in this order.
For the female fruit fly with genotype sc-, ec+, cv-/sc+, ec-, cv+, which of the following
gametes are double-crossover types?
sc-, ec-, cv- and sc+, ec+, cv+
During the spermatogenesis in an XY human individual, if there is non-disjunction for the sex
chromosome in meiosis I but not in meiosis II, what kind of sex chromosomes are expected to be
seen in the four spermatids at the end? (O means no sex chromosomes)
XY, XY, O, O
Below is a pedigree of a rare disease. Which of the following statements is correct?
Statement #1: The diseased trait is most likely to be autosomal dominant.
Statement #2: The mother in the first generation must be heterozygous.
Statement #3: Based on the information here, we are not able to tell whether or not the
unaffected children in the second generation are carriers.
#2 and #3
For an individual with genotype A,b/a,B, where the recombination frequency of two genes is 0.2,
what is the probability that its gamete has the genotype A,B?
0.1
A plant with either purple or white flowers. For the underlying gene, the purple allele P is
dominant to the white allele p. The plant’s pollens show two morphologies, long or short. For the
underlying gene, the long allele L is dominant to the short allele l.
We made the following experiment to estimate the genetic distance between these two genes. We
crossed a homozygous recessive plant (ppll) with a heterozygous plant (PpLl) showing purple
flowers and long pollens. The offspring’s phenotypic data are shown below. The total is 1000.
What is the recombination frequency between these two genes?
purple flower, long pollen: 50
purple flower, short pollen: 440
white flower, long pollen: 460
white flower, short pollen: 50
10%
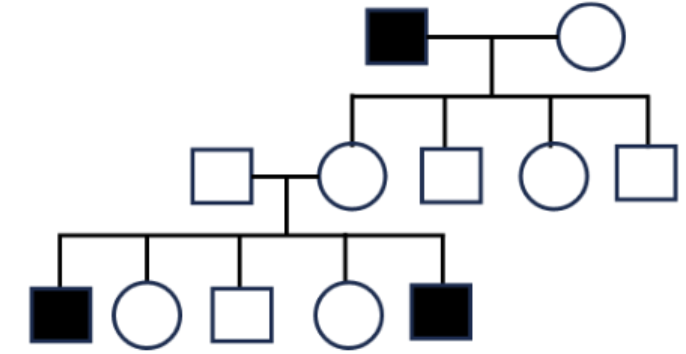
Below is a pedigree of a rare disease. What would be the most likely inheritance mode?
X-linked recessive
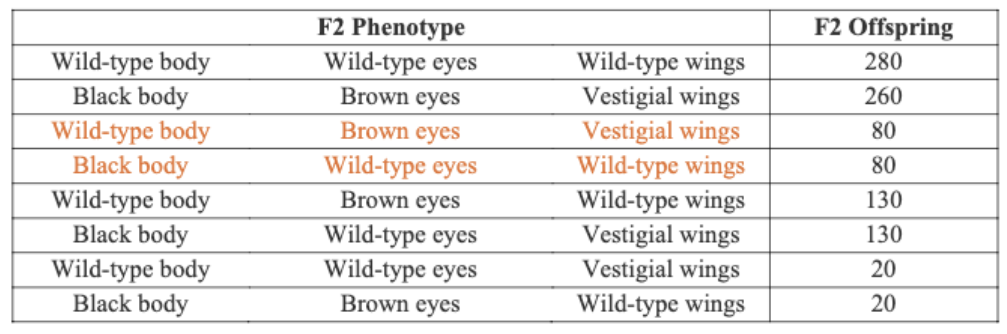
Three genes b, bw, and vg are on the same chromosome in fruit flies. The mutant and recessive
phenotypes related to three genes are black body color (b-), brown eyes (bw-), and vestigial
wings (vg-). All of the three related wild-type phenotypes are dominant. We studied the order of these three genes by the crosses below. We first crossed wild-type pure-line males and pure-line females expressing the three mutant phenotypes. All the F1 females were wild-type. Then, we made a cross between F1 females and pure-line males with the three mutant phenotypes. In total, 1000 F2 females were collected and phenotyped, and the data are shown below. Based on the data, which gene is in the middle?
vg
Which of the following repairs a double strand break of DNA?
non-homologous end joining
Which of the following describes the expected temperatures in a standard polymerase chain
reaction cycle (starting with denaturation)?
95°C → 55°C → 72°C
From what we learned from the Luria-Delbruck experiment, what is the nature of mutations?
Mutations are random and appear spontaneously in all kinds of environments
What are the three steps of mRNA modification in eukaryotes?
5’ capping by a methylated guanine, removing introns, and 3’ polyadenylation
Which of the following is an error-prone DNA repair system?
SOS repair system
When examining a conditional mutant E. coli, scientists found that, in certain conditions,
supercoiled DNA strands remain after replication, which is never completed. Which of the
following proteins is most likely to be mutated in this mutant?
gyrase (topoisomerase)
When a mutation has no fitness effects, it is called a(n) ______.
neutral mutation
Which of the following statements about the T4 phage ‘s lytic cycle is FALSE?
The phage DNA is integrated into the host chromosome.
In E. coli, which of the following repair mechanisms distinguish template DNA strand from new
DNA strand using DNA methylation?
Mismatch repair
Which of the following mating allows the conjugation that will not produce recombinants but
convert recipients to donor strain?
F^+ x F^-
A point mutation that creates a new stop codon is called a ______.
nonsense mutation
Which type of mutation is generally caused by replication slippage?
insertion or deletion
Which of the following best describes the transcription initiation in bacteria?
An RNA polymerase core enzyme and a sigma factor assemble as an RNA polymerase holoenzyme, which then binds to a promoter
In Hershey & Chase’s experiment, they used bacteriophage T2 to infect bacteria. They used P
isotope to label DNA or used S isotope to label protein. Which of the following statement
correctly decribe where they found the isotopes in the experiment?
Statement #1: P isotope is found outside the infected bacteria.
Statement #2: P isotope is found within the next generation of bacteriophage.
Statement #3: S isotope is found within the infected bacteria.
Statement #4: S isotope is NOT found within the next generation of bacteriophage.
#2 and #4
One student performed an experiment in which two auxotrophic strains were placed on different sides of the filter on Davis’ U-tube. DNAse was added to remove all the DNA molecules in the
environment (the DNA within bacteria or bacteriophage is not affected). In the end, the student
found that one side of the tube developed prototrophs. What best explains the transfer of genetic
information in this case?
transduction
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the DNA replication in bacteria versus
eukaryotes?
Statement #1: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear and thus subject to end-replication
problem, while bacterial chromosomes are circular and thus not.
Statement #2: Eukaryotic chromosomes have many origins of replication, while bacterial
chromosomes typically has only one origin of replication.
Statement #3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are replicated in the dispersive mode, while
bacterial chromosomes are replicated in the semiconservative mode.
#1 and #2
We extracted DNA from human cells and analyzed DNA composition. Among the four most
common nitrogen-containing bases, we find that the percentage of adenine is 30%. Using
Chargaff’s rule, what would be the best guess about the percentage of thymine?
30%
What are the roles of DNA ligase and restriction enzymes in making recombinant DNA?
DNA ligase generates the covalent bonds of the phosphodiester backbone, while restriction enzymes break those bonds
Streptomycin (str) and tetracycline (tet) are two different antibiotics. For a prototroph strain of E.
coli with genotype strR tetS , at which of the following media can it grow? R denotes antibiotic
resistance; S denotes antibiotic sensitivity.
Medium #1: Glucose minimal medium
Medium #2: Glucose minimal medium with streptomycin
Medium #3: Complete medium with tetracycline
#1 and #2

To amplify the boxed DNA region below, which pair of primers should be used in PCR?
Primers 1 and 4
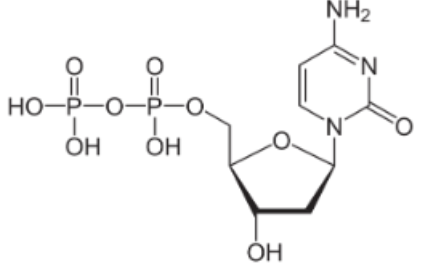
The base is cytosine. What is the abbreviated name of this molecule?
dCDP
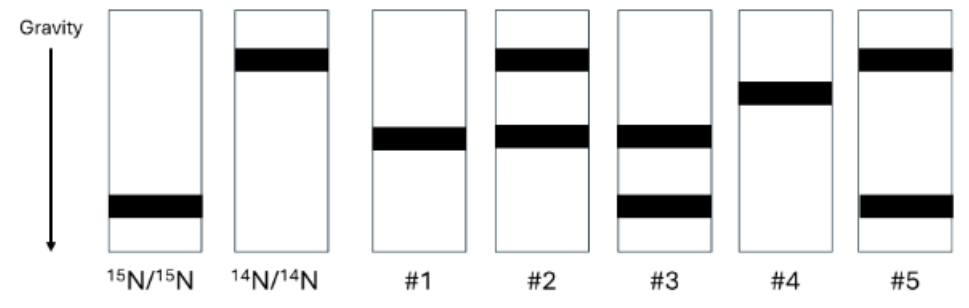
In Meselson–Stahl Experiment, they first grew E. coli in the medium with 15 N, a heavy isotope
of nitrogen, and then moved the E. coli in the medium with 14 N for several generations. Below is
a figure showing multiple possible band patterns for the result of this experiment. The two leftist
panels show the band pattern for E. coli growing in the medium with 15 N and 14 N for a long time,
respectively. Given that the DNA duplication follows the semiconservative model, what would
be the expected patterns for E. coli that moved from the medium with 15 N to the medium with
14 N for two generations?
#2
Tautomeric shift is one of the common reasons for point mutation. For example, cytosine is
regularly complementary to guanine. But sometimes cytosine can have a tautomeric shift to be in
an imino form, and the cytosine in an imino form can be complementary to adenine.
Now, let us consider a tautomeric shift in the following scenario. With a tautomeric shift in a
cytosine, a T-A base pair would generate a C(imino form)-A pair in DNA replication. If this
glitch is not fixed, in the next round of DNA replication, the cytosine can change back to its
regular form and pair with G in this position. In the end, this entire process leads to a ______
point mutation.
T-A to C-G
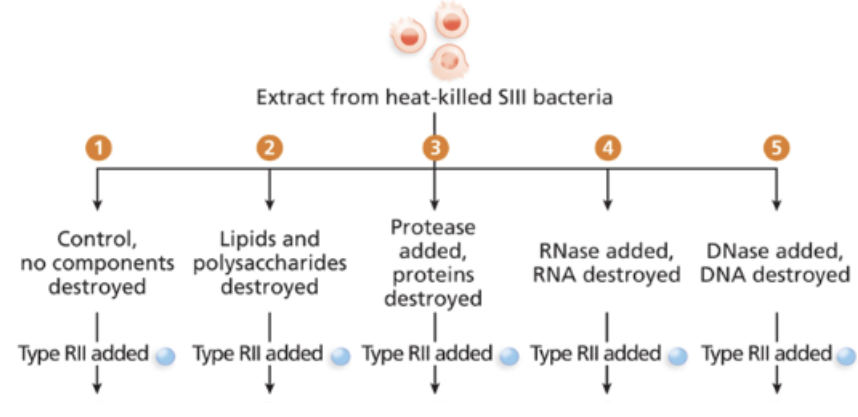
The dead S strain and living R strain of bacteria were used in five different treatments in Avery,
MacLeod, & McCarty’s experiment (see figure below). If RNA was the most critical component
of the genetic material, what would be the expected result?
Living S strain found in treatments #1, #2, #3, and #5 but not in #4.
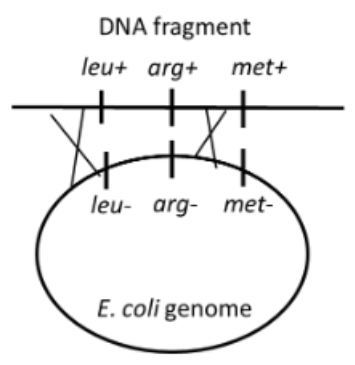
Leucine (leu), arginine (arg), and methionine (met) are three different amino acids. We expose a
competent auxotroph strain of E. coli with mutant genotype leu- arg- met- to DNA fragments
with wild-type alleles leu+ arg+ met+ for transformation. If the two crossovers as shown in the
figure below happen during the transformation, at which of the following media can the
transformant grow in the end?
Medium #1: minimal medium with leucine
Medium #2: minimal medium with arginine
Medium #3: minimal medium with methionine
#3 only
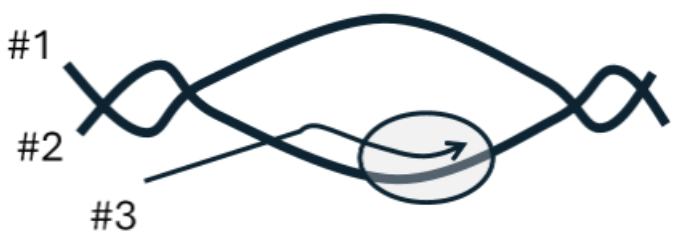
Below is diagram for a replication bubble. The grey circle represents where the new RNA polymerization happens, and the arrow represents the direction of RNA synthesis. #1, #2, and #3 label one end of a polynucleotide chain. Which is 5’ end?
#1 and #3
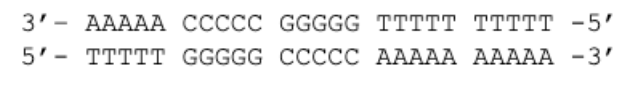
If the top strand is the template strand, what will be the RNA product after the transcription of
the following DNA?
5’– UUUUU GGGGG CCCCC AAAAA AAAAA -3’
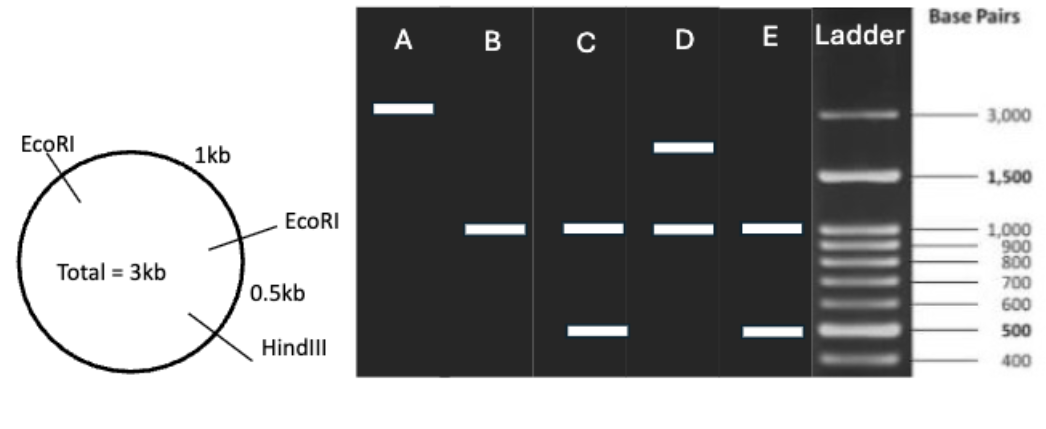
We have plasmid DNA with two EcoRI restriction sites and a HindIII restriction site as shown below. The entire plasmid is 3000 base pairs (3kb) long. We digest the plasmid DNA thoroughly by EcoRI and analyze the digested sample by gel electrophoresis with the ladder DNA. Which of the lanes A-E best represents the expected result from the digested sample?
D
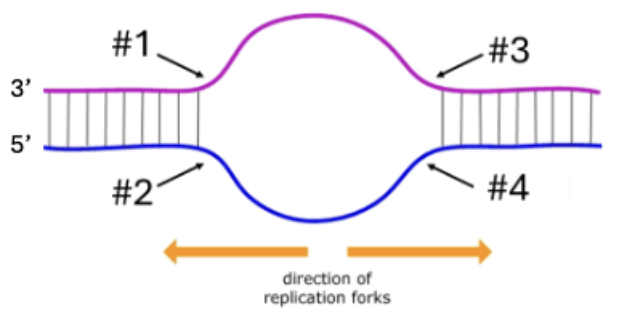
The diagram below depicts a replication bubble with two replication forks. The moving
directions of the two replication forks are indicated. Given the directions of replication and the
orientation of the two DNA strands, which arrow points out the location of a lagging strand, #1,
#2, #3, or #4?
#1 and #4
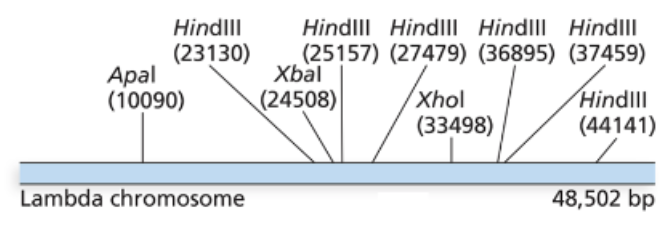
Below is the genome of Lambda phage (48,502 bp in total, ~48.5kb). The physical locations of
various restriction sites on the genome are also labelled in parentheses. If we treat the lambda
phage’s DNA by the restriction enzymes XbaI and XhoI, after fully digestion, what are the
expected number of fragments?
3
Genetic code is ________, as no codon specifies more than one amino acids.
not ambiguous
Which of the following is cis-acting in eukaryotic gene expression regulation?
enhancer
_____expression means continuous gene expression regardless of environmental factors.
Constitutive
Genetic code is ________, as more than one codon may specify a particular amino acid.
degenerate
Which below is a protein with a DNA-binding domain in eukaryotic gene expression regulation?
activator
Tryptophan is called a(n) ______ in the gene expression regulation of trp operon.
co-repressor
Which of the following mutations is expected to increase gene expression?
gain-of-function mutation on an enhancer
Which of the following is correct for Trp operon when tryptophan is in the environment?
Tryptophan-repressor protein complex binds to the operator; expression is off.
______ is the study of the phenotypic changes (e.g., gene expression) from the alterations NOT
at the sequence level of DNA.
Epigenetics