OTD711 Final Prep
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Which of the following best describes a therapeutic activity as an intervention?
Client practices manipulation of nuts & bolts to prepare to return to work role as a mechanic
Client uses theraputty to build hand strength to return to work role as a mechanic
Client receives paraffin treatment on hands to decrease pain to prepare to return to work role as a mechanic
Client receives joint mobilizations to restore mobility in hands to prepare to return to work as a mechanic
Client practices manipulation of nuts & bolts to prepare to return to work role as a mechanic
You see a pt for a 60-minute tx session. You complete 32 mins of neuromuscular reed (97112), 15 mins of ther-ex (97110), and 13 mins of ther-ac (97530). How many total units will you be billing?
5 units
2 units
3 units
4 units
4 units
As an OTR, which of the following do you need to consider when determining which patients you will assign to a COTA?
Knowledge and skill level of the COTA
State and national regulatory requirements
Payor requirements
All of the above
None of the above
All of the above
You see a pt for a 60-min tx session. You complete 21 mins of neuro re-ed (97112), 22 mins of ther-ex (97110), and 17 mins of ther-ac (97530). How many total units will you be billing?
4 units
3 units
2 units
5 units
3 units
Which of the following best describes the action that occurs in a healing wound during the proliferative phase?
Wound closure occurs thru epithelialization
Inflammatory response causes vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation
Collagen fibers remodel
Histamine initiates the inflammatory response
Wound closure occurs thru epithelialization
When utilizing PAMs, it’s important to consider depth of the anatomical structure that you are trying to treat. For therapeutic ultrasound, you can alter the intensity of the tx to adjust your depth of tx. Which of the following choices is correct.
1 MHz = 1-3 cm in depth
3.3 MHz = 1-3 cm in depth
1 MHz = 7-8 cm in depth
3.3 MHz = 3-5 cm in depth
3.3 MHz = 1-3 cm in depth
Juan presents to your clinic seeking OT services with complaints of pain in his right hand. Upon further examination of the affected area and interview with the client, you find out that he fell down the stairs 2 days ago and has had significant pain and bruising of his right index finger and thumb. Based on what you know about Juan’s condition, superficial heat PAMs are indicated for tx of his pain.
True
False
False
Based on SMART goal principles, choose the best goal from the following:
Pt will decrease pain to improve function with overhead ADL tasks.
Pt will increase shoulder flexion by 20 degrees to improve function with overhead ADL tasks without pain within 4 weeks.
Pt will improve score on QuickDASH to increase independence with ADL tasks within 2 weeks
Pt will dress his lower extremities independently
Pt will increase shoulder flexion by 20 degrees to improve function with overhead ADL tasks without pain within 4 weeks.
By which method does ultrasound produce a thermal heat effect?
Conversion
Conduction
Convection
Transfusion
Conversion
Which of the following is categorized as a CPT code specific to OT?
97110: neuromuscular re-education
L3807: Wrist-Hand-Finger Orthosis (WHFO)
S06.2: Traumatic Brain Injury
R27.9: Lack of coordination
97110: Neuromuscular re-education
Allen’s Test will show which of the following?
Nerve impingement of the hand
Flexor tendon tightness
Impaired circulation in the hand
Pain in the arm
Impaired circulation in the hand
Which of the following motor impairments will result from cubital tunnel compression?
Loss of wrist extension
Loss of finger flexion
Claw hand
Loss of elbow flexion
Claw hand
Lateral epicondylitis and radial tunnel syndrome can have the same symptoms of pain in the forearm and elbow.
True
False
True
You receive orders for a pt who sustained a low median nerve injury (complete laceration) at the wrist level approx. 2 years ago without repair. You anticipate the following posture of the hand:
Claw hand with atrophy of the interossei and inability to fully extend the ring and small finger
Thenar muscle/webspace atrophy as well as difficulty opposing the thumb
Wrist drop with inability to extend the wrist and digits limiting functional grasp
Star Trek hand with separation of the digits in extension between the middle and ring finger
Star Trek hand with separation of the digits in extension between the middle and ring finger
Your patient sustained a proximal phalanx fracture of the 4th finger. The surgeon elected for ORIF of the fracture and has now ordered: “Stable fracture: Progress pt ROM/strength based on your judgement”. Based on the information above, when can you begin gentle AROM as an intervention to supported eventual occupational performance?
3-7 days post-op
2-3 weeks post-op
Not enough information to determine
1 month post-op
3-7 days post-op
Scapular winging is caused by weakness in which of the following muscles?
Subscapularis
Teres Major
Serratus Anterior
Supraspinatus
Serratus Anterior
You are completing an evaluation of an individual that complains of weakness in their hand, particularly when using eating utensils or trying to start their car with a manual key. Upon further evaluation, you also note a (+) Froment’s sign. This subjective and objective information is most consistent with which of the following?
Ulnar nerve involvement with weakness or paralysis of the adductor pollicis
Median nerve involvement with weakness of the adductor pollicis
Radial nerve involvement with weakness of the abductor pollicis longus
Ulnar nerve paralysis with weakness of the dorsal interossei
Median nerve involvement with weakness of the adductor pollicis
A patient is referred to you post-op after a massive open RTC repair involving the supraspinatous & infraspinatous tendons. Pt is on post-op day 7 and your orders state “Eval & treat s/p RTC repair. Follow conservative protocol”. Which of the following will you implement at your eval and first tx session?
Heat modalities for pain; AAROM of shoulder through full ROM, 20-30 degrees of ER/IR; passive pendulums & AROM of adjacent joints for home program
Cold modalities for pain; PROM of shoulder - approx. 30-40 degrees in all planes of motion; passive pendulums & AROM of adjacent joints for home program; one-hand ADL techniques
Ultrasound for pain management; AROM of shoulder below 90 degrees elevation, 20-30 degrees ER/IR in scapular plane of motion; passive pendulums & AROM of adjacent joints for home program
Cold modalities & TENS for pain; grade III mobilizations of glenohumeral joint; passive pendulums & pulleys for home program; one-hand ADL techniques
Cold modalities for pain; PROM of shoulder - approx. 30-40 degrees in all planes of motion; passive pendulums & AROM of adjacent joints for home program; one-hand ADL techniques
When treating a pt with an elbow fx, you can be very aggressive with the PROM.
True
False
False
What is the primary muscle involved with subacromial impingement?
Deltoid
Subscapularis
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Supraspinatus
One of the most common causes of musculoskeletal disorders in the workplace is improper body positioning. Which of the following strategies best reduces the risk of ergonomic injuries?
Increasing repetition to improve efficiency
Using adaptive tools to minimize force and strain
Maintaining a static posture throughout the workday
Reducing work breaks to enhance productivity
Using adaptive tools to minimize force and strain
An office work complains of wrist pain after prolonged computer use. What is the best ergonomic recommendation to prevent further strain?
Position the keyboard below elbow level to encourage wrist flexion
Keep wrists extended on firm desk surface for support
Maintain wrists in a neutral position with soft wrist supports
Reduce arm support to increase shoulder engagement
Maintain wrists in a neutral position with soft wrist supports
A worker recovering from a back injury undergoes a Functional Capacity Evaluation (FCE). What is the primary purpose of this assessment?
To provide a permanent disability rating
To determine the worker’s ability to meet job demands
To assess the worker’s pain tolerance levels
To evaluate the efficiency of the workplace layout
To determine the worker’s ability to meet job demands
A factory worker is required to lift heavy boxes as part of their job. What is the safest ergonomic fitting technique?
Bending at the waist while keeping the legs straight
Holding the load away from the body to improve balance
Squatting with knees bent and lifting with the legs
Twisting at the torso while lifting to increase efficiency
Squatting with knees bent and lifting with the legs
A company implements standing workstations for employees to reduce sedentary behavior. Which of the following is the best ergonomic recommendation for prolonged standing?
Use an anti-fatigue mat and alternate foot positioning
Stand in a locked-knee posture for increased stability
Keep feet positioned close together to minimize movement
Avoid shifting weight to reduce strain on one leg
Use an anti-fatigue mat and alternate foot positioning
Which of the following would be the best transfer for a pt with a C7 complete SCI with stage 2 sacral wounds?
Sliding Board with assist
Hoyer lift
Stand pivot transfer with a hemi-walker
Stand pivot transfer with a standard walker
Hoyer lift
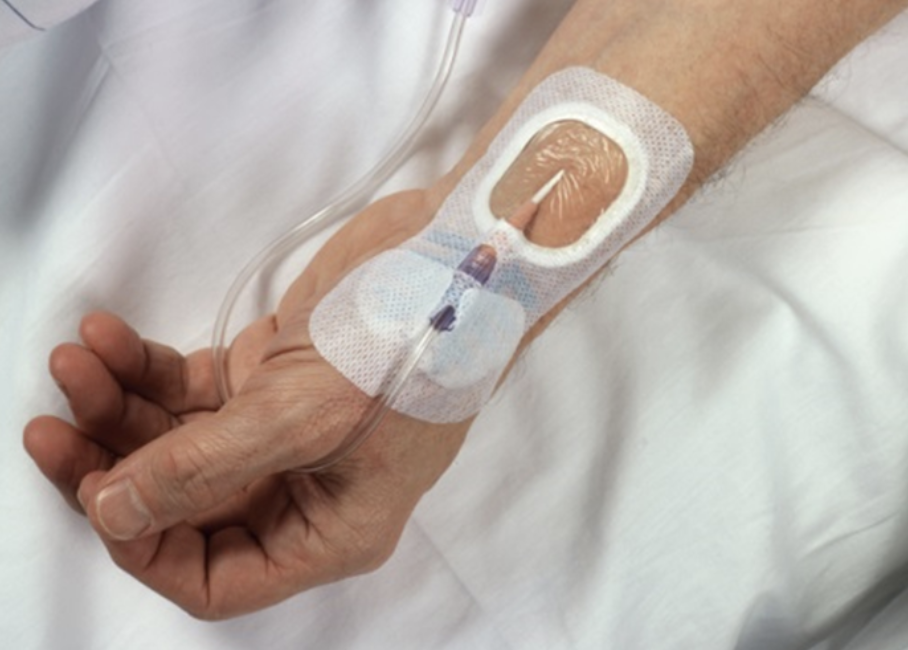
What is the name and purpose of the below picture?
Arterial line; measures arterial BP; can be used to draw blood and deliver medications
Central line (Central Venus Catheter); allows long-term access to blood stream to administer meds
Intravenous (IV) line; allows administration of meds and fluids
Arterial line; measures arterial BP; can be used to draw blood and deliver medications
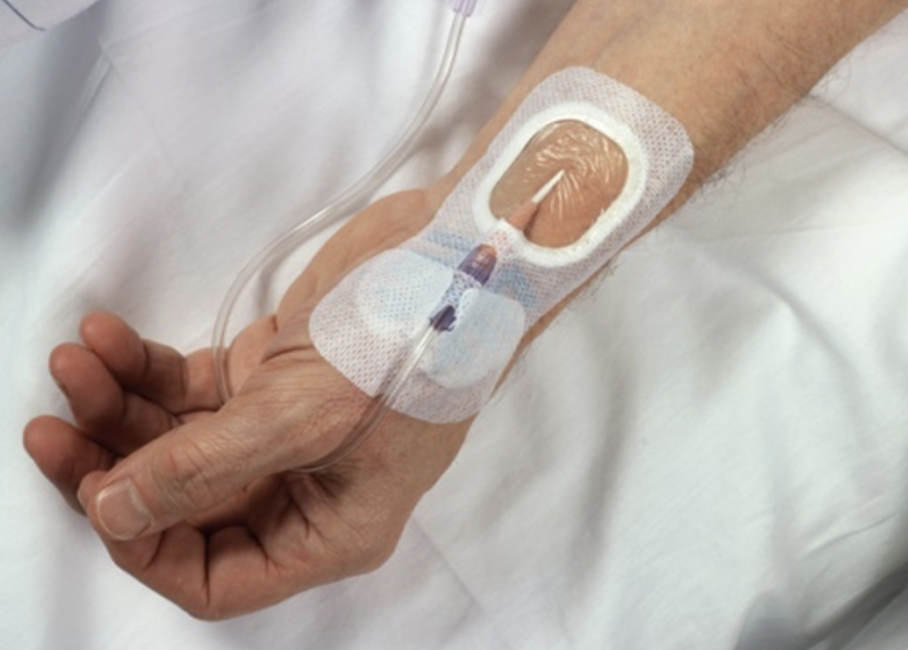
Which of the following is true of this device?
Provides continuous compression to return venous blood to the heart
Can be removed when the pt is up and out of bed
Are typically discontinued when pt becomes mobile
All of the above
All of the above
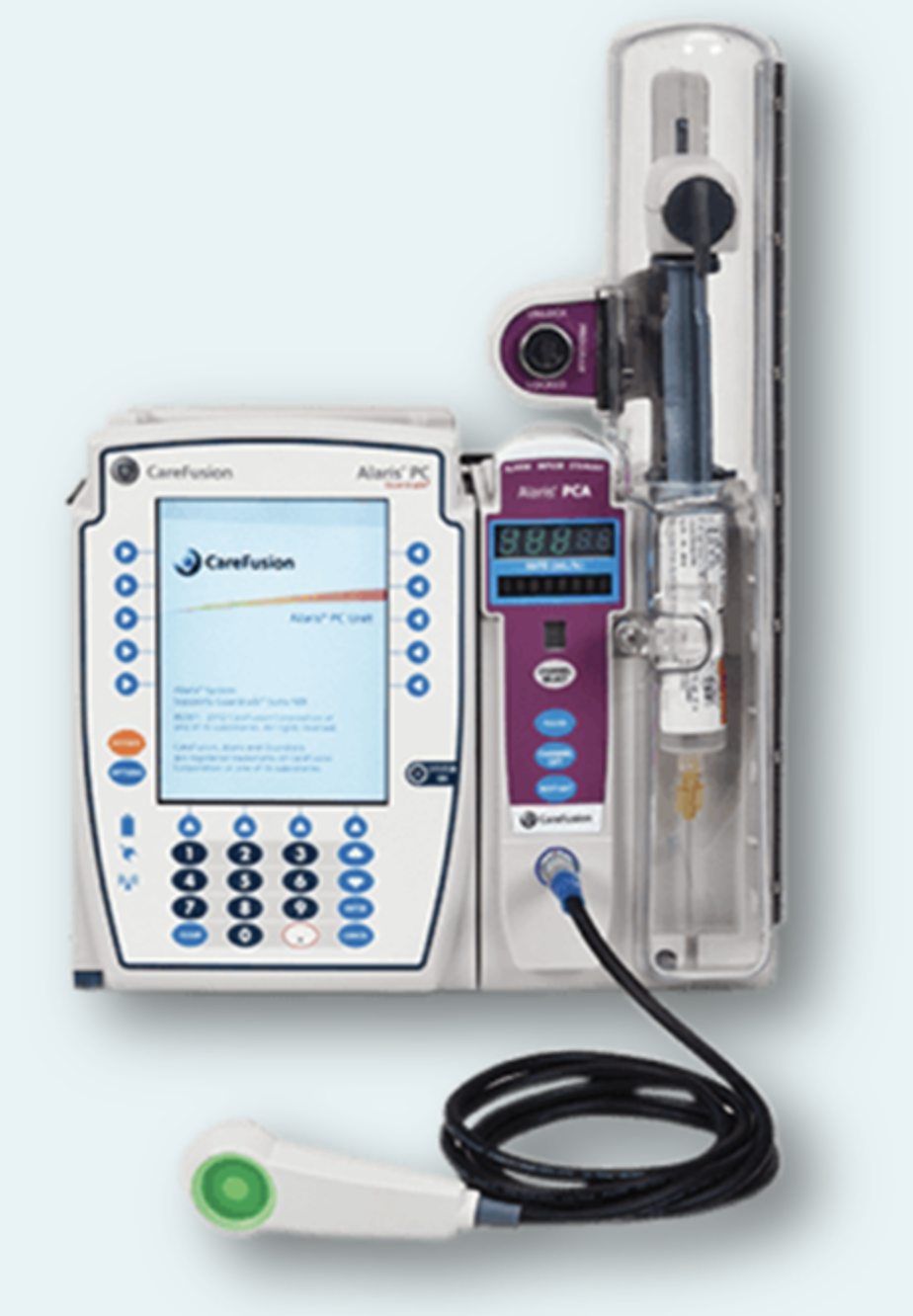
When you enter the room, you see the following device on the IV pole. What is the name of the device and what does it tell you about your pt?
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) device, your pt is experiencing pain
G-tube, your pt is being tube fed
A wound vacuum, your pt had a surgical procedure and the wound is being drained to an external device
CPAP, your patient is on O2
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) device; indicates your patient is able to self-administer pain relief.
Your pt has experienced a CVA and has a flaccid RUE. She has 4/5 strength in her RLE but due to impaired sensation has limited feeling in her right leg and poor standing balance. When you enter the room she is sitting at EOB and states she’d like to go to the dining room. Which of the following is best transfer for this pt?
Stand pivot transfer with a hemi walker on her L side
Stand pivot transfer with a standard walker
Stand pivot transfer with a straight cane
Sliding board transfer
Stand pivot transfer with a hemi walker on her L side
Which of the following would be an effective treatment for a pt with a C7 SCI to improve self-feeding.
Fabricate a short opponens orthotic to allow for tenodesis to pick up finger foods
Universal cuff to provide wrist stability
Pt will not be able to feed self with this level of injury
Both A and B
Both A and B
Which of the following medical complications do you need to be concerned with when work with a pt with a T2 SCI?
Autonomic dysreflexia
Impaired temp regulation
Skin integrity
All of the above
All of the above
Upon chart review you see your pt was diagnosed with a C6 SCI to the central portion of the spinal cord (central cord syndrome). What would you expect to see when you meet the pt?
Loss of motor fxn but full sensation intact
Intact sensation but loss of motor fxn
Motor fxn that is worse in the UE than the LE
Motor fxn that is worse in the LE than the UE
Motor fxn that is worse in the UE than the LE
Which of the following may be used for a pt who has a pressure wound?
Roho wheelchair cushion
Tilt in space wheelchair
Sand bed
All of the above
All of the above
Your pt experienced a C6 (AIS B) SCI and has developed a Stage 2 pressure wound on his coccyx. Which is the best transfer to complete with him?
Stand pivot with walker
Sliding board
Hoyer lift
Stand pivot with quad cane
Hoyer lift
Which of the following is the best way to help decr. orthostatic hypotension?
TED hose
Slow transitions with time to allow for BP regulation
Tilt table
All of the above
All of the above
You are working in an OP clinic and your pt arrives reporting symptoms consistent with autonomic dysreflexia. What should be your plan of action?
Transfer them from sitting to supine
Look to see if you can find noxious stimuli and quickly fix it
Keep them in an upright position
Both B and C
Both B and C
As you enter the room and your pt (C5 injury) reports a pounding headache and is flush in the face. You take her BP and find that is is 165/90. Which of the following conditions would you be concerned about?
Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypertension
Autonomic dysreflexia
Cardiac arrest
Autonomic dysreflexia
Which of the following levels of injury would require mechanical ventilation?
C3
C5
T2
All of the above
C3
Your pt experienced a C5 SCi. He presents with hemiplegia and decr. light touch and proprioception on the right side of his body and loss of pain and temp on the left side of his body following injury. Which of the following diagnosis would fit this presentation?
Posterior cord syndrome with more damage to the right side of the cord
Posterior cord syndrome with more damage to the left side of the cord
Brown Sequard syndrome on the right side of the cord
Brown Sequard syndrome on the left side of the cord
Brown Sequard syndrome on the right side of the cord
Decerebrate and decorticate rigidity are abnormal postures that may occur as a result of a TBI due to damage to the motor pathways of the brain. Which of the following statements is true regarding these abnormal postural patterns?
Decorticate rigidity is related to damage to the cerebral hemispheres of the brain and presents with spastic flexion of the UE
Both A and C are correct
Decerebrate rigidity is related to damage to the structures of the brain stem and presents with spastic extension of the UE
Individuals with decerebrate rigidity typically have a better prognosis than those with decorticate rigidity
Both A and C are correct
__________ approach focuses on enabling the client to obtain motor recovery thru occupational performance using real objects, environments, and meaningful occupations.
Dynamic interaction
Occupational
Wolf Motor
Task-oriented
Task-oriented
Which of the following is not a guiding principle when providing OT services with individuals with cognitive dysfunction?
Outcome measures should be based on overall occupational performance as opposed to cognitive testing
Remediation of individual cognitive impairments is generalizable to improved occupational performance
Evals and assessments should focus on occupational performance specific to the individual
OT and client as active partners to develop an intervention program to meet individual needs
Remediation of individual cognitive impairments is generalizable to improved occupational performance
Which of the following approaches reflect the Multicontext Treatment Approach guided by Toglia’s Dynamic Interactional Model?
Activity analysis to increase treatment activity demands and improve performance
Self-monitoring techniques during intervention to improve client awareness of strengths and weaknesses
Treatment activities based on client’s interests and goals
All of the above
All of the above
_______ attention supports tasks that require vigilance and the capacity to maintain attention over time; often measured by the time spent on a task.
Long-term
Shifting
Sustained
Divided
Sustained
___________ memory is involved in skill performance; it involves a blend of cognitive, motor, and perceptual skills.
Implicit
Episodic
Short-term
Procedural
Procedural
The ability of the brain to reorganize and develop new pathways is known as _________.
Plasticity
Learned non-use
Motor learning
Shaping
Plasticity
Which of the following concepts reflect the dynamic systems theory and heterarchical model of motor control?
Each subsystem (component) is critical to support engagement in occupation
Higher motor systems in CNS control the subordinate lower centers
Dynamic interaction between client factors, context, and occupations
A and C only
A and C only
__________ is a treatment technique involving the forced use of a hemiparetic extremity post-neurological injury.
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT)
Biofeedback
Neuromuscular re-education
Neurodevelopmental therapy (NDT)
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT)
Why might changes in visual processing cause a corollary change in cognitive performance?
Because the visual system is the primary system we use to acquire information about our environment and guides our decision making process
Because the visual system provides us with good acuity
Because the visual system gives us the “big picture”
Because the visual system allows us to identify objects in our environment
Because the visual system is the primary system we use to acquire information about our environment and guides our decision making process
________ is a neurogenic disorder where the body’s own immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system.
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Muscular Dystrophy
Parkinson’s
ALS
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis has three clinical subtypes. Which type is associated with a quicker progression and problems with dysphagia and dysarthria?
Progressive bulbar palsy
Progressive spinal muscular atrophy
Primary lateral sclerosis
Primary medial sclerosis
Progressive bulbar palsy
Your pt with ALS is experiencing frequent “twitches” in his arm and hand and asks you what this might be. What are they most likely describing?
Fasciculations
Muscle spasms
Muscle fatigue
Spasticity
Fasciculations
You receive a referral for a client with a diagnosis of ALS and during your assessment you notice a significant decrease in their grip and pinch strength and MMT is 3/5 (Fair). The client is concerned and asks what they should do. What is an appropriate intervention for you to provide?
Education on compensation and adaptation for reduced grip and pinch strength
Education on caregiver assistance with daily tasks
Education on progressive resistive strengthening program
All of the above
Education on compensation and adaptation for reduced grip and pinch strength
A 74-year-old man with myasthenia gravis has been referred to you for evaluation and intervention. While completing the occupational profile, you learn that he is easily fatigued and short of breath during activity. An appropriate intervention would be:
Training in pacing strategies
Strengthening program
Task modifications and adaptations
All of the above
All of the above
The ________ form of MS (10% of MS population) is distinguished by a downward course with episodes of exacerbations or remission.
Secondary-progressive
Primary-progressive
Relapsing-remitting
Progressive-relapsing
Primary-progressive
________ is the most common chronic disease involving a disorder of chemical transmission at the nerve-muscle synapse, or neuromuscular junction.
Myasthenia Gravis
Huntington’s Disease
ALS
Peripheral Neuropathy
Myasthenia Gravis
What are common psychosocial issues seen with clients diagnosed with Huntington’s disease?
Emotional lability
Suicidal thoughts
Depression
All of the above
All of the above
____ muscular dystrophy affects only males, and the age of onset is between 3 and 5 years.
Duchenne
Becker
Mytonic
Limb girdle
Duchenne
MS is a progressive neurological disease that damages the ______ in the CNS.
Muscle fibers
Axonal synapsis
Neurons
Myelin sheath
Myelin sheath