Parts of the nervous system (1/19-1/26)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
glia
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
synapses
tiny gaps between dentrites and axons of different neurons
neurons
behavior arises from coordination of ______________ (cells). even if they are few in number
neurons, complex, functions
More ________ --> more ___________ circuits --> more complex ________
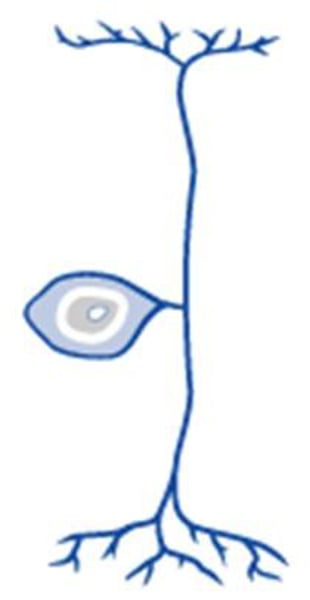
bipolar neuron
a neuron with one axon and one dendrite attached to its soma
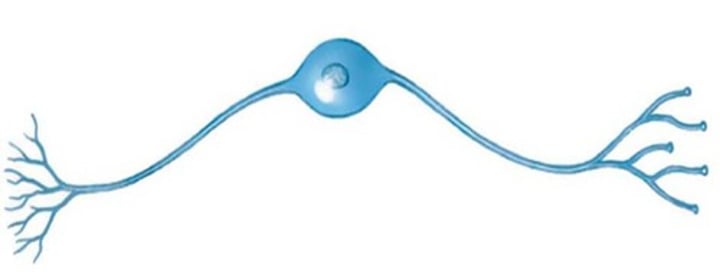
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
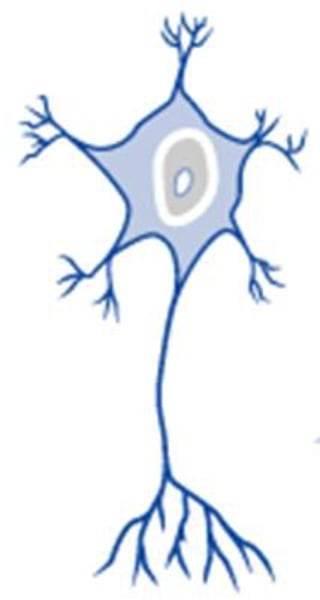
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
dendrite
input zone on neuron, can recieve info from multiple sources
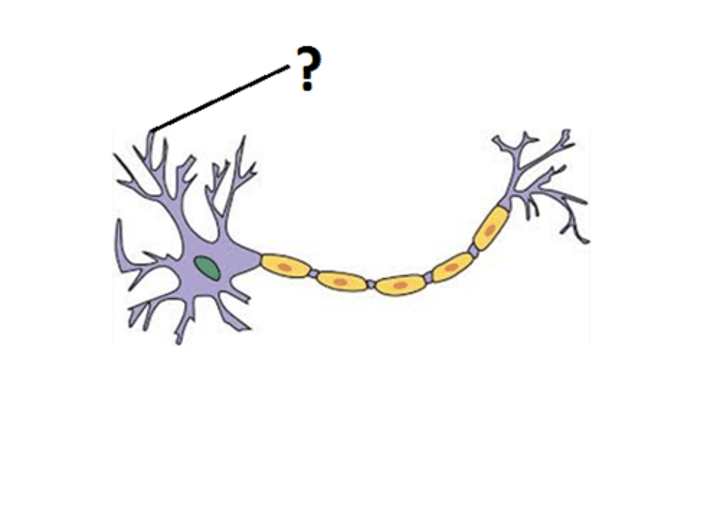
dendritic spines
increase surface area, increases ability to receive signals
cell body (soma)
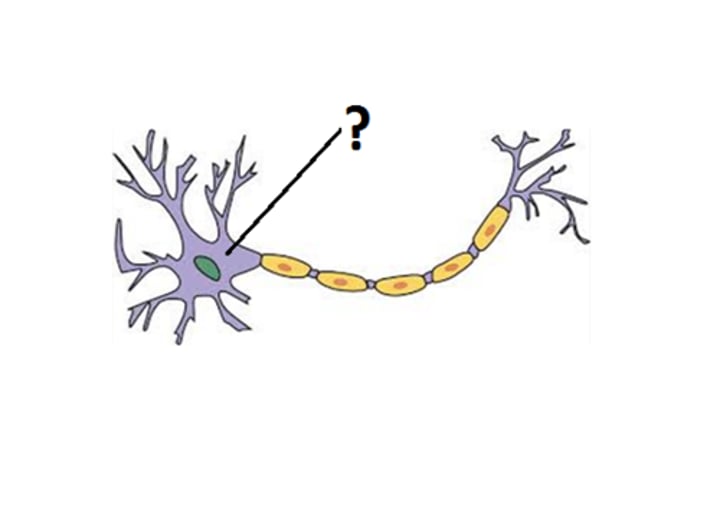
nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
organelles contained in the cell body
axon hillock (axon initial segment) (integration zone)
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
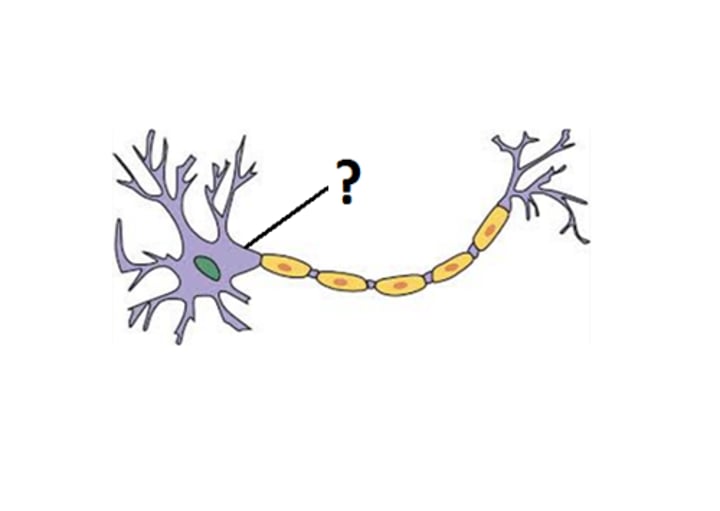
axon hillock
-integrates incoming signals from the cell body
anterograde transport
- movement down the axon away from soma
- via action potentials or motor proteins holding vesicles
retrograde transport
movement up the axon toward the soma
- uses motor proteins
- never action potential
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
- output zone
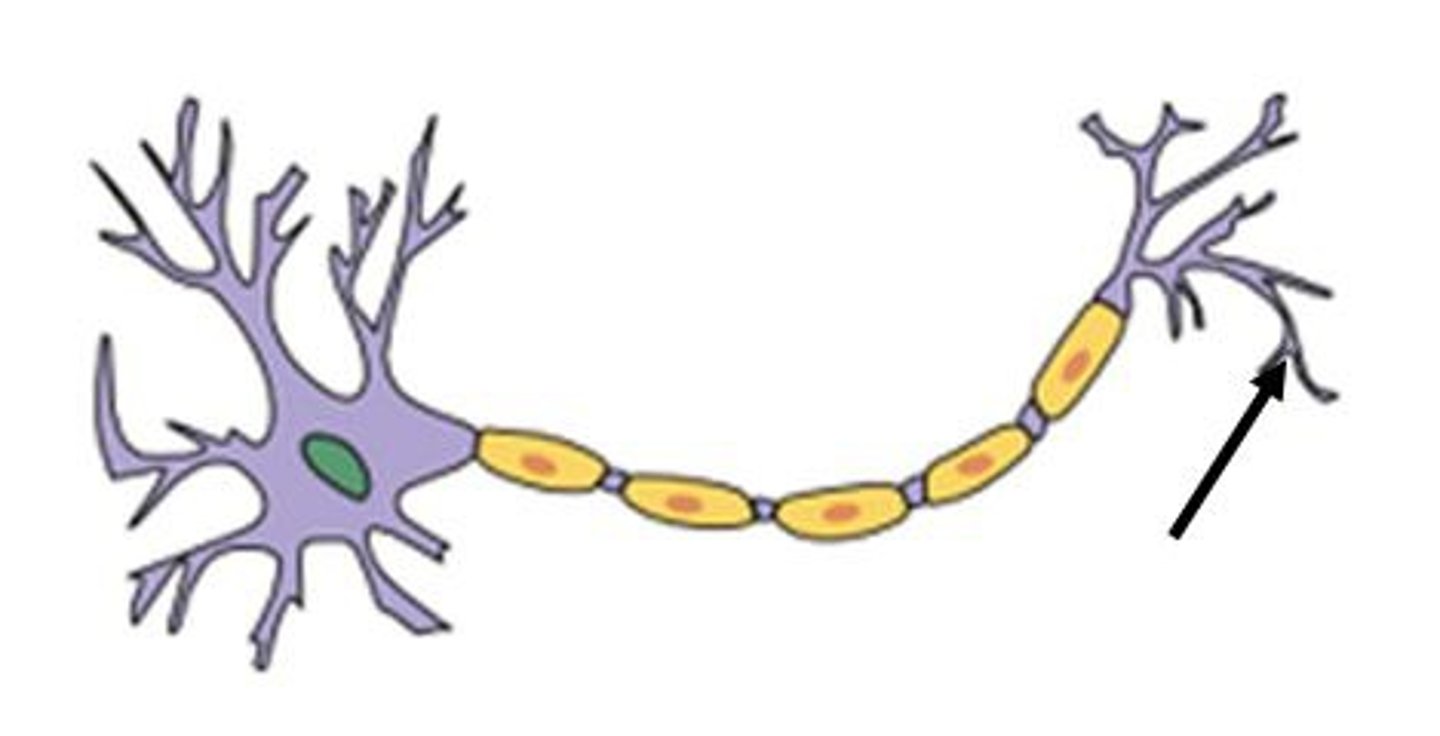
axon
conduction zone
- where info can be transmitted over great distances
synaptic vesicles and mitochondria
presynaptic terminal contains ....
mitochondria
postsynaptic terminal contains ..
glial cells
cells which support and enhance neural activity
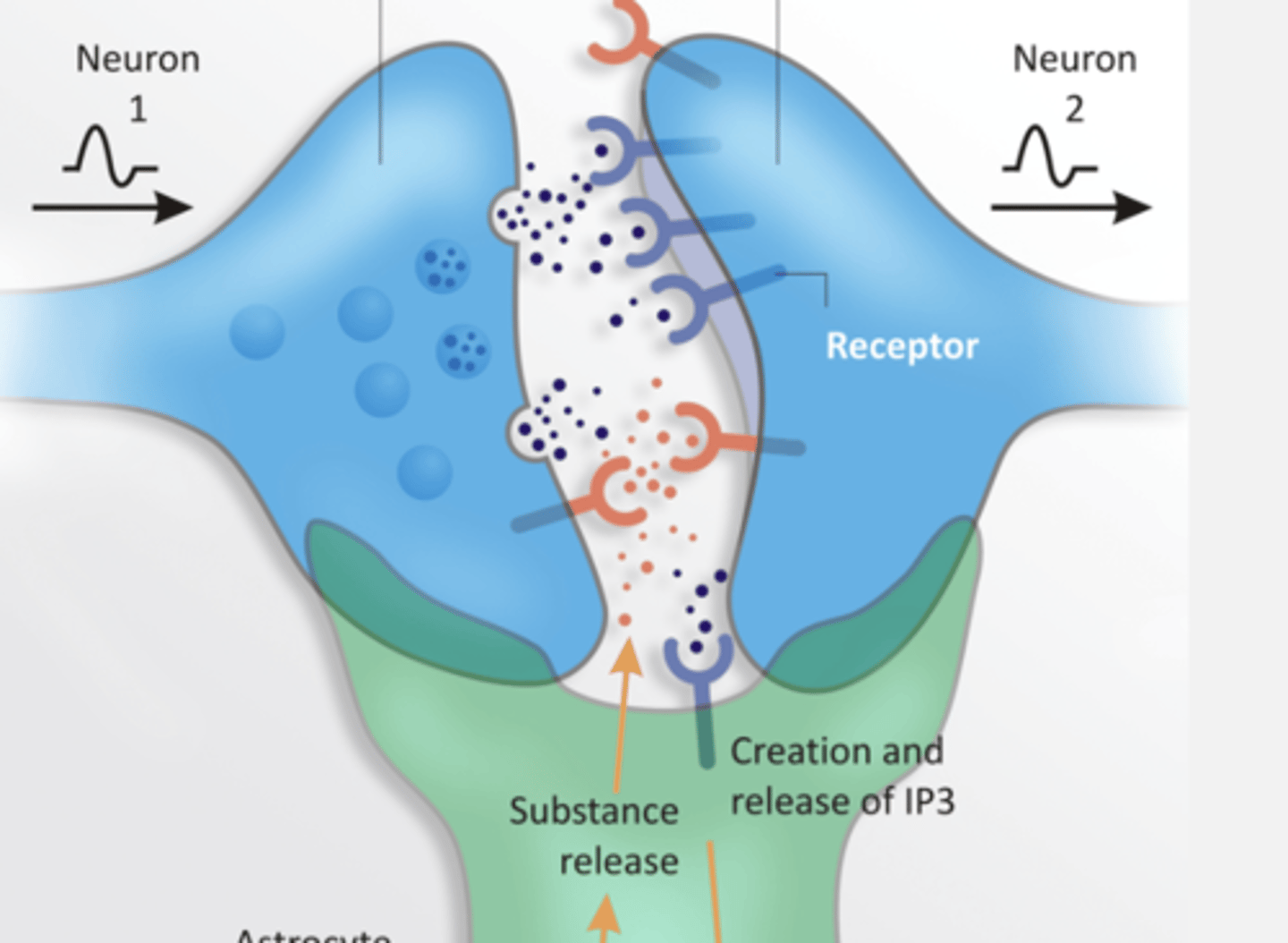
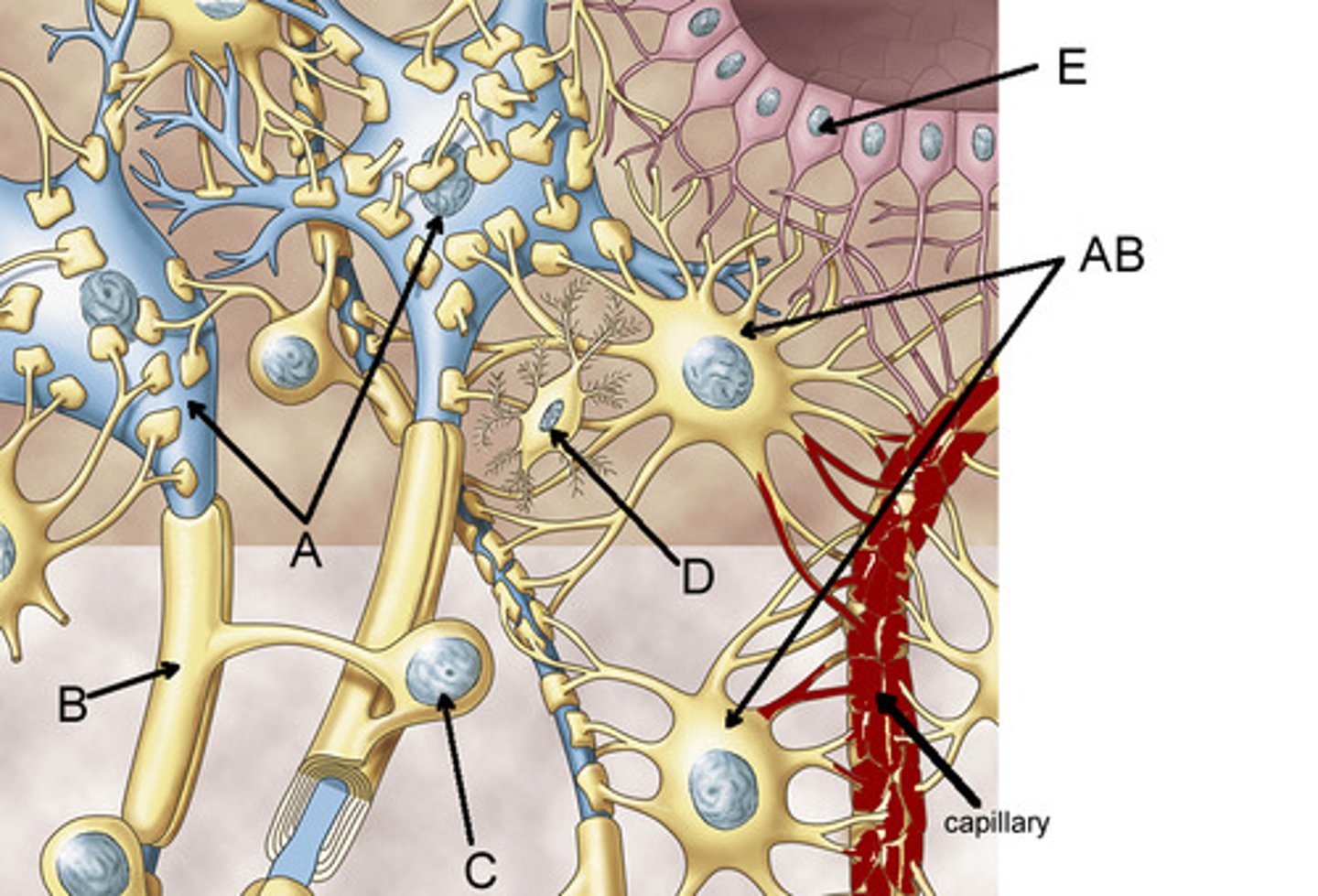
Astrocytes
-glial cell
- Wraps around pre and post synaptic cells
- star shaped cells that help form the BBB by sitting between capillaries and neurons
- support the metabolic and biochemical needs of neurons
- directly regulate synaptic signaling (tripartite synapse)
- react to brain injury
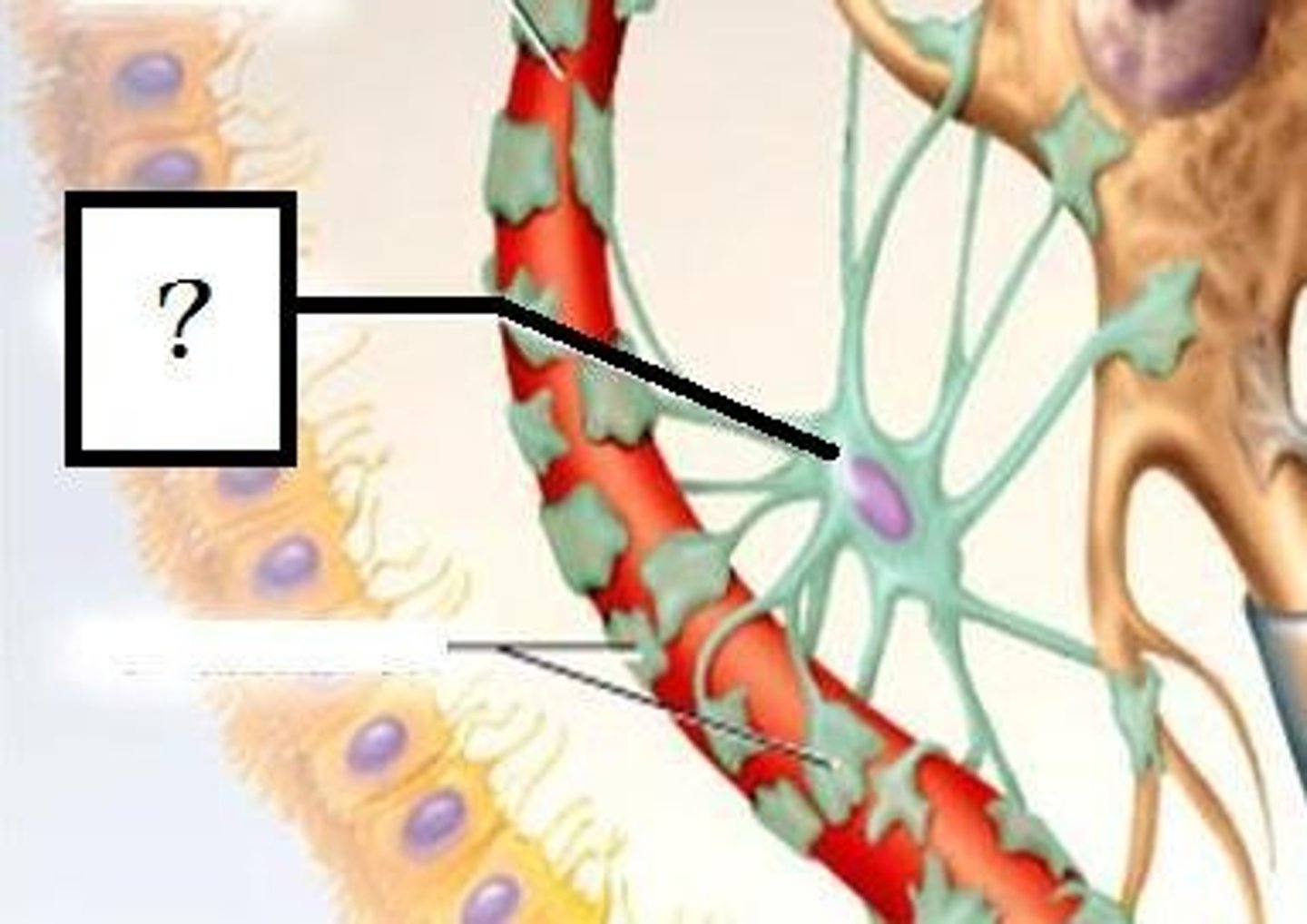
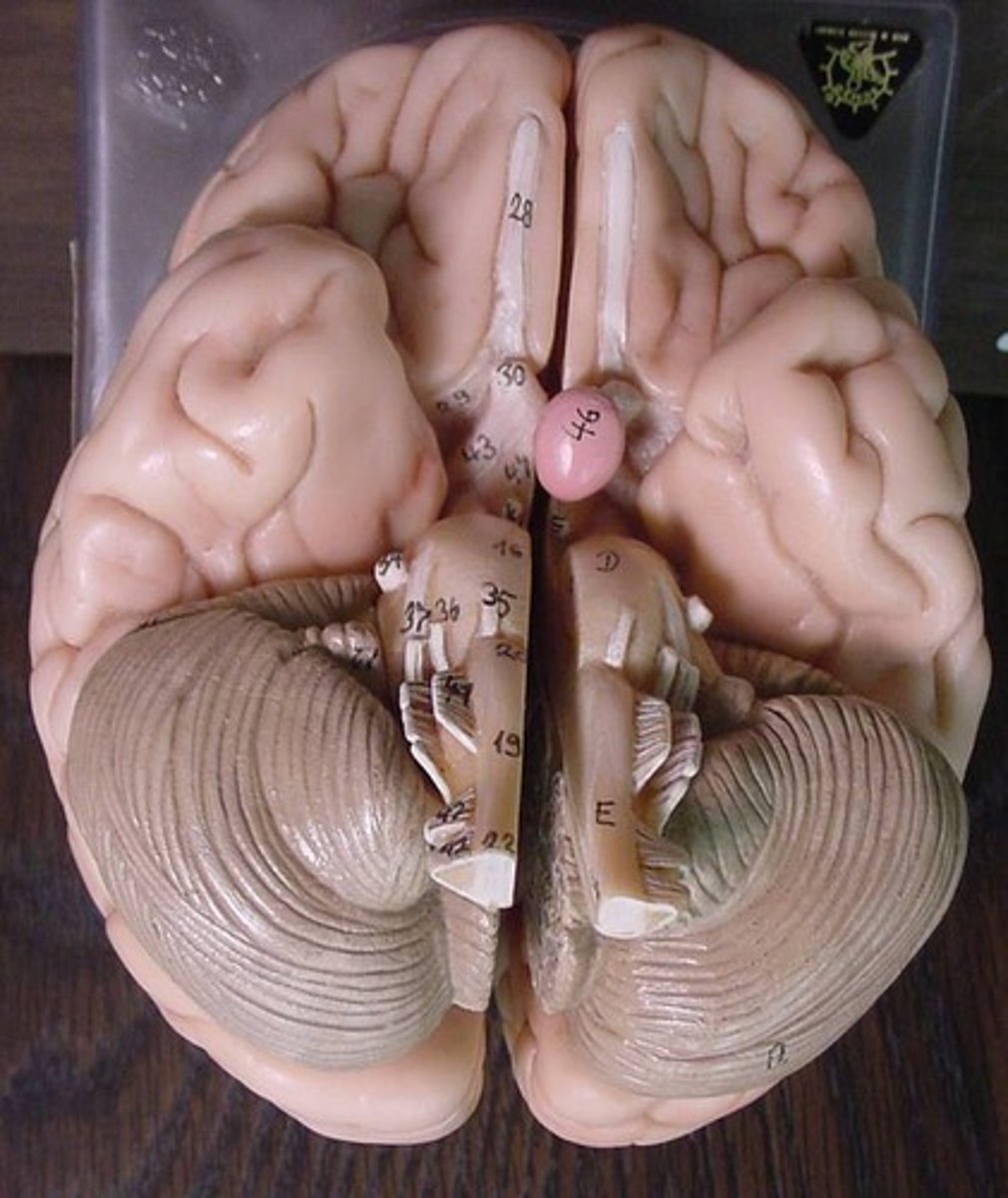
presynaptic terminal, postsynaptic terminal, astrocyte
label:
- left blue
- right blue
- bottom green
Oligodendrocytes
- glial cell
- forms myelin sheath IN CNS
- have node of ranvier
- can attach to a small portion on multiple axons
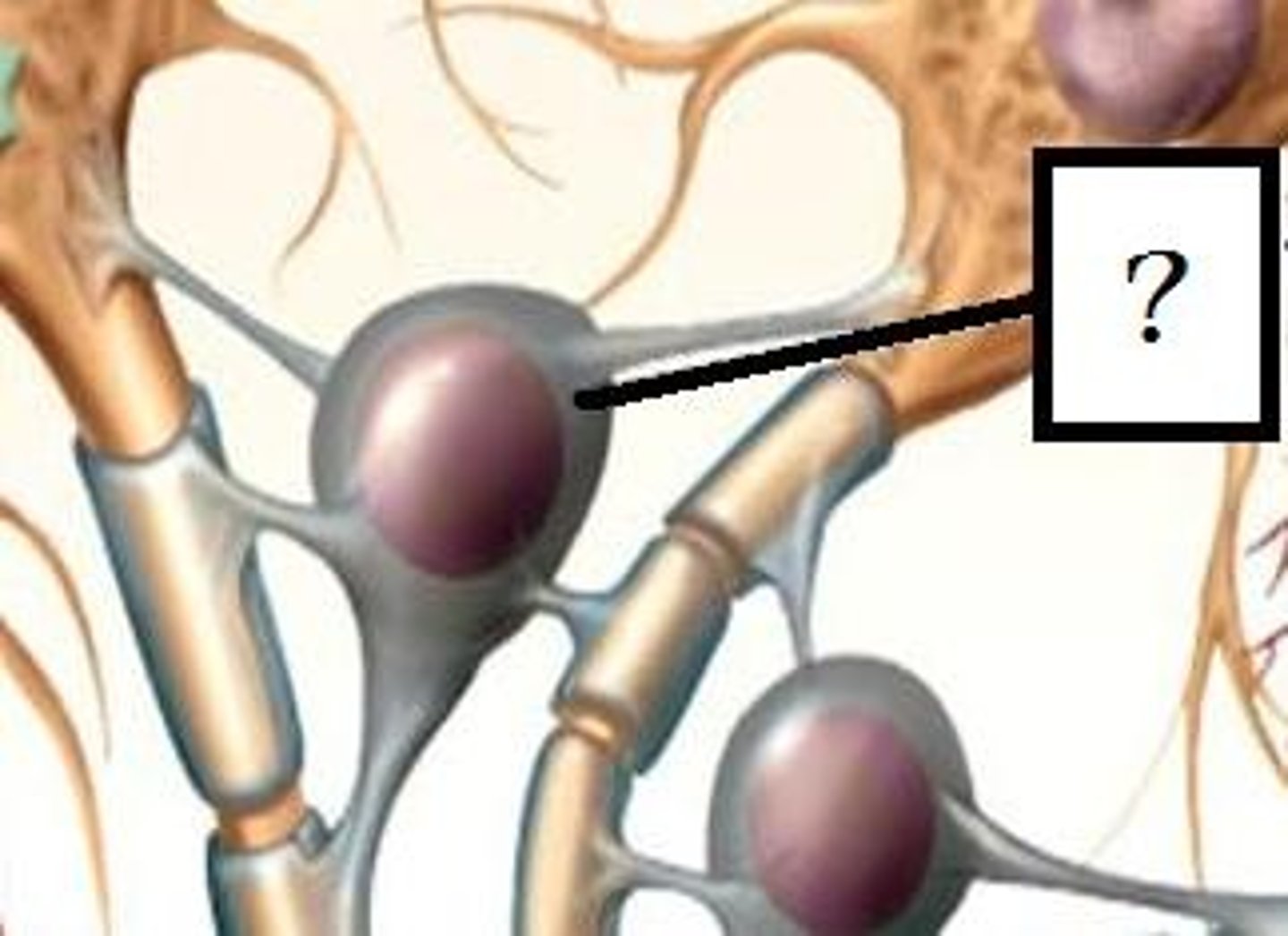
Schwann cells
- glial cell
- myelinates cells in PNS
- not found in the brain
- have node of ranvier
- can only attach to one axon portion
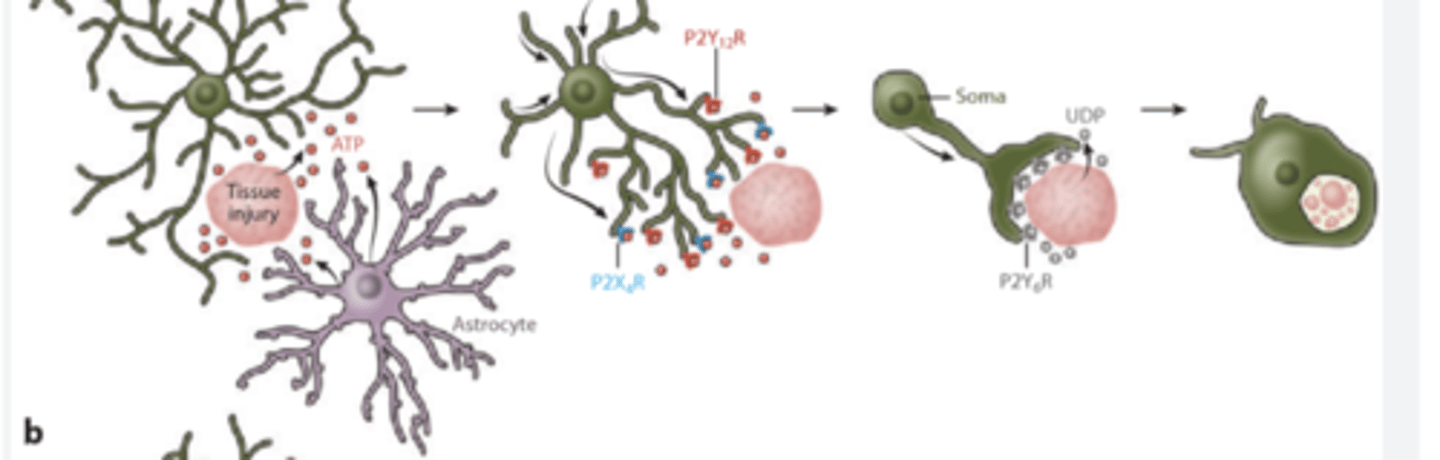
Microglia
- immune cells
- produce inflammatory response
- Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
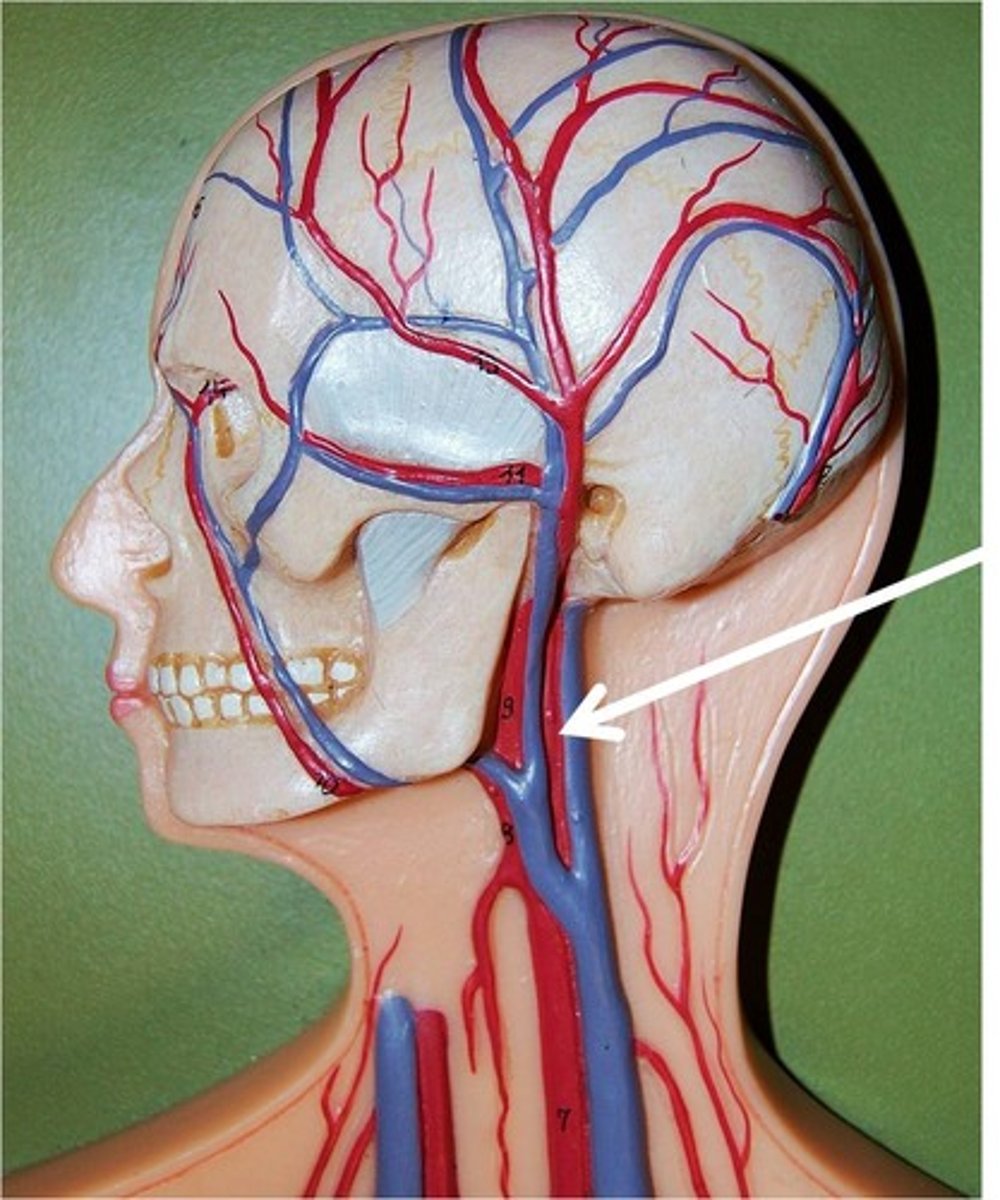
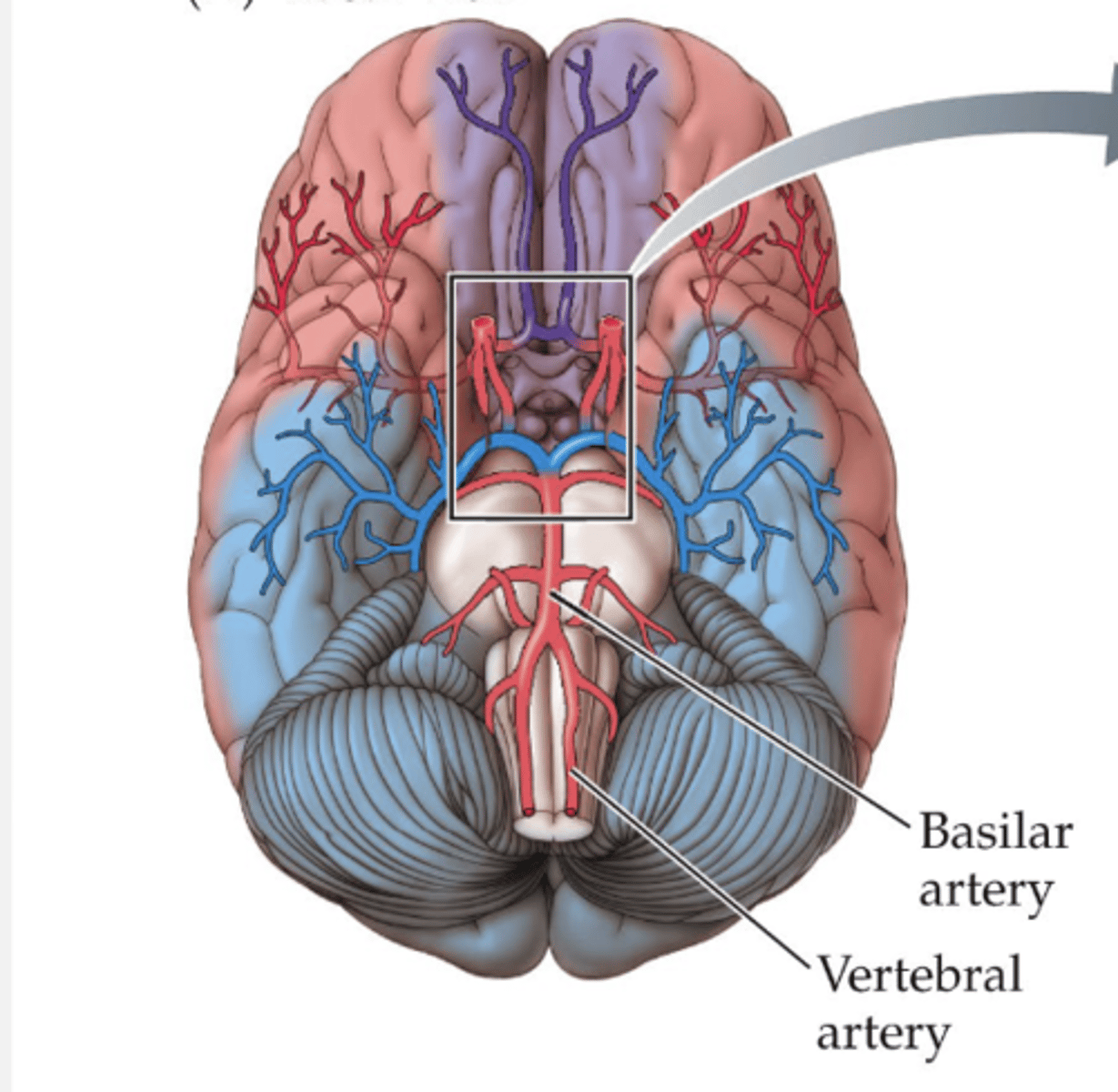
carotid arteries
major arteries to the brain
circle of willis
A structure at the base of the brain that is formed by the joining of the carotid and basilar arteries.
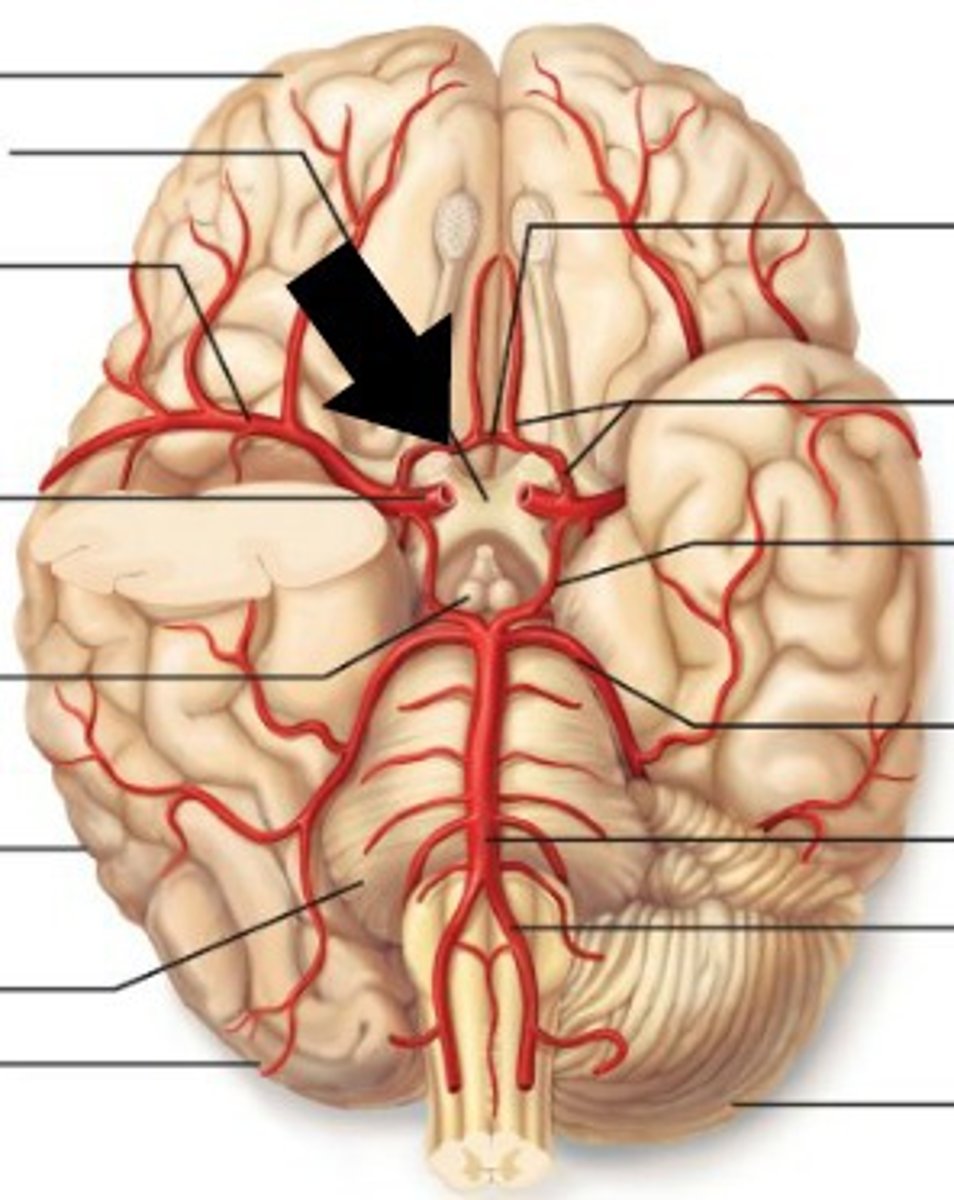
anterior cerebral artery
purple cerebral artery
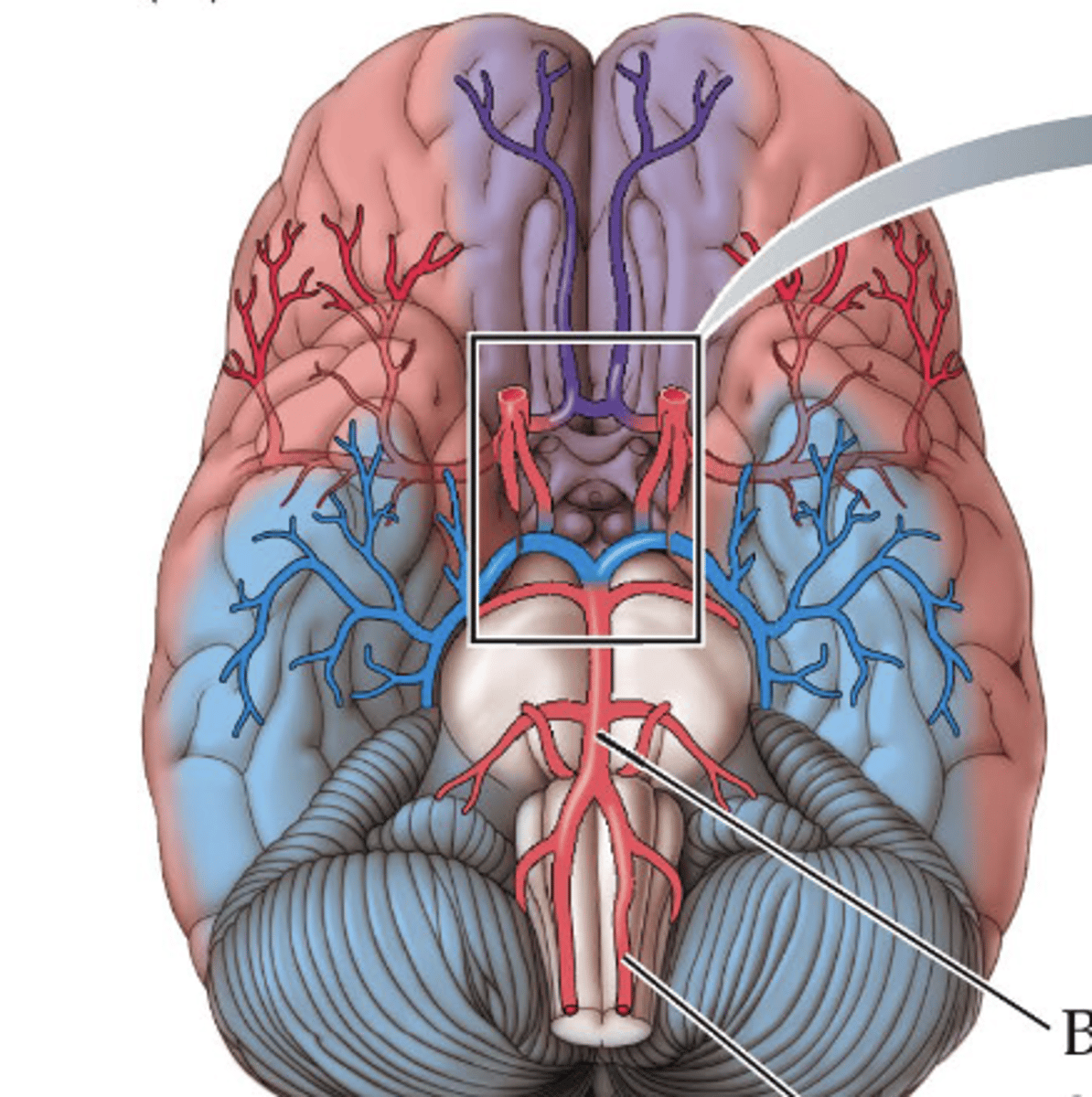
middle cerebral artery
red cerebral artery
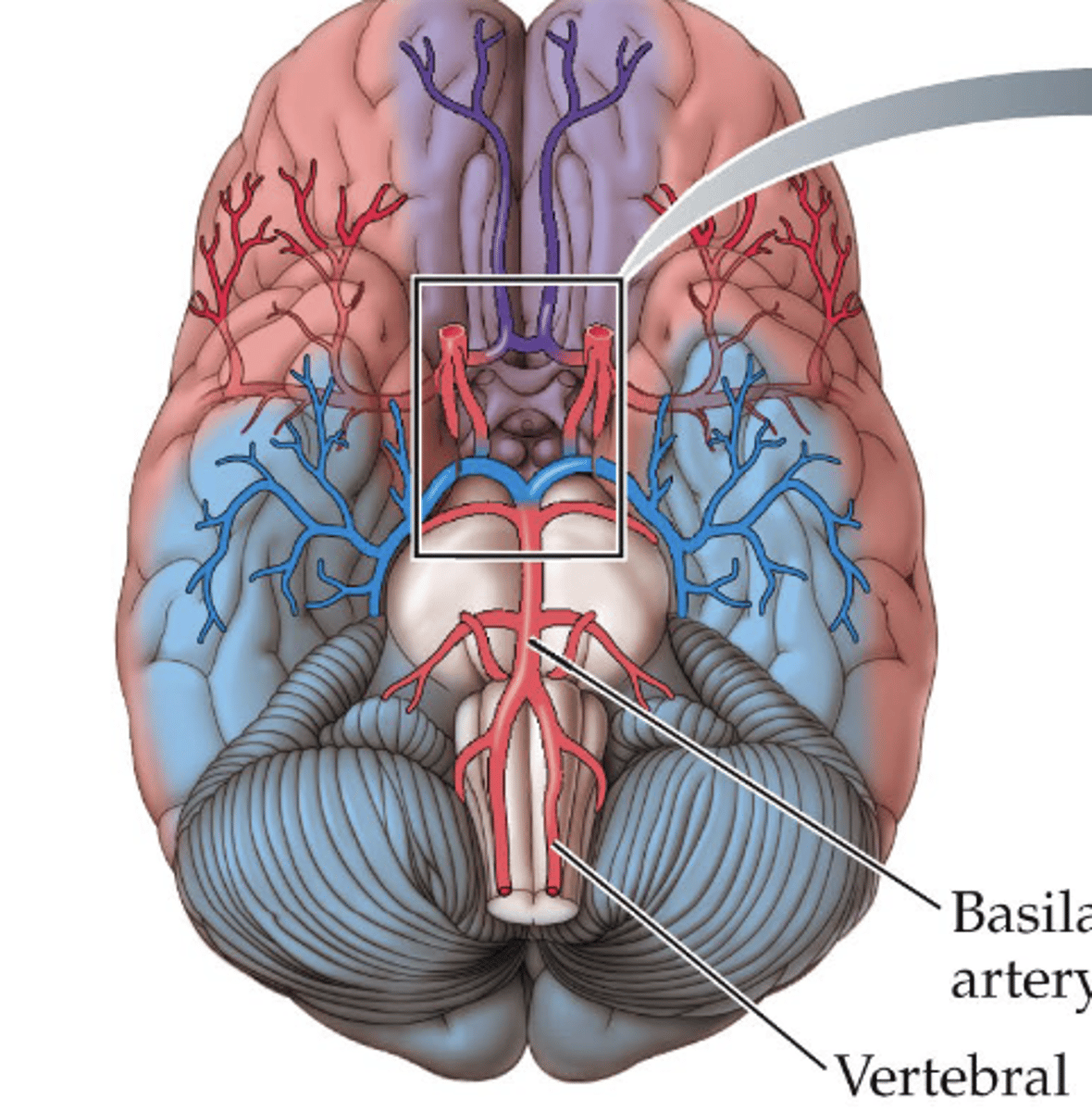
posterior cerebral artery
blue cerebral artery
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
result of higher resistance in brain capillaries that restrict passage of large molecules
endothelial cells
tightly bound cells forming the blood brain barrier
hemorrhage stroke
Occurs when a rupture in an artery allows blood to leak into the brain
ischemic stroke
clots or other debris prevent blood from reaching a region of the brain, causing it to die
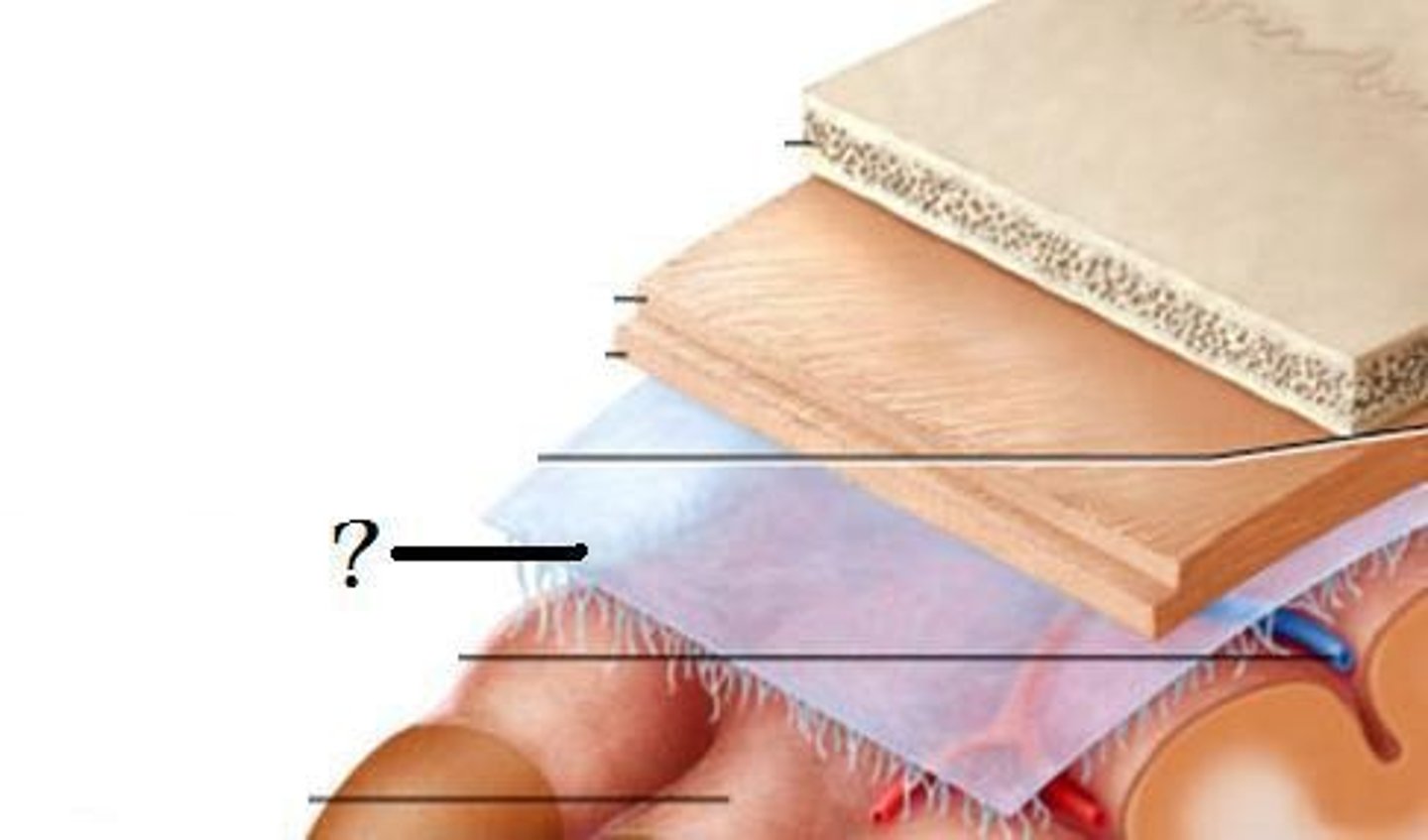
skull
dura mater
archinoid mater
pia matter
brain
layers of the meninges (skull --> brain)
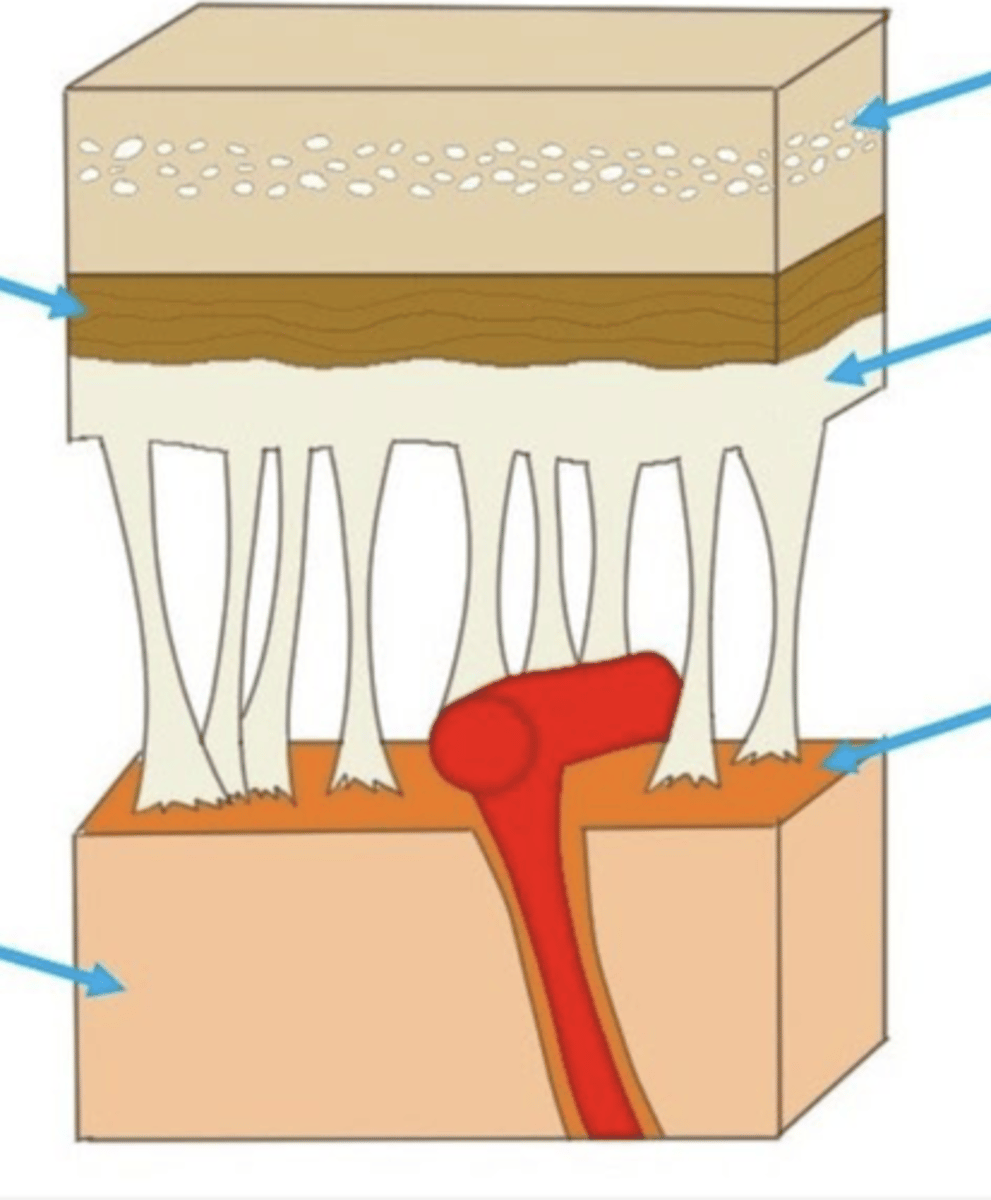
meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
subarchnoid space
below the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater, contains CSF
ependymal cells
E
- lines the meninges
- form lining of ventricles
- secretes cerebrospinal fluid
ventricles
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon (middle line)
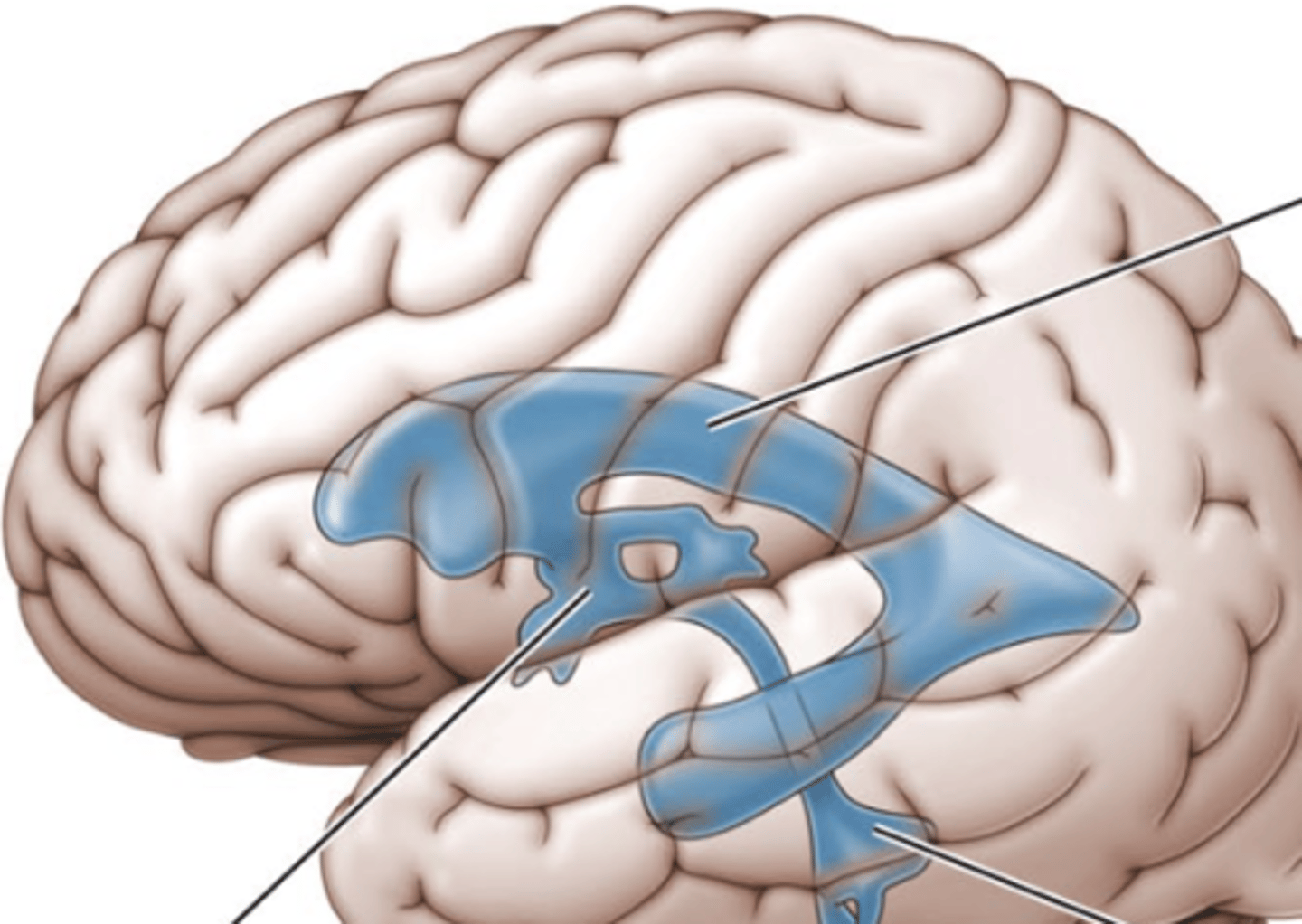
lateral ventricles
A set of paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres. (top line)
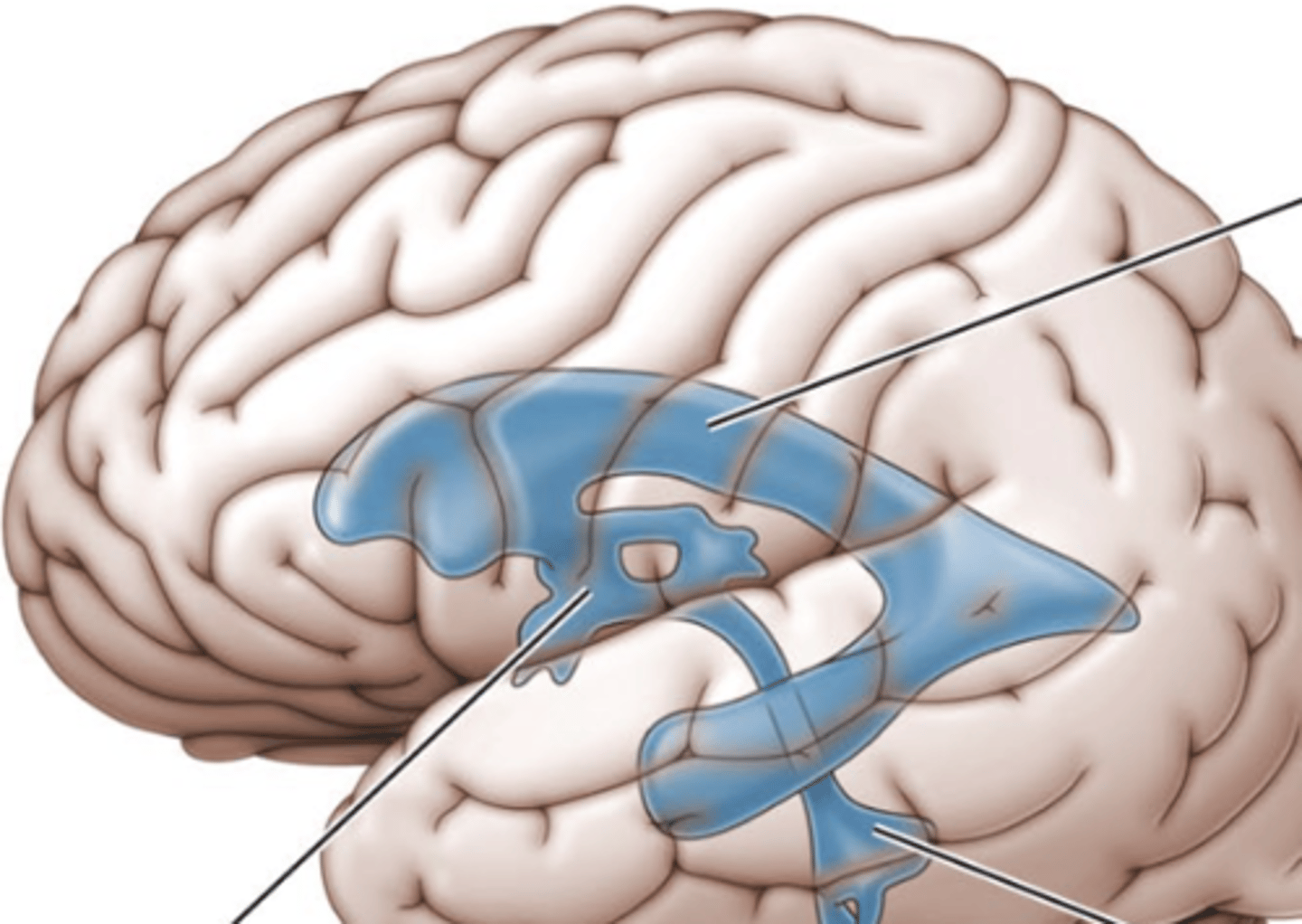
fourth ventricle
small triangular chamber between pons and cerebellum (bottom line)
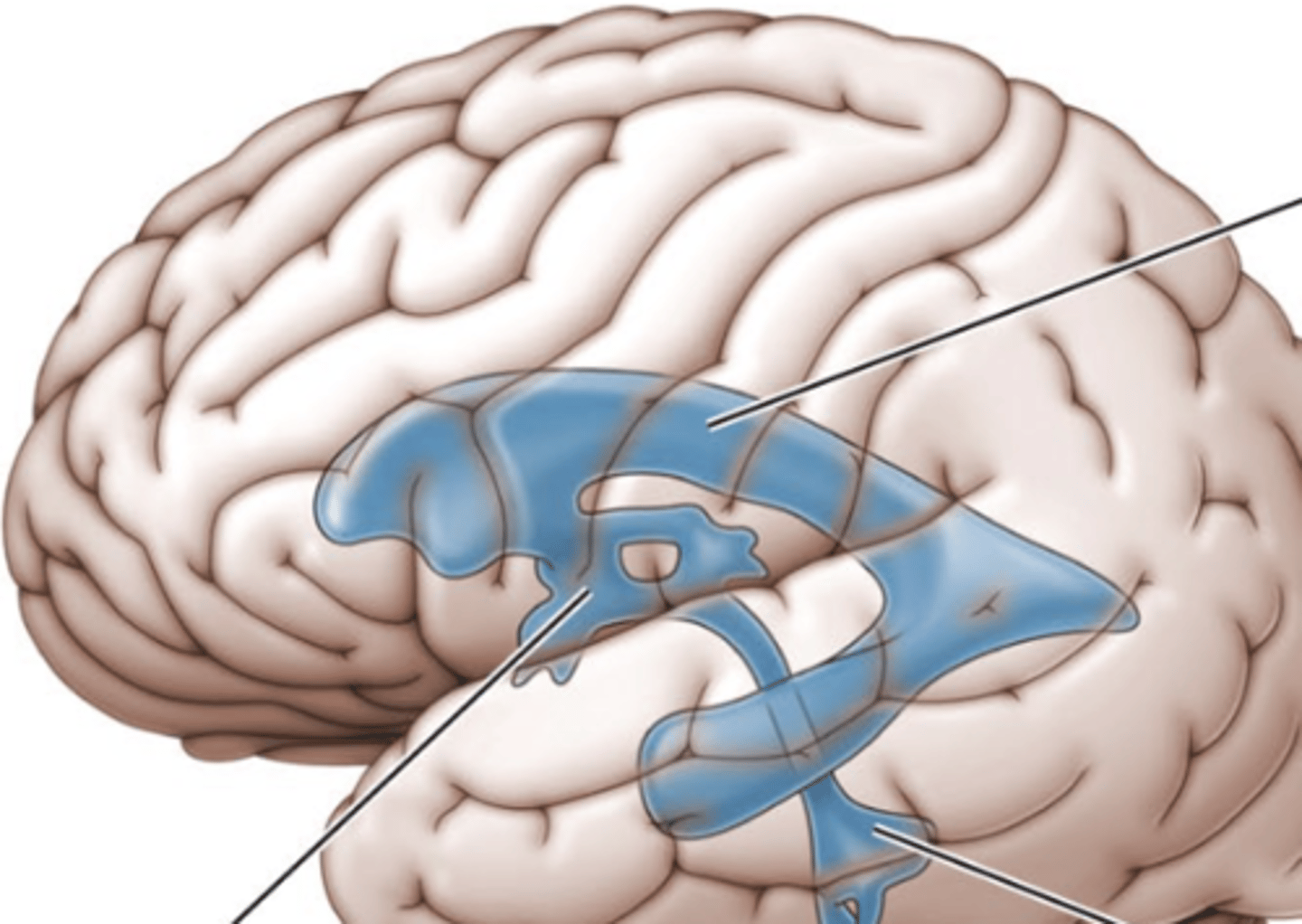
choroid plexus
a membrane lining the ventricles produces cerebrospinal fluid
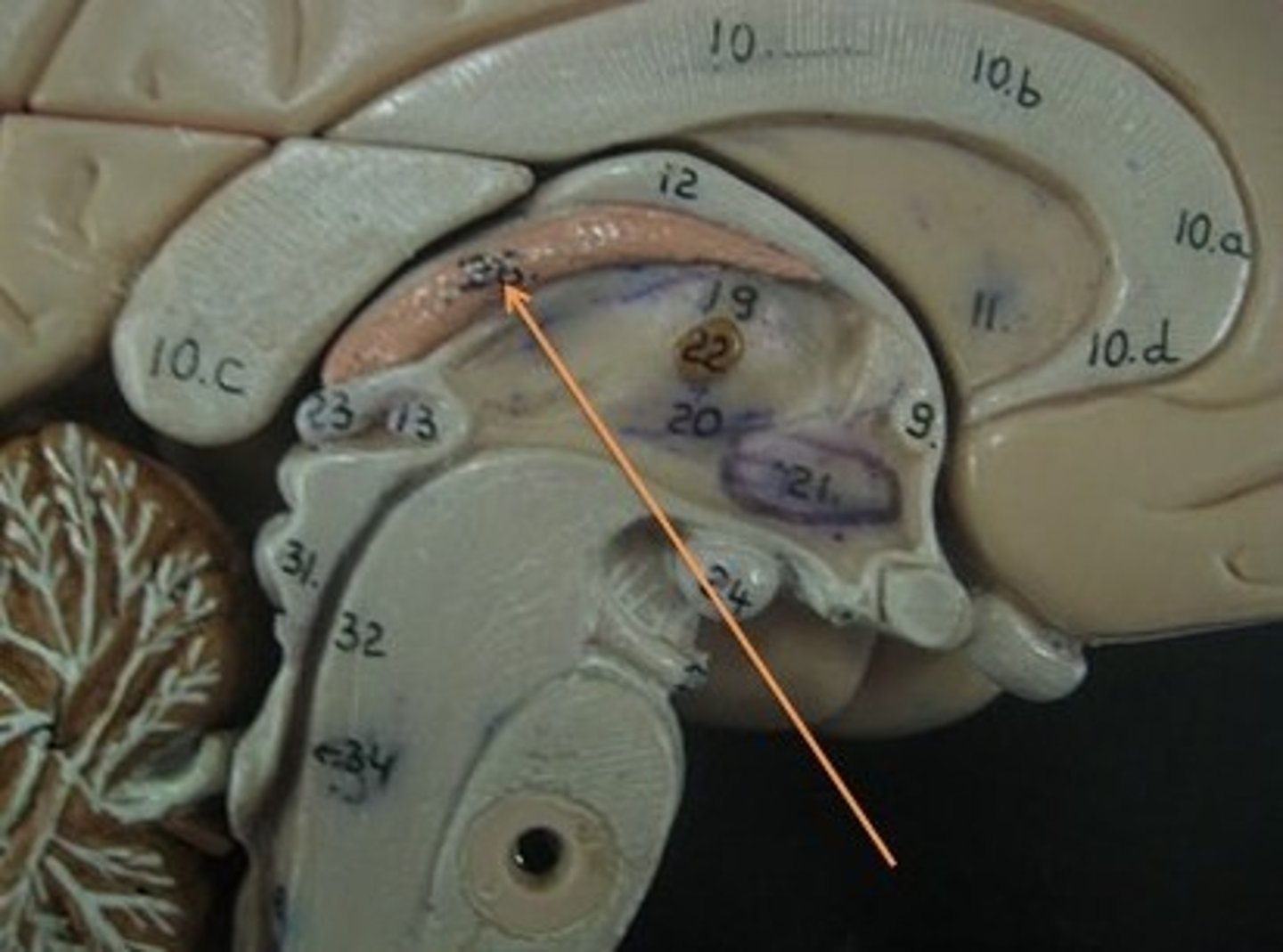
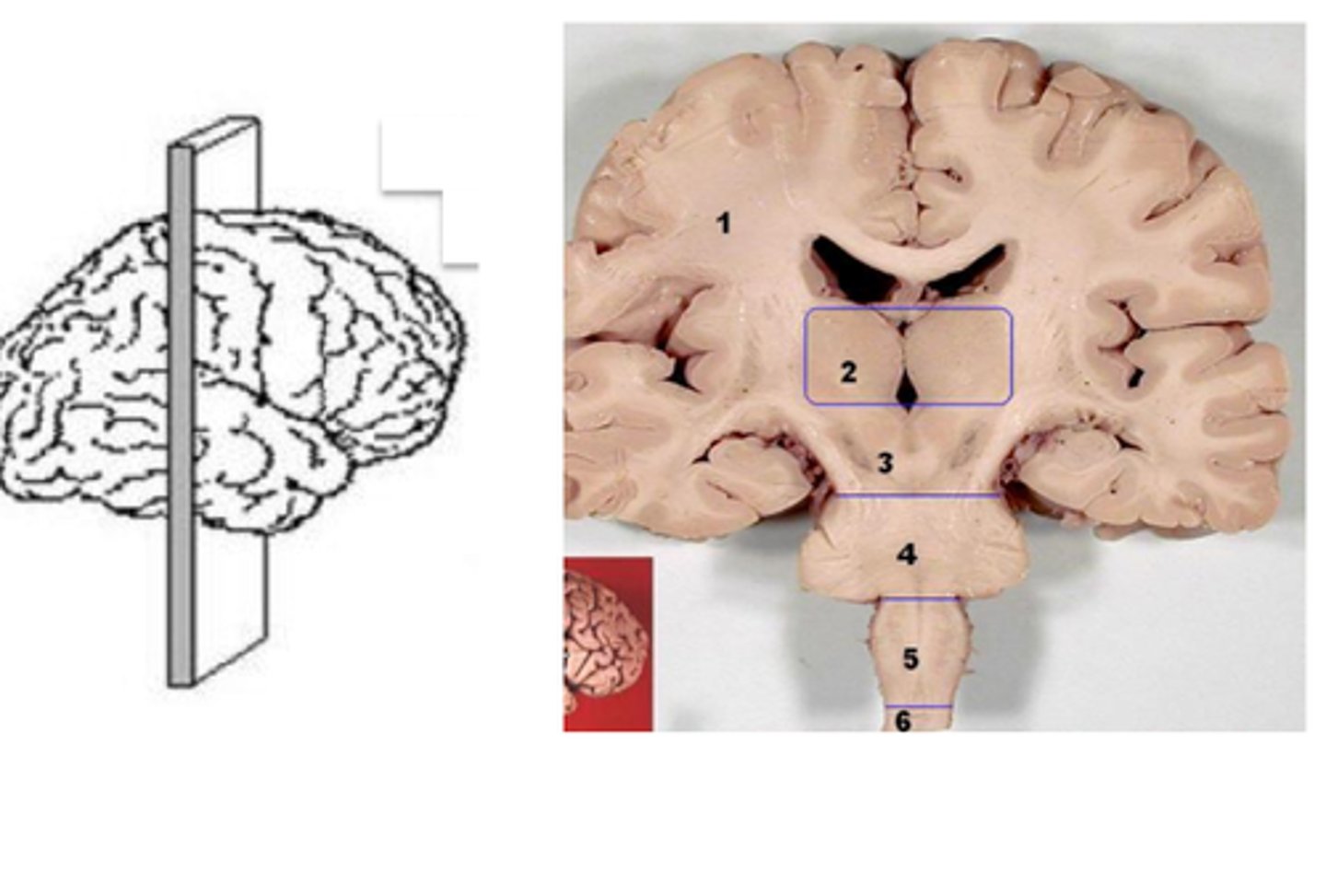
coronal plane
divides body into front and back
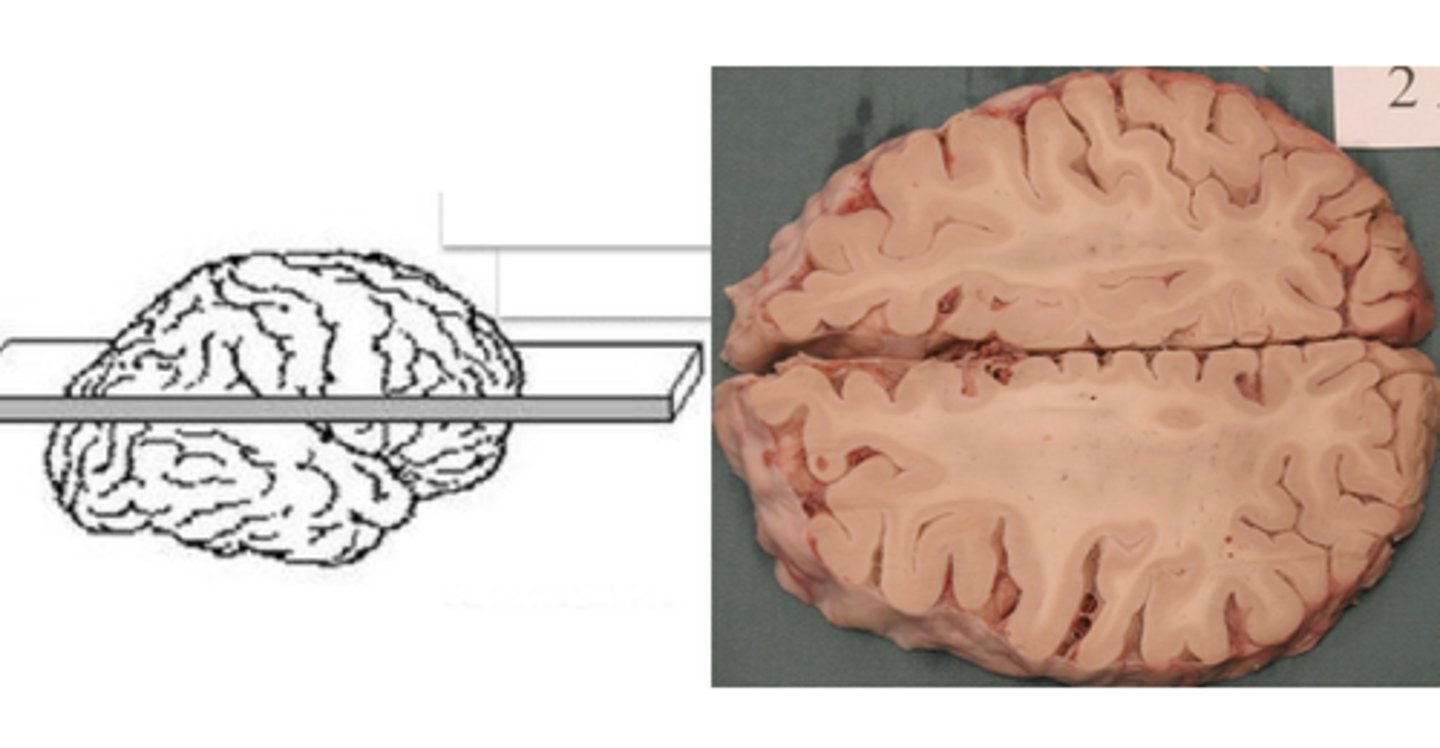
horizontal plane
a plane that shows brain structures as seen from above
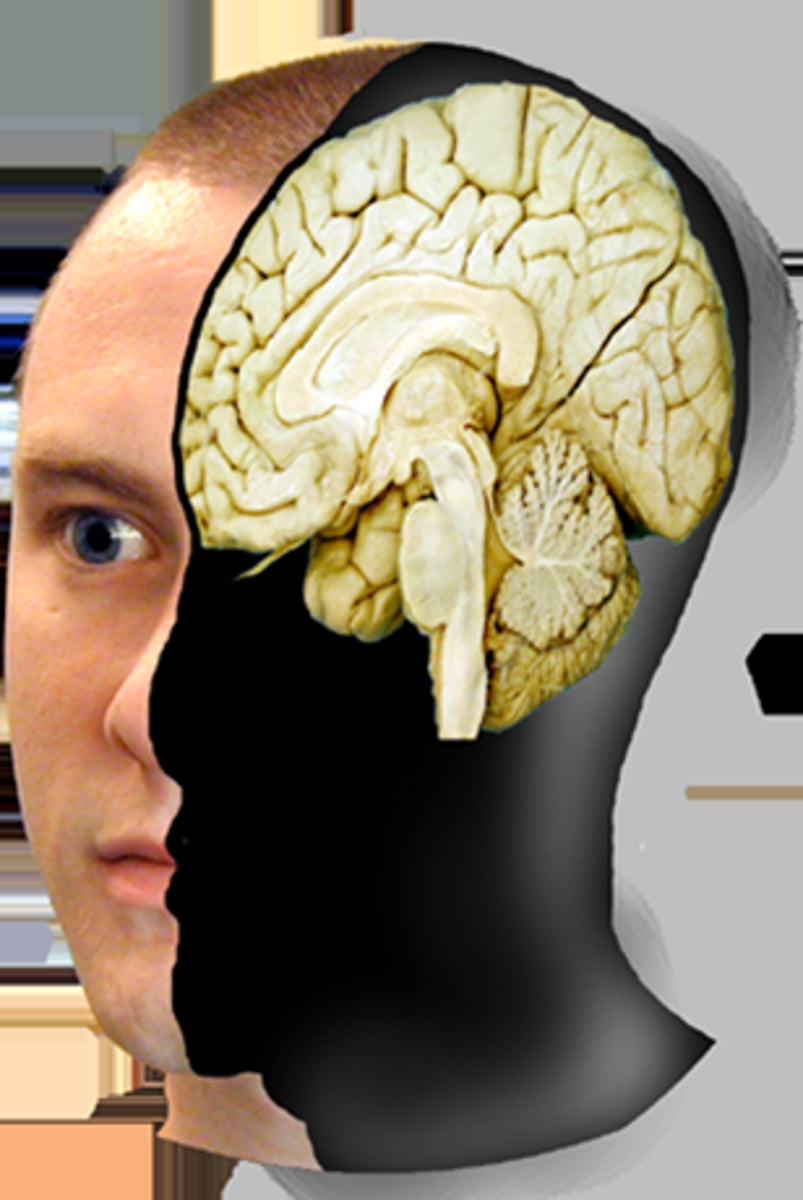
sagittal plane
divides brain into left and right
anterior / rostral
front of brain
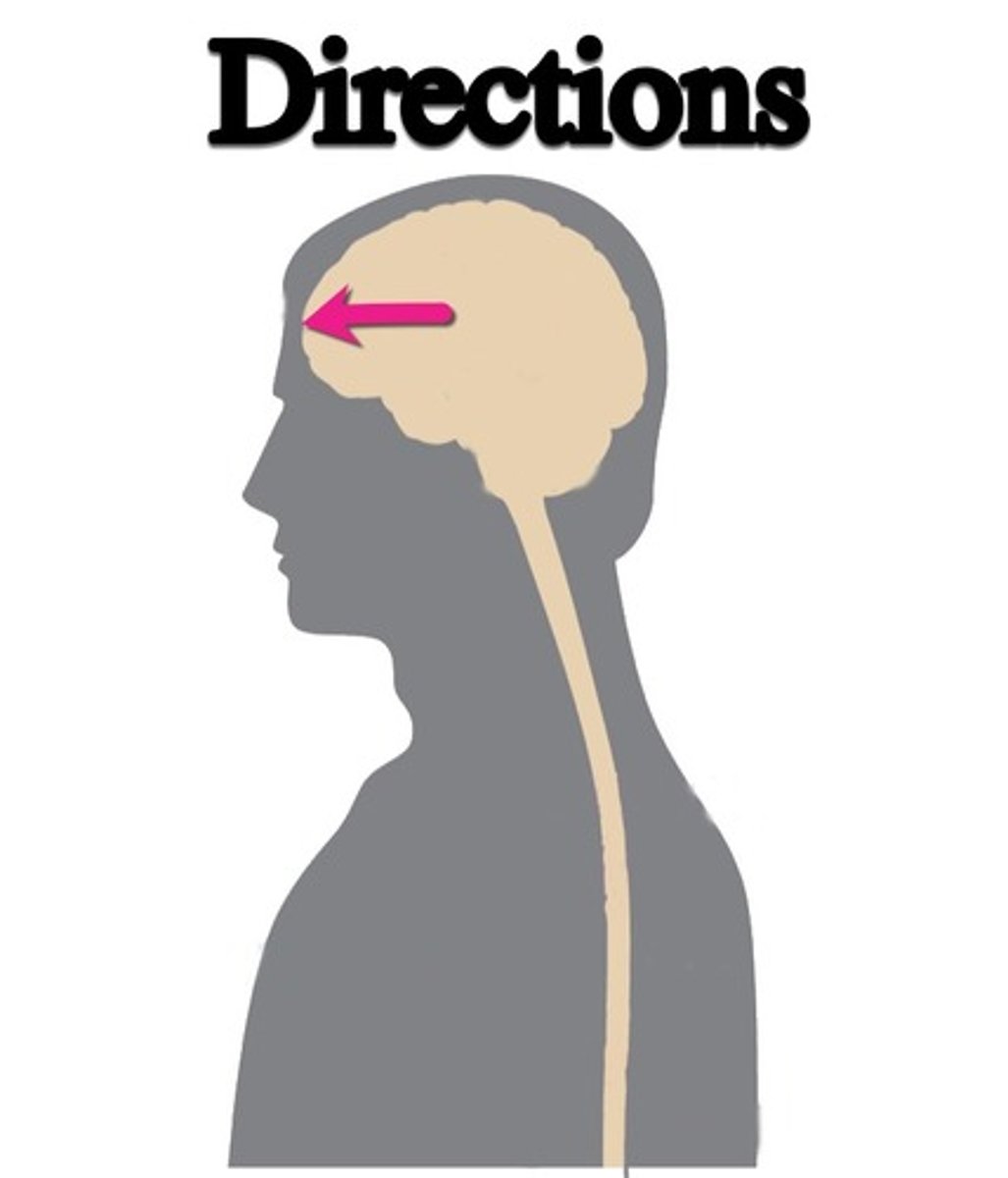
posterior or caudal
back of brain
ventral (brain)
towards the bottom of the brain
dorsal (brain)
top of brain
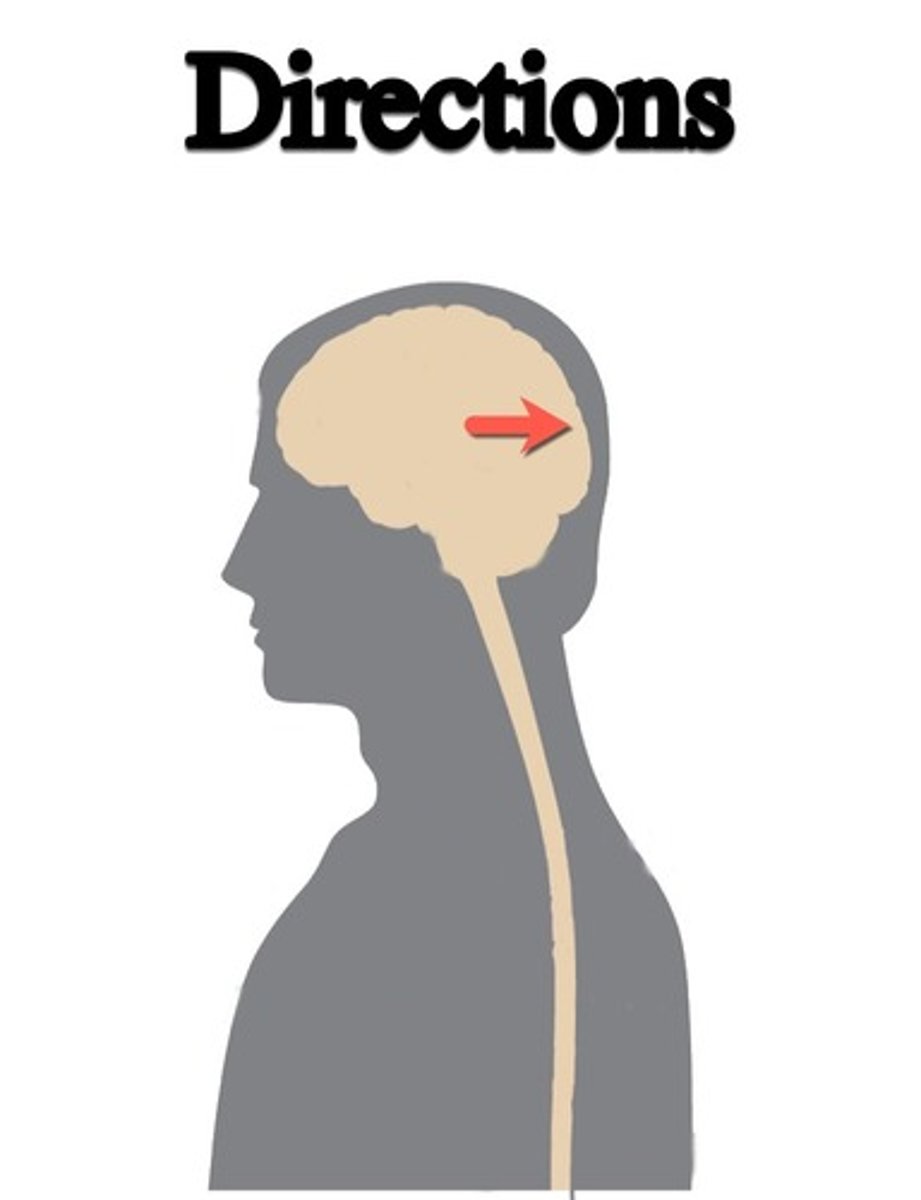
lateral (brain)
side of the brain
medial (brain)
toward the midline of the brain
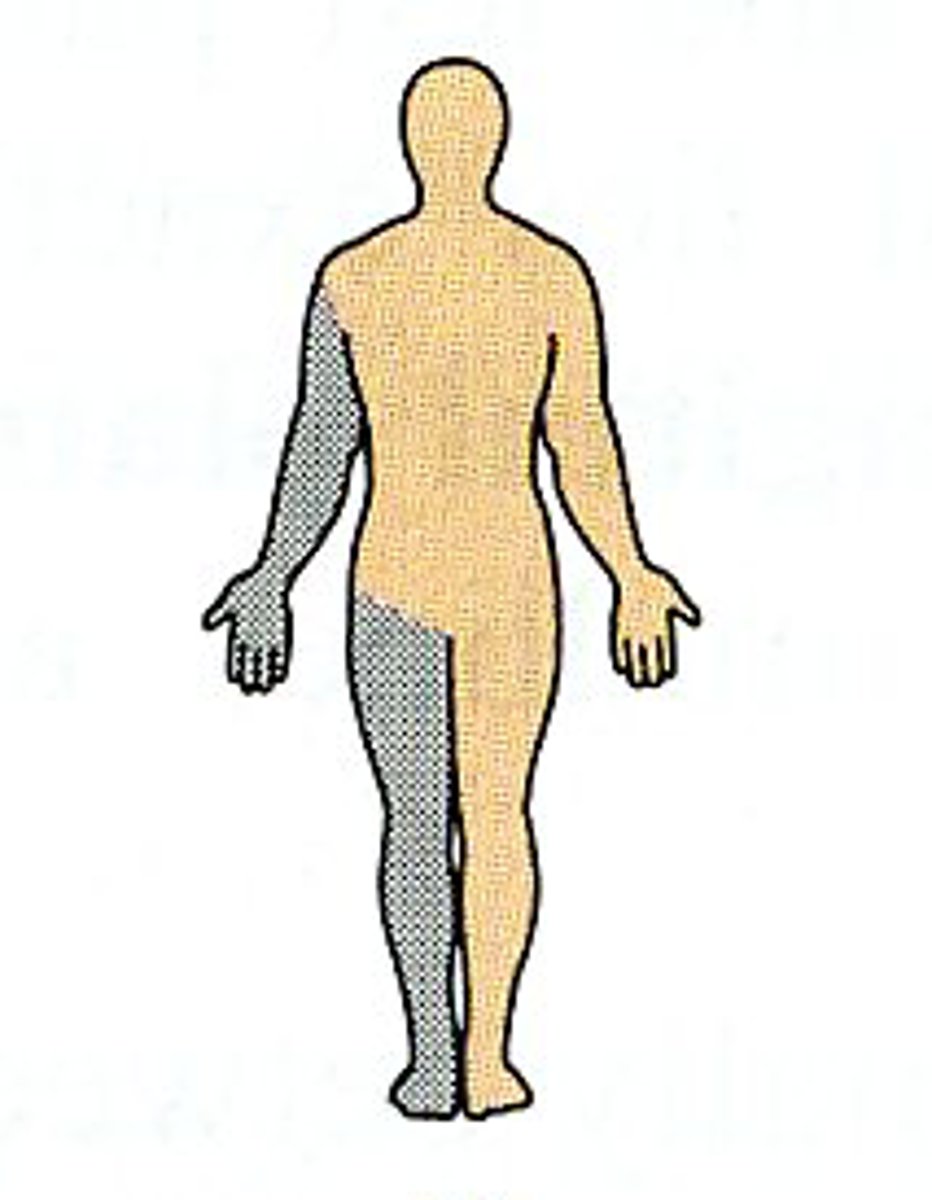
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
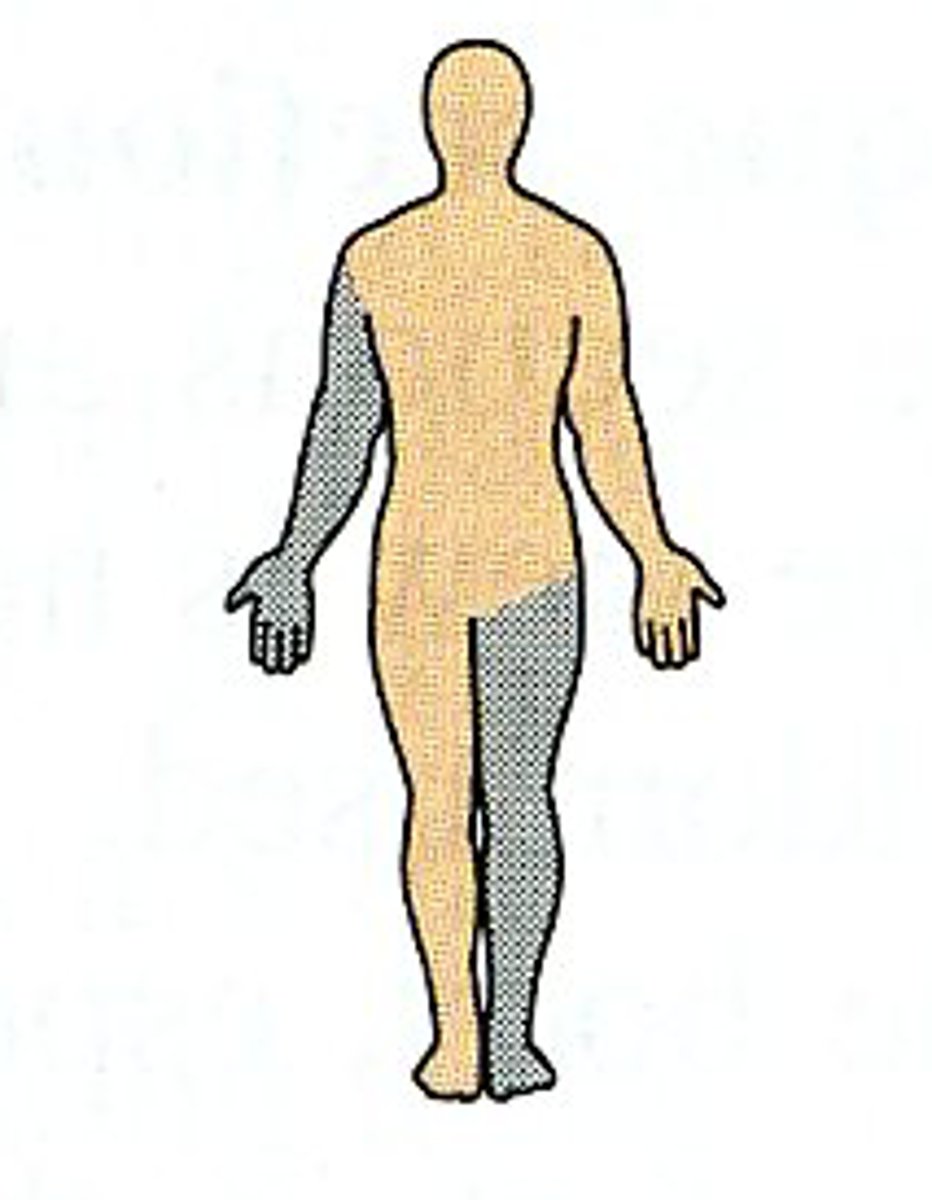
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
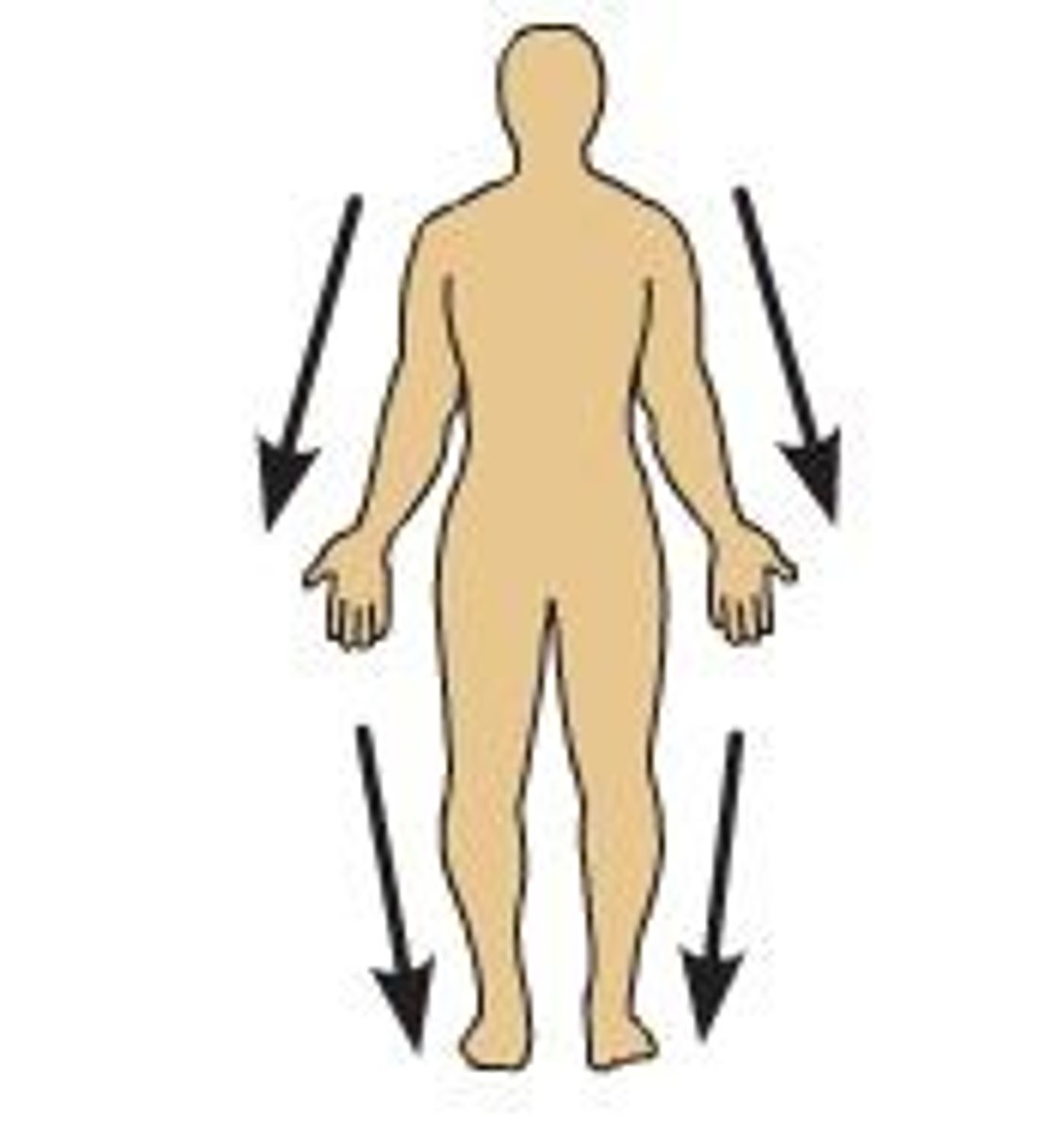
Distal
away from the point of attachment
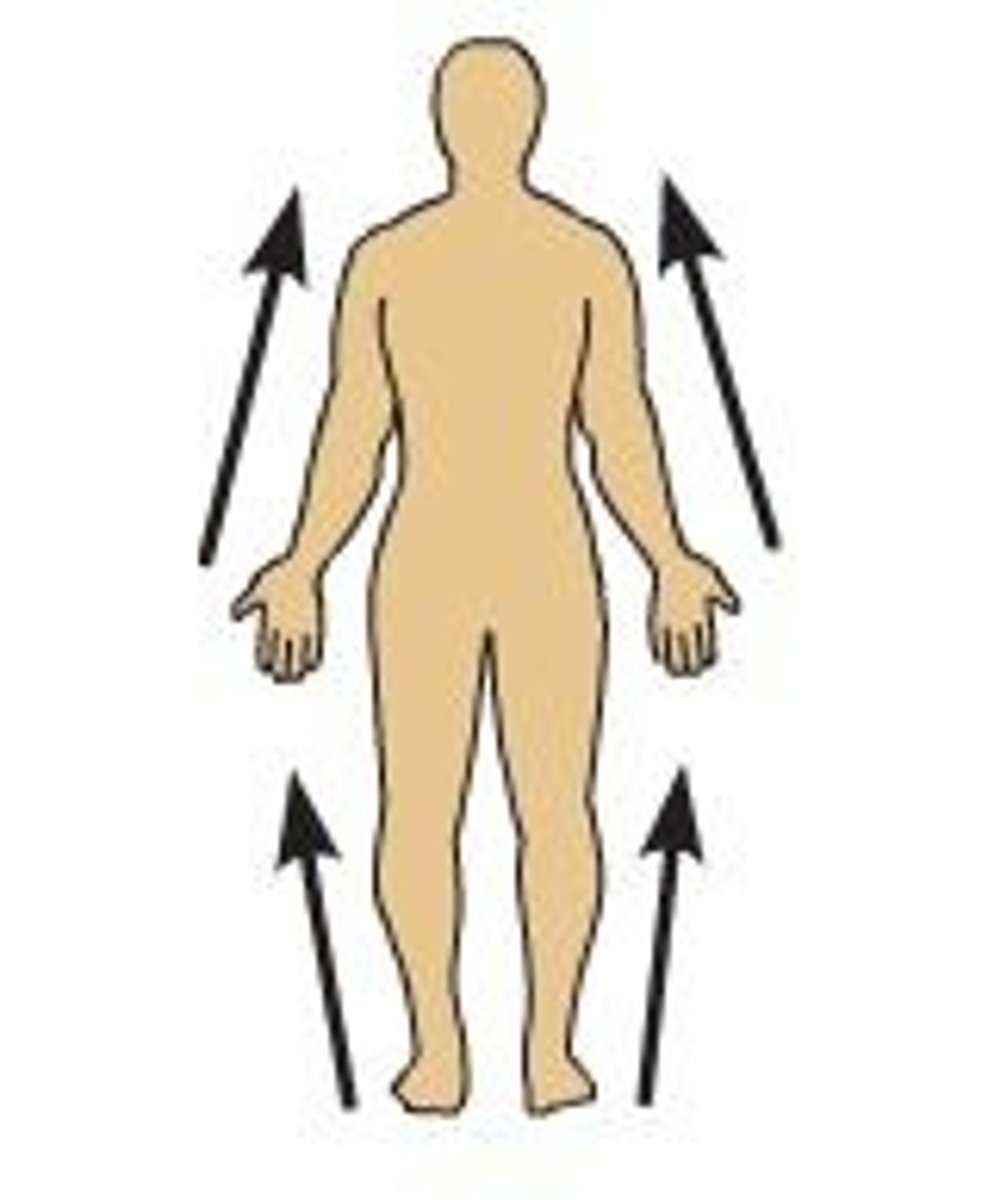
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
PNS
all parts of the nervous system found outside the skull and spinal column
CNS
brain and spinal cord
Sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteric
3 divisions of the autonomic nervous system
divisions of the PNS
somatic and autonomic
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter which heavily influences sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
ACh (acetylcholine)
neurotransmitter which heavily influences the parasympathetic nervous system
enteric nervous system
a division of the autonomic nervous system consisting of nerve cells embedded in the lining of the gastrointestinal system (not as important for us)
somatic nervous system
- Division of PNS
- controls voluntary movements
- consists of nerves from CNS to skeletal muscles
- Sensory input and motor output
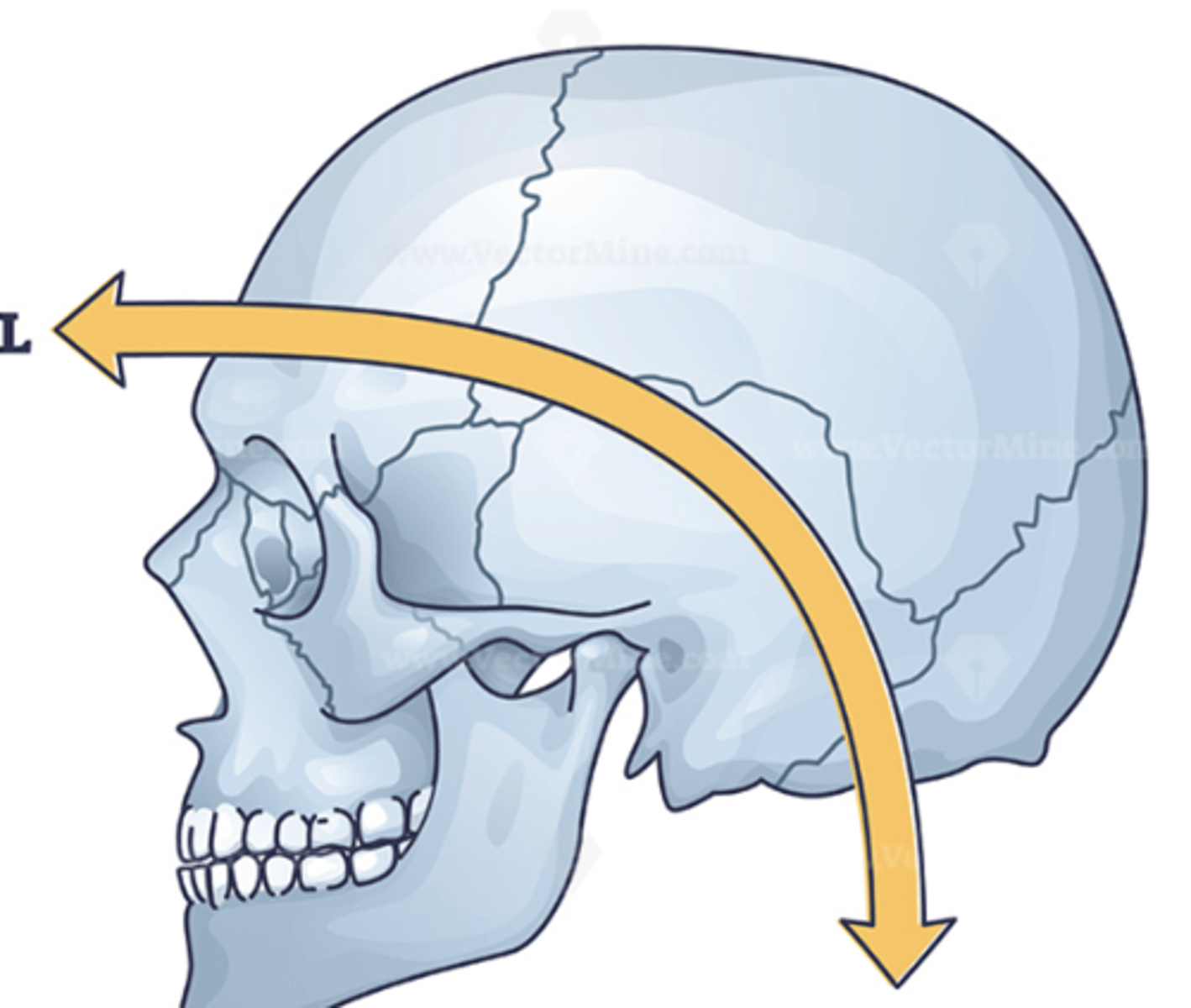
rostral
toward the forehead or nose
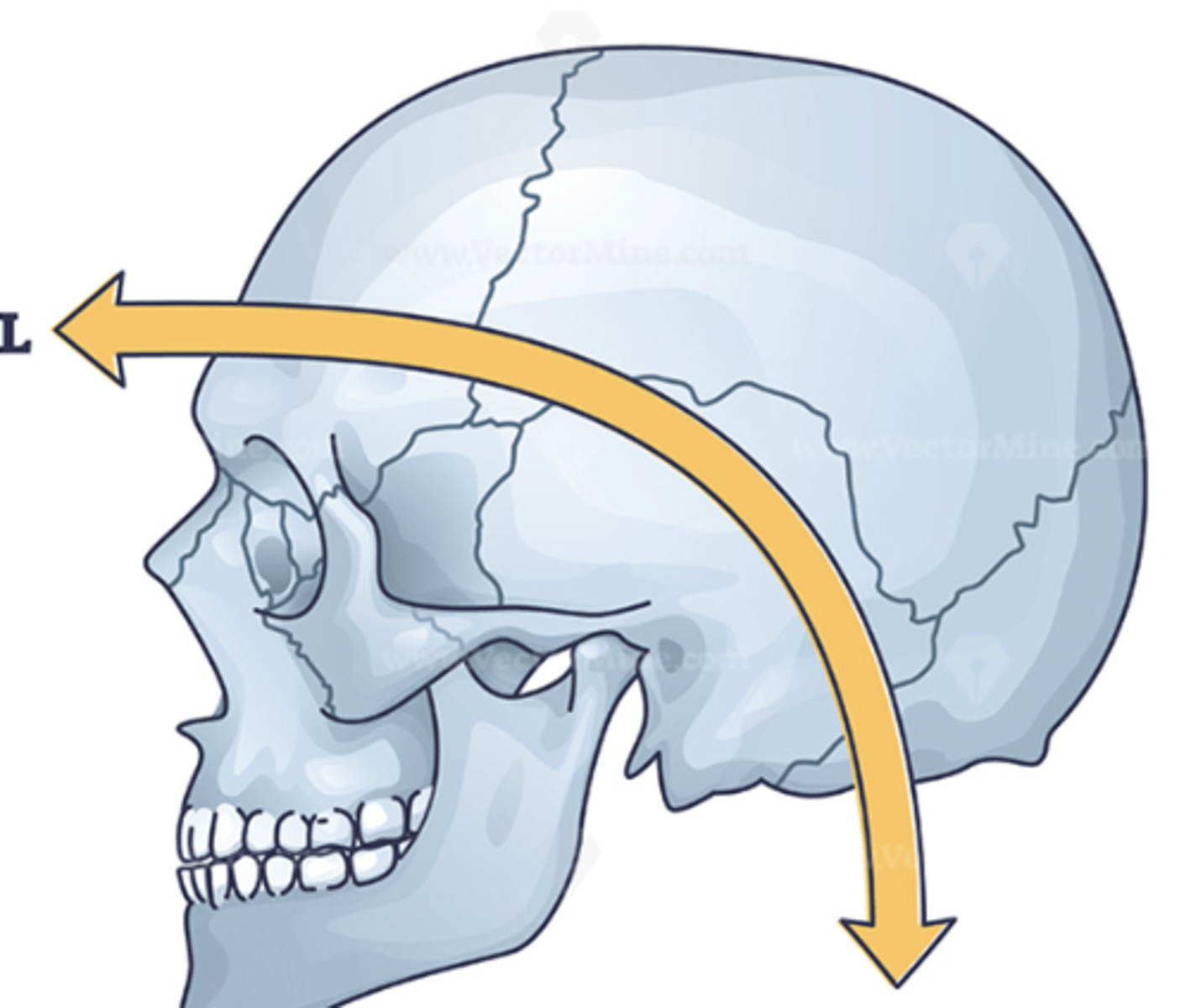
caudal
toward the tail
CNS
responsible for:
- senses
- initiating movement
- attention, cognition, thought, affect, mood
- other life essential functions (breathing, hunger)
automatic, complex
As you move from tail (caudal) to nose (rostal) of the CNS, functions carried out generally become less ____________ and more ____________
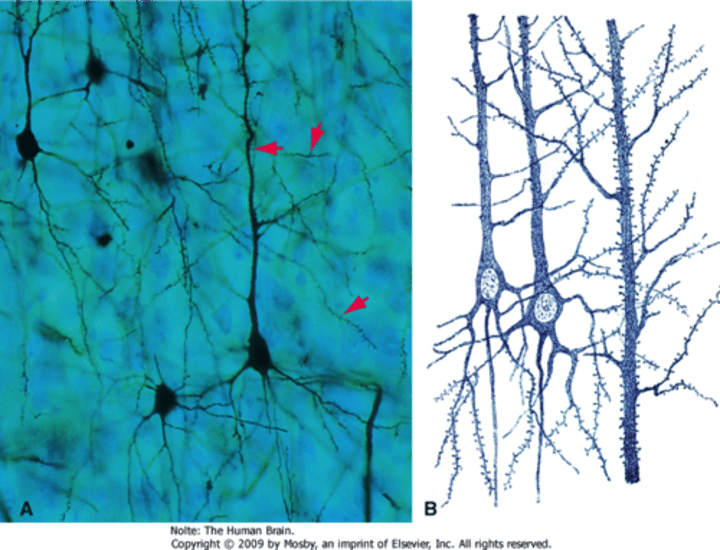
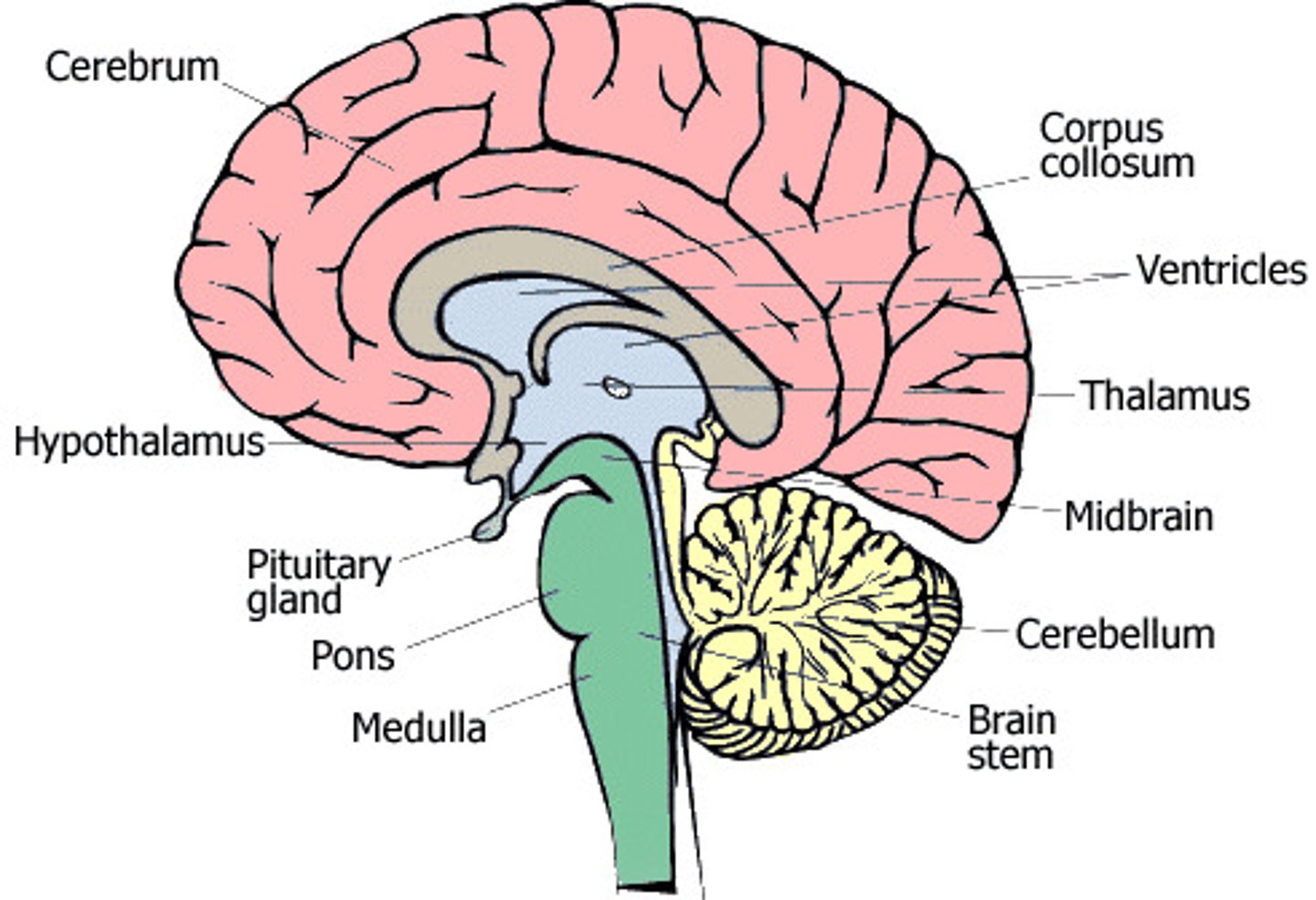
cerebral cortex
outer region of the cerebrum, containing sheets of nerve cells; gray matter of the brain

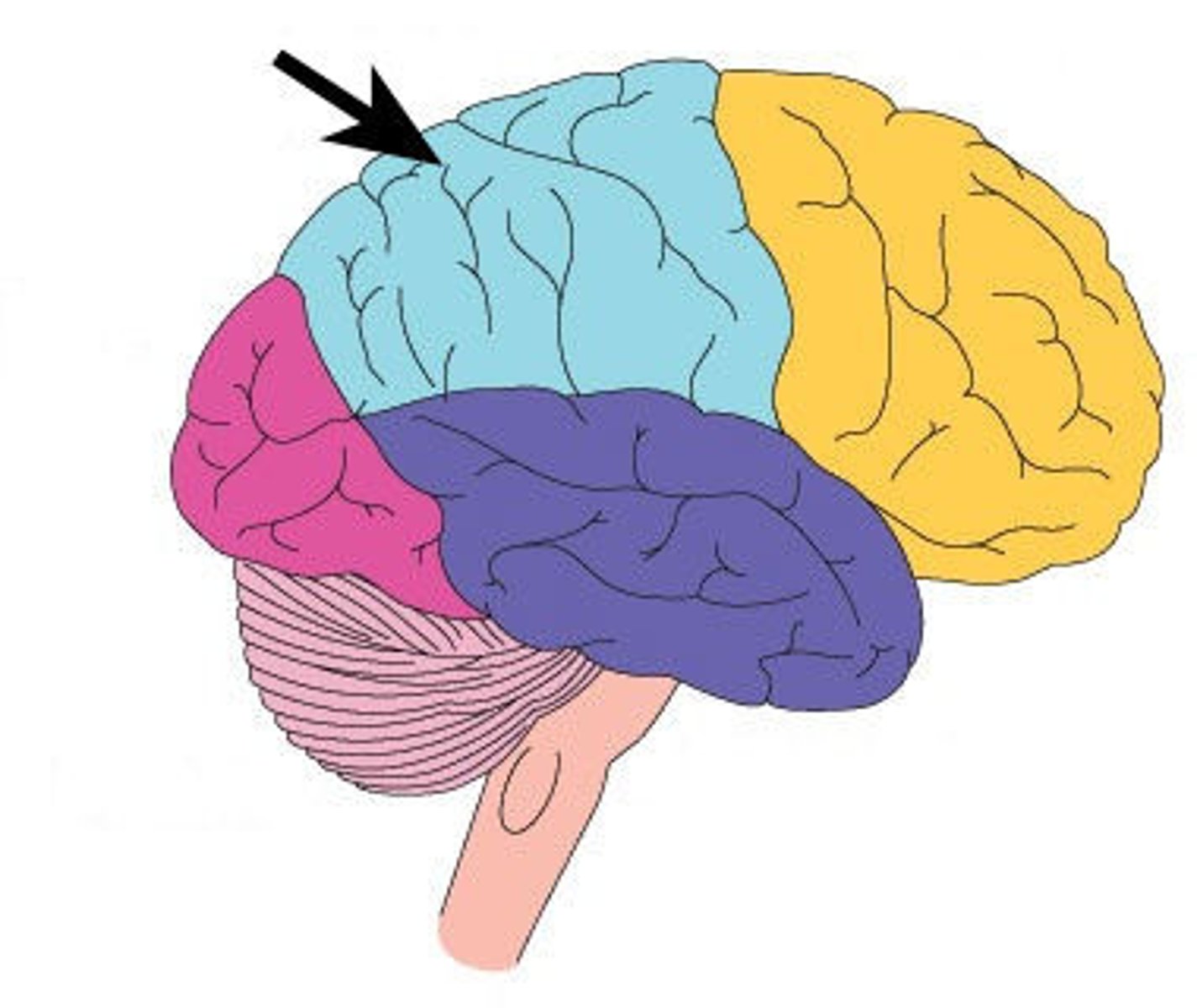
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
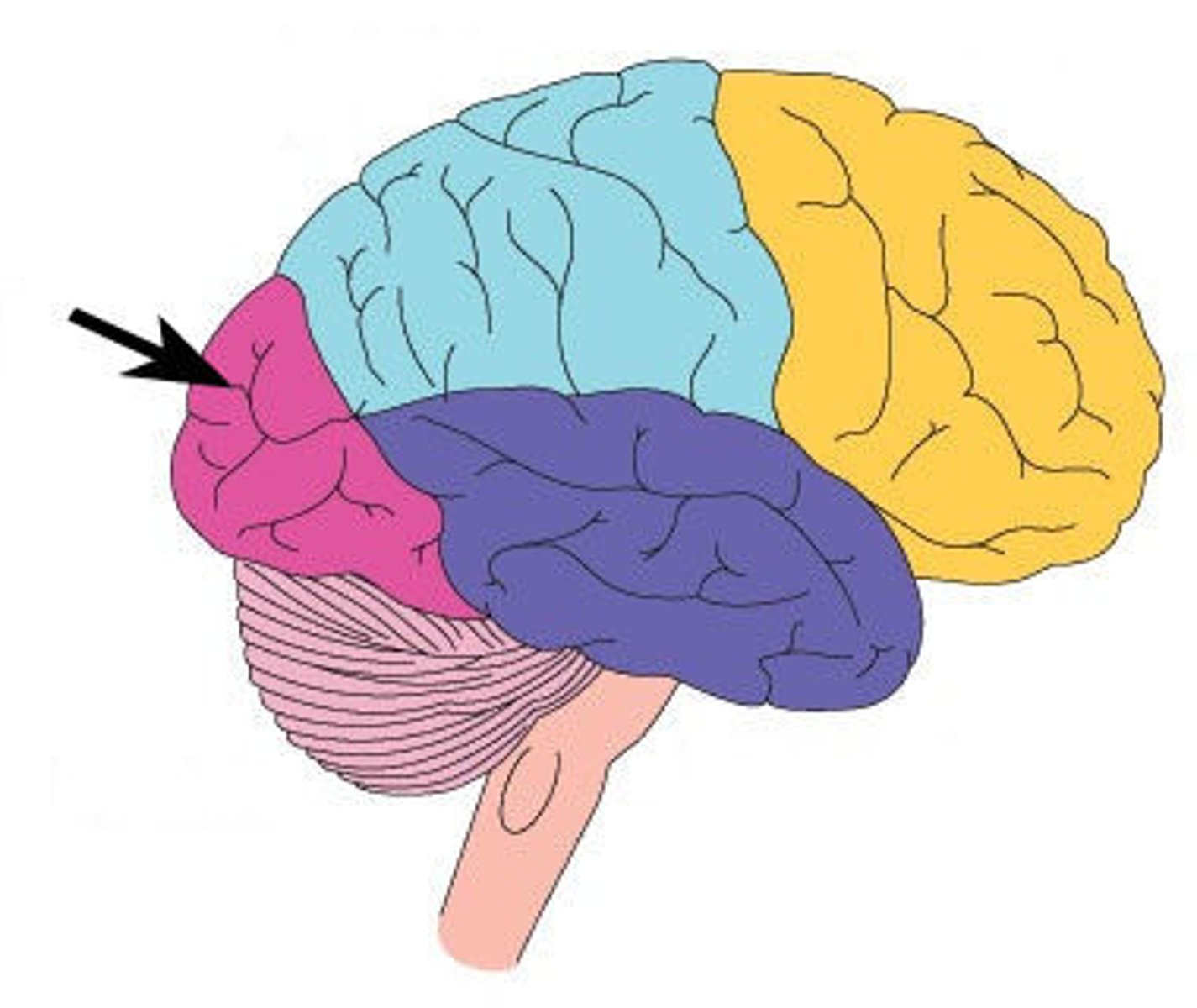
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
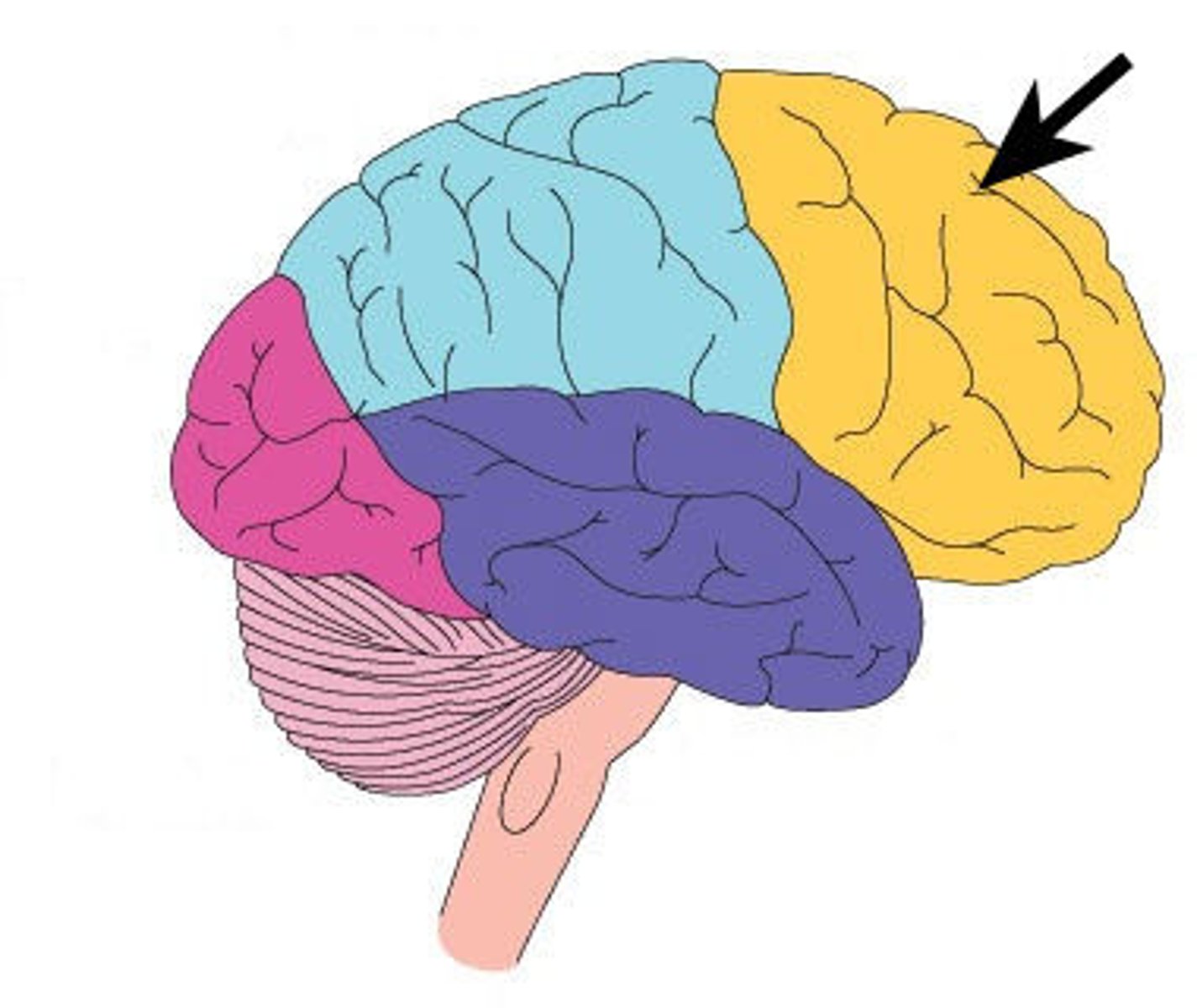
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
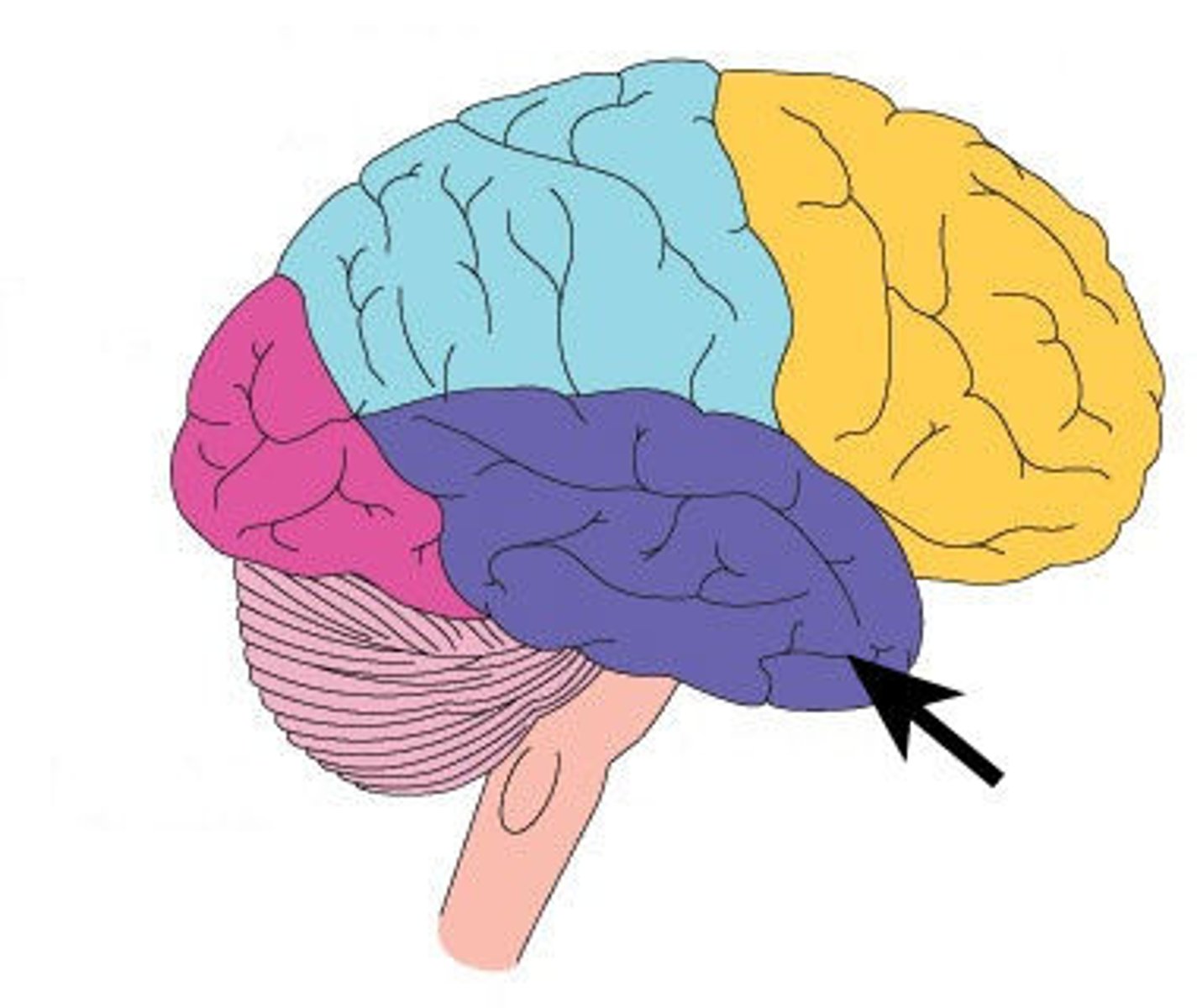
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
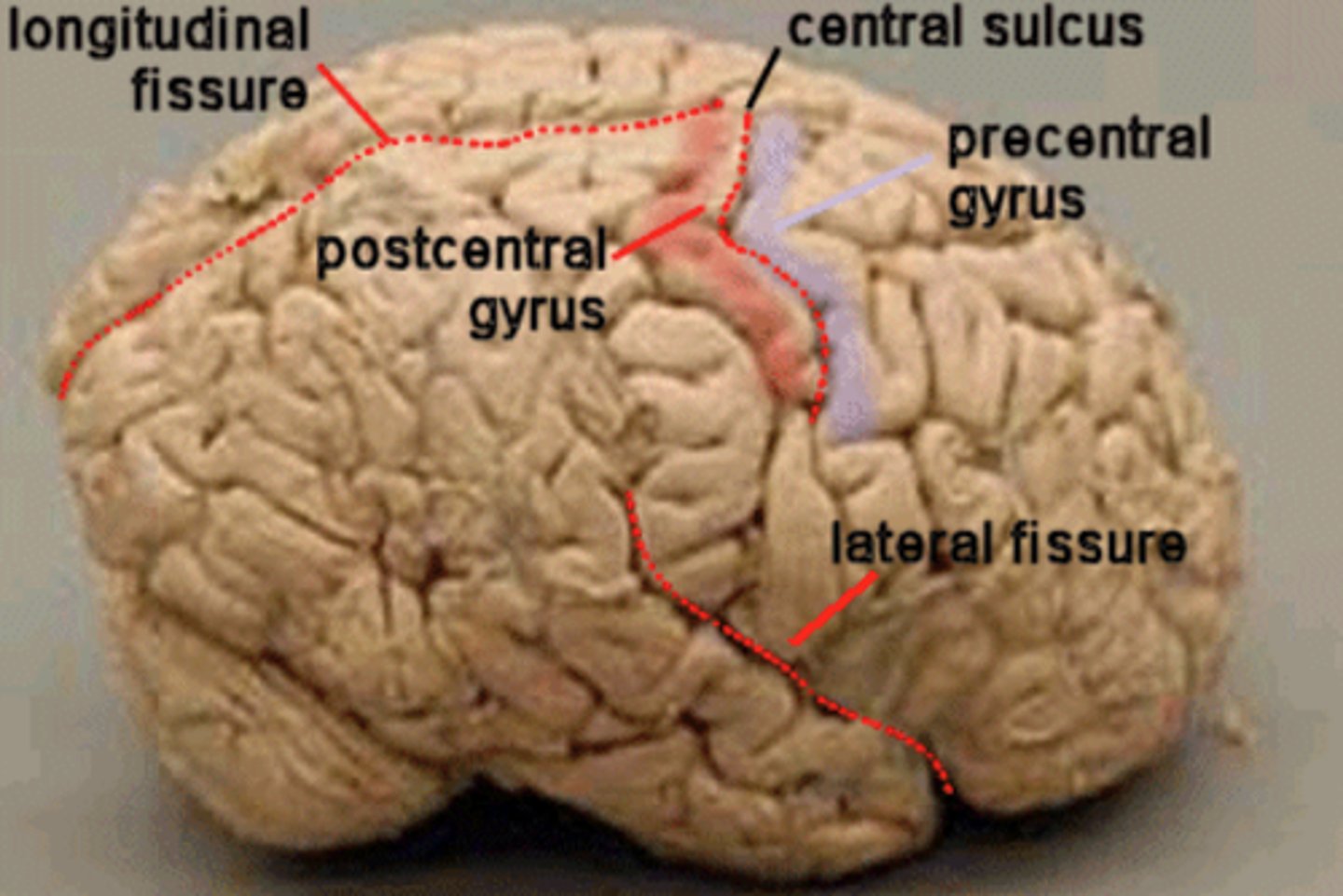
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
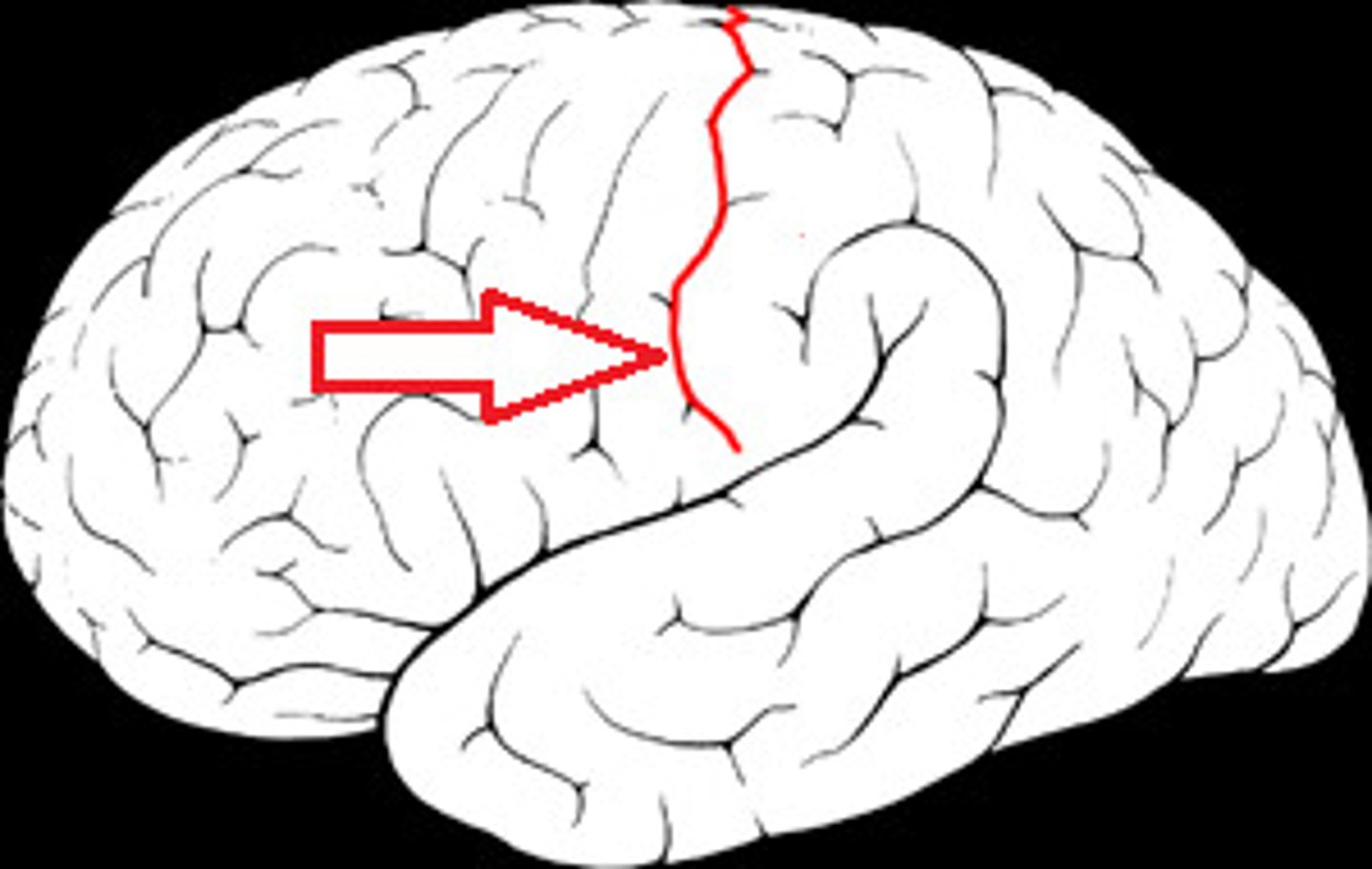
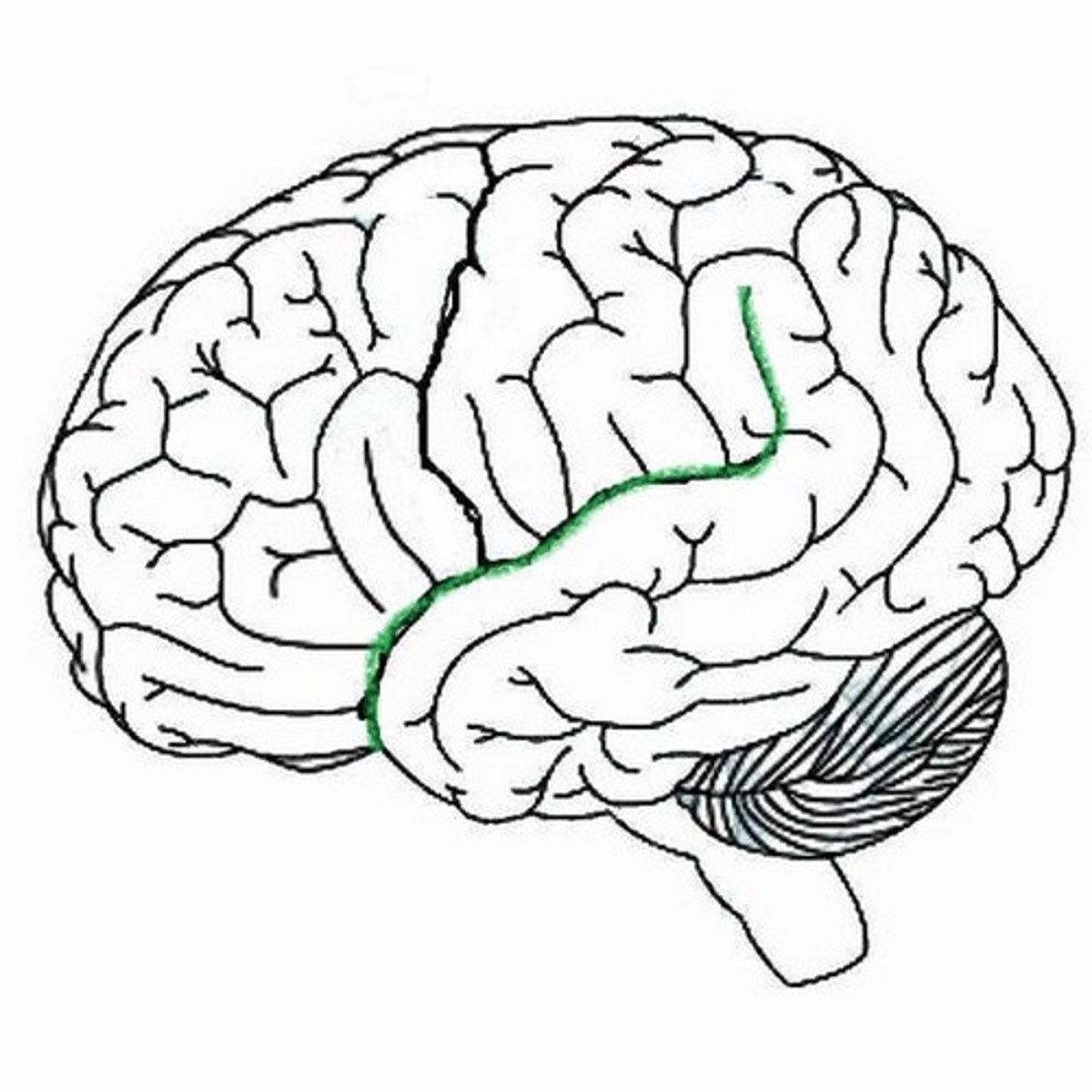
Sylvian fissure
Separates the temporal from the frontal lobe, and the temporal from the parietal lobe
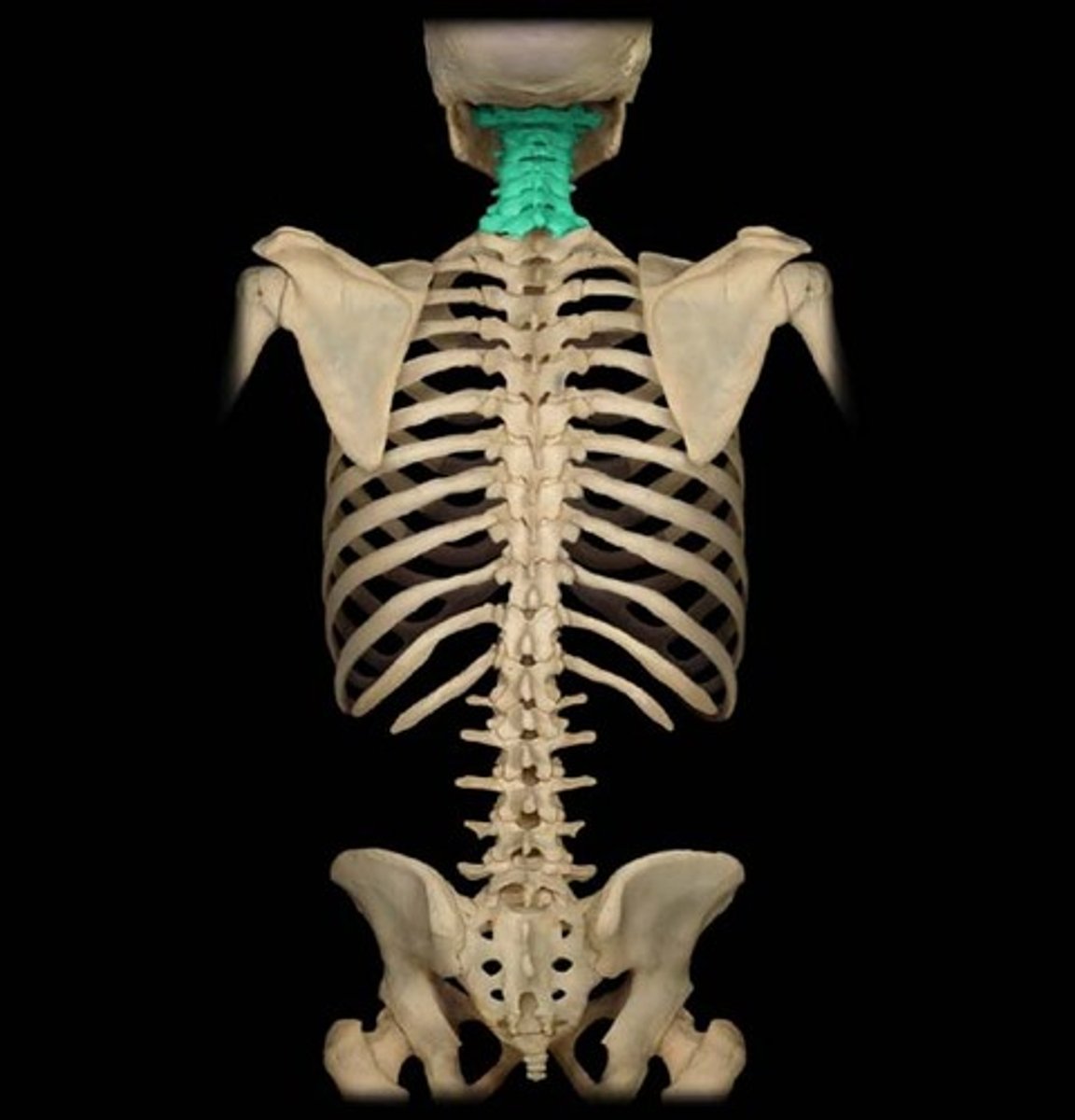
cervical
region in the spinal cord which controls sensation and movement in the neck
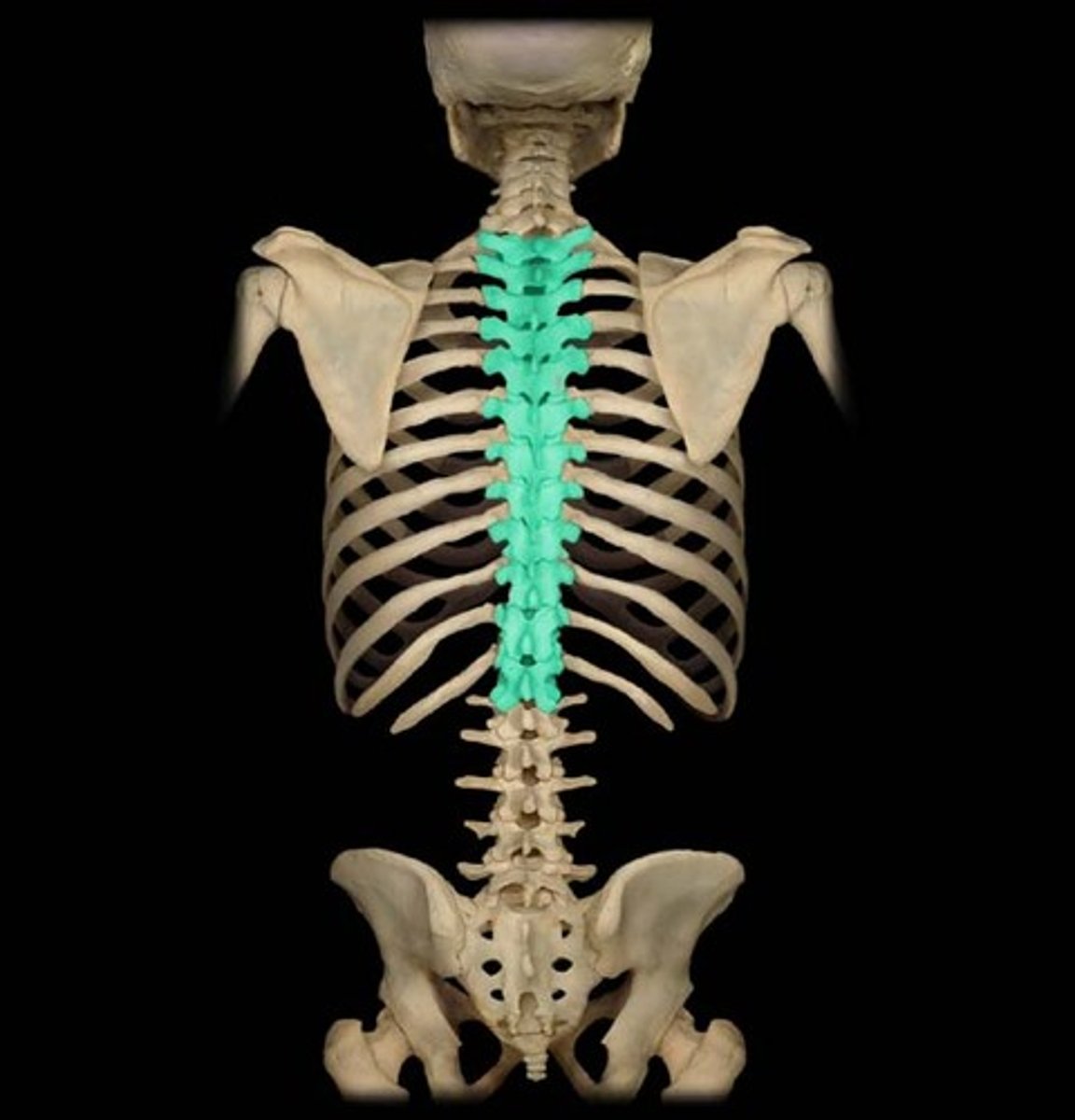
thoracic
region in the spinal cord which controls sensation and movement in the trunk
lumbar
region in the spinal cord which controls sensation and movement in the lower back
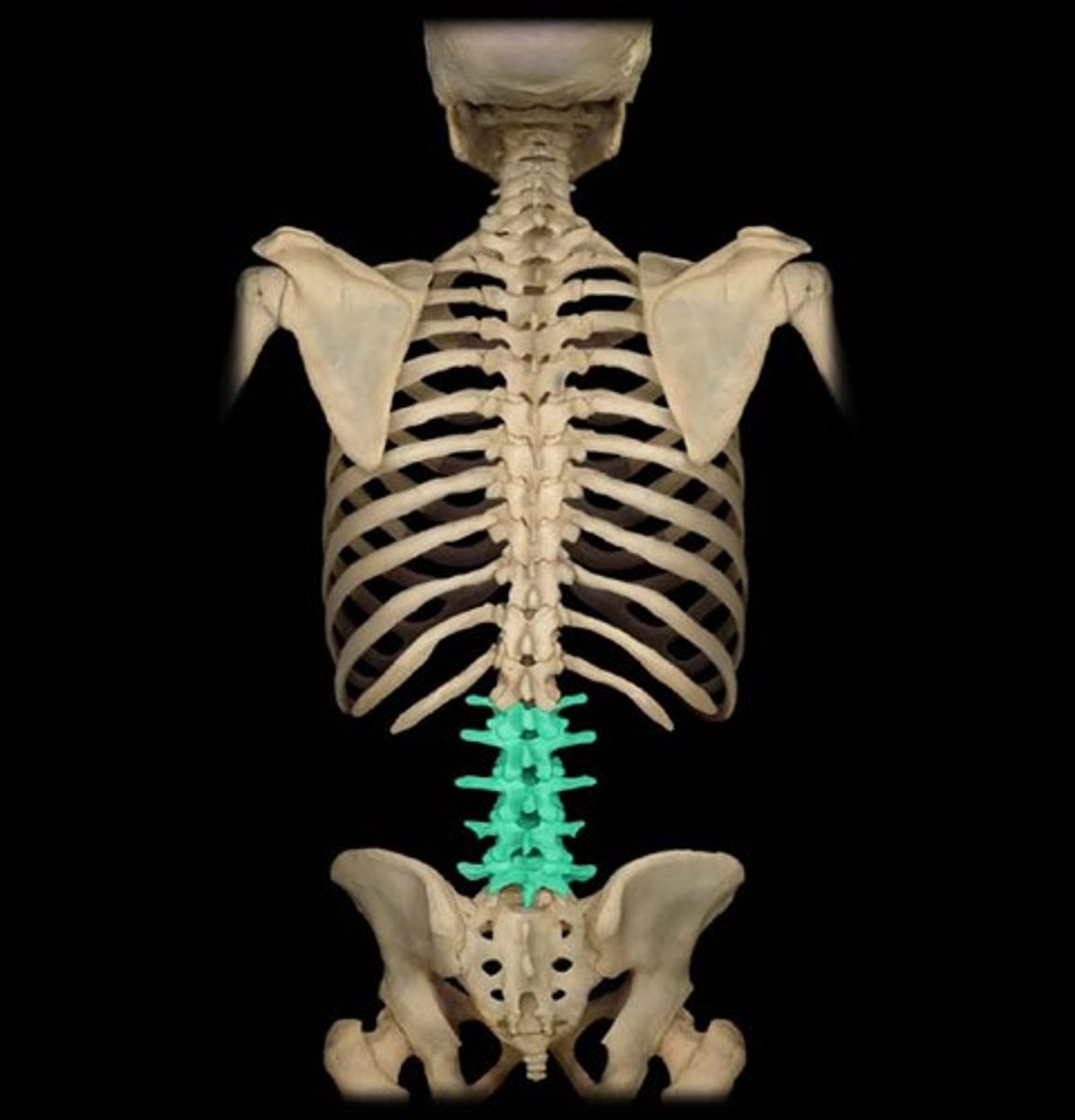
sacral
region in the spinal cord which controls sensation and movement in the pelvis
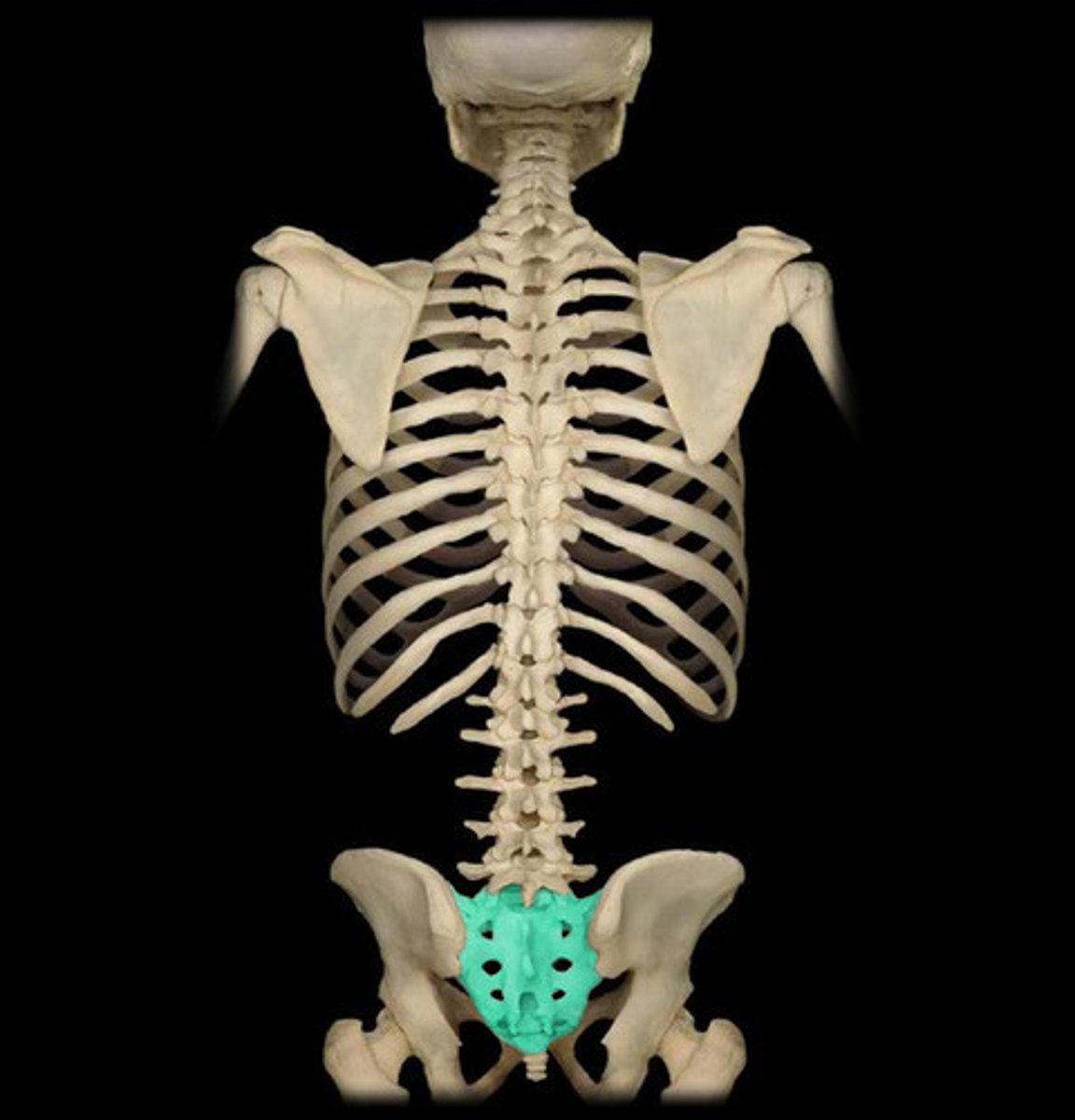
coccygea
region in the spinal cord which controls sensation and movement in the bottom
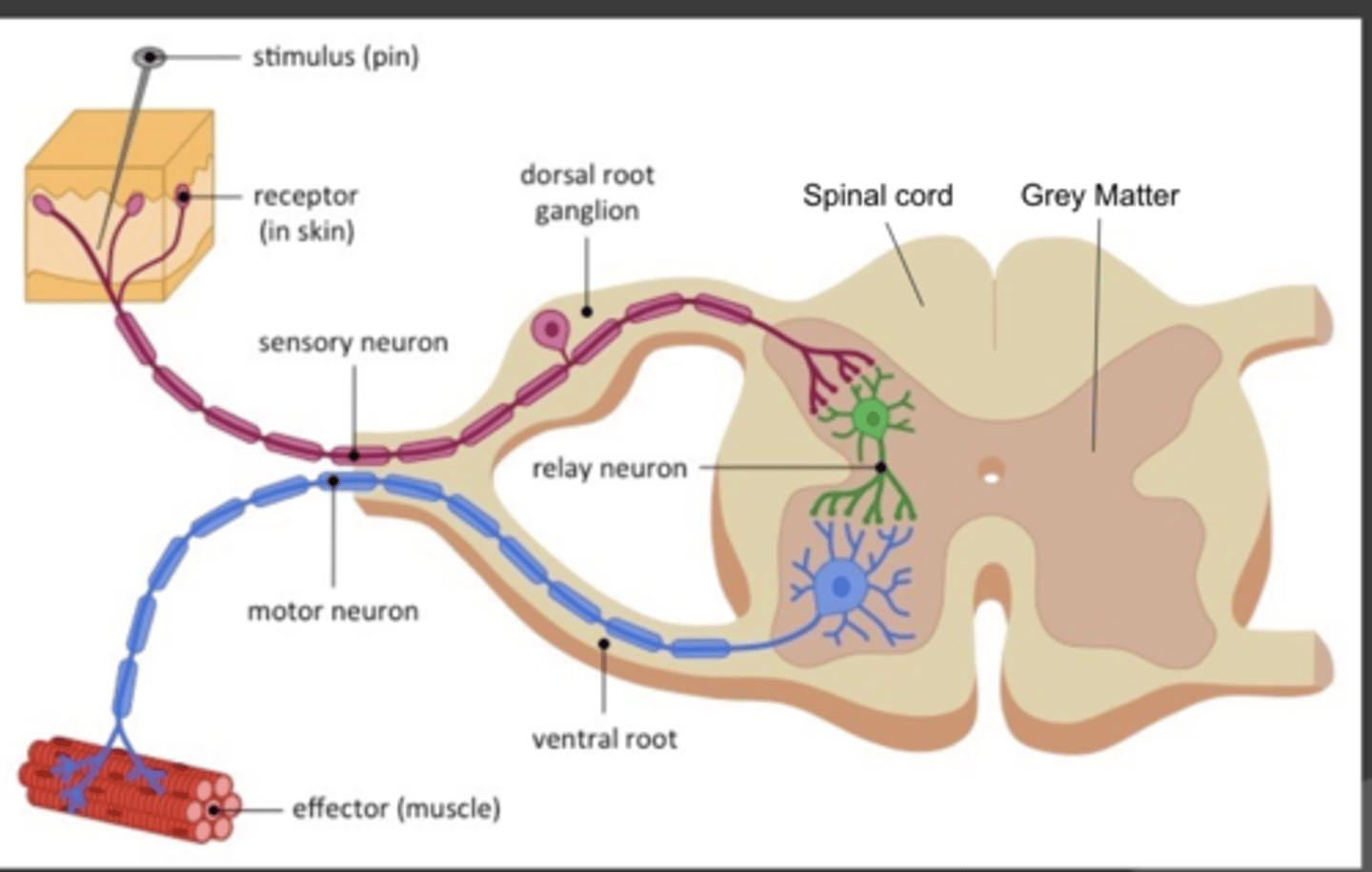
Doral root ganglion
- sensory input in spinal reflex
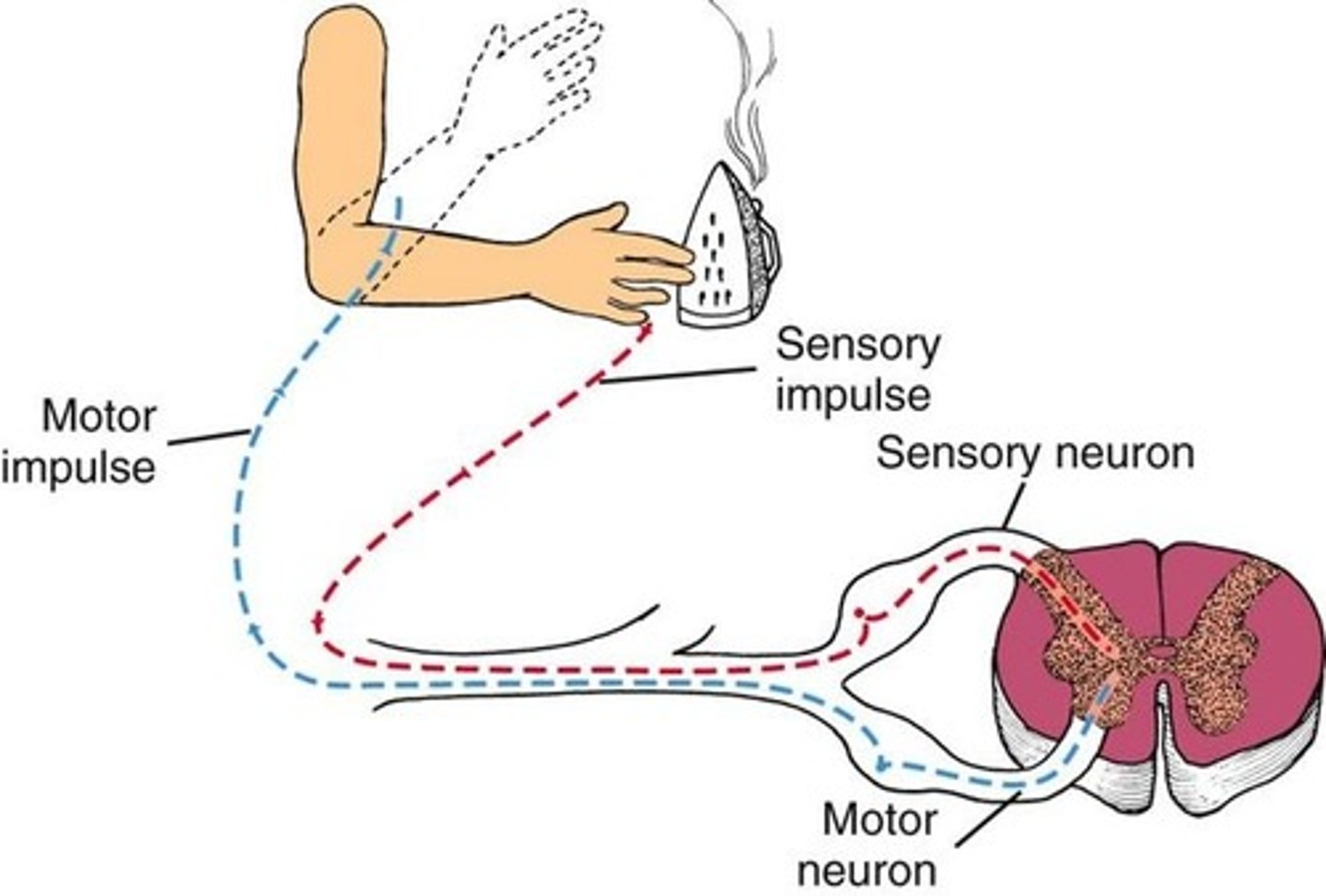
ventral root ganglion (spinal cord)
- motor output neurons in spinal reflex
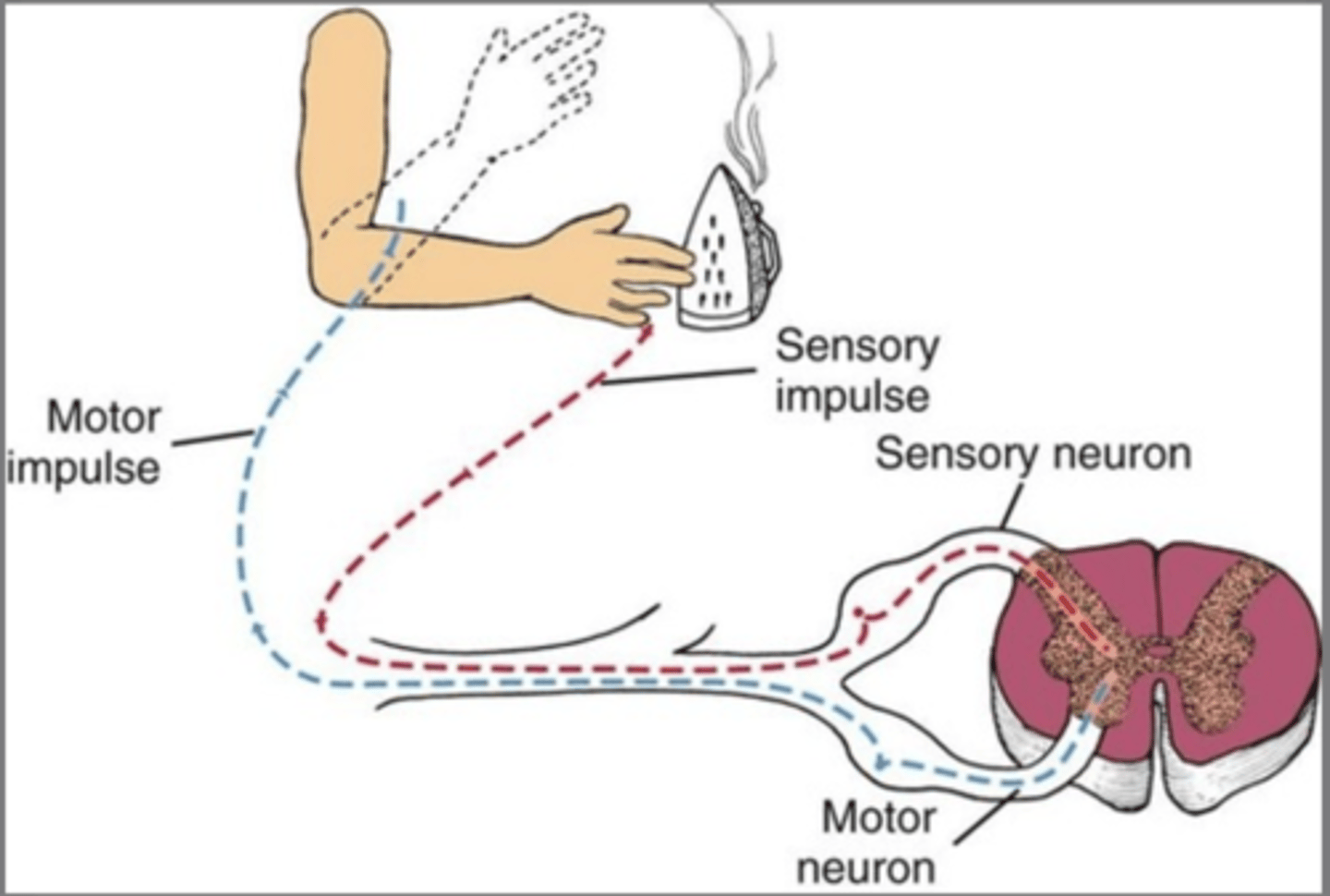
relay neuron
the nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons
sulcus (sulci)
a groove in the cerebral cortex
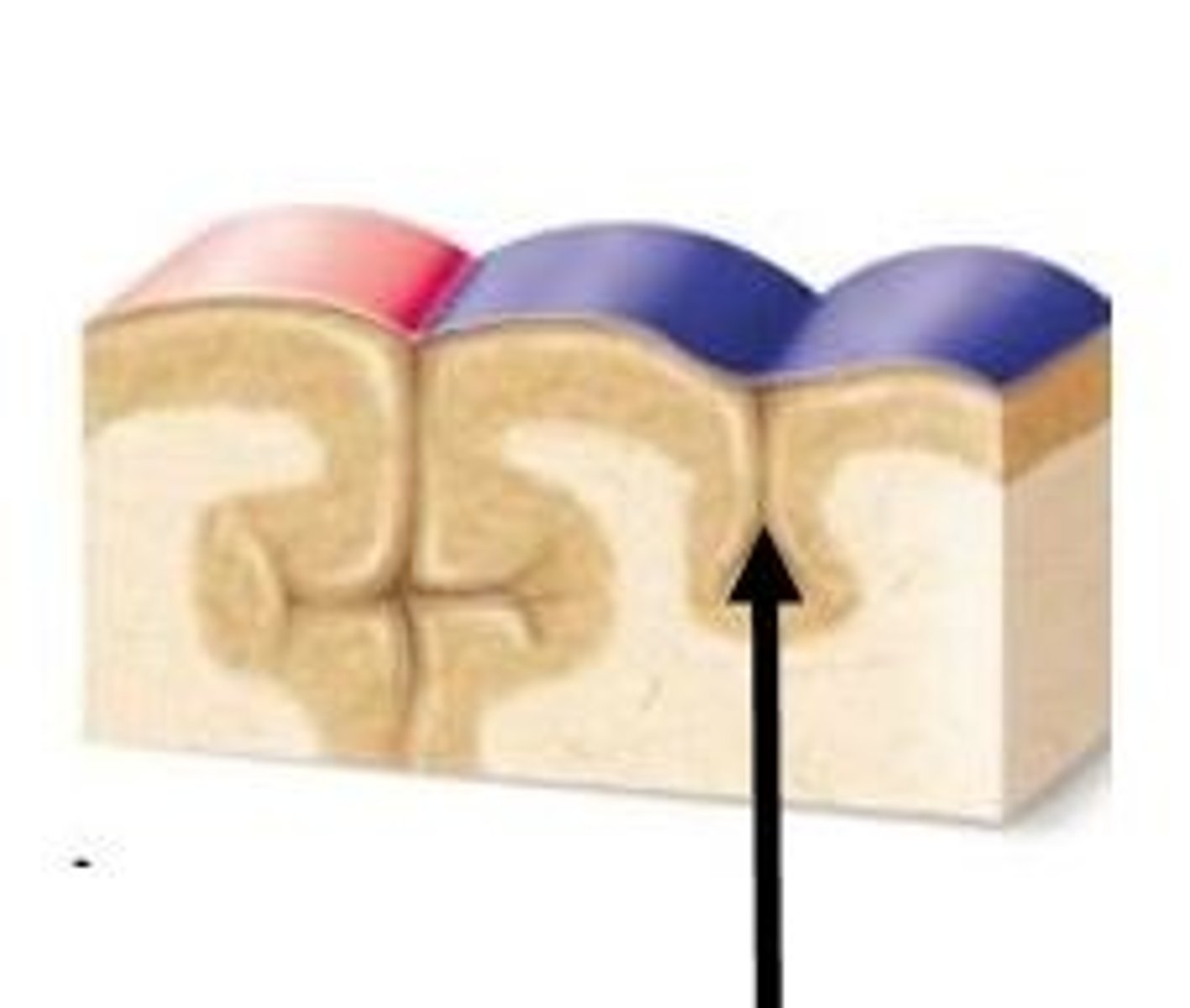
gyrus (gyri)
rounded elevation on the cerebral cortex
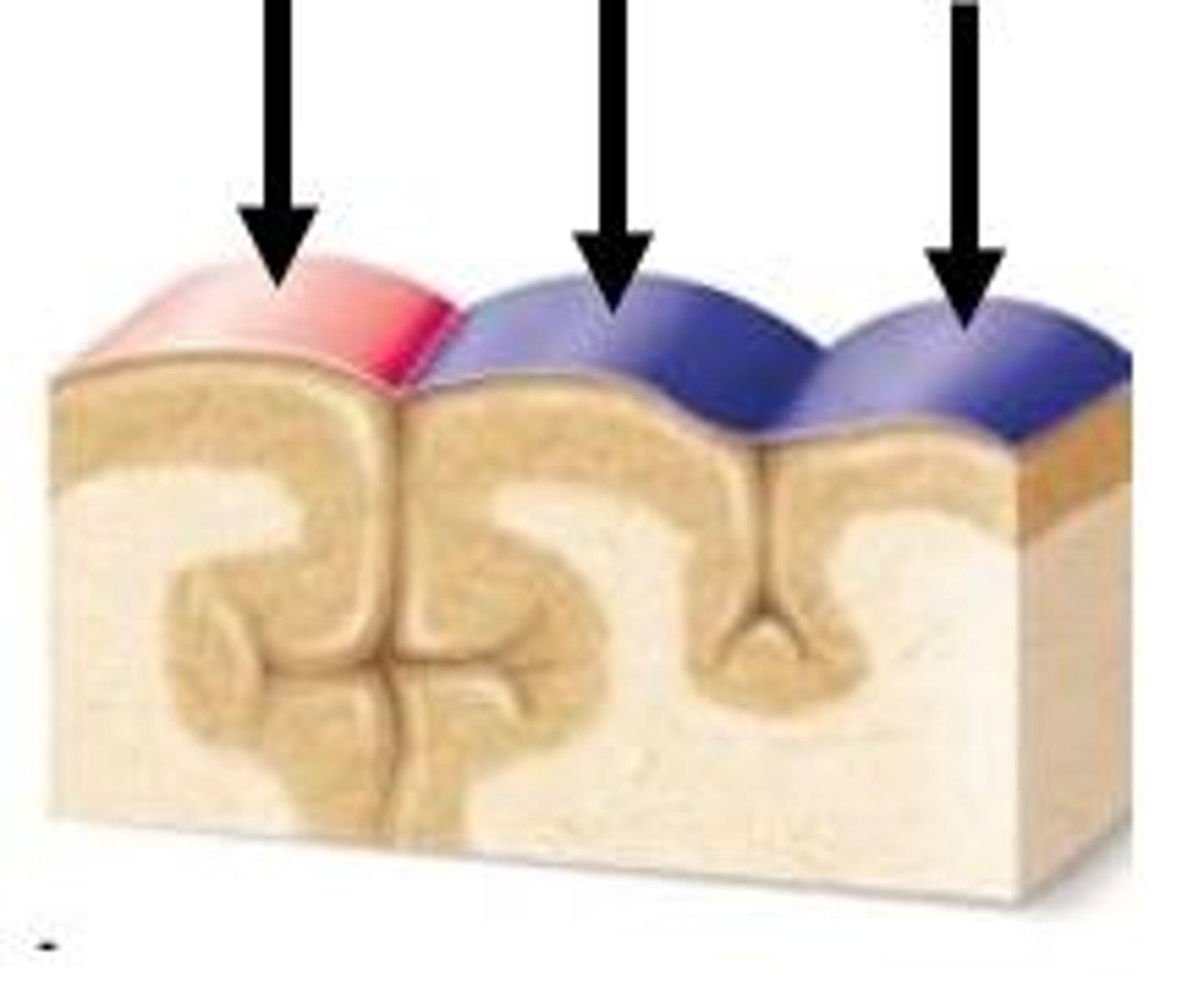
surface area, size
going up the evolutionary ladder, ___________ and _____________ of the brain increases
cell bodies, dendrites, myelin
grey matter consists of __________ and __________, which lack ___________
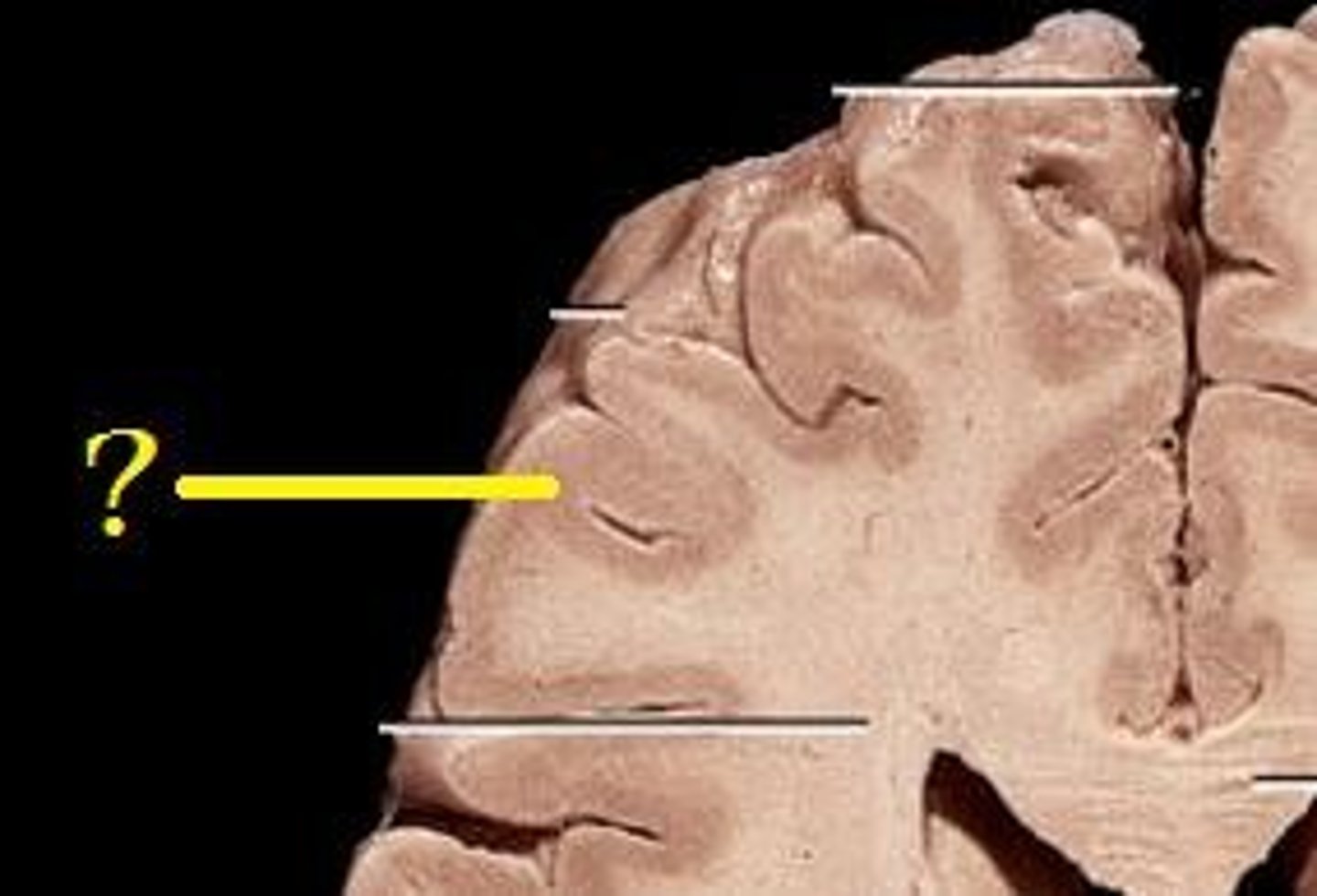
axons, myelin
white matter consists of _____________ wrapped in ________________
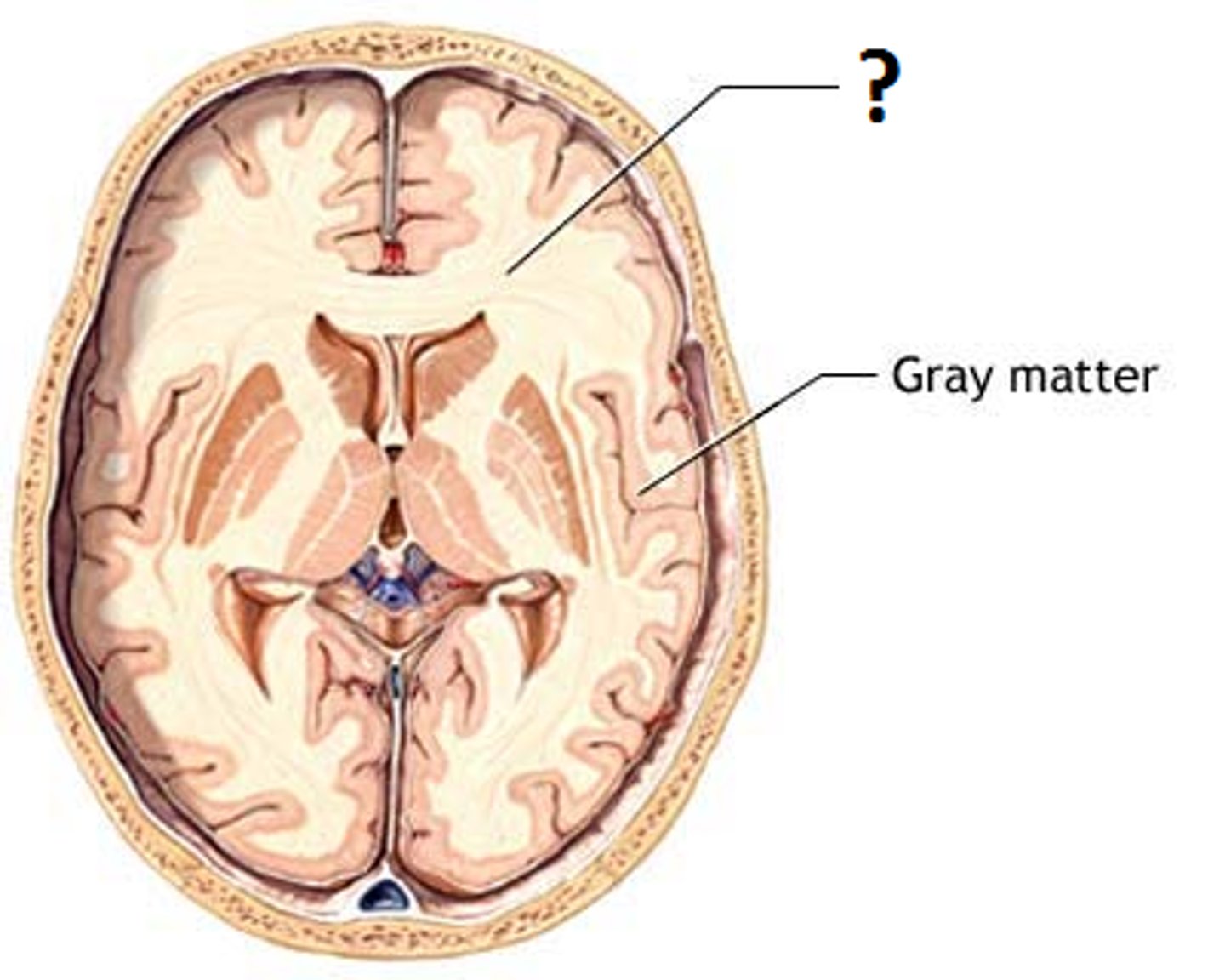
axon tracts
- group of axons traveling together
- in white matter
- cortical and subcortical regions communicate with each other using these
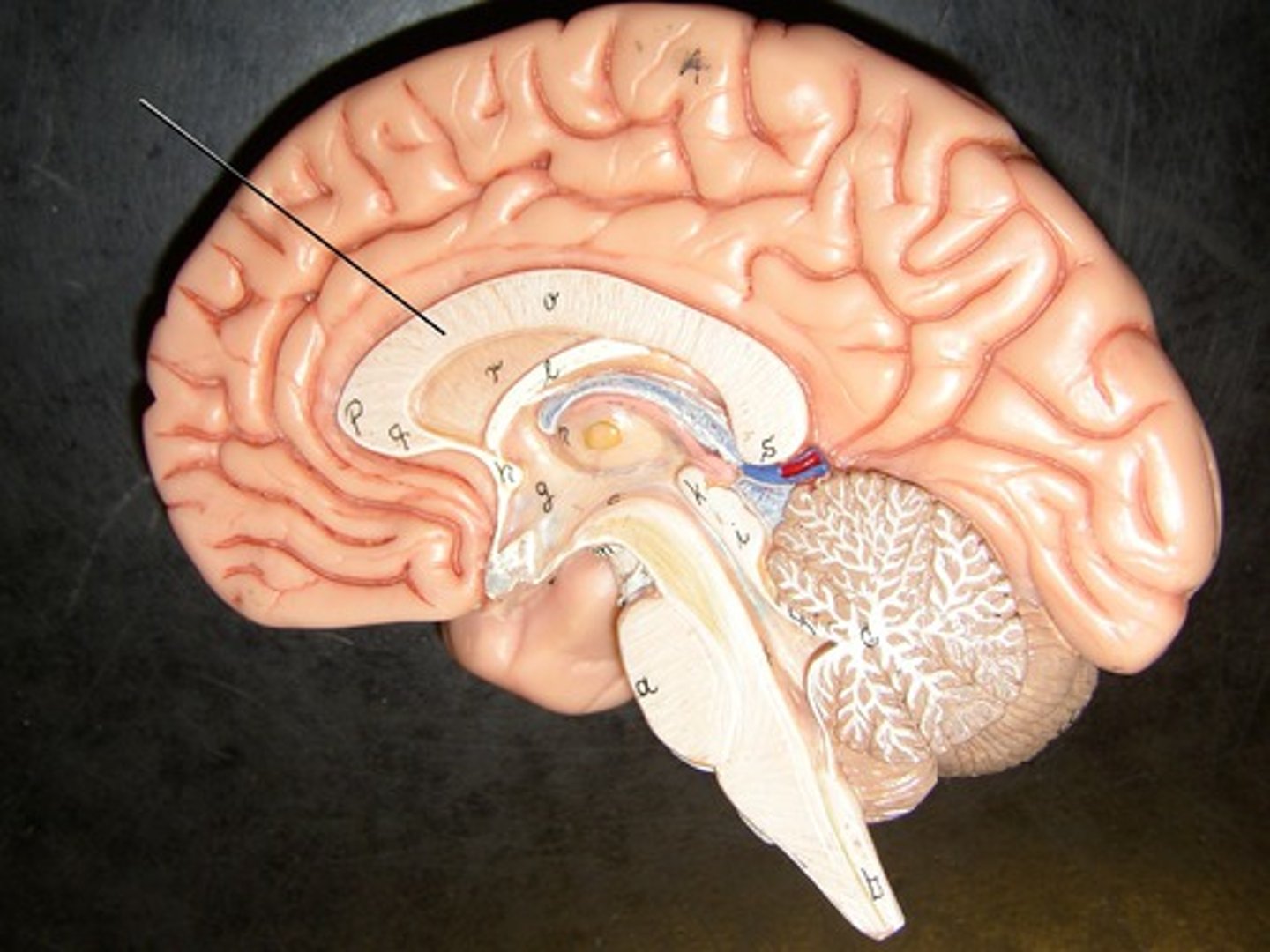
corpus collosum
axon tract that joins the two hemispheres
sensory, motor, associative
Cortical regions are divided into ____________, ___________, and ______________ processing areas
sensory cortex
involved in processing sensory input. receive strong input from sensory organs
- primary sensory cortex
- visual cortex
- auditory cortex
motor cortex
involved in driving movements or generating motor responses. makes strong connection to the spinal cord
- primary motor cortex
associative cortex
involved in cognitive operations that are intermediate between sensing stimuli and acting upon them
- parietal lobe
- temporal lobe
- prefrontal cortex
olfactory bulb
the brain center for smell, located below the frontal lobes
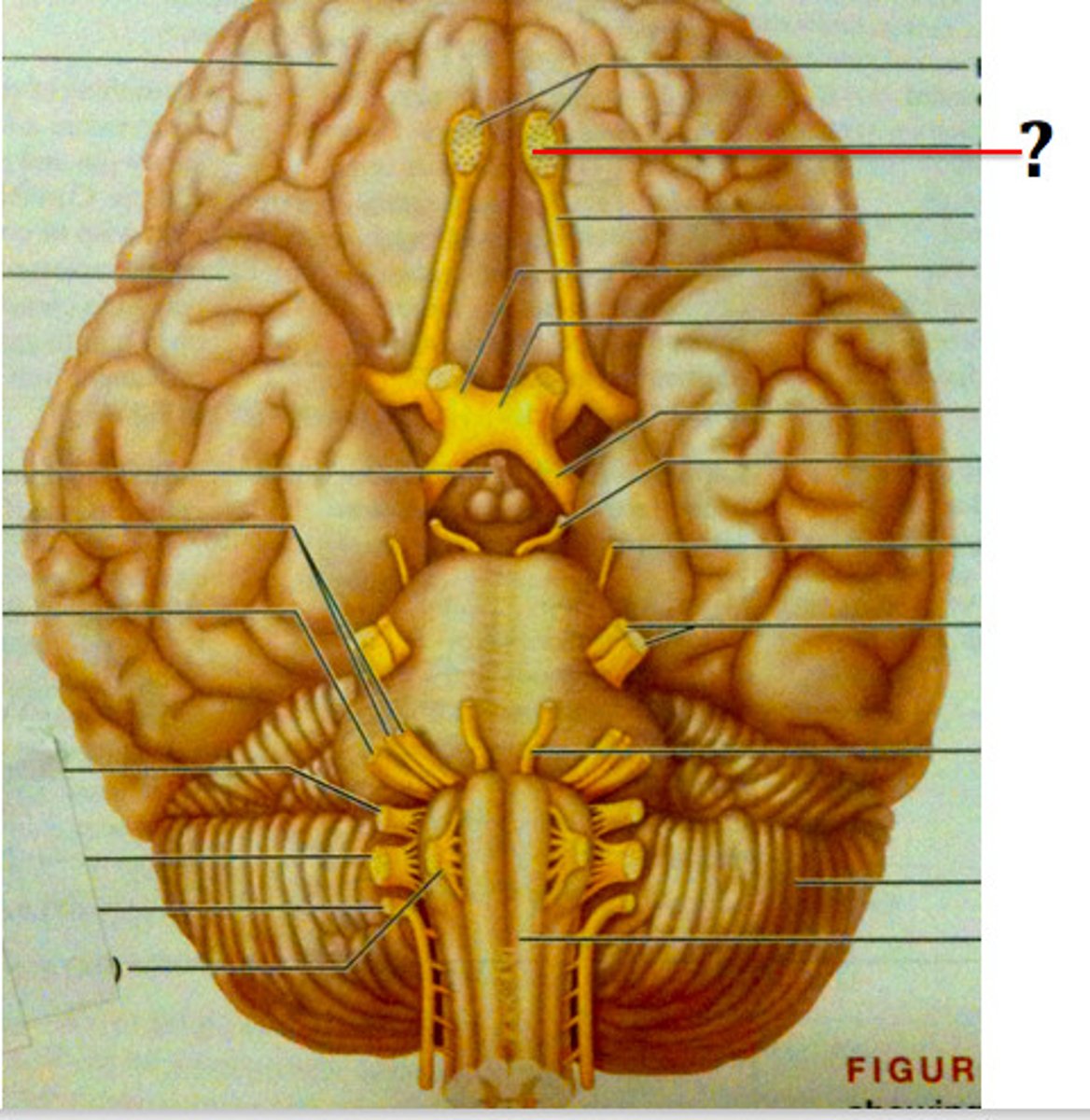
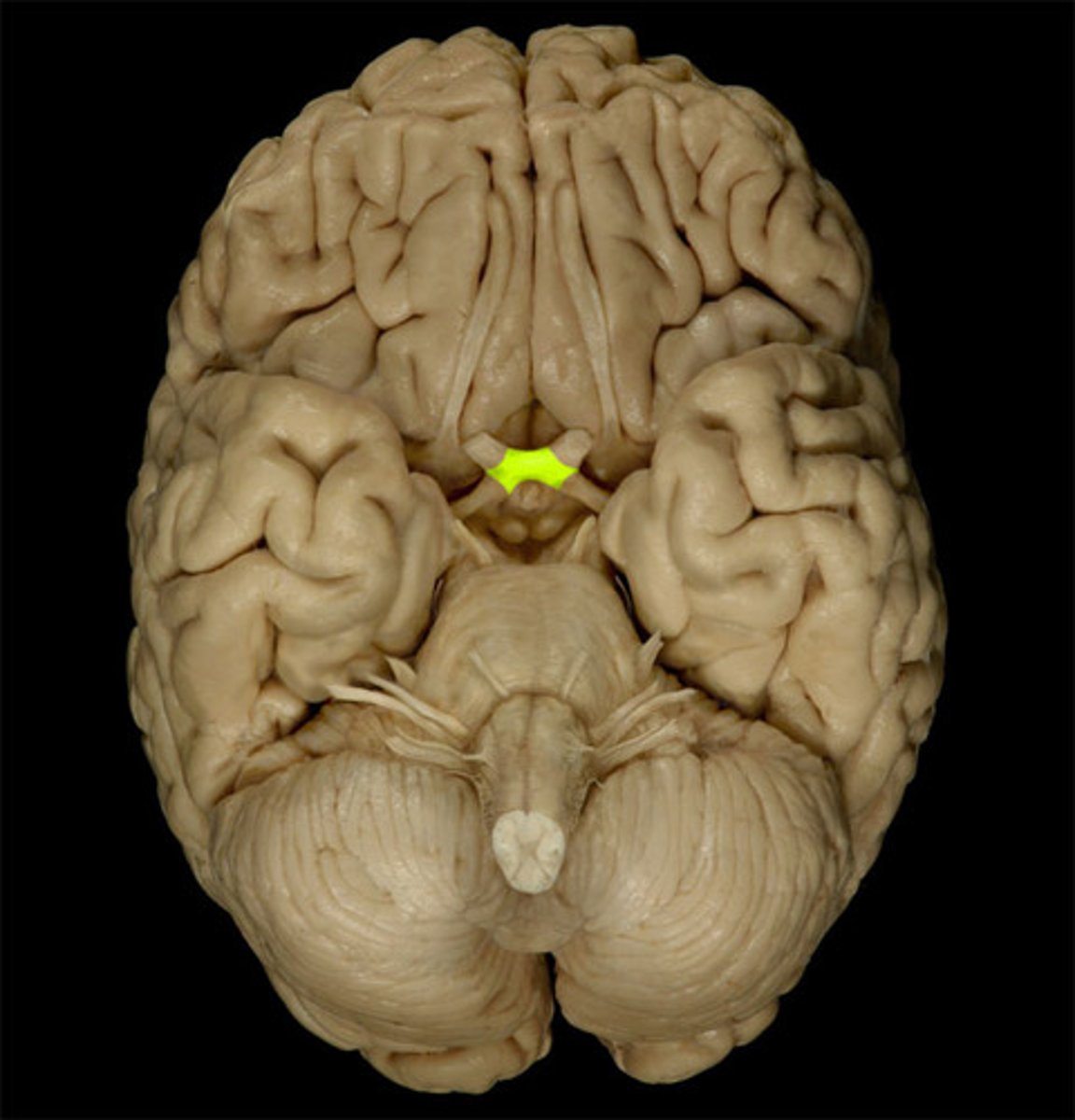
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain