study guide vascular lower leg 04/30
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
The common femoral vein lies ?
In the scarpa triangle aka the femoral triangle , medial to the cfa
Which vein is shorter on the right side, oriented vertically, and ascends posteriorly and then laterally to its companion artery?
The right common iliac vein
Angle correction of the Doppler signal is not necessary during a lower-extremity venous duplex examination because of which one of the following reasons?
Not necessary because peak venous velocity does not provide any clinical information in lower extremity duplex imaging
Which perforator vein is from the greater saphenous vein in the distal thigh?
Dodd perforator
The femoral vein ascends in which location?
Ascends through the inguinal region coursing through deep throughout the medial thigh
Adequate pressure has been applied to compress a vein when:
The artery is deformed , collapsed
A pulsatile venous signal is normal in which veins
Jugular, subclavian , innominate & svc
The compression technique is not used for __________ thrombus.
Free floating
A potentially lethal complication of acute DVT is
When it becomes dislodged from the vein wall and propagate which can cause risk for PE
Signs and symptoms of acute DVT include
Phlegmasia alba dolens, plegmasia cerulea dolens,pain ,warmth,redness and edema
In the presence of incompetent valves, the sudden release of distal augmentation produces
Retrograde blood flow
Ischemic rest pain implies critical ischemia of the __________________ limb when patient is at rest.
Distal
Define: respiratory phasicity
Blood flow velocity changes with respiration
Define: perforating veins
Connect the superficial and deep venous systems
Define:augmentation
The blood flow velocity increases with distal limb compression or with the release of proximal compression
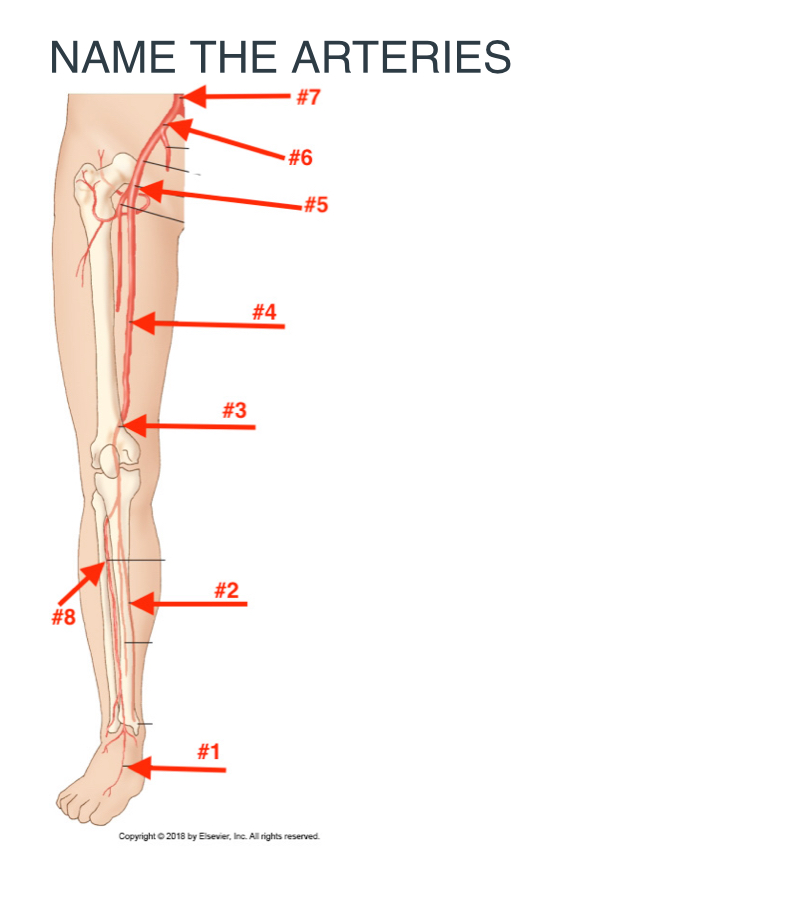
Name the arteries
Doralis pedis artery
posterior tibial artery
popliteal artery
Femoral artery
Common femoral artery
Common iliac artery
Abdominal aorta
Anterior tibial artery
During arterial duplex imaging, Doppler signals are obtained using a ___________ angle.
45-60 degree angle
Which one of the following statements best describes ultrasound compression therapy of pseudoaneurysms?
Treatment of pseudo aneurysms is commonly accomplished by using compression therapy through thrombin injection which may be attempted if the neck if the aneurysm can be clearly identified on the arterial imaging , pressure is then applied to skin ,using the transducer with the goal of impending blood flow into the aneurysm
Which one of the following is most likely to produce a palpable thrill?
A dialysis access graft
Which one of the following imaging characteristics indicates a significant (greater than 50% diameter reduction) arterial narrowing during lower-extremity arterial imagining
Increase of peak systolic velocity of greater than 100% compared with the proximal adjacent area
Most patients describe claudication as which one of the following?
Cramping of the leg muscles
The profunda femoris artery lies __________ and __________ to the superficial femoral artery (SFA).
Posterior and lateral
The major branches of the popliteal artery are the _________ and _________ arteries.
Anterior and posterior tibial arteries
Segmental pressures of the lower extremity tend to ____________ the extent of the disease.
Underestimate
The calf pulse volume waveform normally has greater amplitude than the thigh waveform because of which one of the following? A sequential changes B superficial femoral disease, see cuff, artifact D intermediate ischemia E a&c
E
Exercise testing of the lower-extremity arterial system is performed on a treadmill on a __________ grade.
10-12%
Ankle pressures that fall after exercise and return to baseline in 5 minutes suggest which one of the following?
Single segment occlusive disease
The left iliac vein is usually mildly compressed by which one of the following anatomic vessels?
Right iliac artery
Which one of the following is not one of the three factors of the Virchow triad?
Lysis
The longest vein in the body is which one of the following?
Gsv
Perforating veins connect the superficial and deep venous systems. Blood flow in the perforating veins is normally from the ___________________ to the _______________.
Superficial system and deep system
This chronic process of this syndrome is a complication that may follow DVT.
Post thrombiotic syndrome
Venous blood flow is normally from the ____________________ veins to the ____________________ veins.
Superficial and deep
Venous valves are important in maintaining blood flow from the peripheral veins to the central veins.
True
Deep veins are typically larger than superficial veins, as they must support a larger blood volume. T/F
True
The ________________ is a superficial vein that travels along the anteromedial portion of the thigh and calf.
Gsv
The __________________ originates on the dorsum of the foot and travels anterior to the medial malleolus, and ascends the anteromedial side of the calf and thigh
Gsv
The small (lesser) saphenous vein is a superficial vein that travels along the midline portion of the posterior calf. The small saphenous vein typically drains into the _______________________.
Popliteal vein
Deep veins are typically smaller than superficial veins. T/F
False
Deep veins are typically larger than superficial veins, as they must support a larger blood volume. T/F
True
Venous valves are present in which veins
Superficial veins, perforator veins and deep veins
Saphenous veins are deep veins. T/F
False
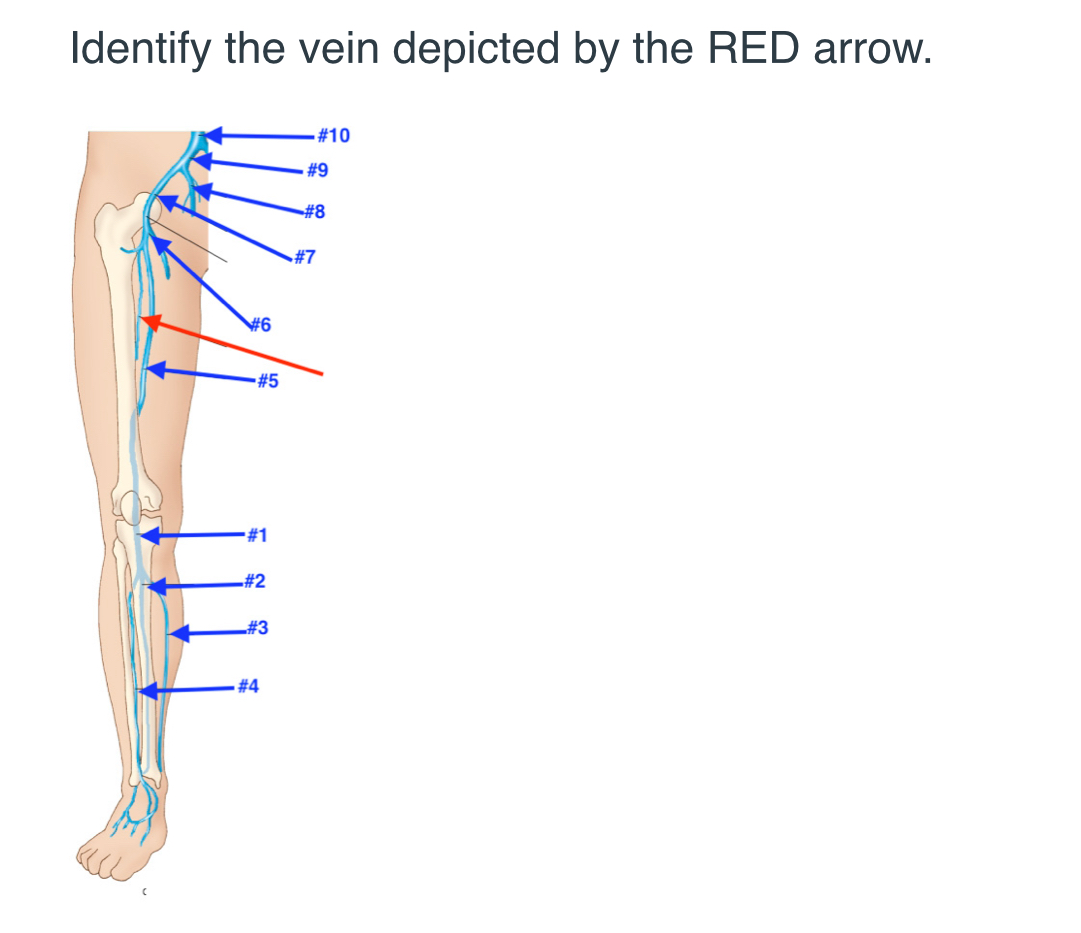
Deep femoral vein
Saphenous veins are superficial veins. T or f
True
The _________________ are a set of paired veins that drain the posterior compartment of the lower leg and originate from the plantar veins (superficial and deep) of the foot.
Posterior tibial veins
The __________________originates from the popliteal vein in the distal thigh at the hiatus of the adductor magnus muscle, at the level of the adductor (Hunter’s) canal.
Femoral vein
The _______________ drains the blood of the lower leg and originates from the confluence of the ATVs with the peroneal and PTVs (tibial-peroneal trunk).
Popliteal vein
Lower extremity deep veins have corresponding arteries located in close proximity to them. T or f
True
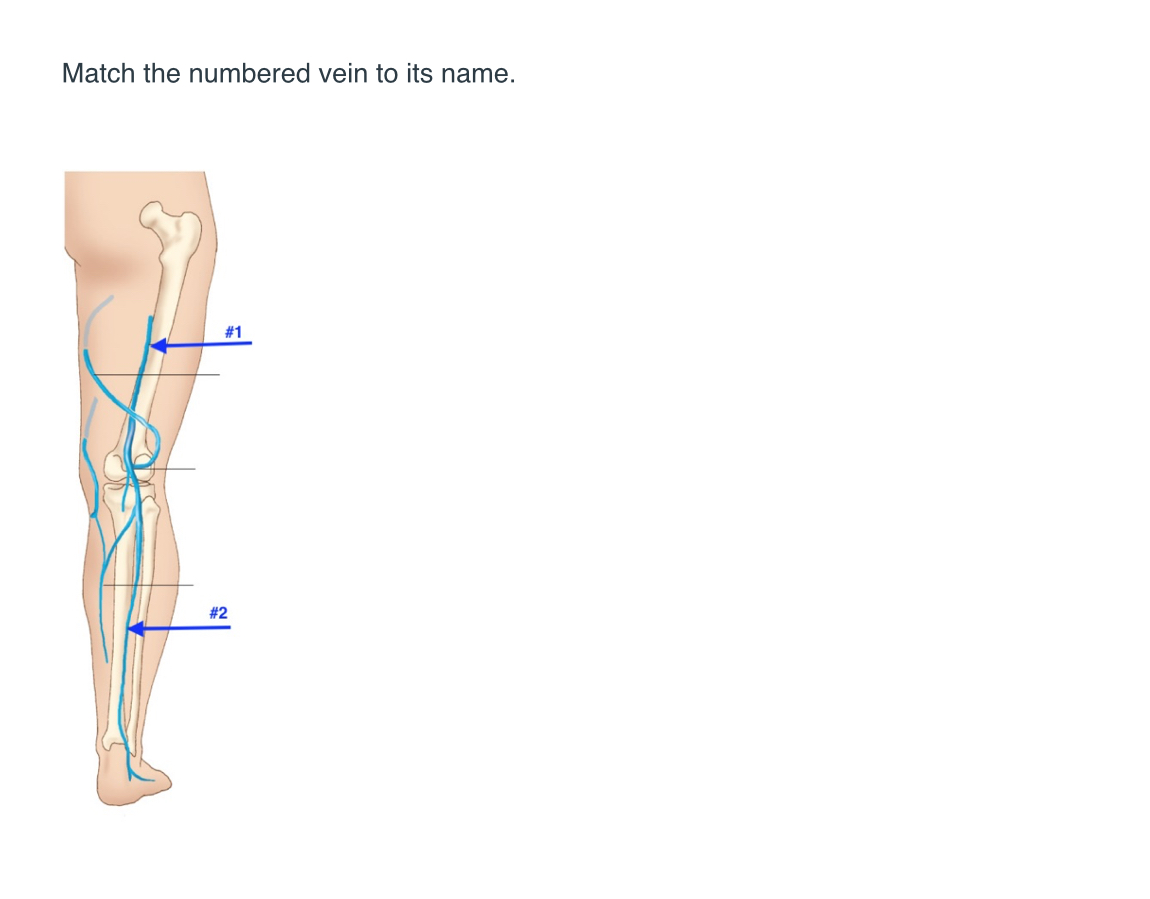
Match name to the number
1. Femoral vein
2.lesser saphenous vein
The external iliac artery terminates at the level of inguinal ligament, where it becomes the common femoral artery. T or f
True
he _______________ arises from the popliteal artery in the proximal calf and travels distally along the lateral calf, into the anterior compartment of the ankle.
Anterior tibial artery
The characteristics of a normal Doppler signal obtained during lower-extremity arterial imaging include
Sharp up slope, triphasic and reversed, flow component, including low, velocity forward, flow and late diastole
A normal pulse volume waveform contains a
Dicrotic notch
To obtain arterial Doppler signals during arterial color Doppler imaging, using a(n) ___________ imaging plane is best.
Longitudinal
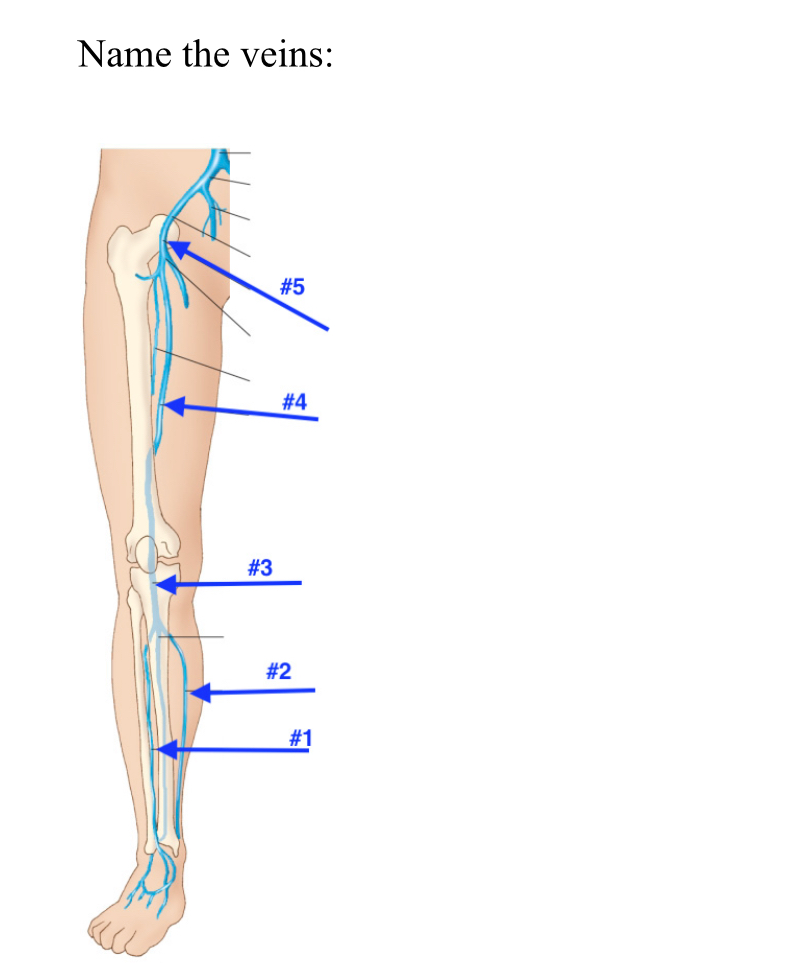
Name the veins
Peroneal vein
Posterior tibial vein
Popliteal vein
Femoral vein
Common femoral vein
The characteristics of a normal venous Doppler signal from the lower extremity include all of the following except:
High pitch pulsability
The most important diagnostic criterion during venous duplex imaging is which one of the following?
How the vein responds to the transducer compression on the skin
The presence of an incompetent venous segment is determined by which one of the following?
Venus reflux on augmentation
The superficial femoral vein is a ______________ vein.
Deep
To obtain venous Doppler signals during venous duplex imaging, using a(n) ___________ imaging plane is best
Longitudinal
Risk factors for deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) include
Deep vein, thrombosis, including age, hypertension, diabetes, tobacco, smoking, and family history of atherosclerosis
Venous valves are observed in which anatomic structures T or f
True
What is the primary reason for conducting noninvasive arterial testing?
To evaluate suspected arterial trauma
Which is not a risk factor for PAD
Low sodium intake
Claudication is best described as
Muscular discomfort due to ischemic during exercise
The ankle brachial index is calculated by
Dividing highest ankle pressure by the highest brachial pressure
Which artery is a continuation of the femoral artery and runs behind the knee?
Popliteal artery
Which test evaluates digital arterial pulses using infrared light reflection?
Photoplethysmography (PPG)
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) is characterized by:
Compression of neural and/or vascular structures at the thoracic outlet
Which of the following is a surgical treatment for PAD?
Bypass grafting
Why are toe pressures preferred over ankle pressures in some patients?
Ankle pressures may be falsely elevated in patients with calcified vessels
Which of the following conditions is characterized by color changes in the digits in response to cold?
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
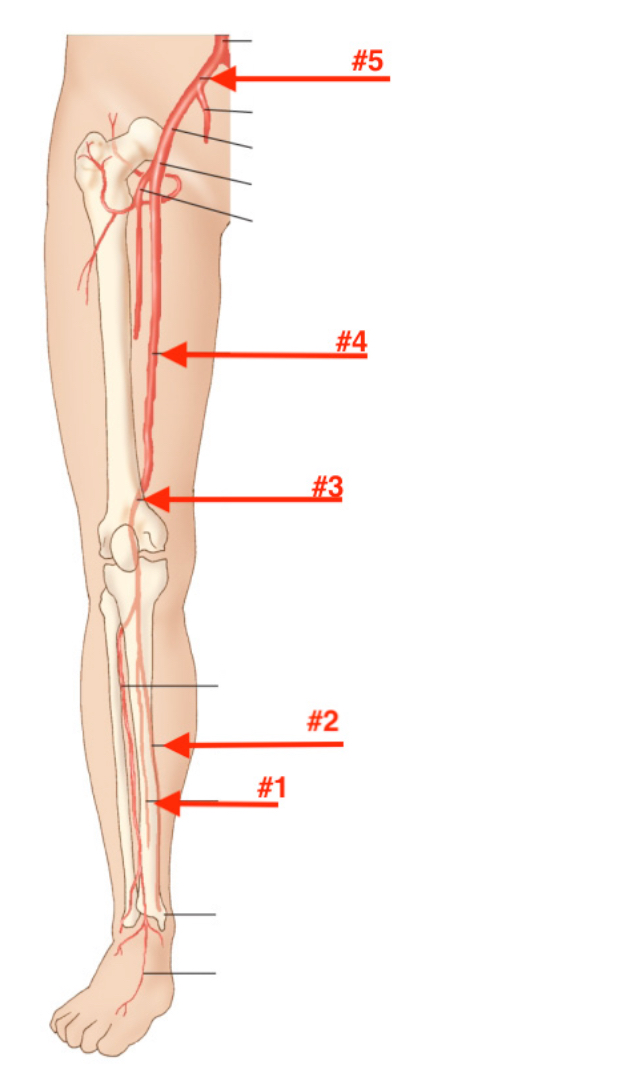
#1 Peroneal artery #2 posterior tibial artery #3 popliteal artery #4 femoral artery #5 common iliac artery
Femoral artery
Courses the length of the thigh through hunters canal and terminates at the opening of the abductor Magnus muscle
Anterior tibial artery
Begins at the popliteal artery and travels down the lateral calf in the anterior compartment to the level of the ankle
Dorsalis pedis artery
Continuation of the anterior tibial artery on the top of the foot
Popliteal artery
Begins at the opening of the abductor Magnus muscle and travels behind the knee in the Popliteal fossa
Profunda femoris artery
Posterior and lateral to the superficial femoral artery
The external iliac artery terminated at the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the _____________ artery.
Common femoral
The artery that is located deep within the calf and travels near the medial aspect of the fibula is the ________________ artery.
Peroneal
The common femoral artery originates beneath the inguinal ligament and terminates by dividing into the femoral artery and the ___________ artery.
Profunda femoris
A continuation of the anterior tibial artery on the top of the foot is the _______________.
Dorsalis pedis
Which artery begins at the opening of the adductor magnus muscle and travels behind the knee?
Popliteal
What is one of the essential questions to answer when performing arterial imaging?
Is disease present in the lower extremity
Which pathology is characterized by abnormal dilation of an artery?
Aneurysm
The subclavian artery transitions into which artery in the upper arm?
Axillary artery
What is a common limitation of lower extremity arterial imaging?
Shadowing from arterial calcification
Which artery originates from the popliteal artery and dives deep into the proximal calf?
Anterior tibial artery
The popliteal artery is best evaluated using which scanning approach?
Posterior longitudinal
Which artery originates from the popliteal artery and dives deep into the proximal calf?
Anterior tibial artery
What is a common limitation of lower extremity arterial imaging?
Shadowing from arterial calcifications
The common femoral artery bifurcates into which two arteries?
Profunda femoris and femoral
Which position is recommended for imaging the aortic bifurcation using duplex ultrasound?
Left decubitus
Which transducer frequency is most suitable for imaging the aortic bifurcation?
2.0 to 3.5 mhz
What is the primary imaging modality used for noninvasive evaluation of peripheral arteries?
What is the primary imaging modality used for noninvasive evaluation of peripheral arteries?
Duplex ultrasound
Which one of the following statements best describes ultrasound compression therapy of pseudoaneurysms?
Usually requires 30 to 60 minutes to be successful
Which one of the following is most likely to produce a palpable thrill?
Dialysis access graft
Most patients describe claudication as which one of the following?
Cramping of the leg muscles
The profunda femoris artery lies __________ and __________ to the superficial femoral artery (SFA).
Posterior ;lateral
The second main branch of the aortic arch is which one of the following arteries?
Left common carotid