Plant structures and their functions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Why are plants called producers?
They produce their own food via photosynthesis
What is biomass
The mass of a living material at a particular stage in a food chain
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
What energy transfer is there in photosynthesis?
There in an energy transfer of light energy to chemical energy stored in the sugars produced
What are four limiting factors of photosynthesis?
Low temperature, dim light and low carbon dioxide concentration all limit the rate of photosynthesis, amount of chlorophyll
How does light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
If there is a low amount light intensity or carbon dioxide the rate of photosynthesis will be slower
If there is a high light intensity or carbon dioxide the rate of photosynthesis will be higher
What is happening when either increasing the light intensity or carbon dioxide amount does NOT increase the rate of photosynthesis?
When either of these factors are high the rate of photosynthesis will not increase because another factor is limiting it from increasing
In this case, temperature would be the limiting factor
How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is an enzymes controlled reaction
When the temperature is low, the molecules and enzymes are moving slower because they have little kinetic energy
Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules and enzymes, causing them to move faster and hit harder
This increases the rate of photosynthesis as there are more successful collisions
At high temperatures, enzymes involved is digestion and synthesis can be denatured, slowing down the rate of photosynthesis
What happens in temperature gets too high for photosynthesis?
If the temperature is too high, enzymes will begin to denature
This decreases the rate of photosynthesis
How are phloem in plants specialised to carry out their function?
Contains sieve tube elements which have very little cytoplasm- this maximises the space for the transport of sucrose and nutrients
Contains companion cells which have lots of mitochondria- these supply energy from respiration for active transport of sucrose into and out of the sieve tubes
How are xylem vessels in plants specialised to carry out their function?
These are dead cells which have no cytoplasm or cell contents- there is more space for water containing mineral ions
They have holes called pits in their walls to allow water and mineral ions to move out
Walls are strengthened with lignin rings making them very strong and prevents them from collapsing
They have no end walls so they form a long tube letting water flow through easily
What is transpiration?
The loss of water by evaporation from the leaves of a plant
What is the movement of water from the roots to the leaves of a plant called?
The transpiration stream
Where are stomata found?
On the lower surface of the leaf
How do stomata work in plants?
They are surrounded by a pair of sausage shaped guard cells
When guard cells take in water they swell causing the stomata to open
When guard cells lose water, they become flaccid and the stomata closes
They close at night because photosynthesis can’t take place, this reduces loss of water
What are the steps of transpiration?
Water enters the roots by osmosis
Water is transported up the stem through the xylem vessel
Water is drawn out of the leaf cells and xylem
Water evaporates from leaves mainly through the stomata
What is translocation?
The transport of sucrose around a plant
What does the phloem transport?
Dissolved sugars
Which direction does water move in transpiration?
Up
Which direction does sucrose move in translocation?
Up and down the plant
What are the steps of translocation?
Sucrose is produced in leaves from glucose formed during photosynthesis
Dissolved sucrose is carried around the plant in phloem
Dissolved sucrose is needed for growth in growing regions
Dissolved sugars are also turned into starch and stored in storage organs for later use
How is a leaf adapted for photosynthesis?
Waxy cuticle on surface and epidermis cells are transparent to let light through
Palisade mesophyll cells are packed with chloroplasts and near the upper surface of the leaf, maximising photosynthesis
Xylem brings water for photosynthesis
Phloem removes sugars made in photosynthesis
Flattened shape of leaf gives a large surface area
How is a leaf adapted to gas exchange?
Air surrounds most of the surface of each cell so that gas exchange can take place over most of the surface
Internal air spaces increase surface area for diffusion of gases
Flattened shape of leaf gives a large surface area
Stomata allow carbon dioxide from air to enter the leaf and allow oxygen from photosynthesis to leave the leaf
How does light intensity affect transpiration?
High light intensity causes stomata to open- this causes the plant to lose water
This increases the rate of evaporation of water from the leaf so more water is taken up to replace this
How does air movement affect transpiration?
Wind blows moist air away from stomata, keeping the diffusion gradient high
The more air movement there is, the higher transpiration rate
How does temperature affect transpiration?
When temperature is high, water molecules have more energy
They move faster, increasing the rate of transpiration
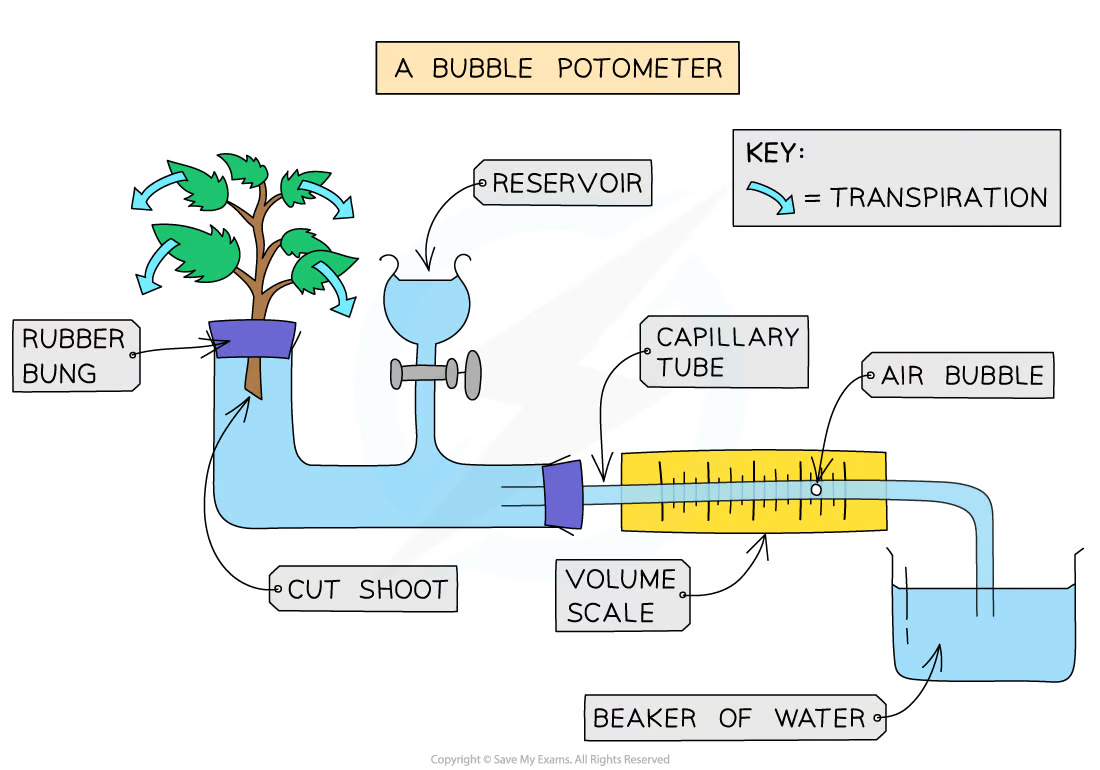
How can a potometer be used to measure the rate of transpiration with this equipment?
Note the position of the bubble on the ruler at the start of the investigation
Note the position of the bubble after a known number of minutes
Use the equation distance moved/time taken to find the rate of transpiration
What is one example of a plant that has adapted to hot and dry conditions in a desert?
Marram grass
How is marram grass adapted to living in a desert?
Stomata sunk in pits to reduce water loss
Waxy cuticle reduces water loss
Rolled leaf to reduce air movement around stomata so less water is lost
Leaf hairs to trap moist air around stomata
How do some plants adapt to tropical conditions where it is wet and has low light intensity?
Large leaves to take in as much light as possible
Stems and leaves that climb up trees to obtain more light, with the plant’s roots still in the ground
Leaves with ‘drip tips’ so water runs off them
How are some plants adapted to waterlogged soil?
Waterlogged soil has no air spaces so root hairs have difficulty obtaining oxygen for respiration
Some plants have spongy tissue in their roots that store oxygen
Fine surface roots that take in oxygen at the water surface
What is a tropism?
A plant’s response to stimulus (a change in the environment) by growing
What is phototropism?
Plants shoots growing towards light
What is gravitropism?
Plant roots growing downwards, towards the pull of gravity
What are auxins and what do they do?
Auxins are plant hormones that causes cells to grow longer
They are affected by light and cause phototropism in shoots and gravitropism in roots
How do auxins work?
In a shoot, auxins are produced near the top of a shoot
When light hits the shoot the auxins move to the shaded side of the shoot
The shoot then bends towards the light
In gravitropism auxins cause the root to grow downwards, away from light and towards gravity
Why does phototropism happen in plants?
So they can get more sunlight for photosynthesis
Why does gravitropism happen in plants?
When the shoots move further down they are able to reach more water and nutrients as well as anchoring themselves which provides stability
What is another name for gravitropism?
Geotropism
How are auxins used in selective weedkillers?
Weed plants compete with crop plants for water and minerals from the soil
Weed plants have broader leaves then crop plants
Broad-leaved plants absorb more of the auxins causing uncontrollable growth, eventually killing the plant
Crop plants get more minerals and water, so they grow better
What is rooting powder and how is it used?
Gardeners take cuttings of plants to grow into new plants
They dip the stalk end into rooting powder
This contains auxins that cause the stalk to produce roots faster, helping the cuttings to grow into fully developed plants
How are gibberellins used by humans?
Gibberellins stimulate germination of seeds, increasing crop yields
They also stimulate flower and fruit production, again increasing the yield
They stimulate stem elongation- when done on crops like sugar cane, this increases it’s yield
They can be sprayed on flowers to produce seedless fruit
They make fruit grow larger
How do humans use ethene for plants?
Ethene hastens the ripening of fruit
If you transport fruits you can transport them as unripe and then use ethene to ripen them
This means that the fruit will not be too unripe to be sold