Glycolysis/ Gluconeogenesis and the Kreb's cycle
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Cori cycle picks up ___ form the blood and coverts it into ___ using gluconeogenisis. The glucose is transported to the blood stream and then the skeletal muscle uptakes it for ___
** learn Cori cycle
lactate, glucose, glycolysis
3 steps of glycolysis that are irreversible use ___ enzyme in gluconeogenisis because there is big ___ ____
different, energy change
in gluconeogenesis , ___ ___ and ___ ____ are used to covert 2 pyruvate to PEP
pyruvate carboxylase, PEP carboxylase
to go from G6P to glucose ___-_-___ is used
Glucose-6-phosphatase
The primary regulators/ inhibitors btwn glycolysis and glucogenysis are ____ and ___
F2,6BP, ATP
___ inhibits hexokinase
G6P
___ and ___ inhibit PFK-1
citrate, ATP
___ and ___ activates PFK 1
AMP, F2,6BP
___ , and ___ ___ inhibits pyruvate kinase
ATP, Acetyl CoA
in gluconeogenysis, what inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
frustose-2,6-bisphosphate and AMP
*** in gluconeogenysis, ___ inhibits pyruvate carboxylase
Acetyl CoA
Kinetics of PFK-1 in the presence of LOW ATP will ___
increase
Kinetics of PFK-1 in the presence of HIGH ATP will the activity is ___ and will increase ___
slow, slowly
Kinetics of PFK-1 in the presence of F26BP will have a ___ velocity
high
Kinetics of PFK-1 in the absence of F26BP will have a ___ velocity
low
F6P to F26BP is converted using ___
PFK-2
*** when is F26BP produced
F26BP and PFK-2 are ___ enzymes
bifunctional
Insulin tells cells to take up ___ out of the blood, metabolize and store it. This ___ the glucose blood levels
glucose, lowers
Glucagon tells cells to ___ metabolizing and ___ glucose levels
stop, increase
what stimulates the phosphorylation of the bifunctional enzyme F26BP?
protein kinase
what is protein kinase stimulated by?
cAMP
where does metabolism take place
mitochondria
Pyruvate crosses the outer membrane of the mitochondria through ___ and crosses the inner membrane via a ___ ___ ___
porins, pyruvate carrier protein
pyruvate dehydrogenase removes ___
electrons
pyruvate decarboxylase removes ___ and it is the first time in the cycle where this happens
CO2
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex converts pyruvate and coenzyme A into ____ ___
acetyl CoA
Coenzyme A is derived from _ __ ___ ___ and central to energy metabolism. it is used as a ___ as is linked to acetyl group through a ___ ___
B vitamin pantothenic acid, carrier, thioester bond
where does the Acetyl group from CoA go to? What is it added to and what does it form?
Kreb’s cycles. Oxaloacetate and forms citrate
what is citrate converted to and with what
isocitrate, aconitase
in the Kreb’s cycle, Isocitrate is ___ and CO2 is ___ to form α-ketoglutarate, using enzyme ____ ____
oxidized, removed, isocitrate dehydrogenase
in the Kreb’s cycle, α-ketoglutarate is ___, CO2 is ___, the Co-A os linked to form succinyl-CoA, using the enzyme ___
oxidized, removed, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
What enzyme adds 2 carbons of acetyl to oxaloacetate to form citrate?
citrate synthase
The bond that holds succinyl to Coa is ___ in energy
high
Succinate is oxidized to ___, using enzyme ___ and uses ___ as an electron acceptor
fumarate, succinate dehydrogenase, FAD
FAD stands for ___ ___ ___ and is a coenzyme that carries ___ or __ from glycolysis and the kreb cycle to the electron transport chain
flavin adenine dinucleotide, protons, electrons
why is FAD used instead of NAD on step 6 of the kreb’s cycle?
the electrons are lower in energy and NAD will not accept them
NADH takes electrons between
C and O
FAD takes electrons between
2 carbons
in the kreb cycle, what enzyme takes fumarate and is converted to malate
fumarate hydratase
In the kreb cycle, what enzyme takes malate and oxidizes it to form oxaloacetate
malate dehydrogenase
in the kreb cycle when the glucose levels are high, ___ acetyl-CoA enters the cycle = ___ in activity
more, increase
*** regulation of the kreb cycle
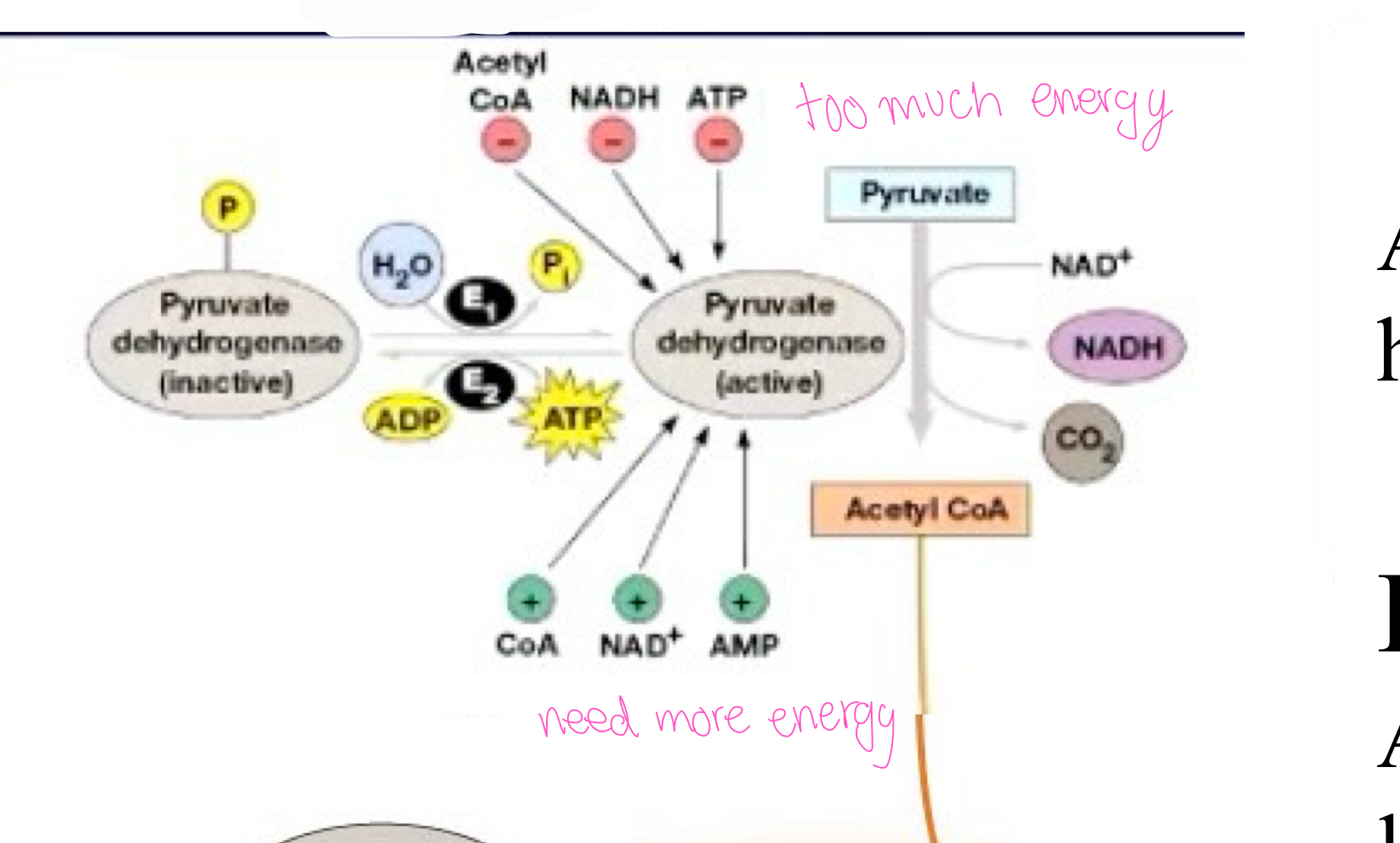
E2= PDH kinase Activity increased by ___ ATP/ADP ratio
high
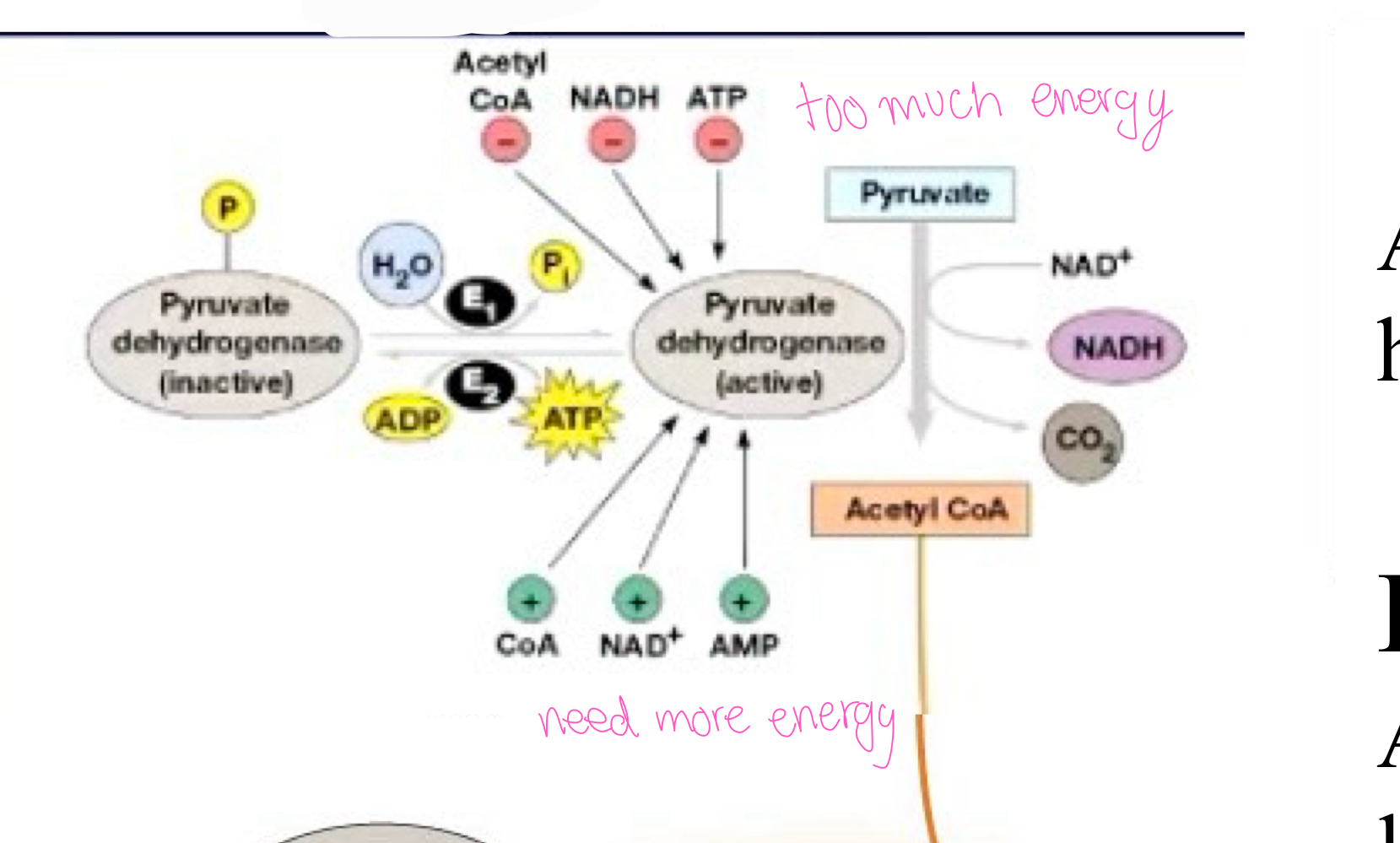
The main function for regulator of pyruvate dehydrogenase is to
phosphorylate
E1= PDH phosphatase Activity increased by ___ ATP/ADP ratio
low