4.1 international economics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
globalisation
refers to the growing interdependence of countries and the rapid change it brings about
characteristic of globalisation
movement towards free trade of goods and services
free movement of labour and capital
free interchange of technology and intellectual capital
factor contributing to globalisation
improvements in transport and infrastructure
improvements in IT and communications
trade liberalisation
TNCs
international financial markets
impacts of globalisation on consumers
consumers have more choice- wider range of goods available all around the world
lead to lower prices as firms take advantage of comparative advantage and produce in countries with lower costs
lead to rise in prices
loss of culture
impacts of globalisation on workers
some gain others lose
increased migration
inequality
sweatshops
impacts of globalisation on producers
firms are able to source to more countries
reduces risk of collapse of the market
firms who are unable to compete internationally and will lose out
impacts of globalisation on governments
may receive higher taxes
maximise gains and minimise losses
impacts of globalisation on the environment
increased demand for raw materials
more emissions
globalisation may aim to tackle climate change
impacts of globalisation on Economic growth
increases investment within countries
TNCs may bring world class management techniques and technology
political instability
comparative advantage
Countries should specialise in goods at which they produce the lowest opportunity cost
absolute advantage
a country can produce a good more efficiently than its competitors, using the same amount of resources
assumptions and limitations of the theory
comparative advantage assumes there are no transport costs- these could lower or prevent any comparative advantage
assumes costs are constant and there are no economies of scales
goods are assumed to be homogenous
assumes factors are perfectly mobile- no tarrifs or other trade barriers
depends on the terms of trade between countries
advantages of specialisation and trade
show how the world output can be increased
allows countries to benefit from economies of scale
Different countries have different factors of production and so trade allows countries to make use of factors of production, or the things produced by these factors, which they otherwise may have been unable to
greater competition
disadvantages of specialisation of trade
lead to over dependence
cause structural unemployment- jobs are lost to foreign firms
the environment will suffer- transport
Patterns of trade
refers to changes in a country’s imports and exports
Factors influencing the pattern of trade
comparative advantage
impact of emerging economies
growth of trading blocs and bilateral trading agreements
changes in relative exchange rates
comparative advantage
countries will trade where there is a comparative advantage to trading
there has been a recent growth in the exports of manufactured goods fro developing countries to developed countries
because developing countries have gained an advantage in the production of manufactured goods due to their lower labour costs
emerging economies
countries grow at different rates and when they grow they are more likely to need to import more goods and services than before exporting more to pay for this
emerging economies take up a larger proportion of a countries imports and exports than they had previously
trading blocs and bilateral trading agreements
these increase the level of trade between certain countries and so influence the pattern of trade
because trade increases between these countries and decreases between others
Relative exchange rates
affects the relative prices of goods between countries
prices are an important factor in determining whether consumers buy goods and so a change in price will affect the pattern of trade
terms of trade
prices
measures the rate of exchange of one product for another when two countries trade
tells us the qty of exports that need to be sold in order to purchase a given level of imports
calculation of terms of trade
(average export price index/ average import price index) x100
factors influencing a country’s terms of trade
an improvement in the terms of trade will be caused by a rise in export prices or fall in import prices
short run- exchange rates, inflation and changes in demand/ supply of imports or exports
improvement in productivity
changes in incomes
impacts of changes
if imports and exports are inelastic- improvements to the current account on the balance of payments
if its elastic it would worsen the current account
improvement in terms of trade is likely lead to a fall in GDP- rise in price of exports, exports fall
trading blocs
a group of countries within a geographical region that trade together with reduced or eliminated trade barriers
preferential trading areas
where tariff and other trade barriers are reduced on some goods traded between member countries
free trade areas
two or more countries in a region agree to eliminate trade barriers on all goods from other members
customs union
acceptance of a common external tariff against non members
common markets
free movement of goods, services, capital and labour
significant level of harmonisation of micro economic policies
common policies such as common agricultural policy
monetary unions
adopting the same currency
exchange rate is monitored and controlled by one central bank
EU zone
o The European Central Bank distributes notes and coins, sets interest rates, maintains a stable financial situation and manages the foreign currency reserves.
o In the EU, the governments agreed not to exceed a fiscal deficit of more than 3% and not to have a National Debt of more than 60%.
for monetary unioun to be successful there should be free movement of labour, capital mobility and wage and price flexibility
economic union
the final step of economic integration
there will be a common market with coordination of social,fiscal and monetary policy
advantages of free trade
Encourages increase specialisation, and this increases output, according to comparative advantage
this specialisation also helps firms to benefit from economies of scale, causing lower prices and costs
Firms can grow larger by creating customer market, economies of scale will be increased further over time as countries expand
Firms inside the bloc are protected from cheaper imports from outside, e.g those in the EU are protected from chinese imports
disadvantage of free trade
-Countries ae no longer to benefit from trade with countries in other blocs and the blocs are likely to distort world trade, reducing the benefits of specialisation
-There may be a reduction in competition as inefficient firms are driven out of the business and the market becomes oligopolistic
-They distribute the gains from trade unequally with developed countries often gaining most and developing being impacted little
Trade creation and diversion
trade creation is when trade is created by the joining of a trade union. It is when consumption shifts from a high cost domestic producer to a low cost partner producer higher cost domestic producer to a low cost partner producer
trade diversion is when consumption shifts from low cost producer outside the trading bloc to a higher cost producer within it
tariff diagram
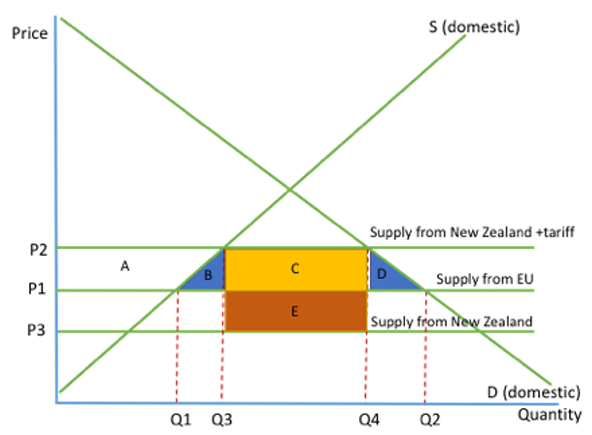
role of WTO
bring about trade liberalisation
ensure countries act according to the trade agreements they have signed
conflicts with the WTO
regional trade agreements contradict WTO’s principles
complement the trading system and the WTO strives to ensures non-members can trade freely and easily with members of a trade bloc
it ignores the developing countries
reasons for restrictions
job protection- governments may be concerned that allowing imports will ean domestic producers will lose out to international firms
protection from unfair competition- around the world different rules apply meaning that producers in different countries can produce at different prices
Terms of trade- restrictions will reduce supply of good and lead to a fall in the price recieved by the importer
tariffs
taxes on imported goods
quotas
limits placed on the level of imports allowed into a country
subsidies to domestic products
payments to domestic producers which lower their costs
impact of protectionist policies on consumers
there are higher prices for consumers as they are unable to buy imports at the cheaper price
raises the price of domestic producers as goods and services needed for the production of these goods may also suffer from import controls
impact of protectionist policies on producers
less competition so can sell more goods at a higher price
foreign producers will lose out as they are limited in where they can sell their goods
impact of protectionist policies on workers
the market would reallocate resources and create new jobs
impact of protectionist policies on governments
gain tariff revenues and are politically popular and can lead to an inefficient economy
balance of payments
A record of all the financial transactions that occur between a country and the rest of the world
the current account
It records the net income that an economy gains from international transactions
Current transfers are typically payments at government level between countries e.g. contributions to the World Bank
causes of current account deficits
Relatively low productivity
high value of the country’s currency
high rate of inflation
Non-price factors such as poor quality and design
how to reduce imbalances on the current account
expenditure switching- use of protectionism (tarriffs or quotas)
expenditure reducing- reduce ad, deflationary fiscal policy
supply side policies- aim to improve factors of production to raise output
do nothing- floating exchange rate acts as a self correcting mechanism
benefits of expenditure switching
Successful in changing the buying habits of consumers
by switching consumption on imports to consumption on domestically produced goods
costs of expenditure switching
Protectionist policies lead to retaliation by trading partners
may consist of reverse tariffs which will decrease exports- trumps tariffs
benefits of expenditure reducing
Deflationary fiscal policy reduces disposable income
leads to a fall in the imported goods and services
improves deficit
costs of deflationary fiscal policy
Deflationary fiscal policy dampens domestic demand which can cause output to fall
when output falls GDP growth slows and unemployment may increase
benefits of supply side policies
Improves quality of products and lowers the cost of production
help the level of exports to increase
reducing the deficit
Cons of supply side policies
Policies tend to be long term so the benefits may not be seen for some time
they usually involve government spending in the form of subsidies and this always carries an opportunity cost
Floating exchange rate
Supply and demand for a currency determines the exchange rate
excess demand= prices to rise
Fixed exchange rate
A country’s central bank intervenes in the currency market to fix the exchange rate
Managed exchange rate
The free market determines the value of a currency but also central banks will intervene from time to time to keep currency value in a desired range
Factors influencing exchange rate
interest rates- hot money flows
inflation rate- value of imports and exports
net investment- FDI into countries
The current account- trade surplus= appretiation of the pound