L2: Synaptic plasticity
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Long term depression and synaptic tag hypothesis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
For synapses to be plastic there needs to be…
poteniation
And
Depression
Why is this?
allows more flexible neuronal network
If synaptic plasticity only enhances synaptic connection→ synaptic efficacy would everntually saturate
THEREFORE: depression mechanisms are also required
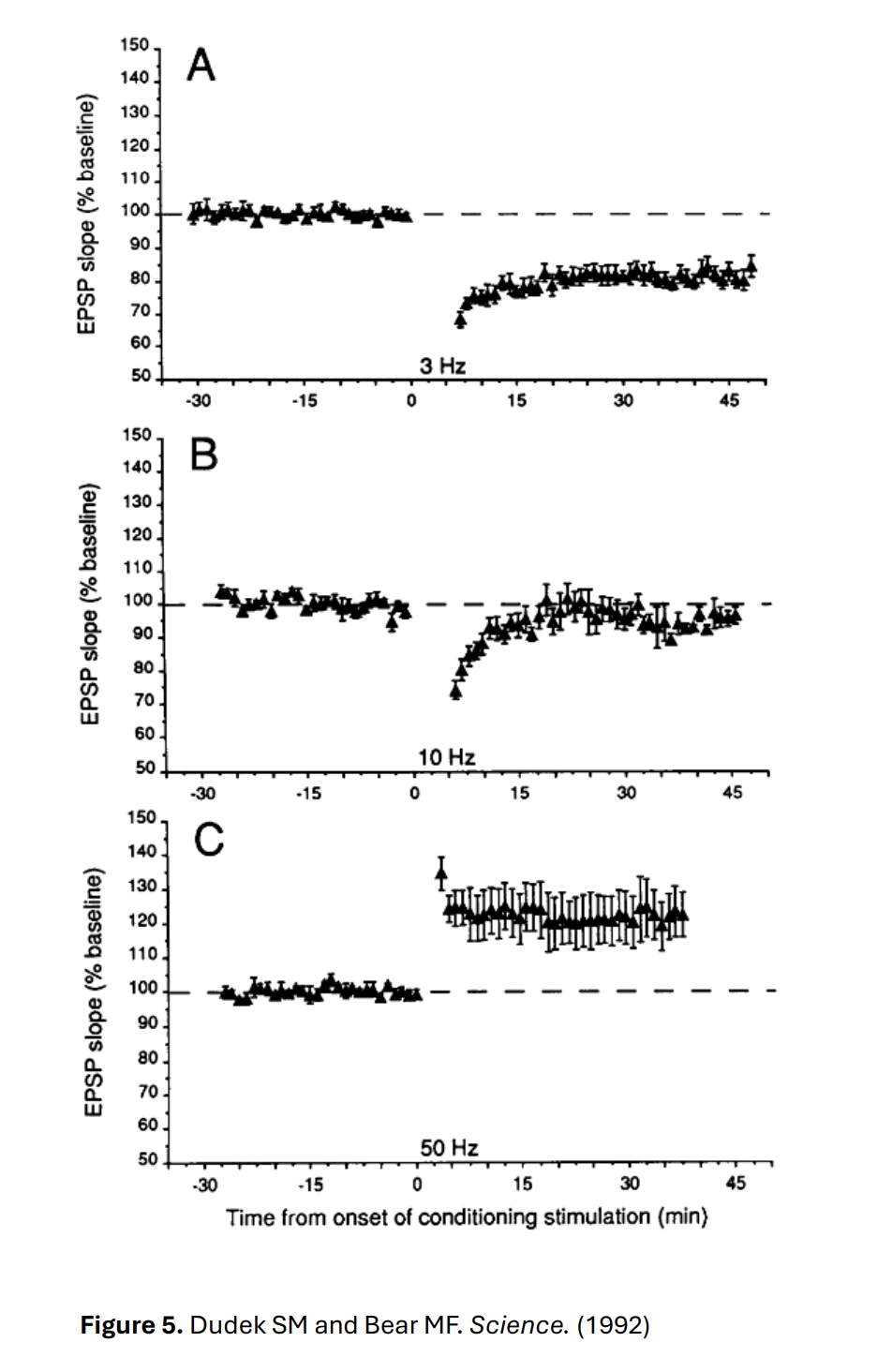
One protocol to induce long term depression in hippocampal Schaffer collaterals-CA1 connection
Low frequency stimulation
(in contrast to high frequency stimulation that induce NMDAR LTP)
But what does ‘low’ frequenecy actually mean?
Still higher than the baseline synaptic transmission
just lower than the high stimulation
Numbers of frequencies for baseline and LTD
Baseline→ frequnecy of 0.1Hz→ one stimulation of presynaptic neuron e.g Schaffer collaterals per second)
For LTD→ 1 Hz→ for a total of 900 stimuli
although can be higher
Following induction, stimulation frequency is decreased back to…
Baseline 0.1 Hz
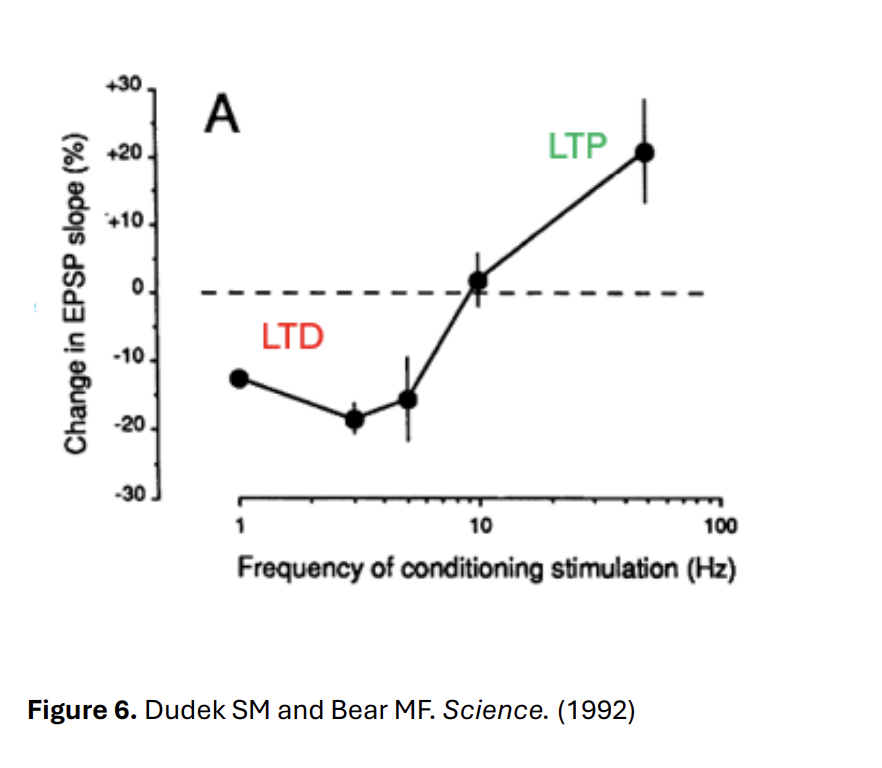
Different frequencies that can be used as ‘low frequency’ LTD protocol (put in graphs here)
1Hz
3Hz
10Hz→ no depression is induced→ slope of EPSP increases back to baseline level→ following an initial drop
50Hz→ induced LTP
THEREFORE→ there is a frequency threshold for LTD and LTP generation
graph shows that is is around 10Hz
Both LTD induction and high freqency LTP induction in the CA1 region of the hippocampus are…
NMDAR dependent
but if they both depend on the same mechanism of Ca2+ entry through NMDARs→ how does frequency of stimulation translate to LTD or LTP??
How does low frequency cause LTD and not LTP, using NMDARs?
low freuency stimulation→ increases Calcium entry via NMDARs
BUT→ extent of calcium elevation is lower than for LTP induction with HFS
Therefore: different cellular mechanism
lower Caclium entry activates certain phosphatase
this is because they have a higher affinity for Ca2+ than the CamKII from LTP did
result in endocytosis of AMPARS from postsynaptic site
Decreasing the EPSP
Decrease in AMPAR levels is the expression of low frequnecy LTD
opposite of expression of NMDAR-dependent LTP→ where there was increase in AMPAR component
Looking back at LTP protocols→ NMDAR-dependent LTP protocol result in…
potentiation of synaptic transmission
→ for up to an hour
THEREFORE: EARLY LTP
Why referred to as early LTP?
one hour post induction→ synaptic strength goes back to what it was at baseline levels
What is late LTP
when potentiation of synaptic strength persists
for several hours
How is late LTP caused?
increasing the number of HFS protocols applied:
larger and more rapid increase in Ca2+ entry in the post-synaptic cell
activates protein kinase A (and CamKII)
translocates to the soma and then nucleus
activates transciption factor Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding protein (CREB)
Binds to cAMP response elements (CRE)
in regulatory region of target genes to initiate their transcription
mRNA transcripts transported
into proteins in the cell body
or transported along with translated proteins to dendrite for translation
What genes are upregulated
over 80 genes potentially upregulated
as a result of Late LTP
What is the overall effect of these genes/proteins?
maintain the increase in AMPAR expression
for a longer period
As there are many dendrties distally and proximally to the soma→
how do these mRNA transcripts and newly translated proteins locate the dendritic spine that that LTP was induced in?
Importance of this
LTP is input specific
mRNA transcripts are proteins need to find their way to location where early LTP was induced
so they can maintain it to the late LTP phase
and not translocate to a spine where no LTP was induced
must be something to do with early LTP?
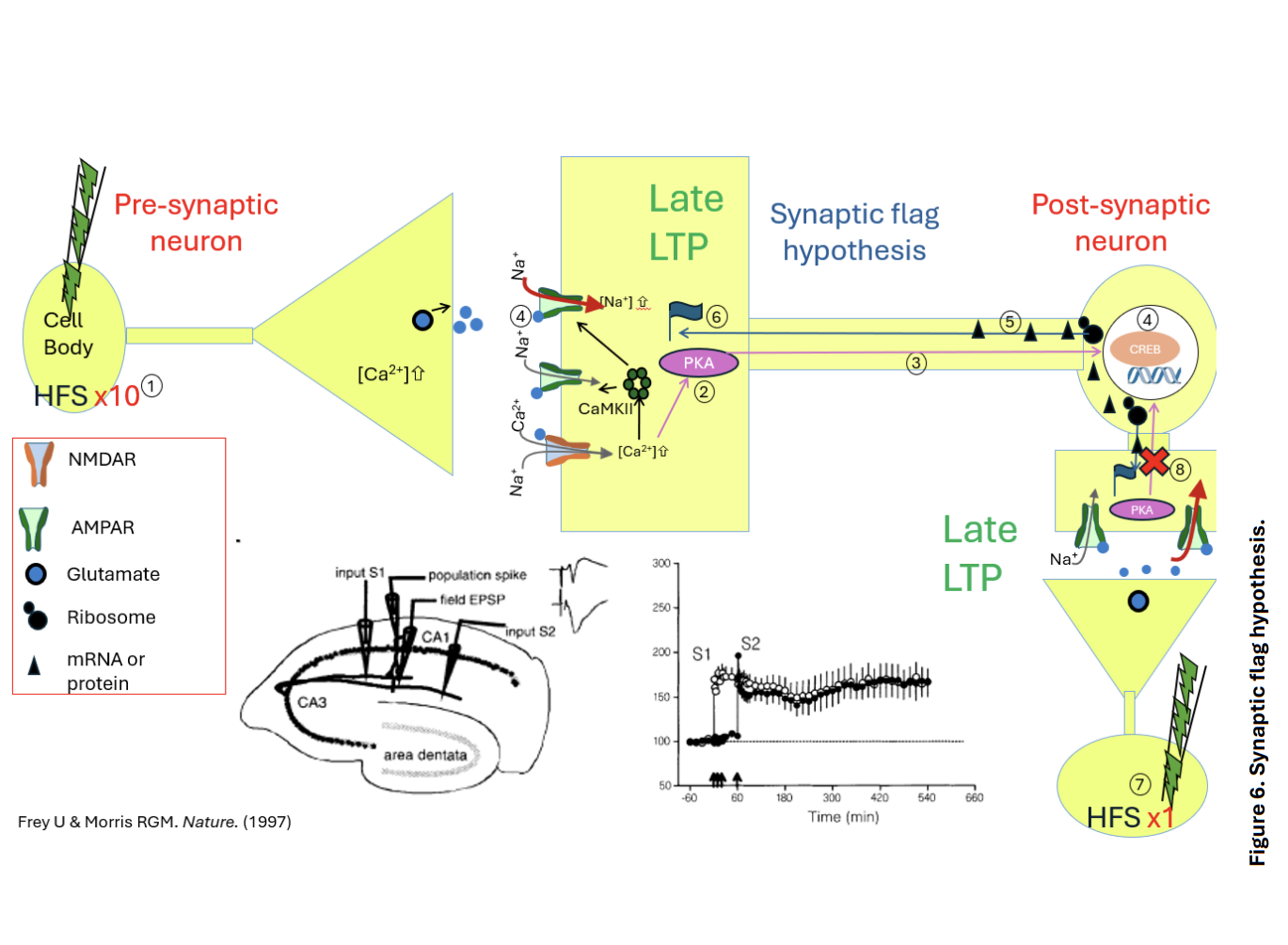
Hypothesis→ Synaptic Flag Hypothesis
unknown tag/flag is only present following early LTP induction
tag/flag draws the mRNA and proteins to that specific location
What is this flag?
Actin?
Actin binding proteins?
Why thought to be actin/actin binding proteins
During early LTP we get an increase in both
AMPAR expression
size of the spine→→ this growth is supposed by an increase in actin cytoskeleton
What does this growth of spine cause?
attract new mRNA transcipts and proteins
to the location of the enlaged spine
When does the spine and actin cytoskeleon enlargement occur?
during early phase of LTP
hypothetically→ provides the expression of the tag
Late LTP also requires…
Protein kinase A translocation
and
gene transciption
Evidence for this:
Experiment:
When first induced late LTP via 10 x HFS protocol in one pathway
After 1 hours→ induced only early LTP in a different pathway via 1xHFS protocol:
Result→ early LTP was converted to late LTP
Why is this?
The flag was expressed by 1xHFS protocol but not→gene transcription
however
the new mRNA transcripts and proteins are provided by the first 10xHFS stimulated pathway
THEREFORE: as the second pathway has the flag available
the mRNA transcripts and proteins can also translocate to tis dendrite
→ maintain the LTP to a later phase