2. Experiments and randomized clinical trials
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Experimental
#1
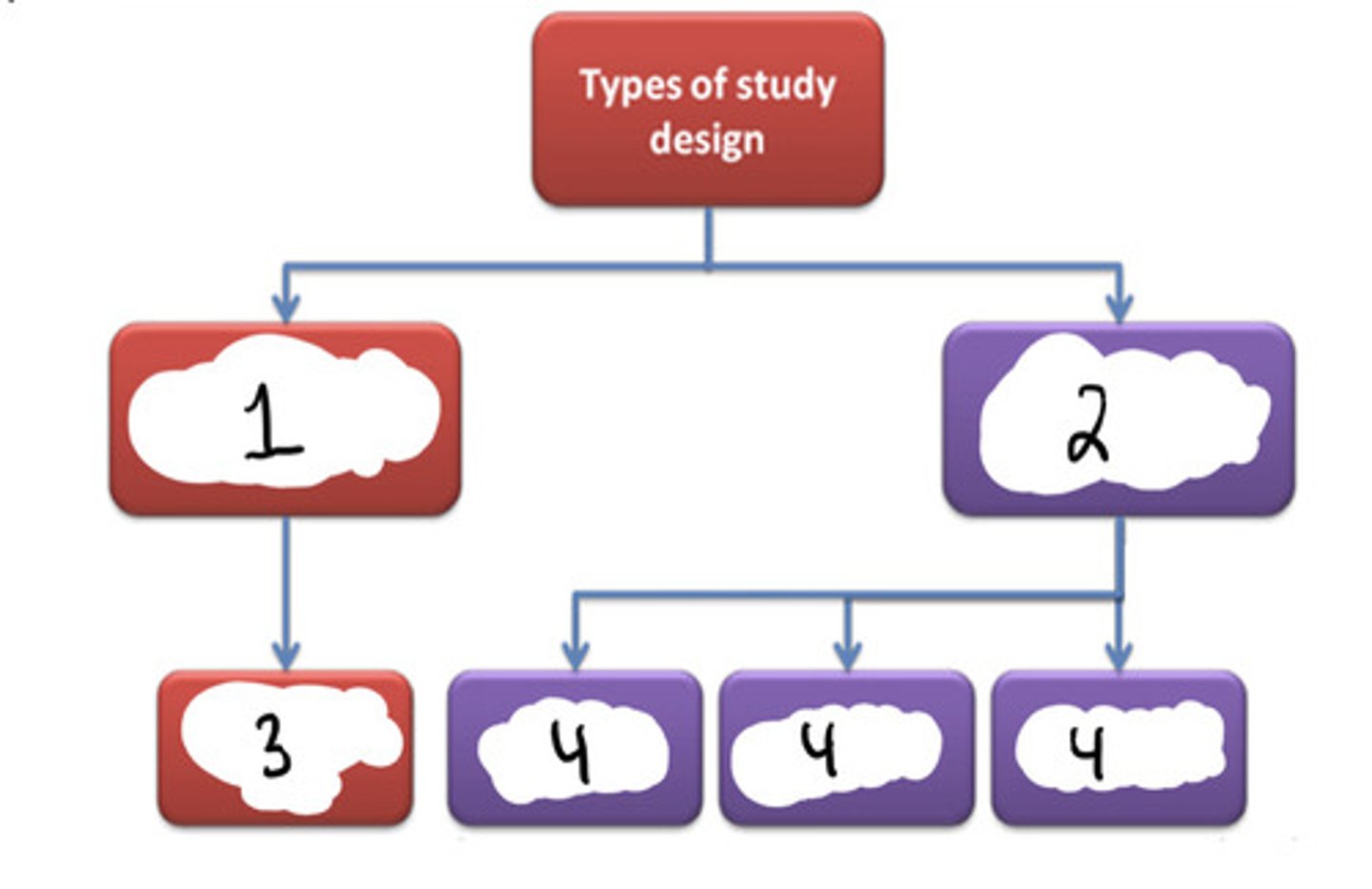
Observational
#2
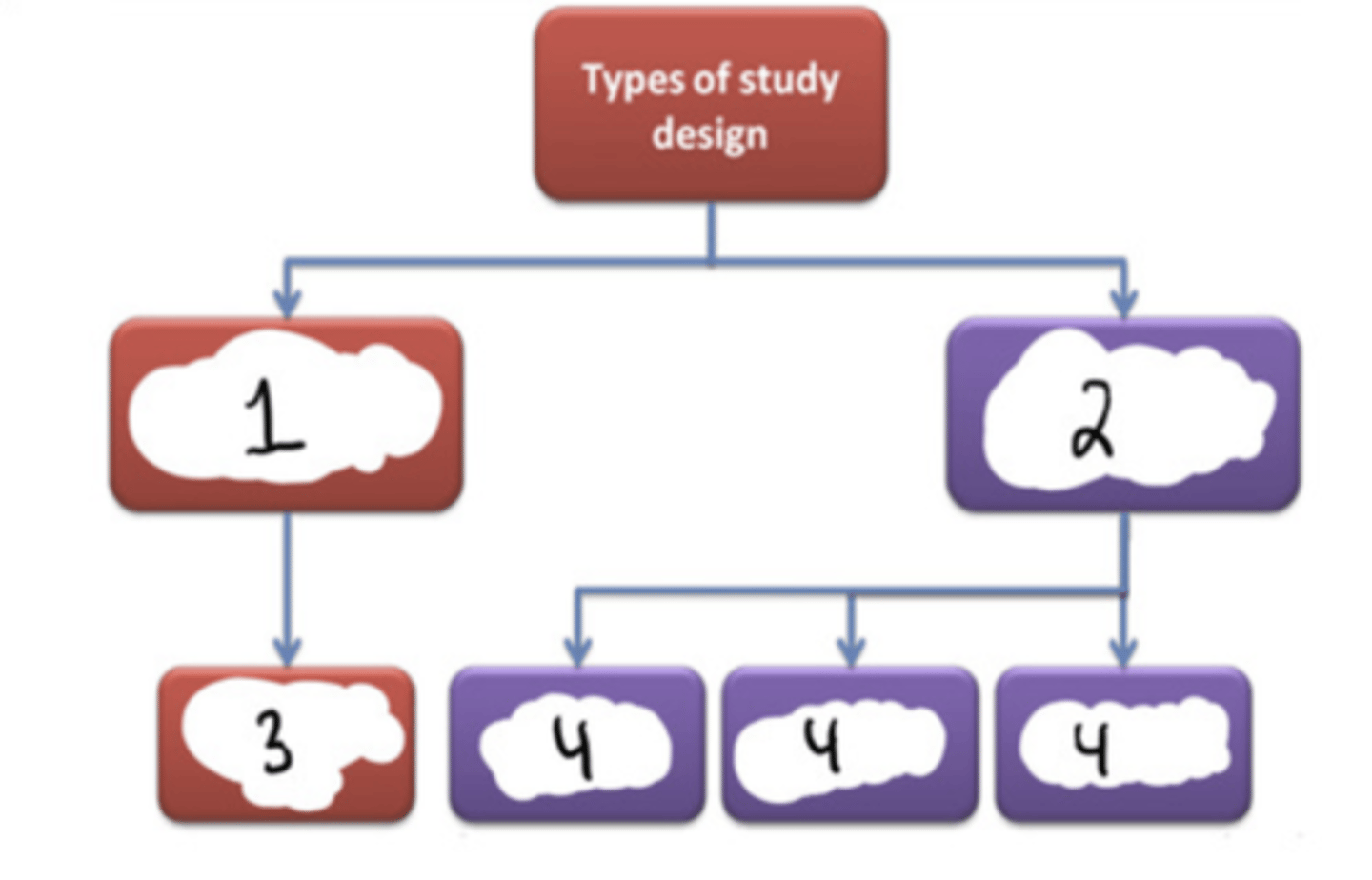
Randomized controlled trial (RCT)
#3
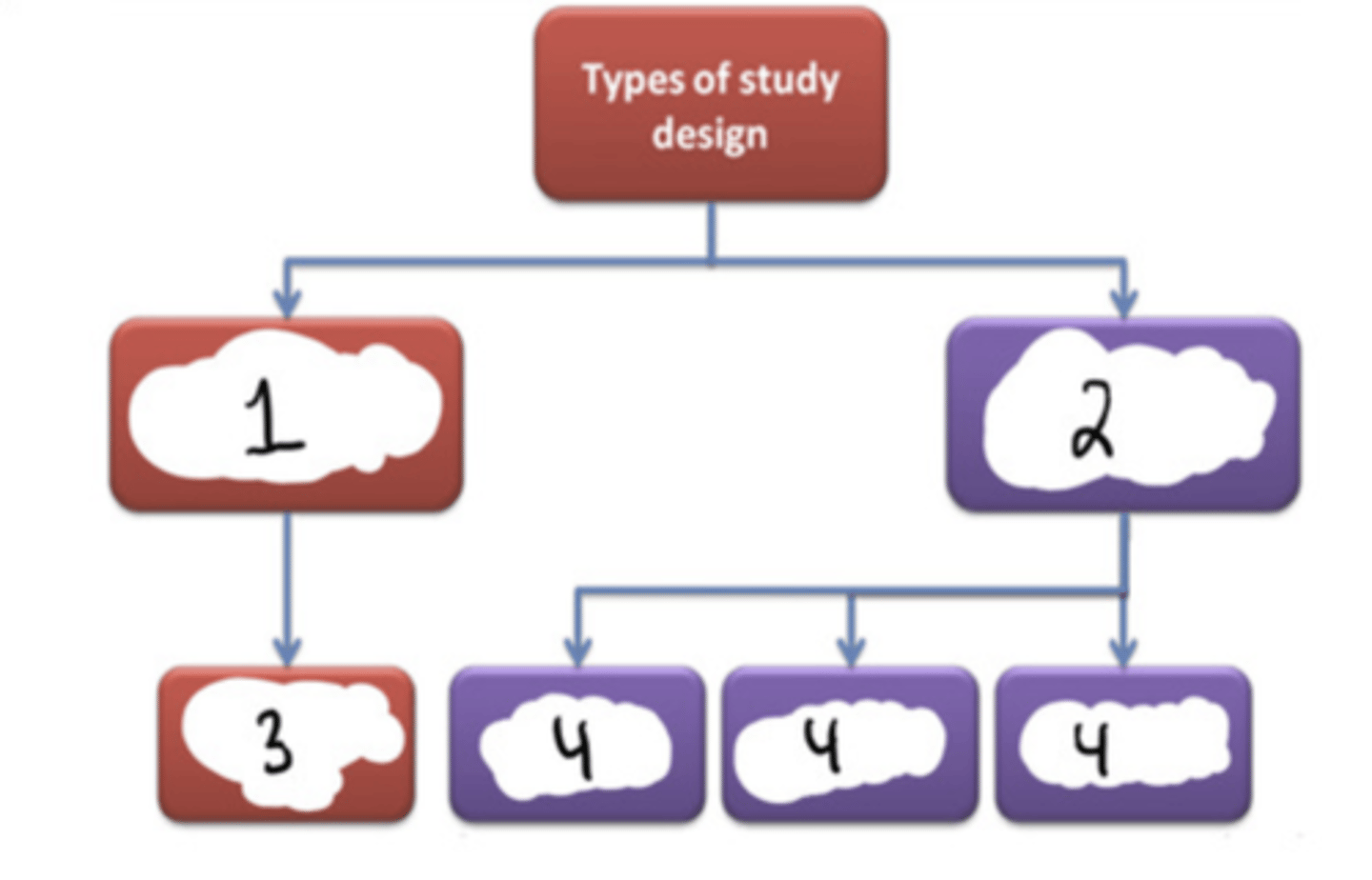
Cohort (longitudinal) + case-control + cross-sectional
#4
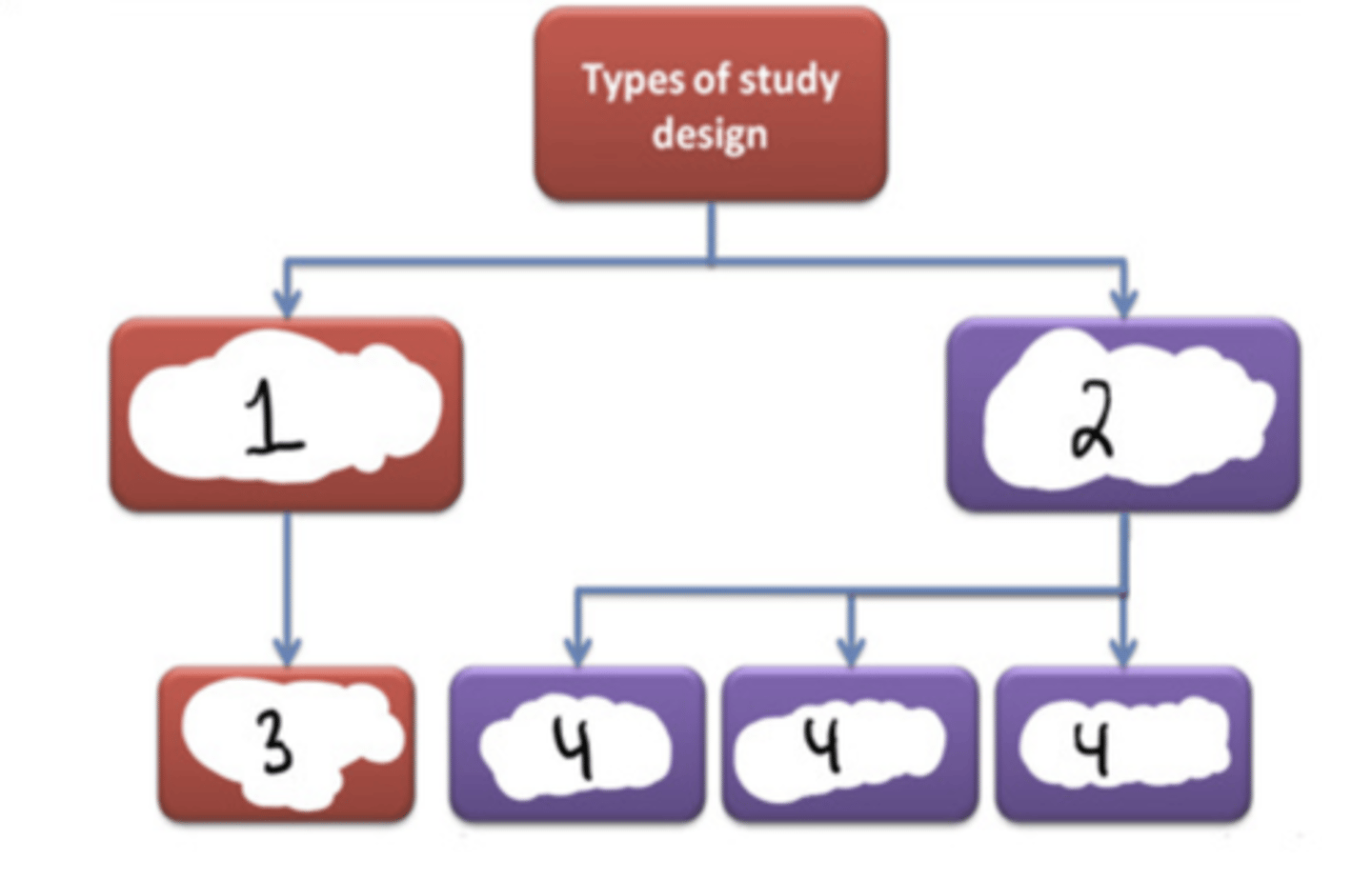
F (randomized clinical trials are a subset of experimental studies)
T/F: Experimental studies are a subset of randomized clinical trials
To answer a "clinical question"
What is the purpose of an RCT?
Equipoise
What term is defined as: You honestly do not know the answer to the question you're are posing; you have reasonable doubt in your mind.
T
T/F: With RCTs, true "equipoise" is important
treatment; comparable control groups
With RCT's they assess the efficacy of a ___ compared against a
F
T/F: in RCTs you cannot use client owned animals
-same population for control group
-randomization of intervention
-fully blinded
-identical tx and outcome measurements
4 Essential components of RCTs
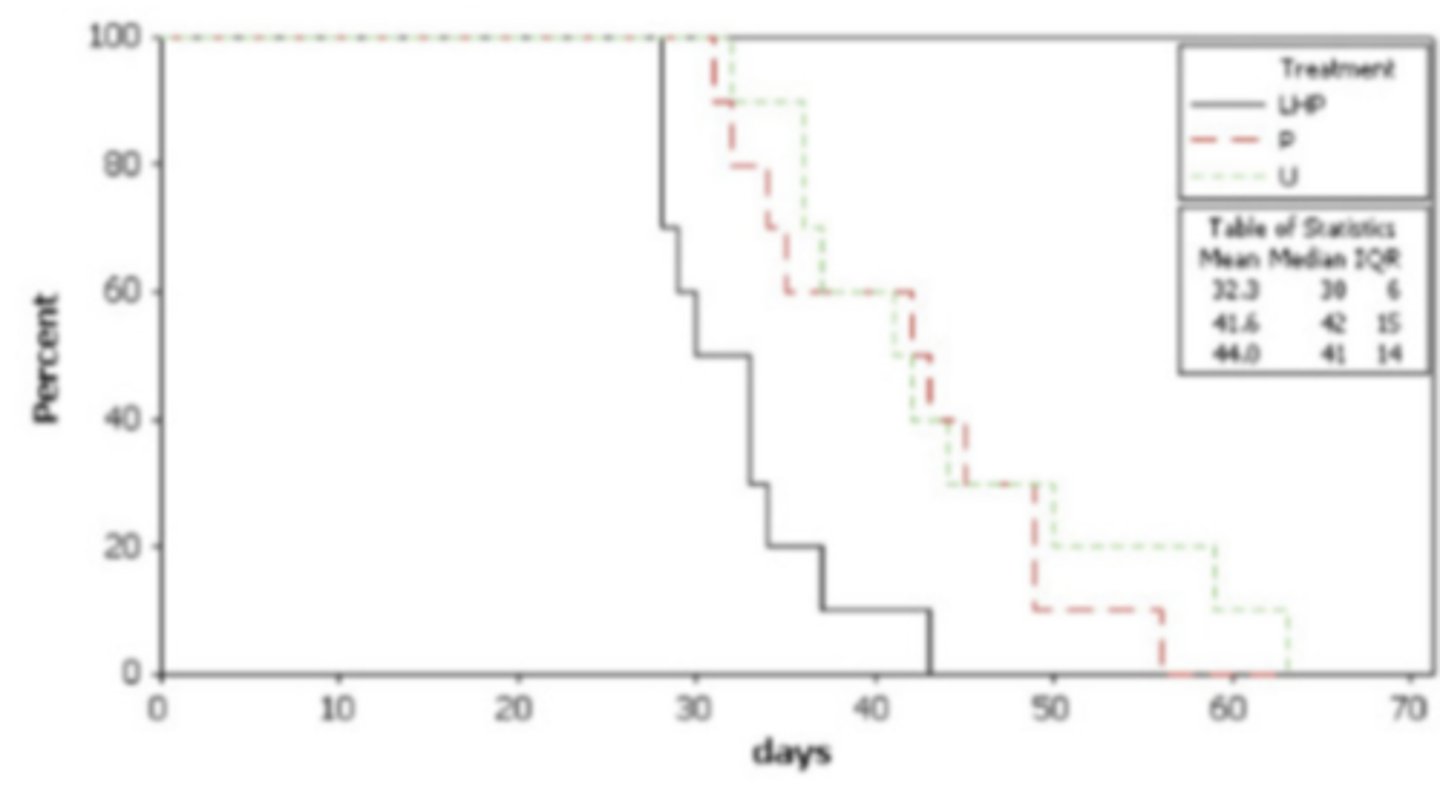
Time to event graph (aka Kaplan Meyer graph aka step graph)
What is this and how do you interpret it?
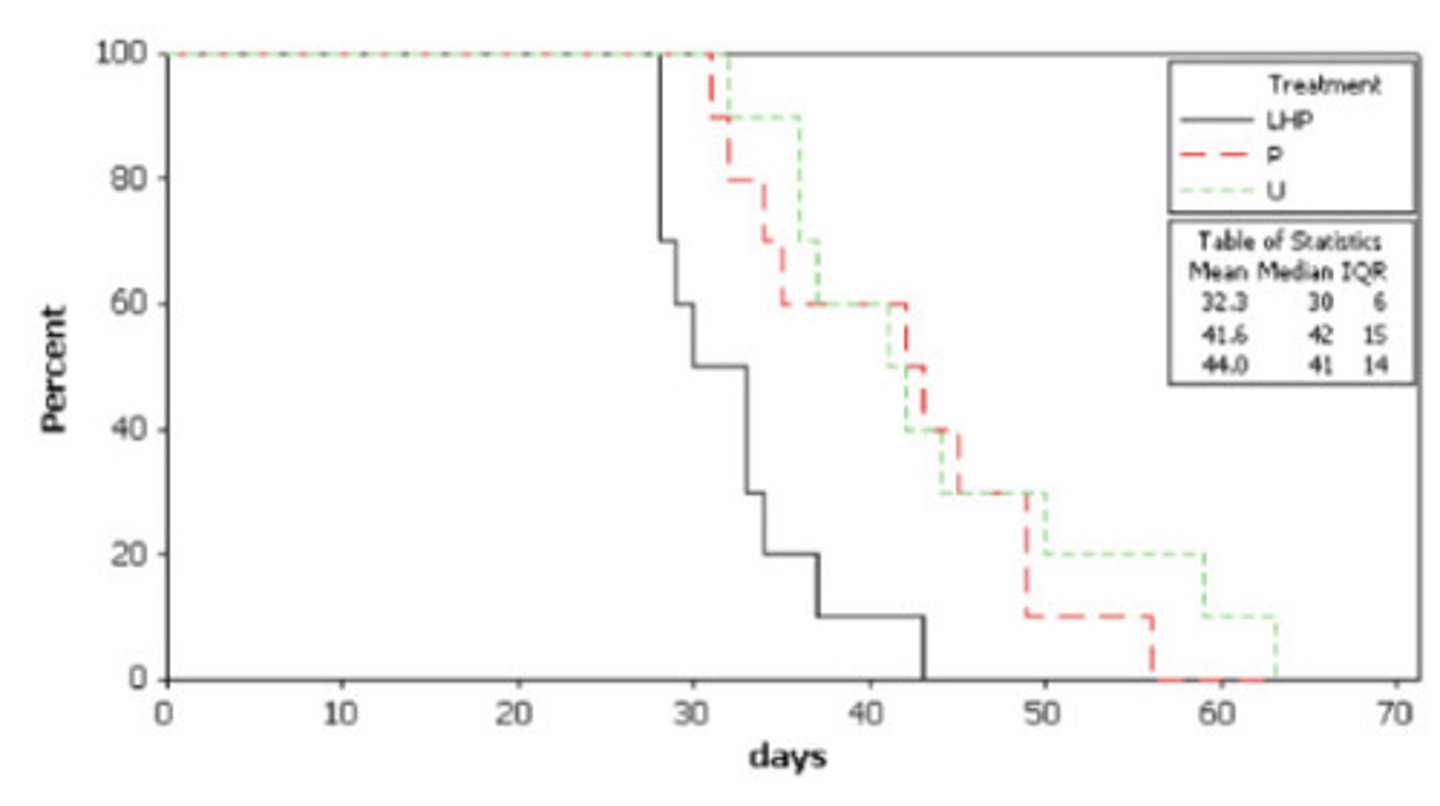
animals healing
What do the downward lines mean
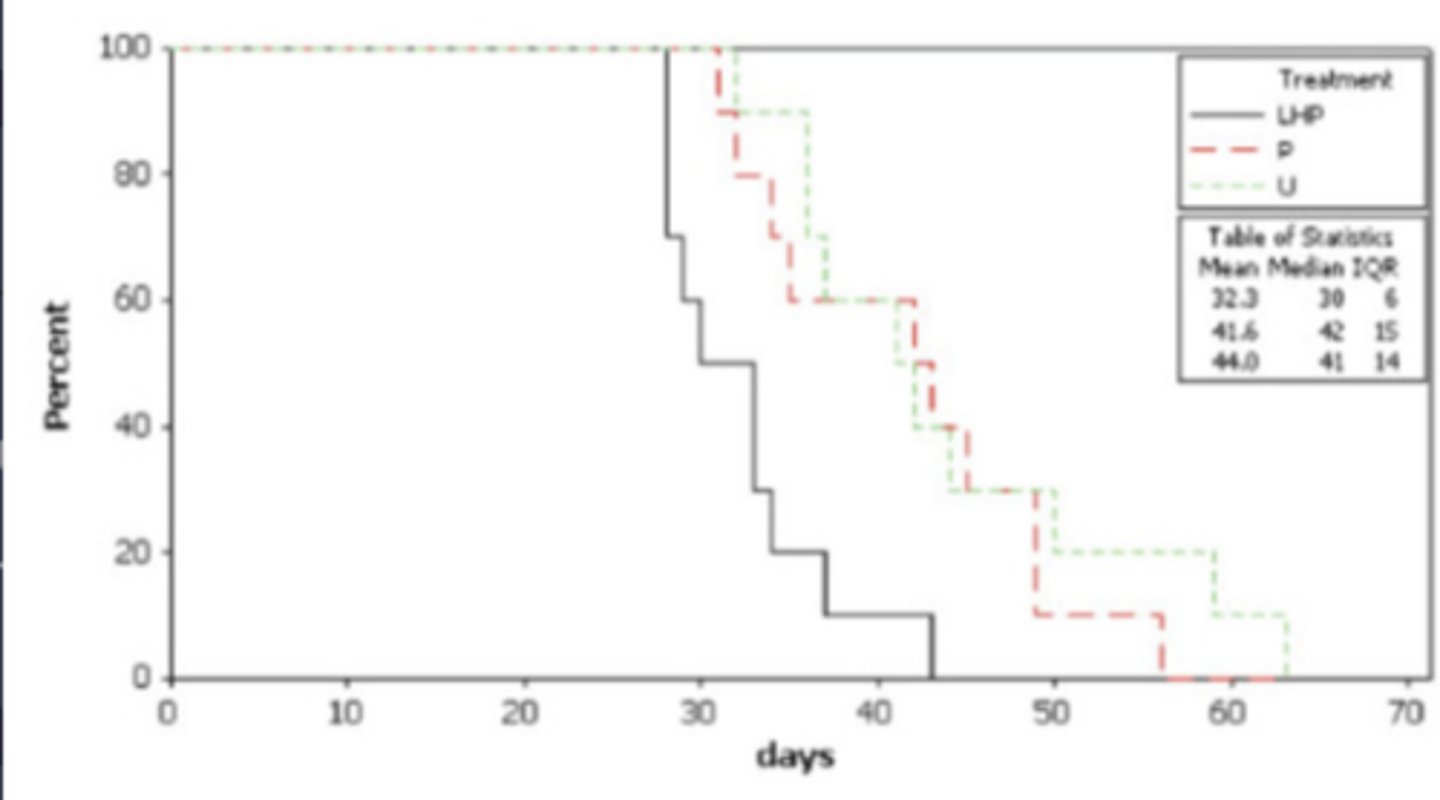
healed faster
What does the black line indicate when compared to the others
- Conduct a background literature search
- Statement of justification
- Statement of the objective and hypothesis
- Identify the "outcome" variable
- Define the experimental unit
- Define the study population
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Consult a statistician
- Sample size calculations
- Recruit and enroll subjects
- Random allocation
- Identify other sources of bias
- Data collection
- Data analysis
- Publish the study
List the steps for a RCT.
To provide the reader with a reason for the study
(Why did they do the study?)
What is the purpose of a statement of justification?
Specific, measurable
The hypothesis should be ________ and ________.
- Clinical relevance of the study ("so what?")
(Ex: We predict that drug X is more effective at reducing the time of illness by more than two days)
What is the "outcome" variable?
What you are performing the experiment on
(- Usually, it is the individual animal
- Can be groups of animals or parts of animals)
What is the experimental unit?
The study population
(If the study population is too narrow/too specific, the results will only be good for that population and cannot be generalized)
What directly determines the generalizability of the study?
- Clearly specifies what specific animals will be included in the study
- Clearly specifies what will exclude specific animals from the study
(How were the subjects selected? How do you justify excluding animals?)
What is the inclusion and exclusion criteria?
Stop and consult a statistician
After the study is planned, what do you want to do befoe actually starting the study?
- Simultaneous enrollment
- Sequential enrollment
What are the 2 methods for recruiting and enrolling subjects?
Simultaneous
What type of enrollment is this: used when the outcome of interest is common and all study participants can be selected at the same time.
Sequential
What type of enrollment is this: used for rare cases, where cases are enrolled as they become available.
To reduce bias + to help ensure comparable study groups
What is the main reason for random allocation?
Random allocation
What is the most important method of bias control
- Blinded all participants
- Randomization
- Standardization of all methodologies throughout the study
How can you identify/prevent other sources of bias?
Data quality
What is the most important practical consideration for the researcher?
False — this will result in publication bias. A well-planned and conducted study should be published regardless of the result.
T/F: You should only publish a study if the results are significant.