Year 10 GCSE Chemistry - Separating Mixtures
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Boiling point
Temperature at which a substance turns from liquid into a gas
Chromatography
Method in which a mixture of (often coloured) substances is separated, relying on a mobile and stationary chemical phase
Crystallisation
When crystals form during evaporation of a solvent from a solution
Dissolution (derivative of verb 'dissolve')
When a solvent and solute mix to form solution
Evaporation
Liquid turning into gas
Filtration
Separates solid insoluble substances from a liquid
Fractional distillation
Method for separating a mixture of liquids with different boiling points
Insoluble substance
One that will not dissolve
Melting point
Temperature at which a substance changes from the solid to liquid state
Mixture
Two or more different substances not chemically bonded together
Pure substance
Single element or compound
Simple distillation
Method to separate a solvent from a solution
Soluble substance
One that will dissolve in a given solvent
Solute
Substance that dissolves in a solvent
Solution
Mixture formed when one substance dissolves in another
Solvent
Substance that can dissolve a solute to form a solution
How filtration works
Filter paper used has tiny microscopic holes in it that allow small enough particles like water molecules to pass through but prevent too large particles passing like grains of sand
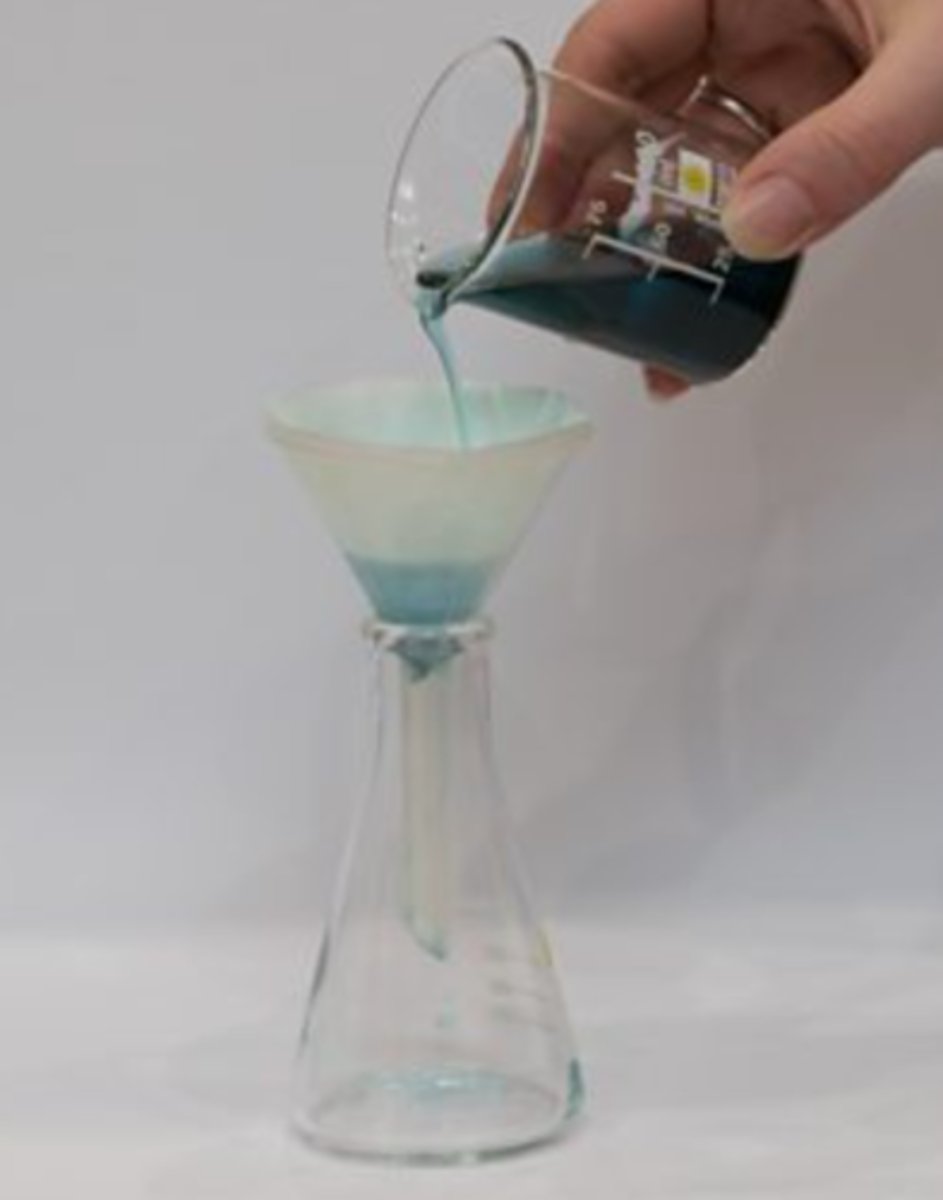

When evaporation is used as a method for separating solutions
When separating a solute from a solution, you evaporate the solvent
How you can safely carry out evaporation as a method for separating a solute from a solution
Slowly, using a water bath
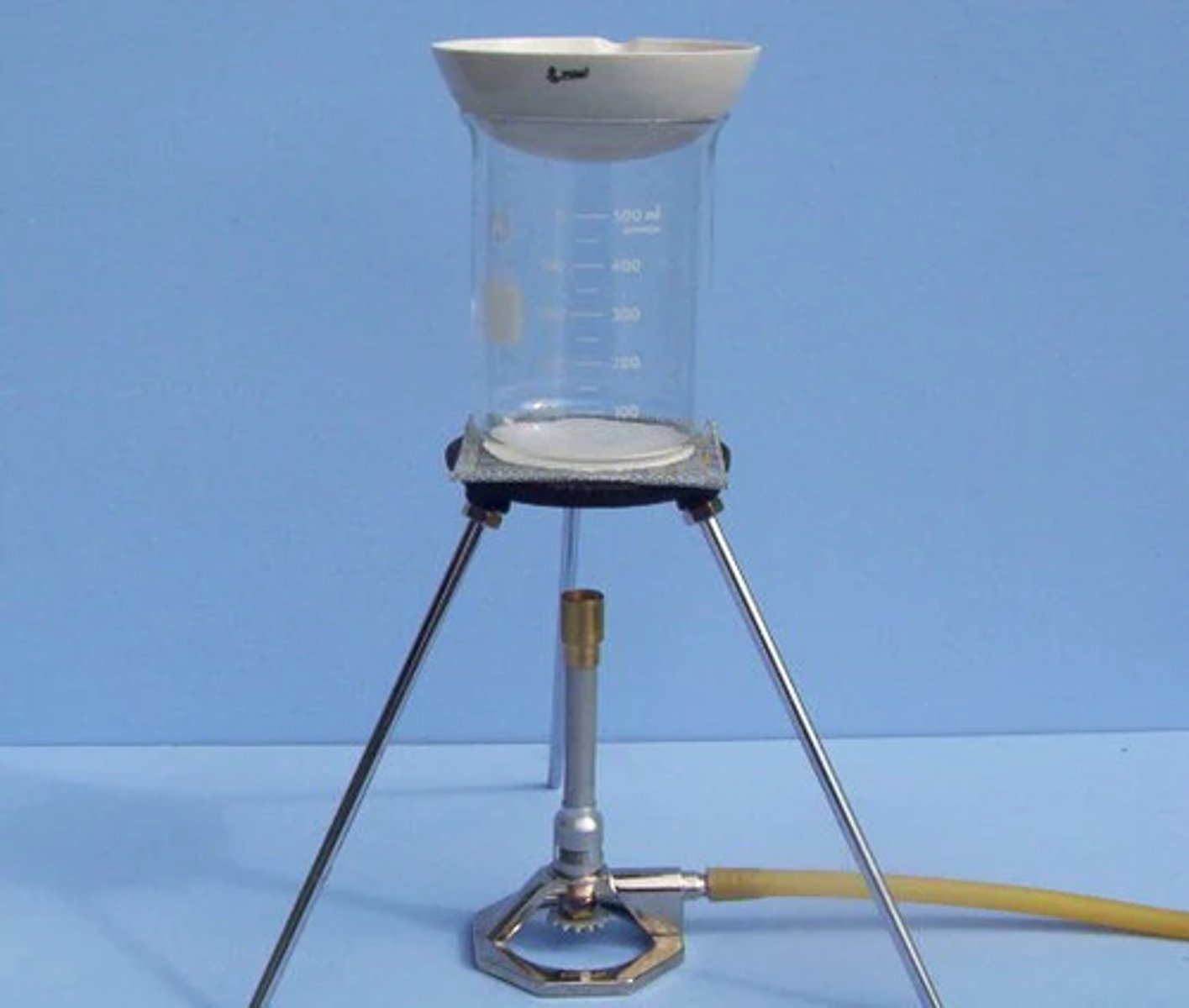

Equipment used in evaporation as a method for separating a solute from a solution, bottom to top
Bunsen burner, tripod and gauze, beaker containing water and evaporating dish containing solution
Gauze
Thin, transparent fabric with a loose open weave placed on top of tripod for support e.g. of beaker in evaporation method for separating solute from solution
What crystallisation results in
Larger, well-formed crystals
Carrying out crystallisation
Evaporate water until the solution becomes saturated and then leave the solution i.e. to crystallise slowly
Saturated solution
One in which no more solute cannot dissolve
What simple distillation is used for
To separate a mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent or one of two different liquids, importantly with different boiling points
What simple distillation allows you to do
Allows you to evaporate and then condense the liquid, rather than letting it escape into the air
Equipment in simple distillation, left to right
Bunsen burner or similar (↑ heat), round-bottom flask, thermometer, Liebig condenser with water in below water out opening and beaker with ideally pure liquid
Simple distillation diagram

Why water in opening is below water out opening in Liebig condenser (in simple distillation)
Ensure water completely fills condenser to optimise cooling efficiency
How fractional distillation is carried out
The fractionating column has a large surface area inside for improved condensation allowing each liquid to be collected separately, stopping other liquids evaporating
Equipment used in fractional distillation, bottom-left to top to right
Bunsen burner or similar (↑ heat), round-bottom flask containing mixture of liquids, fractionating column containing glass beads to increase its surface area, thermometer, condenser (and beaker to collect ideally pure liquid)
Example of mixture of two liquids that may be used in fractional distillation
Ethanol and water
Fractional distillation diagram

Two examples of ways scientists may use chromatography
To tell whether food contains traces of a harmful substance or whether a sample of paint found at a crime scene matches a suspect's car
Type of technique chromatography is
Analysis
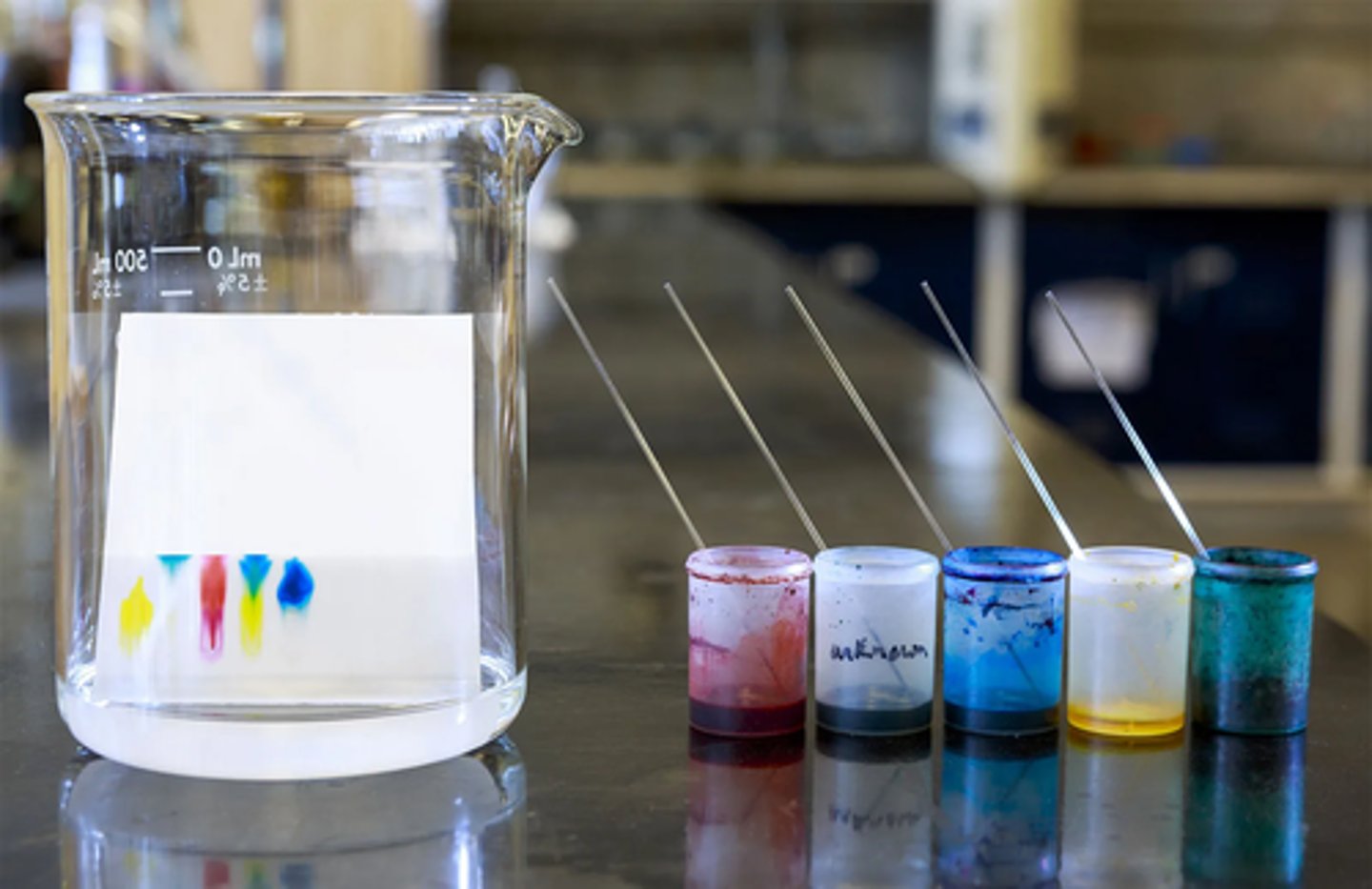
What paper chromatography can be used for
Separating the coloured substances in ink
Stationary phase
One that does not move
Mobile phase
One that moves
Stationary phase in paper chromatography
Absorbent paper
Mobile phase in paper chromatography
Solvent such as water
Thin layer chromatography
Works in same way as paper chromatography but the stationary phase is a thin layer of silica or alumina powder spread over a sheet of glass or plastic, which the solvent travels up, carrying the solute
Chemical formula for silica - word and symbols
Silicon dioxide, SiO2
Chemical formula for alumina powder - word and symbols
Alumina oxide, Al2O3
Diagram of apparatus used for TLC (thin layer chromatography) - revise equipment shown

What Rf values are used for
Compare different spots on a chromatogram
What two spots having the same Rf value and being the same colour means
They are likely to be identical
Stationary phase in gas chromatography
Silica or alumina powder packed into a metal column
Mobile phase in gas chromatography
An unreactive carrier gas such as nitrogen that does not react with the sample
What gas chromatography is used for
Separating the components of a mixture and measuring their quantities
Revise this diagram showing the instruments for gas chromatography

'Phase' meaning in chemistry
Physically distinct form of matter
Phase in chromatography
One of two main components used
Purpose of column oven in gas chromatography
High temperature
What column contains in gas chromatography
Finely divided solid powder such as silica or aluminium oxide, the stationary phase
Explanation of gas chromatography
Sample turns into gas when injected into the column, pushed through by the carrier gas. Different components take different times to travel through the column depending on how strongly they bond to the stationary phase. A detector sends a signal to a computer as each component leaves the column and the computer produces a chromatogram in which each component is a peak plotted against travel time
Solvent front
Furthest point reached by solvent
Rf =
distance substance travelled (spot distance) / distance solvent travelled
Range of Rf values
0 to 1
What Rf stands for
Retention factor
Chromatography for white or colourless mixtures
Process is carried out in the same way but spots do not show up, unless under UV light or using a stain such as iodine
Paper chromatogram image (unfinished)

What x-axis shows on gas chromatogram
Retention time
What y-axis is directly proportional to on gas chromatogram
Quantity of substance
What you can infer from a gas chromatogram with four peaks
It measures a mixture containing four substances
Type of chromatography not mentioned elsewhere in this Quizlet
Column chromatography
Starting line in paper chromatography
Drawn in pencil so that it does not dissolve in the solvent and affect the results, this is where small spots of each sample are placed
What you do once the solvent is near the top of paper in paper chromatography
Paper is taken out of the solvent, the level of solvent is marked and the paper is left to dry
Why substances in a mixture separate
They have different attractions to the stationary phase such as paper and mobile phase such as solvent
Substances have different Rf values in different -
Solvents
Why the water level in the beaker must be below spots in paper chromatography
Prevents the sample dissolving directly into the solvent, rather than being carried up the mobile phase
Watch video? (On chromatography - add a bit if necessary)
What 'pure' refers to in everyday life
Natural substances that have not been processed or changed
What 'pure' means in science
Substance consisting of one element or compound
What mixtures are (pure or impure) and why
Impure, as they contain more than one element or compound
It is difficult to obtain completely -
Pure substances
What liquid is used in the manufacture of computer chips, and why it is not likely pure
'Ultra pure' water, although this is easily contaminated by carbon dioxide from the air
What air is a mixture of
Oxygen, nitrogen and other substances
Why many useful materials are mixtures
Different substances are often deliberately chosen to produce the desired properties
Alloy
Mixture of metals with one or more other elements
What most of the metals we use are
Alloys
Why a mixture of gold and copper is used for jewellery
Pure gold is very soft so this alloy is harder
What a melting point of a pure substance is (answer is not a number)
A single temperature
Melting point of an impure substance
Often less than that of a pure substance and melts over a range of temperatures
How melting points can be used to determine the purity of a substance
The greater the difference between the measured melting point of a substance and its accepted value, the lower the purity of the substance
Melting point of pure stearic acid
69 °C
How melting point is measured with apparatus
A solid is heated and the temperature at which it melts is measured using a thermometer. Alternatively, the temperature of a solid can be measured at regular time intervals and a graph plotted
Why a substance must be heated slowly when finding its melting point
To allow the temperature of the whole sample to increase, so that the melting point is measured accurately
Why it is important to stir the sample when finding its melting point
So it is heated evenly, so that the melting point is measured accurately
Two types of chromatography you can use to tell if a substance is pure
Paper or thin layer chromatography
Four main advantages of thin layer chromatography when determining if a substance is pure
It is quicker, more sensitive, so a smaller a sample can be used, there is a larger range of stationary phases and solvents to choose from and you can scrape an individual spot from a thin layer chromatogram for further analysis, for example by gas chromatography
How scientists discovered what our ancestors ate
By analysing the insides of ancient cooking pots to identify the food substances left behind. Using gas chromatography, they analysed wax from cabbage leaves and compared it to the chromatogram from the contents of the cooking pot and found they matched almost exactly, concluding the ancient pot had been used to cook cabbage
Separation of a mixture can be improved by using what method of chromatography
Two-dimensional chromatography
Two-dimensional chromatography
Uses two different solvents. Chromatography paper or plate is rotated by 90 ° after using the first solvent
Example of what two-dimensional thin layer chromatography can be used to separate
Different plant oils
What you must know to decide on a separation method of a mixture
Some properties of individual components in the mixture
What gas chromatography can be used for
Many different kinds of substance
Even though gas chromatography is versatile, it would not be -
A method you would use in school
Revise table showing methods you could use in school and question
