NURS 3070: ADH1: MODULE 1: Acid-Base and ABG's
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
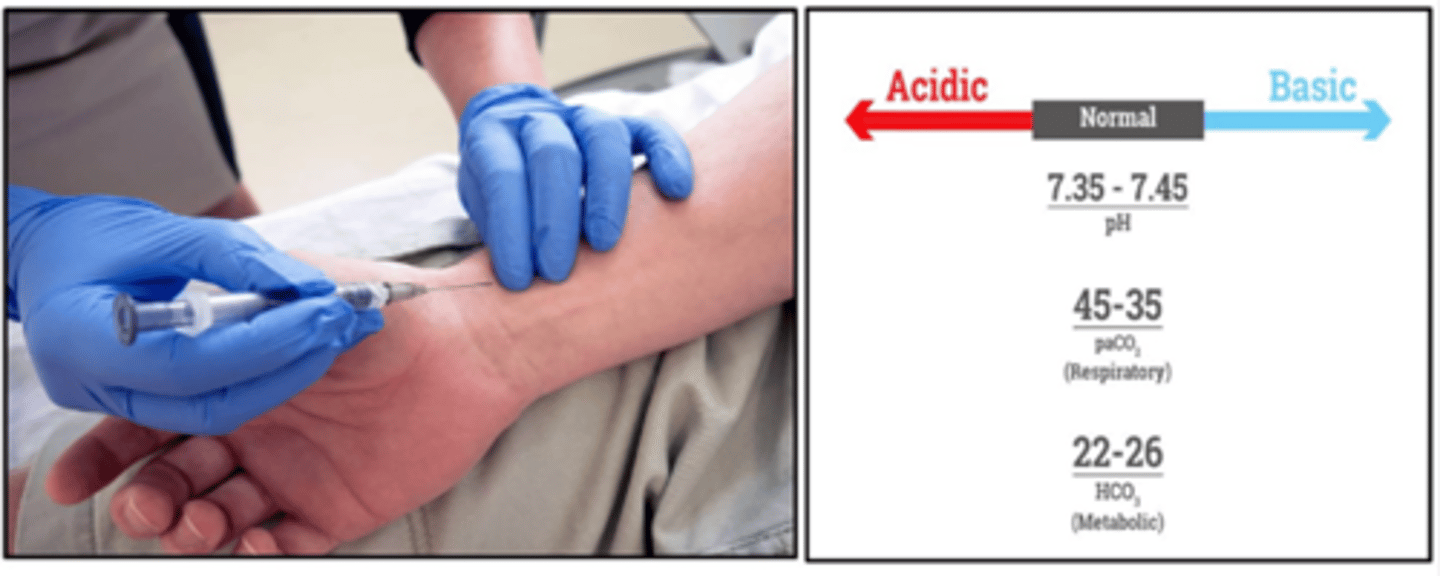
What is the normal pH range?
7.35-7.45
What does a pH less than 7.35 indicate?
Acidosis
What does a pH greater than 7.45 indicate?
Alkalosis
What is the normal PaCO₂ range?
35-45 mmHg
What does a PaCO₂ greater than 45 indicate?
Respiratory acidosis
What does a PaCO₂ less than 35 indicate?
Respiratory alkalosis
What is the normal HCO₃⁻ (bicarbonate) range?
22-26 mEq/L
What does a HCO₃⁻ less than 22 indicate?
Metabolic acidosis
What does a HCO₃⁻ greater than 26 indicate?
Metabolic alkalosis
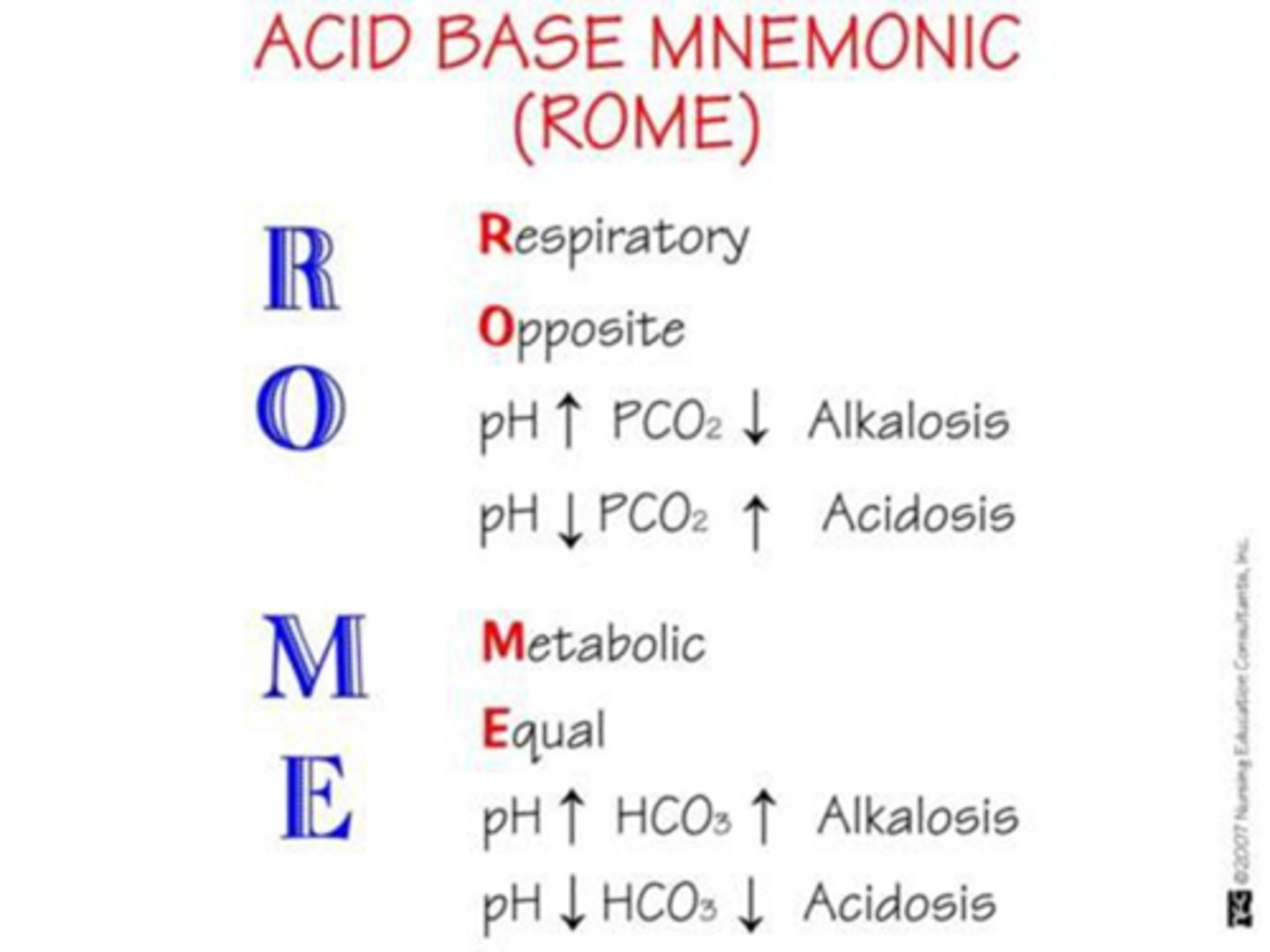
What does ROME stand for in ABG interpretation?
Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal
How do pH and PaCO₂ move in respiratory imbalances?
In opposite directions
How do pH and HCO₃⁻ move in metabolic imbalances?
In the same direction
What does it mean if the ABG is uncompensated?
pH is abnormal, and the other value (PaCO₂ or HCO₃⁻) is normal
What does it mean if the ABG is partially compensated?
pH is abnormal, and both PaCO₂ and HCO₃⁻ are abnormal
What does it mean if the ABG is fully compensated?
pH is normal, but both PaCO₂ and HCO₃⁻ are abnormal
What are the normal values for pH, PaO₂, PaCO₂, SaO₂, and HCO₃⁻ in ABG analysis?
Recognize normal values for pH, PaO₂, PaCO₂, SaO₂, and HCO₃⁻.
What is the significance of the values obtained from ABG analysis?
Explain the significance of these values.
How are O₂ and CO₂ carried in the body and measured?
Describe how O₂ and CO₂ are carried in the body and how they are measured.
How does the pH scale relate to acidosis and alkalosis?
Relate the pH scale to acidosis and alkalosis.
What mechanisms control acid-base balance in the body?
Discuss respiratory and metabolic mechanisms in controlling acid-base balance.
How do you interpret basic ABG values in relation to patient conditions?
Interpret basic ABG values and relate them to patient conditions.
What therapies can be suggested for acid-base correction?
Suggest therapies for acid-base correction.
ROME
Normal Arterial Blood Gas Values
What is the normal pH range?
7.35-7.45
What is the normal PaCO₂ range?
35-45 mmHg
What is the normal bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) range?
22-26 mEq/L
What is the normal PaO₂ range?
80-100 mmHg
What is the normal SaO₂ value?
>95%
What is the first step in ABG diagnosis?
Evaluate pH
What is the second step in ABG diagnosis?
Analyze PaCO₂
What is the third step in ABG diagnosis?
Analyze HCO₃⁻
What is the fourth step in ABG diagnosis?
Determine if CO₂ or HCO₃⁻ matches the alteration
What is the fifth step in ABG diagnosis?
Decide if the body is attempting to compensate
What is the sixth step in ABG diagnosis?
Identify overall imbalance
What does ROME stand for in ABG interpretation?
Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal.
What are the three puzzle pieces of ABG interpretation?
A) Acidosis or alkalosis B) Compensation status (uncompensated, partial, or fully compensated) C) Respiratory or metabolic cause
What are the normal values for pH, PaCO₂, and HCO₃⁻ in ABG interpretation?
pH (7.35-7.45), PaCO₂ (35-45), HCO₃⁻ (22-26).
How do you mark arrows for ABG interpretation?
pH (low = acid, high = base), PaCO₂ (↑ acid, ↓ base), HCO₃⁻ (↑ base, ↓ acid).
What is the first step in interpreting ABGs?
Write down normal values.
What should you do after comparing patient's ABG values to normal?
Check pH → normal, high, or low. If pH normal, check PaCO₂/HCO₃⁻ for abnormalities.
How do you identify acidosis or alkalosis in ABG interpretation?
If pH abnormal, determine direction. If pH normal but one abnormal value, decide which direction it is trending.
How do you determine compensation in ABG interpretation?
pH normal + both PaCO₂ & HCO₃⁻ abnormal → compensated; pH abnormal + both abnormal → partially compensated; pH abnormal + one abnormal → uncompensated.
How do you identify if the cause of an ABG abnormality is respiratory or metabolic?
Only PaCO₂ abnormal → respiratory; Only HCO₃⁻ abnormal → metabolic; Both abnormal → culprit is the one matching pH direction.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.33, PaCO₂ 67, PaO₂ 47, HCO₃⁻ 37?
Respiratory acidosis, partially compensated.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.18, PaCO₂ 38, PaO₂ 70, HCO₃⁻ 15?
Metabolic acidosis.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.60, PaCO₂ 30, PaO₂ 60, HCO₃⁻ 22?
Respiratory alkalosis.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.58, PaCO₂ 35, PaO₂ 75, HCO₃⁻ 50?
Metabolic alkalosis.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.28, PaCO₂ 28, PaO₂ 70, HCO₃⁻ 18?
Metabolic acidosis, partially compensated.
What is the imbalance for pH 7.36, PaCO₂ 58, PaO₂ 50, HCO₃⁻ 33?
Respiratory acidosis with compensation (chronic).
What are common causes of chronic respiratory acidosis?
COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis, CNS depression, neuromuscular diseases.
What are the assessment findings for chronic respiratory acidosis?
Dyspnea, shallow breaths, decreased tidal volume, disorientation, somnolence, tachycardia, arrhythmias.
What are the treatments for chronic respiratory acidosis?
Oxygen therapy, mobilize secretions, positive-pressure ventilation, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, diuretics, antibiotics, sedatives, analgesics.
Case 7
pH 7.50, PaCO₂ 28, PaO₂ 85, HCO₃⁻ 24 → What imbalance is this and what patient scenario fits?
Case 7
Respiratory alkalosis.
-Causes: hypoxemia from pulmonary disorders, anxiety, CNS disorders, mechanical over-ventilation.
-Assessment: tingling/numbness, restlessness, hyperreflexia, tetany, headache, confusion, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting.
-Treatment: correct cause, rebreathing (paper bag), oxygen therapy, bronchodilators
Case 8
pH 7.20, PaCO₂ 28, PaO₂ 81, HCO₃⁻ 18 → What imbalance is this and what patient scenario fits?
Case 8
Metabolic acidosis with respiratory compensation.
Causes: uncontrolled diabetes (DKA), lactic acidosis, starvation, diarrhea, renal failure, shock.
Assessment: drowsiness → coma, deep rapid respirations, hypotension, arrhythmias, flushed skin, GI upset.
Treatment: treat underlying cause, insulin for DKA, glucose for starvation, dialysis for renal failure
Case 9
pH 7.57, PaCO₂ 46, PaO₂ 87, HCO₃⁻ 38 → What imbalance is this and what patient scenario fits?
Case 9
Metabolic alkalosis with partial compensation.
-Causes: severe vomiting, gastric suctioning, diuretics, K⁺ deficit, excess sodium bicarb, mineralocorticoid therapy.
-Assessment: nervousness, confusion, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, nausea, tremors, tetany, tingling.
-Treatment: correct underlying cause, replace K⁺, discontinue offending drugs, treat vomiting