Chapter 8 Part B; Meiosis, Crossing Over, and Chromosome Alterations
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes paired with identical gene loci.
Diploid cells
Cells containing two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Haploid cells
Cells with a single set of chromosomes (n).
Meiosis
Cell division reducing chromosome number to haploid.
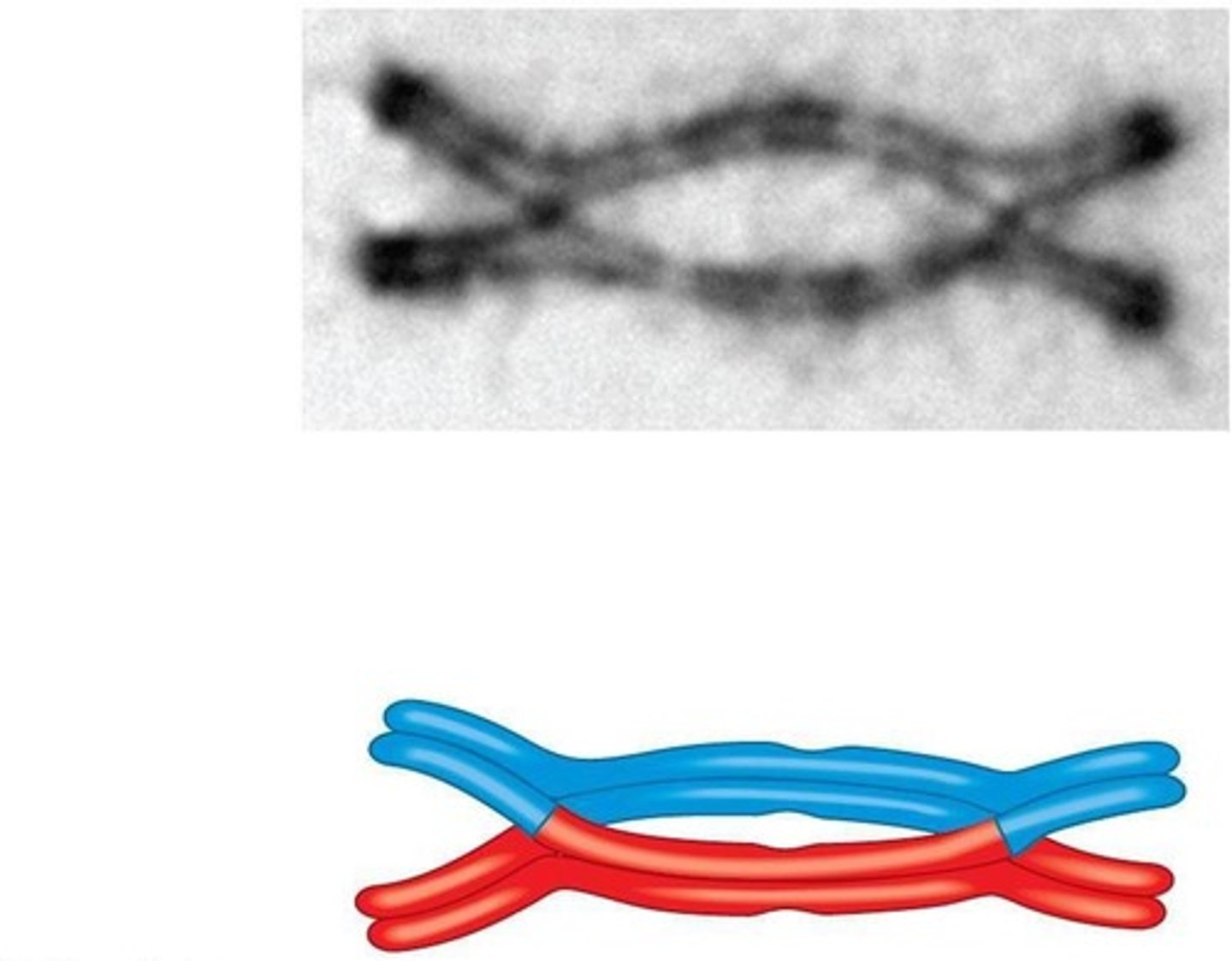
Crossing over
Exchange of segments between homologous chromosomes.
Sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome after duplication.
Gametes
Reproductive cells: eggs and sperm.
Zygote
Fertilized egg, diploid (2n = 46).
Interphase
Phase where chromosomes duplicate before meiosis.
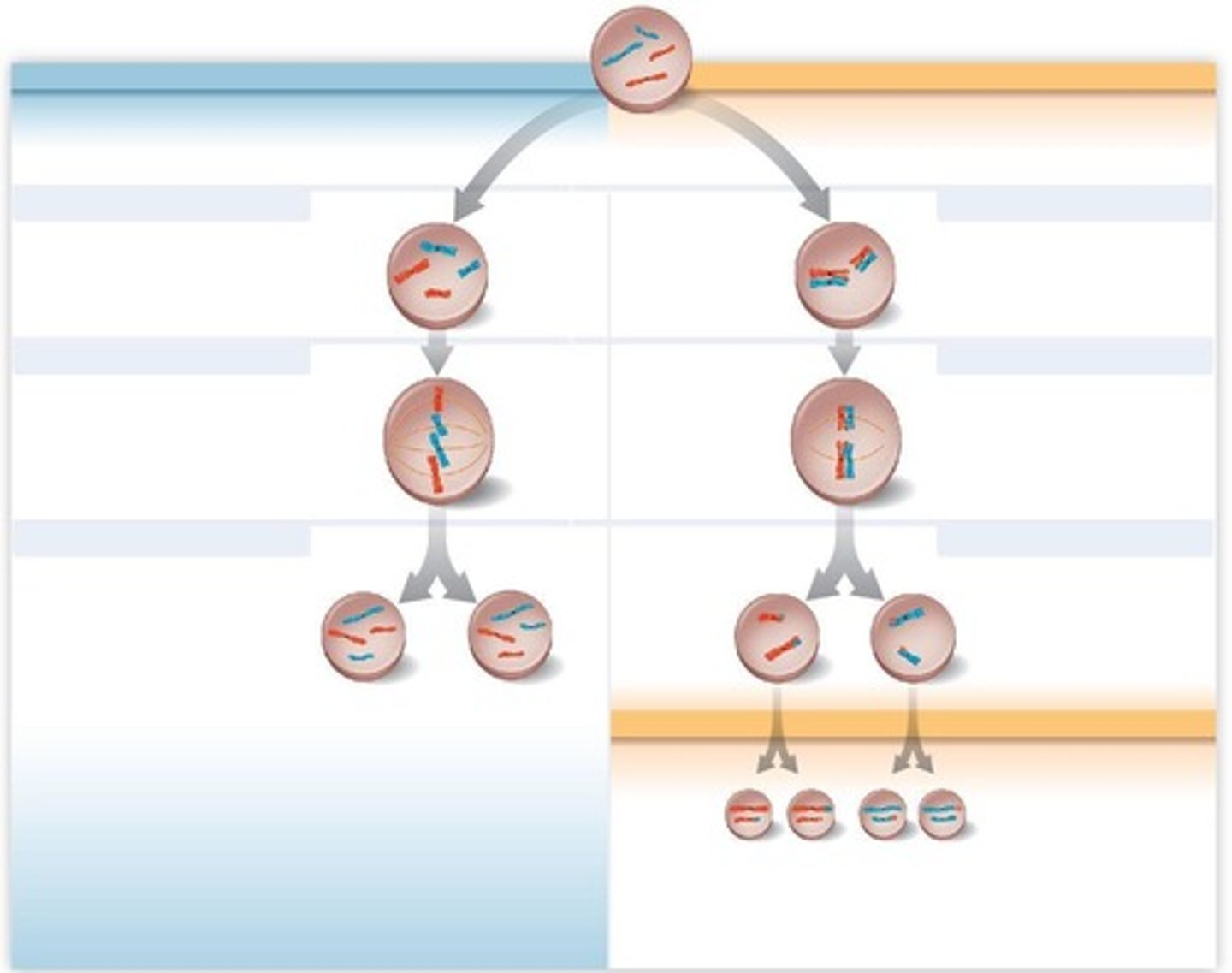
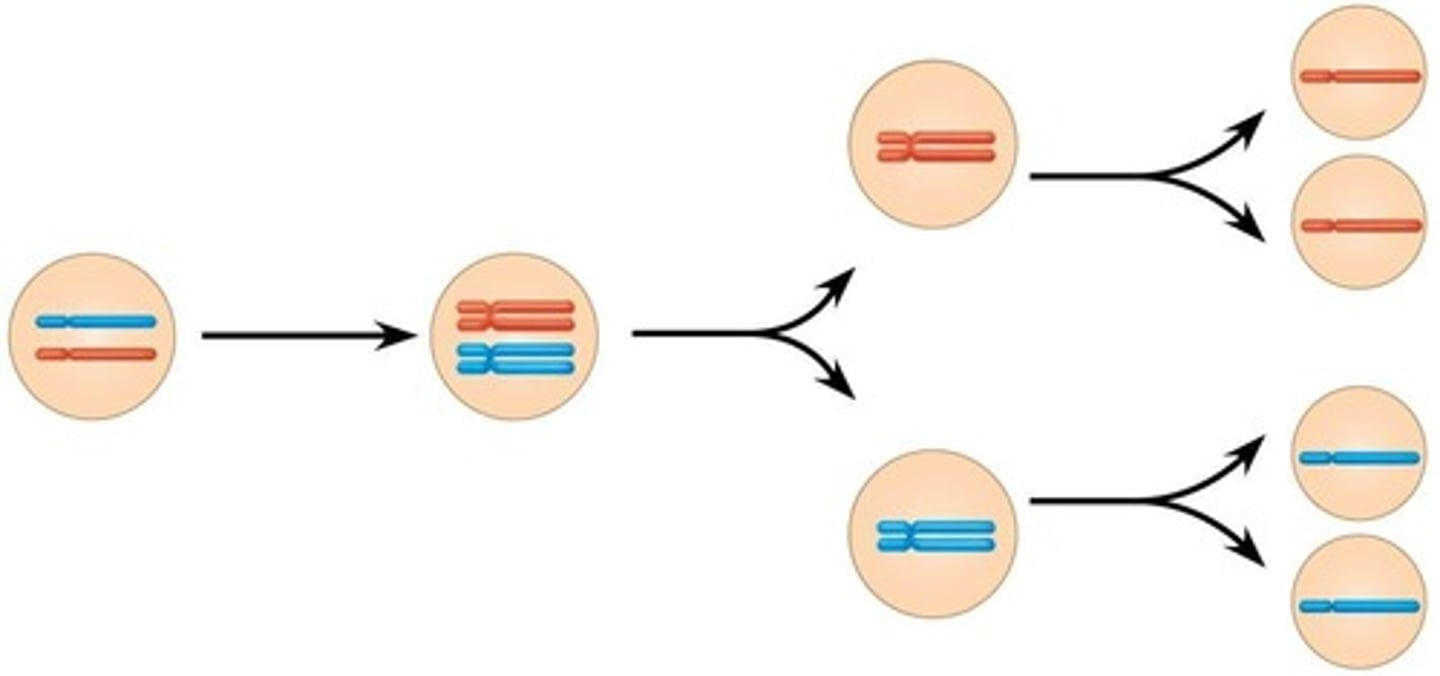
Meiosis I
First division separating homologous chromosomes.
Meiosis II
Second division separating sister chromatids.
Tetrad
Structure formed by paired homologous chromosomes.
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Locus
Specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
Spindle microtubules
Structures that separate chromosomes during division.
Metaphase plate
Equatorial plane where chromosomes align during metaphase.
Telophase
Final stage of cell division, nuclear envelope reforms.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm following mitosis or meiosis.
Somatic cells
Body cells, typically diploid with 46 chromosomes.
Mitosis
Cell division producing two identical diploid cells.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg to form zygote.
Chromatin
Uncondensed form of DNA in the nucleus.
Mitosis
Process producing two identical diploid cells.
Meiosis I
First division of meiosis, reduces chromosome number.
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occurs.
Metaphase I
Homologous chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate, sister chromatids remain attached.
Telophase I
Nuclear membranes form around separated homologous chromosomes.
Meiosis II
Second division of meiosis, separates sister chromatids.
Prophase II
Chromosomes condense, spindle apparatus forms again.
Metaphase II
Sister chromatids align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Telophase II
Nuclear membranes form around four haploid cells.
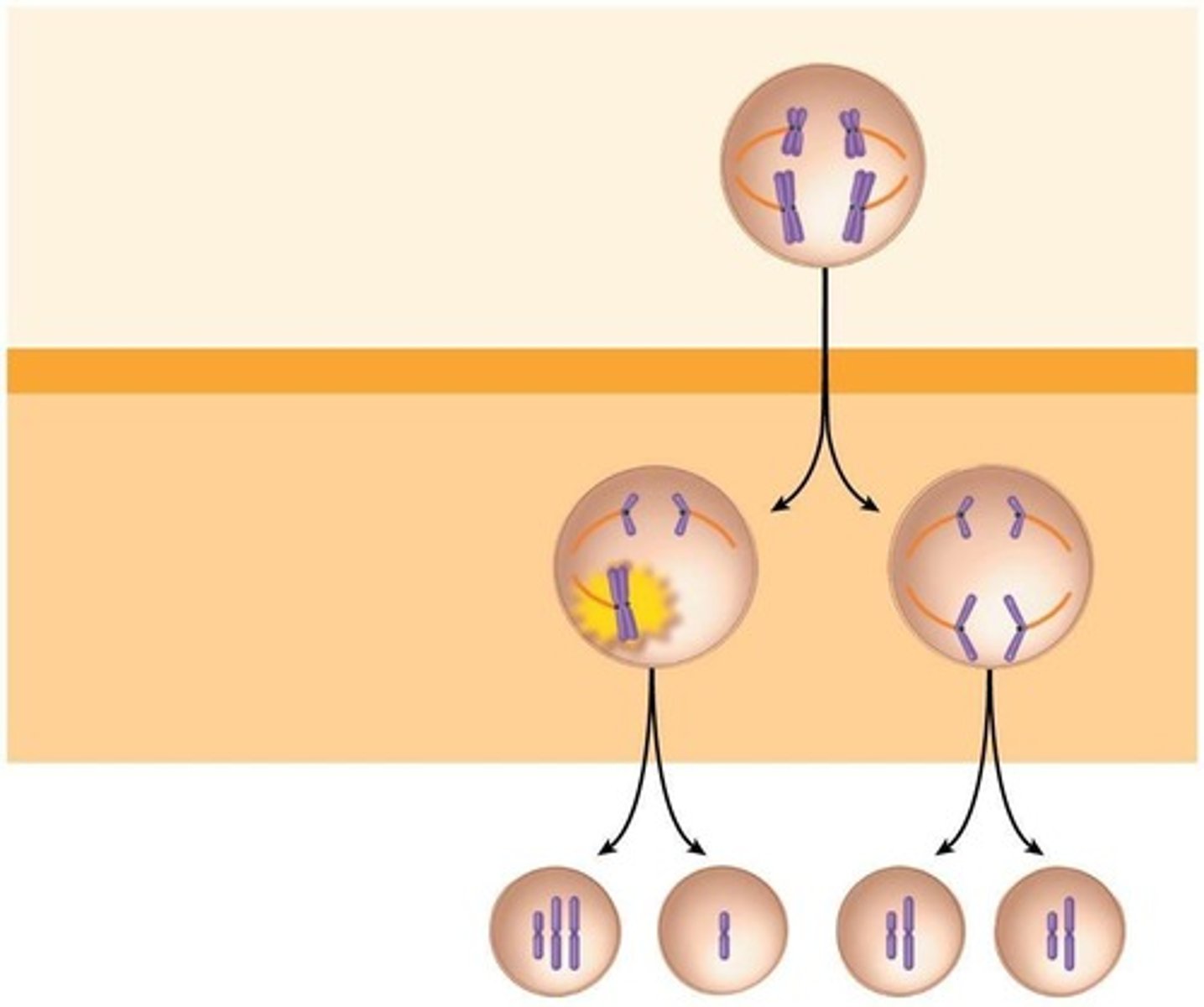
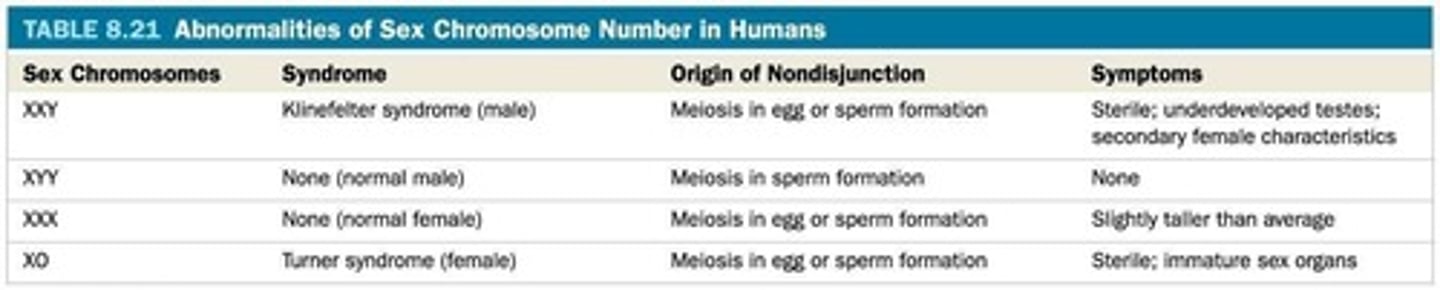
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis.
Gametes
Haploid reproductive cells formed by meiosis.
Crossing Over
Exchange of segments between nonsister chromatids.
Chiasma
Point where homologous chromosomes cross over.
Independent Orientation
Random arrangement of chromosomes during metaphase I.
Genetic Recombination
New combinations of genes due to crossing over.
Haploid Cells
Cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Diploid Cells
Cells with two sets of chromosomes.
Sexual Reproduction
Process producing genetically unique offspring.
Asexual Reproduction
Process producing genetically identical offspring.
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis.
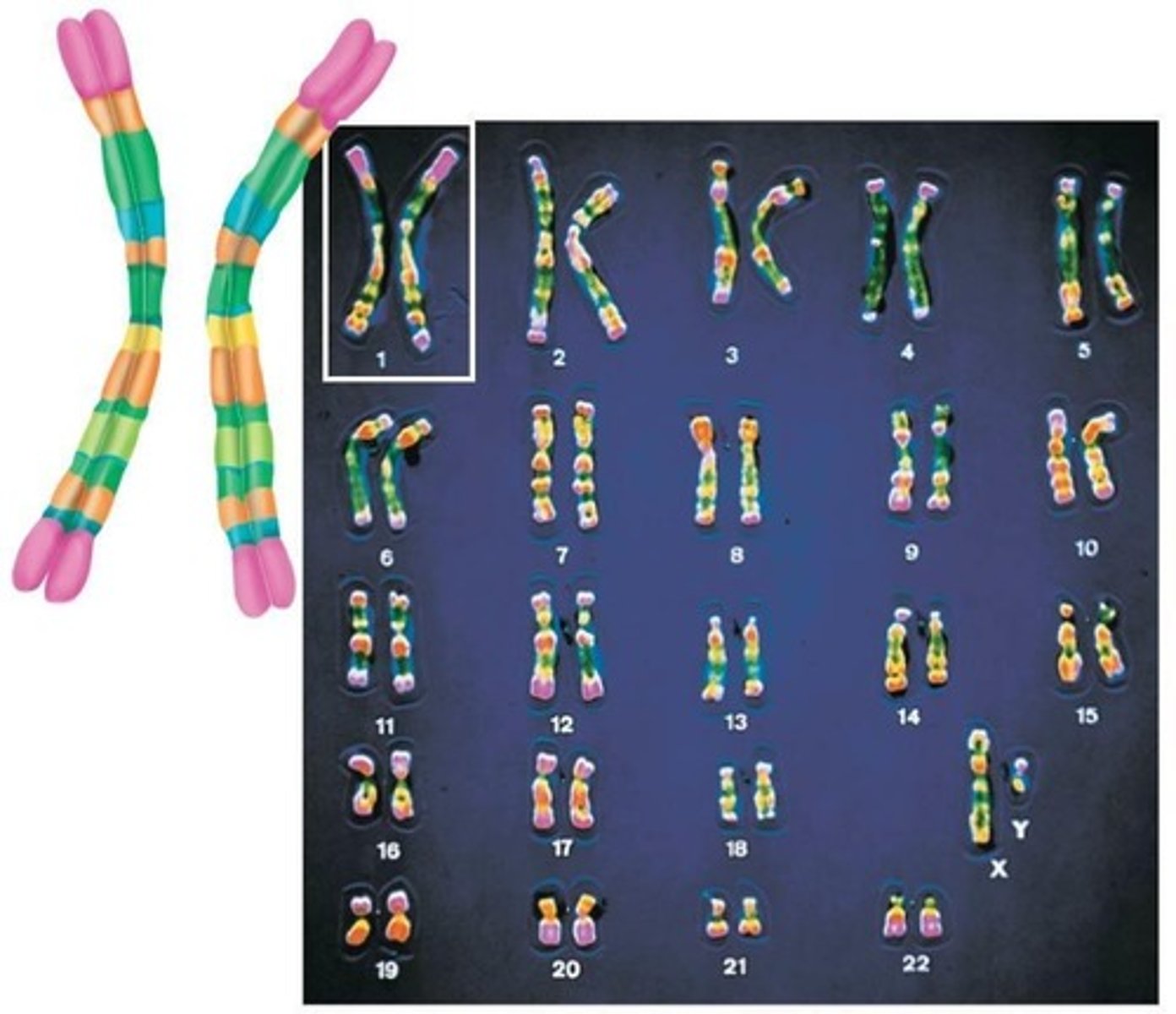
Karyotype
Photographic inventory of an individual's chromosomes.
Trisomy 21
Extra copy of chromosome 21 causes Down syndrome.
Polyploidy
Organisms with extra sets of chromosomes.
Chromosome Breakage
Can lead to deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations.
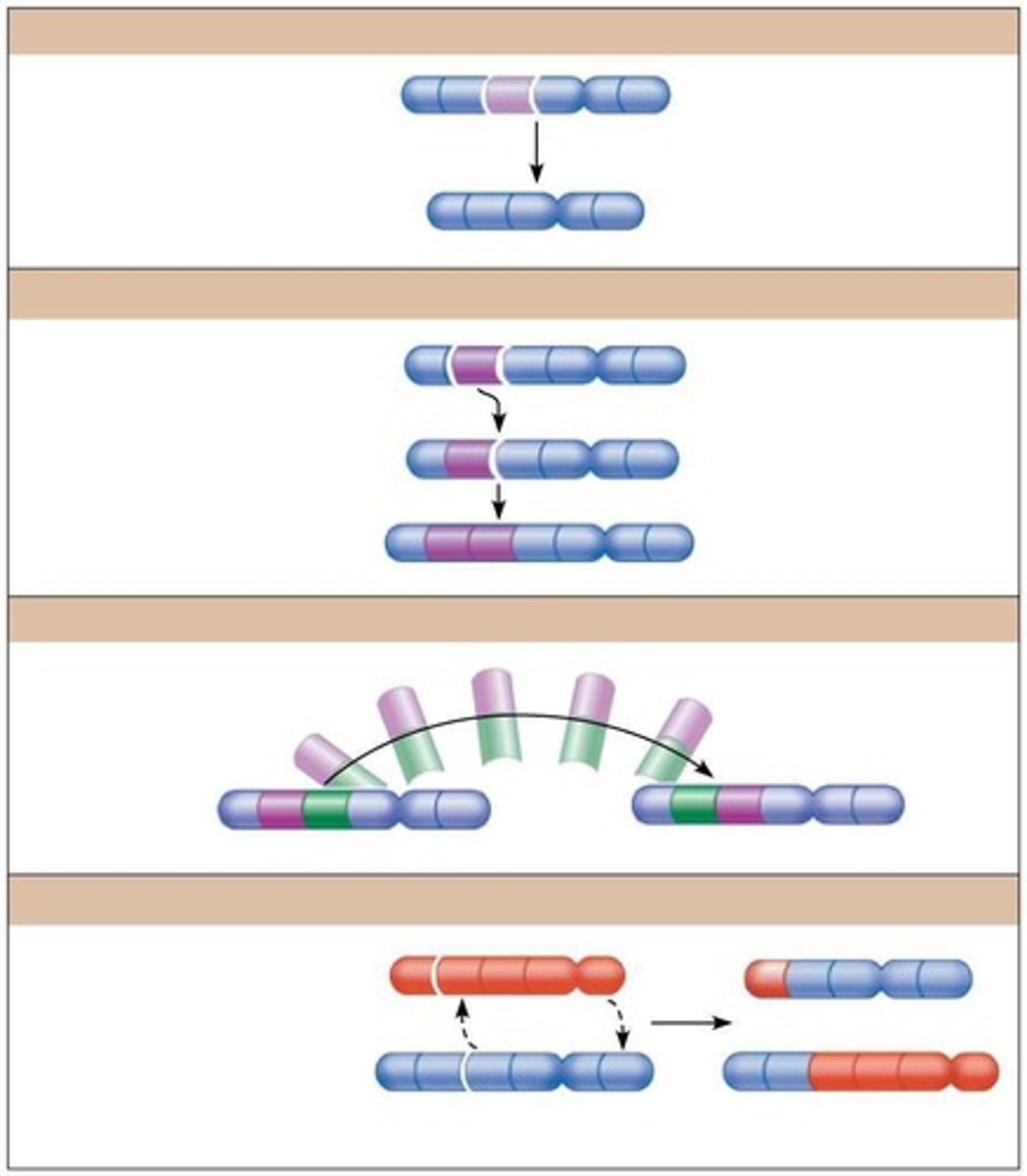
Philadelphia Chromosome
Abnormal chromosome linked to chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Somatic Cells
Body cells that are not gametes.
Gametes
Reproductive cells, either sperm or eggs.
Diploid Cells
Cells containing two complete sets of chromosomes.
Haploid Cells
Cells containing one complete set of chromosomes.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half chromosome number.
Mitosis
Cell division resulting in two identical daughter cells.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome connected at centromere.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosome pairs, one from each parent.
Cell Cycle
Series of events leading to cell division.
Chemical Growth Factors
Substances that regulate cell division.
Anchorage Dependence
Requirement for cells to be attached to a substrate.
Cell Density
Influence of cell population on cell division.
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Alterations in chromosome number or structure.
Down Syndrome Symptoms
Physical and cognitive impairments due to trisomy 21.
Evolution of New Species
Can arise from errors in cell division.