NSO Chap 6
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is the definition of reproduction?
The ability of an organism to produce new individuals of the same species.
What are the offspring of asexual reproduction called?
Clones as they are identical to the parent.
What are a few methods of asexual reproduction?
Binary fission, Budding, Spore formation, Fragmentation and Multiple fission etc.
What is the fastest method of asexual reproduction?
Binary fission, it is even the simplest
What is sexual reproduction?
A male and female are needed to fuse reproductive cells. The male produces sperm and the female a egg or ovum, these fuse to make a fertilised egg.
What is unisexual in animals?
It is where the male produces sperms and the female egg or ova.
What or hermaphrodite or bisexual organisms?
They have both sex organs so individually can sexually reproduce.
What is a zygote?
It is a new cell formed then the sperm and ovum fuse together.
What is fertilisation and what are the 2 types of fertilisation?
Fertilisation is the process of fusion of the sperm and ovum to form a zygote. There is external and internal fertilisation.
What is internal fertilisation?
When fertilisation happens inside a females body , Eg. humans, snakes etc.
What is external fertilisation?
When fertilisation occurs outside the organism, the egg and sperm are realised outside in the environment and then are fertilised. this usually happens with creatures in or close to water. Eg. Frog, Fish etc.
What are animals which lay eggs called.?
Oviparous animals Eg. Lizards, frogs, Etc.
What are animals which give birth to young ones called?
Viviparous organisms, Eg. Rats, Squirrels, Etc. (most mammals are viviparous)
What are the Testes?
They are what produce sperm, when a male reaches puberty pituitary gland is stimulated to produce testosterone(male sex hormone)
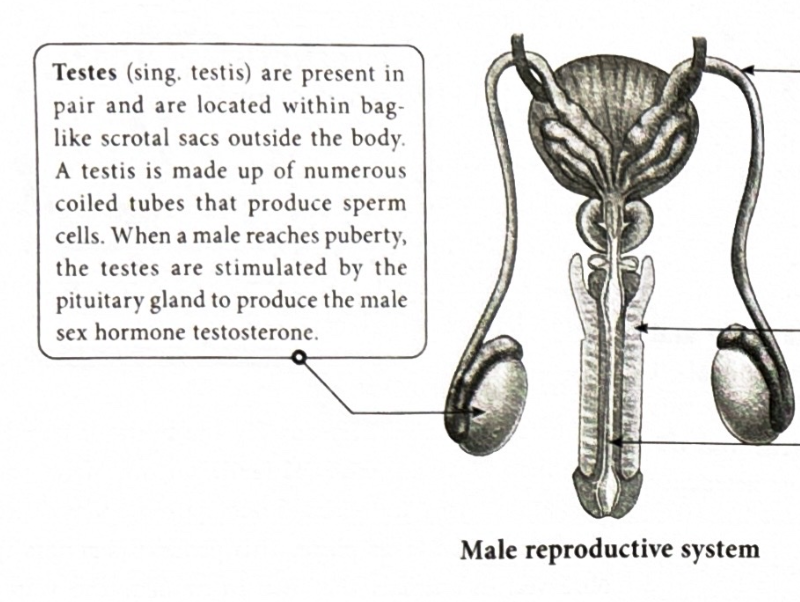
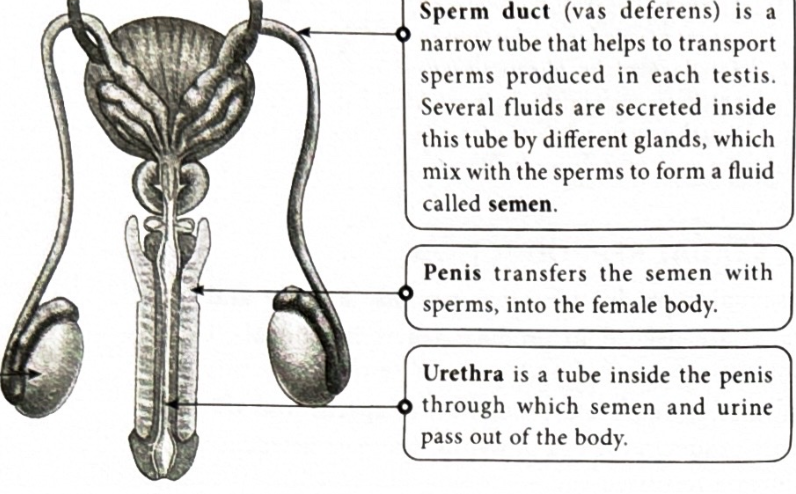
What is a sperm duct(Vas deferens)?
It is a thin tube used for transportation of sperm produced. many different fluids are in the gland which mix with sperm to produce semen.
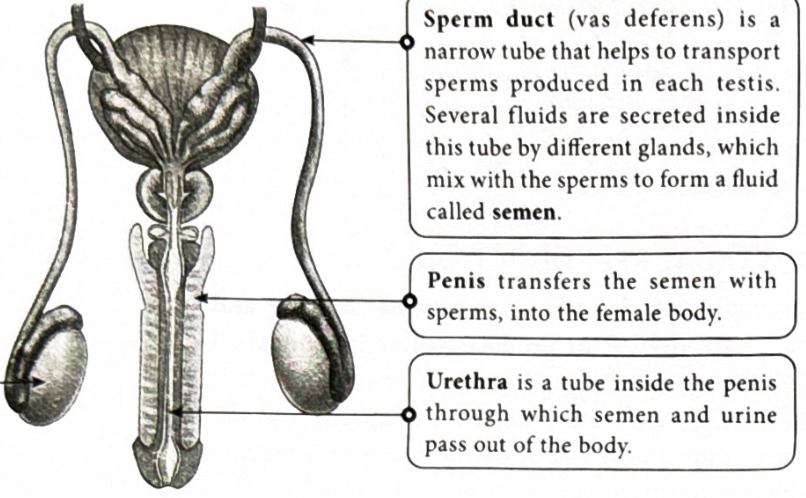
What is a penis?
It transfers the semen with sperm present into the females body
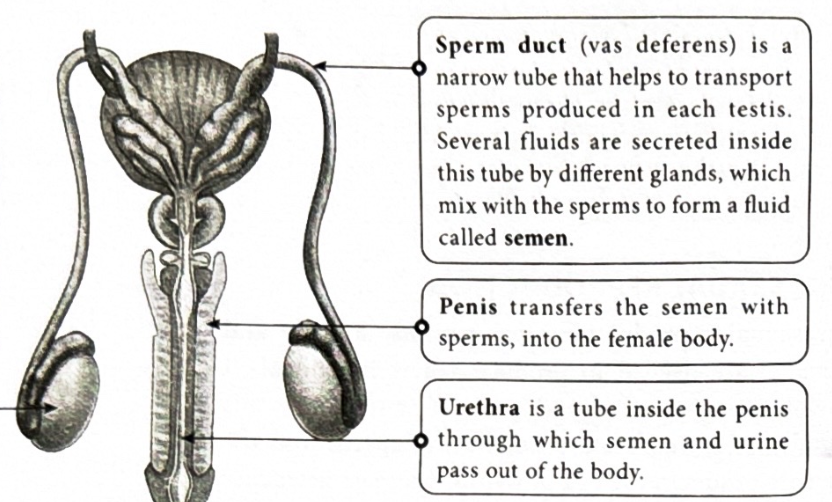
What is a urethra?
A small tube through which urine and semen exit the body.
What are ovaries?
Produce and release eggs(ova), they are about the size of an almond, When a girl reaches puberty they are stimulated by the pituitary gland to produce estrogen(female sex hormone).
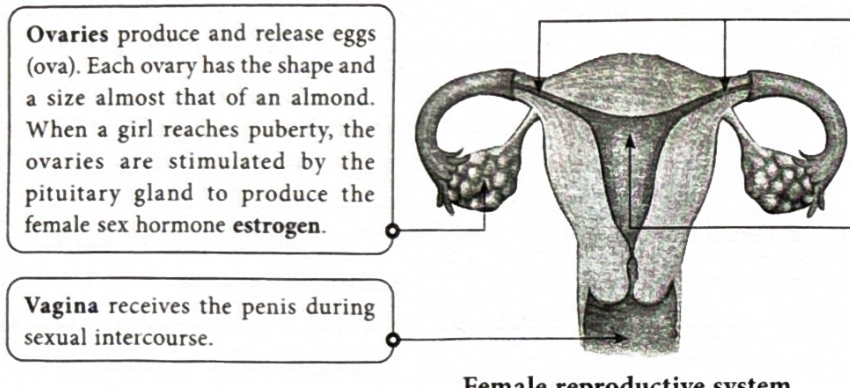
What is a vagina?
It receives the penis during sexual intercourse.
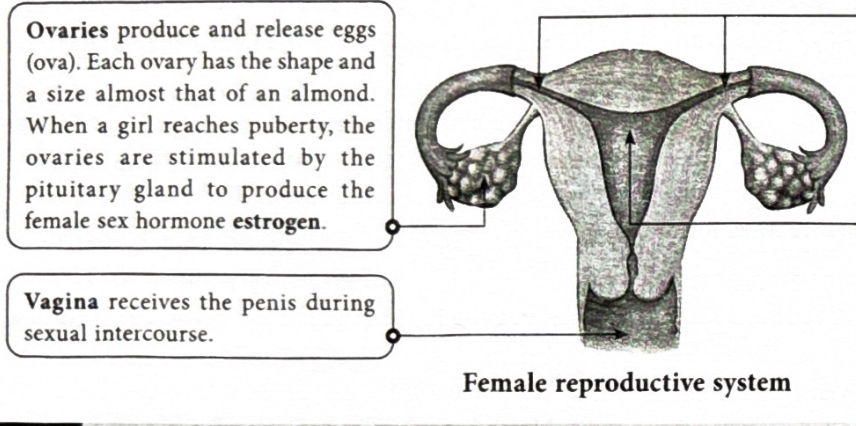
What is a oviduct(fallopian tube)?
It carries the ovum released by the ovary. Fertilisation happens here and a zygote is also formed here.
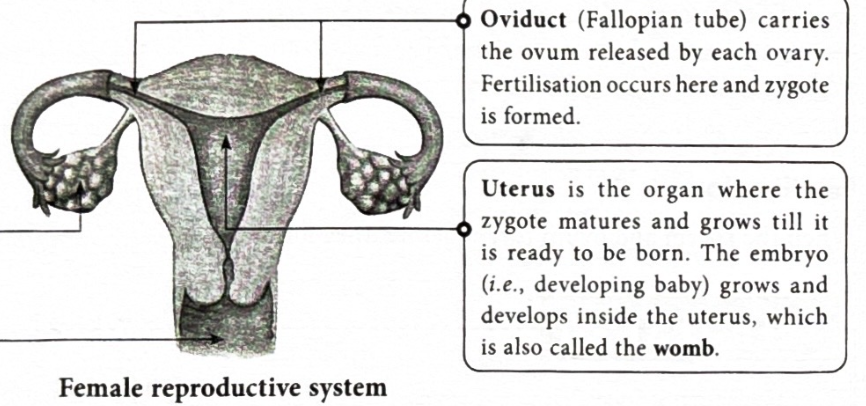
What is a uterus?
It is where the zygote develops and matures, it is also called a womb(when the egg is formed to prepare for a baby the body adds extra layering which is then shed through period if no zygote comes.)
What is the largest and smallest human cell?
Egg, ovum or gamete is largest and sperm is smallest cell
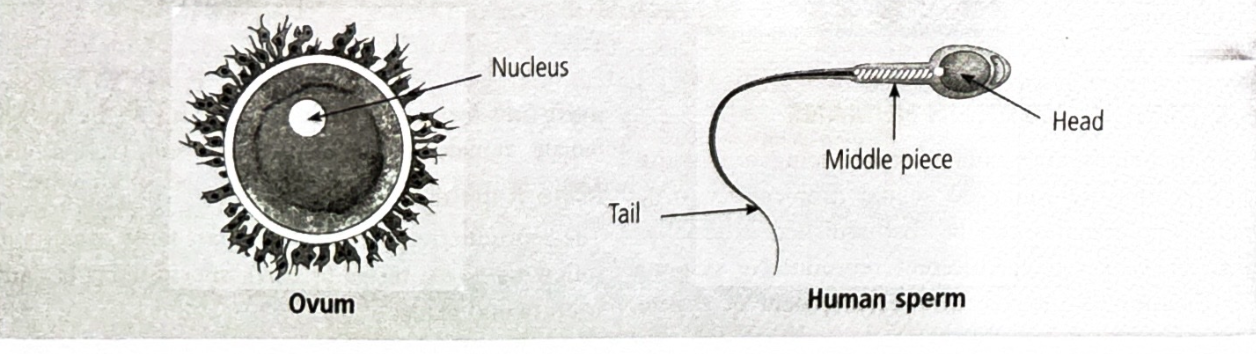
Fertilisation process?
Sperm enters through vagina and heads towards the oviduct passing through the vagina. If there is a egg in the oviduct and the sperm is able to enter the eggs then it is fertilised, both nuecli fuse to form a single neucli and making a zygote.
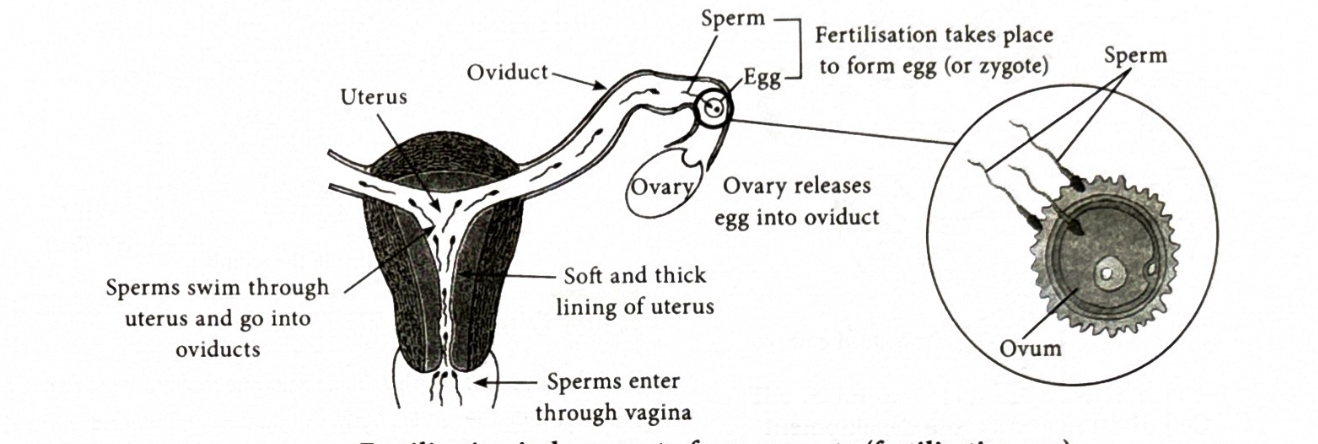
What happens if fertilisation doesn’t happen?
Then the ovum along with the inner uterine lining it expelled from the body, menstruation.
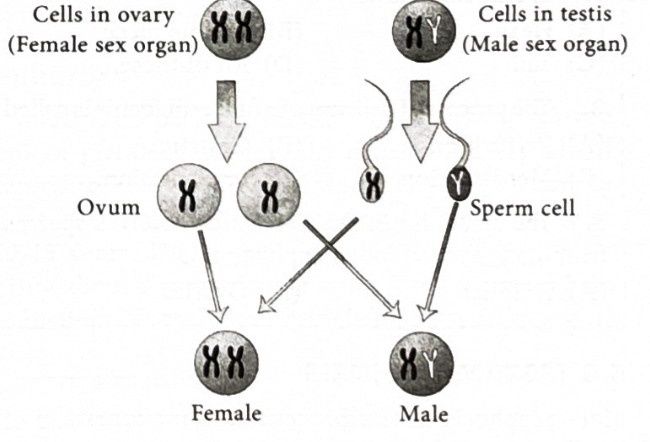
How is the Sex of a baby determined?
There are 2 types of sperm cells, either X chromosome or Y. If the X meets the ovum then its a girl as a girl has XX chromosome but if it is Y sperm then it’ll be a boy as they have XY chromosome
What is a embryo?
It is the zygote which has divided repeatedly to make hundreds of cells.
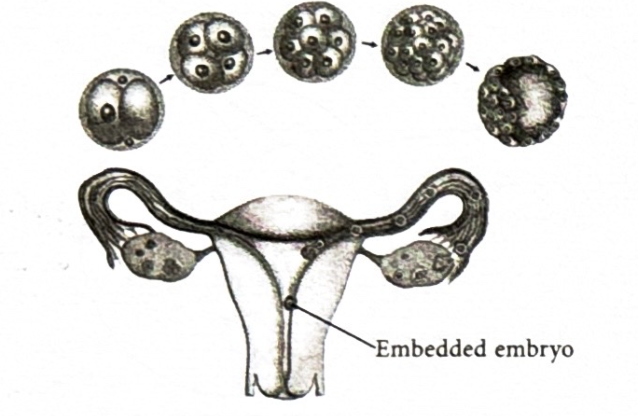
What happens to zygote once it has been converted into a embryo?
It moves down the oviduct and gets embedded in the soft and thick lining of the uterus where it will continue to grow, this is called implantation. Once the embryo is embedded a women becomes “Pregnant”
How does the embryo receive nutrition?
Directly from the mothers blood, in this stage it rapidly grow with all major systems developing.
What is the foetus stage?
When most of the body parts/organs can be identified
What is the gestation period
When the baby grows in the mothers womb for about 40 weeks.
What happens in the gestation period?
It receives nourishment from the placenta.
What is parturition?
When the foetus is fully developed and the uterus begins to contract to push out the baby.
What is metamorphosis?
It is the process of changing larva into a adult with drastic changes.
What are larvae?
Newly hatched younglings of some oviparous animals which do not match there parents.
What are a few animals which undergo Metamorphosis?
Frog, mosquito, butterfly, bees, Etc.
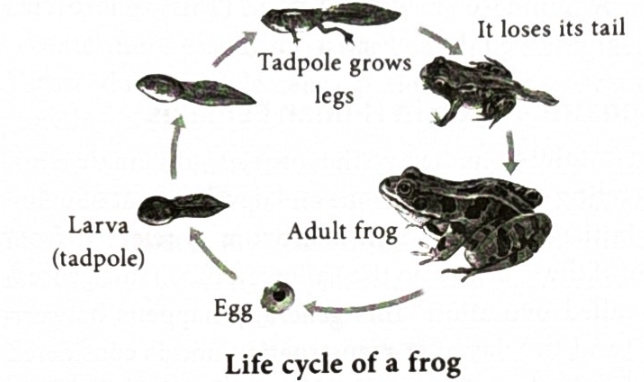
What is the life cycle of a frog?
It starts as an egg and to become into a frog loses its tails and develops lungs and legs.
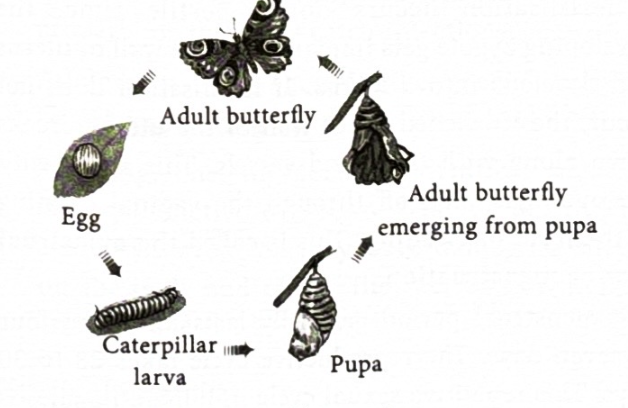
What is the life cycle of a butterfly?
this
What is cloning
Producing an exact copy of an animal through asexual reproduction.
What are genetically identical animals?
Animals which contain the exact same genes, these are also called clones(exact copy of parent).
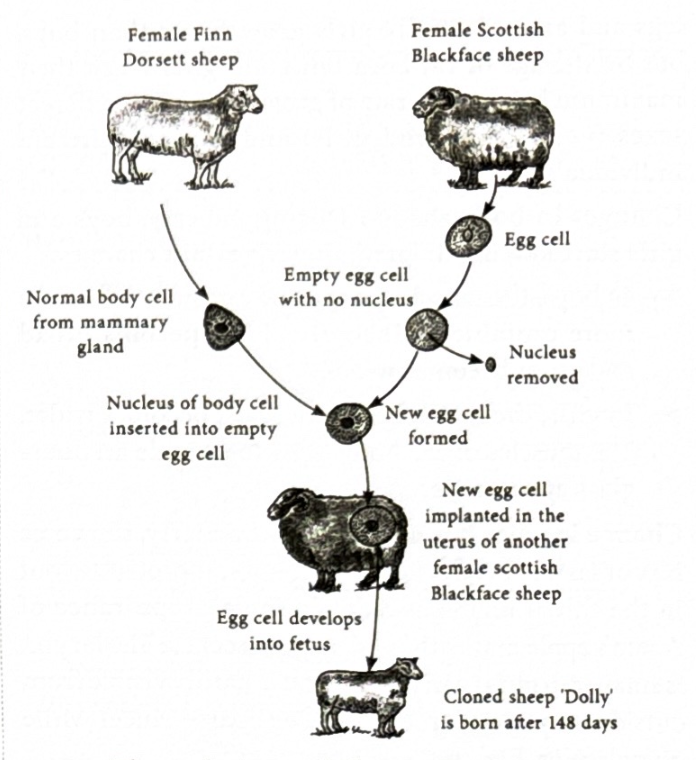
Who cloned the first large animal?
Ian Wilmut and his team at Roslin institute in scotland. Thet cloned Dolly the sheep
Who was the first mammal cloned?
Dolly born on 5th July 1996 from its mother Finn Dorsett sheep
How was dolly cloned?
By replacing the eggs nucleus and adding who you want to clones nucleus from a body cell and implant into a new sheep.
What is adolescence?
A period of growth between 11-18 or 19 years. Between childhood and adulthood. Adolescence begins 1-2 years before for girls.
What is puberty?
A period in life where sexually immatures boys and girls become sexually mature and capable of reproduction. Boys go through between 11-16 and girls 10-15.
What are some changes we go through in puberty?
Increase in height(till 18yrs), Muscle bigger and shoulders and chest broaden/widen. Butt becomes bigger for girls. Deeper voice for boys, produce more sweat(pimples and acne) and maturation of sex organs,
What are some sexual changes we go through in puberty?
Estrogen in females and testosterone in males. For males, pubic hair growth and muscle development. For females enlargement of breast and hips, pubic hair, periods begin.
What is ovulation?
The process when one of the ovaries produce 1 ovum and send it to the fallopian tube(once a month), 11-16 days after menstruation. fertile time period.
What happens before ovulation?
Before the ovum is produced the body prepares itself for a zygote, the inner wall of the uterus thickens.
What happens if fertilisation doesn’t happen?
The thickened inner walls break and with the ovum is shed through the vaginal opening. this is called Menstrual flow or menstruation.
What is the menstrual cycle?
The reproductive cycle lasts about 28-30 days with 4-7 days of periods.
What is a menarch?
The first period of a girls life.
What is menopause?
After the age of about 45-50 the female hormone levels drop drastically and the cycle stops.
What are STD’s?
Diseases which are transmitted through sexual contact, Eg. syphilis, AIDS, gonorrhoea, etc.
What are some things that should be done for good personal hygiene?
All parts/organs should be cleaned properly or they can catch infections, Girls should take more care while on period. Smoking, tobacco, alcohol and drugs should be avoided.
Why should regular physical exercise be done?
To keep the body healthy and fit, we should take walk and exercise(play outdoor games regularly)
What is the endocrine system?
A collection of specialised organs(glands) that secrete chemical substances. these chemical substances are called hormones which go directly in the blood stream.
What are the major glands which make the human endocrine system?
pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries and testes.
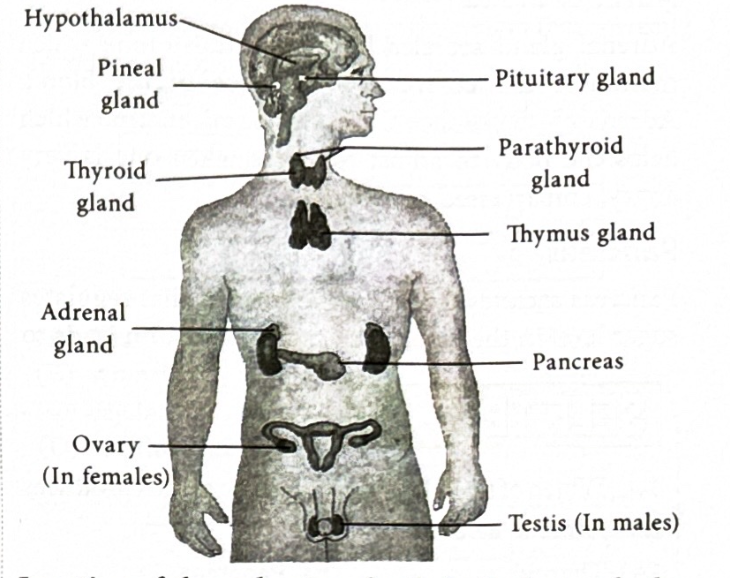
What is the Pituitary gland?
It is also called the master gland as it influences the other glands to function. secretes growth hormones(GH) that help the body grow, it also secretes thyroid stimulating hormone(TSH) and adrenocorticotropic hormones(ACTH).
What is the Pineal gland?
Secretes melatonin hormone which is the sleep hormone. It promotes sleep and becomes more effective in dim/dark light.
What is the Parathyroid gland?
secretes parathormone aka parathyroid hormone(PTH). It regulates calcium and phosphate balance in the body.
What is the thyroid gland?
Secretes thyroxine which controls the metabolism in the body and its deficiency leads to goitres(BK99 jake)
What is the adrenal gland?
Secretes aldosterone which helps maintain salt balance in the blood. Also Adrenaline which helps the body adjust to stress when you are angry, embarrasses or worried.
What are the pancreas?
They secrete insulin which regulates sugar level in blood. Less insulin leads to high sugar aka Diabetes.
What are the ovaries?
secrete estrogen, progesterone, relaxin and inhibin. Estrogen helps the growth of secondary sexual characteristics. Progesterone maintains growth of uterus during pregnancy.
What are the testes?
secrete testosterone which helps the growth of secondary sexual charecteristics and sex organs in males.