Bio: 3.1-3.6 - Cells
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Theory
1. All organisms are made of 1+ cells
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function in a living thing (atoms -> biomolecules -> organelles -> cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems)
3. New cells are made from existing cells
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function in a living thing (atoms -> biomolecules -> organelles -> cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems)
3. New cells are made from existing cells
2
New cards
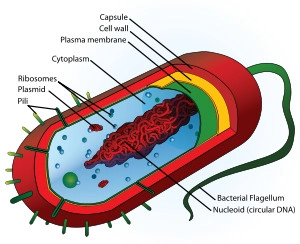
Prokaryote
mostly unicellular bacteria w/ 1 strand of DNA floating as a nucleoid, has no complex organelles and *usually* asexually reproduces
3
New cards
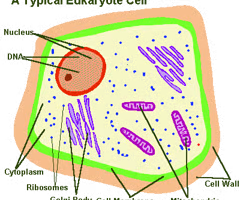
Eukaryote
Mostly multicellular organisms, usually larger and has a nucleus w/ complex membrane-bound organelles, some fungi, *mostly* sexually reproduces
4
New cards
All cells have
cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
5
New cards
Endosymbiotic Theory
complex, eukaryotic cells arose from prokaryotic cells
6
New cards
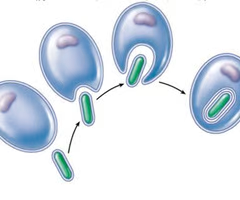
Endosymbiotic Theory Process
1. Prokaryotes existed first 2. In some prokaryotes, the membrane folded inward to make pockets 3. Infolded cell membrane surrounded DNA to make nucleus 4. Some primitive eukaryotes engulfed prokaryote (became mitochondria & created animal cells) 5. Some animals cells engulfed photosynthetic prokaryote (became chloroplast and created plant cells)
7
New cards
Evidence supporting Endosymbiotic Theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts have 2 membranes, their own DNA & ribosomes (same size and shape), and are autonomous (grow & divide on their own like bacteria)
8
New cards
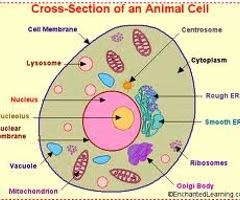
Animal Cells
no cell wall and chloroplast, round-shaped, has centrioles and some have cilia and flagella, has many, small vacuoles, can move
9
New cards
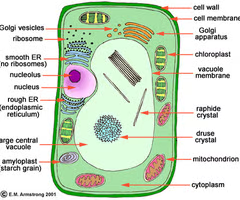
Plant Cells
has cell wall and chloroplast, box-shaped, no centriole, cilia, or flagella, one large vacuole
10
New cards
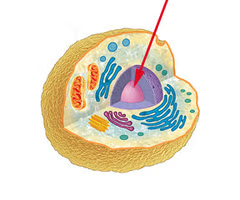
Nucleus
stores DNA and regulates cellular activities
11
New cards
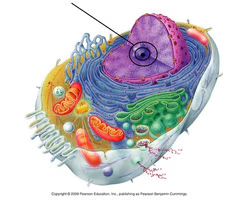
Nucleolus
produces and assembles ribosomes
12
New cards
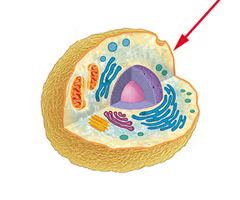
Cell Membrane
Surrounds the cell and regulates what molecules can enter & exit the cell
13
New cards
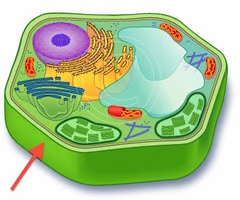
Cell Wall
Provides external support and protection to plants - made of cellulose
14
New cards
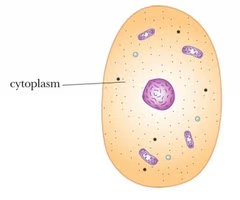
Cytoplasm
Fills up the spaces between the organelles
15
New cards
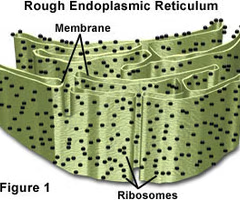
Ribosomes
Produces proteins (rib -> protein)
16
New cards
Rough ER
Produces and stores secretory proteins w/ its ribosomes and bumpy tubes
17
New cards
Smooth ER
Produces and stores lipids w/ its flat tubes (smooth as butter)
18
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies proteins & sends them throughout the cells in vesicles (vesicles = vehicles)

19
New cards
Vacuole
Storage of substances like water & food; many, small in animals, 1 large in plants
20
New cards
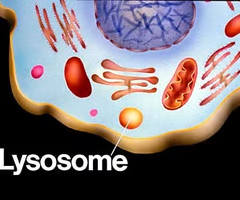
Lysosome
Breaks down cellular waste using enzymes; many in animals, some in plants (lysol = cleans)
21
New cards
Mitochondria
Produces energy by breaking down sugars (cellular respiration) POWERHOUSE
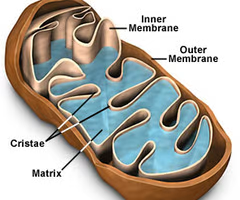
22
New cards
Chloroplast
Uses sunlight to produce sugars (photosynthesis)
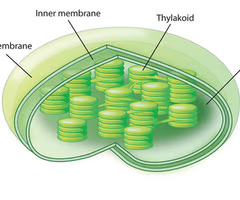
23
New cards
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that provides internal support & roads for vesicles and organelles to attach to
24
New cards
Centrioles
Assists w/ cell division (twizzlers divided into strands)
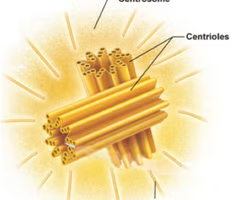
25
New cards
Cilia
Short hairs that help with cellular movement/the movement of fluids (like mucus...)
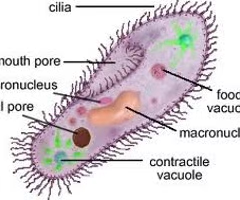
26
New cards
Flagella
a long tail-like structure that aids in cell movement
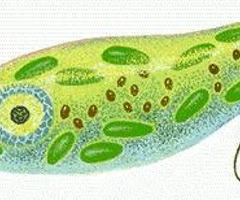
27
New cards
Bacteria Cell
Prokaryotic cell w/ a cell membrane & wall, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, and sometimes flagellum
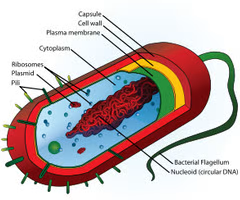
28
New cards
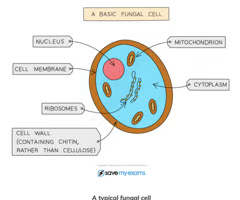
Fungi Cell
Eukaryotic cell w/ cell wall, but no chloroplast (has both animal and plant cell properties)