behavioural ecology
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
behavioural ecollogy definition
interaction between animals & their environments
associative learning
process by which animals take one stimulus and associate it with another
eg. classical conditioning by Ivan Pavlov
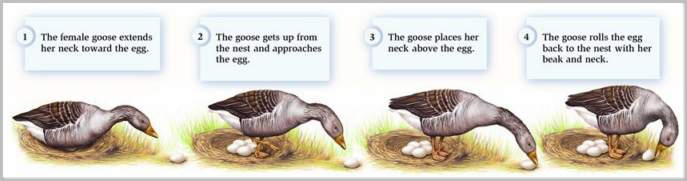
fixed-action pattern (FAP)
innate, preprogrammed response to a stimulus. Once this action has begun, it will not stop until it has run its course
eg. once a goose detects a key stimulus (egg outside nest), it will go through an entire set of movements
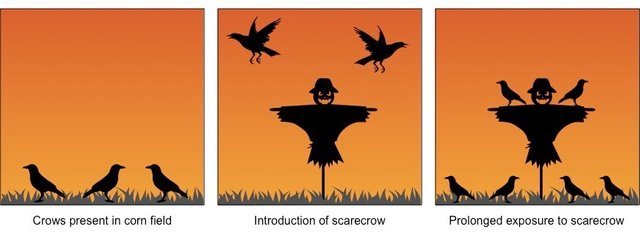
habituation
loss of responsiveness to unimportant stimuli
imprinting
innate behaviour learned during the critical period of life (early in life). Come to recognize (another animal, person, or thing) as a parent or other object of habitual trust, Once imprinting is made, it’s irreversible
eg. when geese are born, they imprint on motion that moves away from them, and they follow it around accepting it as their mother (can be anything)
konrad lorenz, became the mother to a group of young geese bc he was around when the geese hatched and spent the critical period with them (creating mother-baby bond). The geese didn’t recognize their real mother and proceeded to follow lorenz around

insight learning
ability to do something right the first time with no prior experience. Requires reasoning ability — the skill to look at a problem and come up with an appropriate solution

observational learning
ability of an organism to learn how to do something by watching another individual do it first, even if they’ve never attempted it themselves
eg. chimpanzees of the Ivory Coast, who watch their mothers crack nuts with rock tools before learning the technique
operant conditioning
type of associative learning based on trial & error. Association is made between the animal’s own behaviour and a response.
eg. bright coloured lizard with a chemical defence mechanism hopes to use the colouration pattern as an association with the chemical spray through trial and error by the predator