Introduction to Kinesiological Concepts in Physical Therapy
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Kinesiology
The study of movement
Biomechanics
The application of the principles of mechanics to the study of biological systems
Kinematics
The set of concepts that describes the motion of a body, without regard to the forces that cause that motion.
Kinetics
The description of the effects of forces on the body
Linear motion
Translation: All parts of the body move parallel and in the same direction as every other part of the body.
Angular motion
Rotation: A rigid body moves in a circular path around a pivot point. All points move in the same direction (clockwise or counterclockwise). Motion is measured in degrees or radians.
Osteokinematics
The motion of bones relative to the three cardinal planes of the body: sagittal, frontal and horizontal.
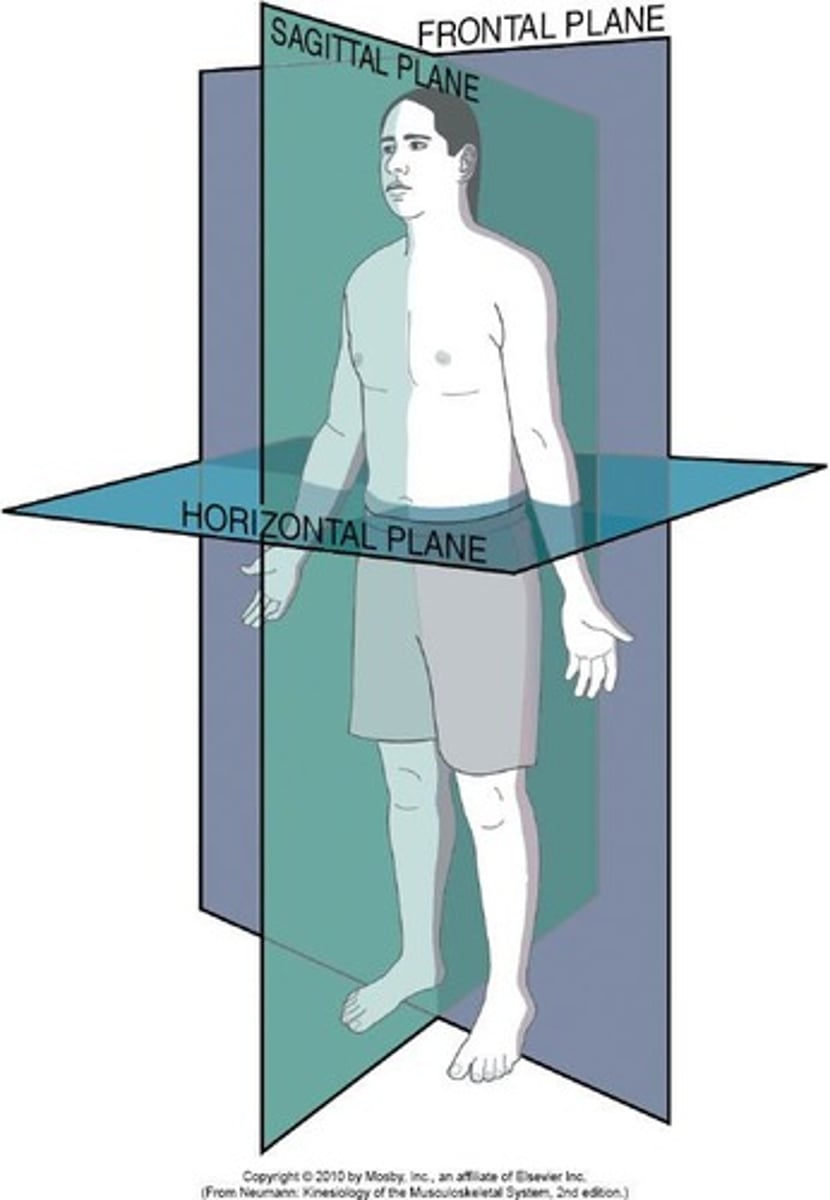
Sagittal Plane
Common motion in this plane is flexion/extension.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Common motion: abduction/adduction.
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
Internal/external rotation.
Axes of Motion
Usually located through the convex bone of the joint. Axes run perpendicular to the plane of motion.
X-axis
Medial-lateral axis.
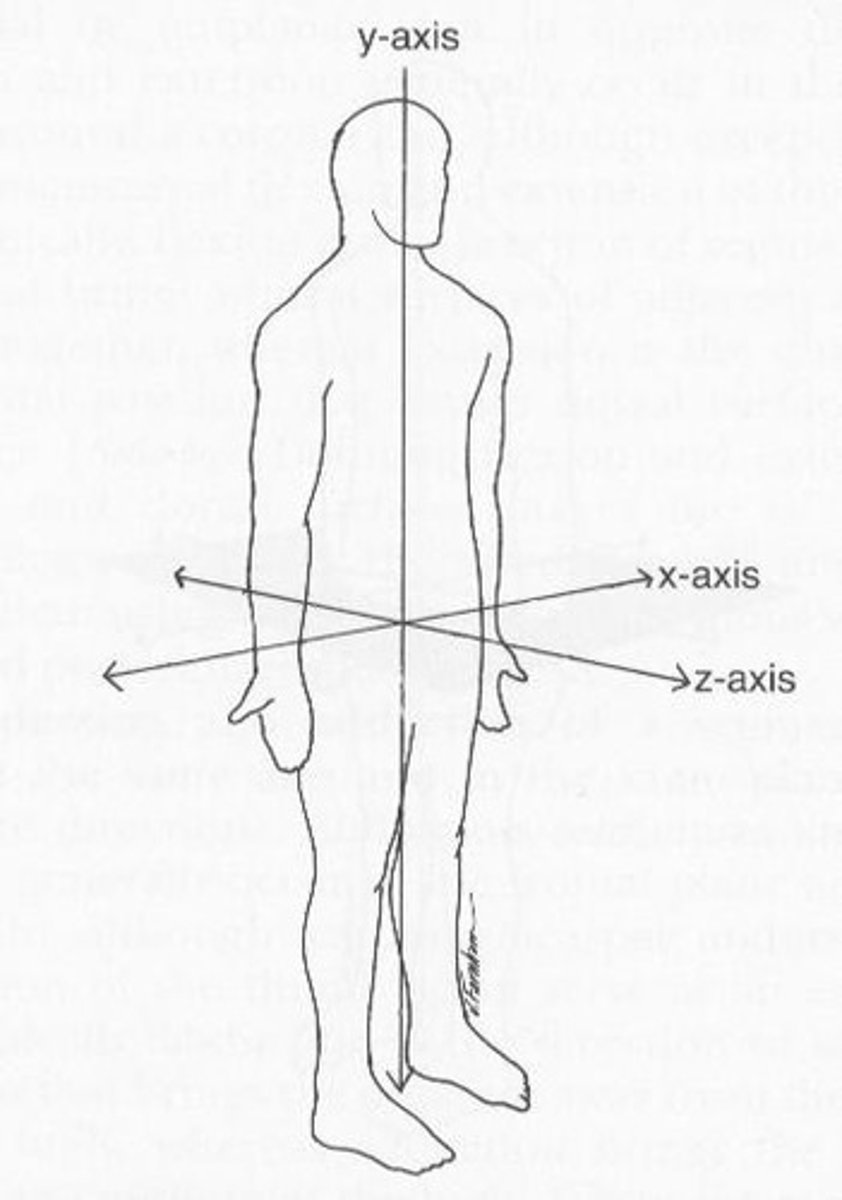
Y-axis
Superior-inferior axis.
Z-axis
Anterior-posterior axis.
Degrees of Freedom
The number of planes through which a joint can be voluntarily moved.
Glenohumeral joint
Movement in 3 planes.
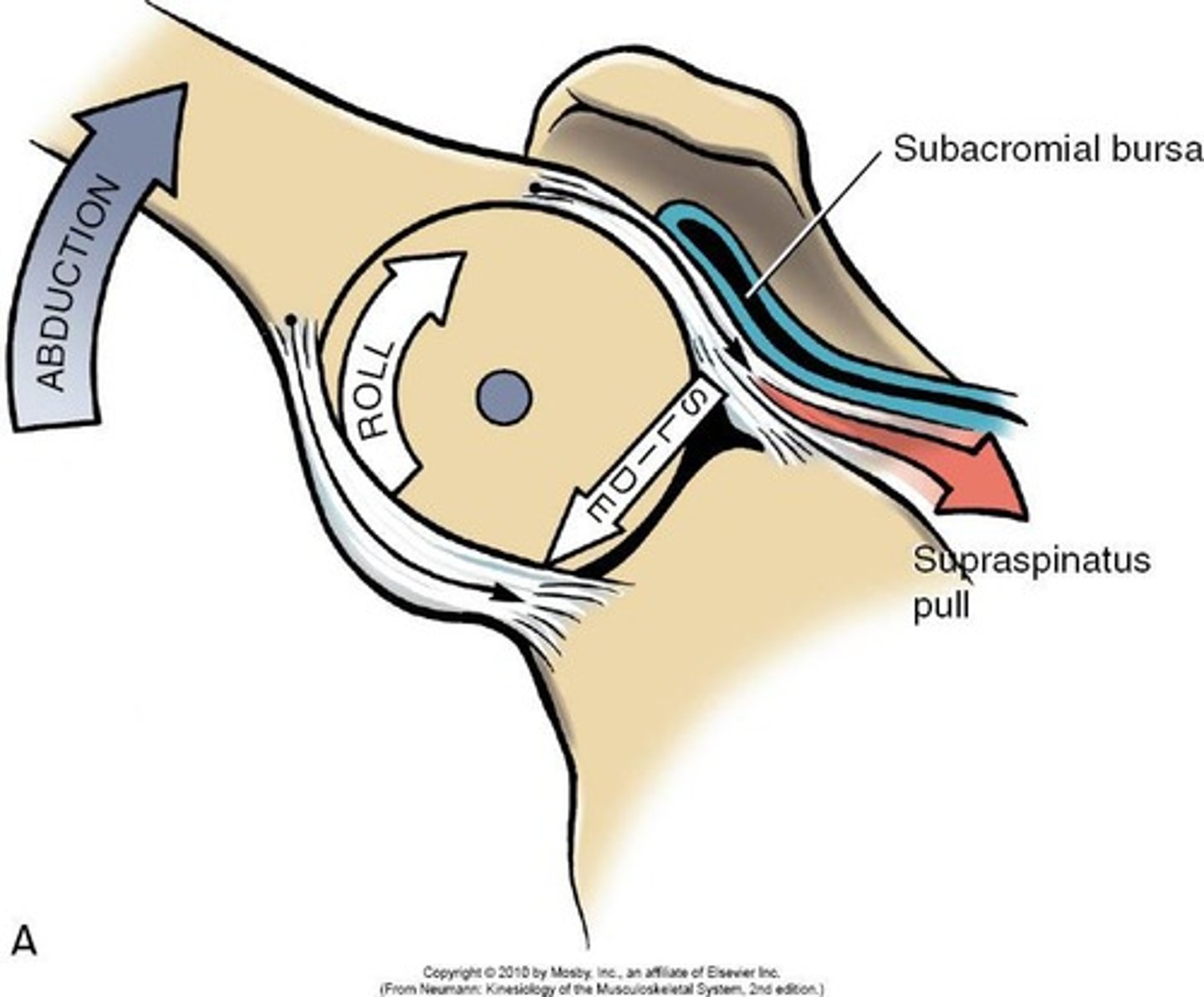
Instantaneous Axis of Rotation
Not stationary; moves slightly throughout the motion.
Open Chain
One joint can move independently of the others; the distal segment is free to move; usually NWB
Closed Chain
Distal end of the chain is fixed or stabilized on a support surface and motion occurs at the proximal segments; usually WB
Forces
Internal forces and external forces that can make us move
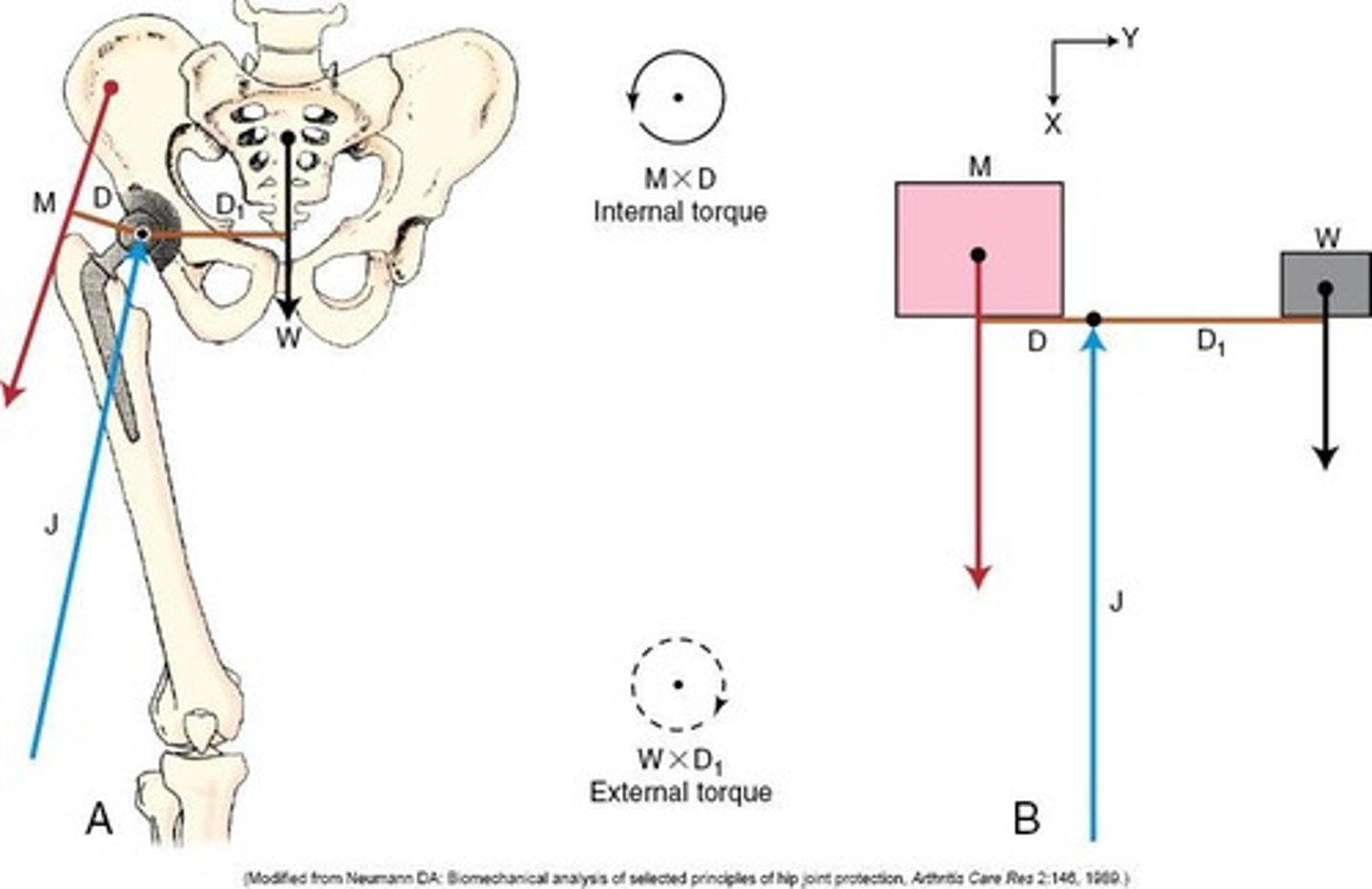
Body Weight
A type of external force calculated as Force = mass x acceleration (F=m x a) or Weight = mass x gravity (W=m x g)
Gravity
The force that pulls objects toward the center of the Earth
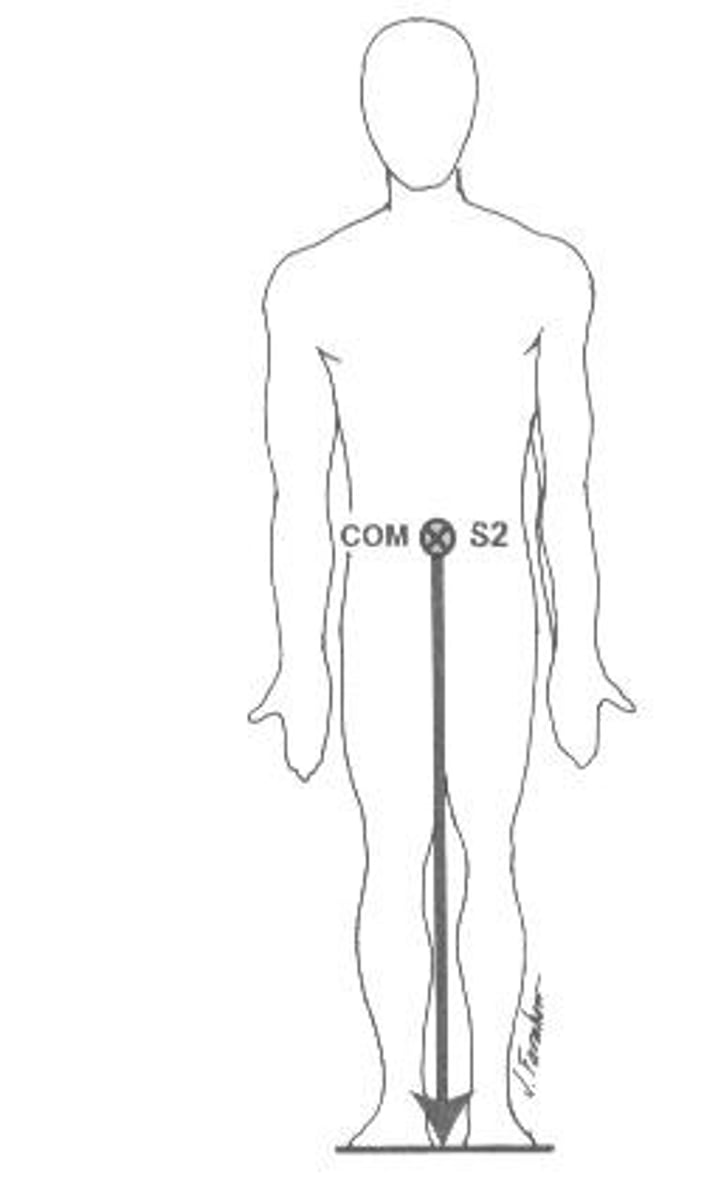
Center of Mass
Point where the mass is evenly distributed in all directions
Center of Gravity
Point in the body through which the resultant force of gravity acts
Line of Gravity
Always vertically downward from the Center of Mass (COM)
Base of Support
The area beneath an object or person that includes every point of contact that the object or person makes with the supporting surface
Tissue Mechanics
The mechanics of materials of human connective tissue (bones, ligaments, cartilage, and tendons)
Load
In tissue mechanics, we refer to force as a load
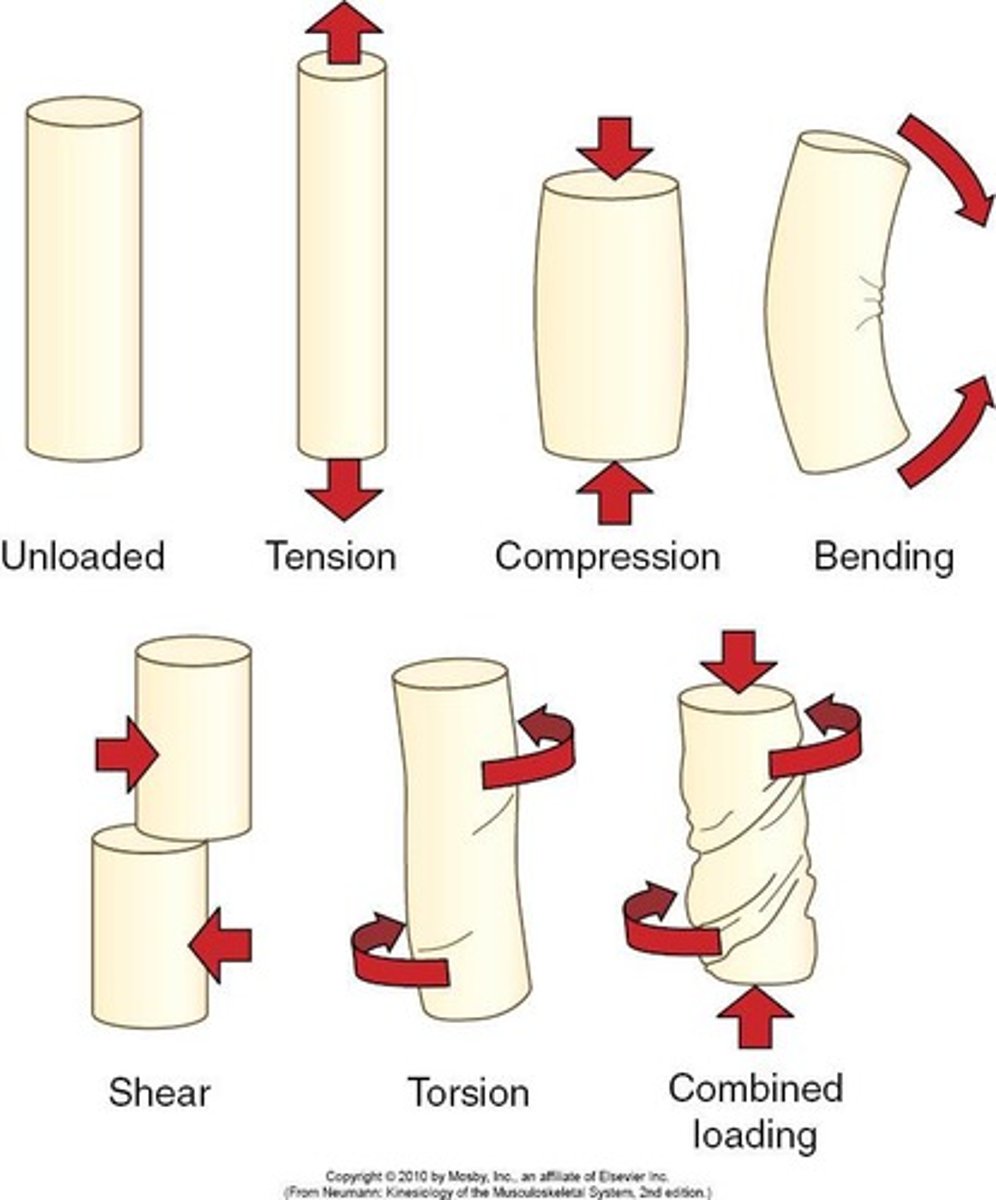
Types of Load
Tension, Compression, Bending, Shear, Torsion
COM Location
Each body segment has a Center of Mass (COM) approximately at the midpoint of the segment
COM Variation
The COM of the body or the lower extremity will change depending upon the spatial orientation of the individual segments