7: Mars
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What high priority science topics about Mars are addressable by Meteorites?
How water could have been brought to earth (panspermia)
internal or surface structure
age dating
What high priority science topics about Mars are addressable by Rovers?
habitability through subsurface exploration
drill down ice to look
What high priority science topics about Mars are addressable by Orbiters?
differences between earth and mars atmosphere
whole mars atmosphere column
alignment of mars magnetic minerals (magnetosphere in past?)
What has been brought back by Mars Sample Return?
igneous and sedimentary rocks by NASA perserverance rover
alkali rich igneous rocks - different to meteorite collection
carbonates - signs of microbial life?
Which country is next going tot collect Mars samples?
China with Tianwen 3 in 2028
500g material
drill and scoop
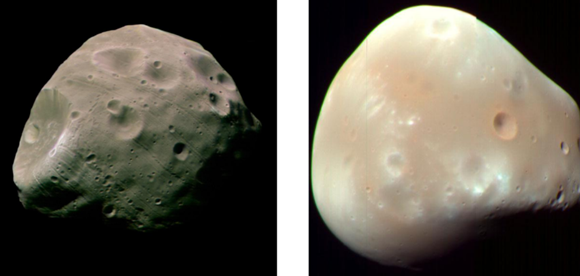
What are the names of Mars’ moons?
Phobos: closest to planet in SS (~600km)
Deimos
Likely captured asteroids
Phobos 1 mission
1988
expected communication failed to occur and the spacecraft failed to operate
Phobos 2 mission
July 12 1988
investigated mars surface and atmos
returned 37 images
Phobos-Grunt Mission
russian mission, 8 Nov 2011
sample return mission
communications lost - failed
programming error
MMX Mission
JAXA sample return mission 2026
2 possible landing and sample collections
~10g samples collected and return - 2029
Describes Mars’ structure vs earth
chemically and isotopically distinct
formed in different part of solar system to other terrestrials
could be stranded planetary embryo
remained much further from sun than earth
differentiated after formation
rocky exterior - iron rich interior
has atmosphere
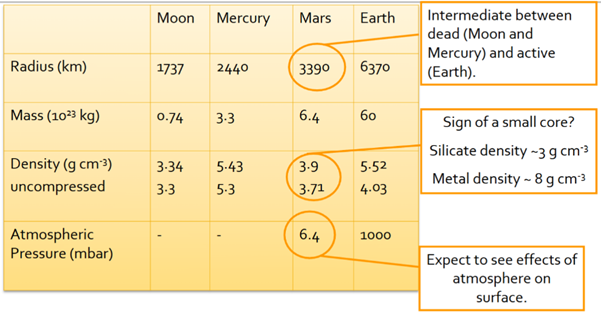
Mars and Magnetic field
does not currently have one
could have in the past if core was molten
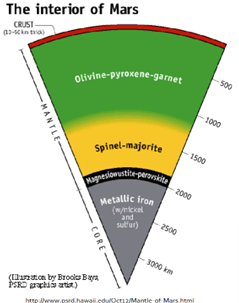
Describe mars interior
complicated layered mantle comp
minerals similar to those of interior earth
partial melting of different melting = volcanoes
inferred from chem structure of martian meteorites
Describe Mars’ crustal make-up
Primary
southern highlands - modified by impacts
Secondary
Volcanic eruption centres - single plate planet
mostly secondary#
tertiary
water lain deposits
volcano-sediment interaction
glacial products
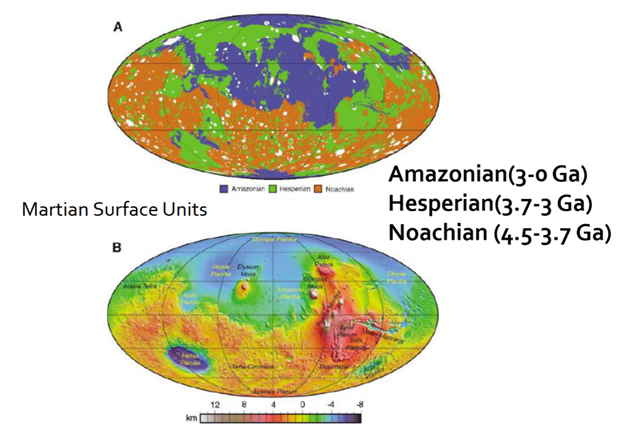
What is the Mars Geological timescale
Noarchian
Hesperian
Amazonian
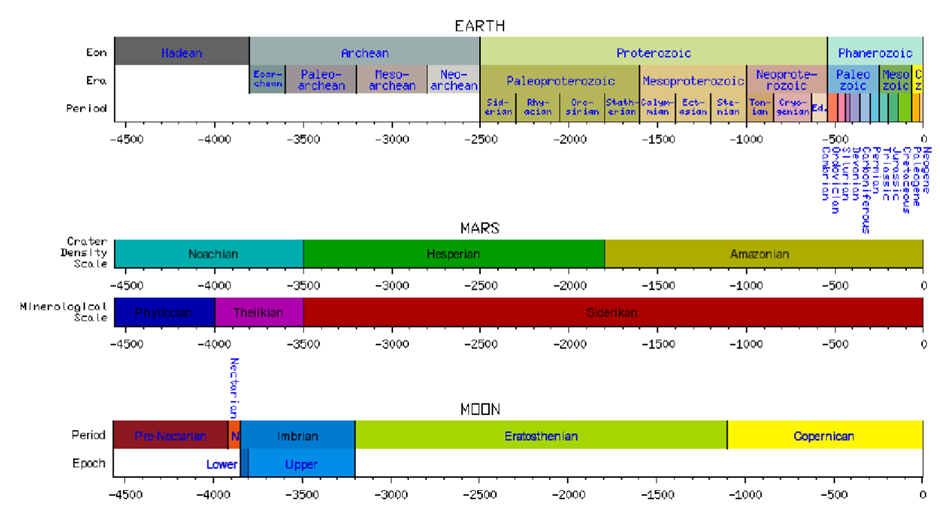
What occured in the Hesperian period?
Early volcanism, little impact cratering
What occured in the amazonian?
small scale volcanism, impact cratering, large scale resurfacing due to aeolian wind processes, tectonics etc.
What happened most recently in Mars timescale?
oxidation of surface, red colour, Fe
What area of Mars’ surface is youngest?
northern hemisphere is youngest
based on counting crater impacts
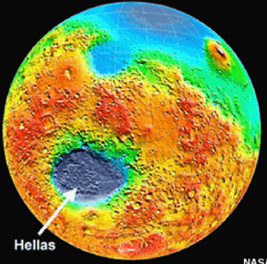
Hellas Planitia
crater in southern hemisphere
over 6km deeo and 2000km in diameter
formed 3.8-4.1Ga
Could have been lake or small sea in past
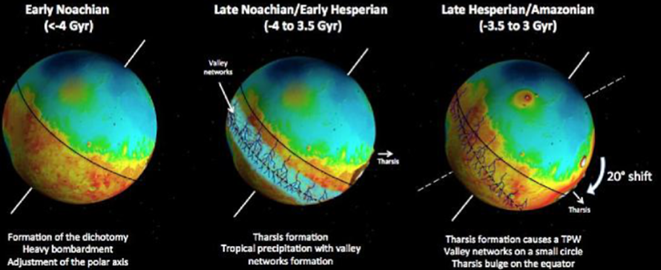
What is the Mars dichotomy?
the two hemispheres geology differ in elevation by 1-3km
NORTH: amazonian in age
Northern lowlands: 32km crust thickness
Southern highlands: 58km crust thickness
could a large impact have stripped the northern hemisphere? Good place for water stability
What is the age range of Mars Volcanic features?
Noachian (>3.7Ga) to late Amazonian (<500Mya)
Olympus Mons
largest mountain in solar system
24km high, 500km diameter
most recent eruption 25Mya
Tharsis region
huge bulge on surface, 4000km across and 10km high
no tectonics to move things around
sustains large vol of melt
tharsis used to be in North - so much volcanism that it has driven mars to rotate on its axes and move tharsis towards the equator
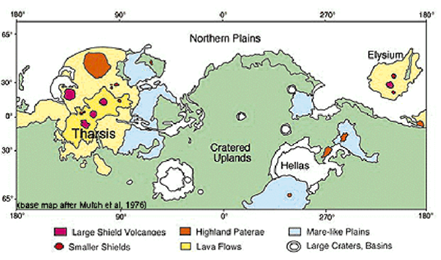
Tholi
dome-shaped edifices that are much steeper and larger than Tharsis shields
central calderas large in proportion to base diameters
densite of impact craters reveal they are older than large shields
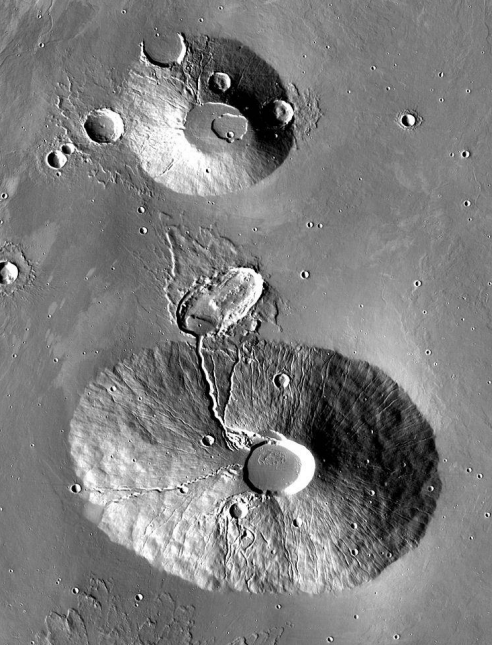
Igneous features of Vallis Marineras
old intrusive mafic dykes
not only lavas erupted in volcanos but also magmas stored in mars’ crust as magma chambers or dyke systems

past volcanism on mars and the corresponding meteor types
effusive volcanism: shergottites and nakhlites
intrusive magmatism: chassignites, ALHA 84001, orthopyroxene
pyroclastic material (?): black beauty meteorite
which earth rock types have been found on mars?
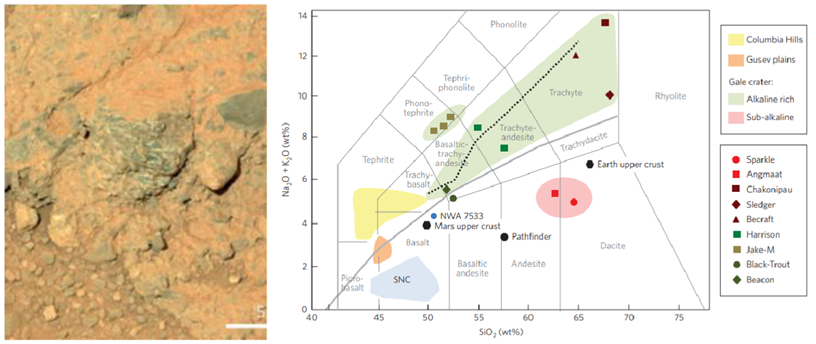
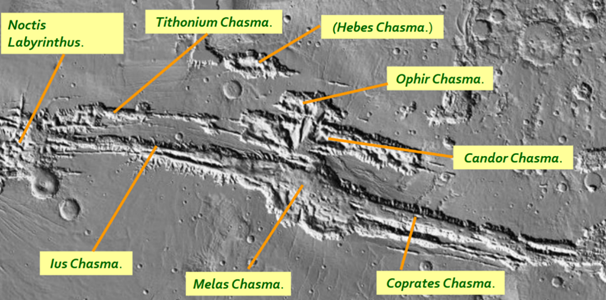
What is the Valles Marineris Formation?
system of canyons 400km long and 2-7km wide
crust stretched, faulted noamrlly, valley floor drops relative to surroundings
modification by landslides and erosion

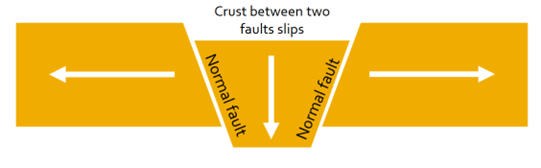
Analysis of Valles Marineris Formation
largest canyon in SS
equitorial
formed in rift faults like the East African Rift valley - made bigger by erosion and collapsing of rift walls
floor may be lake bed sediments, retaining palaeobiological
valley systems feed water into valley floor
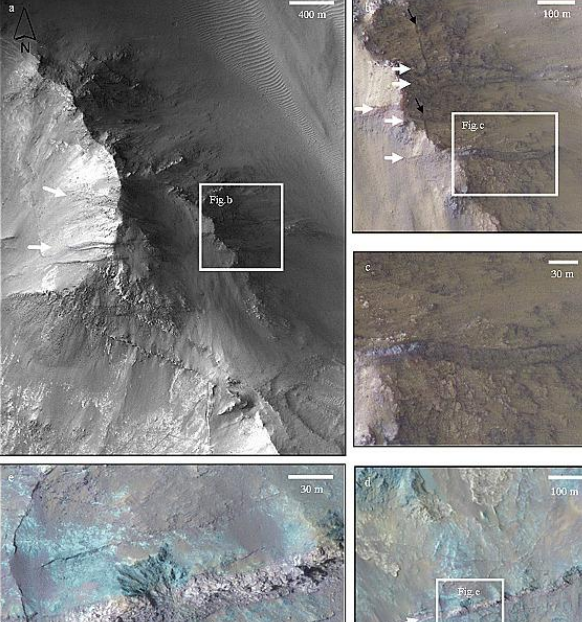
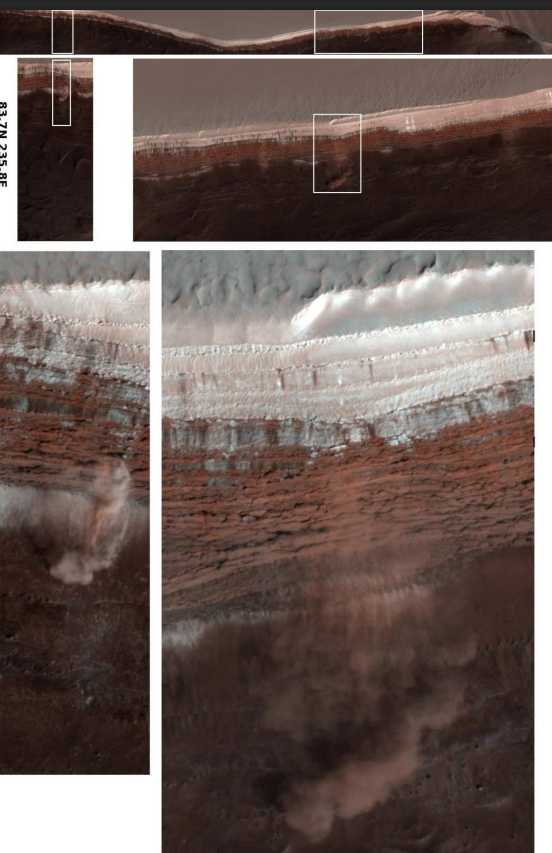
What evidence is there for Mars Quakes?
avalanches on northern polar scarps of Mars

Evidence for fluvial processes on Mars?
flash flood evidence
river systems/valley networks
island creation
deposition of river deposits - delta deposits
mineralogical evidence of water - hematite Fe2O3 - opportunity rover 2023
hematite blueberries - hydroxyl material
sedimentary rocks in fluvial environment
what do hematite blueberries look like?

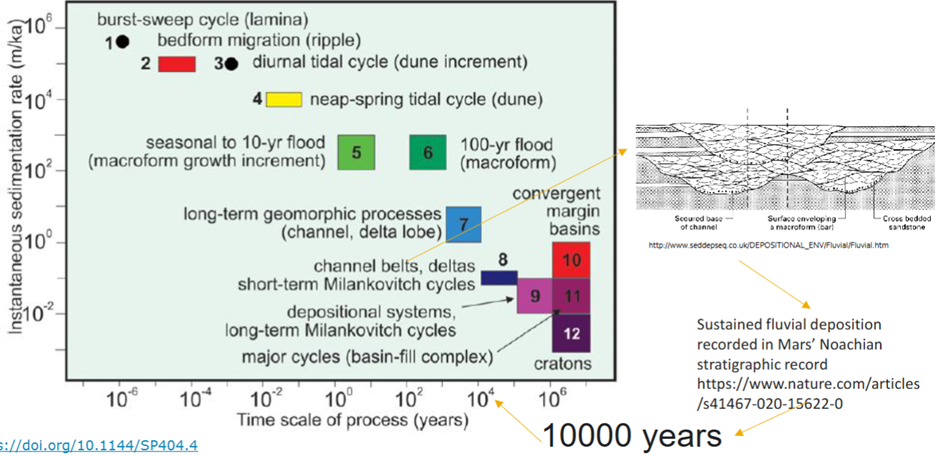
Time for sedimentation on Mars
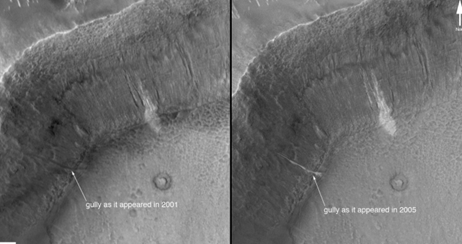
Evidence for recent liquid water on mars?
slipe lines, could be related to seasonal releases of volatiles in walls of impact craters
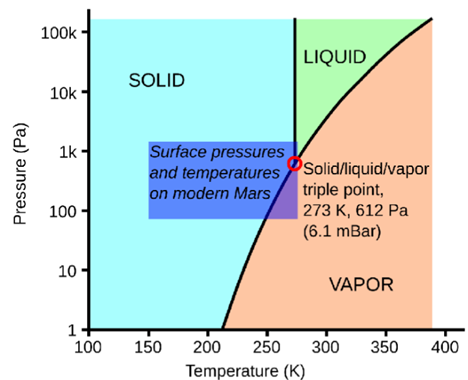
Why is there no water now on Mars?
due to changes in p/T ratios over time
mars exists at a triple junction point o f3 domains on graph shown
ice sublimates
thin atmosphere
What temperature is Mars’ atmosphere?
avg temp: -63C
max temp: 20C
min temp: -140C
What makes up Mars’ atmosphere?
CO2: 95.3%
N2: 2.7%
Ar: 1.6%
O2: 0.13%
H2O: 0.03%
Ne: 0.00025%
What triggers dust storms?
solar heating of surface heats the air above the surface, causing a temp gradient - cooler pulled downwards
wind lifts dust
dust heats up
most storms are localised - only few are global
What features do dust storms form on mars?
Yardangs: wind-abraided ridge found in desert environments - few impact craters - erosion still occuring
Dust devils

Mars environment human implications
dust is an abrasive material
surface radiation
mars quakes
long spaceflight duration (18 months)
Where have organics been found on mars?
found by Viking
found at Gale Crater by Curiosity rover
what evidence is there for past microbial activity on mars?
ALH 84001 meteorite
contained magnetite, carbonite minerals
possible evidence of fossilised microbes - debated
What scientific equiptment was on the viking lander?
two 360 degree cameras
sampler arm up to 30cm
temp, wind, pressure
seismometer
x-ray spectrometer
what was the aim of Viking
experiment to see if bugs in martian sediment were producing carbon that could be tracked as a tracer for respiration - produce carbon that could be detected by a gas spectrometer
What were the results of the Viking experiment?
Gas exchange: O2 emitted by both steralised and unsteralised - no life present within soil
pyrolitic release: both produced no evidence of C14 so no life
label release: steralised samples DID produce radioactive carbon (life?). when more nutrients were added it gave less amounts of carbon - not predicted