Photometry Conceptual Info - Physical Optics Spring 2025
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
electromagnetic
Light is ______ radiation
transmitted
Light is a form of radiant energy that is _____ from a source
380-760nm
visible light spectrum
the visible part of the EM spectrum
What is light referred to as?
radiometry
measurement of radiant energy in terms of absolute power
radiometry
This type of measurement of radiant energy can be used in any portion of the light spectrum
photometry
measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye
radiometry
measurement of absolute power
no
Is the human eye equally sensitive to all wavelengths of light?
photometry
radiometry weighted by the visual response of the "avg" human eye
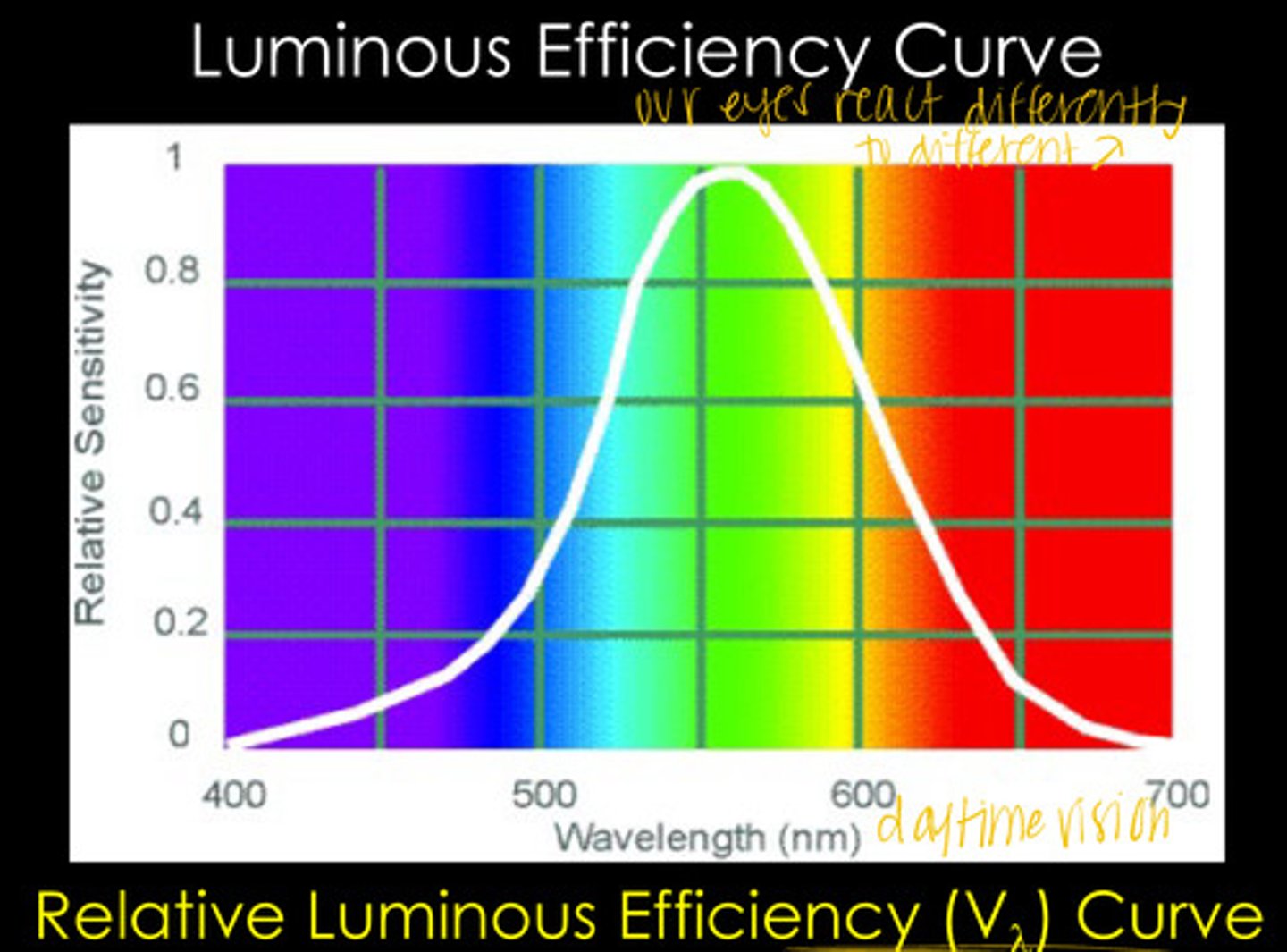
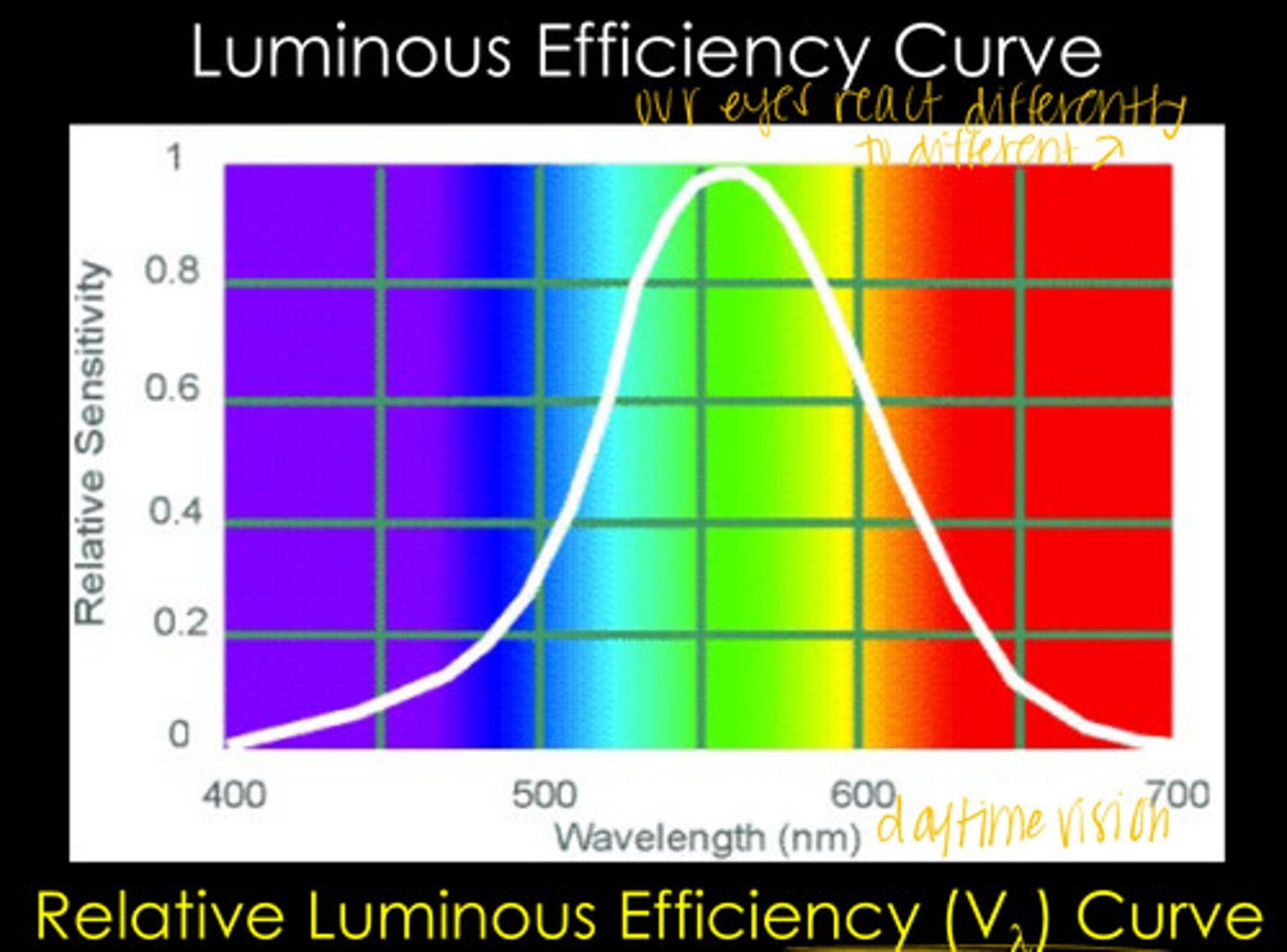
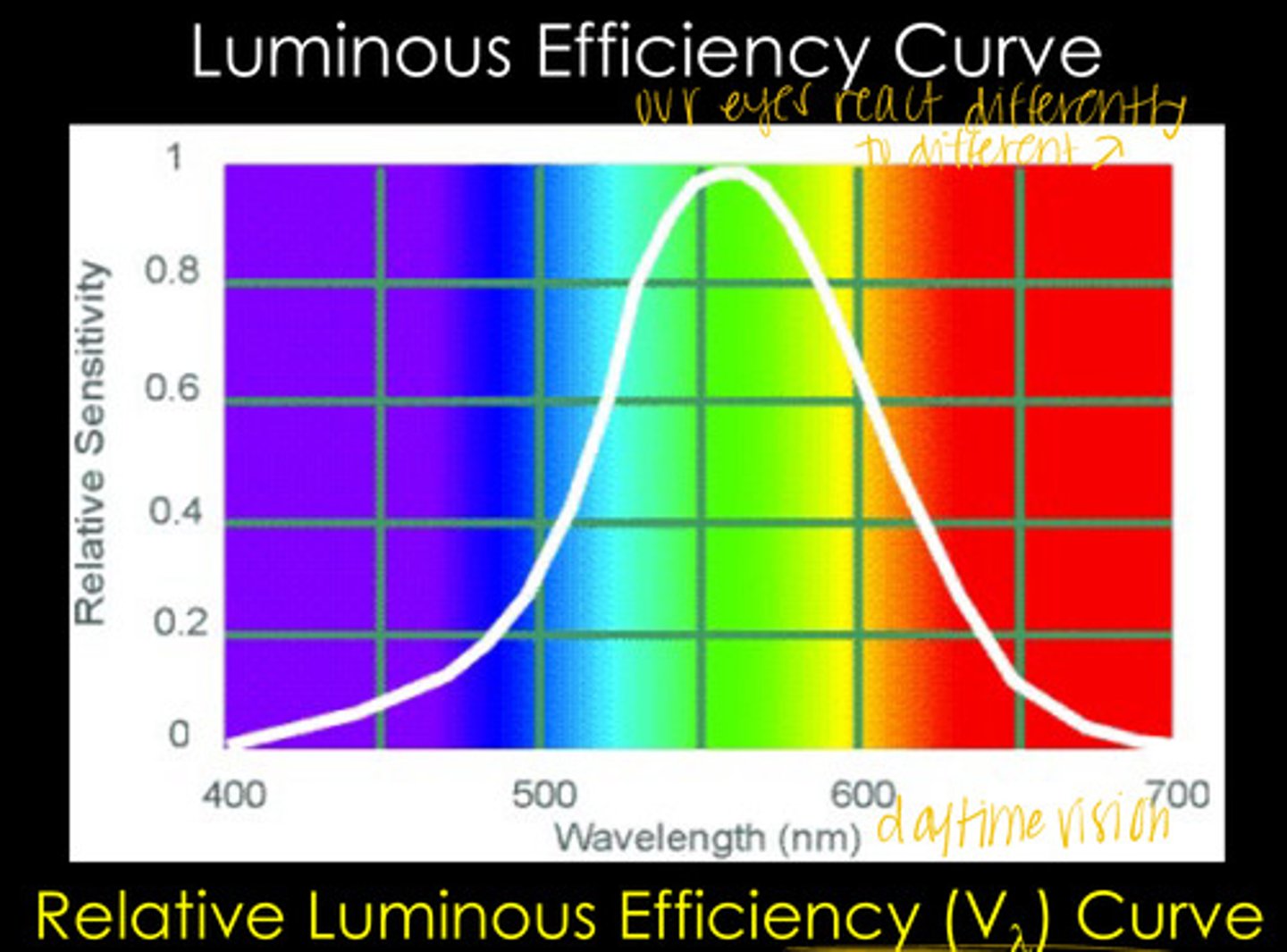
our eyes are unequally sensitive to all wavelengths in the visible light spectrum
What does the Relative Luminous Efficiency Curve show?
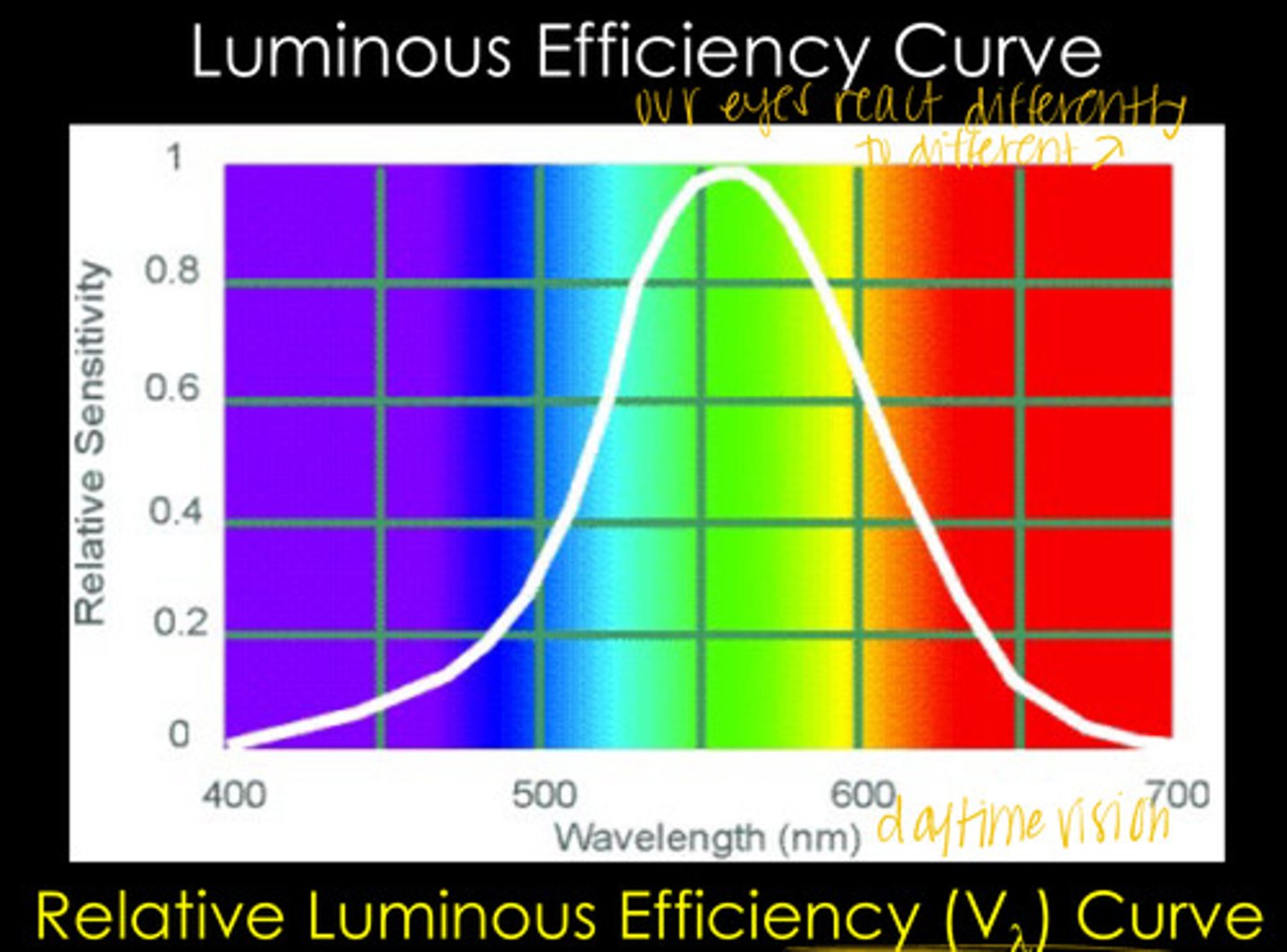
555 - SEAFOAM GREEN BABY
At what wavelength is the human eye most sensitive?
0 - 1
The Relative Luminous Efficiency Curve ranges from ______ to ______ in relative sensitivity
555
Max Wavelength of the Relative Luminous Efficiency Curve
1
What relative sensitivity is associated with wavelength 555 in the Relative Luminous Efficiency Curve?
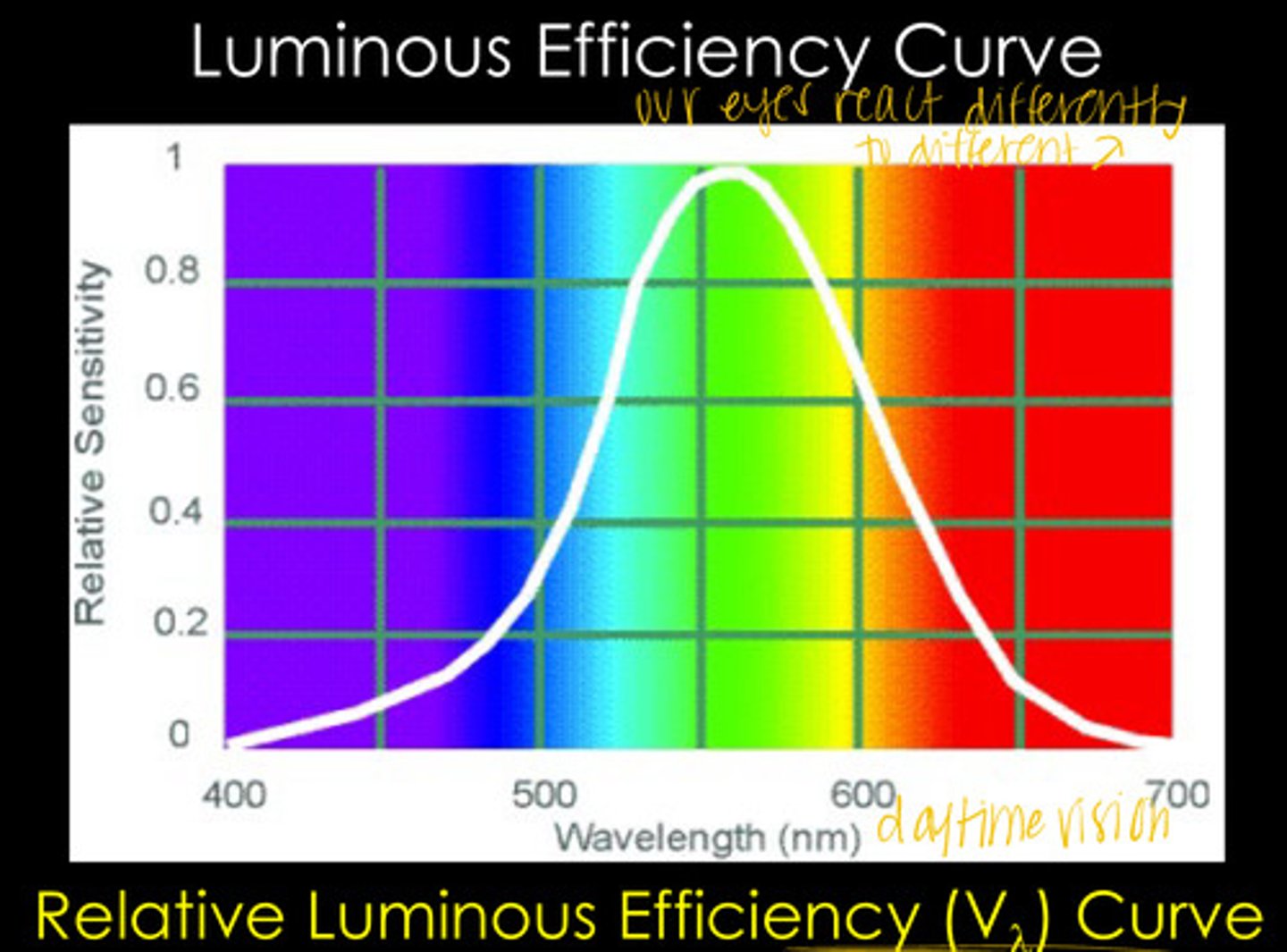
380 and 760
At what wavelengths is the relative sensitivity of the Relative Luminous Efficiency Curve ~0?
683
What is the Kmax of the Absolute Luminous Efficiency Curve?
555 nm
At what wavelength on the Absolute Luminous Efficiency Curve does the Kmax of 683 correlate to?
Joules (radiometry)
Radiant energy is measured in _____? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Talbots (photometry)
Luminous Energy is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Watts (radiometry)
Radiant flux is measured in _____? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Lumen (photometry)
Luminous Flux is measured in _____? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
watt/steradian (radiometry)
Radiant Intensity is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Candela (photometry)
Luminous Intensity is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Watt/steradian/area (radiometry)
Radiance is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
candela/area (photometry)
Luminance is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
point
Radiant Intensity and Luminous Intensity are values measured from a (point/extended) source?
extended
Radiance and Luminance are values measured from a (point/extended) source?
watts/area (radiometry)
Irradiance is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
Lumen/area
Illuminance is measured in ______? Photometry or Radiometry Value?
see pic
What is the symbol for radiant flux?

see pic
What is the symbol for luminous flux?

Ie
What is the symbol for radiant intensity?
I
What is the symbol for luminous intensity?
E
What is the symbol for illuminance?
radiant energy
measurement of all electromagnetic radiation (not just the visible light)
joules
Radiant energy is measured in _____?
energy expended in applying a force of one Newton to move an object a distance of one meter
I Joule = ?
Luminous Energy
measurement of light which is the electromagnetic radiation that affects the visual system
perceived brightness of the human eye
What is luminous energy measured in terms of?
talbot
What is the basic unit of luminous energy?
radiant flux
energy expended over time
watt
What is the basic unit of radiant flux?
lumen
What is the basic unit of luminous flux?
With Planck's equation\
Energy per quantum = hc/λ
How to calculate energy/quantum? Using what equation?
Radiant Flux = Energy per quantum * N quanta/sec
How to calculate radiant flux?
Luminous Flux = Radiant Flux Vλ Kmax
Kmax = 683
How to calculate luminous flux?
4π
How many steradians around a point source?
intensity
angular flux density
produced by a point source ONLY
What is intensity produced by?
-no resolvable area
-project equally into all portions of space
What makes a source a point source?
Radiant Flux / 4π
How to calculate Radiant Intensity from a point source?
Luminous Flux / 4π
How to calculate Luminous Intensity from a point source?
INTENSITY/area
As mentioned, point sources have INTENSITY. What do extended sources have?
intensity/area
the eyes assess brightness on what basis?
radiant and luminous intensity
When there is a point source, what value(s) will you be finding?
radiance and luminance (values are intensity/area)
When there is an extended source, what value(s) will you be finding?
L
What is the symbol for luminance?
Intensity (I) * Area (A)
Luminance (L) = ?
irradiance (radiometry) or illuminance (photometry)
flux falling onto a receiving surface = ?
E
What is the symbol for illumination?
E = I/d^2
I = intensity of point source
d = distance
What is the equation used to find E (illumination)?
decrease in illumination
An increase in distance will lead to an (increase/decrease) in illumination
4 (use the inverse square law)
E = I / d^2
Is the position of light important? If you bring a light 2x as close, it will be _____x brighter
larger
When calculating illumination, a small cosθ will lead to a (larger/smaller) amount of illumination
smaller
When calculating illumination, a large cosθ will lead to a (larger/smaller) amount of illumination
Illumination = (Luminous Intensity/d^2)cosθ
When calculating illuminance from a point source to a receiving surface, what equation should be used?
Illumination = (Luminous Intensity/d^2)cosθ^2
When calculating illuminance from an extended source that is parallel to a receiving surface, what equation should be used?
Illumination = (Luminous Intensity/d^2)cosθ1cosθ2
When calculating illuminance from an extended source that is not parallel to a receiving surface, what equation should be used?
reflects light -- it is a secondary source
Does a luminant object reflect or produce light?
Luminance = pE/π
What is the equation used for luminance of a secondary object?
linear
**a chart with 2x the luminance = can see 2x the letters
There is a ____ relationship between visual acuity and luminance of the chart in log scale
sine^2 law
What law can we use to calculate illumination, if the extended source is circular and the receiving surface is on axis?
E = I / (r^2 + d^2)
What is the equation for the Sine^2 law?
retinal illumination
amount of light falling into a given retinal area
Eret = L * s. (trolands)
What is the appropriate equation for retinal illumination?
yes -- as seen in the equation for retinal illumination
Eret = L * s
With normal retinal viewing, is illumination affected by pupil size?
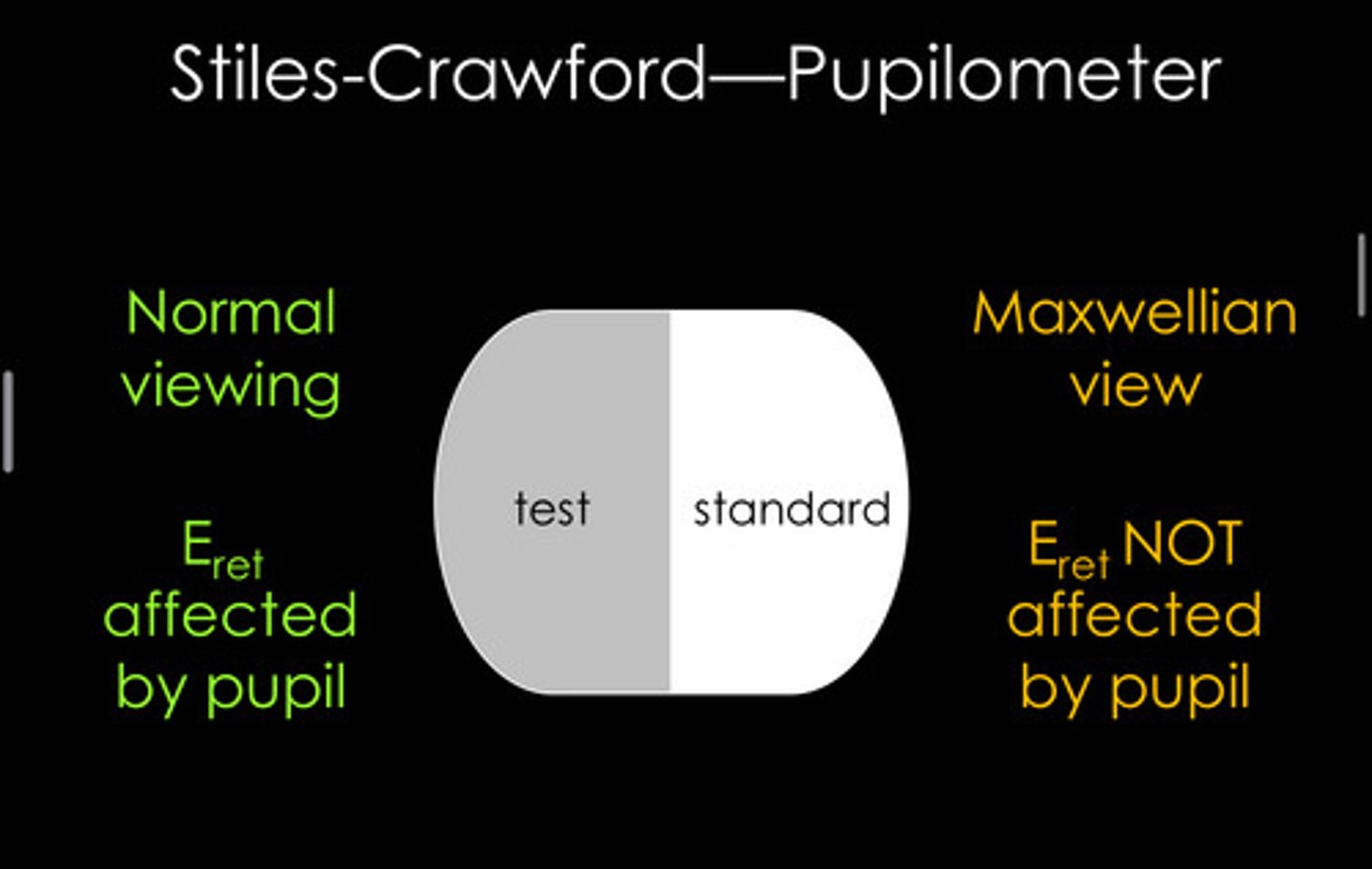
maxwellian view
a large, uniformly bright field
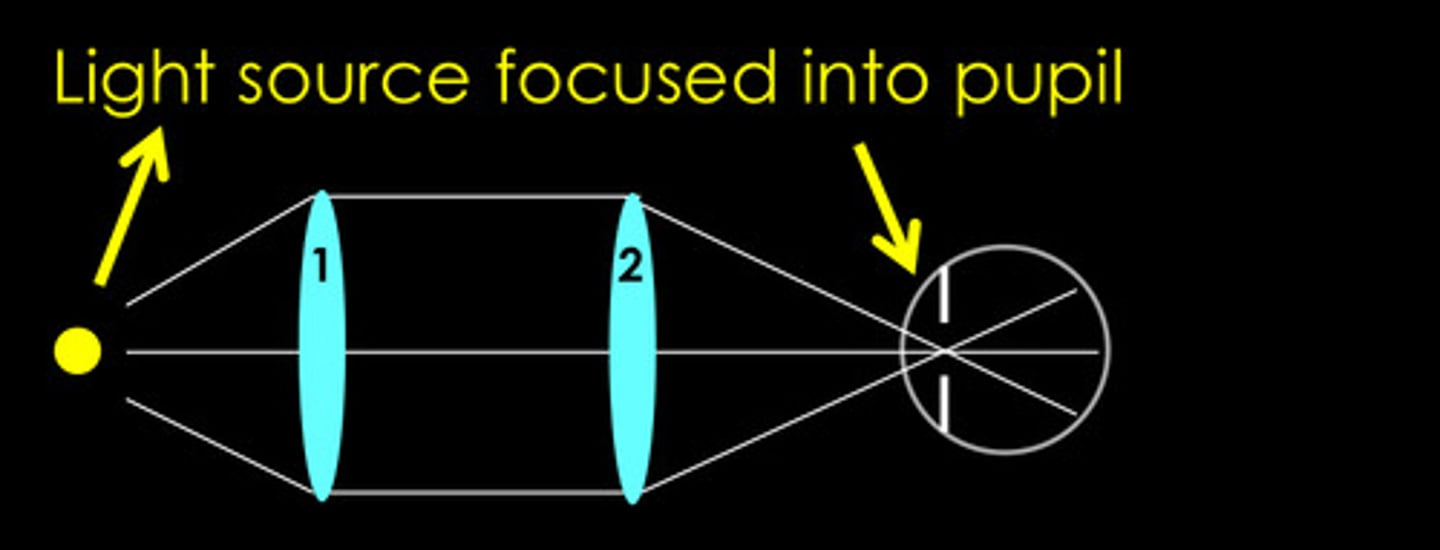
in the plane of the pupil
In a Maxwellian view, where is the light source imaged?
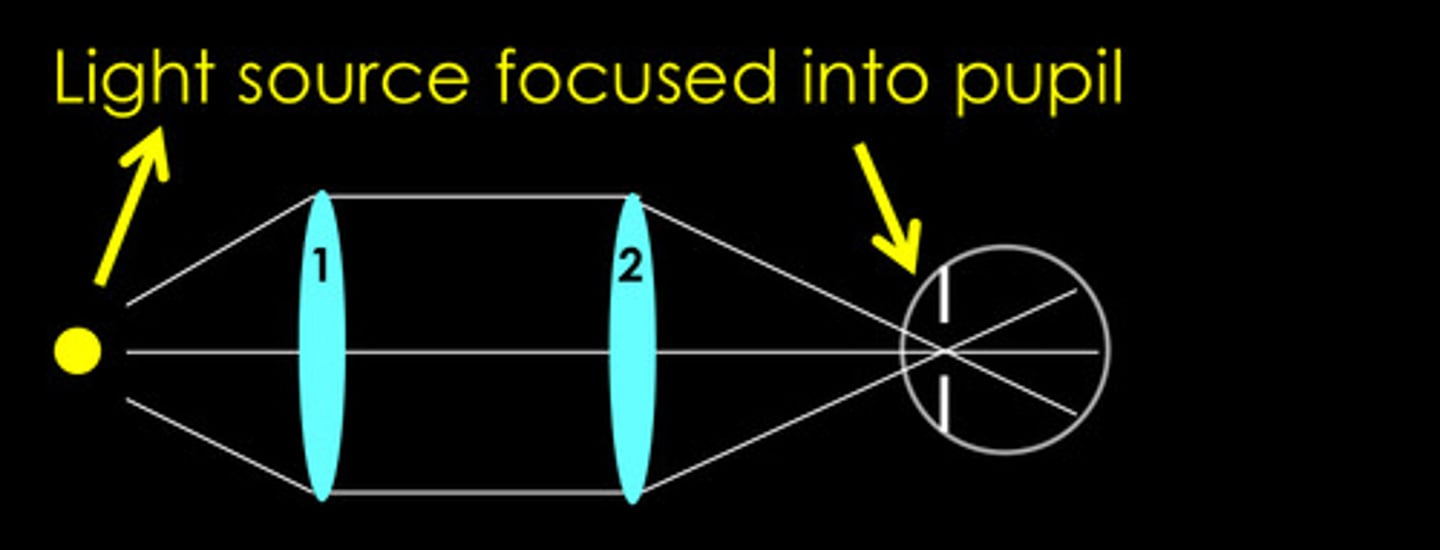
yes, pupil fluctuations do not influence retinal illumination
Does a Maxwellian view of the retina bypass the pupil? What does this mean?
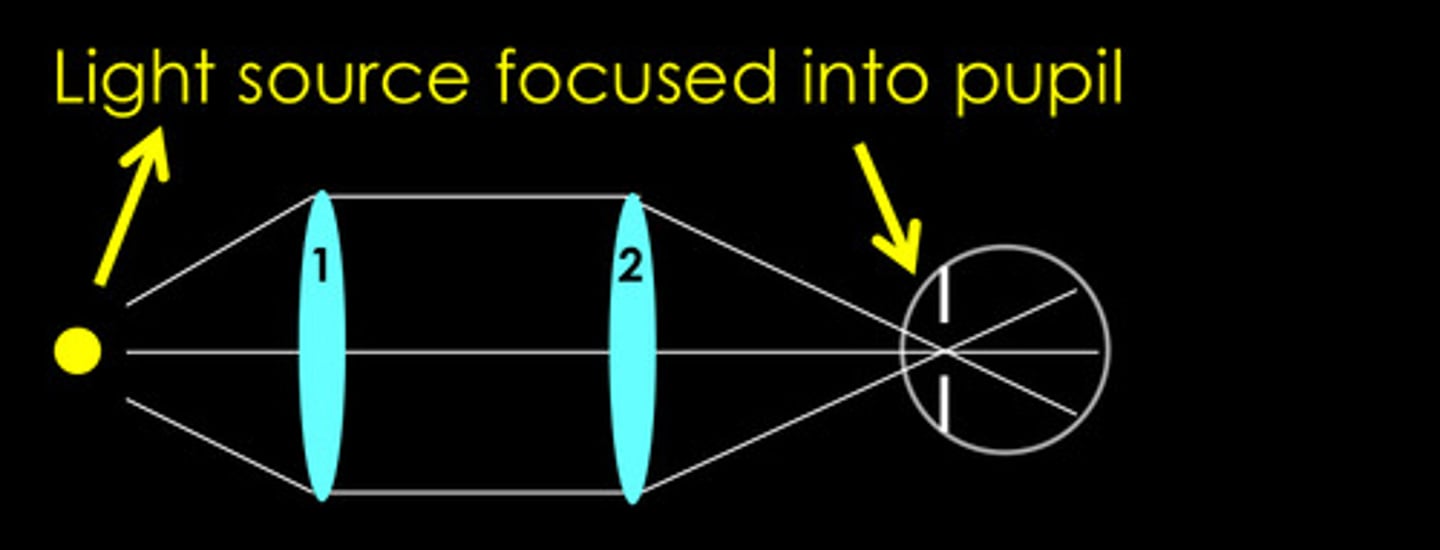
yes
Can a Maxwellian view generate very high levels of light on the retina?
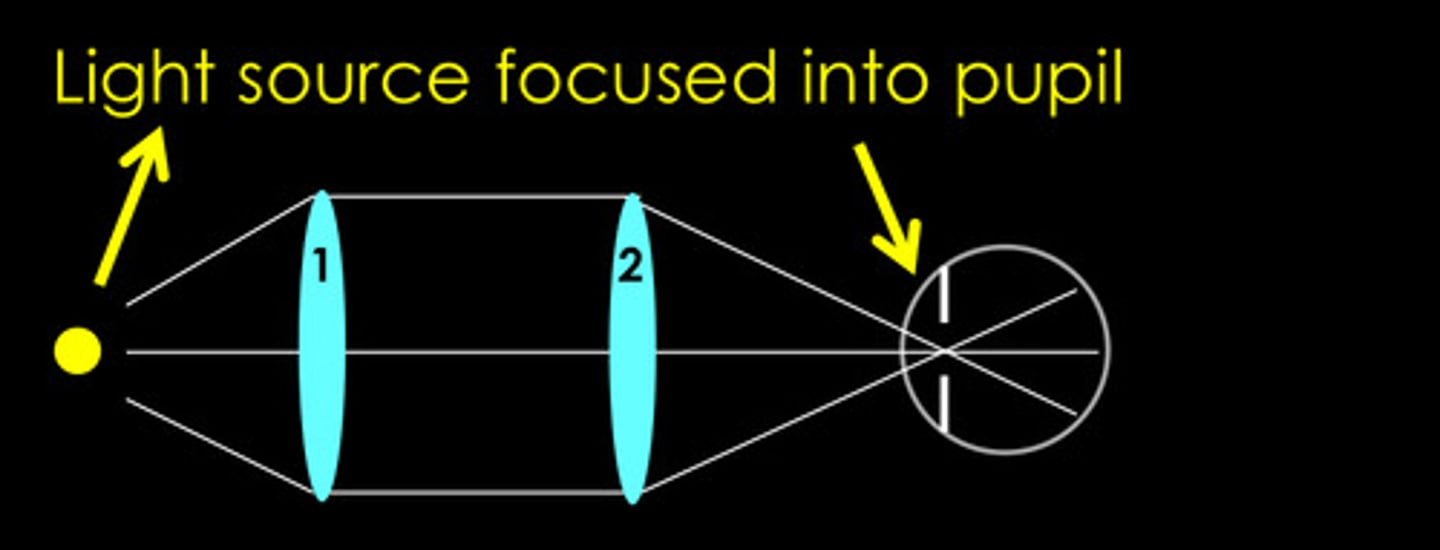
Stiles Crawford (type I)
What phenomenon is this referring to? Light rays traveling through the periphery of the pupil are less effective in stimulating vision than rays passing centrally through the pupil
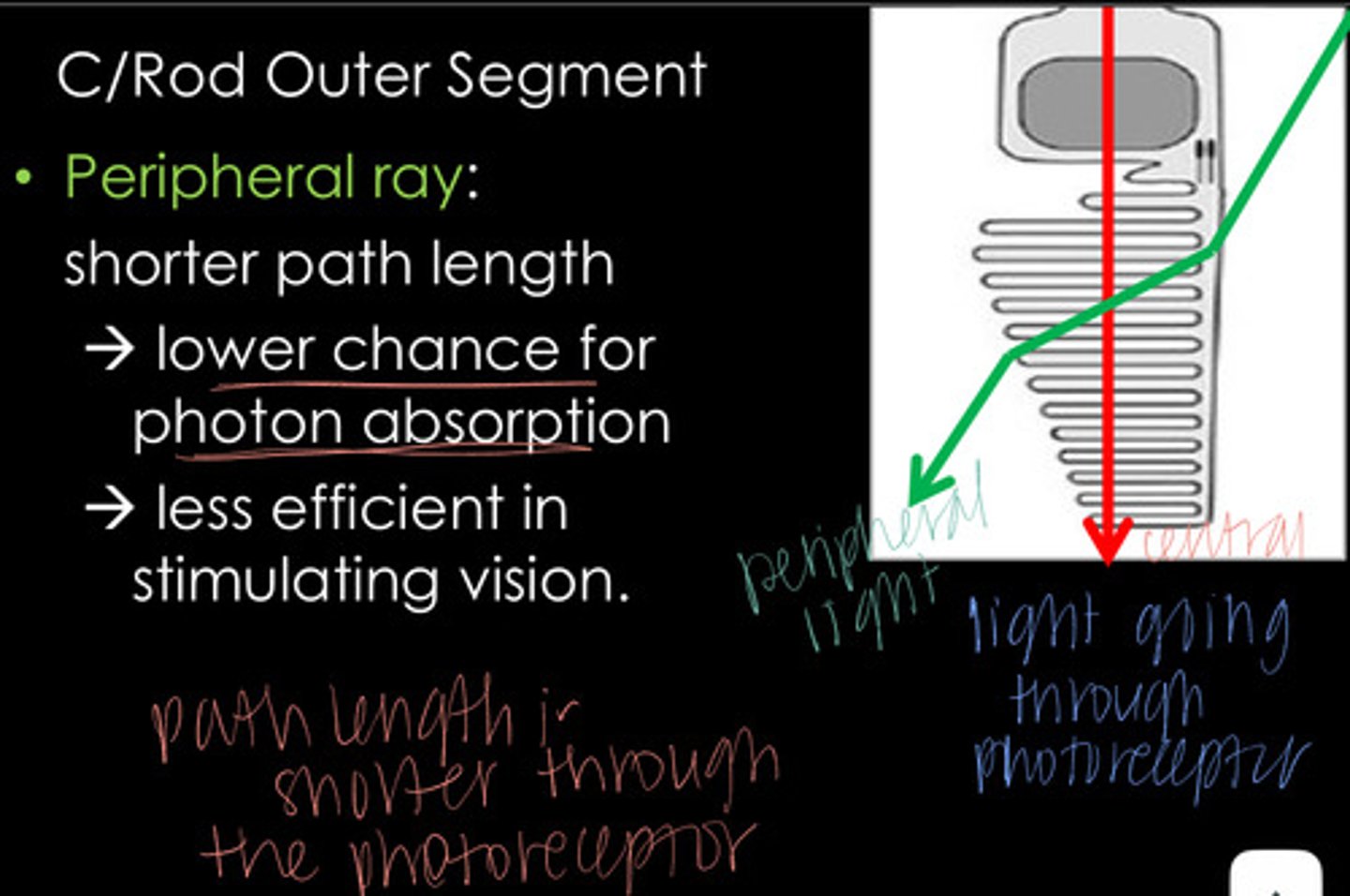
Peripheral rays have a shorter path length through the photoreceptor -- lower chance for photon absorption and less efficient in stimulating vision
Why is the peripheral light rays traveling through the periphery of the pupil are less effective in stimulating vision than rays passing centrally through the pupil?

yes
Is there a wavelength dependency to Stiles-Crawford Effect (type I)?
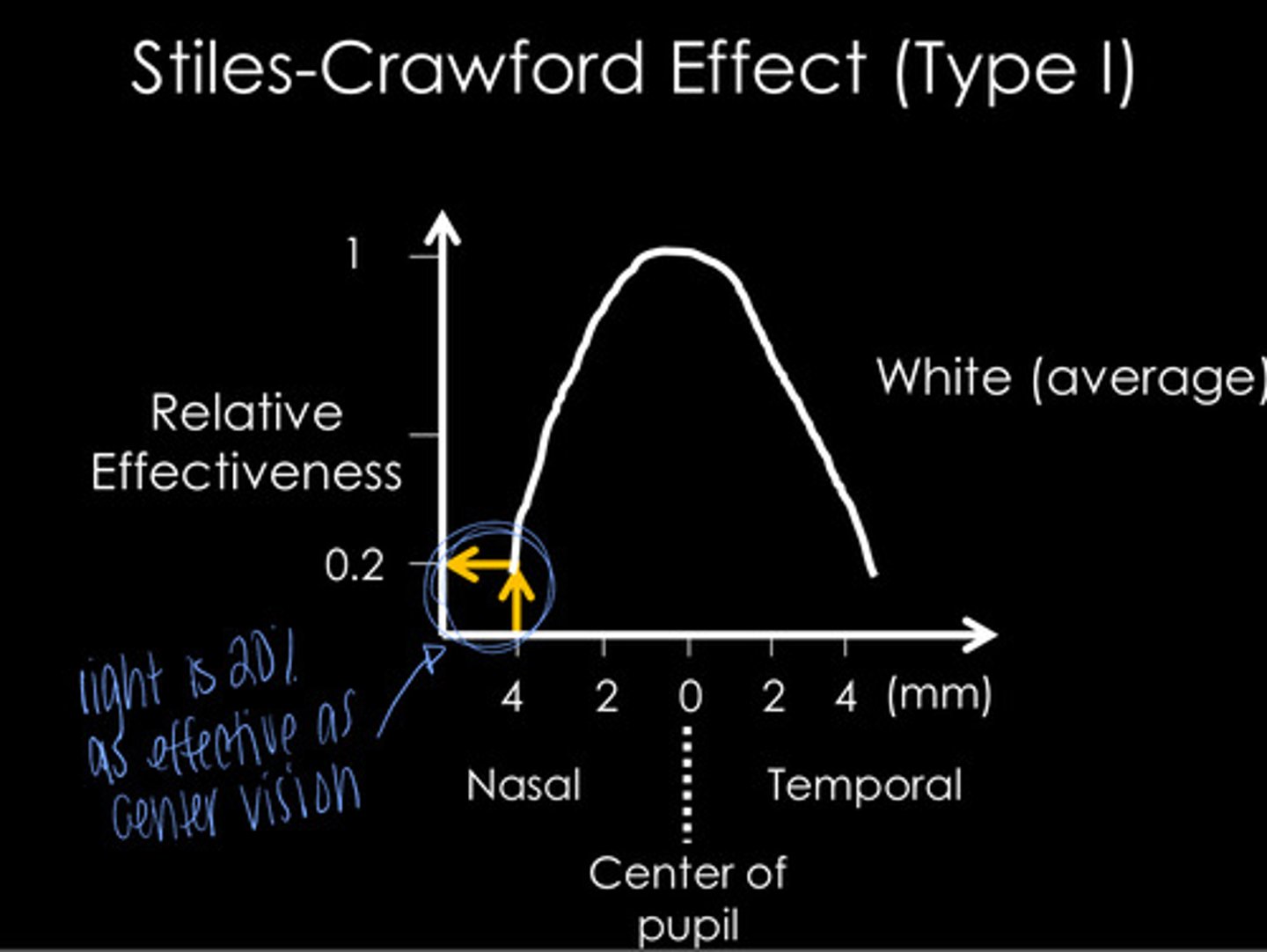
560 nm
In the Stiles Crawford Effect, where is the minimum effect of wavelength (ie -- what wavelength is the peripheral and center photoreceptors going to have the most similar effect)?
The appearance (color) of a monochromatic ray changes depending on where it passes through the pupio
What is the idea behind Stiles-Crawford Effect (Type II)?
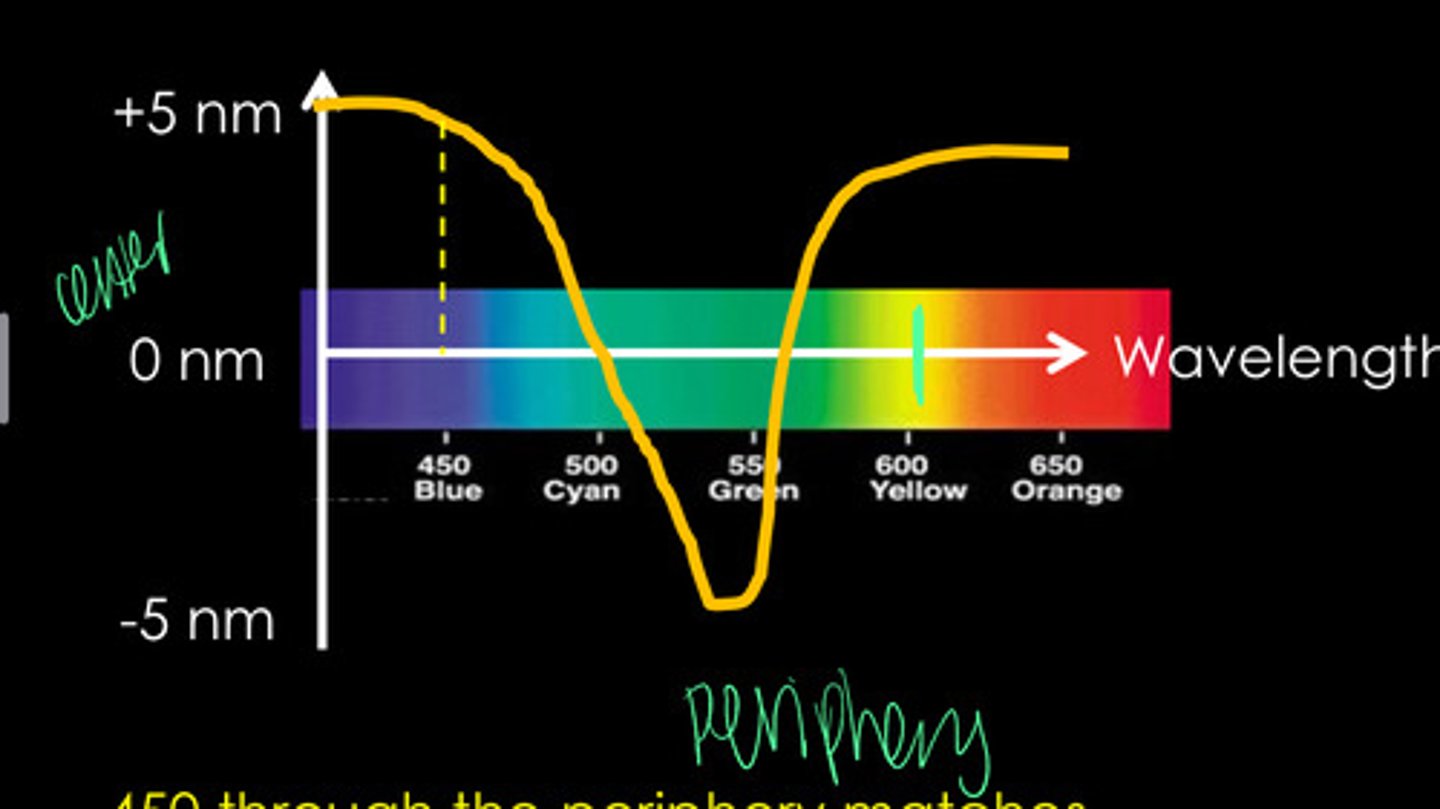
500 and 560
What are the 2 points in a Stiles-Crawford Effect (type II) where there is no change in color from the center of the pupil to the periphery of the pupil?
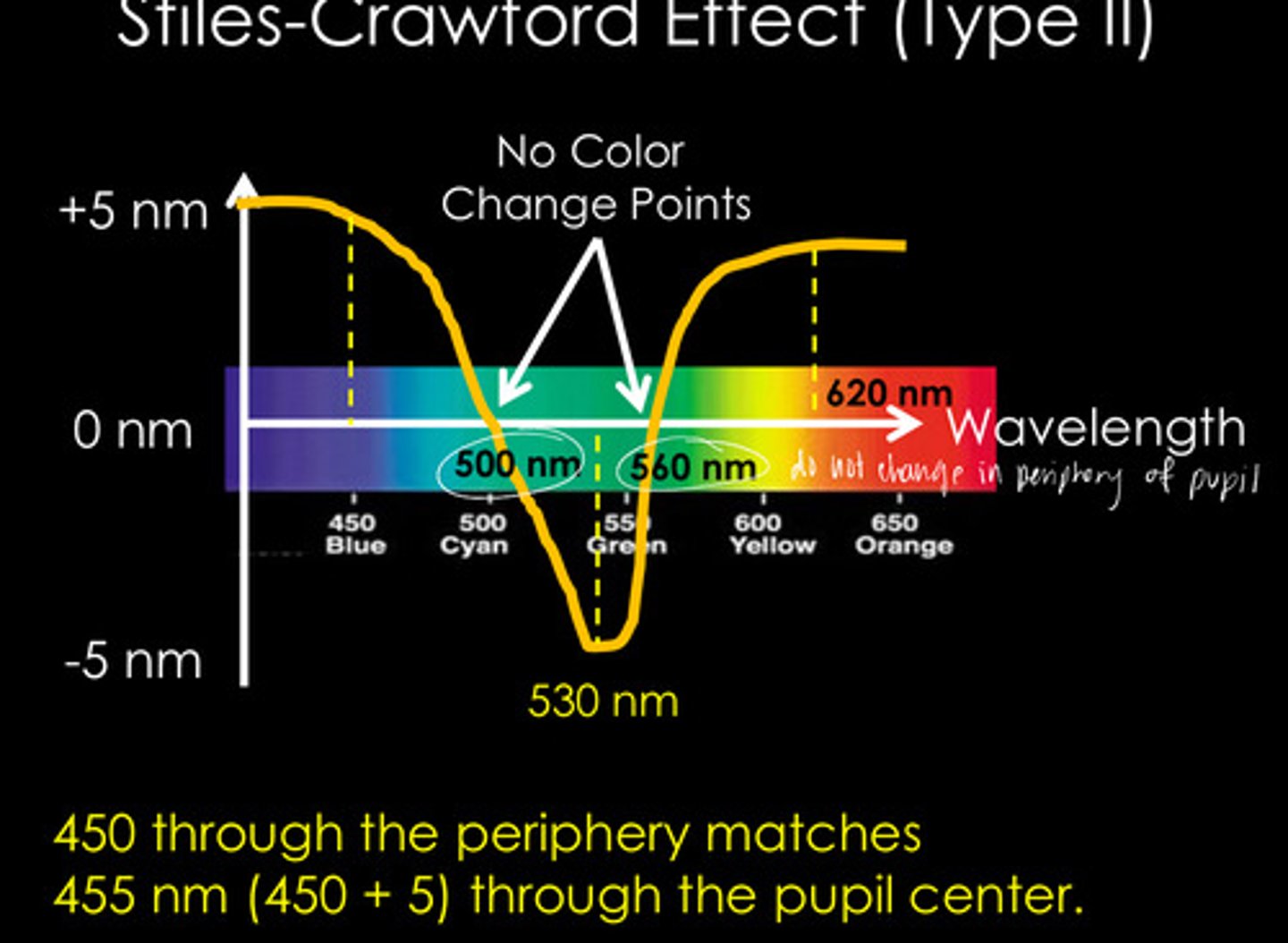
A monochromatic ray passing through the periphery of the pupil would have the appearance of its natural wavelength plus the amount shown on the Y Axis when passed through the center of the pupil
How to calculate the appearance of a peripheral wavelength using Stiles Crawford Effect (type II)?
incandescence light source
the production of light through the thermal excitation of a solid, liquid, or gas
luminescent light source
the production of light by any method other than incandescence
temp (K) and substance
The spectrum distribution of light from the production of light through incandescent method depends on what 2 factors?
1) Planck's Law
2) Kirchoff's Law
3) Stefan-Boltzmann Law
4) Wein's Displacement Law
What are the 4 Law's that describe incandescent light?
blackbody
a theoretical object that is a perfect incandescent source
all incident light on it
What does a blackbody absorb?
Reemitted energy dependent on properties of the black body, not on the incident energy
Does a black body reemit light? Based on what properties?
yes (predicts radiant flux)
Does Planck's Law hold for a blackbody?
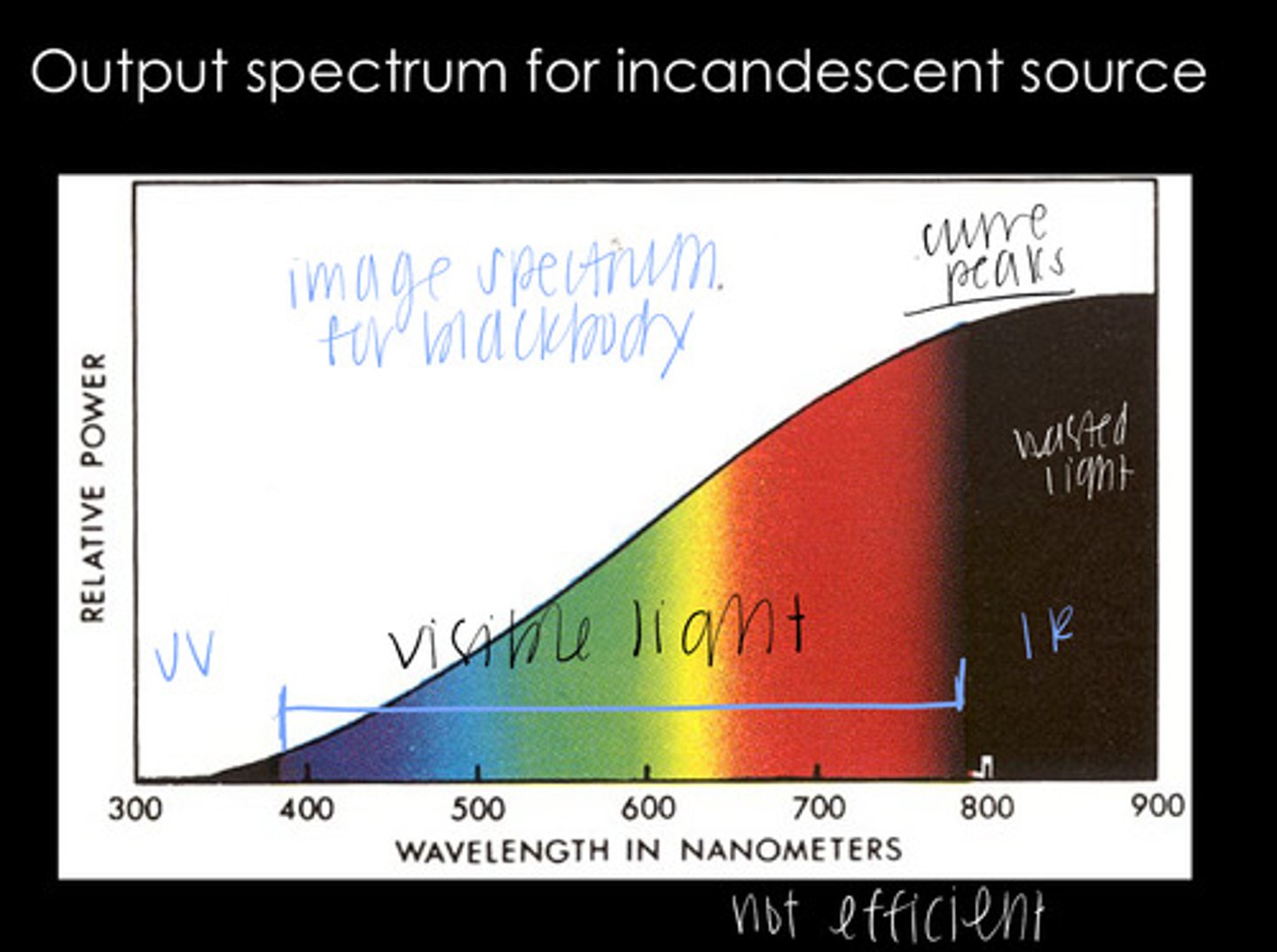
-UV
-visible light
-IR light
Blackbody (incandescent sources) emit what kinds of radiant flux (output spectrum)?
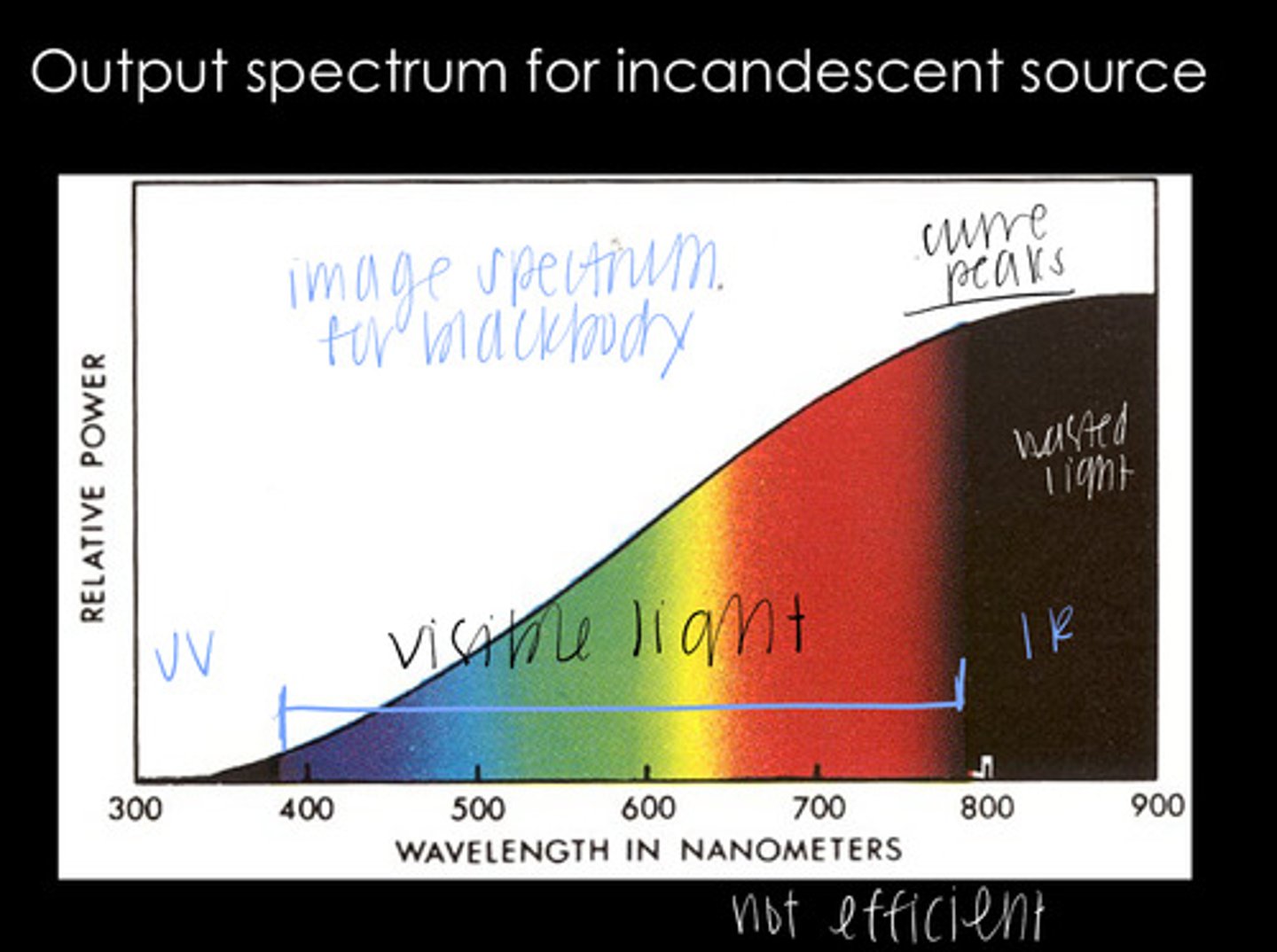
NO -- a lot of wasted light is produced that humans cannot see (IR and UV are at wavelengths humans cannot detect)
Are incandescent light sources efficient?
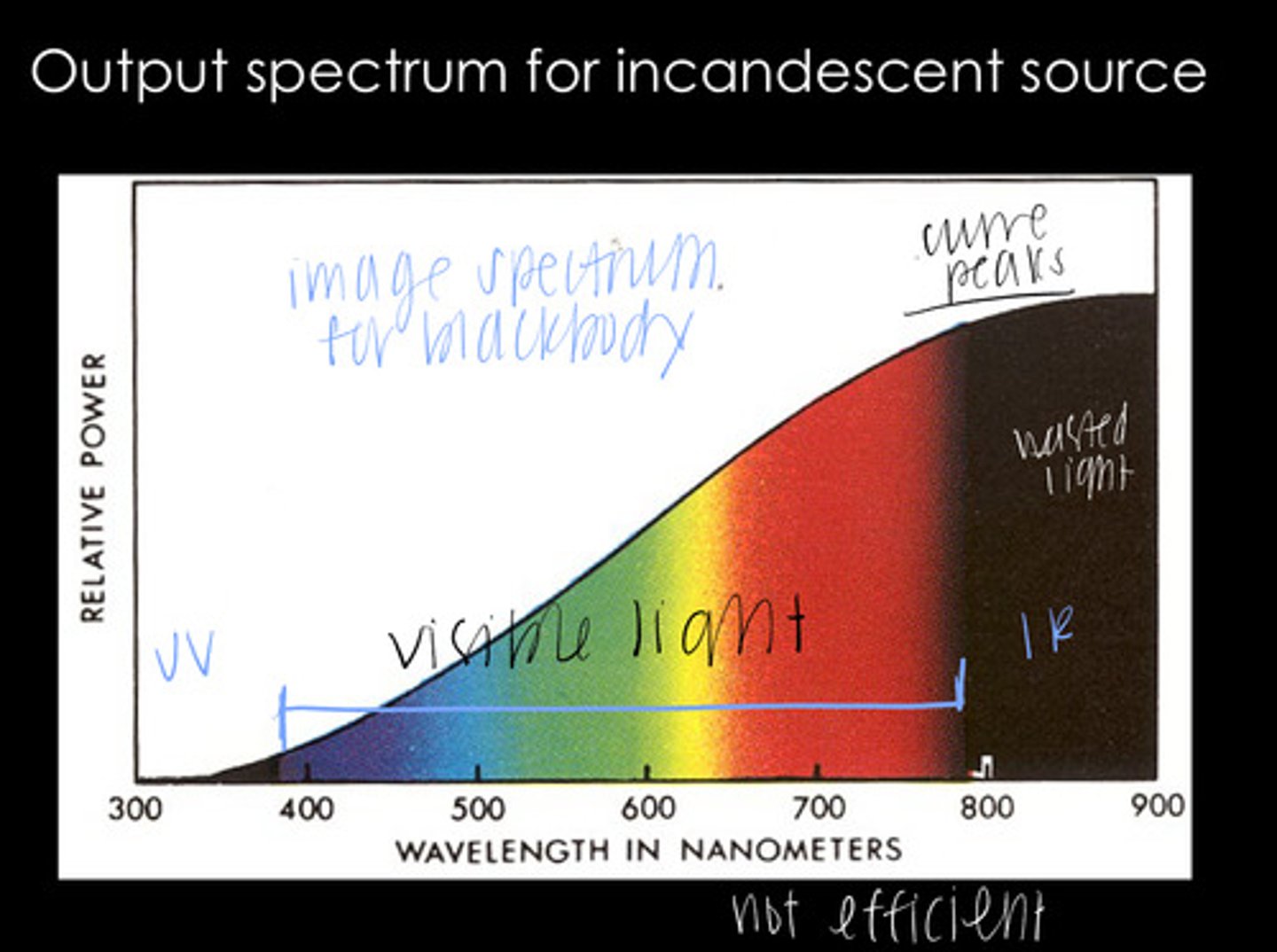
Emissivity = Absorbance
What is the idea of Kirchoff's Law?
Emissivity
Percent of Emitted Radiation (relative to predicted radiation of Planck's Equation)