Organic Alkane Naming
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1 Carbon Atom
Methane/Methyl
2 Carbon Atoms
Ethane/Ethyl
3 Carbon Atoms
Propane/Propyl
4 Carbon Atoms
Butane/Butyl
5 Carbon Atoms
Pentane/Pentyl
6 Carbon Atoms
Hexane/Hexyl
7 Carbon Atoms
1st Step Naming Alkanes
Identify longest (Parent) chain of carbons
If there is competition, choose the chain with the most substituents
Cyclo
Indicates the presence of a ring in the alkane structure
When an alkyl group (substituent) is connected to a ring, the ring is generally treated as the parent
If the ring is comprised of fewer atoms than the rest, it is instead considered a substituent (cycloalkyl group)
2nd Step Naming Alkanes
List and number all substituents
If 1 substituent is present, it should be assigned the lowest number possible
When multiple substituents are present:
give the first the lowest number possible (2,5,5) vs (3,6,6)
If there is a tie, the second should be the lowest possible
If there is still a tie, assign the lowest number alphabetically
If a substituent appears more than once in a compound, a prefix is used to identify how many times it appears:
di = 2
tri = 3
tetra = 4
penta = 5
hexa = 6
Naming Complex Substituents
Place numbers on the substituent going away from the parent chain
Assembling the Systematic Name
Place all substituents in alphabetical order (prefixes except iso don’t count)
hyphens separate numbers from letters & commas separate numbers from each other
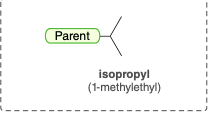
Isopropyl
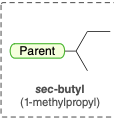
sec-butyl
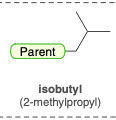
Isobutyl
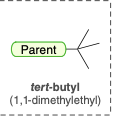
tert-butyl
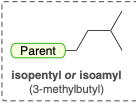
Isopentyl/Isoamyl
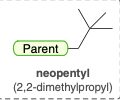
Neopentyl