Lecture 16: Proprioception
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Proprioceptive sensory neurons
all over your body
allows us to know the position of our body, keep balance, and sense muscle tightness
Damage to the proprioceptive system
Only 9 cases in the world! Can't control your arms - while looking to the right side, his left arm just starts flanking around and can hit people

Conflict of visual-proprioceptive cues
Disappearing hand trick
A person putting their hand under a screen. Under the screen there are two cameras, and the person's task is to keep their hands between moving lines. However, one of the cameras slowly move to the right. Even as the participant moves their hand with the camera, it looks like their hand doesn't move at all, even though it's a lot further apart than it feels
Two crossed fingers demo
Stimulating the ‘outside’ parts of your middle and index fingers usually only happens when there are two objects
The unusual positions of your fingers confuses your proprioceptive system
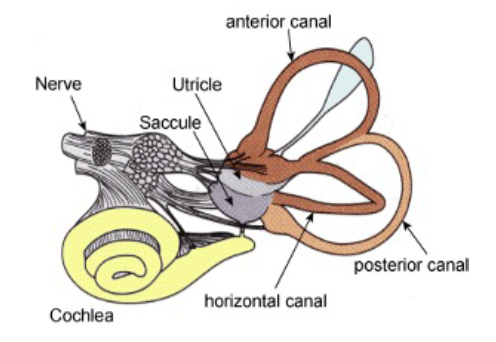
Vestibular system
sense of orientation
exists in the inner ear, using 3 semi-circular canals with fluids that indicate rotational movements
otoliths are in charge of our sense of gravity
Sense of orientation is affected by
verstibular, proprioceptive, and visual cues
sense of pressure - you feel the ground you stand on and the direction your hair is falling
Irvin Rock (1956) ambigious figures study
showed that tilting our head doesn’t change our perception on orientation of images, need to actually rotate the image to see the actual figure
Orientation in face perception
Upright faces are processed better than inverted ones, using the retinal frame of reference
Egocentric
Retinal, head, body
if you see an upside down face and you’re also upside down, it will look normal, thus aligning with your ego view
Allocentric
Enviornemntal, gravitational
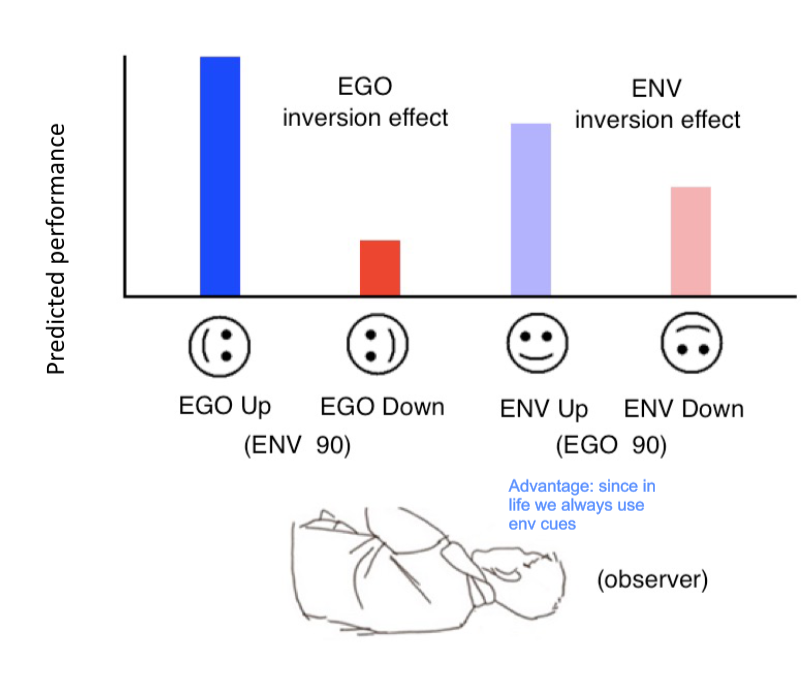
Design to test different reference frames
Rotating the observer and having faces in different orientations (some that align with ego and some with env)
best results when EGO up → env up → env down (not the worst since in life we always use env cues) → ego down
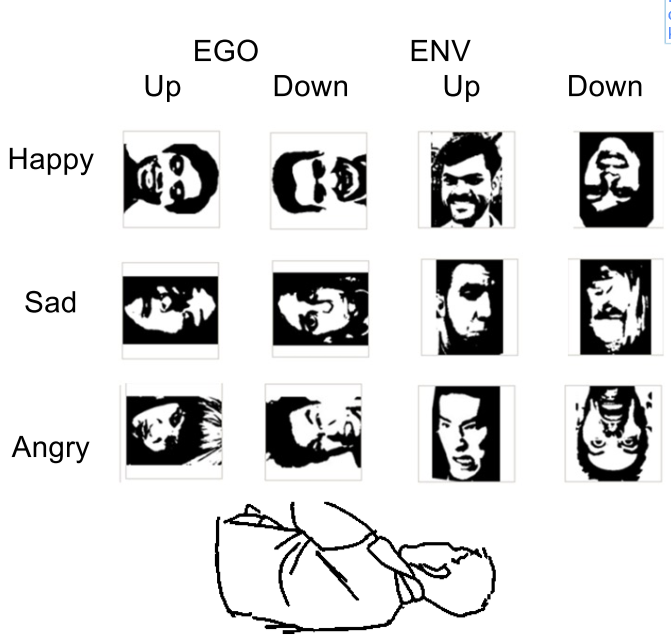
Exp 1: classifying emotional expressions of mooney faces
rotate right/left and classify orienated expressions
Both EGO (large effect) and ENV (small effect) influence facial expression identification
Mooney faces
two toned faces
difficult to recognize since they have shadows, which is used in real life to find orientations
Clock study
Reading clocks is influenced by both EGO and ENV angles
Best reaction times when the clock was mostly aligned to you, but a little bit more upright
Reading study methods
Orientation on reading
Created a bunch of words and non-words to see RT and accuracy of reading based on orientation -- see a word and say if it's a real word or non-word
Reading study results
Person is upright: Symmetric effect of orientation (+- 90) which is unexpected since we read from top to bottom
Person is turned: A big asymmetry now: -90 takes a lot more time than 90. This is because 90 aligns with gravity
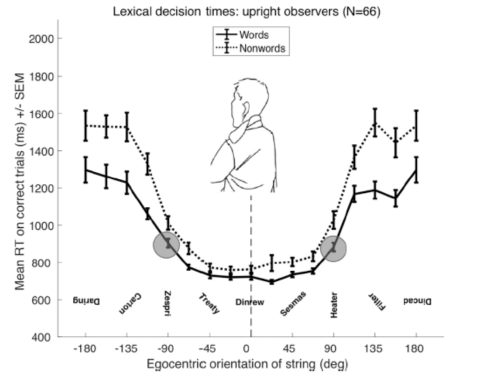
Reading study conclusions
We have more experience reading words upright (aligns with the environment) even when our head is turned
Both the orientation of the words relative to orientation and relative to the environment matter
How do people choose to orient a display screen when their body and head are in non-upright positions?
2 conditions: one with a room as the background and one with a black bg
VR Study conclusions
No VE: preferred screen orientation increased as body rotation increased (halfway between ego and env 0)
World-aligned VE (only screen rotated with the world) = wanted screen to be ENV-aligned
EGO-aligned VE (screen and bg rotated w/ your body) = EGO-aligned
upright body, tilted screen - no correlation
Participant analysis
lots of variety across participants, but each subject was consistent within themselves
the best solution may be to display the screen without a virtual environment and
give users the ability to manipulate the screen’s orientation