Diagnosis of CVD & Genetics – Flashcards (16)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms


What is the Framingham Heart Study?
: A landmark longitudinal study (started in 1948) that identified major CVD risk factors, including hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia, smoking, obesity, and diabetes.
What is QRISK and how is it used clinically?
A UK-based algorithm used to estimate a person’s 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is the significance of “Heart Age” in risk assessment? (hint think jacks heart)
A communication tool to help patients understand risk; a heart age higher than chronological age indicates poorly controlled risk factors.
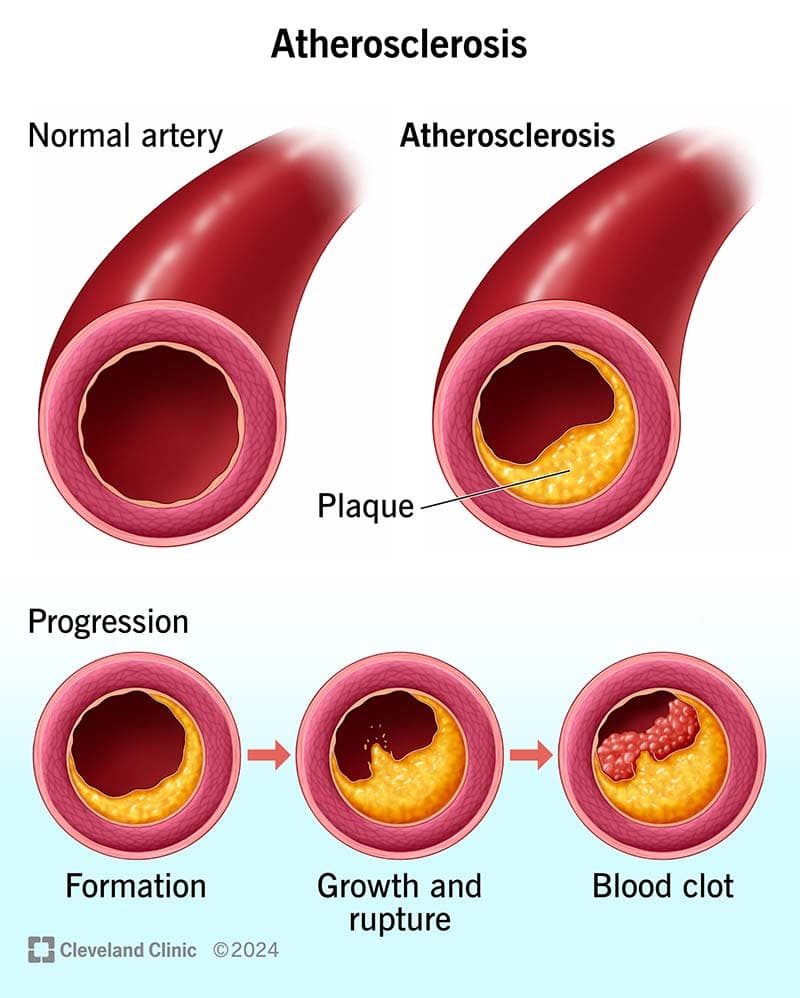
What is Familial Hypercholesterolaemia (FH)?
An inherited disorder causing markedly elevated LDL cholesterol from birth, leading to premature coronary heart disease.
Which genes are most commonly mutated in FH?
LDLR, APOB, PCS9
What is a “proband” in genetic testing?
The first affected individual in a family to be identified and tested to determine the causative mutation.

How does Sanger sequencing work?
A highly accurate, “gold standard” method that sequences small DNA regions (up to ~900 bp) using chain termination.

What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
Massively parallel sequencing that analyses millions of DNA fragments simultaneously, allowing rapid multi-gene screening.
When is NGS preferred over Sanger sequencing?
For initial diagnosis, when screening multiple genes at once (e.g. LDLR, APOB, PCSK9 in FH).
When is Sanger sequencing preferred over NGS?
For cascade testing, to confirm a known family mutation in relatives.
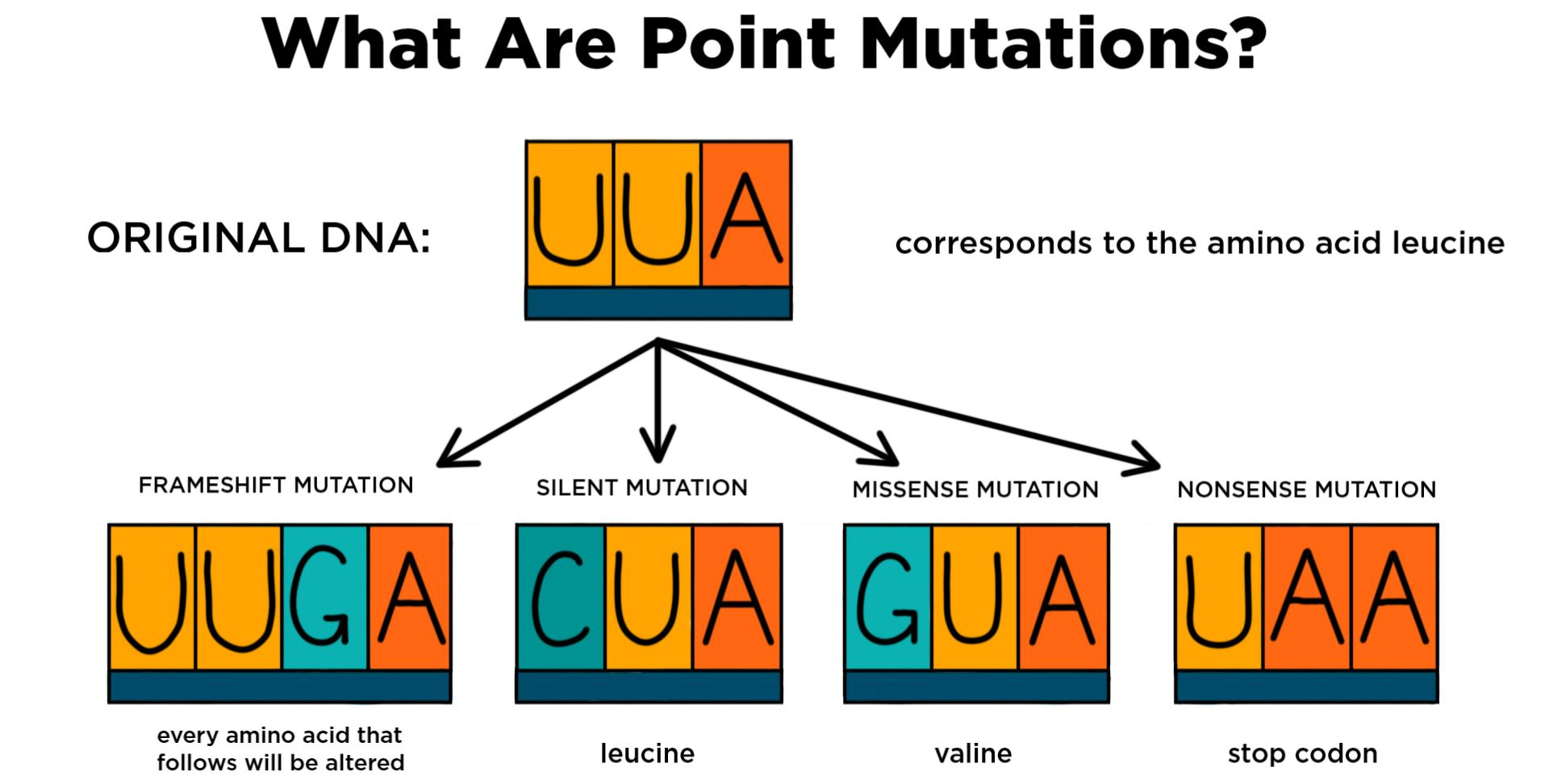
What is a point mutation (SNV)?
A point mutation (SNV) is a single-nucleotide change in DNA that may be silent or alter protein function (silent, missense, or nonsense mutations) and is a common cause of both genetic disease and normal variation.
What is a limitation (“con”) of NGS?
Produces large datasets requiring specialist bioinformatics and significant computing resources for interpretation.
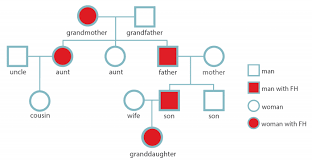
What is cascade testing in FH?
Targeted genetic testing of first-degree relatives of an affected individual to identify others at risk early.
Why is the LDL receptor (LDLR) gene critical?
It encodes the receptor responsible for clearing LDL cholesterol from blood; mutations cause very high LDL levels.
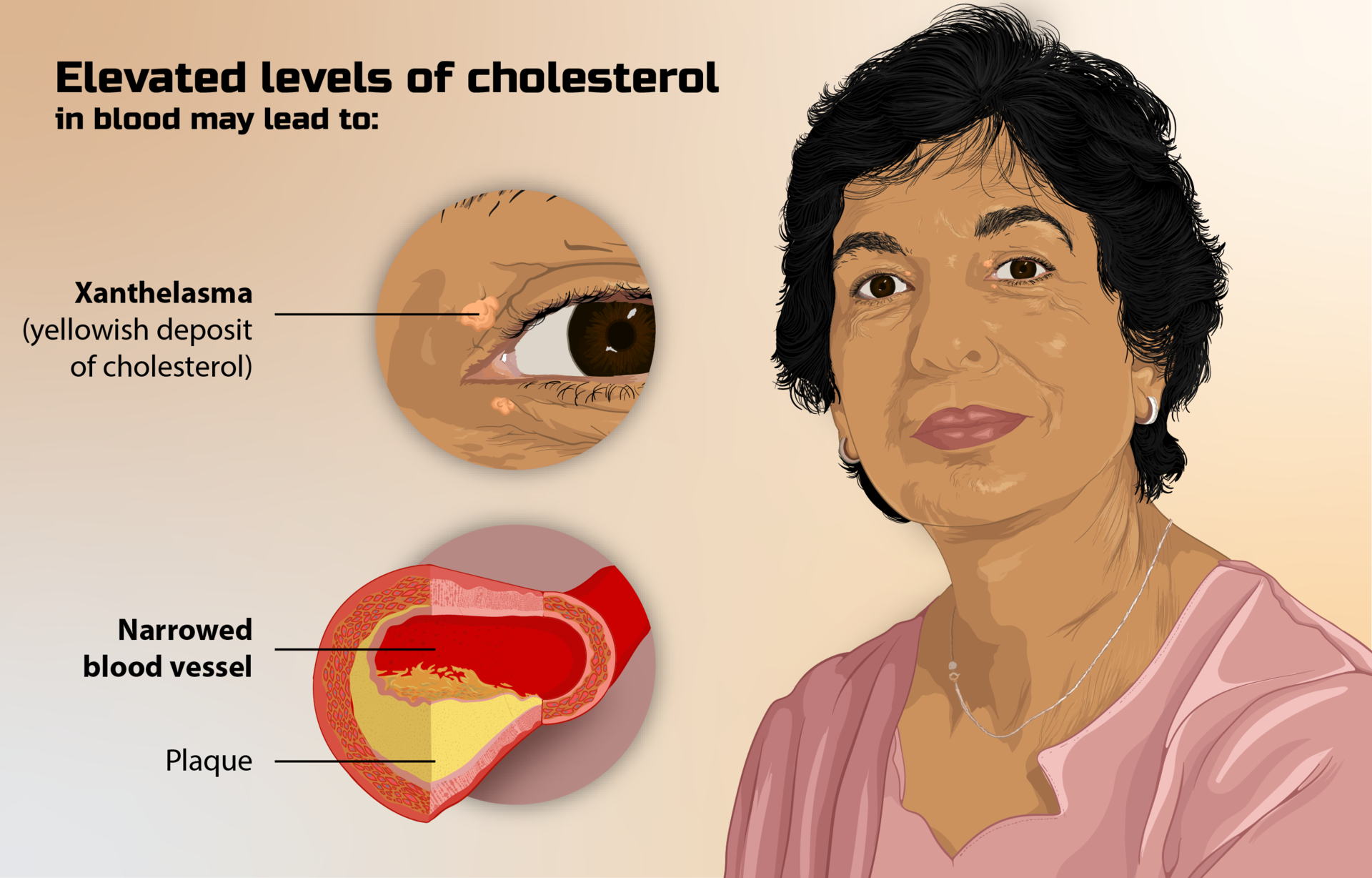
What clinical signs may suggest FH?
Tendon xanthomas and corneal arcus occurring at a young age
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype: The underlying genetic mutation (e.g. LDLR mutation)
Phenotype: The observable effect (e.g. LDL = 18.0 mmol/L)