intro to psychology
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
2 year certificate
psychology technician, works under supervision of licensed psychologist or counselor
4 year certificate
bachelor of arts majored in psychology and can work as a school counselor, nurse, or regional centers
6 year certificate
master of arts, Psy. D. psychologist, can work as social worker, psychiatric nurse, conducting research, or teaching
8-10 years
philosophy doctorate (PH. D.), psychologist. can work in clinical settings, research, or teaching at college level
10 years
medical degree (M. D.) psychiatrist. can perform medical procedures and prescribe medication
psychoanalyst
after master of arts (M. A.) or philosophy doctorate (PH. D.), two additional years of freudian training
clinical psychology (clinician)
diagnosing and treating abnormal problems such as schizophrenia, personality disorders, and severe emotional disturbances. usually in hospital settings
counseling (counselor)
many deal with normal problems such as adjustment issues. usually in private practice settings.
experimental psychology
many involved with conducting basic research in psych. and are faculty members at colleges and universities. commonly referred to as research psychologists.
educational psychology
studying how we learn. they create standardized testing, ACTs, SATs. they focus on relationships between learning and environments
social psychology
explores how our behaviors, feelings, and beliefs are influenced by our interactions with others.
developmental psychology
study of the growth of the lifespan from womb to death. they conduct and apply research in age related behavioral changes as we develop overtime.
industrial/organizational psychology
study and advise on behavior in the workplace, selecting/training employees. many focused and concerned about consumer behavior
forensic psychology
applies both the law and psychology to legal issues. can analyze crime scenes, assist law enforcement with evidence, testimony, and jury selection
sports psychology
incorporates many fields, including biomechanics, physiology, kinesiology, and psychology. they study how psychological factors affect performance and participation, it is not exclusive to sports only
american psychology association
scientific and professional organization that represents psychologists in the U.S. they are responsible for academic citation format.
wilhelm wundt
considered the founder of modern psychology by opening the first psychology laboratory. nicknamed father of psychology. used introspection, first to use scientific method in studying consciousness.
introspection
(used by wilhelm wundt) describing one's conscious experience, careful examination of ones own mental experiences. (self reporting, self reflecting, looking inward).
edward titchener
founder of structuralism and analyzed the intensity, clarity and quality of the parts of consciousness.
structuralism
theory founded by edward titchener that the structure of conscious experience could be understood by analyzing the basic elements of thoughts and sensations. (breaking consciousness into its smallest points)
william james
first american psychologist and author of first psychology textbook. founder of functionalism
functionalism
theory founded by william james that emphasized the functions of consciousness or the way consciousness helps people adapt to their environment
max wertheimer
created gestalt psychology in response to structuralism (edward titchener)
gestalt psychology
psychological perspective made by max wertheimer that emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes. "whole is greater than the sum of its parts"
phi phenomenon
when motion is perceived when there is nothing more than a rapid sequence of individual sensory events. ex: blinking christmas lights
sigmund freud
founder of psychoanalysis (controversial theory about the workings of the mind)
psychoanalysis
sigmund freud's theory of personality, also therapeutic technique that attempts to provide insights into thoughts and actions by exposing and interpreting the underlying unconscious motives and conflicts.
john watson
founder of behaviorism
behaviorism
theory that psychology should only study observable behaviors, not mental processes
B. F. skinner
american behavioral psychologist who developed the fundamental principles and techniques of operant conditioning and devised ways to apply them to the new world.
today, it focuses on learning through rewards and observation
abraham maslow
humanistic psychologist who proposed the hierarchy of needs. self actualization as one of the ultimate psychological needs
carl rogers
humanistic psychologist who developed client centered therapy and stress the importance of acceptance, genuineness, and empathy in fostering human growth.
humanistic psychology
perspective that focused on the study of conscious experience, the individuals freedom to choose, and the capacity for personal growth. striving to reach full potential
jean piaget
pioneer in the study of environmental psychology who introduced a stage theory of cognitive development that led to the understanding of children's thought processes.
biological perspective
focuses on the physical structure and substance underlying a particular behavior, thought, or emotion.
ex: brain chemistry, genetics, glands, etc.
behavioral perspective
focus on how behaviors are based on how we learn observable responses. we learn responses through rewards, punishments, and observations.
cognitive perspective
focuses on how we take in, process, store and retrieve information. cognitive psychologists believe how we think can influence our behaviors.
psychodynamic perspective
focuses on how behavior is affected by unconscious drives and conflicts. behavior is explained through unconscious motivation and unresolved inner conflicts from one's childhood
humanistic perspective
focuses on how healthy people strive to reach their full potential. behavior is explained as being motivated by satisfying needs (safety, hunger, thirst) with the goal of reaching one's full potential once basic needs are met.
socio-cultural perspective
focuses on how thinking or behavior changes in different situations or as a result of cultural influences
evolutionary psychology
focuses on the principles of natural selection to study the roots of behavior and mental processes. combines aspects of biological, psychological, and social aspects of human behavior. behavior is explained by how the behavior may have helped our ancestors survive long enough to reproduce successfully.
methodology
method of asking questions then drawing logical supported conclusions. researchers need to be able to determine if conclusions are reasonable or not. well designed research produces data - supported conclusions
basic research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base. research with the explicit purpose of finding new information.
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles. difficulty applying data from one person to everyone
longitudinal study
a research technique that follows the same group of individuals over a long period. can provide rich source of data. can be quite expensive and difficult to conduct.
cross sectional study
research technique that compares individuals from different age groups at one time. cheaper and easier than longitudinal.
naturalistic observation
a descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation. subjects are not aware of being watched.
laboratory observation
observing and recording behavior in a laboratory environment that allows the researcher to manipulate or control the situation.
correlational study
research project strategy that investigates the degree to which two variables are related to each other. it is IMPORTANT NOT TO IMPLY A CAUSE AND EFFECT RELATIONSHIP between variables. do NOT determine WHY two variables are related.
A could cause B or B could cause A or C could cause A & B.
survey method
research technique that questions a sample of people to collect information about their attitudes or behaviors. relies on self reports; uses surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
scientific method
method of learning about the world through the application of critical thinking and tools such as observation, experimentation, and statistical analysis.
experiment
are research methods in which the researcher manipulates and controls certain variables to observe the effects on other variables. ONLY way to determine cause and effect relationship.
hypothesis
testable prediction of the outcome of the experiment or research
population
entire group of people about whom you would like to know something. total large group being studied.
random sample
sample that fairly represents a population because each member of the population has an equal chance of being included.
random assignment
procedure for creating groups that allows the researcher to control for individual differences among research participants.
control group (control condition)
participants in an experiment who are not exposed to the independent variable. group that is NOT being tested on. they are compared to the experimental group.
experimental group (experimental condition)
participants in an experiment who are exposed to the independent variable. group being tested on. they are compared to the control group
operational definitions
explanation of the exact procedures used to make a variable specific and measurable for research purposes. ex. "generous people are attractive people" how are we going to measure generous and attractive? generous: amount of money donated - $100.
EXAMPLE
if you eat purple M&Ms before a test, then you will get good grades.
population: students in psych class
control group: half of the students NOT eating M&Ms.
experimental group: half of the students eating M&Ms before test.
O.D.: what is considered a good grade? A-B/100%-90%
independent variable: M&Ms
dependent variable: grades/outcome
confounding variable: whether or not the students had studied.
independent variable
variable that the researcher will actively manipulate and if the hypothesis is correct that will cause a change in the dependent variable. cause variable, variable manipulated by the experimenter.
dependent variable
variable that should show the effect of the independent variable. effect variable, variable being measured, outcome/results of the experiment.
confounding variable
variable other than the independent variable that could produce a change in the dependent variable.
confounding variables: environmental differences
are any differences in the experiments conditions -- between the experimental and control groups. they include: temperature, lighting, noise levels, distractions, etc. should be minimum of environmental differences between the two groups, ideally.
single blind procedure
experimental procedure where the research participants are ignorant (blind) to the purpose or expected outcome of the experiment. eliminates subject/participant bias.
double blind procedure
a research procedure in which both the data collectors and the research participants do not know the expected outcome of the experiment.
placebo
inactive substance or condition administered used to control for confounding variable. given to the control group.
replication
repeating the essence of a research study to see whether the results can be reliably reproduced.
research ethical guidelines: informed consent
participants must be informed in advance about the general nature of the research and any potential risks. they have the right to refuse participation or withdraw anytime.
research ethical guidelines: right to be protected from harm and discomfort.
studies involving harm or discomfort can be conducted under specific circumstances, and only with the informed consent of the participants.
research ethical guidelines: right of confidentiality
individual data about research participants should never be discussed or released.
research ethical guidelines: right to debriefing
participants have the right to receive a complete explanation of the research at the end of the study. important if the research involves deception.
reasons for animal research
interest in animal behavior as a topic of study. data from animal studies may apply to humans. easier to do some type of studies (genetics) due to the shorter life span of animals.
care of animals used in research
animals used in research must have clean have clean housing with adequate ventilation, appropriate food, and be well cared for.
statistics
means to make data are more meaningful and provide a method of organizing data so it can be understood.
descriptive statistics
statistics that describe main characteristics of the data.
inferential statistics
statistical techniques used to determine whether the data from two or more groups are the same or different.
measures of central tendency
statistical methods of finding the center of a distribution. THREE METHODS -----> MODE, MEAN, AND MEDIAN.
mode
most frequency occurring core or scores in a distribution. most useful in circumstances where the data can be placed into distinct groups.
ex: 1,5,2,10,9,7,5,1,2,4. the mode is 1, 2, and 5.
mean
arithmetic average of a distribution obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the # of scores.
ex: 1,5,2,10,9,7,5,1,2,4. the mean is: 4.6 (all 10 #s added then divide by 10)
median
middle score in a ranked distribution from low to high scores; half of the scores are above, half of the scores are below.
ex: 1,1,2,2,4,5,5,7,9,10. the median is 4.5. (4+5, 9/2)
range
the difference between the highest and the lowest scores in a distribution.
normal distribution
frequency distribution that is shaped like a symmetrical bell.
skewed
distorted distribution not evenly distributed around the mean.
correlation coefficient
statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between to variables. extent to which two things vary together.
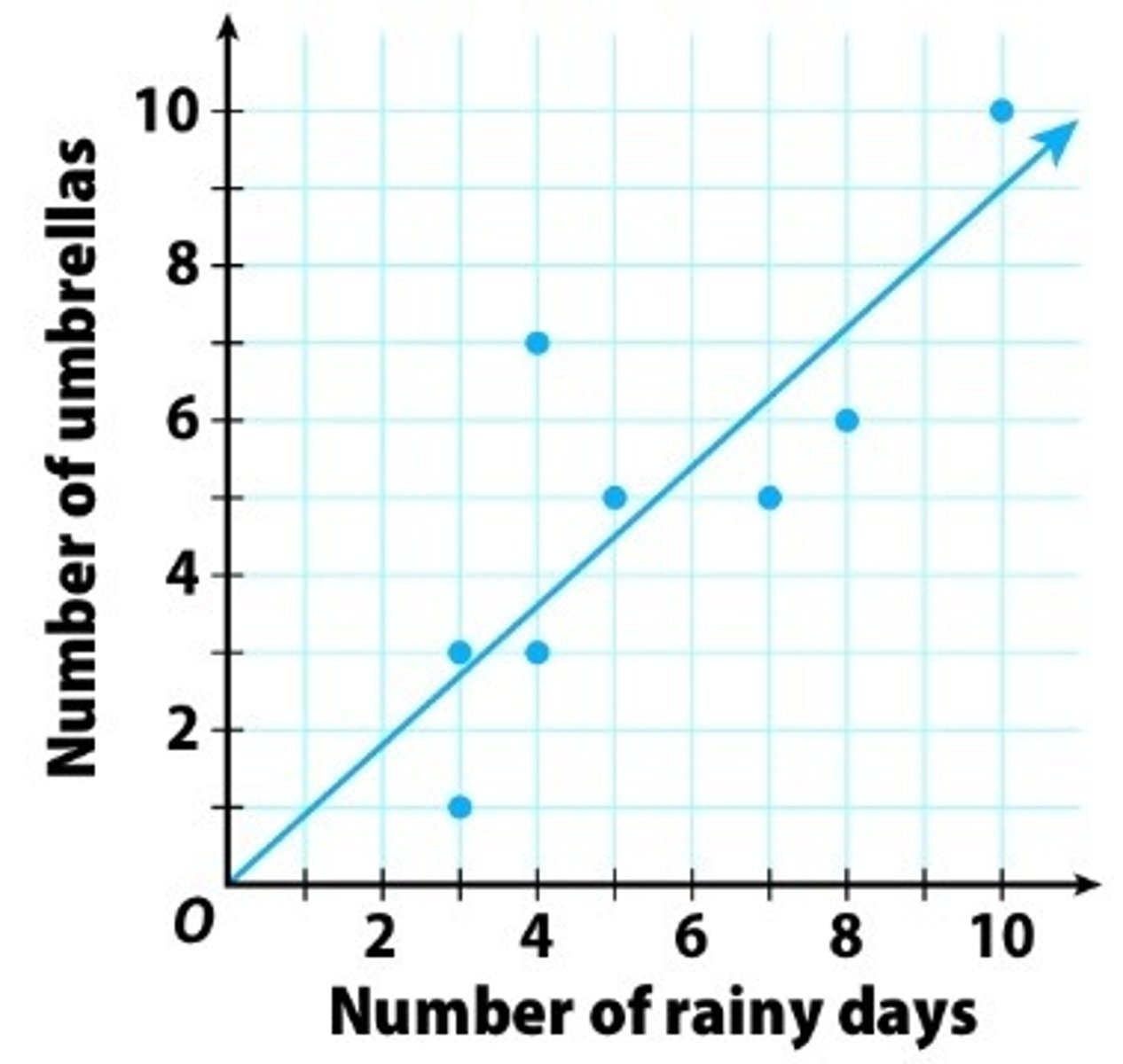
positive correlation
as the value of one variable increases (or decreases) so does the value of the other variable. a perfect positive correlation is +1.0. the closer the correlation is to +1.0, the stronger the relationship.
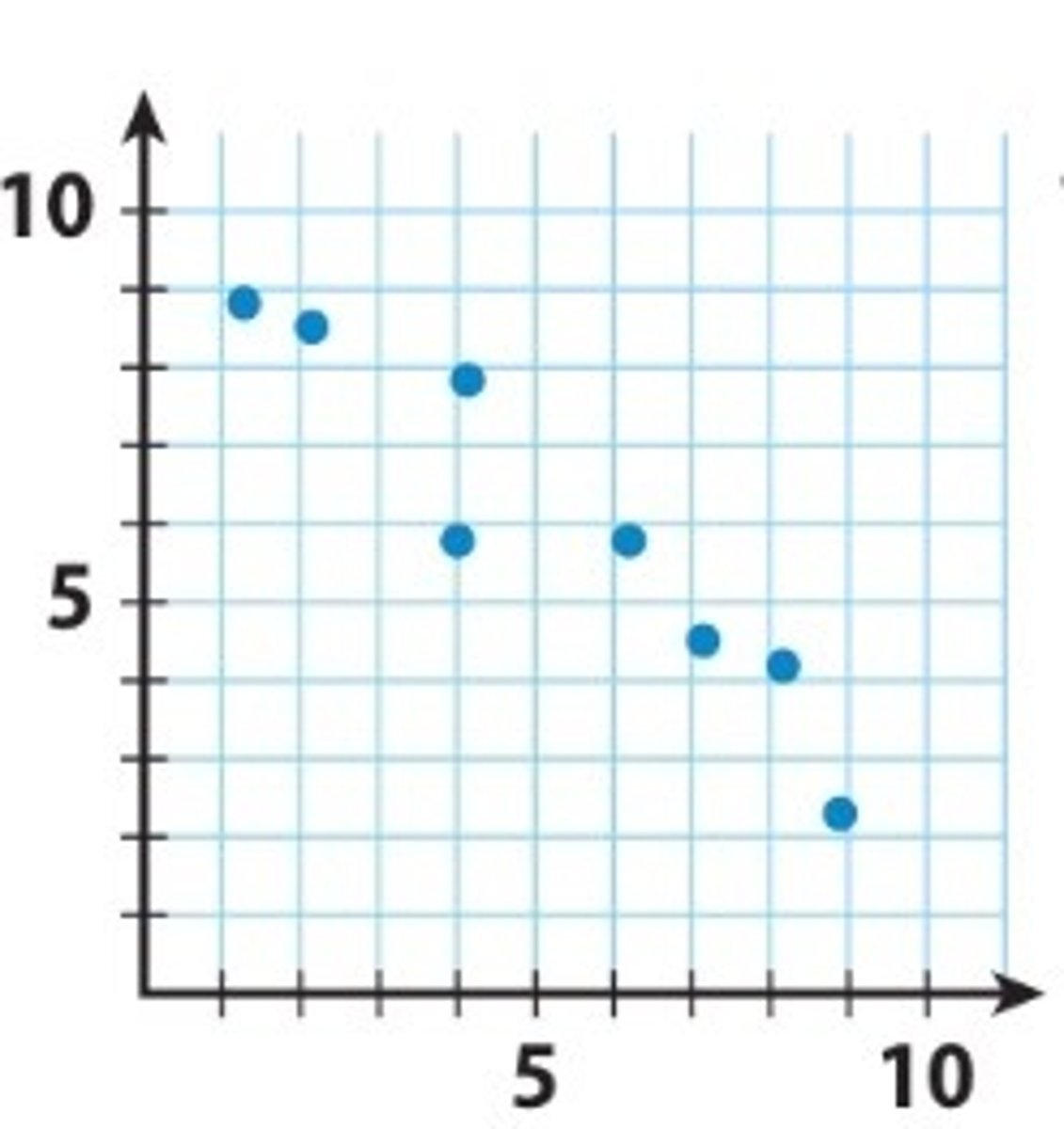
negative correlation
as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases. A perfect negative correlation is -1.0. the closer the correlation is to -1.0, the stronger the relationship.
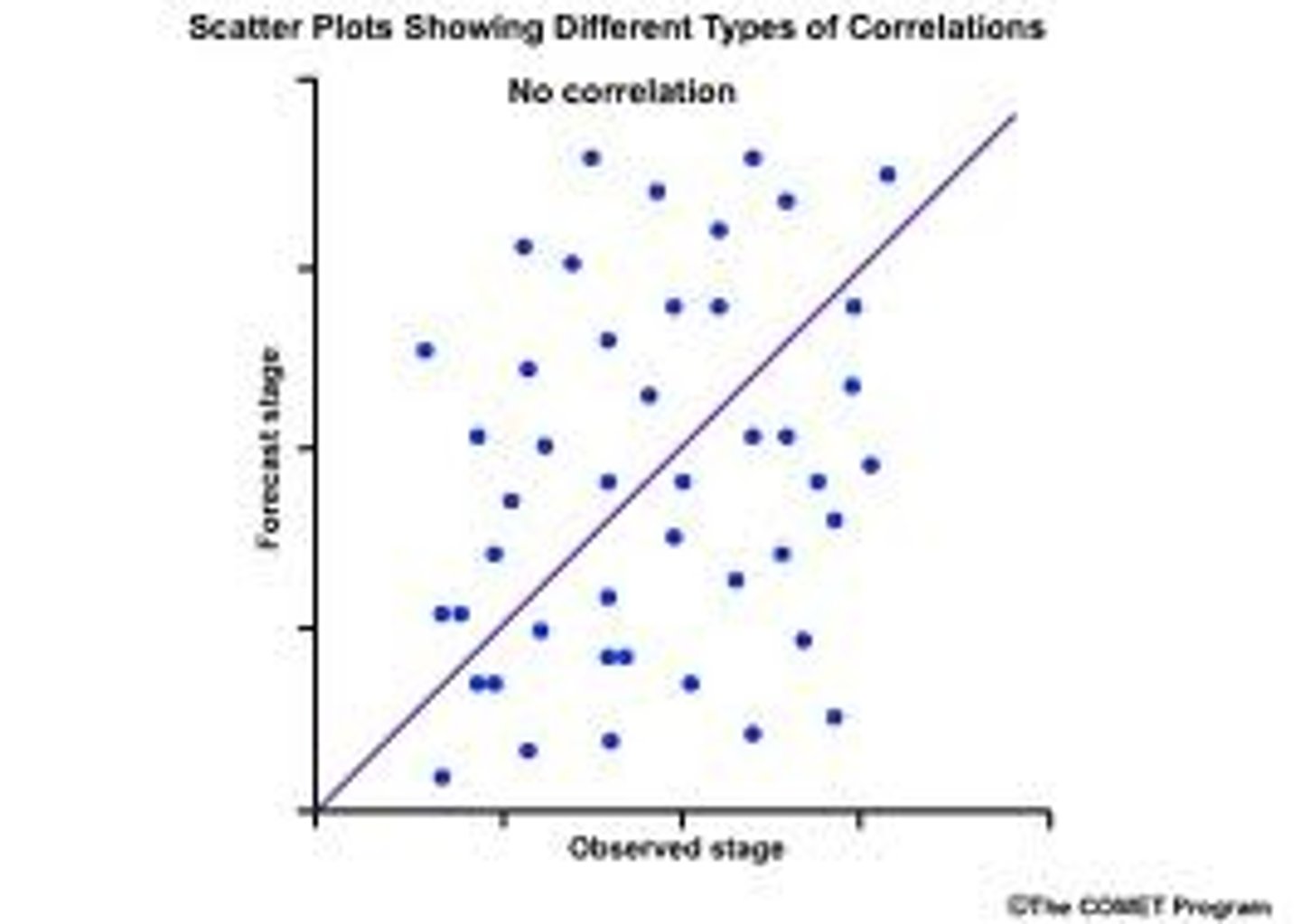
zero correlation
no relationship whatsoever between the two variables.
inferential statistics
statistics that can be used to make a decision or reach a conclusion about data.
statistically significant
possibility that the differences in results between the experimental and control groups could have occurred by chance is no more than 5%.