Muscular System: Key Concepts, Vocabulary, and Microscopic Anatomy
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Origin
The muscle attachment that is not movable or is less movable than the insertion.
Insertion
The movable attachment of a muscle as opposed to its origin.
Epimysium
A connective tissue that wraps around the entire muscle.
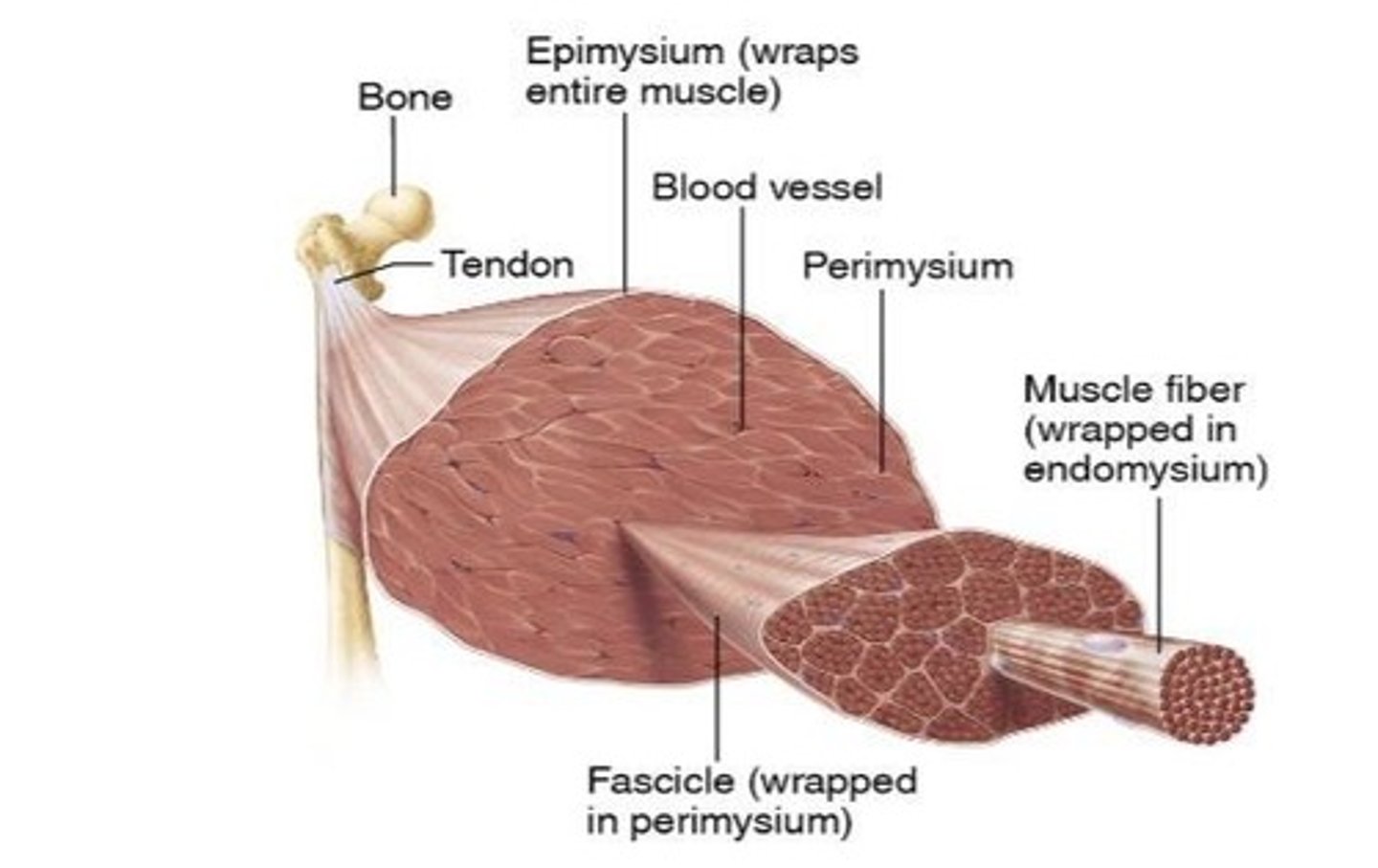
Perimysium
The connective tissue that surrounds individual fascicles within a muscle.
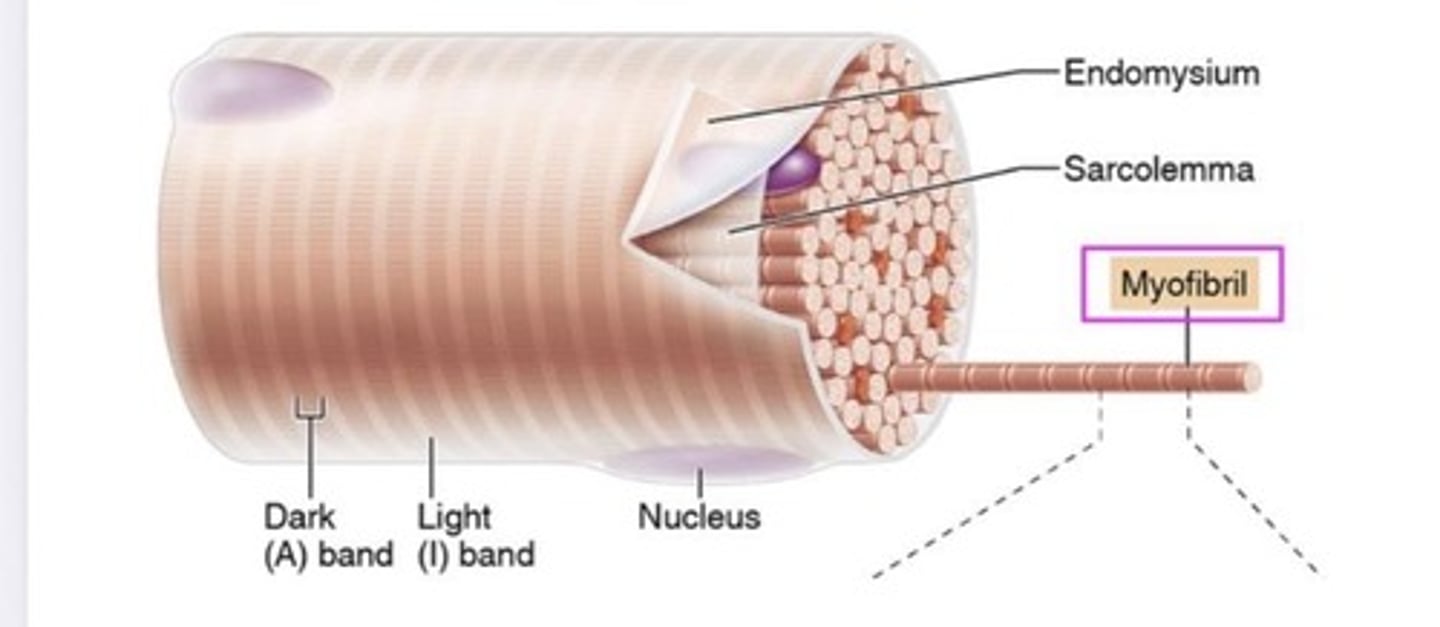
Endomysium
The connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber.
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium.
Tendon
A cord of dense fibrous tissue attaching a muscle to bone.
Aponeurosis
A fibrous or membranous sheet connecting a muscle and the part it moves.
Myofibrils
Complex organelles composed of bundles of myofilaments within a muscle fiber.
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane surrounding a muscle fiber.
Sarcomere
The basic contractile unit of muscle tissue, composed of actin and myosin.
Myofilament
The filaments of myofibrils, composed of proteins, primarily actin and myosin.
Actin
A thin myofilament that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction.
Myosin
A thick myofilament that interacts with actin to produce muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
A specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum that stores and releases calcium for muscle contraction.
Neurotransmitter
A chemical messenger, such as acetylcholine, that transmits signals across a synapse.
Neuromuscular junction
The synapse or junction between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber.
Axon
The part of a neuron that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body.
Synaptic cleft
The gap between the axon terminal of a neuron and the sarcolemma of a muscle fiber.
Action potential
A rapid rise and subsequent fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane.
Motor unit
A motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates.
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that sends signals for muscle contraction.
Sliding filament theory
The theory that explains muscle contraction as the sliding of actin filaments over myosin filaments.
Calcium binds to troponin, ATP binds to myosin head to provide energy
Flexion
A movement that brings two bones closer together.
Extension
A movement that brings two bones further apart.
Abduction
A movement that moves a limb away from the midline of the body.
Adduction
A movement that moves a limb toward the midline of the body.
Circumduction
A circular movement of a limb, where the distal end moves in a circle.
Dorsiflexion
A movement that brings the toes toward the head.
Plantar flexion
A movement that points the toes away from the head.
Opposition
The movement of the thumb to touch the fingers on the same hand.
Cardiac, skeletal, smooth
Name three types of muscle tissue
Branching, uninucleated, chains of cells, striations, intercalated disks
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Hallmarks
Single, tapered, uninucleate, no striations
Smooth Muscle Tissue Hallmarks
Long, cylindrical, multinucleated, striations
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Hallmarks
Produce movement, posture & position, stabilize joints, generate heat
What are the 4 functions of Skeletal Muscle?
Cross at least one joint, bulk of skeletal muscle proximal to joint crossed, 2 attachments: origin and insertion, only pulls, during contraction muscle insertion moves toward origin
What are the 5 golden rules of skeletal muscle activity?
turn sole medially
Inversion
turn sole laterally
Eversion
Palms turn face up
Supination
Palms turn face down
Pronation
Irritability, contractibility, extensibility, elasticity
What are the four special properties of skeletal muscle fibers?
Step 1
AcH is released into the neuromuscular junction by the axonal terminal
Step 2
AcH diffuses across the neuromuscular junction and binds to receptors on the sarcolemma
Step 3
Depolarization occurs, and the action potential is generated
Step 4
The action potential carried deep into the cell causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium
Step 5
Calcium ion concentration at the myofilaments increases, myofilaments slide past one another and the cell shortens
Step 6
As calcium is actively reabsorbed into the sarcoplasmic reticulum its concentration at the myofilament decreases