Semester 1 IB Chemistry year 11
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Relative isotopic mass
The mass of an atom of an isotope compared to 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Relative atomic mass, Ar
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Relative molecular mass, Mr
The weighted mean mass of a molecule compared to 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Relative formula mass
The weighted mean mass of a formula unit compared with 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Equation: Relative atomic mass (of an element) =
[Relative isotopic mass(es) x Relative isotopic abundance(s)] / 100
Amount of substance
The quantity whose unit is the mole
Avogadro constant, Na
The number of atoms per mole of the carbon-12 isotope (6.02 x 10^23 mol^-1)
Mole
The amount of a substance containing as many particles as there are carbon atoms in 12g of carbon-12
Molar mass, Mr
The mass per mole of a substance (gmol^-1)
Equation linking molar mass, mass and number of moles:
Mr = m/n
Mr = Molar mass (gmol^-1)
m = Mass (g)
n = Number of moles (mol)
Empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound
Molecule
A small group of atoms held together by covalent bonds
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
Molar volume
The volume per mole of a gas (dm^3mol^-1) (At room temperature and pressure, the molar gas volume is approximately 24dm^3mol^-1
Molar gas volume equation (at standard conditions)
V = 22.7 x n
V = Molar gas volume ((dm³mol⁻¹)
n = Amount of substance (mol)
Concentration (of a solution)
The amount of solute, mol, dissolved per 1dm³ of solution
Concentration equation
c = n / V
c = Concentration (moldm⁻³)
n = Amount of substance (mol) or mass (g)
V = Volume (dm³)
Standard solution
A solution of a known concentration
Species
Any type of particle that takes part in a chemical reaction
Acid
A species that is a proton donor
Base
A species that is a proton acceptor
Alkali
A type of base that dissolves in water forming hydroxide ions (OH-)
Cation
A positively charged ion
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Acid + Carbonate →
Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Acid + metal →
Salt + hydrogen
Acid + metal hydroxide →
Salt + Water
Hydrated
A crystalline compound containing water molecules
Anhydrous
A substance that contains no water molecules
Waters of crystallisation
Water molecules that form an essential part of the crystalline structure of a compound
Oxidation number
A measure of the number of electrons that an atoms uses to bond with atoms of another element
Oxidation
A loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation number
Reduction
A gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation number
Redox reaction
A reaction in which both reduction and oxidation take place
What does O I L R I G stand for?
Oxidation
Is
Loss
Reduction
Is
Gain
Reducing agent
A reagent that reduces (adds electrons to) another species
Oxidising agent
A reagent that oxidises (takes electrons from) another species
Stoichiometry
The molar relationship between the relative quantities of substances taking part in a reaction
First ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one electrons from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ atoms
Electron shielding
The repulsion between electrons in different inner shells (Shielding reduces the net attractive force from the positive nucleus on the outer-shell electrons)
Successive ionisation energies
A measure of the energy required to remove each electron in turn
Second ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one electron from each ion in one mole of gaseous 1+ ions to form one mole of gaseous 2+ ions
Shell
A group of atomic orbitals with the same principal quantum number, n
Principal quantum number, n
A number representing the relative overall energy of each orbital, which increases with distance from the nucleus
Atomic orbital
A region within an atom that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins
Sub-shell
A group of the same type of atomic orbitals (s, p, d or f) within a shell
Electron configuration
The arrangement of electrons in an atom
Compound
A substance formed from two or more chemically bonded elements in a fixed ratio
Ionic bond
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Giant ionic lattice
A three-dimensional structure of oppositely charged ions, held together by strong ionic bonds
Group
A vertical column in the periodic table (Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties and their atoms have the same number of outer-shell electrons
Covalent bond
A bonded formed by a shared pair of electrons
Lone pair
An outer-shell pair of electrons that are not involved in chemical bonding
Dative covalent (coordinate bonding)
A shared pair of electrons which has been provided by one of the bonding atoms only
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
Permanent dipole
A small difference across a bond that results from a difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms (A polar covalent bond has a permanent dipole)
Intermolecular force
An attractive force between neighbouring molecules
Permanent dipole-dipole force
A weak attractive force between permanent dipoles of neighbouring polar molecules
Hydrogen bond
A strong dipole-dipole an electron deficient hydrogen atom on one molecule and a lone pair of electrons on a different molecule
London forces (dispersion forces)
the weak attractive forces between molecules resulting from the small, instantaneous dipoles that occur because of the varying positions of the electrons during their motion about nuclei
Metallic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons
Delocalised electrons
Electrons shared between more than two atoms
Giant metallic lattice
A three-dimensional structure of positive ions and delocalised electrons, bonded together by strong metallic bonds
Simple molecular lattice
A three-dimensional structure of molecules, bonded together by weak intermolecular forces
Giant covalent lattice
A three-dimensional structure of atoms, bonded together by strong covalent bonds
Period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table (Elements show trended in properties across a period_
Periodicity
A regular periodic variation of properties of elements with atoms number and position in the periodic table
Thermal decomposition
The breaking up of a chemical substance with heat into at least two chemical substances
Displacement reaction
A reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from an aqueous solution of the latter's ion
Precipitation reaction
The formation of a solid from a solution during a chemical reaction (Precipitates are often formed when two aqueous solutions are mixed together)
Describe the line emission spectrum of hydrogen.
A series of dark lines of light of an exact frequency on a black background. The lines get closer together (converge) as frequency increases.
How are emission spectra produced?
Photons are emitted from atoms as excited electrons return to a lower energy level.
What is the shape of an s orbital?
spherical
What is the shape of a p orbital?
dumbbell shaped
In an emission spectrum what does the limit of convergence at higher frequency correspond to?
first ionisation energy
describe a continuous spectrum
Radiation spread over all wavelengths/frequencies
describe a line spectrum
radiation emitted (or absorbed) at specific wavelengths/frequencies
What is the Aufbau principle?
electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first
What is Hund's rule?
Electrons will fill an unoccupied orbital before they pair up.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
an atomic orbital can contain a maximum of 2 electrons with opposite spin
PV=nRT what are the units for each variable
P=Pa
V=m³
n=mol
T=K
R = 8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
how to convert volume in cm³ to volume in m³?
volume in cm³/10⁶= volume in dm³
How to convert from C to K
Temperature in C +273 = temperature in K
homogeneous
a process involving substances in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gaseous)
heterogeneous
a process involving substances in different phases (solid, liquid, or gaseous).
Percentage yield =
(actual yield/theoretical yield) x 100
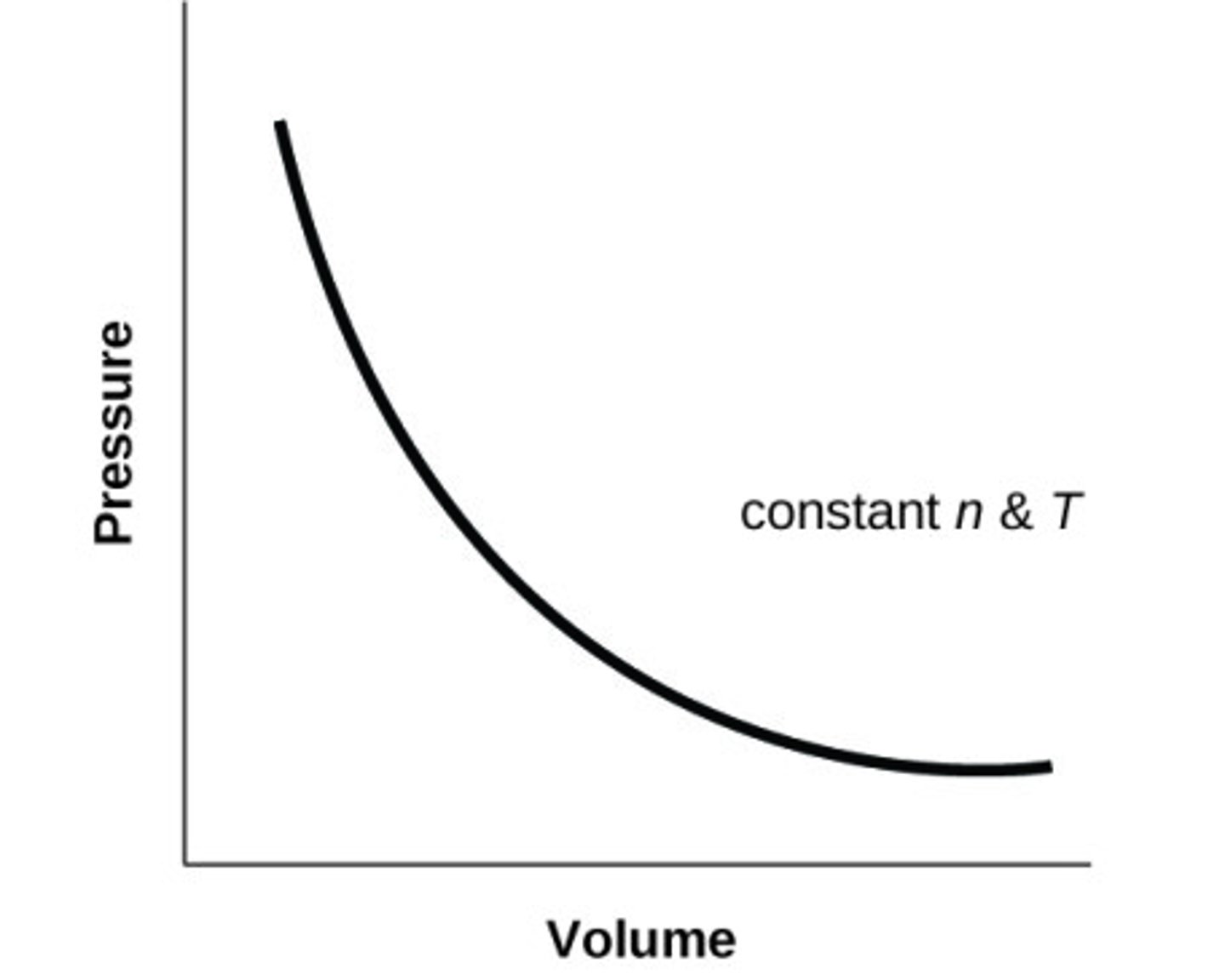
Sketch P against V for an ideal gas at constant T (and n)
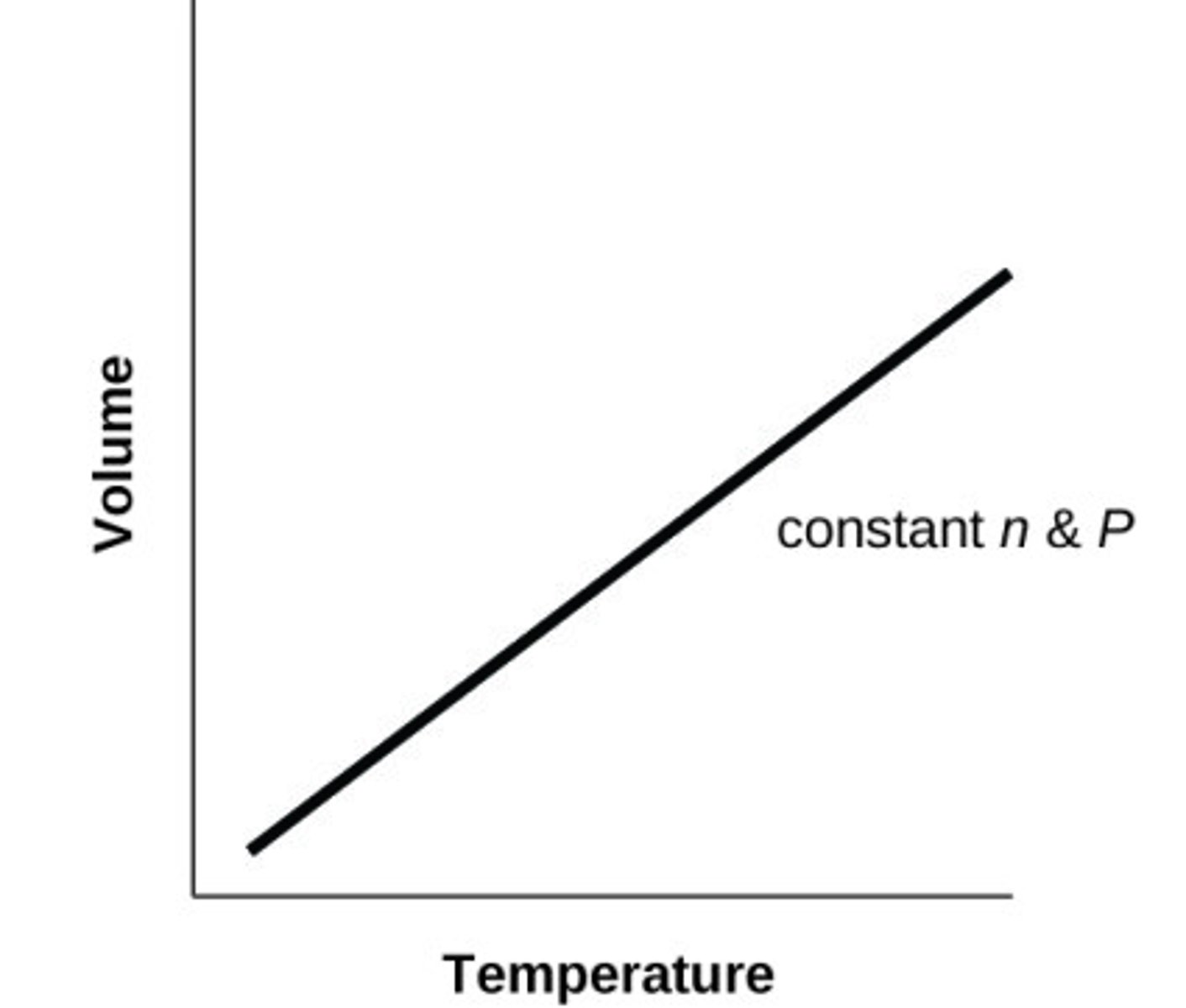
Sketch V against T for an ideal gas at constant P (and n)
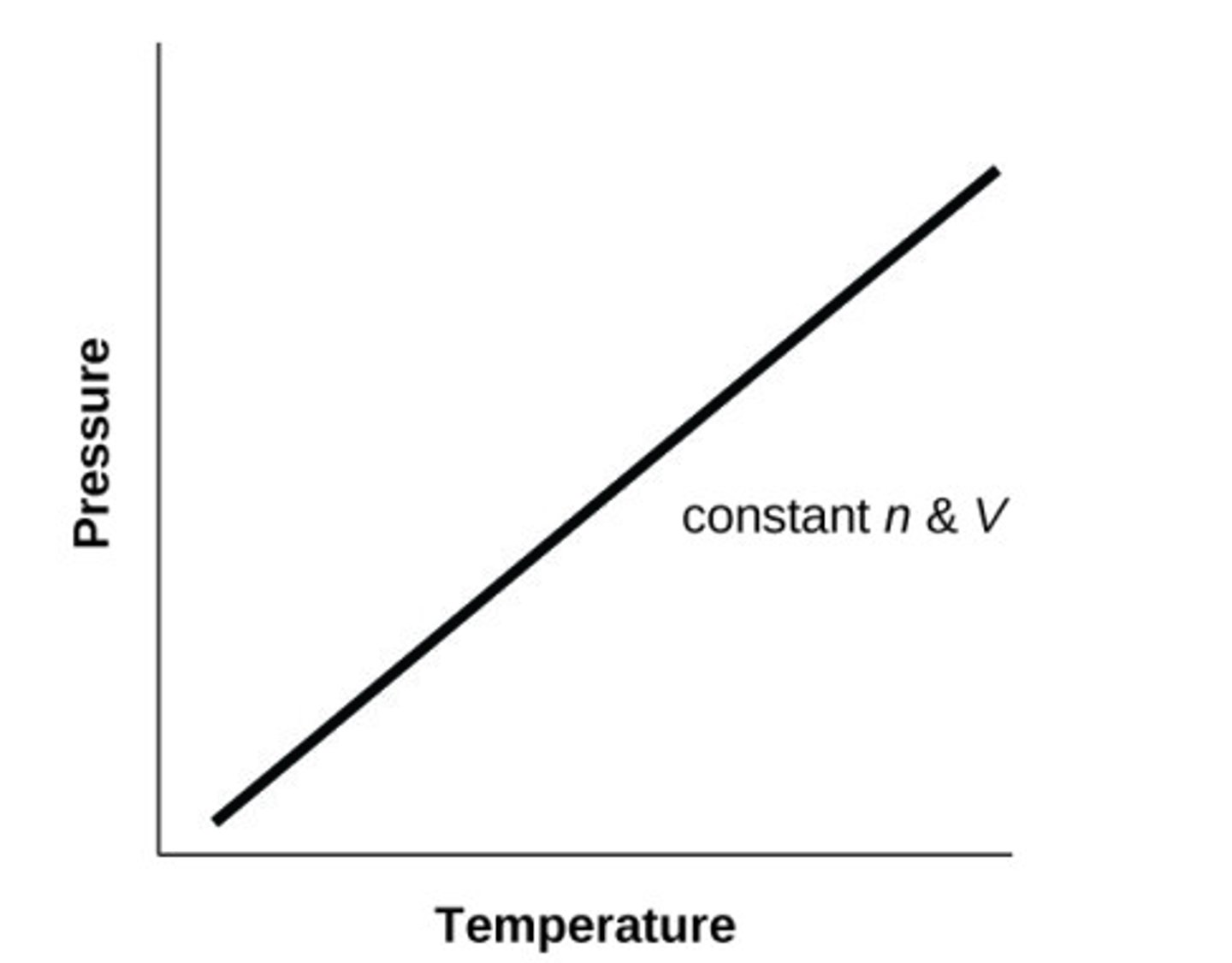
Sketch P against T for an ideal gas at constant V (and n)
Why gases behave as ideal gases at low temperatures
The closer the gas is to being a liquid then the less it behaves like a real gas as the particles themselves are moving slower, are more closely spaced and take up more of the 'empty' volume of the gas
what is the limiting reagent?
The reactant in a chemical reaction that limits the amount of product that can be formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed
How does an σ bond formed?
by the direct head-on/end-to-end/axial overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms
How is a pi bond (π) is formed?
by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
How do you calculate Formal charge
(Number of valence electrons)-½(Number of bonding electrons)-(Number of non-bonding electrons)
How do you use formal charge to detemine the most likely lewis structure?
The Lewis (electron dot) structure with the atoms having FC values closest to zero
What hydrid orbital is present in a carbon atom with 4 σ bonds
sp³
What hydrid orbital is present in a carbon atom with 3 σ bonds and 1 π bond?
sp²
What hydrid orbital is present in a carbon atom with 2 σ bonds and 2 π bond?
sp
Which bonds are present in a C≡C bond
1σ bond and 2π bonds