Acute Kidney Injury Pathophysiology - Zhang
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the 3 categories of AKI?
prerenal, instrinsic, postrenal
What defines the pathophysiology of prerenal AKI?
renal blood HYPOperfusion
long answer: decreased renal blood perfusion (renal hypoperfusion) (no damage to the parenchymal/functional tissue of an organ, diff from the connective and supporting tissue)
What defines the pathophysiology of intrinsic/renal AKI?
ischemia or toxins
long answer: structural damage to kidney, most commonly tubule from ischemic or toxic insult (acute tubular necrosis, ATN)
What defines the pathophysiology of postrenal AKI?
obstruction of urine flow downstream from kidney
What are the causes of renal hypoperfusion with systemic arterial hypotension?
instrinsic volume depletion (ie. GI loss: V/D, diuretics…)
decreased effective circulating blood volume (ie. decreased cardiac output or systemic vasodilation/sepsis)
What are possible causes of prerenal AKI?
NSAIDs, ACEi, ARB, Cacineurin imhibitors
which renal hypoperfusion is most commonly associated with renal artery occlusion?
renal hypoperfustion WITHOUT systemic hypotension (aka. drug-induced)
Patients at risk for prerenal AKI are particularly susceptible to changes in the _____ and _____ arteriolar tone
afferent, efferent
What meds can cause drug-induced prerenal AKI?
ACE-i/ARB, NSAID
Most cases of intrinsic AKI can be ID’d with ________
tubular damage (acute tubular necrosis, ATN)
What are possible causes of intrinsic AKI?
ATN nephrotoxins (endogenous or exogenous toxins or contrast dye) and ischemia
The most common causes of postrenal AKI is what?
prostatic process/hypertrophy (hypertrophy/Benign prostatic hyperplasia, cancer, infection)
Which of the following is most likely the cause of intrinsic AKI?
hypovolemia (decreased in blood volume)
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
prostate hypertrophy
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
Which of the following is most likely the cause of prerenal AKI?
hypovolemia (decreased in blood volume)
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
prostate hypertrophy
hypovolemia (decreased in blood volume)
Which of the following is most likely the cause of postrenal AKI?
hypovolemia (decreased in blood volume)
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
prostate hypertrophy
prostate hypertrophy
In terms of the diagnosis of AKI, what indicates prerenal AKI?
urine Na < 20, specific gravity > 1.018
In terms of the diagnosis of AKI, what indicates intrinsic AKI?
urine Na > 40, specific gravity < 1.012
In terms of the diagnosis of AKI, what indicates postrenal AKI?
urine Na > 40, specific gravity variable
Which diuretic is most likely to cause allergic reaction to patients allergic to sulfa?
furosemide
mannitol
erythonic acid
furosemide
Prostate hypertrophy is a major cause for ______ AKI
postrenal
Which of the following is most likely a cause of intrinsic AKI?
hypovolemia (decreased blood volume)
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
prostate hypertrophy
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
Which of the following is most likely a cause of prerenal AKI?
hypovolemia (decreased blood volume)
medications that induce acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
prostate hypertrophy
hypovolemia (decreased blood volume)
Urine sodium (45mmol/L) and urine specific gravity (1.010) indicate the possibility of ______ AKI.
intrinsic
Urine sodium (17mmol/L) and urine specific gravity (1.022) indicate the possibility of ______ AKI.
prerenal
If prerenal AKI caused by hypovolemia is left untreated, _____ AKI may occur.
intrinsic
MOA of loop diuretics
inhibit NKCC2, induce expression of cyclooxygenase COX-2
Of the loop diuretics, which increases renal blood flow?
furosemide
Why is furosemide more commonly used compared to the other loop diuretics?
lower cost, PO and Parenteral, reasonably safe
What are the benefits of torsemide and bumetanide over furosemide?
more predictable oral bioavailability, higher potency
Please arrange the loop diuretics in terms of potency
Bumetanide > torsemide > furosemide
Please arrange the loop diuretics in terms of predictability in terms of oral bioavailability:
torsemide and bumetanide > furosemide
Which loop diuretic is recommended for patients with allergy to sulfonamides?
ethacrynic acid
What are the side effects of loop diuretics?
electrolyte imbalance, metabolic alkalosis, hyperuricemia, otoxicity, allergic/other reactions
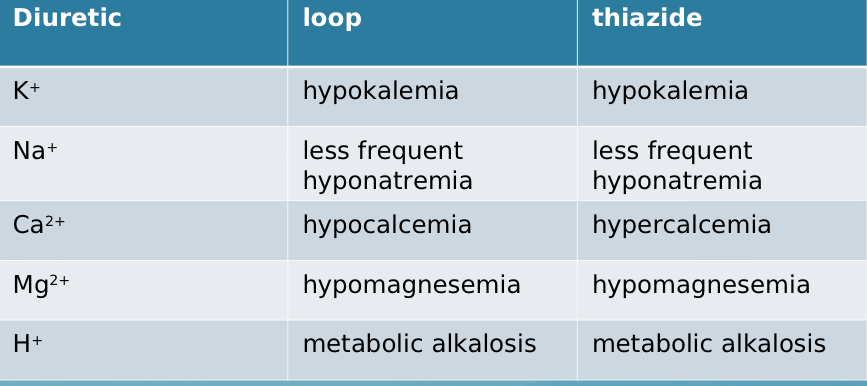
Comparing loop vs thiazide, which causes hypo-/hyperkalemia?
both cause HYPOkalemia
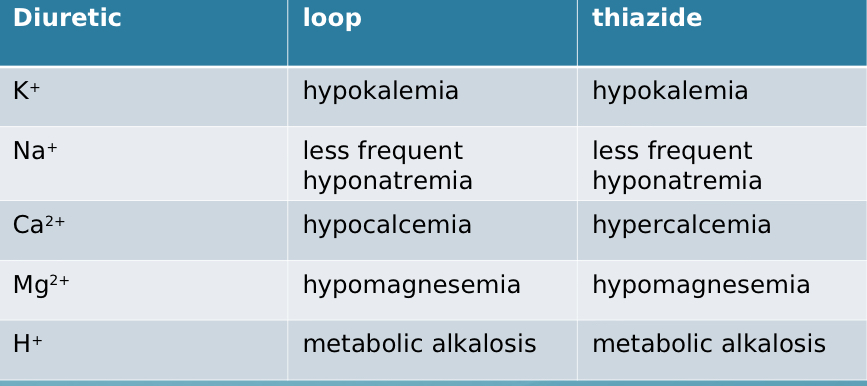
Comparing loop vs thiazide, which causes hypo-/hypernatremia?
both cause less frequent hyponatremia
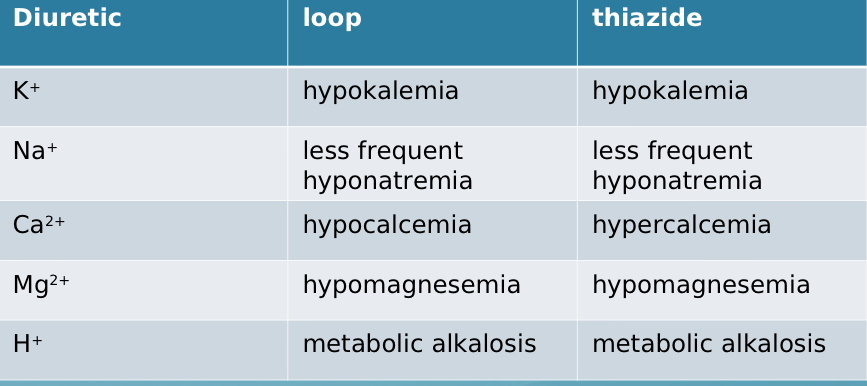
Comparing loop vs thiazide, which causes hypo-/hypercalcemia?
loop - HYPOcalcemia, thiazide - HYPERcalcemia
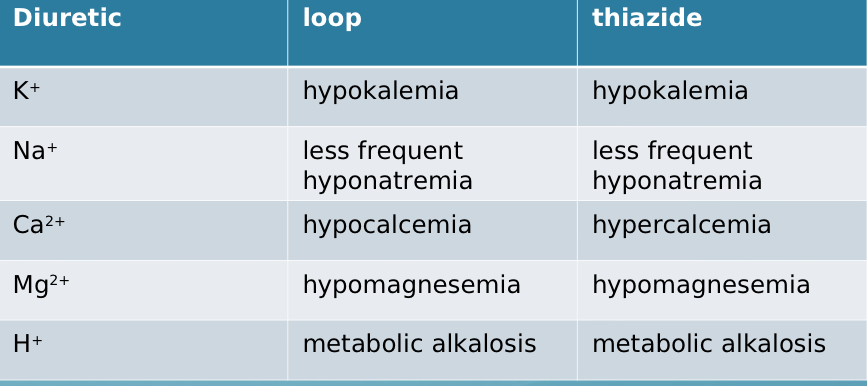
Comparing loop vs thiazide, which causes hypo-/hypermagnesemia?
both cause hypomagnesemia
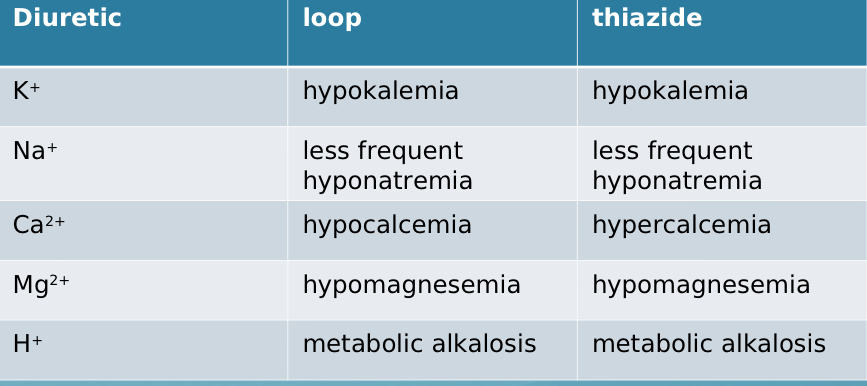
Comparing loop vs thiazide, which causes H+ imbalance (metabolic acidosis or metabolic alkalosis)?
both cause metabolic alkalosis
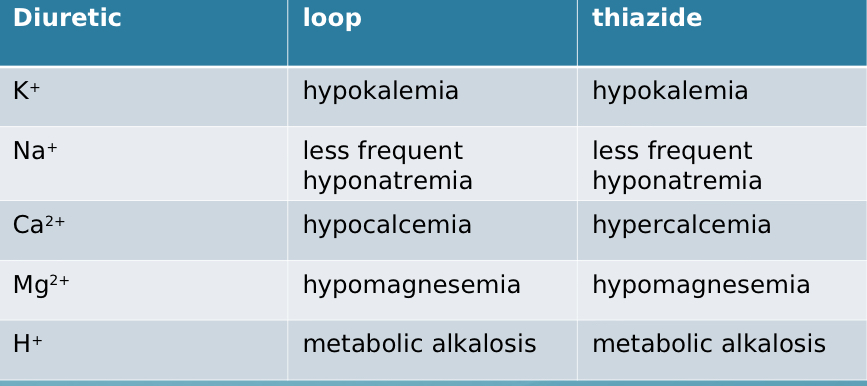
Comparing loop vs thiazide, what is the only difference in electrolyte imbalance?
calcium