BIOL 2403 - A&P - Minich - Chapter 2 notes - Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Matter
Anything that occupies space
Energy
ability to do work of cause change
Matter is composed of ....
Atoms
Atoms are composed of .....
3 types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons
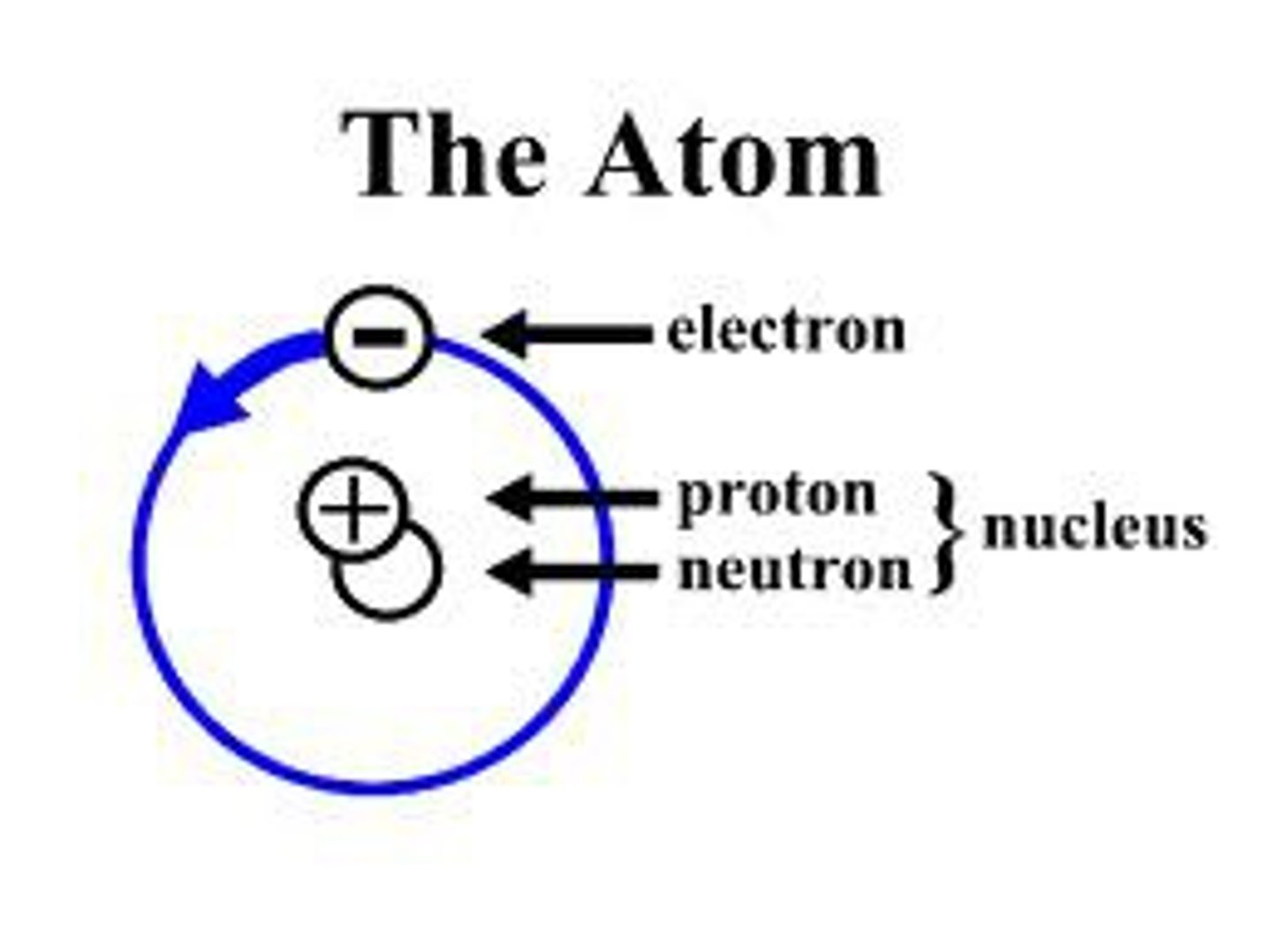
Neutrons are _____ charged
neutrally
Protons are ______ charged
Positively
Electrons are ________ charged
Negatively
Electrons are located on different ________ of the electron cloud
orbitals
the number of _______ electrons determine an atoms behavior
valence
Valence electrons of reactive atoms interact with other atoms to form various _____
Compounds
How many elements have been discovered?
118
how many elements occur in nature?
92
How many elements are present in living organisms?
25
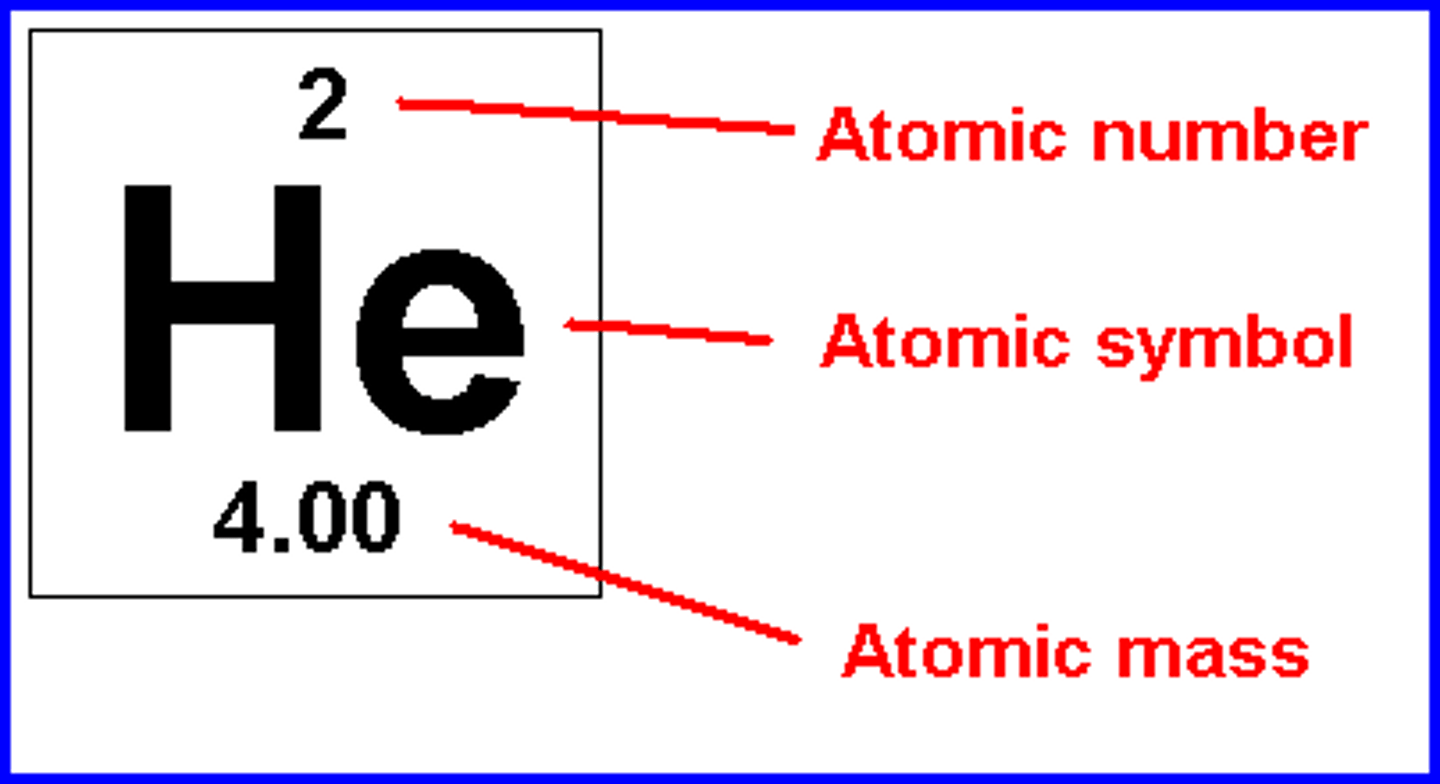
-The atomic number contains the number of _____
-the atomic mass is the number of ____________
protons, protons and neutrons
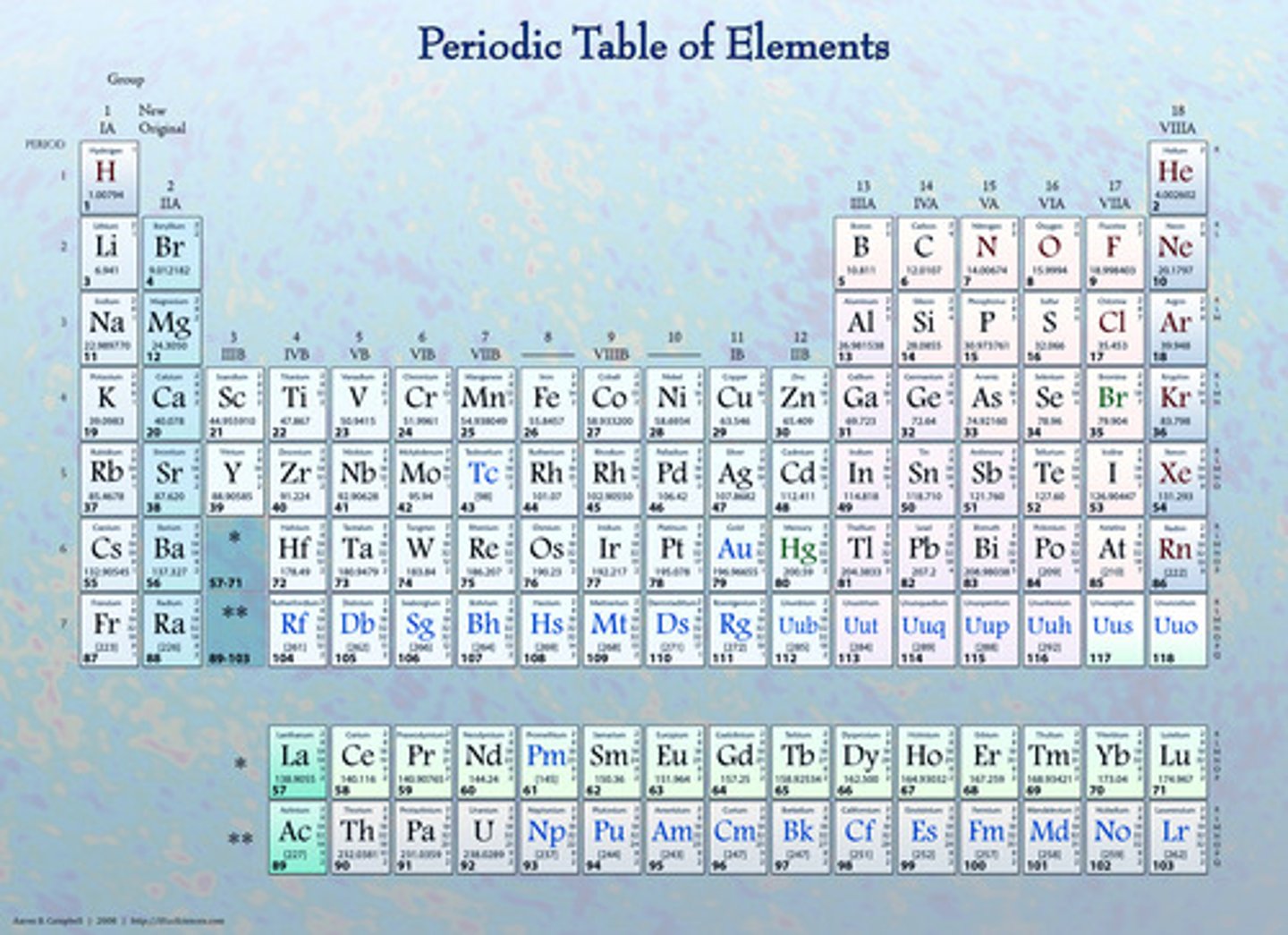
in the periodic table, periods are _________ (direction) and they indicate __________
side to side ; number of orbitals
in the periodic table, groups are _________ (direction) and they indicate_____________
up and down ; number of valence electrons
Each atoms behavior is determined by the number of __________
Valence electrons
What does the octet rule state?
That an element must have 8 valence electrons to be considered stable
What are the exceptions to the octet rule?
Helium and hydrogen. They only need 2 valence electrons
Inert/complete atom
when an atom is stable and does not need to interact with other atoms (only in group 8 - noble gasses)
reactive/incomplete atom
when an atom does not have a complete outer shell and needs to interact with other atoms
compound
when two or more incomplete atoms bond (ionic or covalent)
ionic bonding
between a metal and non-metal
covalent bonding
between two non-metals
ions
atoms or groups of atoms with a positive charge or negative charge (often times written like Na+ or Na-)
ions with a positive charge
Cations
ions with a negative charge
Anions
how are ions formed?
by giving or taking electrons in order to achieve chemical stability
Metals tend to _____ electrons and become cations (+)
Give
non-metals tend to ______ electrons and become anions (-)
take
positive and negative ions experience powerful attraction called __________________________
ionic bonding
Major function of Sodium ion (Na+)
signaling in nerve and muscle tissues
Major function of Potassium ion (K+)
signaling in nerve and muscle tissue
Major function of calcium ion (Ca^2+)
Hardness of bones, muscle contractions, blood clotting
Major function of hydrogen ion (H+)
determines pH
Major function of Phosphate (PO4^3-)
Bone hardness, component of DNA, RNA, ATP
Major function of Chloride (Cl-)
Signaling
Some ions reach stability by ___________ electrons, otherwise known as covalent bonding
Sharing
The number of ______ each atom will form = the number of electrons needed to complete the outer shell
Bonds
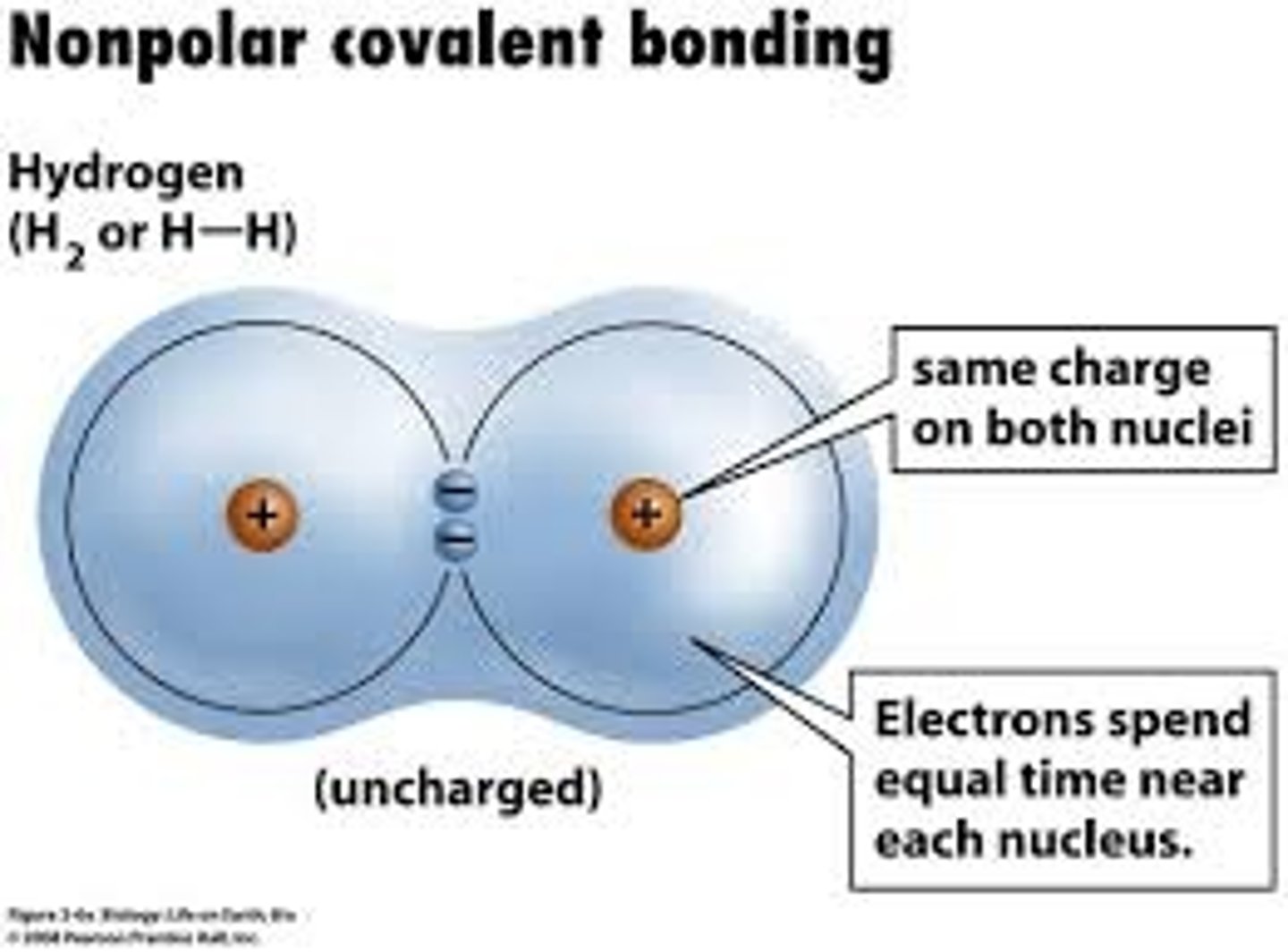
non-polar covalent bonding
Two atoms share equally
When does non-polar covalent bonding occur?
between atoms of the same element or between C-H atoms
polar covalent bonding
Two different atoms share unequally
The closer to _________ (element) the closer the electron pull
Helium
as the result of covalent bonding, complex particles called __________ are formed
molecules
polar molecules are formed when....
polar covalent bonds are arranged in a way that produces a molecule that has one end positive, while the opposite end is negative
non-polar molecules are formed when....
a.) all bonds non-polar covalent
b.) polar covalent bonds are arranged in a way that no opposite charges exist on the opposite ends
Amphipathic molecules are....
large molecules that is polar in one location and non polar in another location
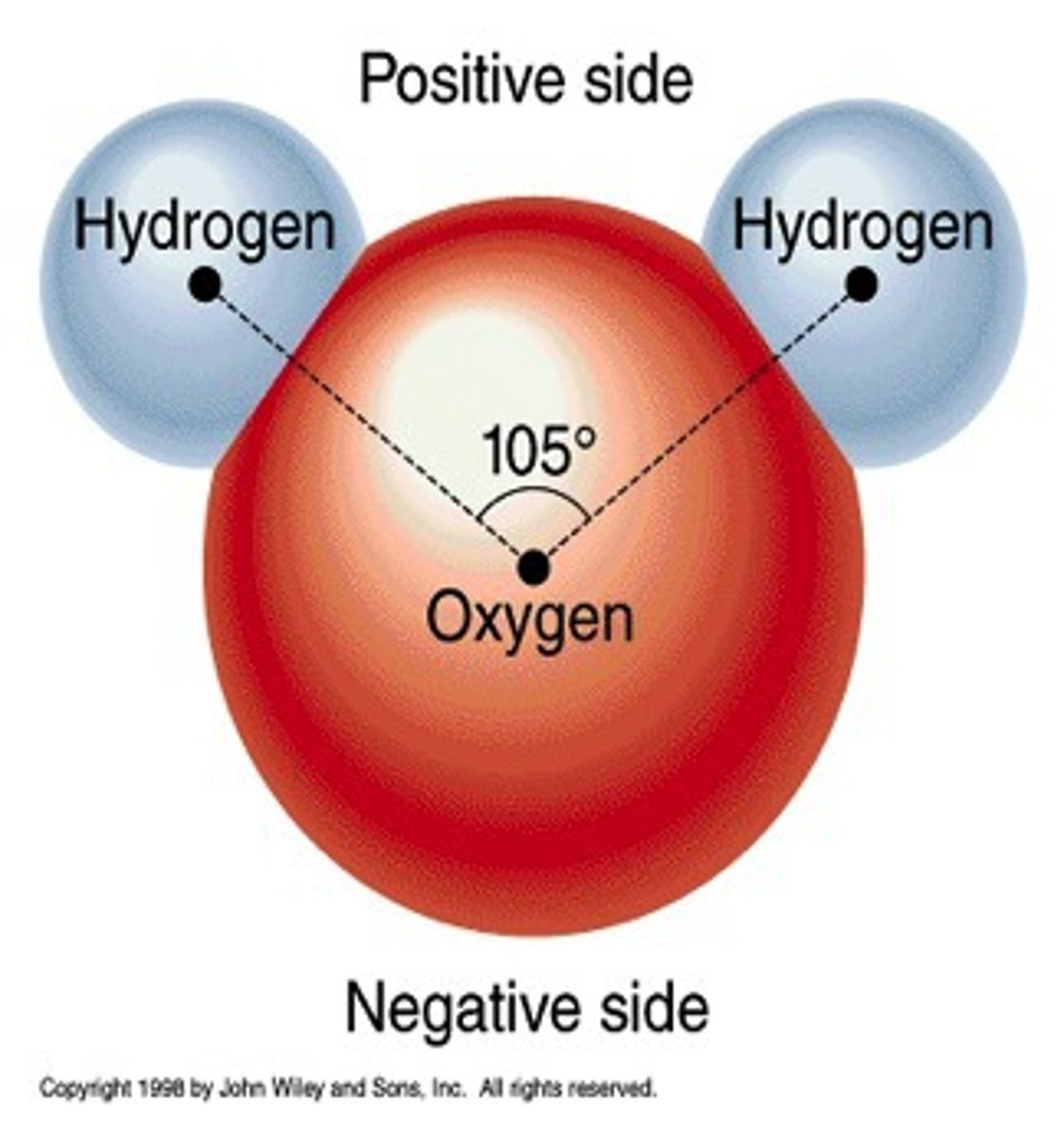
Structure of water
dipolar. Oxygen has two partial negative charges while hydrogen has one partial positive charge
hydrophobic
does not like water - nonpolar molecules
hydrophilic
likes water - some polar molecules
amphipathic
one part likes water and the other part does not -
both polar and nonpolar molecules
functions of liquid water in the body
transport (blood)
lubricates (serous fluid)
cushions (cerebrospinal fluid)
What is pH
a measure of the relative amount of hydrogen concentration in a solution
pH less that 7 is _____
acidic
pH greater than 7 is ______
basic
acid has a _____ concentration of H+
higher
Bases have a _______ concentration of H+
lower
Buffer
a single substance or group of substances that prevent pH changes by adding or decreasing H+
biochemistry
the study of the chemistry of life
What are the two substances found in living organisms?
organic and inorganic
Organic substances ______ carbon
contain
inorganic substances _______ carbon
Don't contain
what are the four classes (biomolecules) of organic substances
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
carbon needs ___ electrons to satisfy the octect rule, so it can form ___ bonds arranged in a great variety of molecules: _______, ________, _________.
4; 4; chains, branched chains, rings
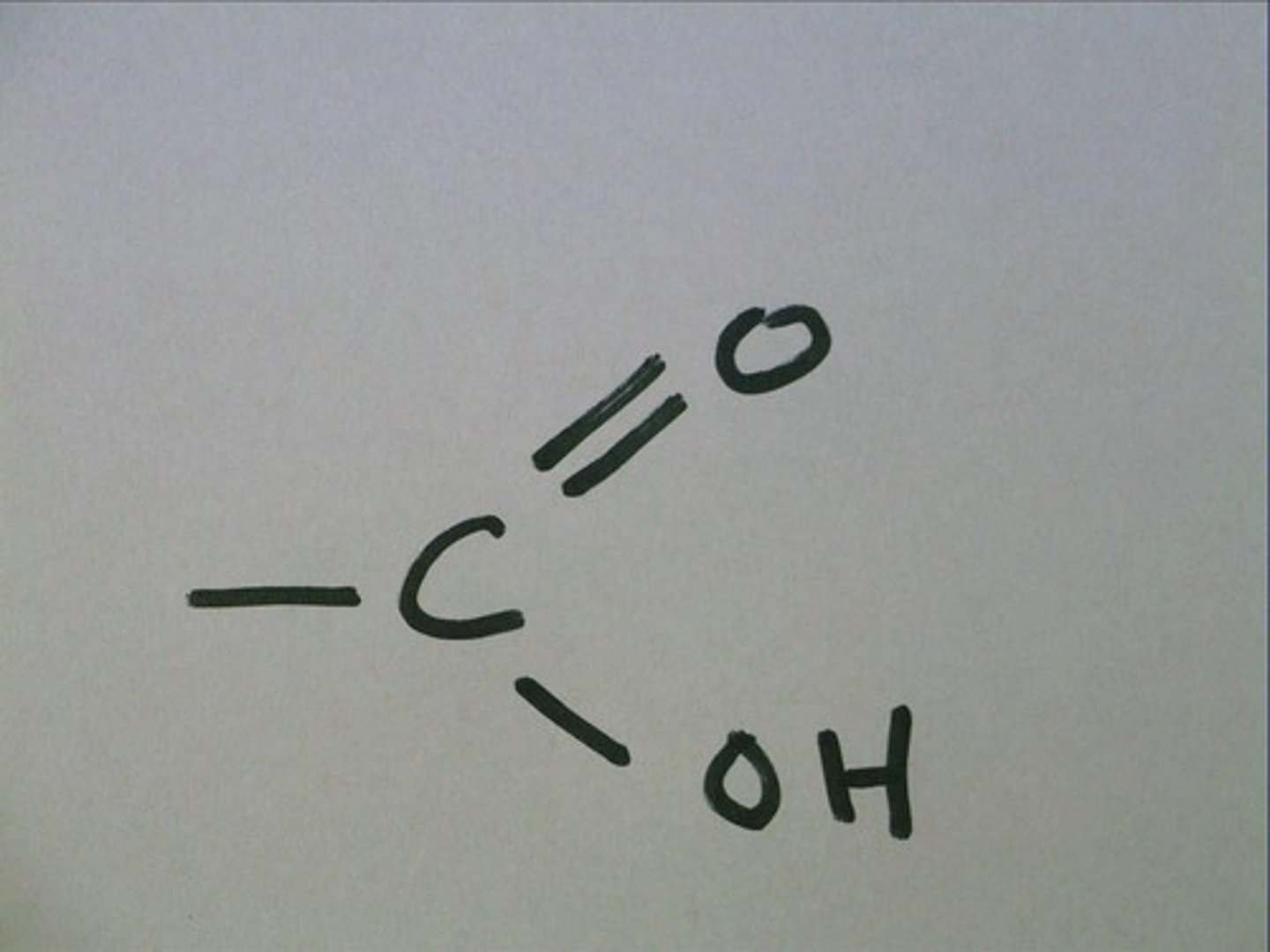
What does carboxyl look like?
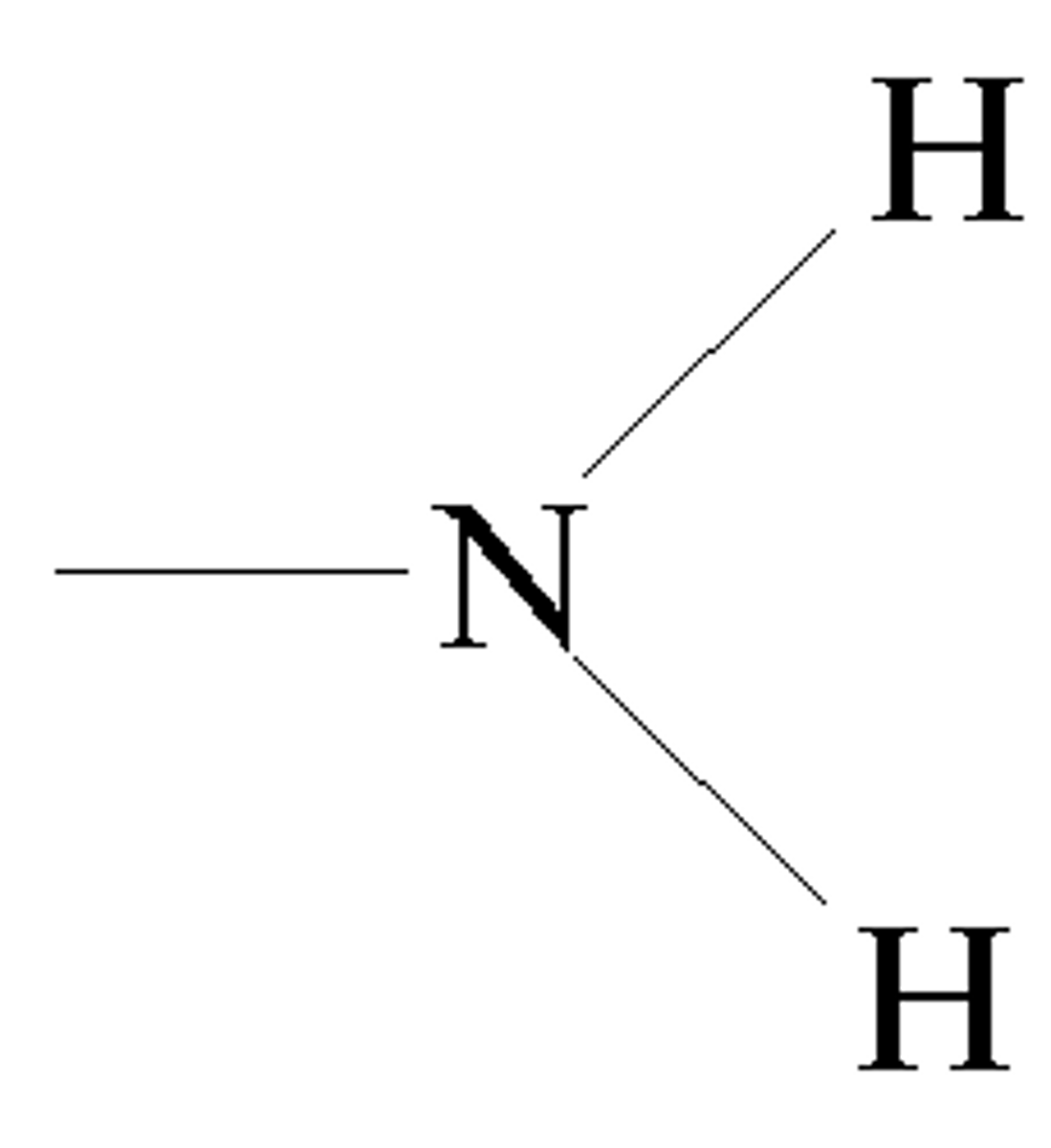
What does Amine look like?
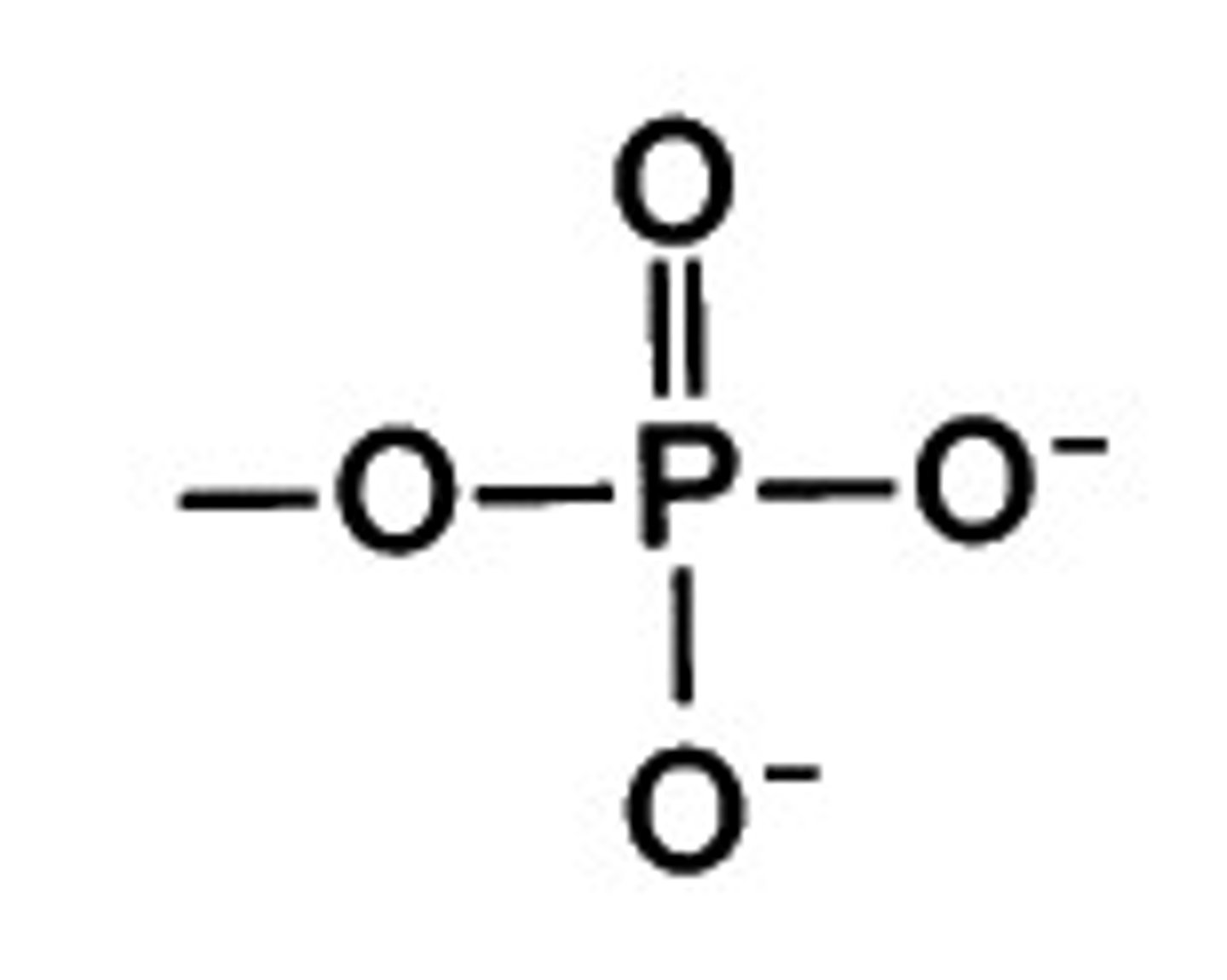
What does a phospate look like?
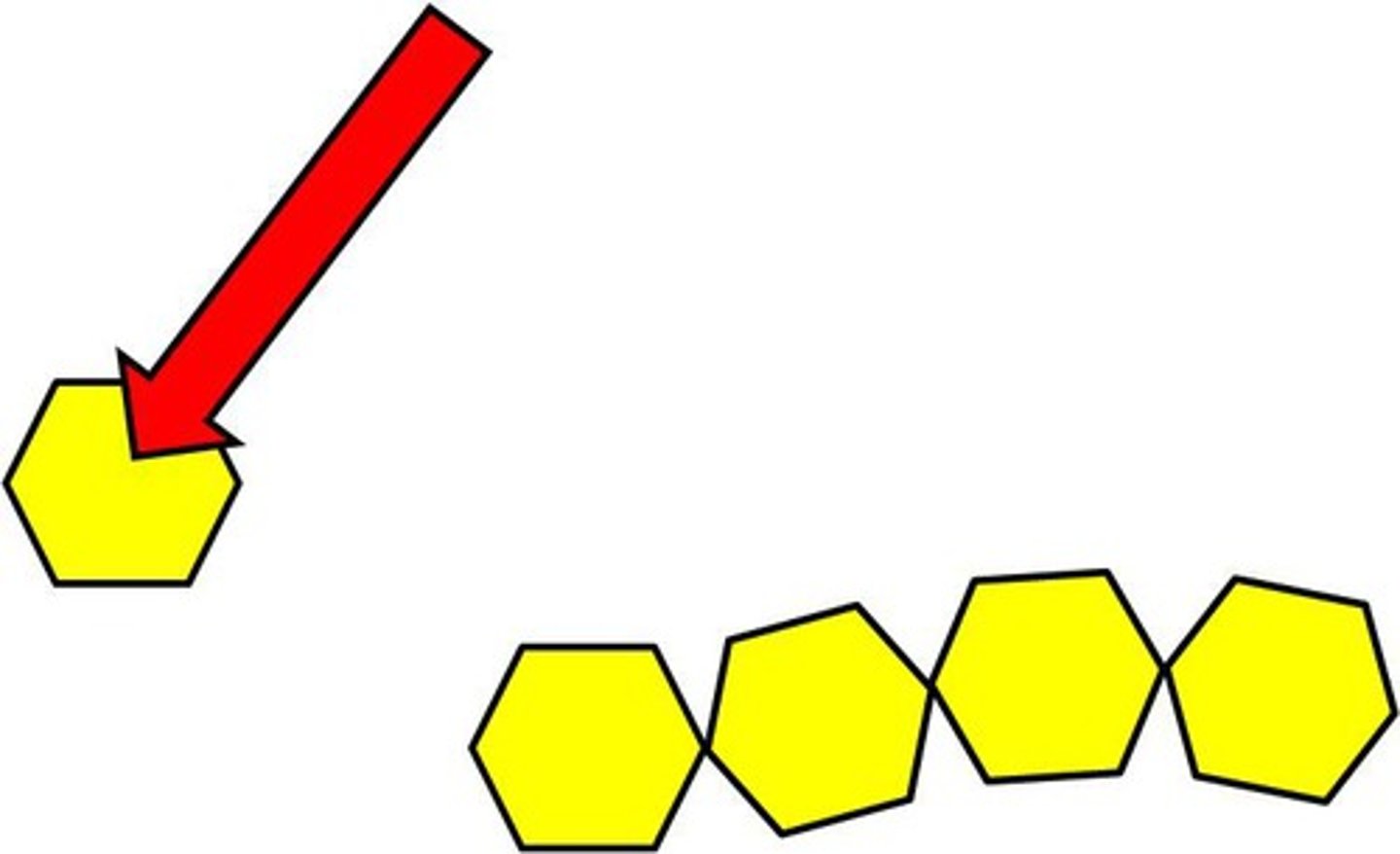
monomers
small molecules (one unit)
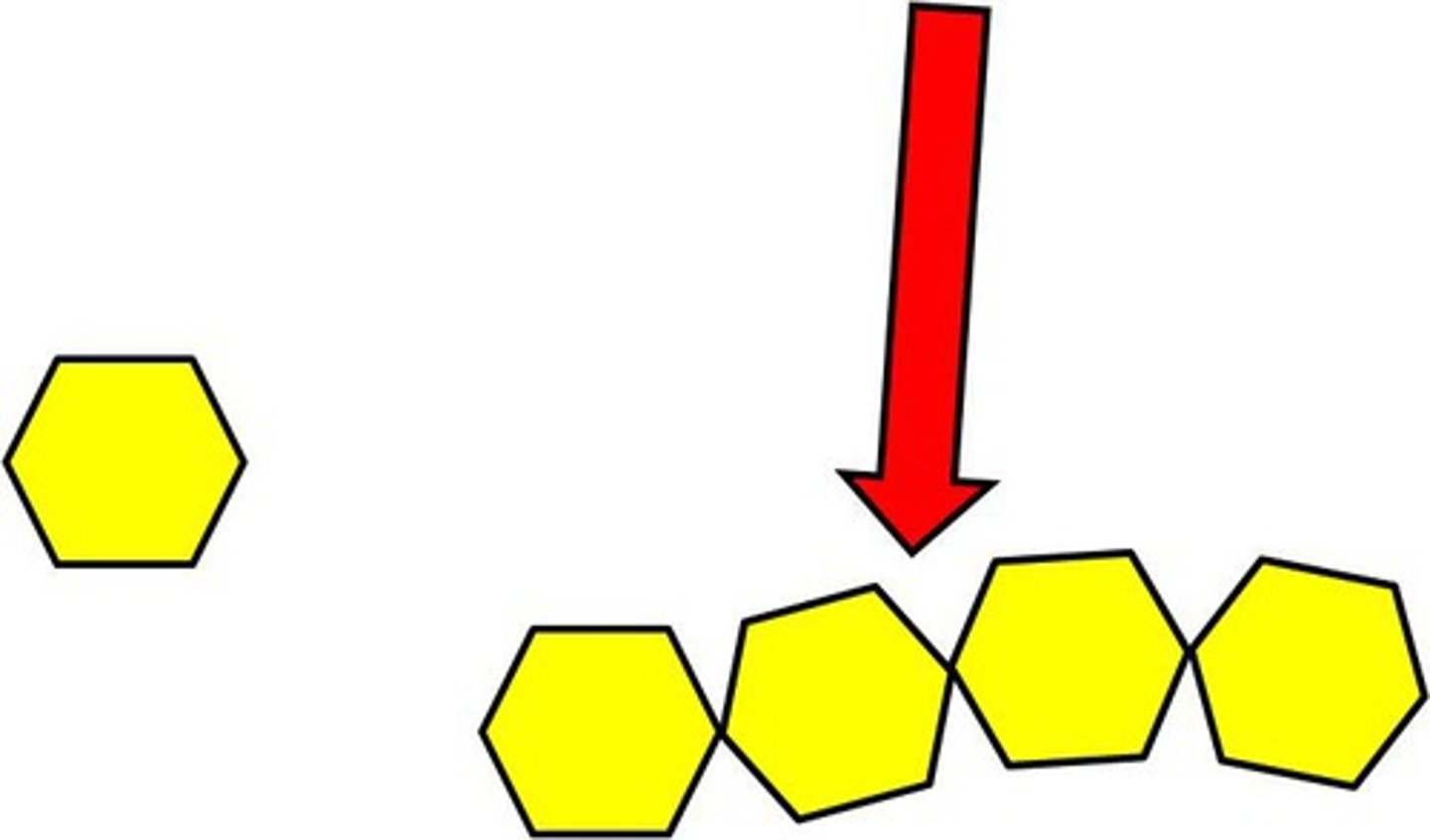
Polymers
large small molecules (many units)
Carbohydrate function
-Major source of energy
-structure and support
If a word ends in -ose it is a _________
carb
-saccharides means _______
carbs
Glucose
C6H12O6
hexagon
major source of energy
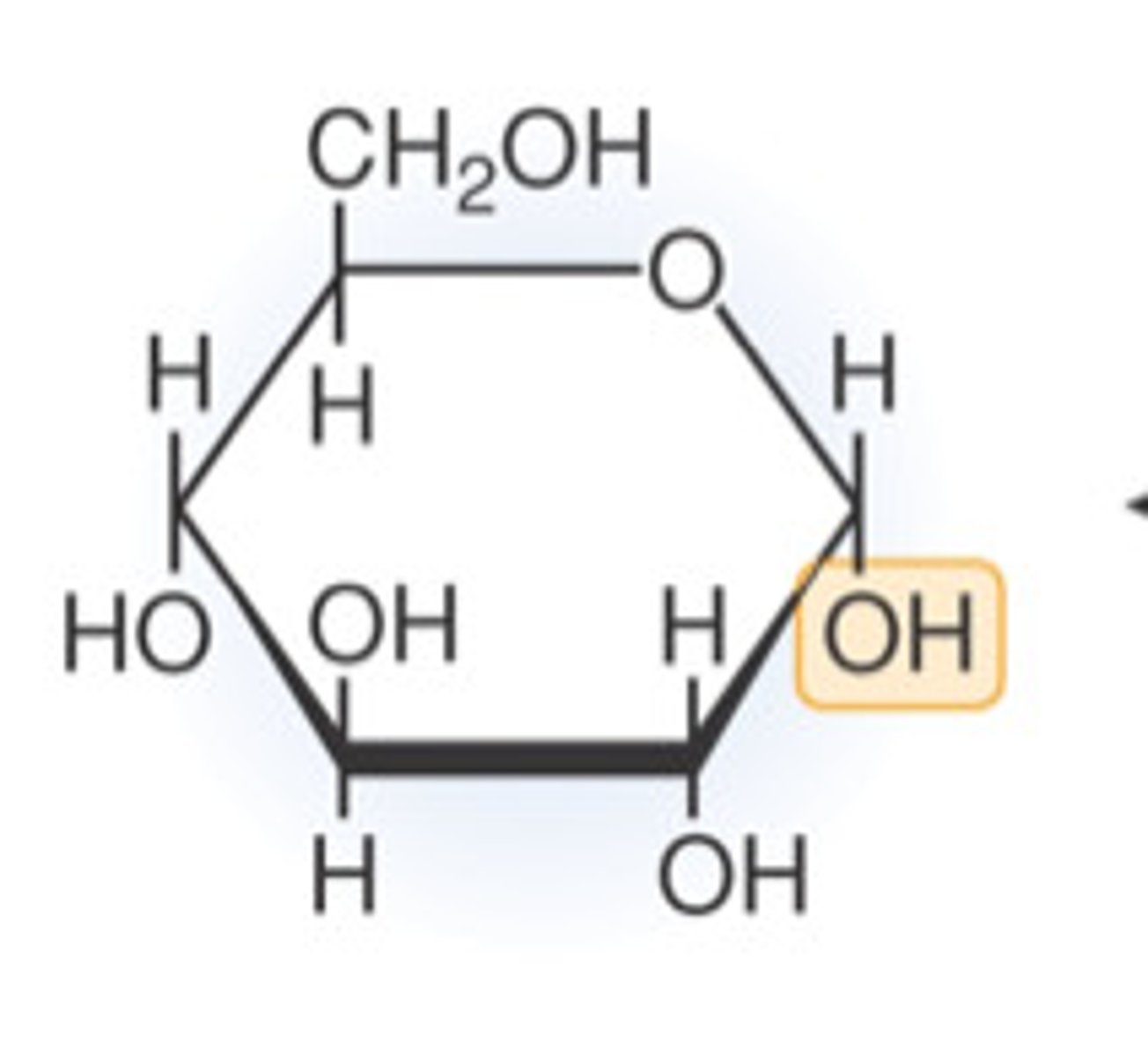
Fructose
monosaccharide
C6H12O6
pentagon
source of energy
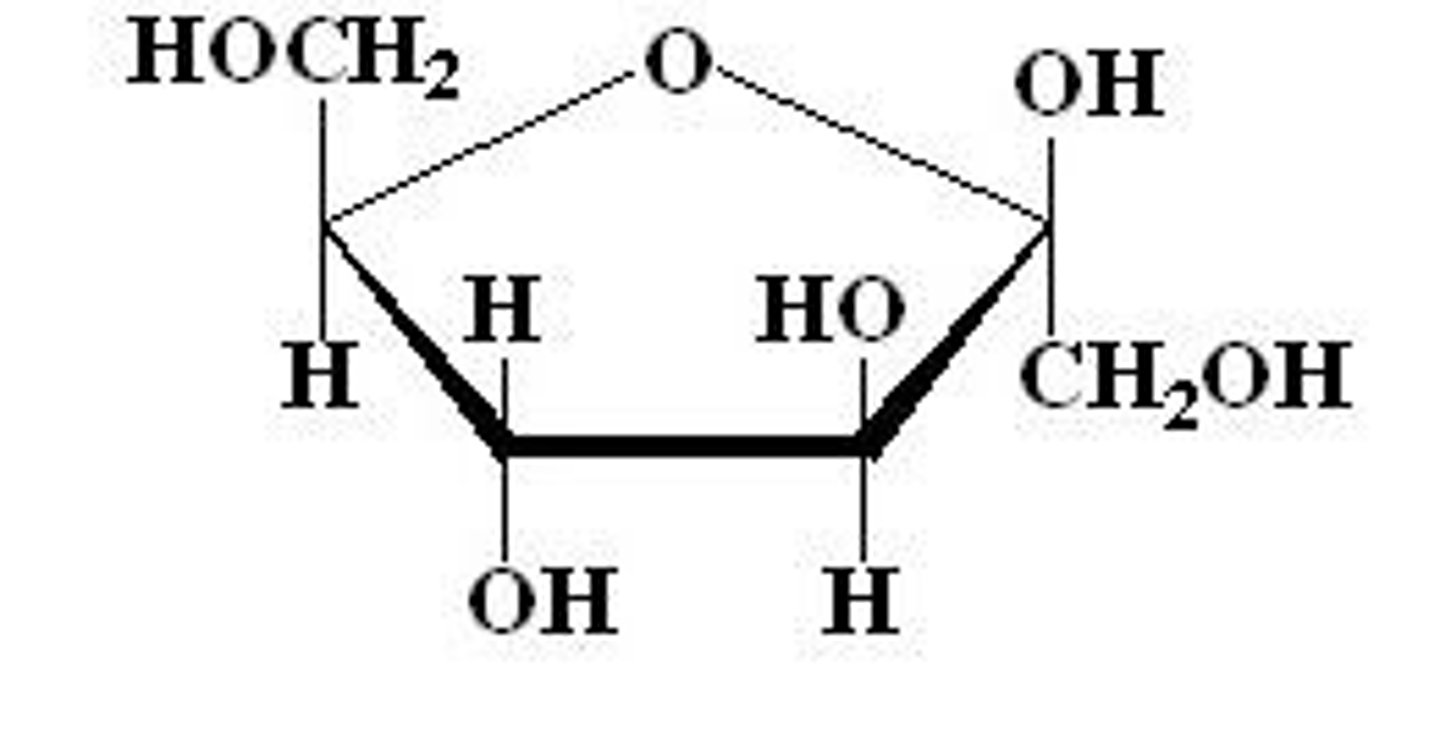
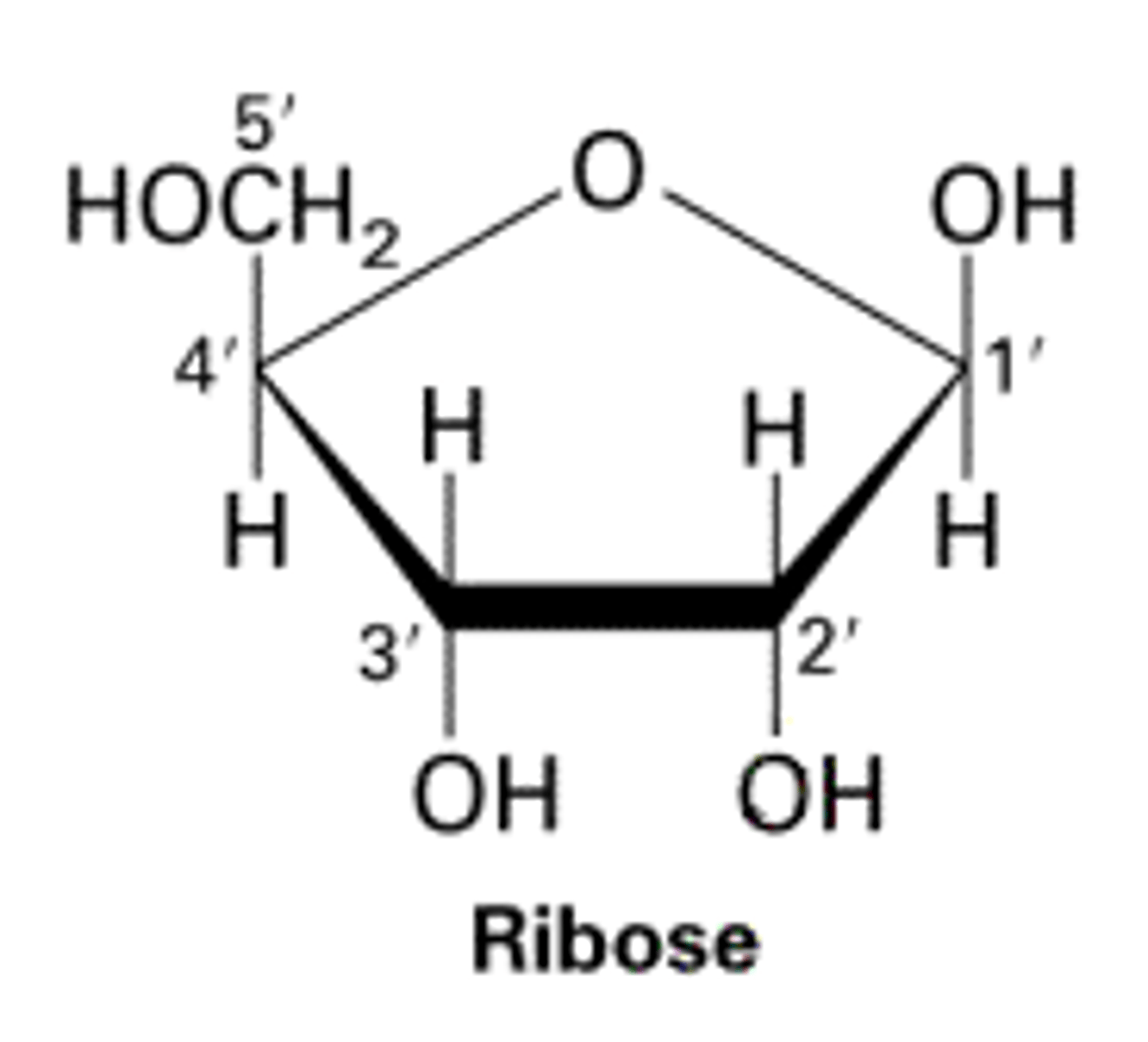
Ribose
monosaccharide
C5H10O5
component of RNA
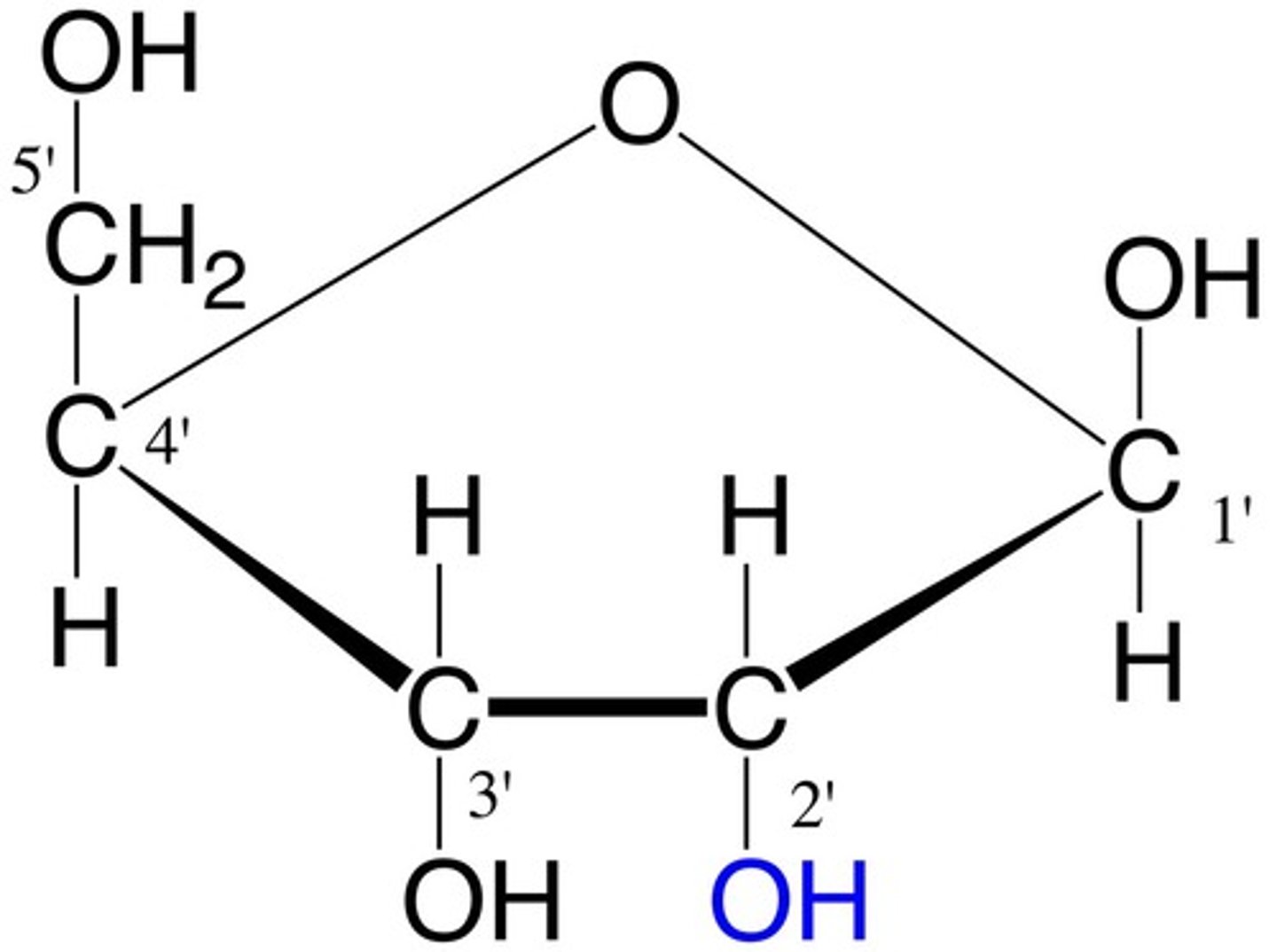
Deoxyribose
monosaccharide
C5H10O4
component of DNA
*DEOXYRIBOSE DOES NOT HAVE THE BLUE OH BUT RIBOSE DOES*
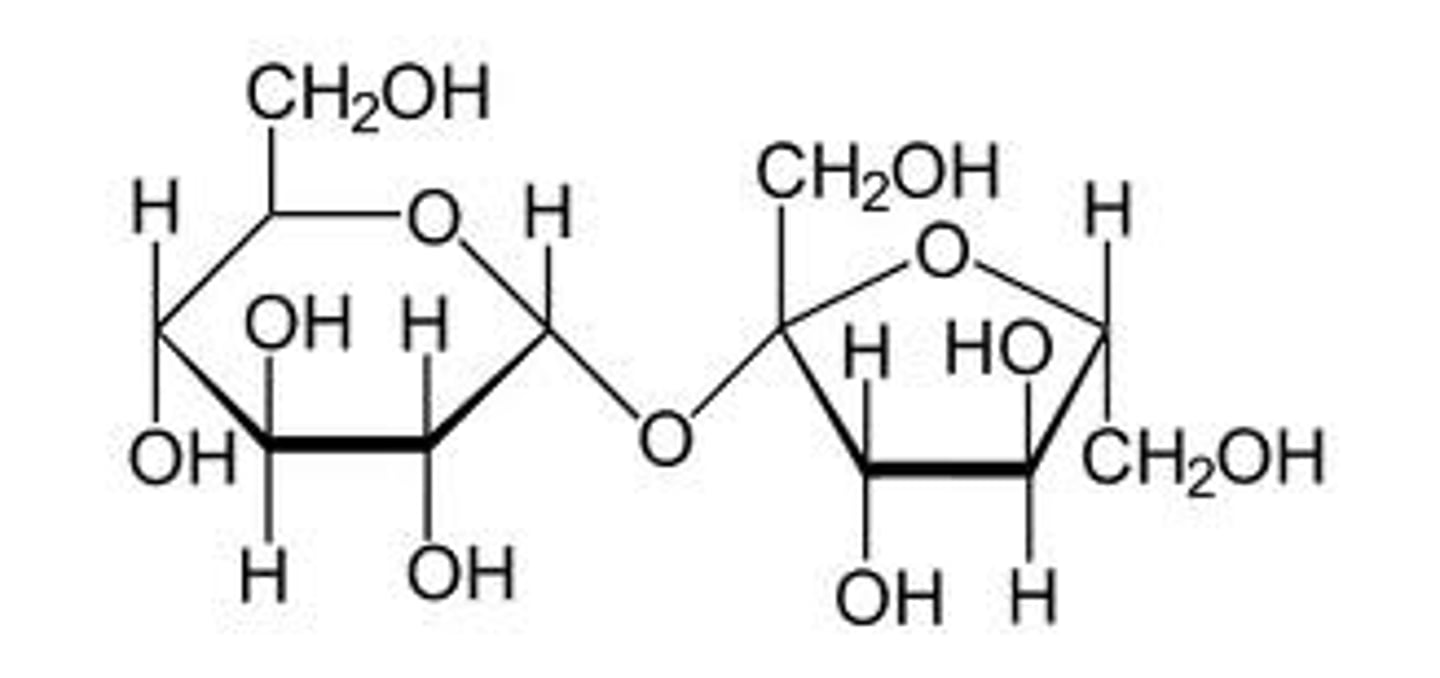
Sucrose
Disaccharide
made of glucose and fructose
source of energy
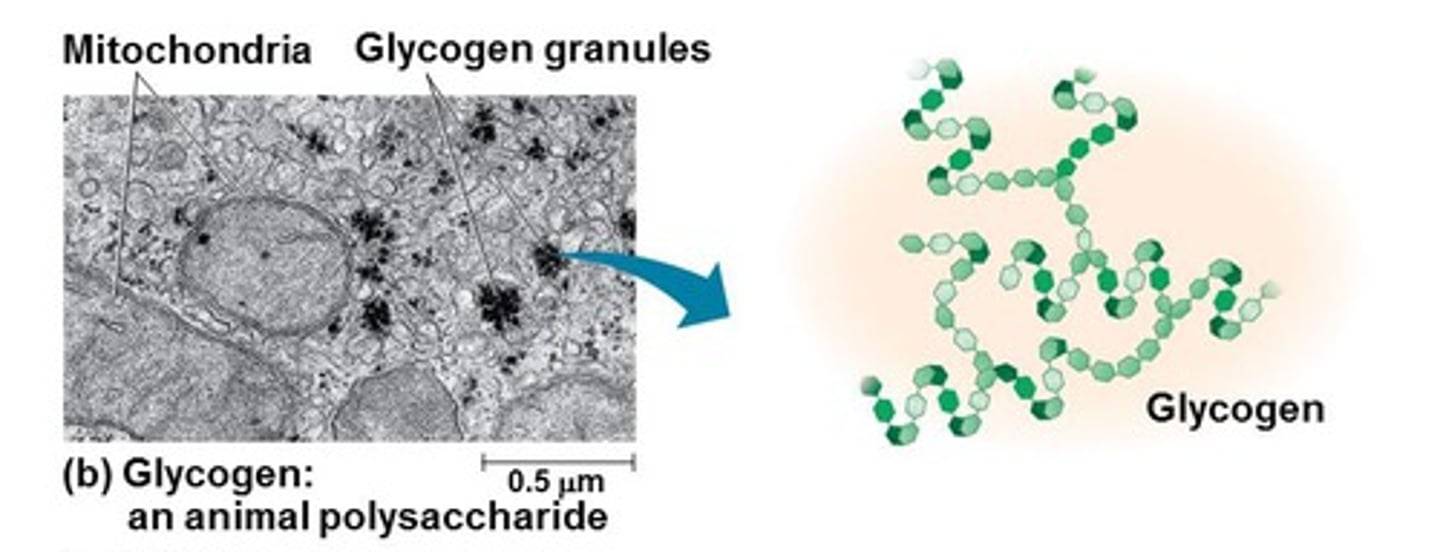
Glycogen
branches
energy storage (animals - liver and skeletal muscle)
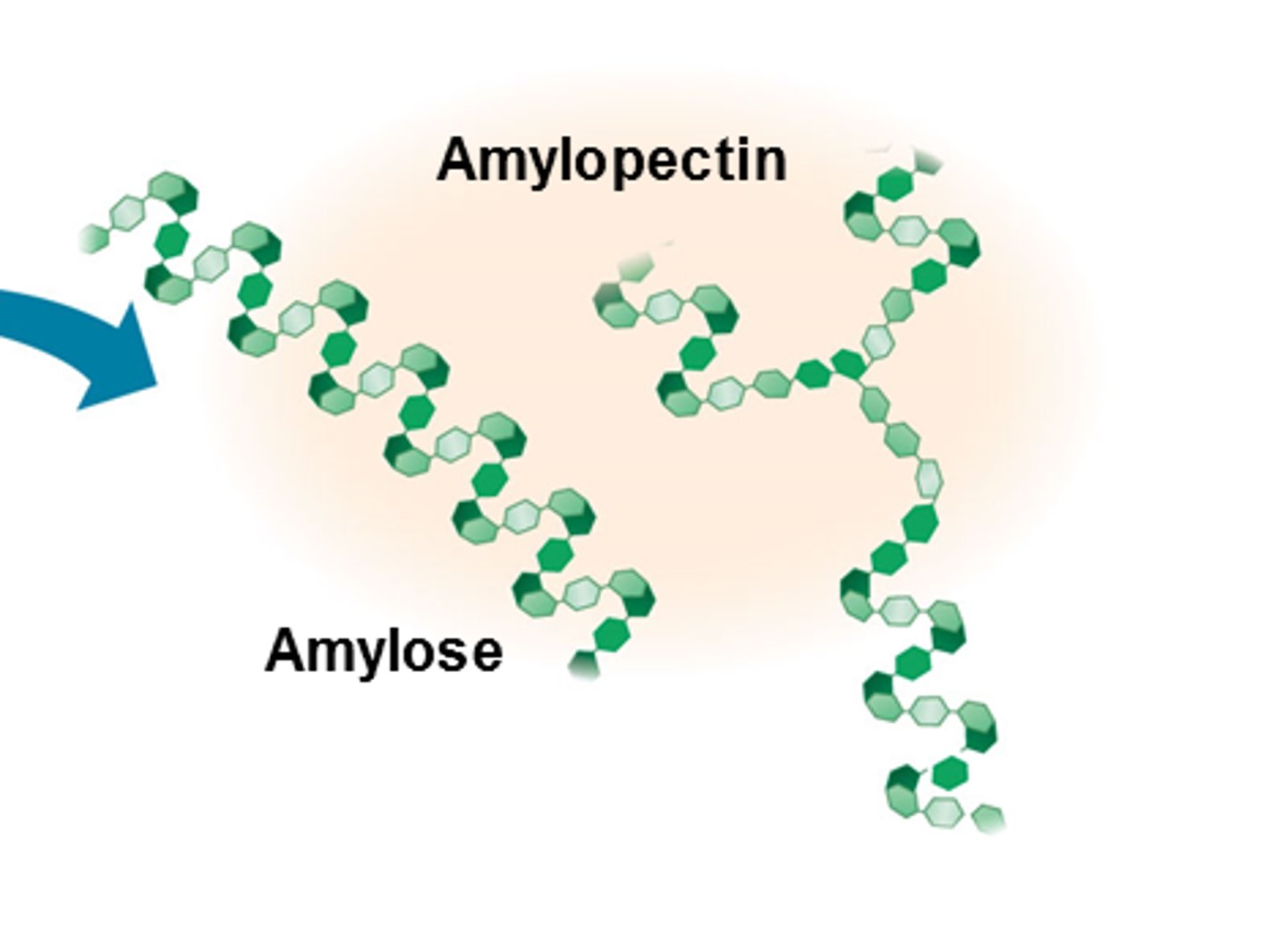
Starch
String
energy storage (plants - stems and roots)
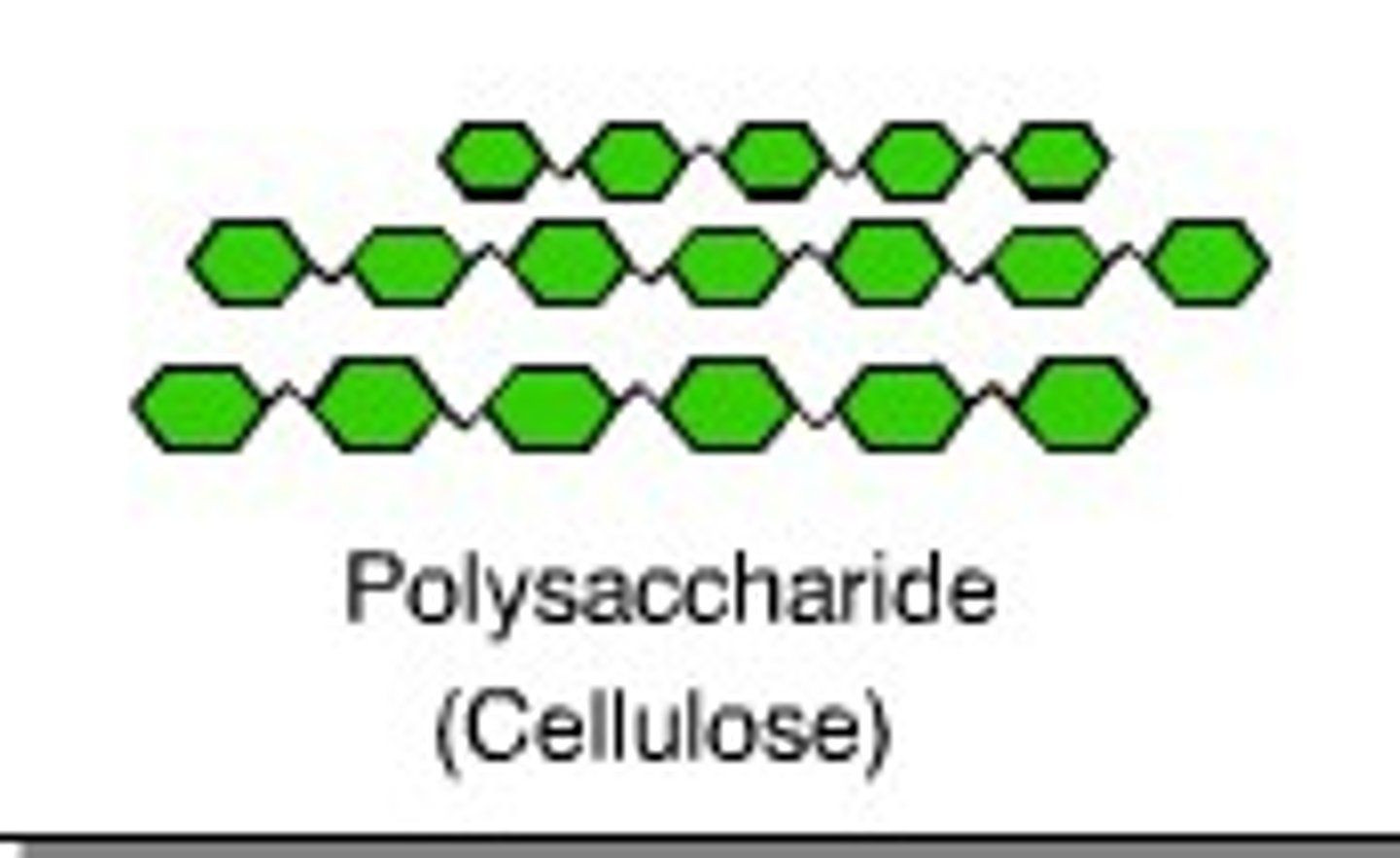
Cellulose
structural molecule (supports plant cells)
Lipids are diverse but one common feature is that they are ________
Hydrophobic
Triglycerides (fats, oils)
long term energy storage + insulation + cushioning
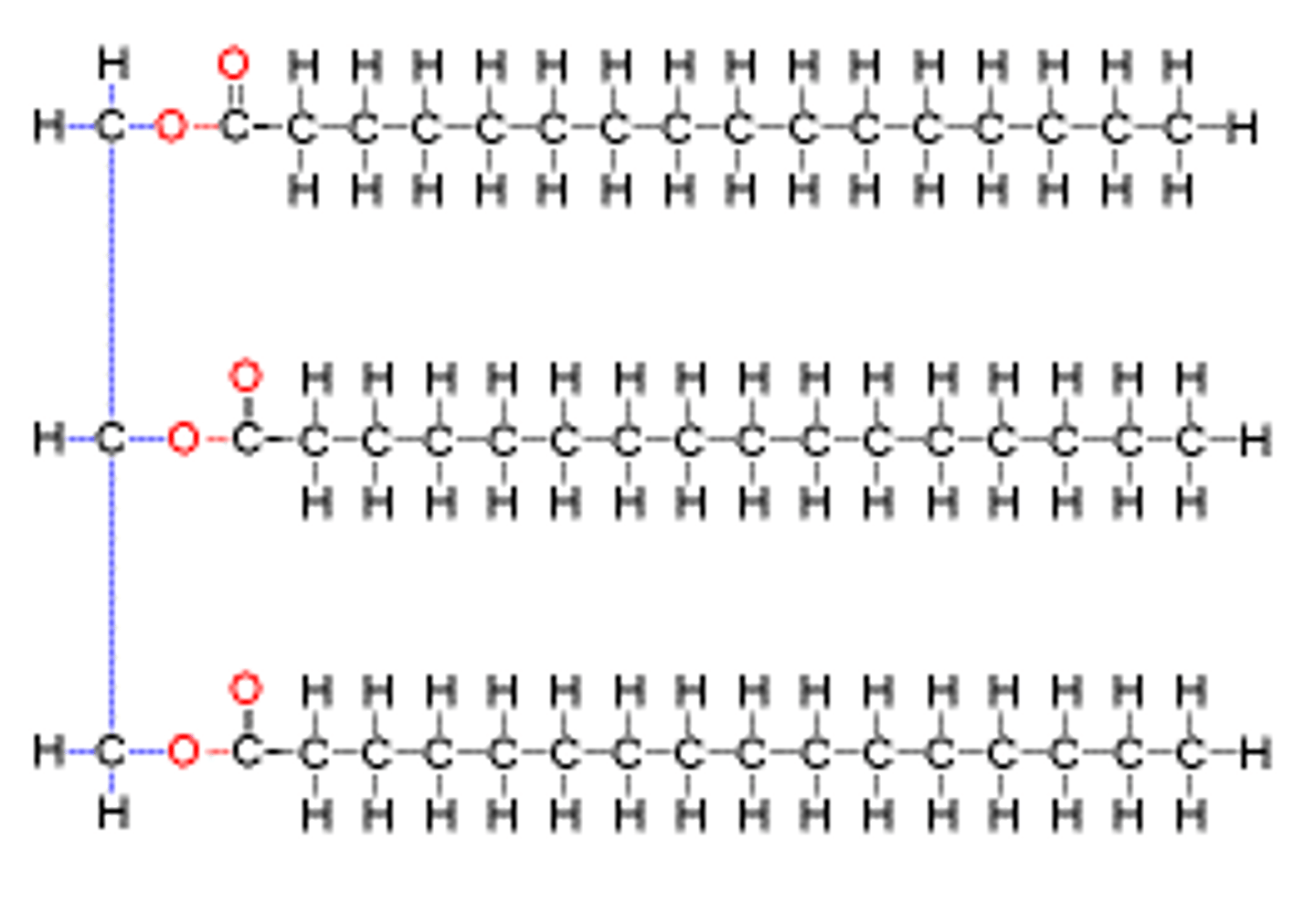
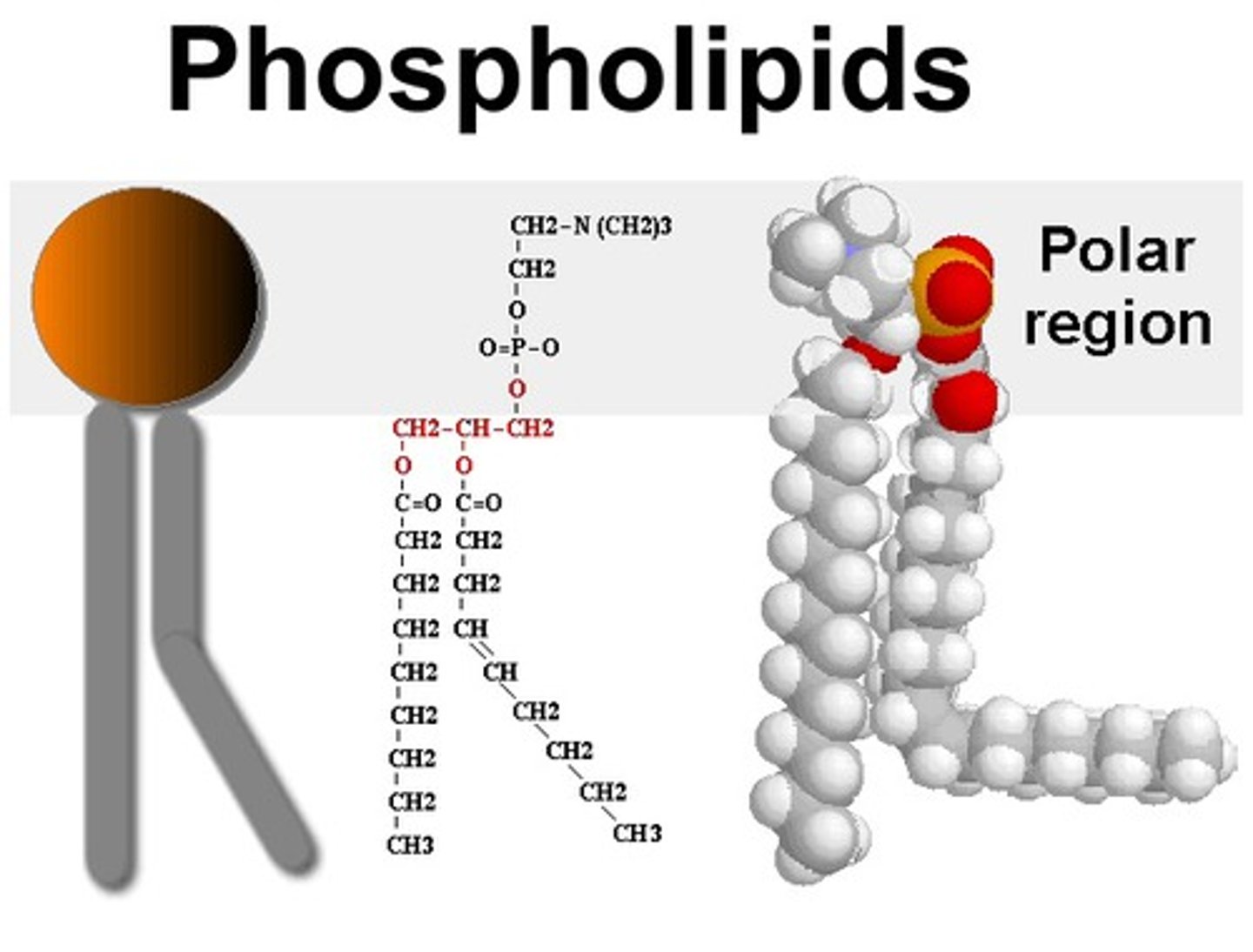
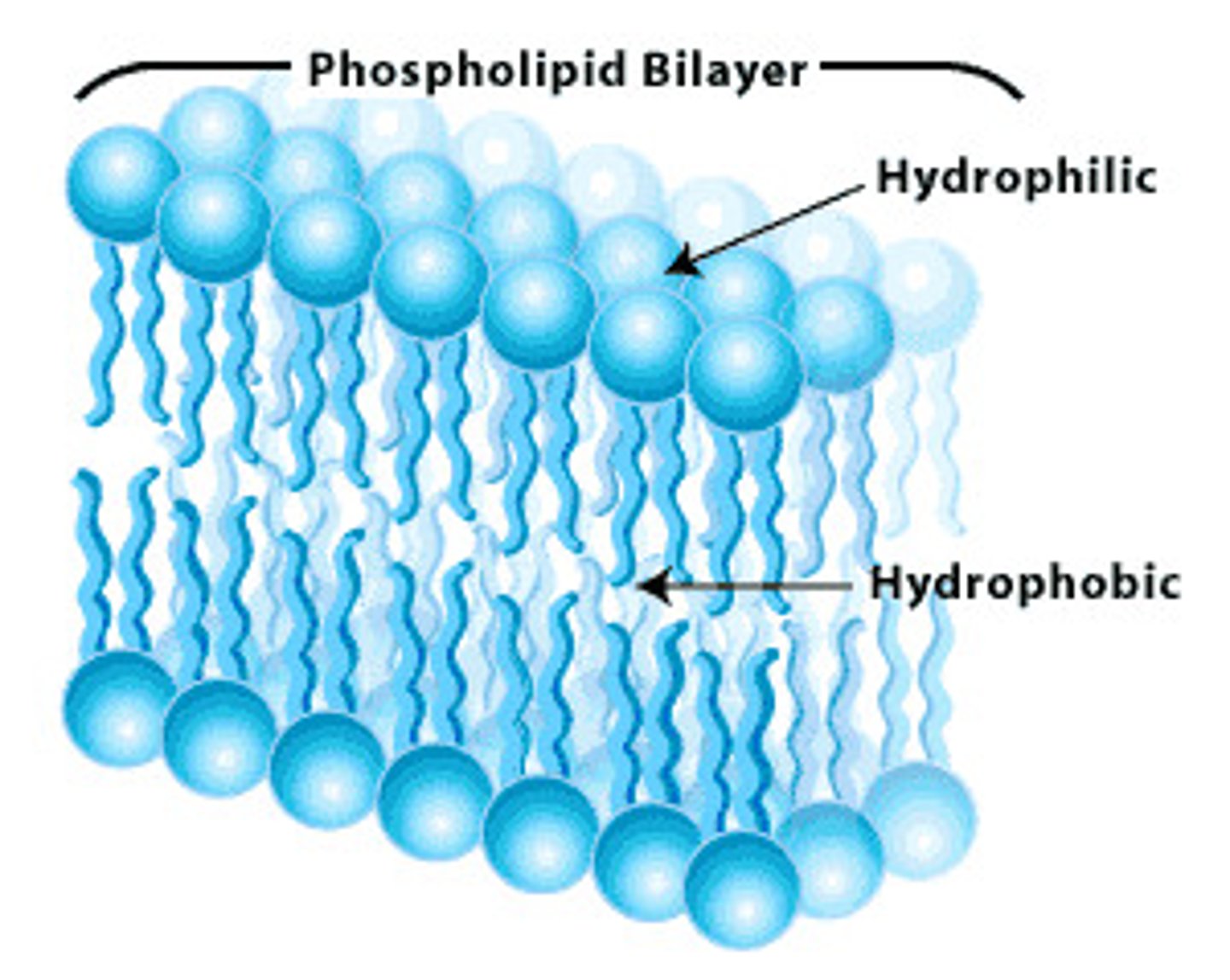
Phospholipid
Major component of cell membranes
Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
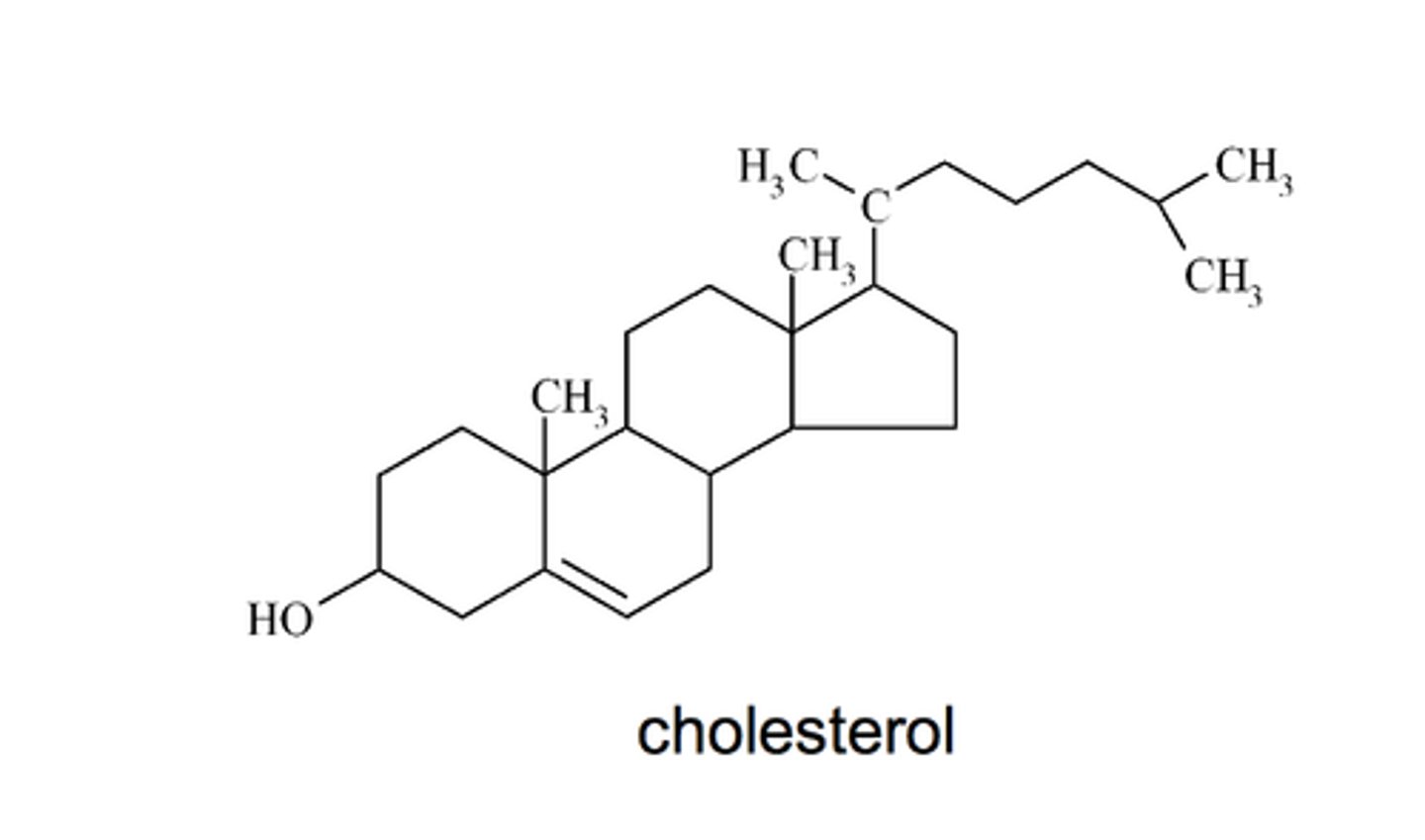
steroids
component of cell membranes + some hormones + vitamin D
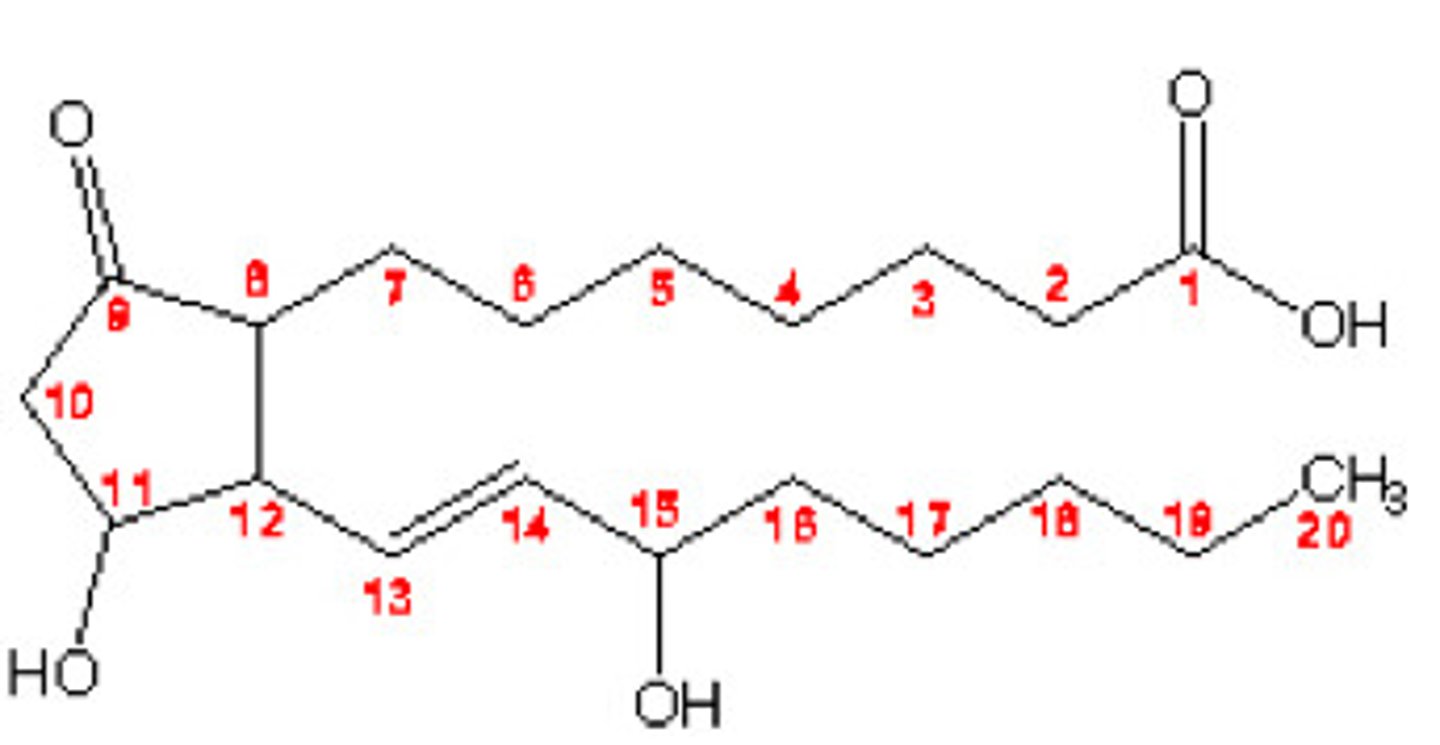
Eicosanoids
local signaling molecules aiding various body systems
there are greater than _____ proteins in a human body
10,000
What are the functions of proteins
1. structure
2. transport (other molecules)
3. regulate (cellular processes)
4. fight (diseases)
5. catalyze (chemical reactions in a cell - enzymes)
6. cause movement
7. provide energy (LAST RESERVE)
All proteins are ________ composed of one or more stands of ________________ monomers held by _________ bonds
polymers; amino acid; peptide
R-groups (of a protein) determine ________ of amino acids
behavior
different R-group within 20 amino acids _____ with each other and surrounding _______. This interactions cause each protein to fold to fold into a precise, unique 3-D structure (protein _______)
interact; water; conformation
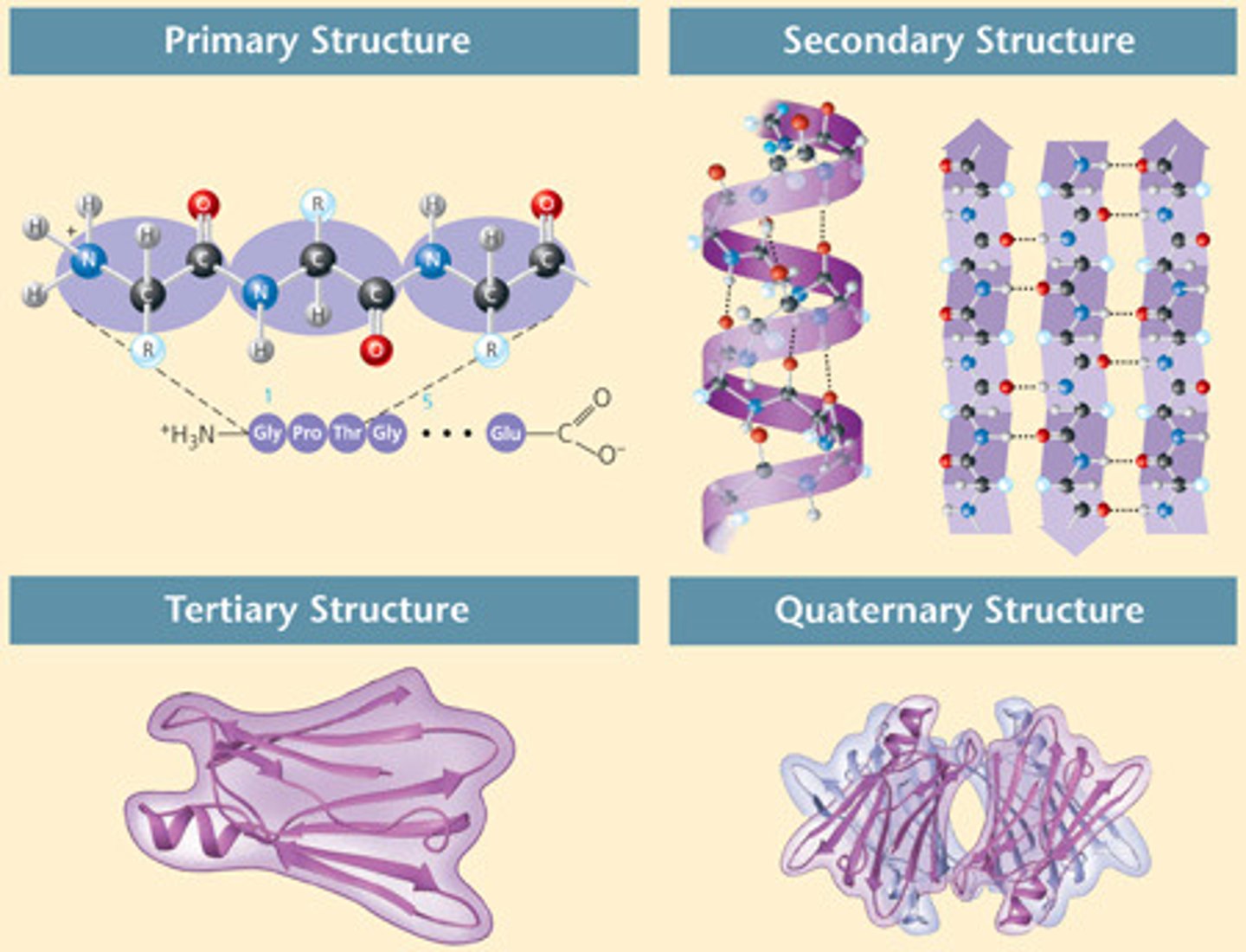
Primary protein structure
step 1
a specific sequence of AA within a chain (polypeptide)
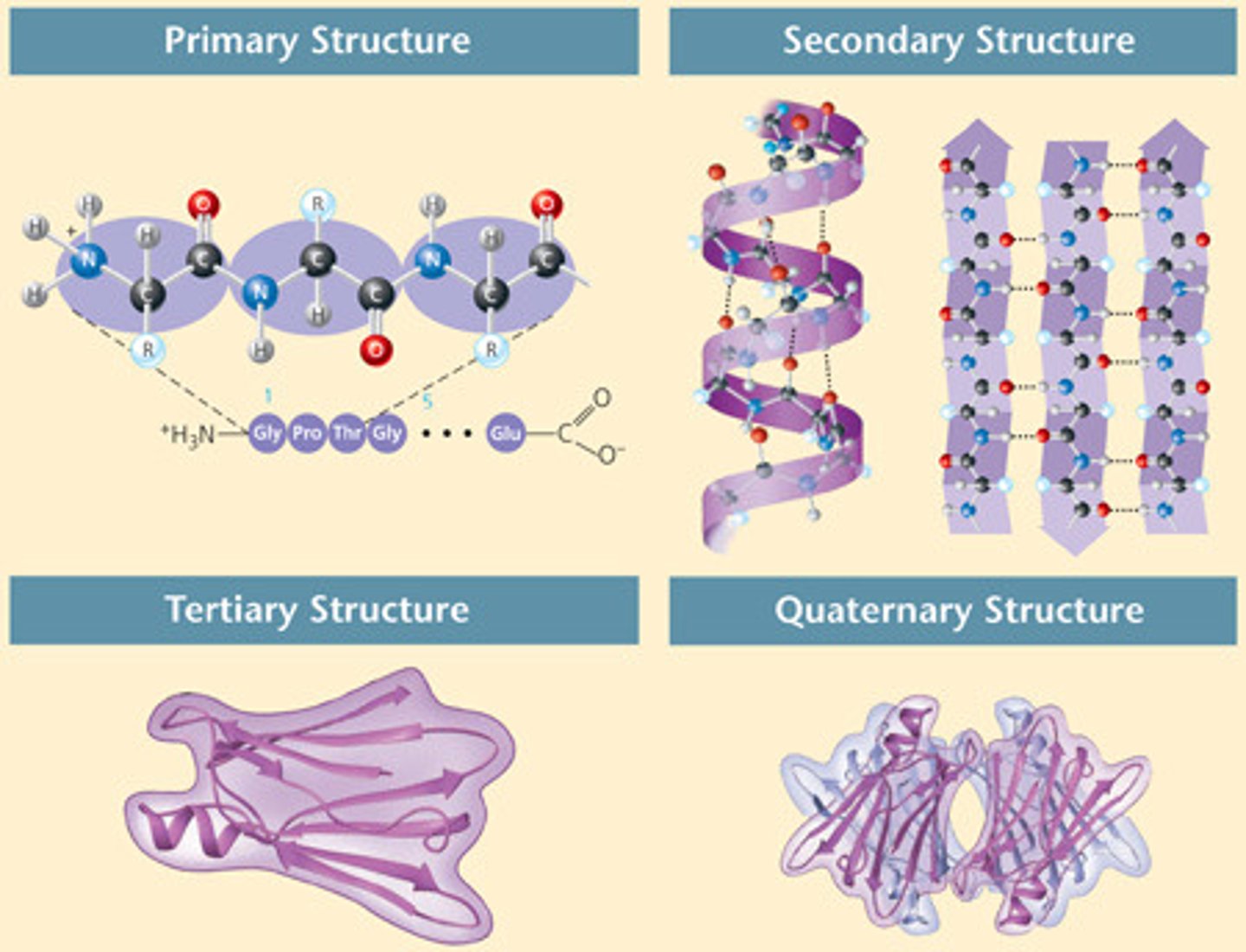
Secondary protein structure
step 2
folding of a polypeptide section into repeating patterns due to the hydrogen bonding between various amino acids
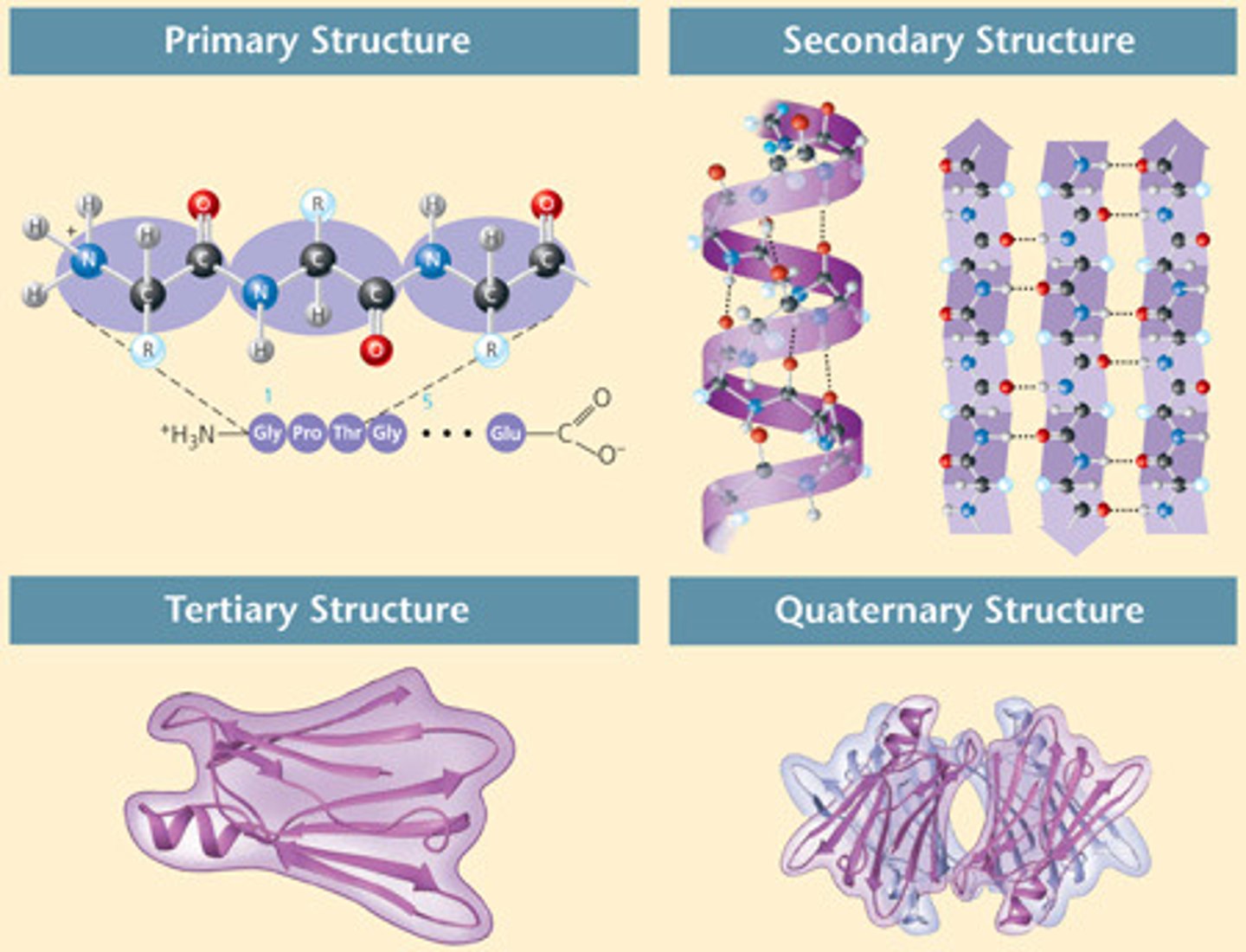
tertiary protein structure
step 3
overall shape of a polypeptide chain - globular or fibrous
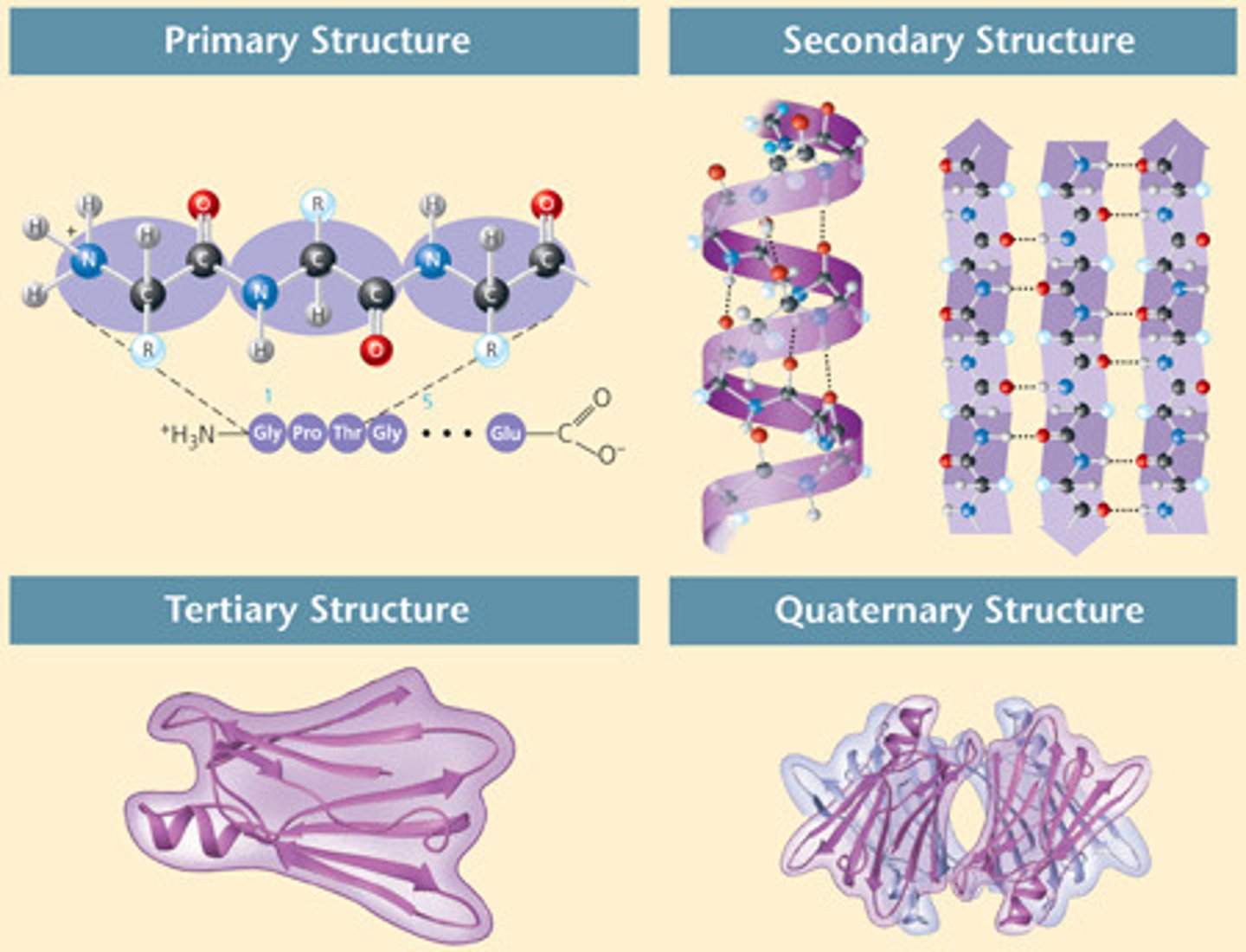
quarternary protein structure
step 4
shape produced by combination of several polypeptide chains
protein functioning
every protein must be precisely folded into a correct 3-D shape (conformation) to do its job for the living organism
What happens when there is an unfavorable change in temp or vibration interfere with intramolecular bonding
it can cause the protein to loose its shape
the process of a protein losing its shape is called _________
denaturation
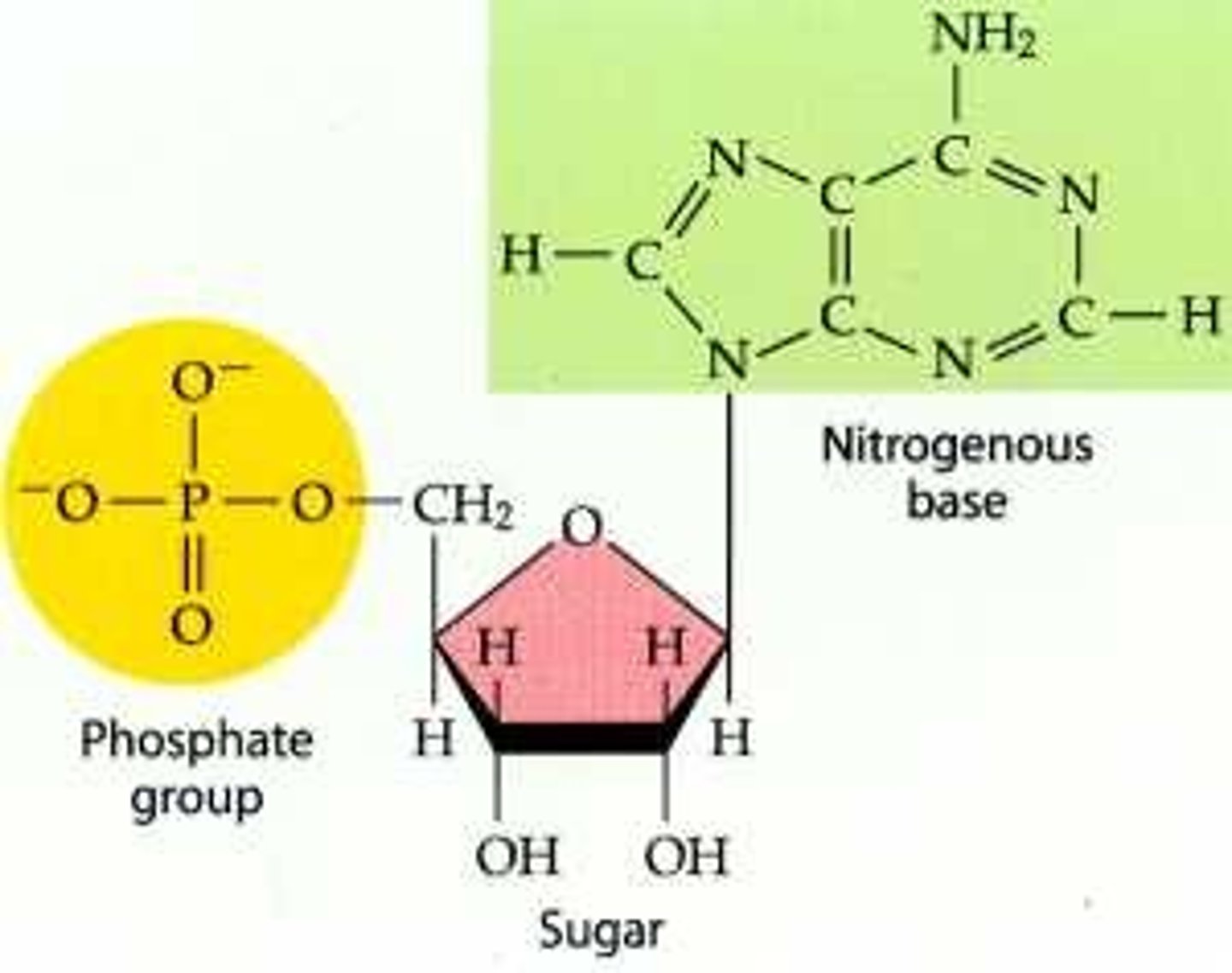
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
-store and transmit genetic info
-determine the types of proteins synthesized within cells
nucleic acids are _____ composed of ________
polymers; monomers
What is a nucleic acid composed of?
phosphate, 5-carbon sugar, nitrogen base