APUSH Textbook - Chapter 15
1/314
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
315 Terms
What was the main focus of the Reconstruction era?
To redefine freedom and citizenship for former slaves and their white allies in the post-Civil War South.
Who were some prominent Black leaders that participated in discussions about freedom in January 1865?
Ulysses S. Houston, James Porter, and James D. Lynch.
How did Garrison Frazier define slavery?
As one person receiving the work of another by irresistible power and not by consent.
What did Garrison Frazier believe was necessary for true freedom?
To have land and the ability to work it by their own labor.
What was Special Field Order 15?
An order issued by General Sherman that set aside land for Black families, offering them forty-acre plots and mules.
What phrase originated from Sherman's Special Field Order 15?
Forty acres and a mule.
What was the Freedmen's Bureau?
A federal agency established to assist freed slaves during the Reconstruction era.
What significant amendment was ratified in 1868?
The Fourteenth Amendment, granting citizenship and equal protection under the law to all persons born or naturalized in the U.S.
What did the Fifteenth Amendment accomplish?
It granted Black men the right to vote.
What were Black Codes?
Laws enacted in the South to restrict the rights of newly freed Black Americans.
What was the impact of Radical Reconstruction?
It led to significant political and social changes, including the establishment of Black schools, churches, and institutions.
What was the significance of the Colfax Massacre in 1873?
It was a violent event that highlighted the racial tensions and backlash against Reconstruction efforts.
What did Congressman James A. Garfield question about freedom in 1865?
Whether freedom was merely the absence of slavery or included other rights such as civil rights and property ownership.
How did African Americans' understanding of freedom differ from that of white Americans during Reconstruction?
Blacks sought not only the absence of slavery but also equal rights, opportunities, and the ability to participate fully in society.
What role did family play in the lives of freed Black Americans?
The family became central to the post-emancipation community, with efforts to reunite separated family members and strengthen family ties.
What was the Tenure of Office Act of 1867?
A law intended to restrict the president's power to remove certain officeholders without the Senate's approval.
What was the outcome of the impeachment trial of President Johnson in 1868?
He was acquitted and remained in office, but the trial highlighted the political conflicts of the era.
What was the significance of Hiram Revels in 1870?
He became the first Black U.S. senator, representing Mississippi.
What was the Enforcement Acts of 1870-1871?
Laws aimed at enforcing the rights of African Americans and curbing the violence of groups like the Ku Klux Klan.
What did the Reconstruction Act of 1867 do?
It divided the South into military districts and outlined the process for readmitting Southern states into the Union.
What was the impact of the Slaughterhouse Cases?
They limited the scope of the Fourteenth Amendment and weakened federal protections for Black citizens.
What was the Bargain of 1877?
An informal agreement that resolved the disputed 1876 presidential election and effectively ended Reconstruction.
What did the Radical Republicans aim to achieve during Reconstruction?
They sought to ensure civil rights for freed slaves and to transform Southern society.
What was the role of Black churches during Reconstruction?
They served as centers for community organization, education, and political mobilization.
What challenges did African Americans face during Reconstruction?
They faced violence, discrimination, and the eventual rollback of many rights gained during the period.
What did many Black women prefer to do after the Civil War?
Devote more time to their families than had been possible under slavery.
What was considered a badge of honor for Black men after emancipation?
Seeing their wives remain at home.
What compelled a higher proportion of Black women to work for wages?
The dire poverty of the Black community.
What religious institutions did Blacks abandon after emancipation?
White-controlled religious institutions.
How many Black Methodists worshiped in biracial South Carolina churches before the Civil War?
42,000.
By the end of Reconstruction, how many Black Methodists remained in biracial churches?
Only 600.
What role did the independent Black church play in the community?
It served as a place of worship, education, social events, and political gatherings.
How many Black ministers held public office during Reconstruction?
Approximately 250.
What did the Family Record lithograph depict?
An idealized portrait of a middle-class Black family with scenes of slavery and freedom.

What was the significance of education for freedpeople?
It was seen as the next best thing to liberty.
What motivated Blacks to seek education after the Civil War?
Desire to read the Bible, prepare for the economic marketplace, and participate in politics.
Which university was an exception that admitted Black students before the Civil War?
Wilberforce University in Ohio.
Name three Black colleges that proliferated during Reconstruction.
Fisk University, Hampton Institute, and Howard University.
What did Frederick Douglass say about the right to vote?
He stated that slavery is not abolished until the Black man has the ballot.
What did Douglass imply about democracy and voting rights?
Excluding any group from voting meant branding them with the stigma of inferiority.
What did former slaves believe was essential for their freedom?
Landownership.
How did former slaves view their right to land?
They believed they had acquired it through their unpaid labor.
What was the economic condition of the South in 1870 compared to before the Civil War?
The value of property was 30 percent lower than before the war.
What did many white southerners struggle with after emancipation?
Accepting the reality of emancipation and the loss of their slaves.
What was the perspective of southern planters on Black freedom?
They defined it in the narrowest manner, believing it was a privilege rather than a right.
What did the victorious Republican North envision for the reconstructed South?
A society resembling the North with public schools, small towns, and independent farmers.
What principle was central to the Republican North's vision of freedom?
The antebellum principle of free labor.
What did Sidney Andrews observe about education among Black laborers?
Many were studying spelling books during their free time.
What was the significance of the term 'freedom ballots'?
They were organized by Blacks to demand the right to vote.
What did the Alabama Black convention declare about property?
That it was nearly all earned by the sweat of their brows.
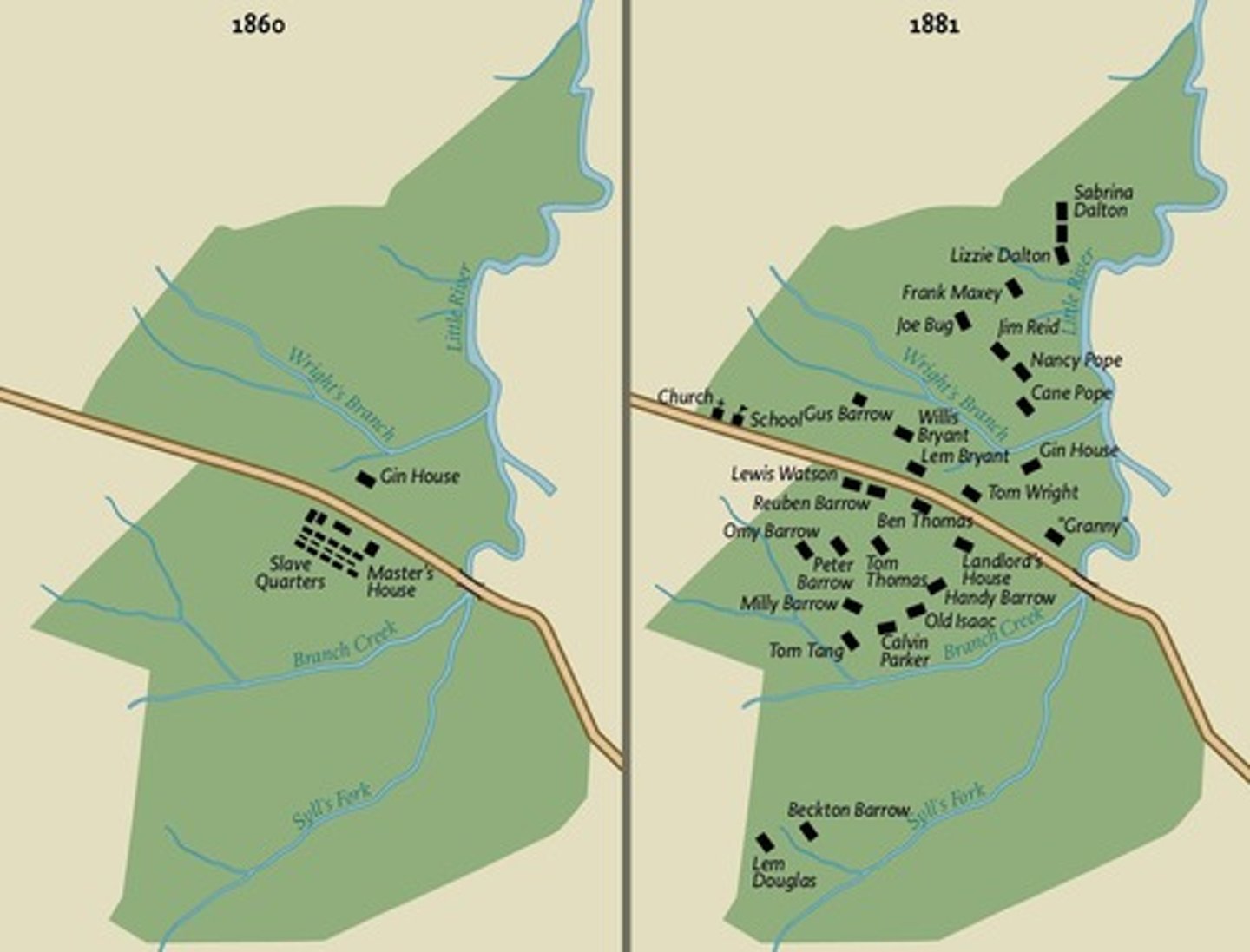
How did the Barrow plantation change from 1860 to 1881?
Slaves lived in communal quarters near the owner's house, while former slaves as sharecroppers lived scattered across the plantation.
What did the term 'free labor' imply in the context of the reconstructed South?
Emancipated Blacks would enjoy the same opportunities for advancement as northern workers.
Who proclaimed that America would become a greater republic based on free labor?
Carl Schurz
What was the main conflict regarding labor in the South after the Civil War?
Planters sought a labor system close to slavery while former slaves demanded economic autonomy and land.
What agency was established by Congress in March 1865 to help former slaves?
The Freedmen's Bureau
Who directed the Freedmen's Bureau?
General O. O. Howard
What were some responsibilities of the Freedmen's Bureau?
Establishing schools, providing aid to the poor, settling disputes, and securing equal treatment in courts.
What did General William T. Sherman say about the expectations of the Freedmen's Bureau?
He expressed doubt that they could fulfill even one-tenth of the expectations.
What significant painting by Winslow Homer portrays the dignity of Black women in the South?
The Cotton Pickers
How many schools did the Freedmen's Bureau help coordinate by 1869?
Nearly 3,000 schools serving over 150,000 pupils.
What was the primary failure of the Freedmen's Bureau regarding land?
The failure to distribute land to former slaves.
What did President Andrew Johnson order regarding federal land in 1865?
He ordered nearly all land in federal hands to be returned to its former owners.
What was the response of former slaves to the return of land to former owners?
They expressed disbelief and protested for their promised homesteads.
What labor system emerged as a compromise between Blacks' desire for land and planters' demand for labor?
Sharecropping
What was the sharecropping system?
A system where Black families rented parts of plantations, dividing the crop between worker and owner.
By 1880, what percentage of agricultural labor in the South was sharecropping?
Sharecropping had become the dominant form of agricultural labor.
What economic system forced farmers to pledge part of their crop as collateral for loans?
The crop lien system.
What happened to many white farmers after the Civil War?
They fell into dependency as sharecroppers due to economic hardships.
What was the plight of Black farmers compared to white farmers in the postwar South?
A higher percentage of Black farmers rented land rather than owned it.
Who was Matt Brown and what does his case illustrate?
A Mississippi farmer whose increasing debt illustrates the struggles of sharecroppers.
What did freedmen insist was essential to the meaning of freedom?
Land ownership.
What did the Freedmen's Bureau achieve in education?
It helped to finance and coordinate education for Black children.
What was the general sentiment among freedpeople regarding their economic condition after the Civil War?
They felt betrayed and believed they had not improved their condition from slavery.
What was the task system in labor?
A system where workers were assigned daily tasks, completing them ended their responsibilities for the day.
What did the Freedmen's Bureau fail to achieve in economic relations?
It struggled to provide meaningful economic opportunities for former slaves.
What was the impact of the decline in farm product prices on sharecroppers?
It severely limited their economic opportunities.
What was the significance of the Freedmen's Bureau's existence from 1865 to 1870?
It represented an early attempt at government social policy in support of freed slaves.
What did the Freedmen's Bureau agents face in their efforts to assist freedpeople?
Daunting responsibilities and high expectations.
What did the Freedmen's Bureau do regarding health care?
It assumed control of hospitals and expanded medical care to both Black and white southerners.
What was the long-term effect of the failure of land reform on African Americans?
A deep sense of betrayal that persisted long after Reconstruction.
What was the financial situation of Matt Brown, the Mississippi farmer?
He began with a debt of $226 in 1892, which increased to $402 by 1893 despite producing cotton worth $171.
What did Matt Brown's last entry in the merchant's account book signify?
It signified his death, with the last entry being for a coffin.
What did the freedmen petition to President Andrew Johnson in 1865?
They petitioned for the right to obtain land that had been distributed to them but was being returned to former owners.
What was the main concern of the freedmen regarding land ownership?
They believed that owning land was essential for the enjoyment of freedom and protection of their rights.
What was the nature of the sharecropping contract in 1866?
It involved laborers working on white-owned land for a share of the crop, with many restrictions on their freedom.
What were the laborers required to do under the sharecropping contract?
They had to plant, cultivate, and raise crops under the management of the landowner and were responsible for their own living expenses.
How did the contract limit the freedom of the laborers?
It bound them to obey the landowner's orders and penalized them for disobedience, limiting their autonomy.
What social changes occurred in the South after the Civil War?
The South saw the emergence of new social classes, including landowning employers, sharecroppers, and urban entrepreneurs.
What was the economic situation of southern cities after the Civil War?
Southern cities experienced remarkable growth, with railroads enabling direct trade with the North.
What stereotype did planters hold about former slaves?
They believed former slaves were lazy and lacked ambition, thinking freedom meant no labor.
What efforts did former slaves make to gain independence after emancipation?
They sought to reconstruct family life and withdrew women and children from field labor to gain more independence.
What was the role of the Freedmen's Bureau during Reconstruction?
It was established to assist freed slaves in transitioning to freedom, including land ownership and education.
What was a common outcome for freed slaves regarding land ownership?
Few former slaves were able to acquire land and most ended up as sharecroppers.
What did the freedmen argue about their rights compared to former landowners?
They argued that their rights as free people should be considered before those of former landowners who had been in rebellion.
What was the significance of the petition drafted by the freedmen?
It highlighted their desire for land ownership and equal rights in the post-Civil War South.
What did the sharecropping contract stipulate about labor hours?
Laborers were required to work ten hours a day on average, with penalties for lost time.
How did the sharecropping system affect the economic status of Black laborers?
It often kept them in a cycle of debt and poverty, limiting their economic mobility.
What was the impact of Reconstruction on Black and white southerners?
Reconstruction brought profound changes, creating new social classes and altering economic dynamics.
What did the freedmen believe about land monopoly?
They believed it was injurious to their advancement and sought government provision for land ownership.
What were the conditions of the sharecropping contract regarding supplies?
Laborers had to pay for any supplies provided by the landowner out of their share of the crop.