Pediatric Oral Pathology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Developmental anomalies of the oral mucosa
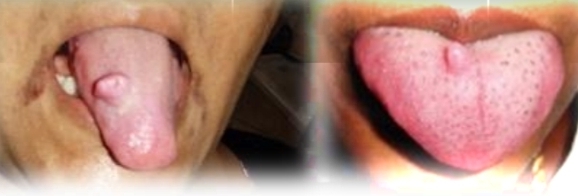
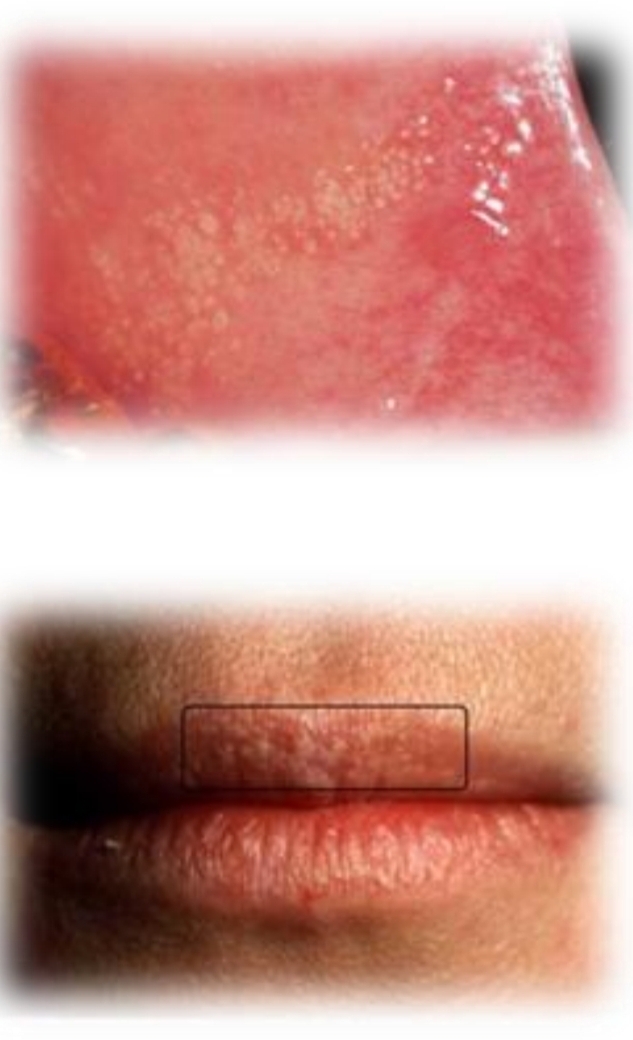
Fordyce granules
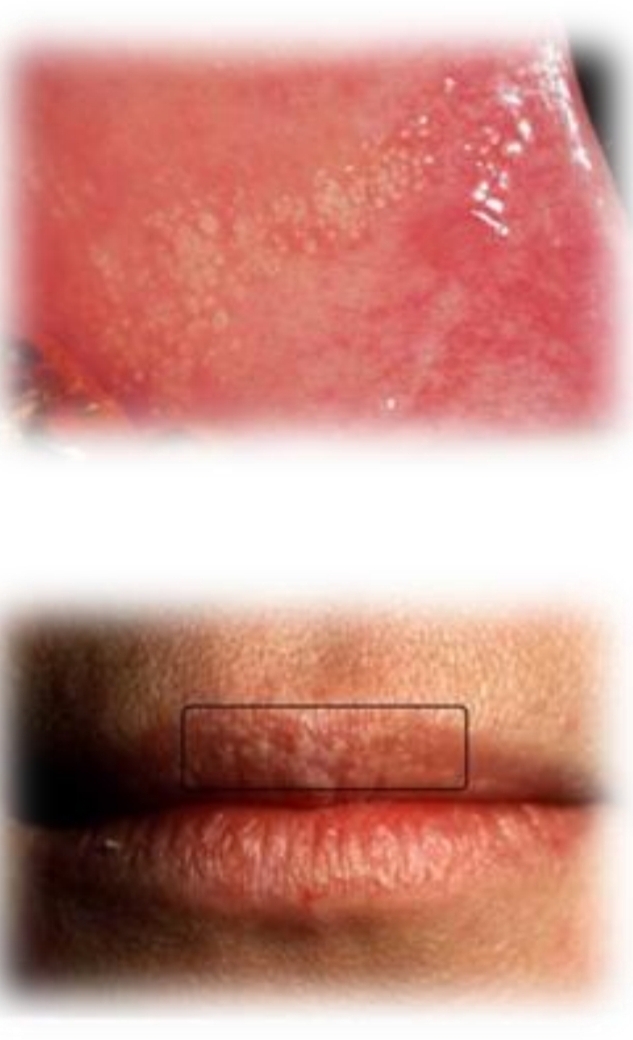
Small yellow-white multifocal papules. Discrete or clustered.
Asymptomatic
Second decade of life (puberty)
Male predilection
Found on:
Bilateral buccal mucosa
Retromolar pad
Upper lip vermilion
Fordyce granules
Oral sebaceous glands
May increase in size
No treatment - can laser for cosmetics
DD - Frictional keratosis, scar formation, pustules
White lesions of the oral mucosa
Frictional keratosis
Morsicatio Buccarum
Leukoedema
White sponge nevus
Linea alba
Scar formation (Cicatrix)
Chemical burn
Pseudomembranous candidiasis (thrush)
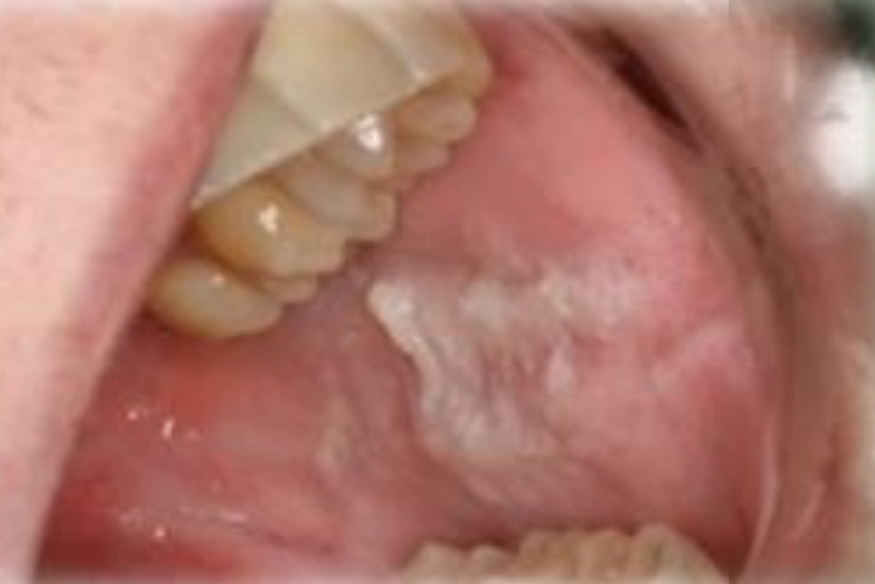
Localized to diffuse white rough/shredded patches, adherent.
Asymptomatic
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Mucosa adjacent to occlusal plane: Buccal, labial mucosa, lateral tongue, attached gingiva
Ask: History of habits and ortho appliances?
Frictional keratosis
Chronic biting/sucking habits
Irritation from orthodontic appliances
Fractured teeth
Tooth brushing
Treatment - eliminate cause, lesion will regress
DD - Leukoedema, linea alba, smokeless tobacco keratosis, cinnamon contact, stomatitis, lupus erythematosus
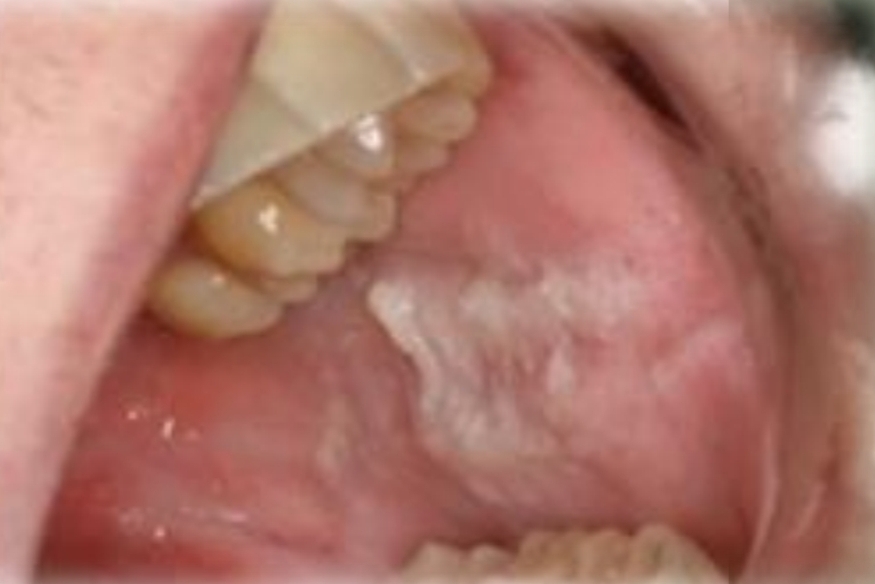
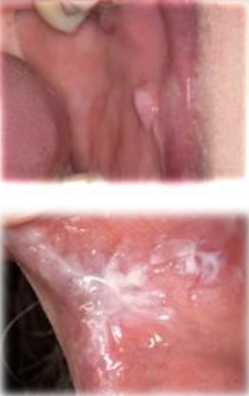
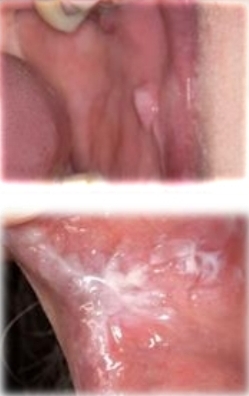
Whitish formation that comes off when rubbing, with superficial mucous tearing.
Small whitish epithelial desquamation, that leave erythematous areas between them.
Asymptomatic
No gender bias
Early childhood/puberty
Found on:
Buccal mucosa
Labial mucosa
Lateral border of tongue
Ask: Chewing habit or Anxiety? Look for adjacent poor restorations + signs of bruxism.
Morsicatio buccarum
Reactive lesion from poor fitting restoration
Mucosa chewing habit in anxiety or bruxism
Treatment - Correct habit - night splints and oral shield. (If iatrogenic correct restoration)
DD - Frictional keratosis, Leukoplakia, lichen planus, pseudomembranous candidiasis
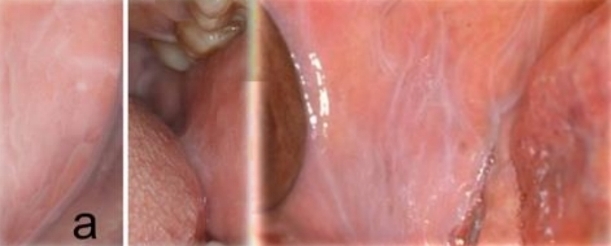
Widespread, filmy white, wrinkled mucosa - Adherent.
Dissapears when stretched
First and second decades
No gender bias
More common in black children
Found on:
Bilateral buccal mucosa
Labial mucosa
Soft palate
Leukoedema
Common variant of normal mucosa
More pronounced in cigarette smokers
No treatment
DD - Frictional keratosis, Linea alba, White sponge nevus
White plaques that are diffuse, symmetric, corrugated or velvety. Adherent
Asymptomatic
First decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Bilateral buccal mucosa
Labial mucosa
Ventral tongue
Floor of mouth
Soft palate
White Sponge Nevus
Autosomal dominant skin disorder - keratin defect
Extraoral sites may be involved
Reaches full expression during adolescensce
Treatment:
None required
Retinoids, topical tetracyclines, systemic penicillin (partially effective)
Surgery most effective
DD - Leukoedema, Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis, frictional keratosis, Hyperplastic candidiasis, Syndrome related leukoplakia
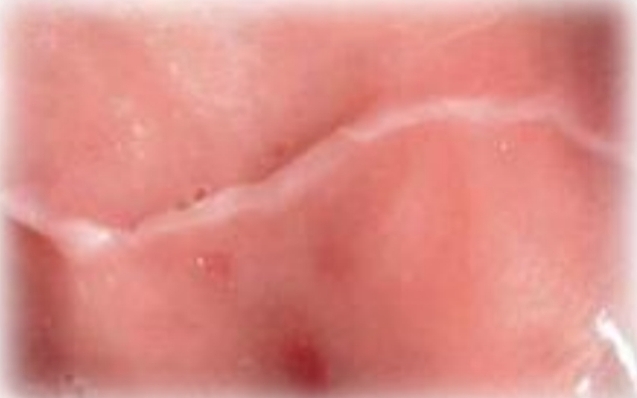
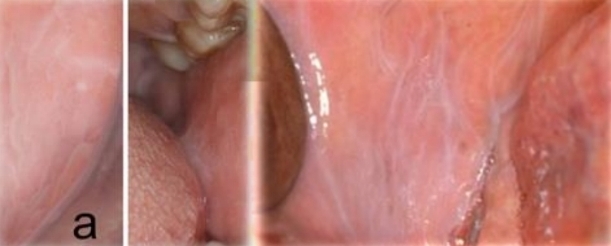
White line, may be scalloped
Asymptomatic
No gender bias
Any age after eruption
Found on:
Bilateral buccal mucosa
Along occlusal plane
Linea alba
Biting irritation / sucking habit
May be associated with leukoedema
No Treatment - may spontaneously regress
DD - Cinnamon contact stomatitis, scaar formation, Cheek biting keratosis
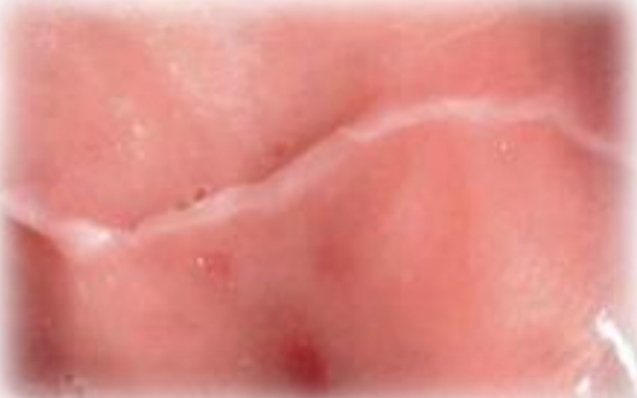
White or pale pink line, or smooth irregular patch with crosshatch or starburst pattern
Asymptomatic
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Any site; common on labial mucosa, lip vermillion, tongue
Ask: history of trauma or surgery?
Scar formation (cicatrix)
Oral trauma or surgery
May represent child abuse or self-mutilation
Treatment - none, unless cosmetic concern or restricts function (then scar revision)
DD - Cinnamon contact stomatitis, Cheek biting keratosis
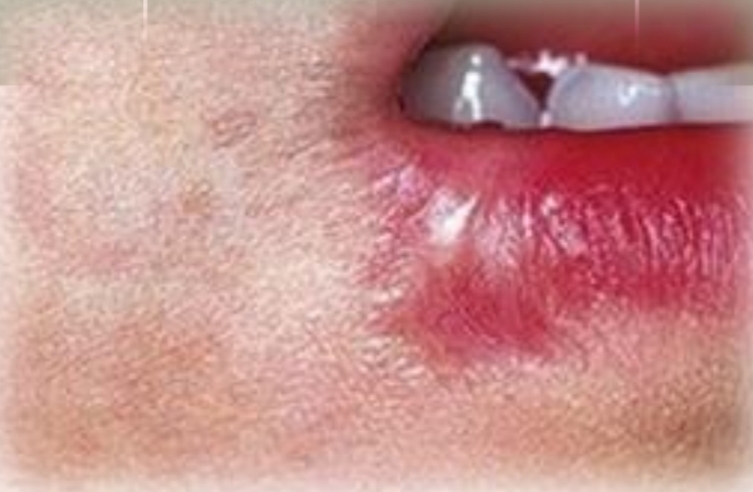
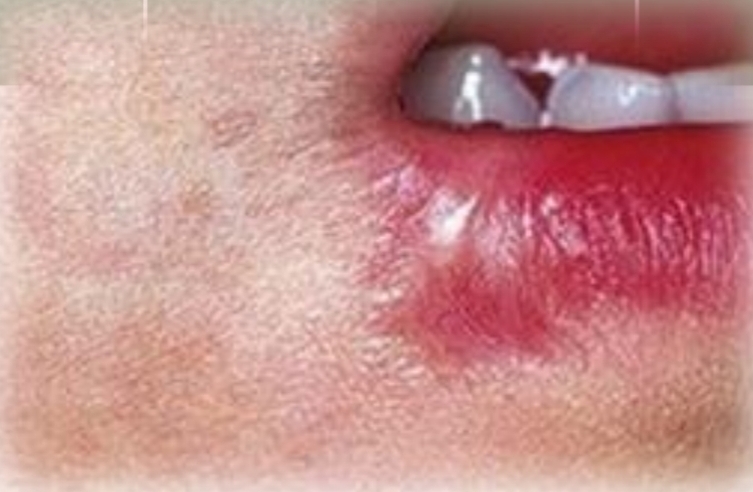
Localised or widespread, white nonaderent plaques and erythematous erosions or ulcers
Tender/Painful
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Any site, common on lips, tongue buccal mucosa, gingiva
Ask: Use of any topical medicine/chemicals or mouth rinse?
Chemical burn
Chemicals and drugs, including dental:
Inappropriate use of mouth rinses, topical anesthetics, phenol, formocresol
Treatment - Identify and remove cause, and symptomatic relief
DD - Plaque, Pseudomembranous candidiasis, Coated tongue, Mucosal sloughing, Mucous patch of syphilis
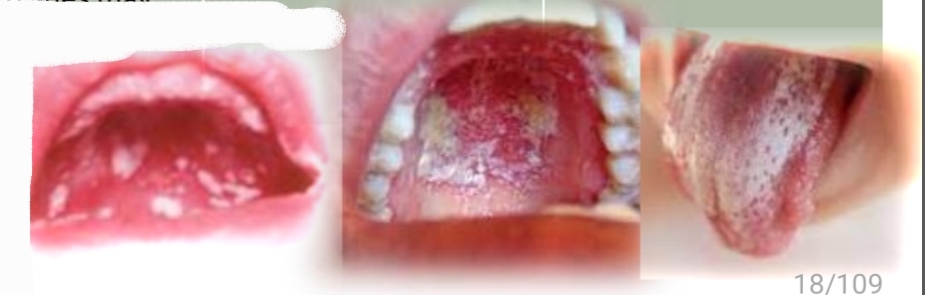
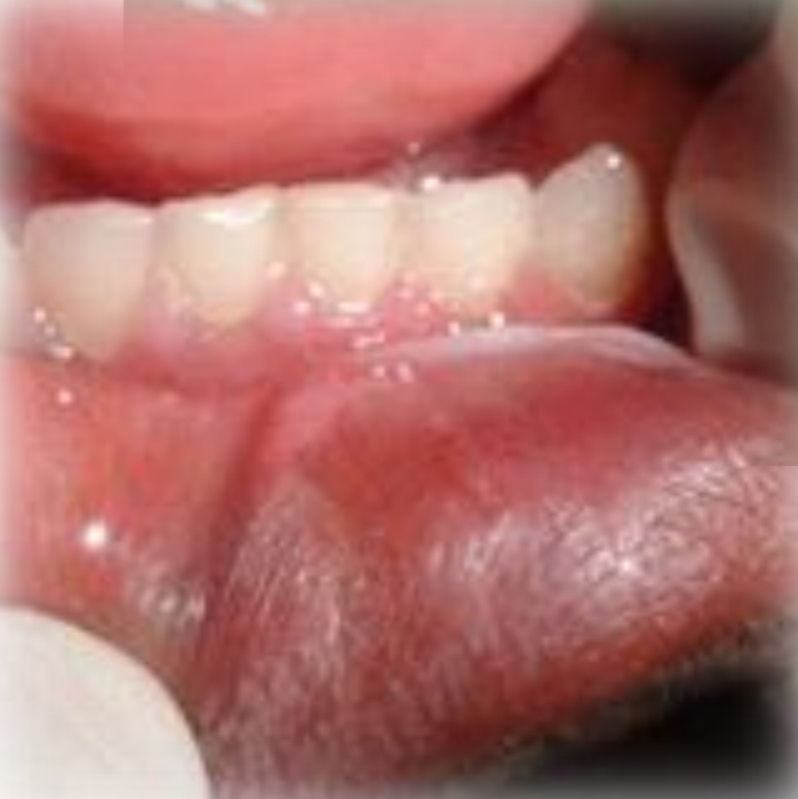
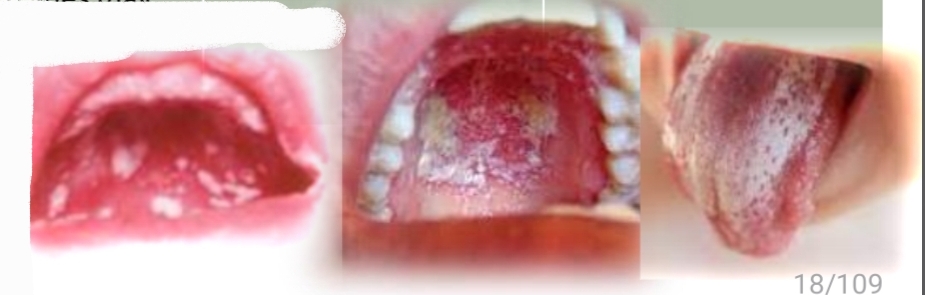
Widespread, white spots or plaques that wipe off leaving red base
Mild burning sensation
Any age, esp. infancy
No gender bias
Found on:
Any mucosal site - common on buccal mucosa, tongue and palate
Ask: Taking any medications, if infant - pacifiers, diaper rash? Orthodontic applianes? Immunosupressive condition?
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis
Candida albicans fungus (and other species)
Contributing factors: antibiotics, steroids, immune supression
Orthodontic appliances and toothbrushes may harbour fungus
Treatment - Antifungals, proper oral hygiene. Reccurance if cause not eliminated
DD - Plaque, Chemical burn, Coated tongue, Mucosal sloughing, Superficial lip and cheek biting, Koplic spots of rubeola
Pigmented lesions of the oral mucosa
Petechiae, ecchymosis, hematoma
Erythematous candidiasis
Oral melanotic macule
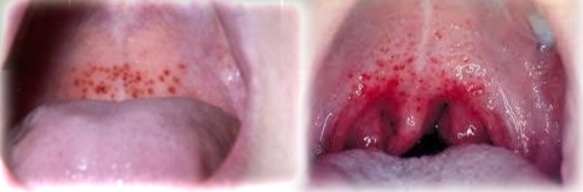
Localised to diffuse pinpoint spots/patches/swelling with smooth surface. Red, blue or black depending if early or late lesion.
May be tender
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Buccal mucosa
Lips
Lateral tongue
Soft palate
If multiple Lesions are present, what must we exclude?
Petechiae, Ecchymosis, Hematoma
If multiple lesions, must exclude:
Child abuse
Bleeding disorders
Infectious mononucleosis + other viral infections
No treatment - spontaneously resolve
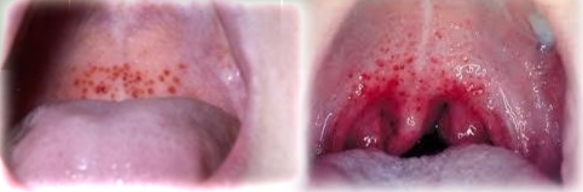
Multiple red macules to diffuse red patches
Depapillation of tongue
Burning sensation
Possible angular chelitis
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Palate, Buccal mucosa, dorsal tongue
Ask: medications, palatal coverage appliance, check medical history. In infant, use of pacifier?
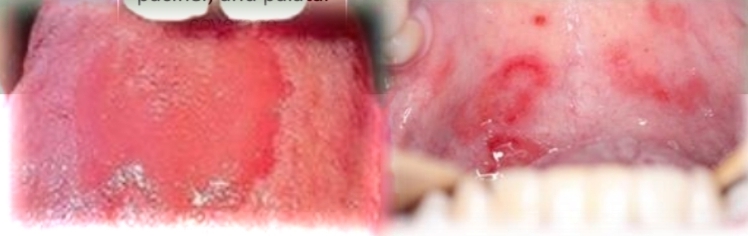
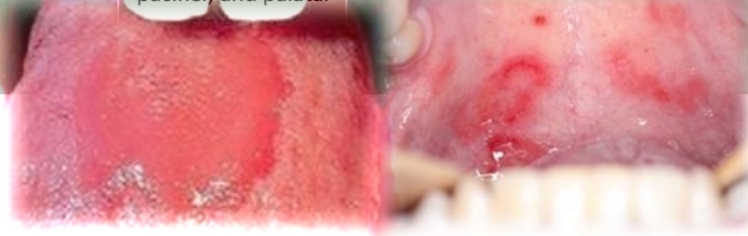
Erythematous candidiasis
Candida albicans and other species
Contributing factors: Antibiotics, immunosupression, xerostomia, pacfier, palatal coverage appliance
Treatment - Antifungal medication and proper oral hygiene. May recur if cause not eliminated or managed
DD - Contact allergy, Traumatic erythema, Erythema migrans, Thermal burn, Anemia
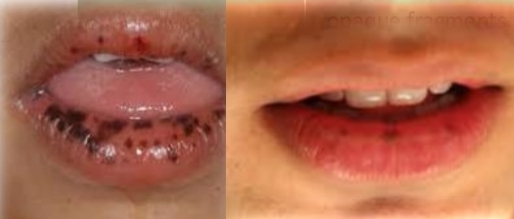
Brown/ black oval macule with smooth surface and well defined to irregular margins.
Potential opaque fragments in radiograph
First and second decades
Female predilection
Found on:
Lower lip vermillion, Buccal mucosa, Gingiva
Oral melanotic macule
Most common oral pigmentation of fair complexioned children
Multiple lip macules in Peutz-jeghers syndrome
Treatment - None unless menalocytic neoplasm cannot be excluded. Otherwise (if not neoplasm), no potential for malignant transformation.
DD - Amalgam/graphite tatoo, Melanocytic nevus, Smokers melanosis, Late eccymyosis
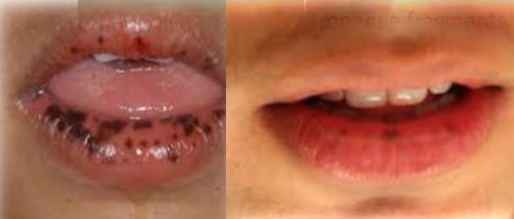
Ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa
Apthous ulcer
Traumatic ulcer
Contact allergy
Erythema multiforme
Painful recurrent ulcers. Can be 1-5 superficial and <1cm or multiple deep >1cm. Can also be herpetiform.
First and second decade
Female prediliction
Found on:
Buccal, labial mucosa most common
Non keratinized mucosa
Apthous Ulcers
T-cell mediated reaction
Trauma and ortho are factors in children
Genetic predisposition
Association with systemic disease, food sensitivities, nutritional deficiencies
Minor variant: 1-5 superficial oval ulcers <1cm. Resolves 7-10 days
Major variant: Multiple deep ulcers >1cm. Resolves in 2-6 weeks
Herpetiform variant: Showers of multiple small ulcers
Treatment - Topical anaesthetics and coating agents for symptomatic relief, Corticosteroids (t+s), chlorhexidine rinse, laser treatment, nutritional supplement. Major varients heal with scarring
DD - Traumatic ulcer, Secondary herpetic ulcer, Chrons disease, Behcet syndrome, Celiac disease, neutropenic ulcer, PFAPA syndrome, Gastroesophageal reflux disease
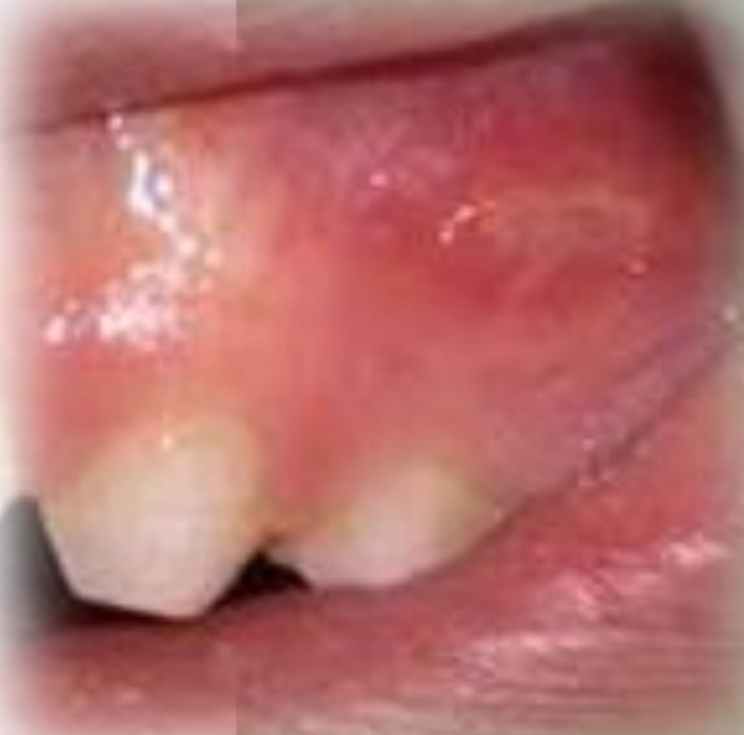
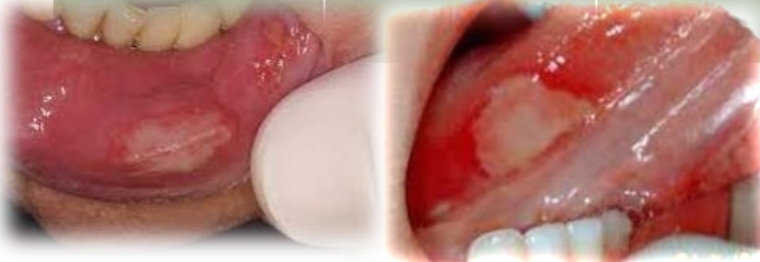
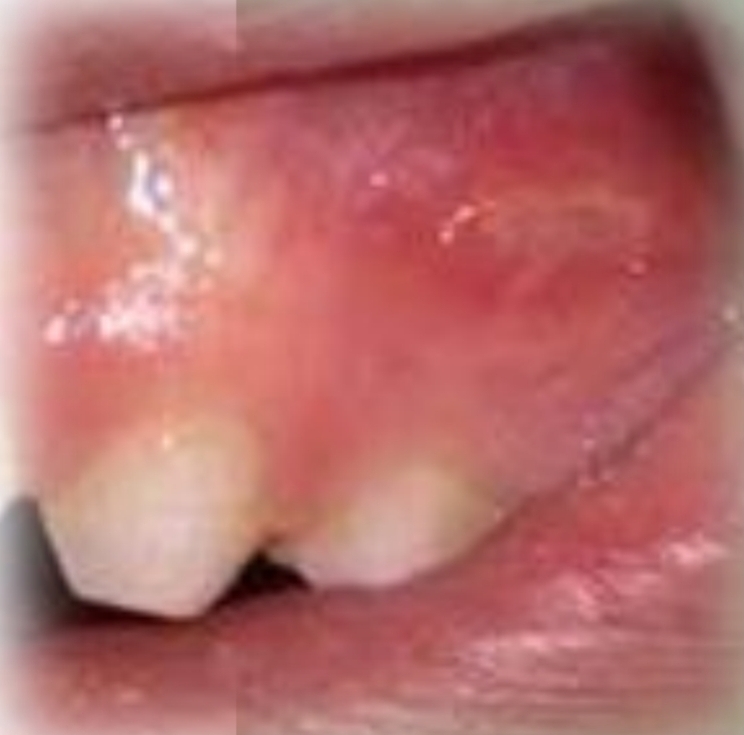
Single (usually), large ulcer, variable shape and irregular margins. Shallow or deep
Painful
First and second decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Lateral tongue, Buccal mucosa, lips and gingiva, ventral tongue
Ask: Recent injury to site?
Traumatic ulcer
Most common oral ulcer
May indicate:
Child abuse
Neurologic impairment
Factitial injuries when peristent and recurrent
Treatment - Typically heals in 1-3 weeks. Symptomatic relief, eliminate cause. Factitial ulcers are diagnostic problem. May heal with scarring.
DD - Apthous ulcer, Mucosal burn Secondary herpetic ulcer, Contact allergy
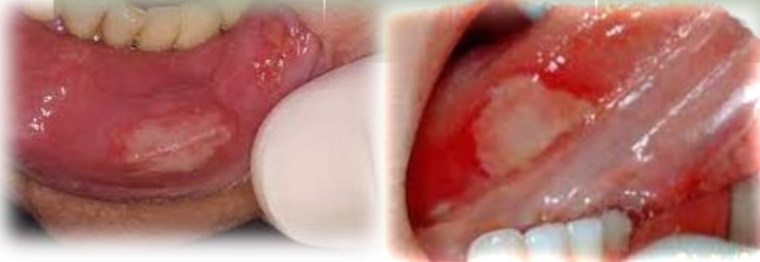
Focal or widespread erythema, with vesicles and ulcers.
Burning sensation and pain
First and second decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Any mucosal site
Ask: Use of new oral hygiene products/topical medications/cosmetic products? New/ rarely eaten food?
See if any dental materials near site
Contact allergy
Mucosa coming into contact with allergens - food/dental materials/ oral hygeine products/topical medications/ cosmetic products
Treatment - Identify (patch testing helpful) and eliminate allergen. Topical steroids for symptoms
DD - Mucosal burn, Secondary herpetic ulcer, Apthous ulcer, Angular cheilitis, Erythema multiforme
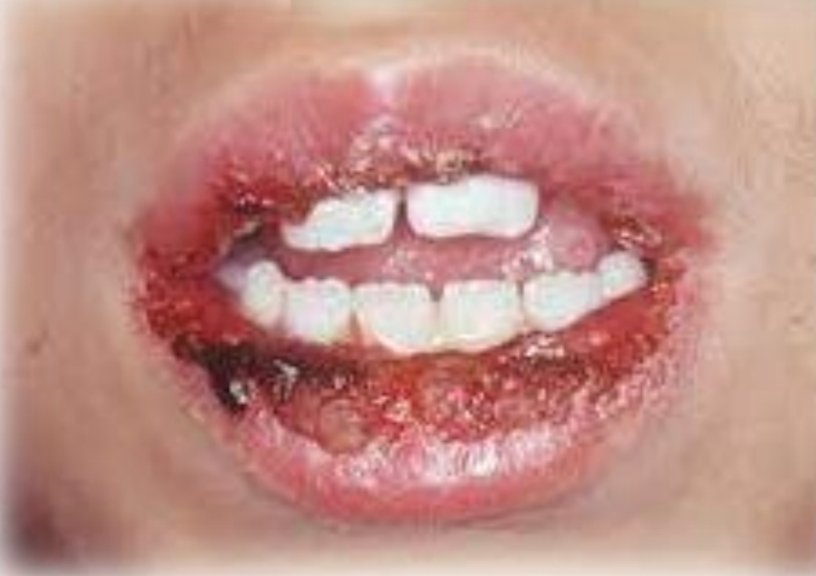
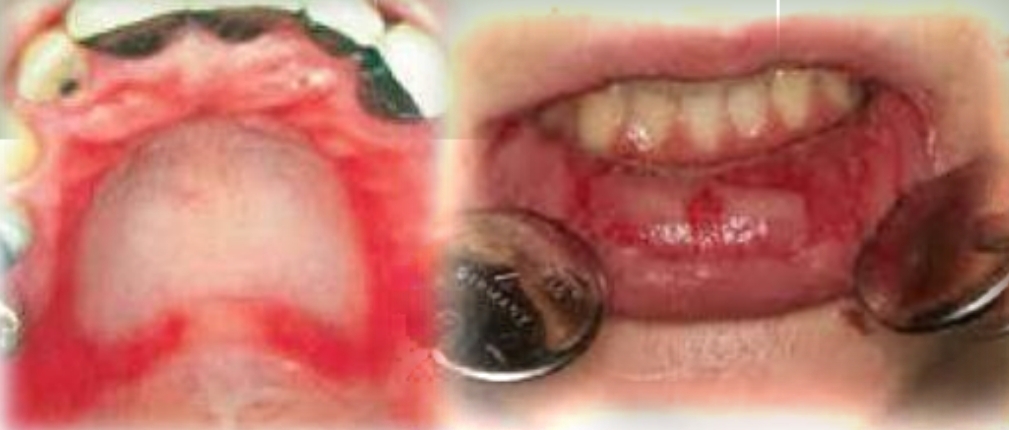
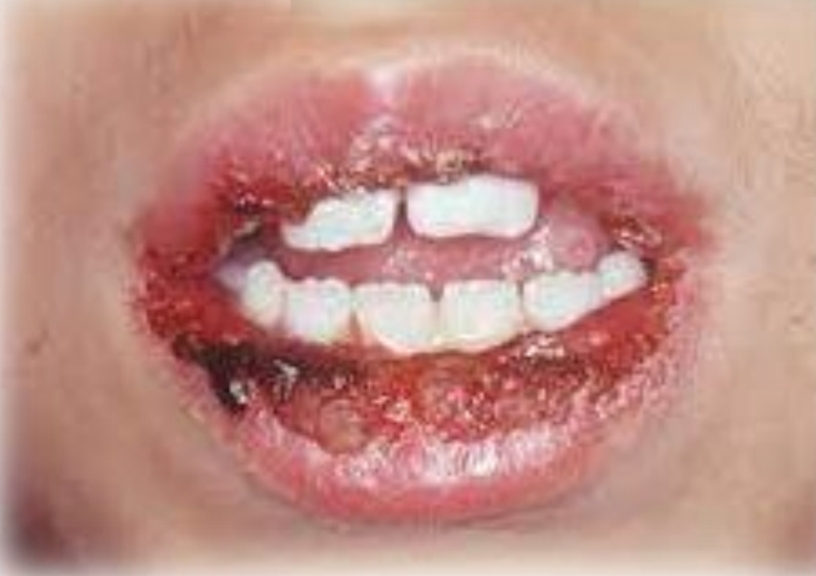
Widespread and painful, red macules, vesicles, bullae and ulcers. Blood crusted lesions on lips. Target lesions on skin.
Acute onset, fever, malaise
Second decade
Male prediliction
Found on:
Oral lesions: Lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, soft palate
Skin ‘Target’ lesions on: Extremities and head and neck region
Erythema multiforme
Common precipitating factors:
HSV
Medications
Major and minor forms exist
Treatment - Withdrawl of medication, lubricate lips, symptomatic relief. Hospitalization of severe. Reccurences common if triggered by HSV
DD - Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis, Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, Apthous major ulcers, Chemical burn
Papillary lesions of the oral mucosa
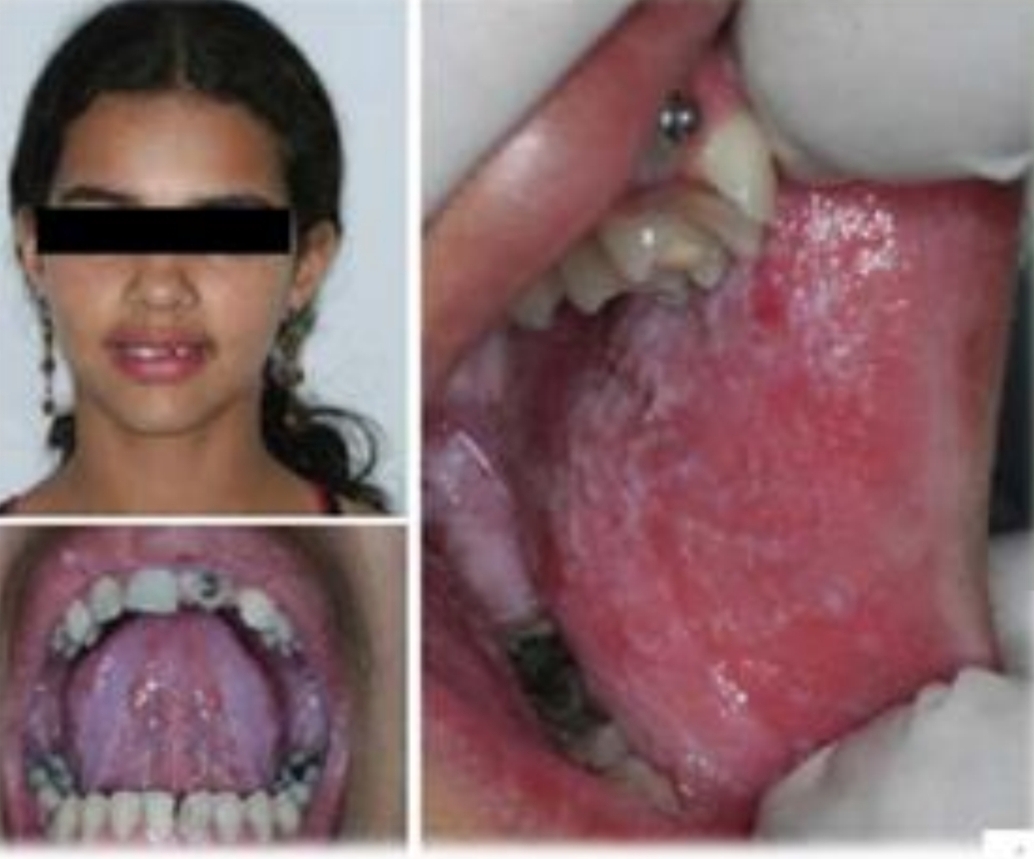
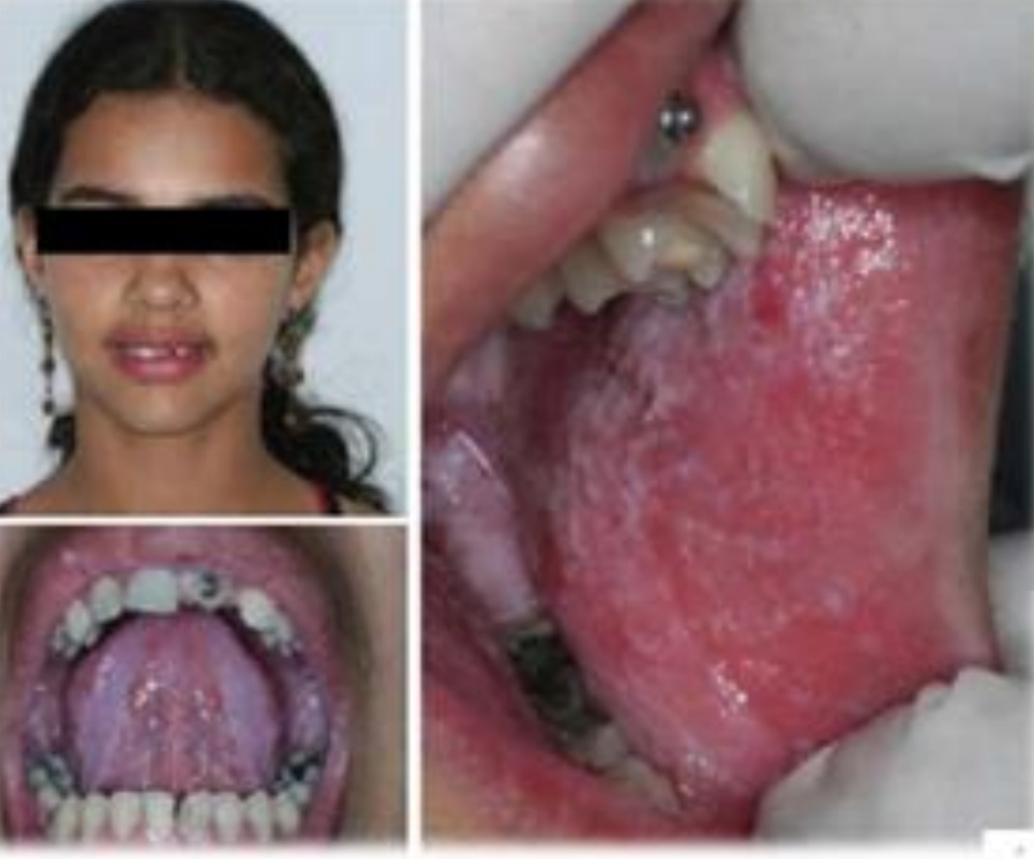
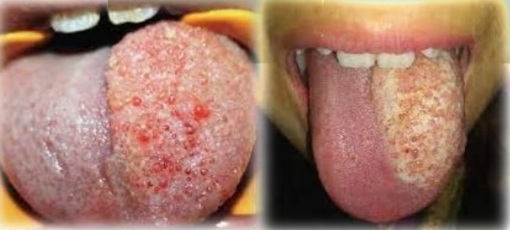
Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia (Hecks disease)
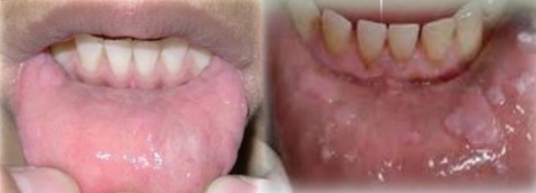
Multifocal sessile papules and nodules with pink grainy/stippled surface. Lesions coalesce. Cobblestone appearance.
Not tender
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Labial and buccal mucosa and tongue
Ask: Family history of same condition? Living conditions? Diet? Oral hygeine habits?
Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia (Hecks disease)
HPV 13, 32
Genetics
Poor hygeine, crowded living conditions and nutritional deficiencies
Treatment - Excisional biopsy, laser ablation. Reccurence common, but may spontaneously regress. No malignant transformation
DD - Verruca vulgaris, Conyloma acuminata, Multiple hamartoma syndrome, Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome
Tumor like lesions of the oral mucosa
Irritation fibroma
Mucosal neuromas (multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome, type 2b)
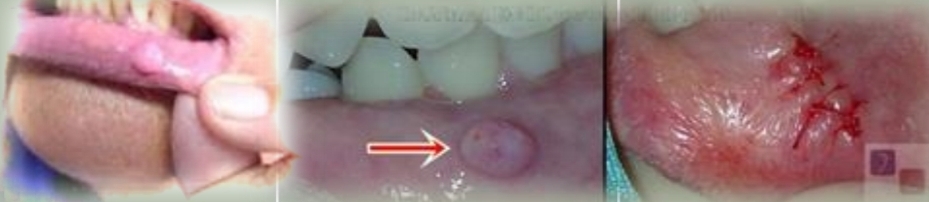
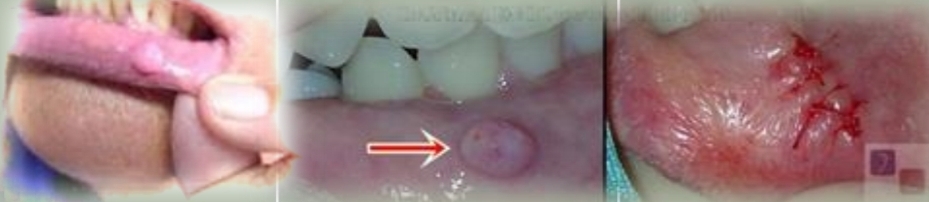
Pedunculated or sessile nodule, has a pink smooth surface, firm and non tender. Doesnt grow beyond a certain size
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Buccal and labial mucosa
Tongue
Attached gingiva
Irritation fibroma
Reactive hyperplastic lesion caused by chronic trauma and mimics tumor.
Limited growth potential
Treatment - Excisional biopsy, may reccur if irritation continues.
DD - Fibrosing mucocele, Peripheral ossifying fibroma, Giant cell fibroma, Benign submucosal neoplasm.
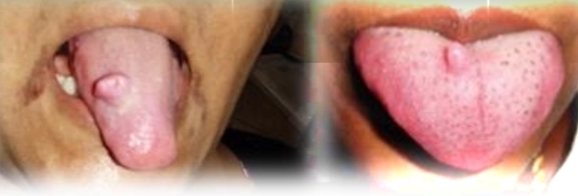
Multiple pink papules and nodules, soft and nontender. Marfanoid body type (disproportionately long limbs, fingers toes). Narrow face, full lips.
First decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Labial and buccal mucosa
Anterior tongue
Gingiva
Conjunctiva and eyelids
Mucosal neuromas (Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome, type 2B)
Autosomal dominant syndrome (genetic).
Other stigmata include pheochromocytoma, medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland
Treatment - Surgical excision of neuroma for cosmetics. Aggresive thyroid cancer develops in second decade - refer patient for testing and possible preventative surgery.
DD - Neurofibromatosis, Focal epithelial hyperplasia, Multiple hamartoma syndrome
Developmental anomalies of the tongue
Fissured tongue (scrotal tongue)
Ankyloglossia
Lingual thyroid
Bifid tongue
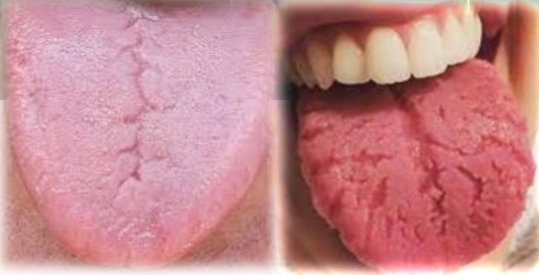
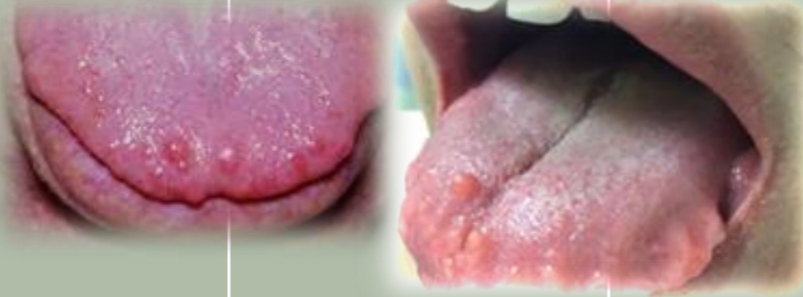
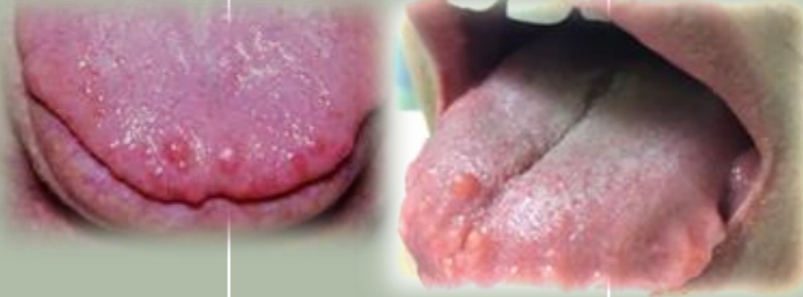
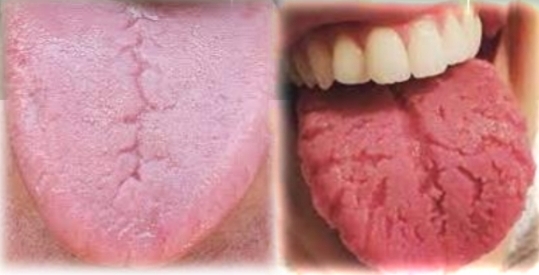
Deep central groove in tongue, multiple short furrows, fissured.
Tender if irritated. May be seen with erythema migrans. Possible halitosis.
First and second decades
No gender bias
Found on:
Dorsal and lateral tongue
Fissured tongue (scrotal tongue)
Polygenic or autosomal dominant trait
Down syndrome
Dry mouth
Diabetes
Becomes more prominent with age
Treatment - Brush/scrape tongue (proper oral hygiene). Cant cure but hygeine may reduce prominence.
DD - Erythema migrans, Macroglossia with crenations, Hemihyperplasia of tongue, Orofacial granulamatosis
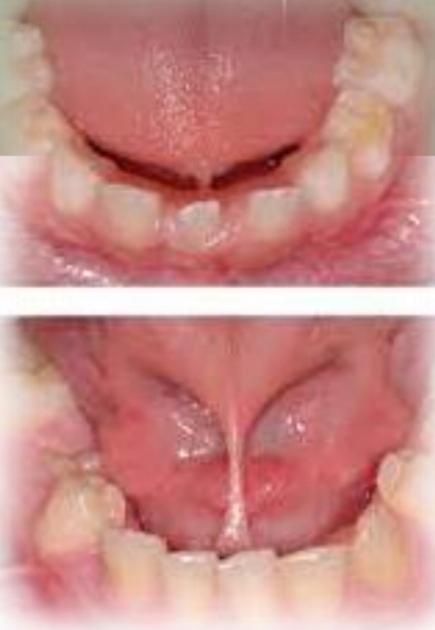
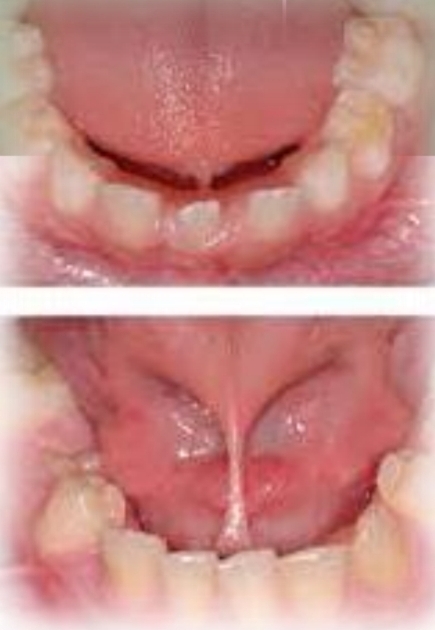
Short and thick lingual frenum, or attachment of fremum to tip of tongue - may cause a slight cleft at tip
Present at birth
No gender bias
Found on:
Ventral tongue
Floor of mouth
Ankyloglossia (tongue tie)
Can cause:
Language and swallowing problems
Lower incisor gingival recession
Treatment - Frenectomy
DD - bifid tongue, microglossia
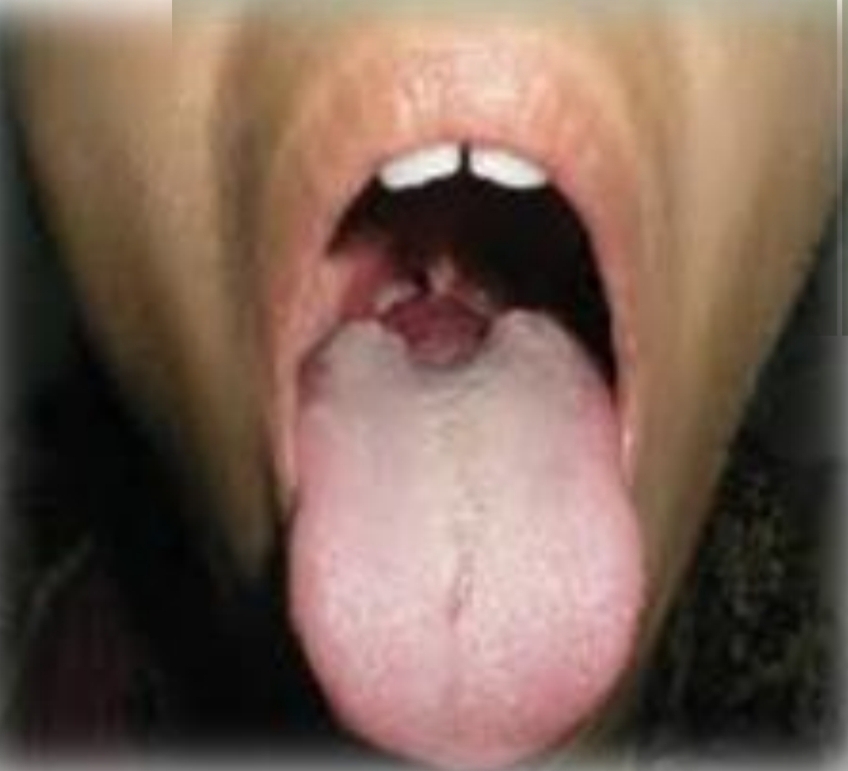
Nodular mass with smooth pink or red surface. Potential suffering from dysphagia, dysphonia or dyspnea
Second decade - symptoms developed during puberty or pregnancy
Female prediliction
Found on:
Midline base of tongue
Thyroglossal duct cys (in neck midline)
Lingual thyroid
Normal thyroid absent in 70% of cases
Cause of infantile hypothyroidism
Carcinomas arise in <1%
Treatment - thyroid hormone therapy, excision or radioactive iodine ablation
DD - Lymphoid hyperplasia, Hemangioma, Lymphangioma, Epiglotis
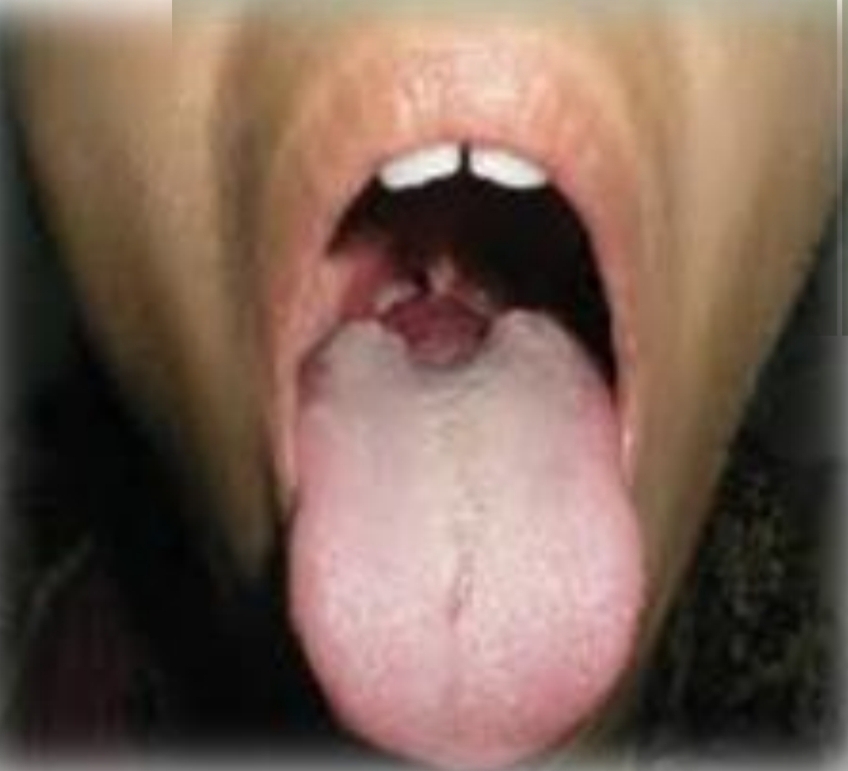
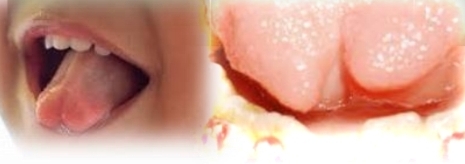
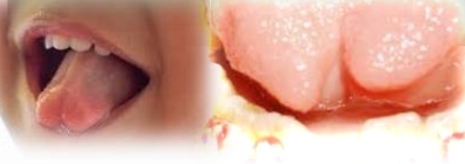
Deep groove in midline of dorsal tongue.
Bifid Tongue
Rare congenital anomaly, lack of fusion of the two lateral parts of the tongue
Most common partial cleft
Treatment - None required, possible accumulation of food debris and bacteria at base of cleft - clean well to avoid irritation.
DD - Partial ankyloglossia
White lesions on tongue
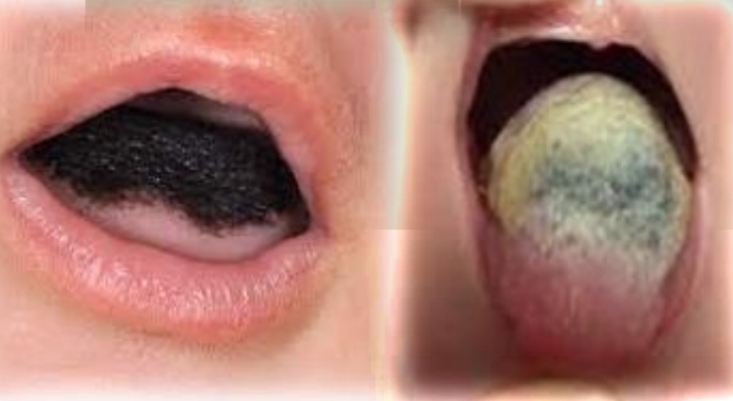
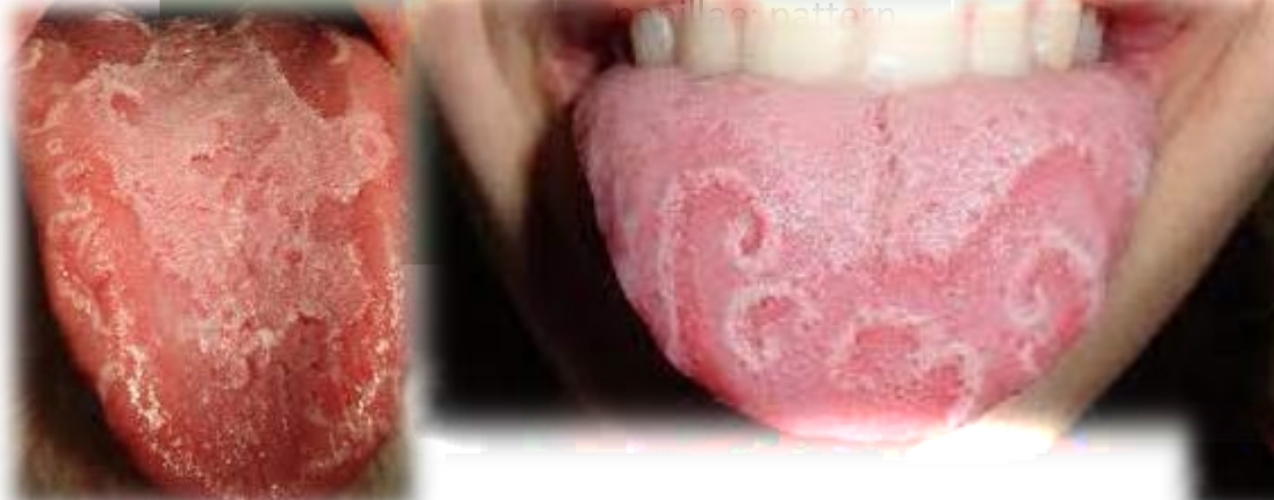
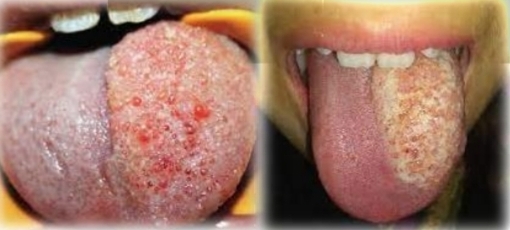
Hairy tongue
Coated tongue (furred tongue)
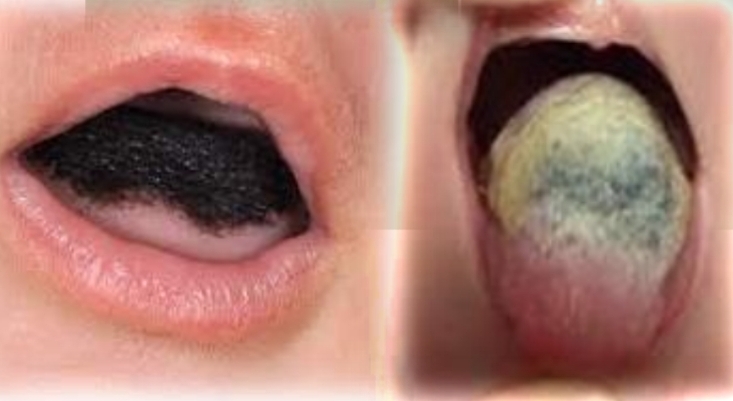
Cream to brown discolouration of tongue, with diffuse elongation of filliform papillae. Possible halitosis
Second decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Dorsal tongue
Ask: Smoking? Oral hygiene habits and use of mouth rinses? Use of antibiotics?
Hairy tongue
Associated with cigarettes, poor oral hygeine, antibiotics, dry mouth, overuse of mouth rinses.
Coated tongue more common in children
Treatment - Eliminate cause, Brush tongue
DD - Coated tongue, Frictional keratosis, Hyperplastic candidiasis
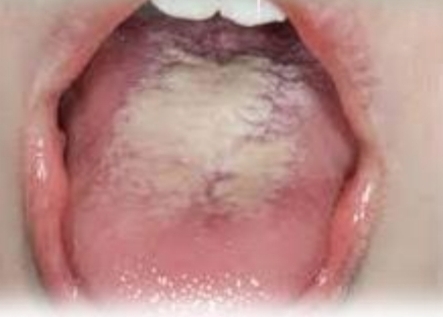
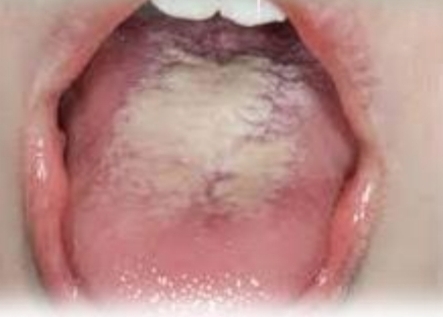
White or yellow nonadherent coating on dorsal tongue, potential halitosis
Asymptomatic
First and second decades
No gender bias
Coated tongue (furred tongue)
Common, associated with mouth breathing, febrile ilnesses dehydration and poor oral hygiene
Treatment - Brush tongue and adequate hydration. Tends to reccur
DD - Pseudomembranous candadiasis, Hairy tongue, White strawberry tongue
Pigmented lesions of the tongue
Erythema migrans (benign migratory glossitis) “Geographic tongue”
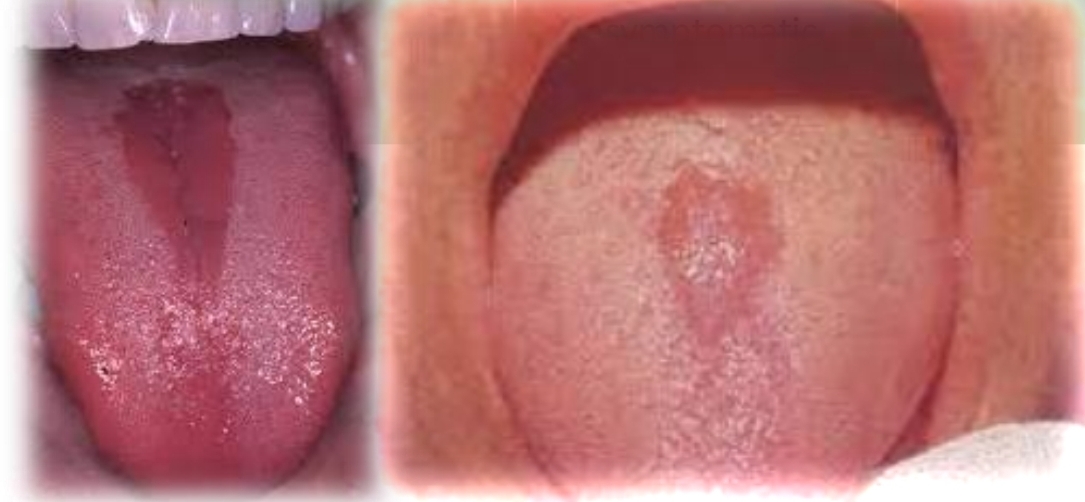
Median romboid glossitis
Lymphangioma
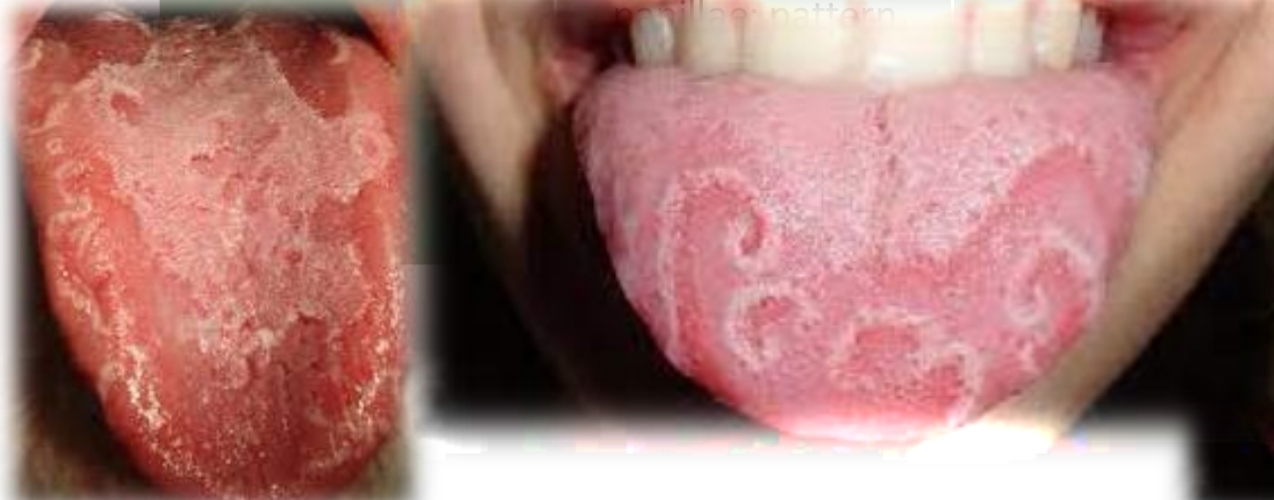
Multiple oval oral circular red patches on tongue with white scalloped border, loss of foliform papillae and pattern changes.
May be burning sensation
May occur with fissured tongue
First and second decades
Female prediliction
Found on:
Dorsal and lateral tongue, rarely at other mucosal sites
Erythema migrans (benign migratory glossitis) “Geographic tongue”
More common in children
Treatment - none required. Topical steroids in symptomatic cases Avoid hot or spicy foods.
DD - Median rhomboid glossitis, Contact allergy, Erythematous candidiasis, Transient lingual papillitis, Lichen planus
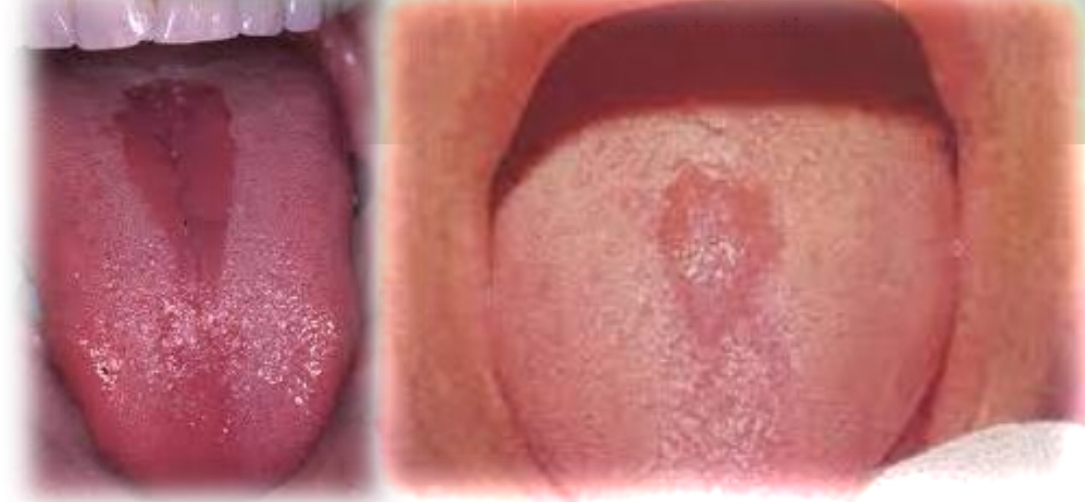
Localized red depapilated patch on midline of posterior dorsal tongue. Oval to rhomboid shape, smooth or lobulated durface. May be seen with kissing lesion
Asymptomatic
First and second decades
No gender bias
Median rhomboid glossitis
Caused by candidal infection, may palatal erythema (kissing lesion) may be present.
Treatment - Antifungals and proper oral hygiene
DD - Erythema migrans, Contact allergy, Hemangioma, Lingual thyroid
Localised/diffuse, translucent/red/purple swelling with smooth/pebbly surface. Soft and compressible.
Crepitus may be palpated
Infancy, detectable by 2 years
Found on:
Oral sites - tongue, lip, buccal mucosa
Up to 75% on head and neck
Lymohangioma
May cause - Malocclusion, dysphagia, respiratory problems
Variants - Cystic hygroma and neonatal alveolar lymphangioma
Can also cause airway obstruction and death with large neck or tongue lesions
Most cases detected by 2 years old
Treatment - Surgical excision, reccurances are common
DD - Hemangioma, Squamous papilloma, Lingual papillitis, Mucocele, Plunging ranula
Tumor and tumor like lesions of the tongue
Neurofibroma
Single of multiple nodules with smooths surface. Discrete or diffuse, and can be soft or firm on palpation.
Nontender
Second decade
No gender bias
Found on:
Tongue, buccal mucosa, vestibule and palate
Syndrome lesions occur at any site, especially skin
Neurofibroma
Neurofibromatosis is autosomal dominant trait with neurofibromas, Cafe-a-lait macules, axillary freckling and lisch nodules on iris.
5% malignant transformation of syndrome type
Treatment - Surgical excision if solitary lesion, Selective excision of syndrome type.
DD - Neurilemmoma, Mucosal neuroma, Irriation fibroma, Benign submucosal neoplasm, Salivary gland neoplasm