Blood Vessels: Types, Structure, and Function in Circulatory System
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Blood Vessels
These are tubes or channels that carry blood throughout our body.
Types of Blood Vessels
There are three types of blood vessels—veins, arteries and capillaries.
Artery
Carries blood away from the heart.
Vein
Carries blood back towards the heart.
Capillary
Assists in the exchange of substances between the blood and tissues.
Artery Structure
It has the thickest wall of all three, allowing it to withstand the high pressure created by the heart.
Capillary Structure
It has the thinnest wall to allow substances such as oxygen and sugars to pass through its wall—into or out of the blood.
Vein Structure
It is less muscular and stretchy than an artery, so blood moves through it with low pressure.
Vein Valves
It also has a special valve that helps blood go only one way.
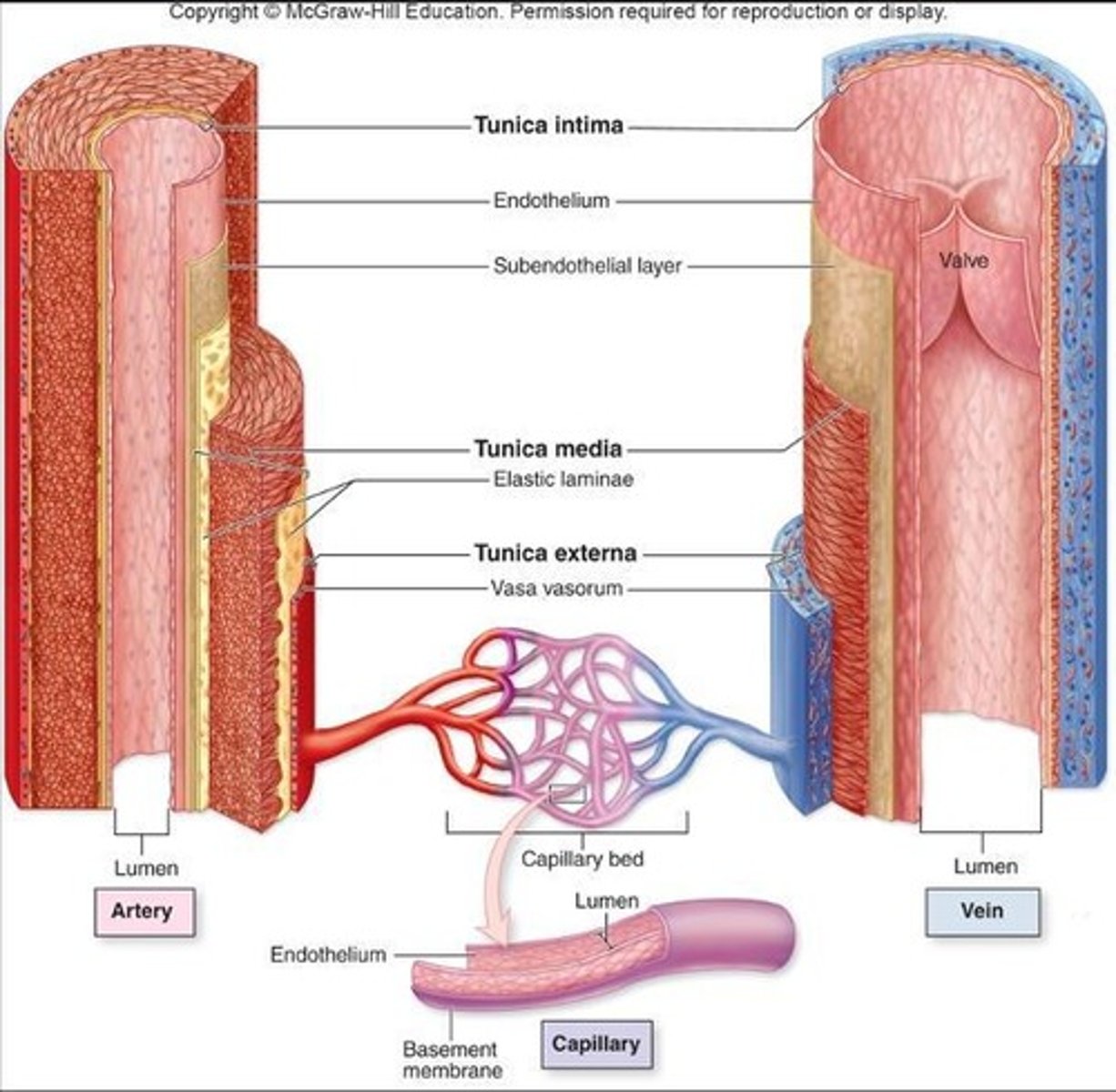
Wall of a Blood Vessel
The vessel wall is made of layers called tunics.
Tunica Media
Middle layer made of muscle responsible for vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
Tunica Externa
Outermost layer that helps anchor vessel to other structures.
Tunica Intima
Innermost layer made of endothelium with a smooth inner lining.
Vaso Vasorum
Very large blood vessels have Vaso Vasorum in this layer (blood supply for the blood vessel!).
Arteries vs. Veins
Arteries have a narrower lumen and thicker wall in general; veins have a wider lumen and thinner wall.
Arteries Characteristics
Keeps shape without blood in vessel; Valves NEVER present.
Veins Characteristics
Collapses without blood in vessel; Valves USUALLY present.
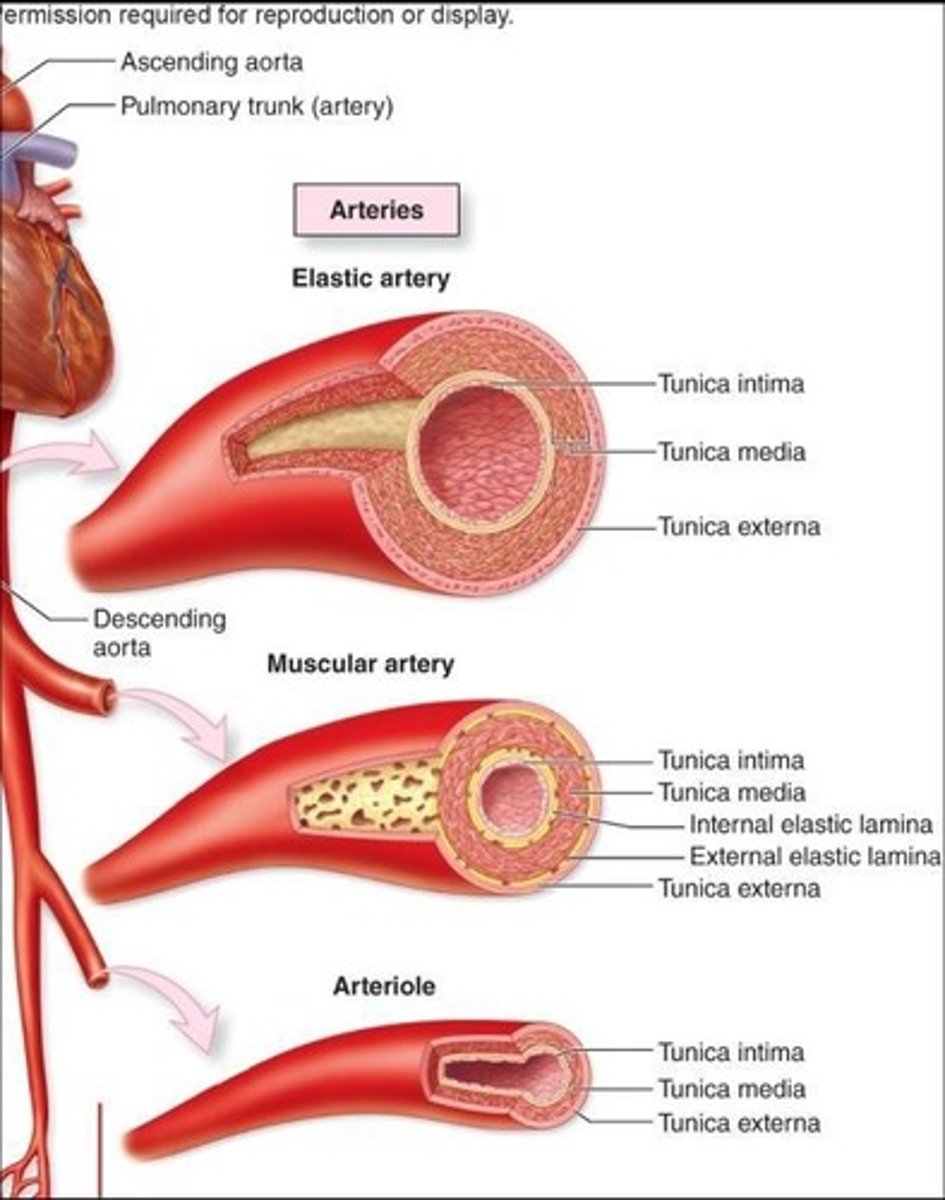
Elastic Arteries
Largest, AKA conducting arteries; lots of elastic fibers for stretch and recoil.
Muscular Arteries
AKA distributing arteries; thicker tunica media.
Arterioles
Smallest; play a major role in regulating blood pressure and flow.
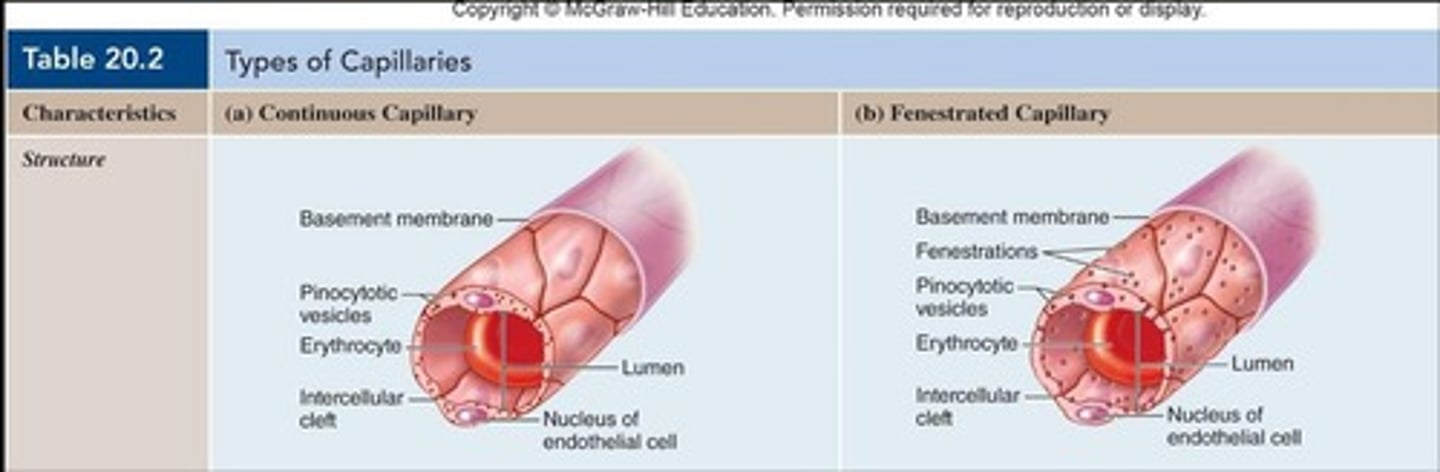
Continuous Capillaries
Most common type; complete lining with intercellular clefts for passage of small materials.
Fenestrated Capillaries
Complete lining but extremely thin areas called fenestrations to allow for passage of larger materials like nutrients.
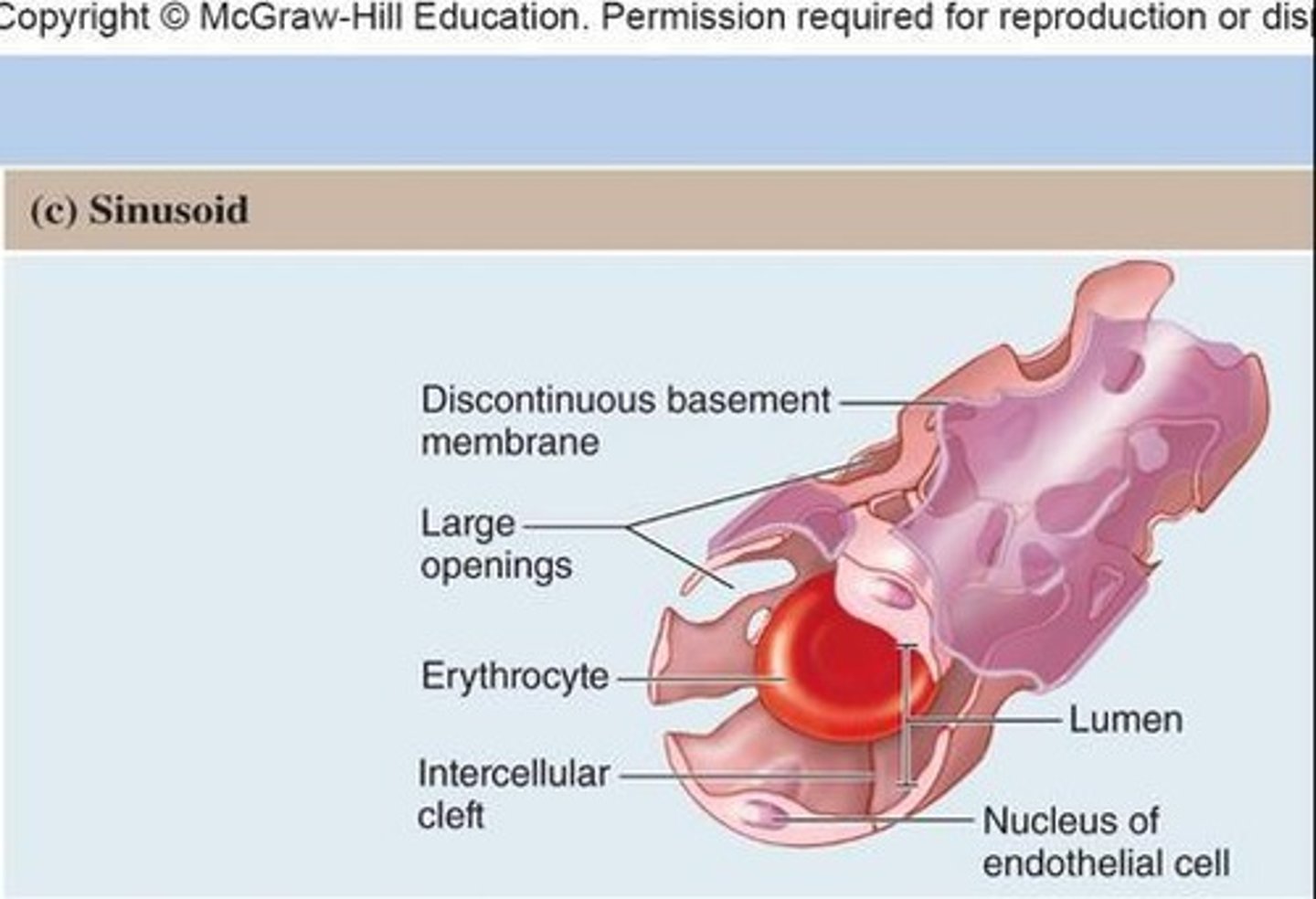
Sinusoids
Most permeable type; incomplete lining with gaps for blood cells and large substances to pass through.
Exchange at Capillaries
Delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells at the capillary bed and picking up wastes and carbon dioxide from those same cells.
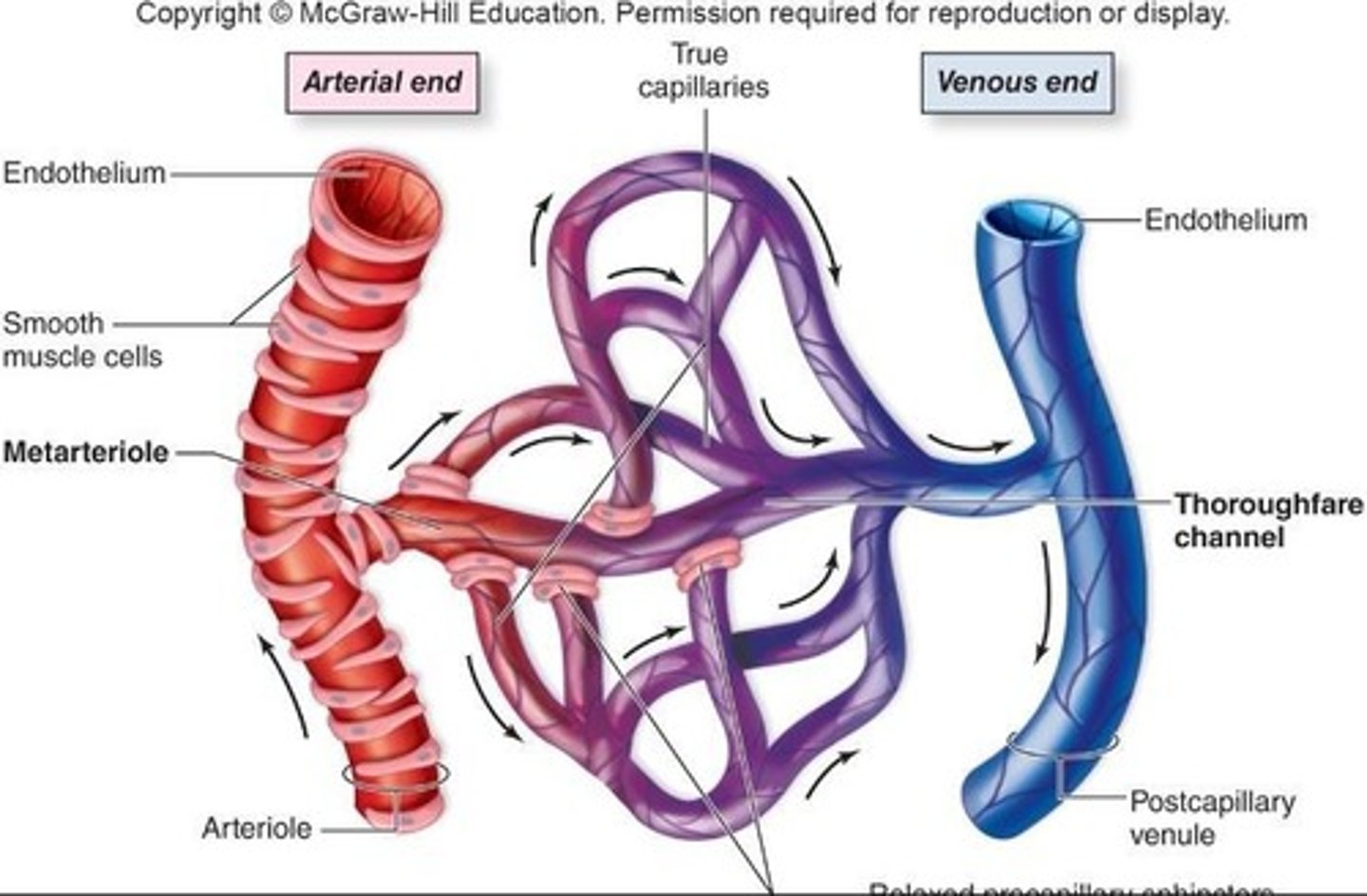
Metarteriole
Bringing in oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to deliver to cells surrounding the capillaries.
True Capillaries
Actually do the delivery/exchange; they pick up the waste from the cells.
Venule
At the end of the capillary bed, it collects waste from the true capillaries.
Diffusion in Exchange
Nutrients and oxygen leave blood and move out to interstitial fluid/tissues; carbon dioxide and wastes leave tissues/interstitial fluid to go into blood.
Veins as Blood Reservoirs
Veins serve as blood reservoirs (basically places to store blood).
Blood Shifting in Veins
Blood can be shifted from venous reservoirs into circulation with increased physical exertion.
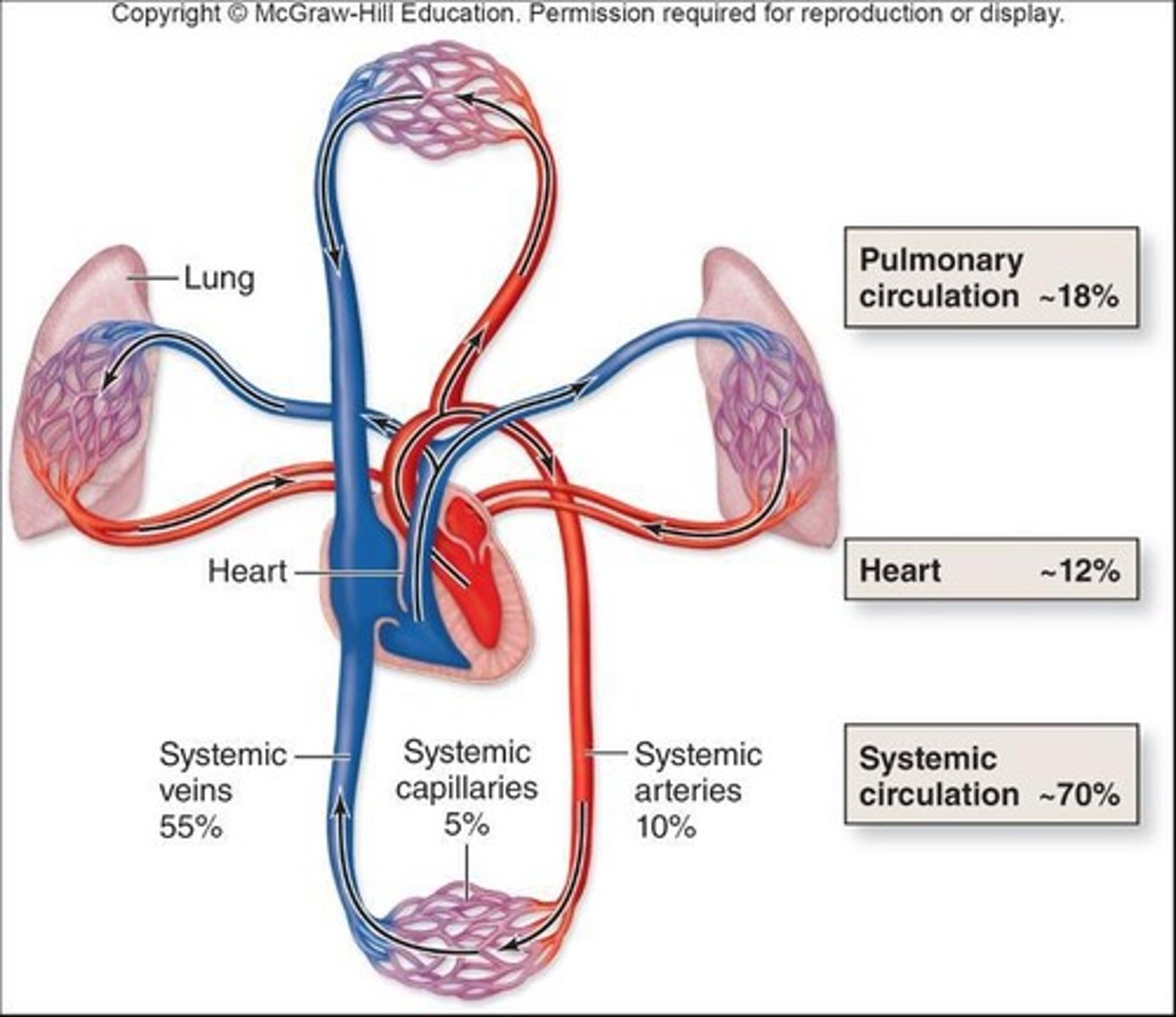
Circulatory System Function
Delivers oxygen and nutrients to the body, while also removing wastes.
Blood Vessels Pathways
Blood vessels can have direct or less direct pathways.
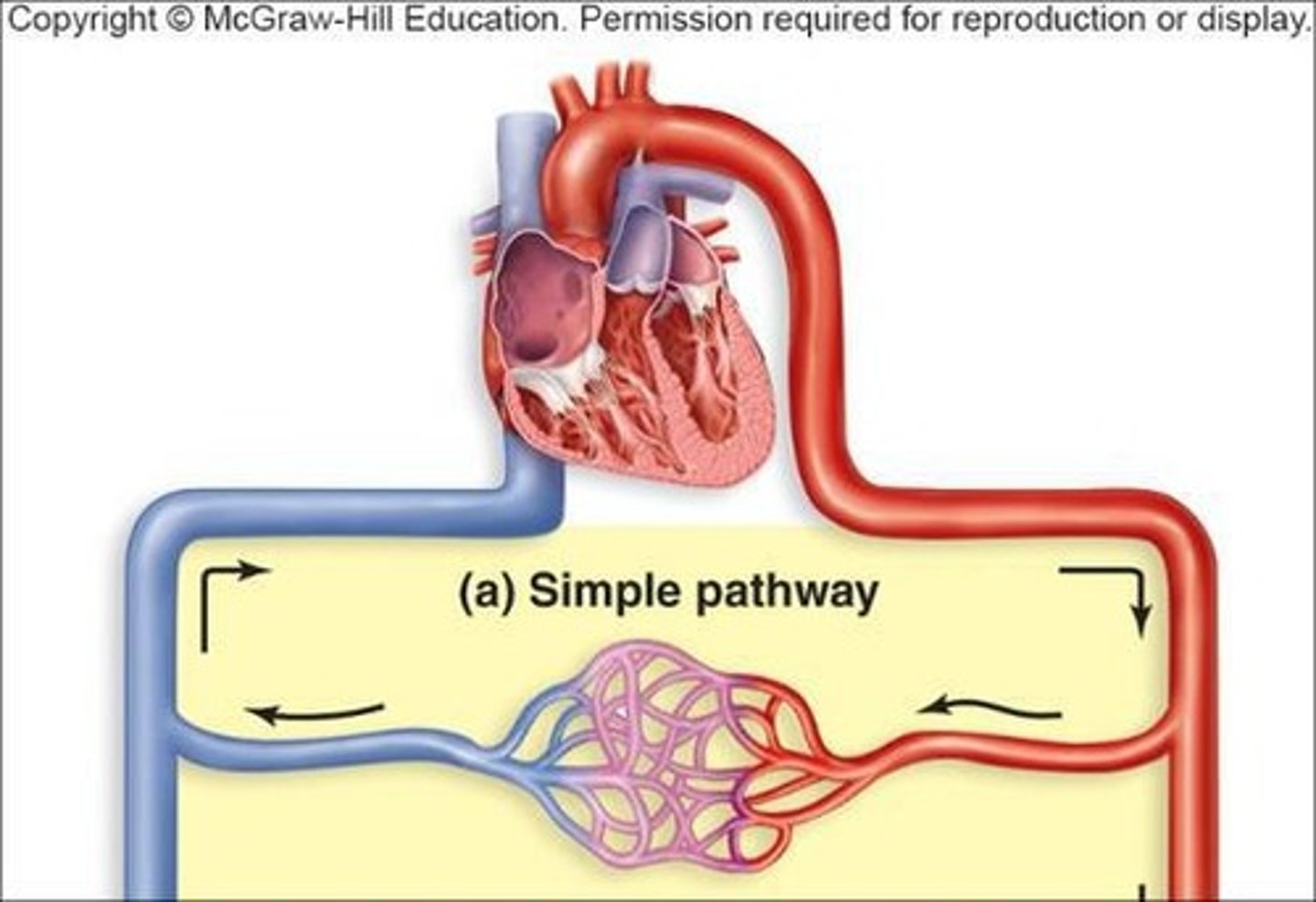
Simple Pathways
A simple pathway consists of one artery, a capillary bed, and one vein per organ/body region.
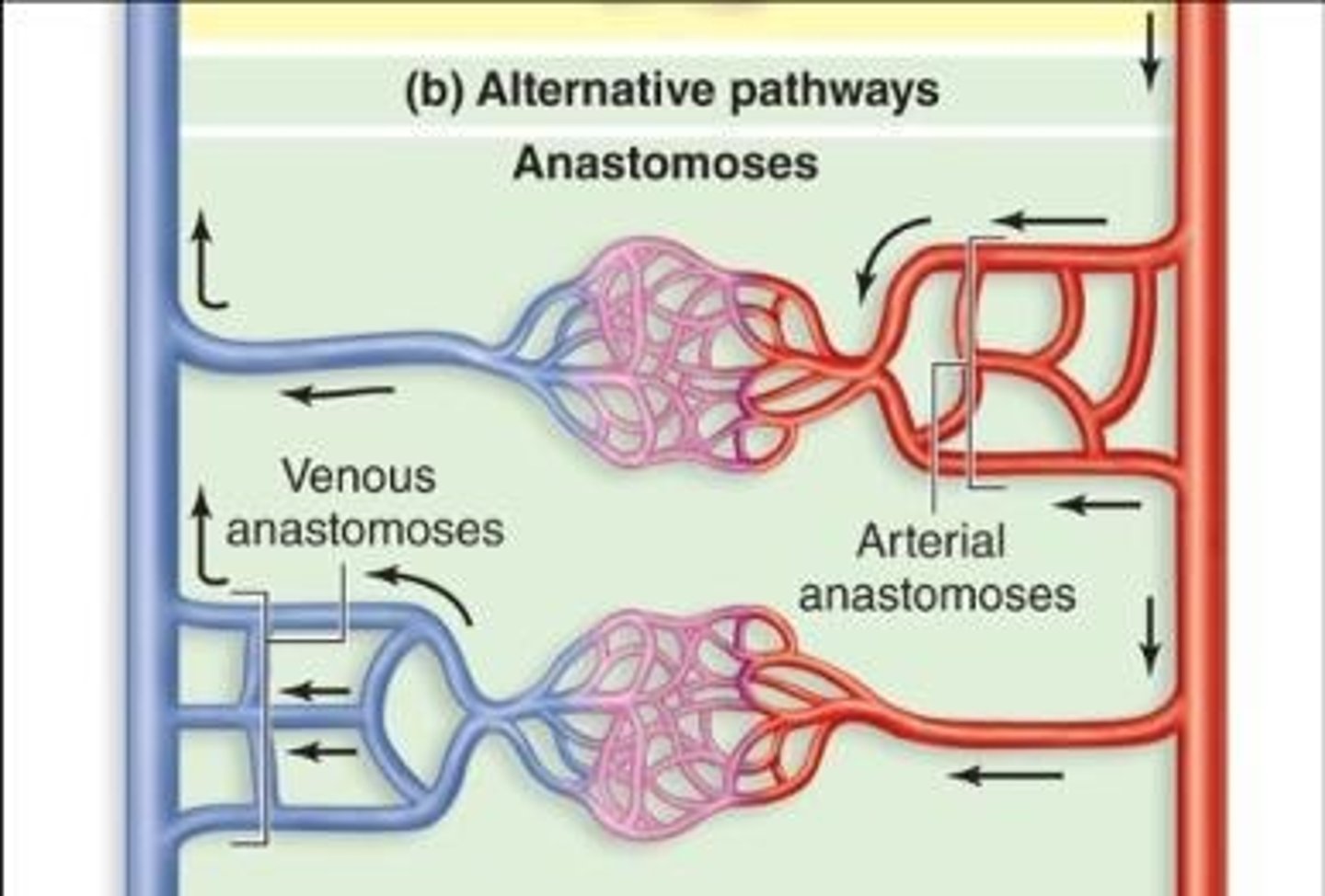
Anastomosis
Anastomosis is the joining together of blood vessels.
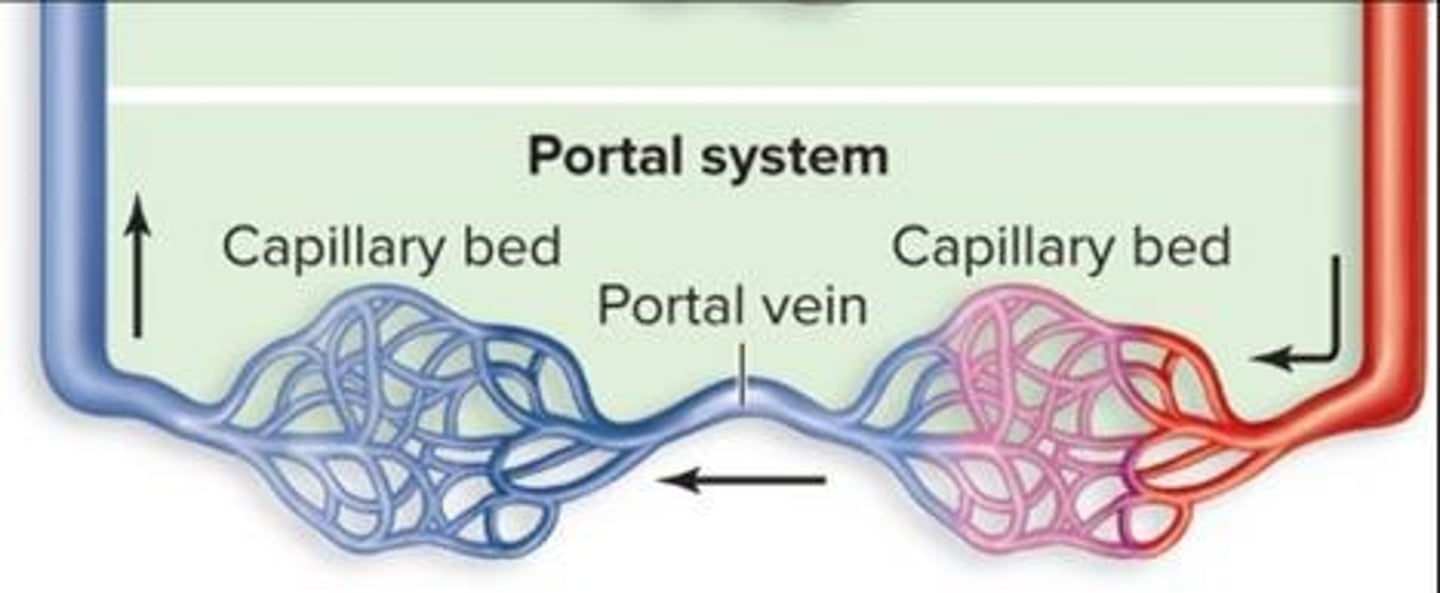
Portal System
A portal system directs venous blood through the capillary bed of an organ, like the liver, before going to the heart.
Cross-Sectional Area
Cross-sectional area refers to the diameter of a vessel's lumen.
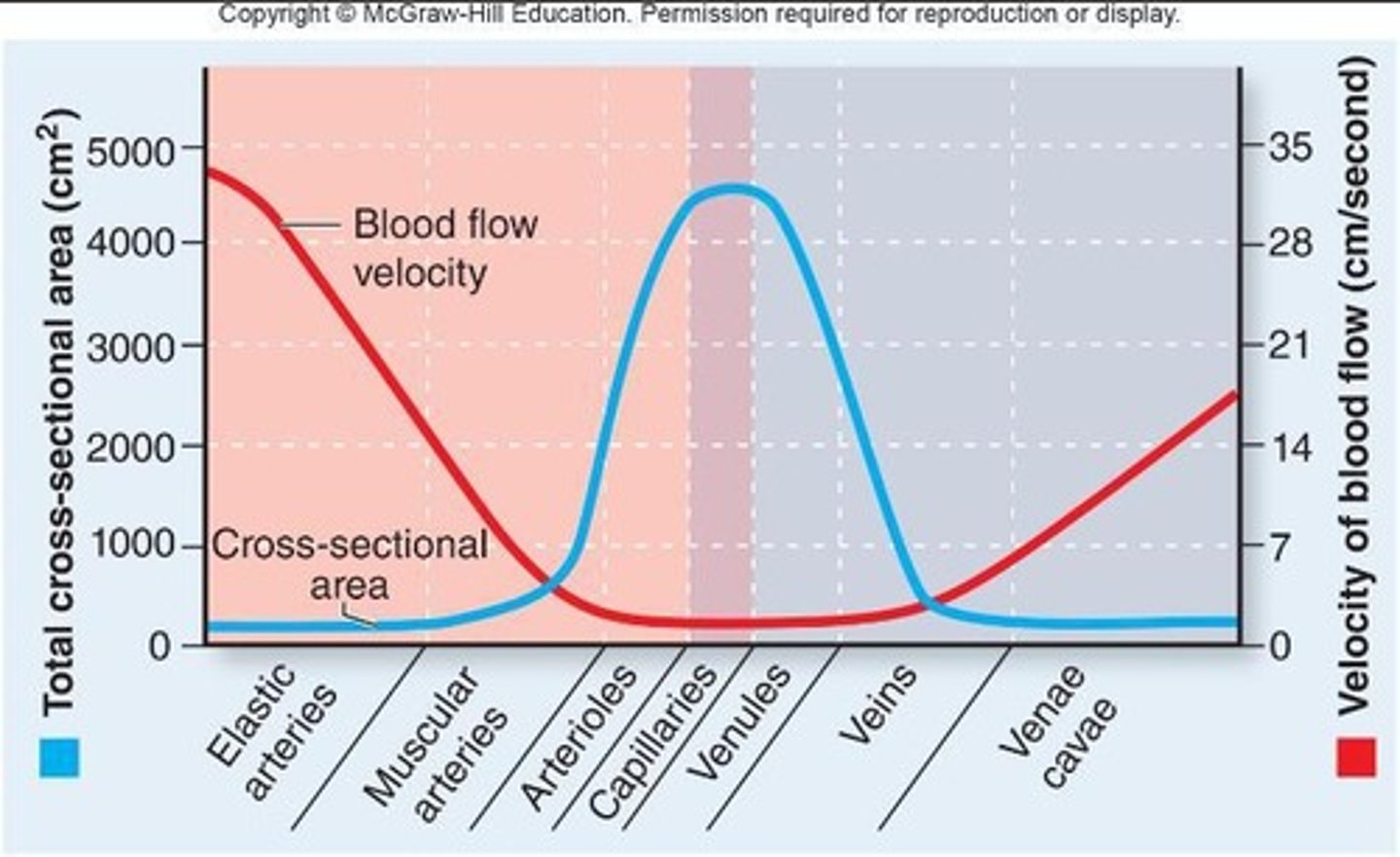
Total Cross-Sectional Area
Total cross-sectional area is the aggregate lumen diameter across the total number of a type of vessel.
Blood Flow Velocity
The relationship between total cross-sectional area and velocity of blood flow is inverse.
Fastest Blood Flow
The fastest blood flow occurs in arteries because the total cross-sectional area is relatively small.
Slowest Blood Flow
The slowest blood flow occurs in capillaries because the total cross-sectional area is large.
Bulk Flow
Bulk flow is the movement of large amounts of fluids and dissolved substances at the capillaries driven by a pressure gradient.
Filtration
Filtration is the process that occurs at the arterial end where fluid and small solutes move out of the blood.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption is the process that occurs at the venous end where fluid and small solutes move back into the blood.
Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
NFP is determined by the balance of hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure.
Hydrostatic Pressure (HP)
Hydrostatic pressure is the physical force exerted on a fluid by a structure, promoting filtration.
Colloid Osmotic Pressure (COP)
Colloid osmotic pressure is the pull of water back into tissues by the tissue's concentration of protein.
Reabsorption Rate
About 85% of the fluid is reabsorbed, while the other 15% is picked up by the lymphatic system.
Local Blood Flow
Local blood flow is the blood delivered to a specific tissue, dependent on various factors.
Vascularization
Degree of vascularization of tissues affects local blood flow.
Myogenic Response
Myogenic response is the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle in response to stretching of the vessel wall.
Local Regulatory Factors
Local regulatory factors, such as vasodilators and vasoconstrictors, alter blood flow.
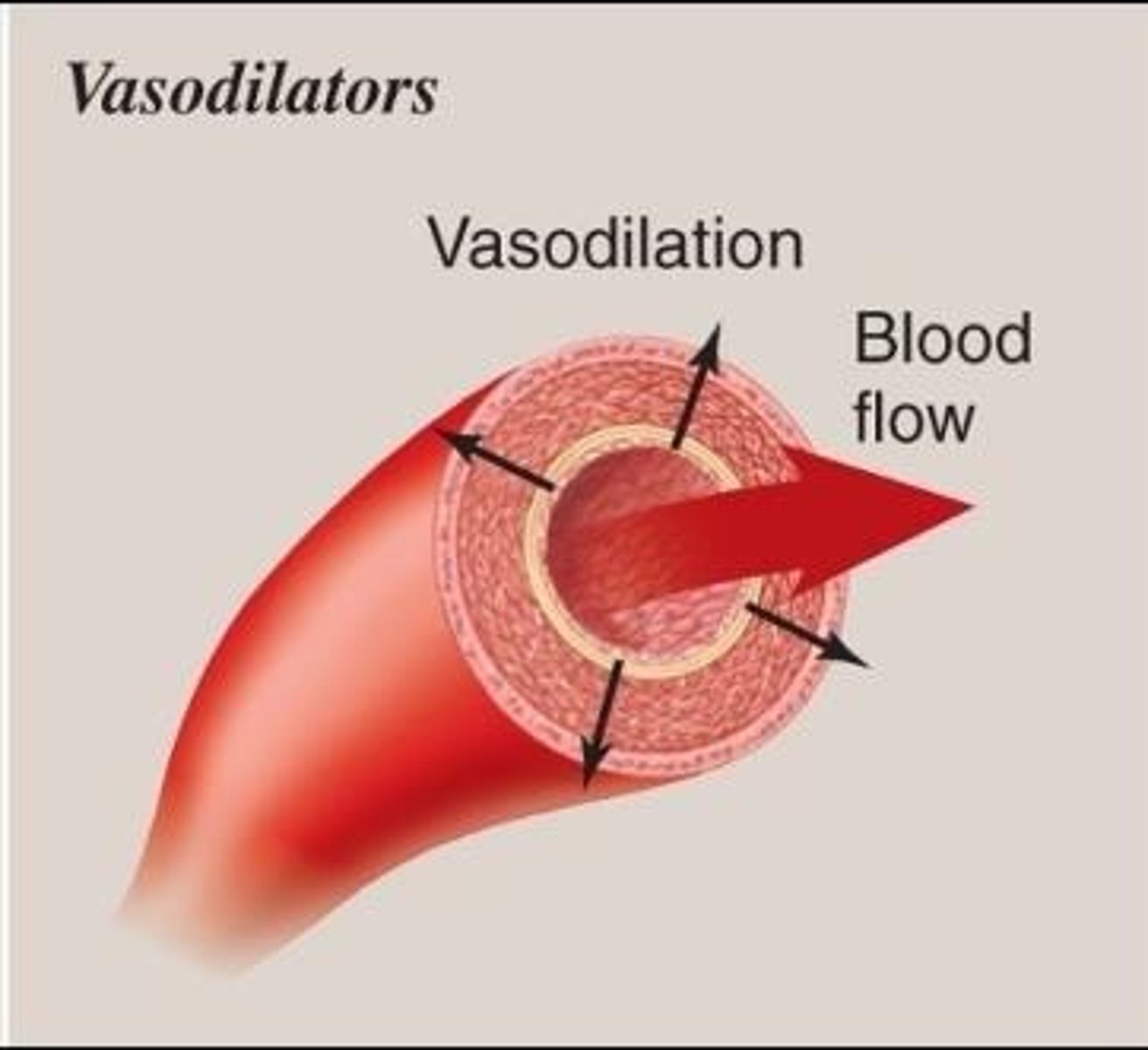
Vasodilators
Vasodilators are substances that cause smooth muscle relaxation, enlarging the lumen and increasing blood flow.
Vasoconstrictors
Vasoconstrictors are substances that cause smooth muscle contraction, narrowing the lumen and decreasing blood flow.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force per unit area that blood exerts against the inside wall of a vessel.
Arterial Blood Pressure
Arterial blood pressure is pulsatile/throbbing due to ventricles contracting and relaxing.
Systolic Pressure
Systolic pressure is the highest pressure occurring during ventricular systole.
Diastolic Pressure
Diastolic pressure is the lowest pressure occurring during ventricular diastole.
Pulse
Pulse is the rhythmic throbbing of an arterial wall as blood is being pumped, indirectly determining heart rate and blood pressure.
Common carotid
An artery located in the neck.
Radial artery
An artery located near the wrist.
Popliteal artery
An artery located at the back of the knee.
Capillary Blood Pressure
The pressure in capillaries that is high enough to promote exchange but not to damage fragile capillaries.
Venous Blood Pressure
The pressure in veins, which is lower than in arteries and not pulsatile.
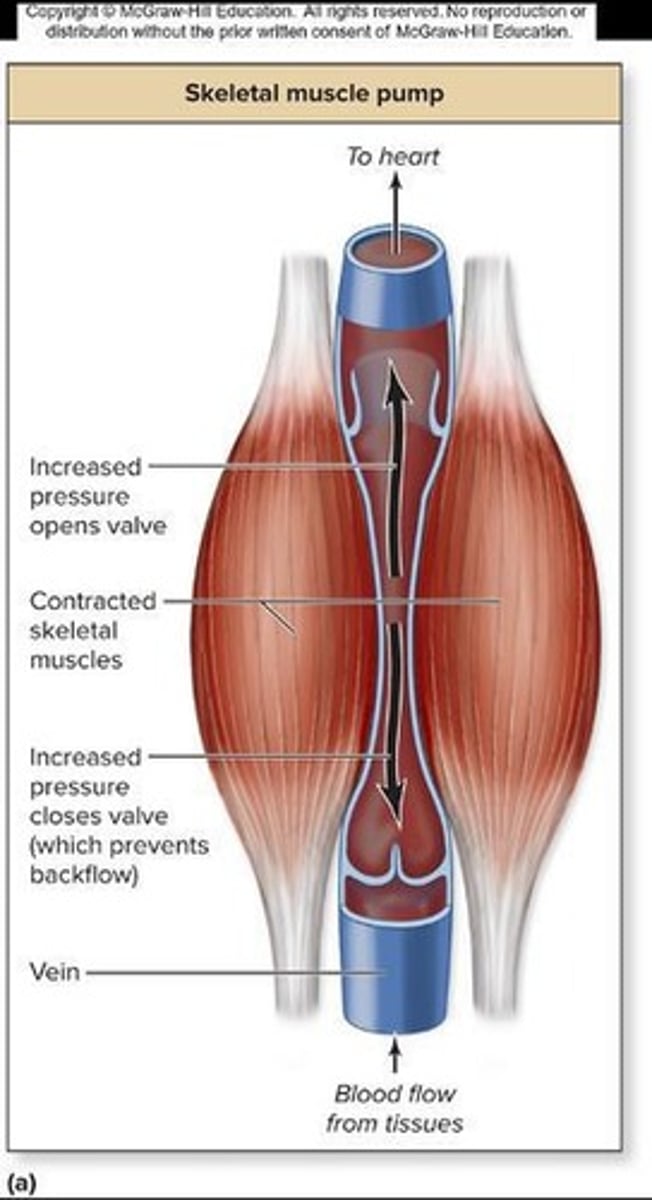
Valves
Structures in veins that allow one-way movement of blood.
Skeletal muscle movement
A mechanism that helps move blood through veins.
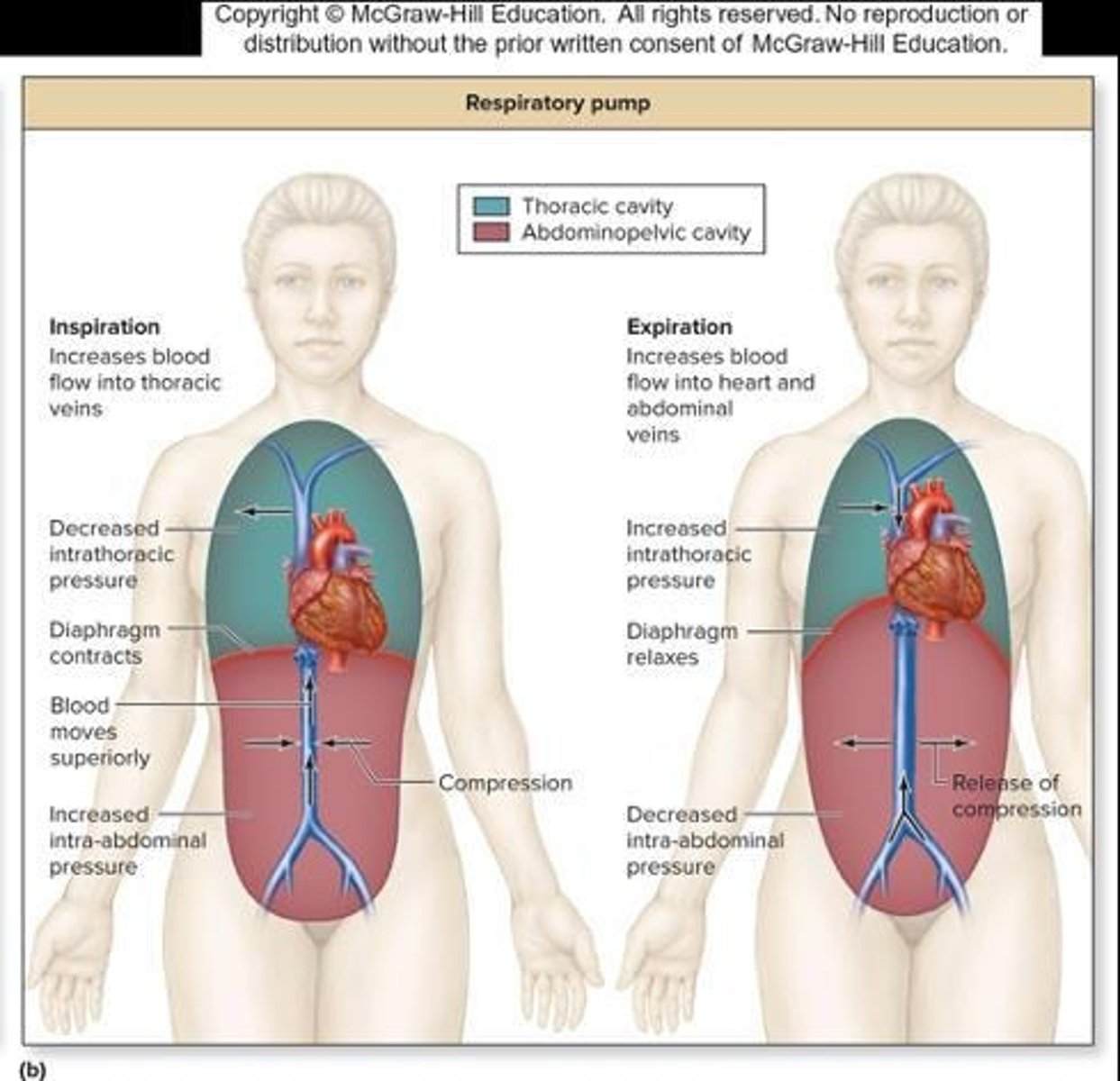
Respiratory pump
The movement of lungs that aids in blood flow through veins.
Resistance
The friction force blood encounters due to contact between blood and vessel walls.
Viscosity
The resistance of fluid to its flow, which increases with dehydration and decreases with anemia.
Vessel length
A factor affecting resistance; longer vessels result in more resistance.
Lumen size
A factor affecting resistance; smaller lumen radius results in more resistance.
Total blood flow
The overall flow of blood affected by cardiac output and resistance.
Cardiac Output
The amount of blood the heart pumps, which affects total blood flow.
Vasodilation
A decrease in resistance that increases total blood flow.
Vasoconstriction
An increase in resistance that decreases total blood flow.
Tissue perfusion
The process of delivering blood to tissues, which requires adequate blood pressure.
Pressure
Depends on cardiac output, resistance and blood volume.
Short-term mechanisms
Regulate blood pressure through the nervous system.
Long-term mechanisms
Regulate blood pressure through the endocrine system.
Baroreceptors
Detect stretch in blood vessel wall.
Chemoreceptors
Detect high carbon dioxide, low pH, and very low oxygen.
Cardiovascular center
Located in the medulla oblongata, it regulates cardiac output.
Cardiac center
Regulates cardiac output.
Vasomotor center
Controls vasoconstriction and vasodilation of vessels.
Angiotensin II
A powerful vasoconstrictor regulated by the endocrine system.
Aldosterone
Increases absorption of water in the kidney to maintain blood volume.
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
Increases water absorption in the kidney and can cause vasoconstriction.
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Released by the heart, causes vasodilation and increases urine output.
Renin-angiotensin system
A hormone system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Blood clot in a vein due to heart disease or immobility/inactivity.
Aneurysm
Occurs when part of arterial wall thins and balloons out, prone to rupture.
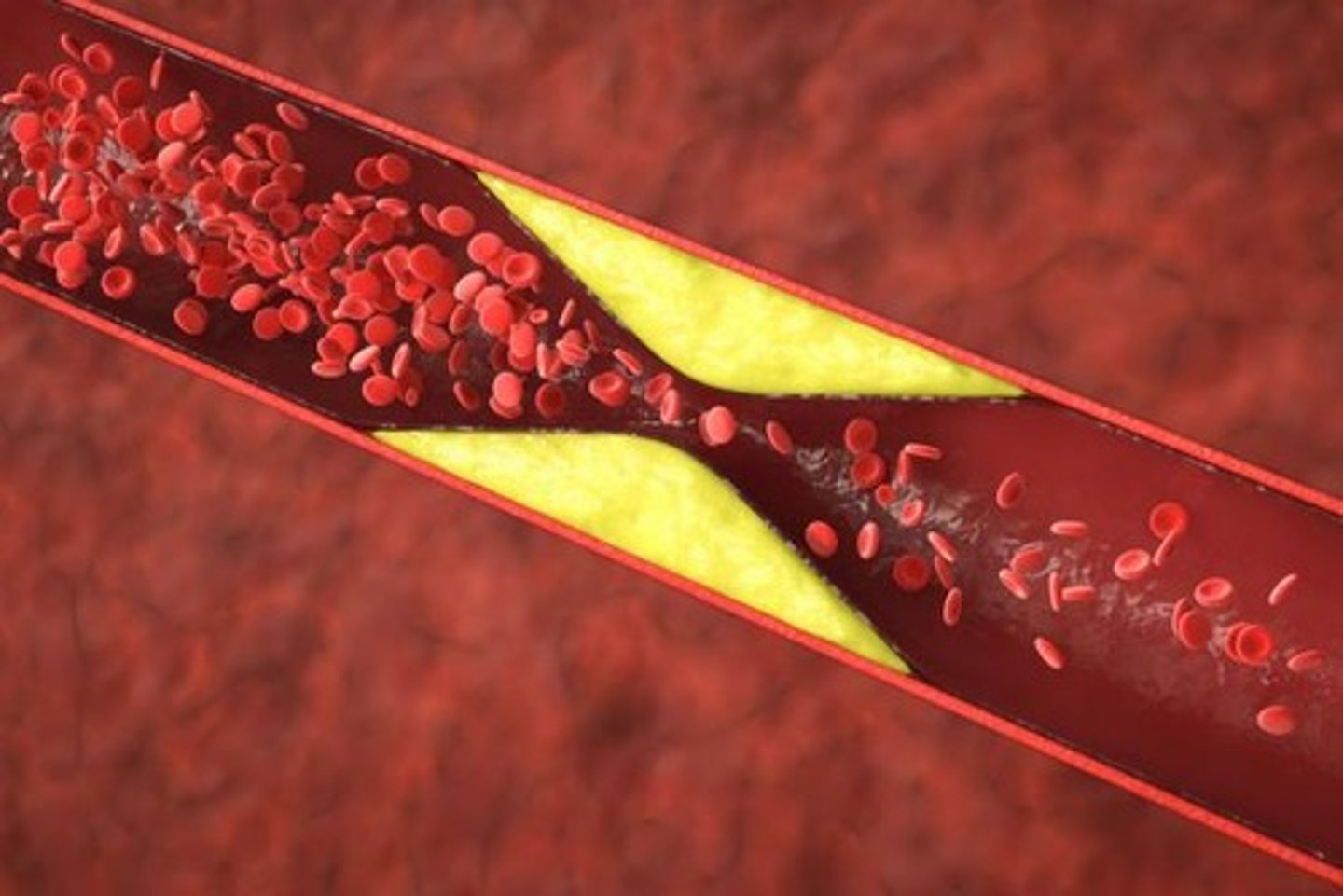
Atherosclerosis
Progressive disease of elastic and muscular arteries, associated with high fat diets.
Pulmonary embolus
A potential complication of deep vein thrombosis.
Kidney
Maintains blood volume and blood pressure by producing renin.
Renin
Enzyme that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
ACE
Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
Angiotensinogen
Precursor to angiotensin I, released into the blood.
Plaques
Narrow the lumen and block blood flow in arteries.