anatomy lab 1
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
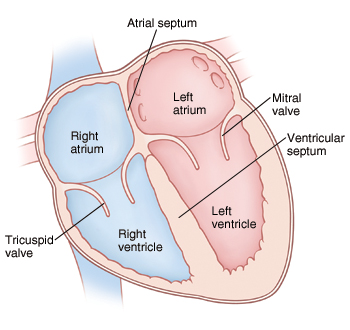
4 chambers of the heart
right atrium , left atrium , left ventricle, right ventricle
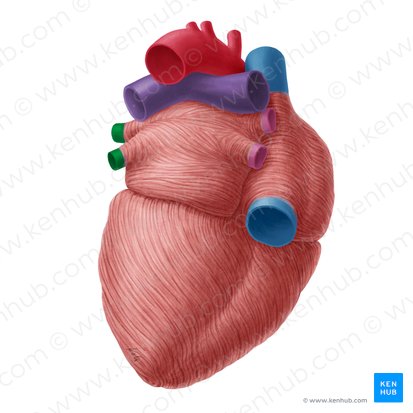
what is this - posterior view
(above left ventricle)
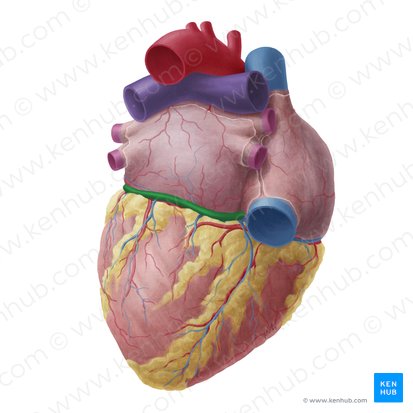
coronary sulcus
what is this - anterior view
(above left ventricle)
coronary sulcus
what is this
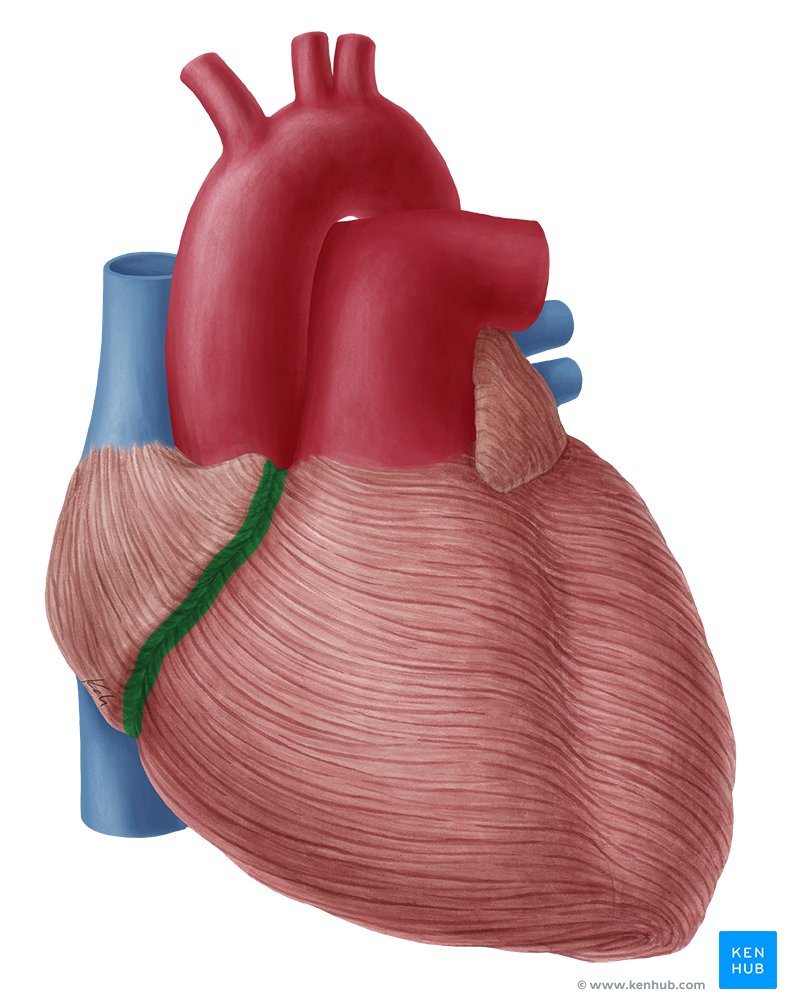
anterior interventricular sulcus
(seperates the two ventricles on the anterior side)
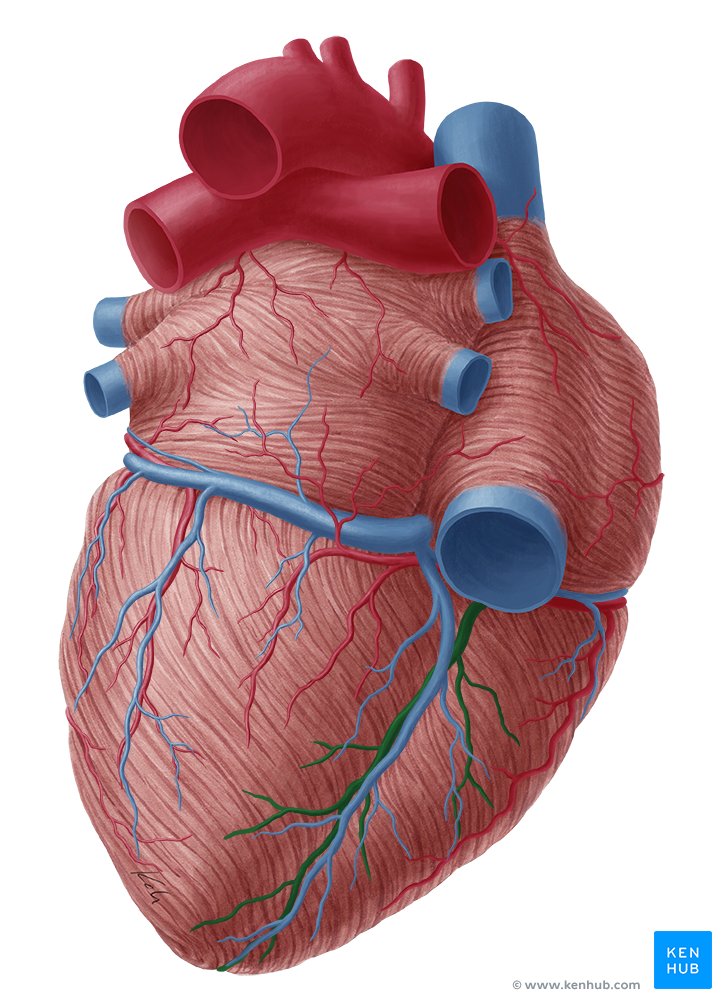
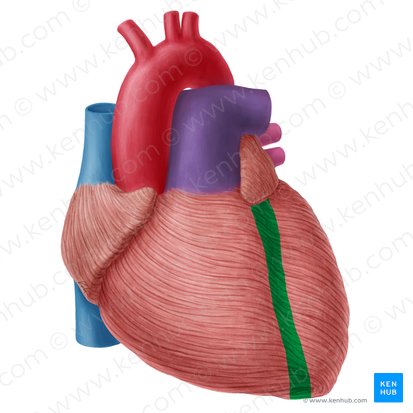
what is in green
posterior interventricular sulcus
what is this
apex of the heart
where is the base of the heart
at the top of the heart, opposite the apex
function of right atrium (behind right auricle)
Receives deoxygenated venous blood from Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava, and Coronary Sinus. and pumps it into right ventricle
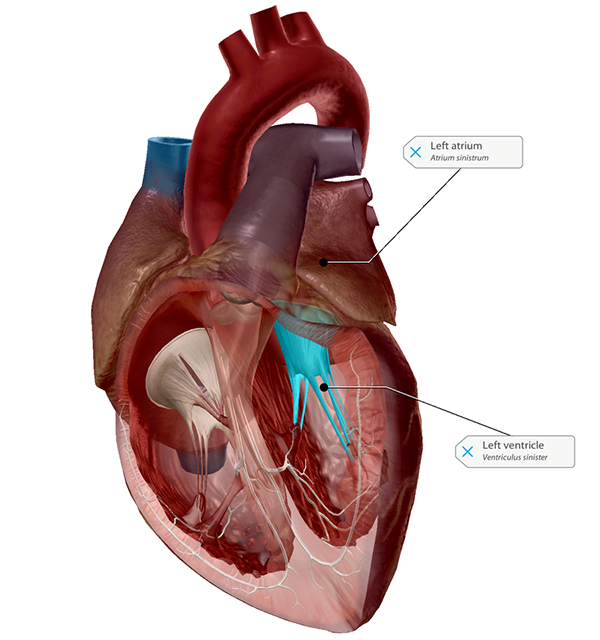
function of left ventricle (mostly posterior)
Thickest wall; strong trabeculae & papillary muscles
Pumps oxygenated blood → body (aorta)
receives blood from the left atrium.
left atrium function
Receives oxygenated blood from lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle.
right ventricle function
Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs through pulmonary valve into pulmonary trunk to the lungs
receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium.
Interatrial Septum function
Separates right & left atria; contains fossa ovalis which allows for fetal blood flow.
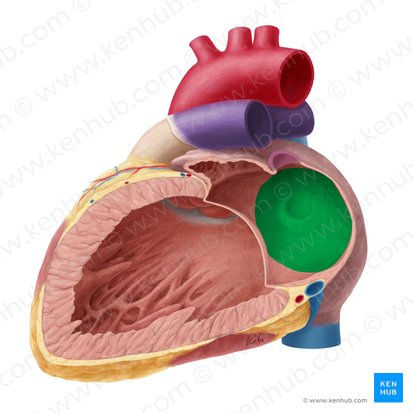
what is this
interatrial septum separating the atria.
anterior view
what is this
interatrial septum
posterior view
interventricular septum function
Thick wall that separates ventricles and supports conduction system
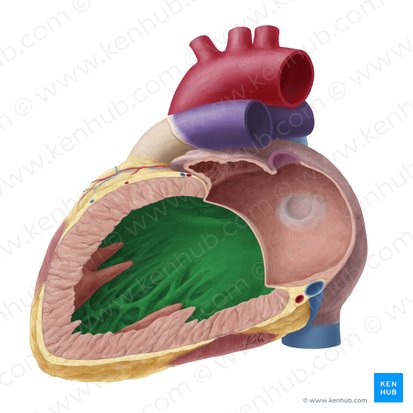
what is this
interventricular septum
posterior view
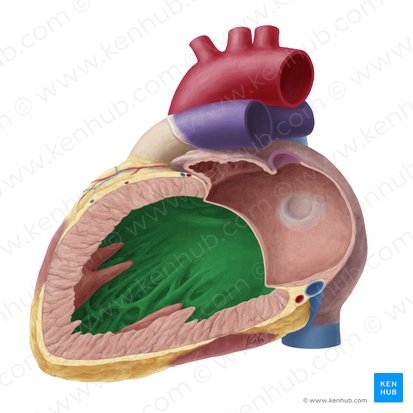
what is this
interventricular septum
lateral view
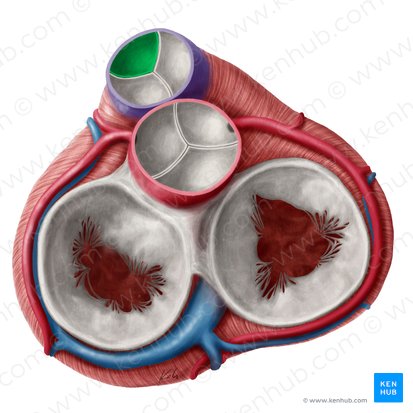
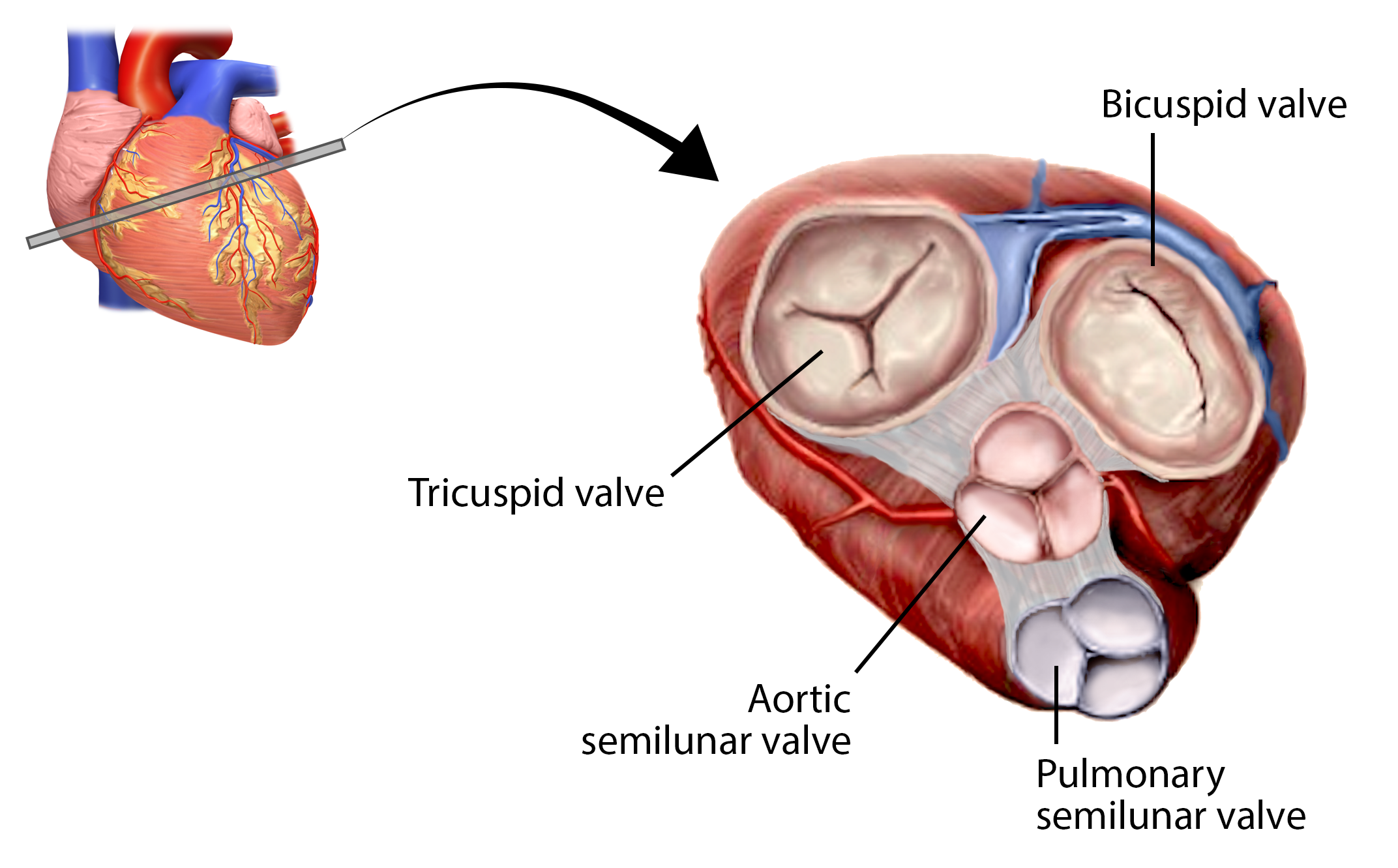
Tricuspid Valve (Right atrioventricular valve) function
Prevents backflow to right atrium during ventricular contraction.
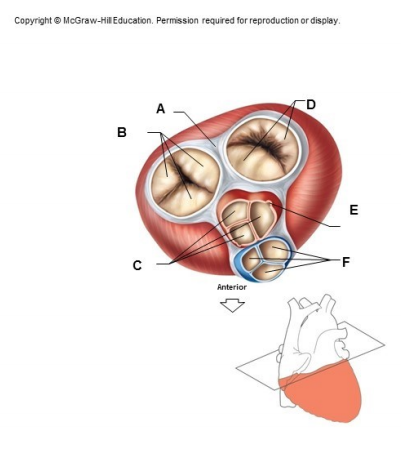
what is structure B
tricuspid valve
between right atrium and right ventricle
bicuspid (mitral) valve
Prevents backflow to left atrium during ventricular contraction.
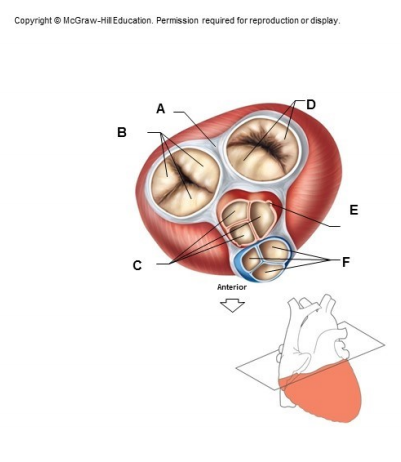
what is structure D
bicuspid/mitral valve
located between the left atrium and left ventricle
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve function
prevents backflow from pulmonary artery into right ventricle.
Prevents blood return from pulmonary artery
what structure is this
pulmonary semilunar valve
located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
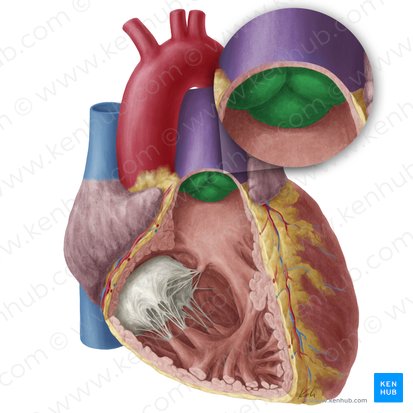
aortic semilunar valve function
Prevents blood return from aorta into left ventricle.
prevents backflow from aorta into left ventricle.
right and left auricles
The auricles are pectinated muscle structures that form a pouch on the exterior surface of the heart.
They increase the capacity of the atria, allowing for greater blood volume.
what are these structures in purple
right and left auricle
left auricle overlaps what
pulmonary trunk
right auricle overlaps
ascending aorta.
right ventricle coverage
Forms most of the anterior surface of the heart.
behind the sternum.
left ventricle coverage
Forms the left inferior border and part of the apex.
visible from the left and slightly posterior
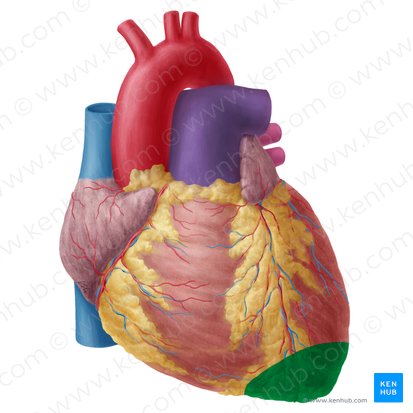
heart apex
formed by left ventricle
formed anteriorly, inferiorly, and to the left
what does the surface of right ventricle show
trabeculae carneae and conus arteriosus (smooth upper region leading to pulmonary trunk).
how is left ventricle diff from right ventricle
Thicker myocardium compared to right ventricle.
apex has point of what
Point of maximal impulse (PMI) on chest wall.
anterior interventricular sulcus contains what
great cardiac vein
Anterior interventricular artery (LAD), and small cardiac vein.
what does the coronary sulcus do
Separates the atria from the ventricles and contains important blood vessels.
what does coronary sulcus contain
Right & left coronary arteries,
coronary sinus
FRONT VIEW
superior vena cava function
Returns blood from head & upper limbs
superior vena cava location
enters the top of right atrium
(front view)
Ascending Aorta → Aortic Arch vessel function
Sends oxygenated blood to systemic circulation
Pulmonary Trunk → Pulmonary Arteries function
Sends deoxygenated blood to lungs
Pulmonary Trunk → Pulmonary Arteries location
anterior
Arises from right ventricle
Ascending Aorta → Aortic Arch vessel
anterior
Emerges from left ventricle
what enters left atrium
Four pulmonary veins
what forms most of the base of the heart
left atrium
what is the location of coronary sinus
lies on the posterior side
coronary sulcus location
large venous channel - Drains cardiac veins into right atrium.
pulmonary veins funciton
carry oxygenated blood to the left atrium from the lungs.
superior and inferior vena cava function
carry deoxygenated blood from the body and return it to the right atrium.
aortic arch → descending aorta
passes posteriorly into thoracic aorta
what seperates the ventricles
interventricular septum, a posterior groove
what does interventricular septum contain?
posterior interventricular artery (from RCA)
what does right atrium contain
pectinate muscles.
what does right ventricle received blood from
tricuspid valve from right atrium
what does the interior of right ventricle contain
trabiculae carne, papillary muscles, and conus arteriosus
where do trabiculae carne, papillary muscles and conus ateriorsus lead to
pulmonary valve
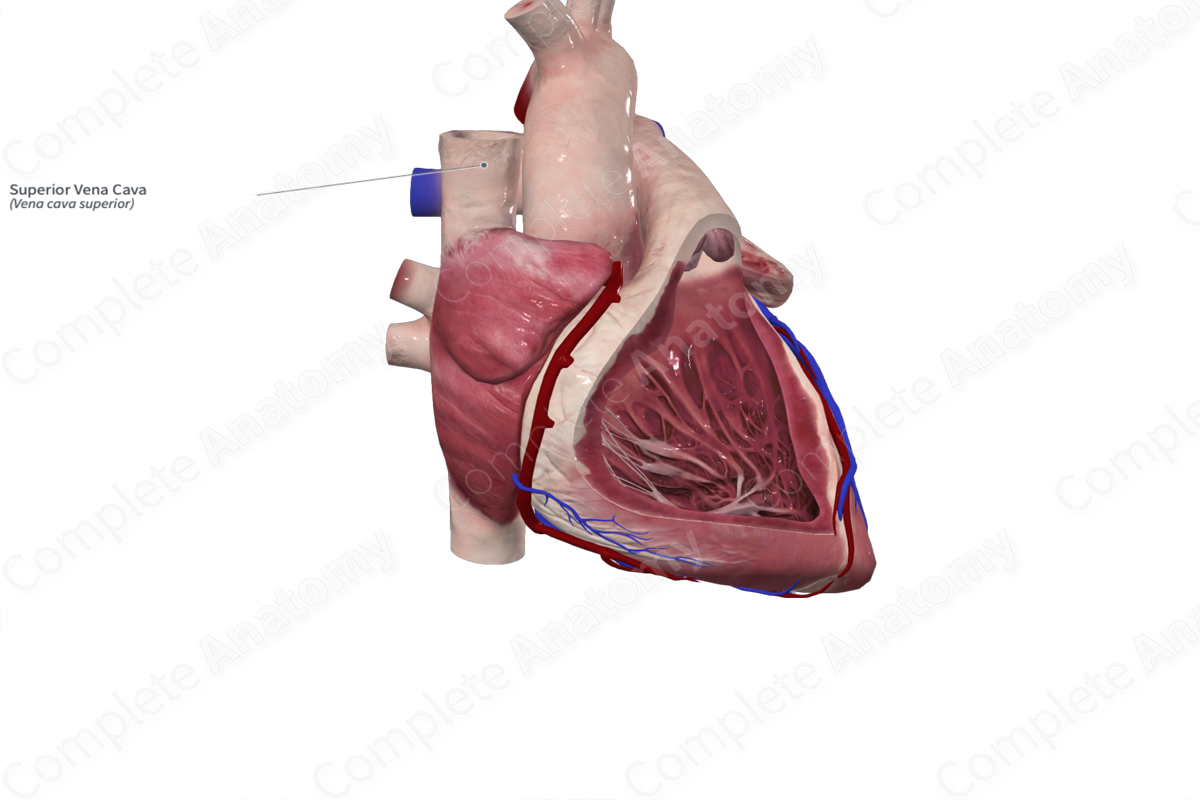
what is the blue structure
superior vena cava
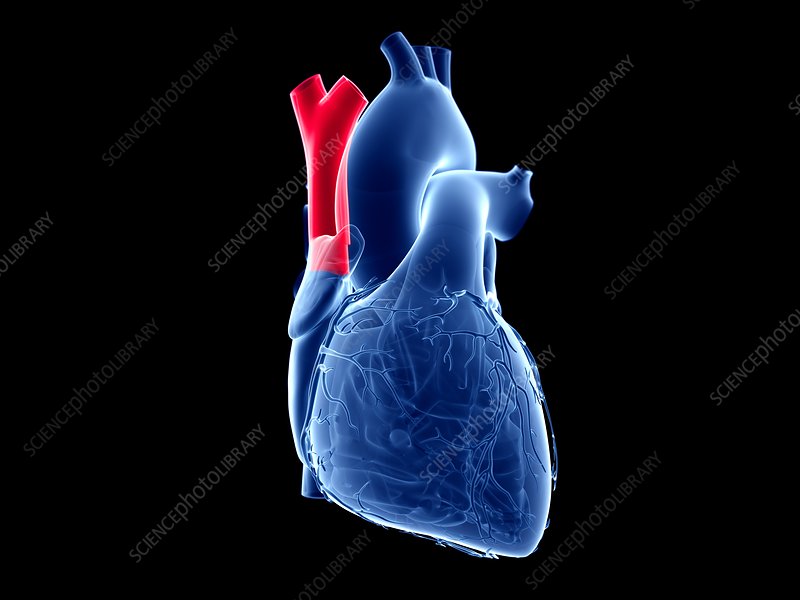
what is this structure
also svc
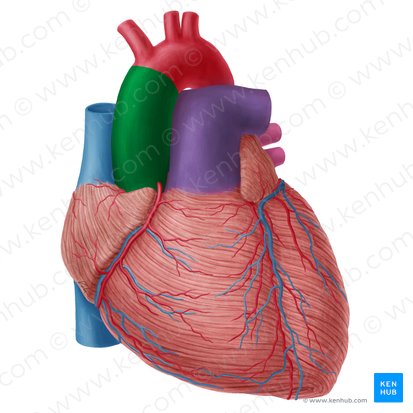
what structure is highlighted in green
inferior vena cava
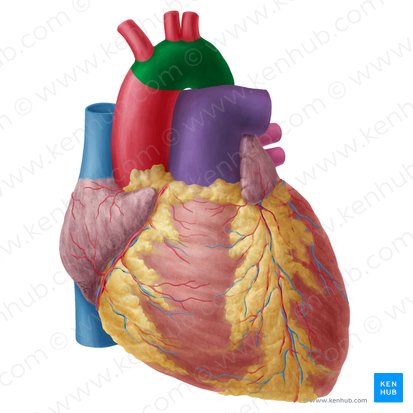
what structure is highlighted in green
ascending aorta
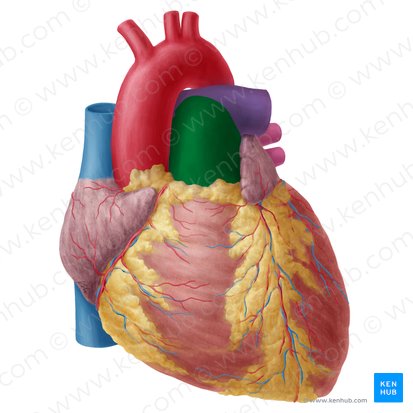
what is the structure in green
aortic arch
what is the structure in green
pulmonary trunk
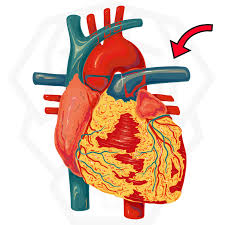
what structure is being pointed to
left pulmonary artery
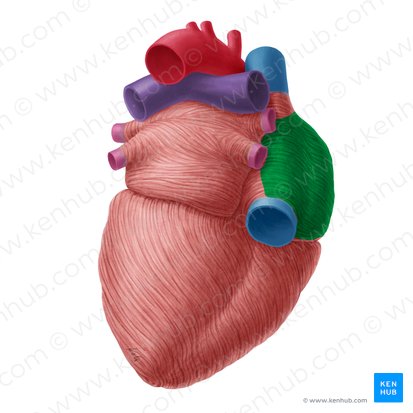
what structure is in green
right atrium
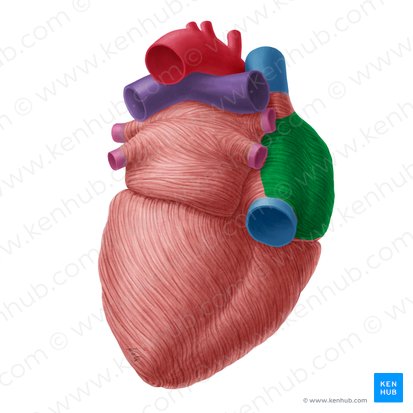
what structure is left to the green
left atrium
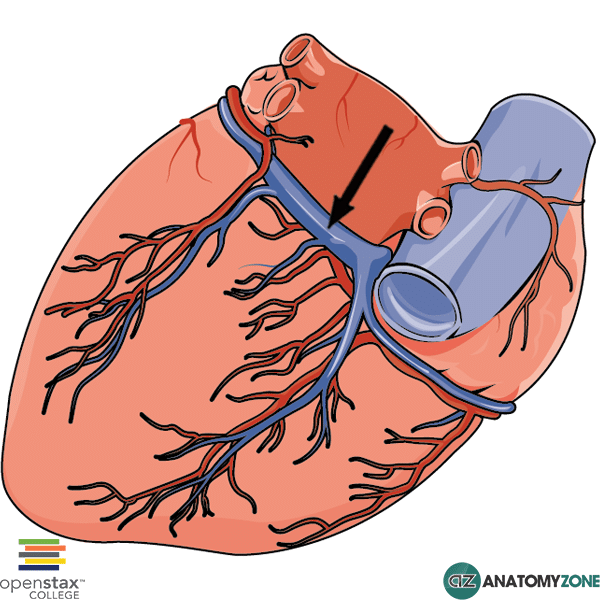
what is being pointed to in this picture
coronary sinus
what are the structures in green and pink
2 left and 2 right pulmonary veins
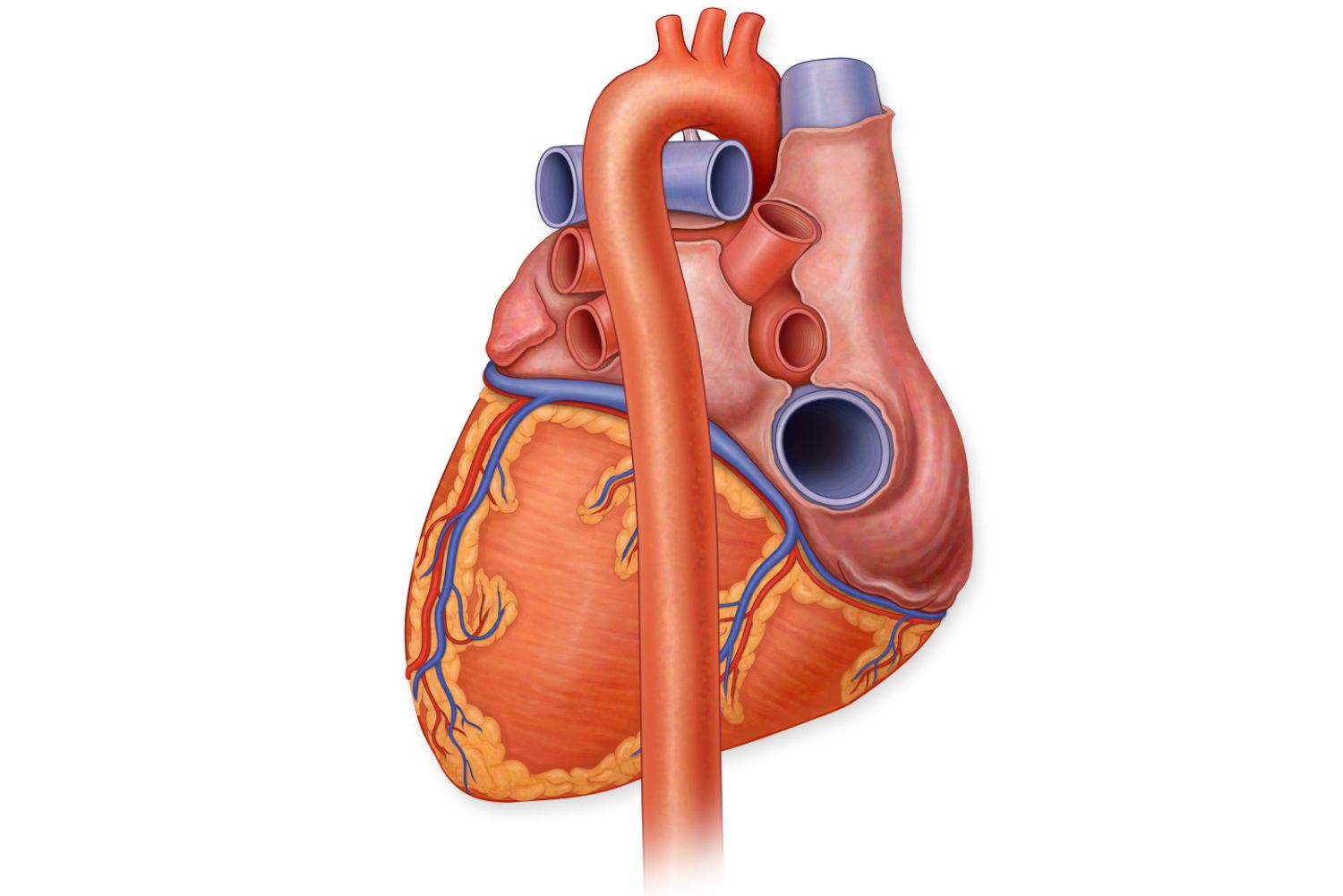
what is the long structure
descending aorta
Inferior Interventricular Sulcus
groove on posterior side that seperates the ventricles
where does inferior interventricular sulcus lie
Lies near the diaphragmatic surface of the heart.
function of inferior interventricular sulcus
pathway for major coronary blood vessels that supply the ventricular myocardium.
what does the inferior interventricular sulcus contain
Posterior Interventricular Artery (branch of the right coronary artery).
Middle Cardiac Vein which drains into the coronary sinus.
left atrioventricular valve names
bicuspid or mitral valve
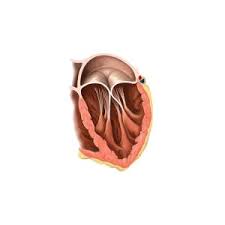
what is the name of this structure at the top
bicuspid/ left atrioventricular/ mitral valve
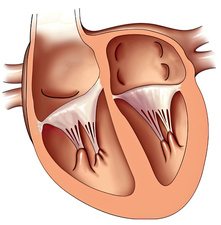
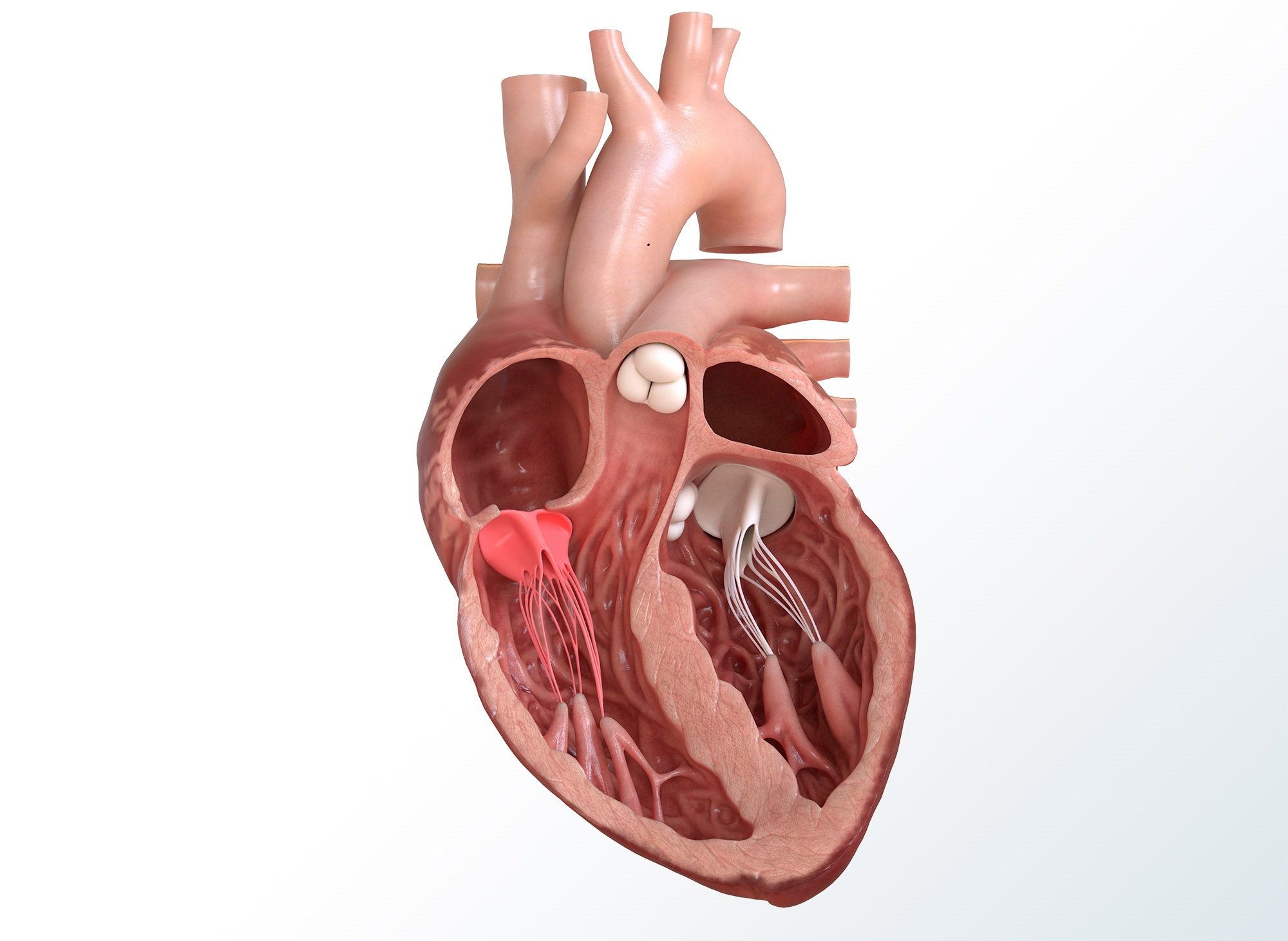
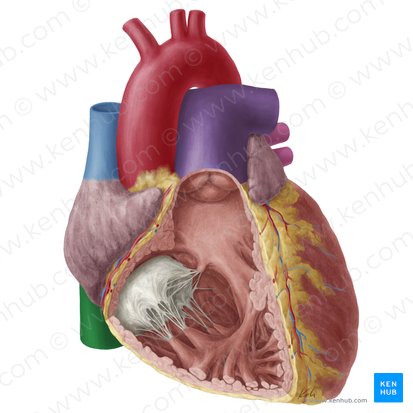
what are the name of the white stringy items
chordae tendineae
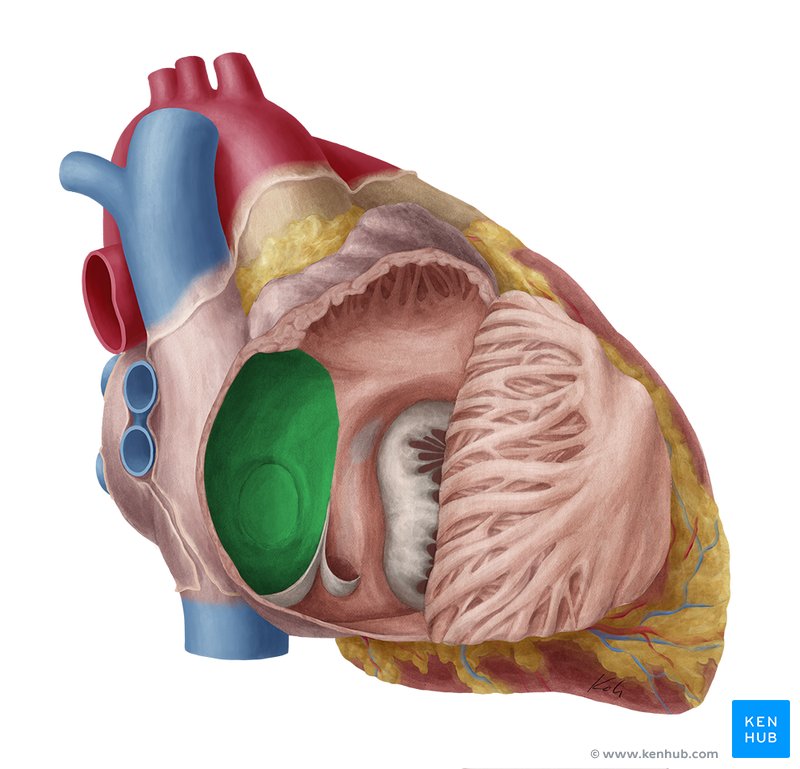
fossa ovalis
a depression in the interatrial septum that is a remnant of the fetal foramen ovale.
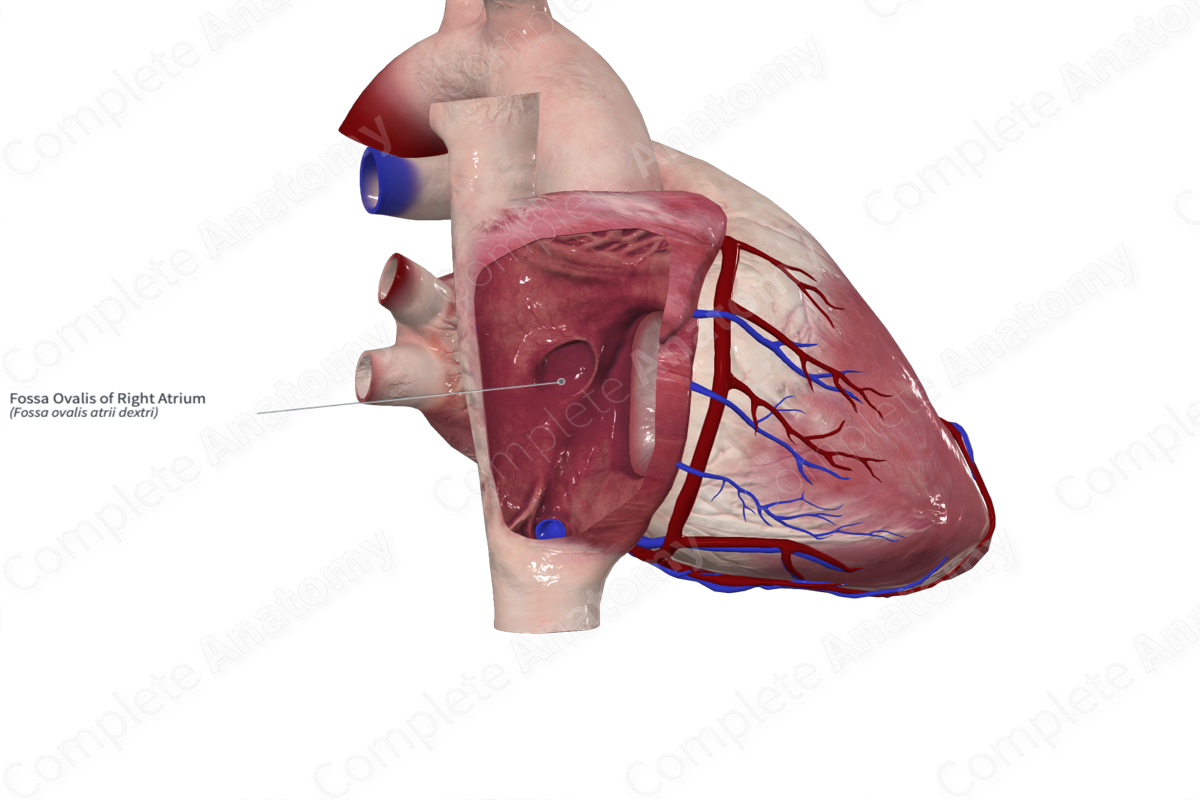
what is this
fossa ovalis
intratrial septum funciton
prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in left and right atrium
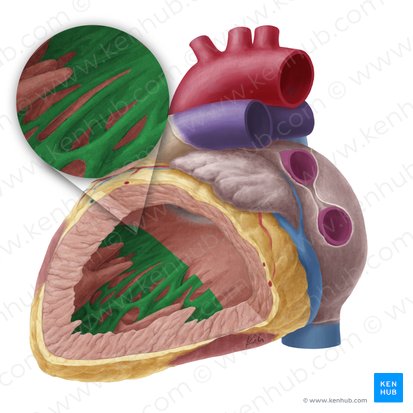
what structure is in green
trabeculae carnae
where are trabeculae carnae
Ridges of muscle on ventricle wall.
what do chordae tendineae do
string-like muscles that anchor the valve cusps
papillary muscles function
cone shaped
They anchor the valve flaps in place during contraction and make sure they close tightly during each heartbeat.
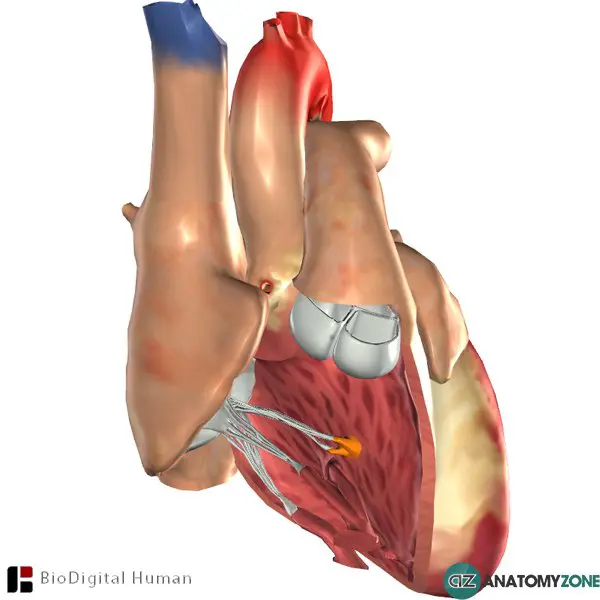
what is the structure in orange
papillary muscles
aortic vestibule function
smooth-walled outflow tract guides blood from the left ventricle toward the aortic valve
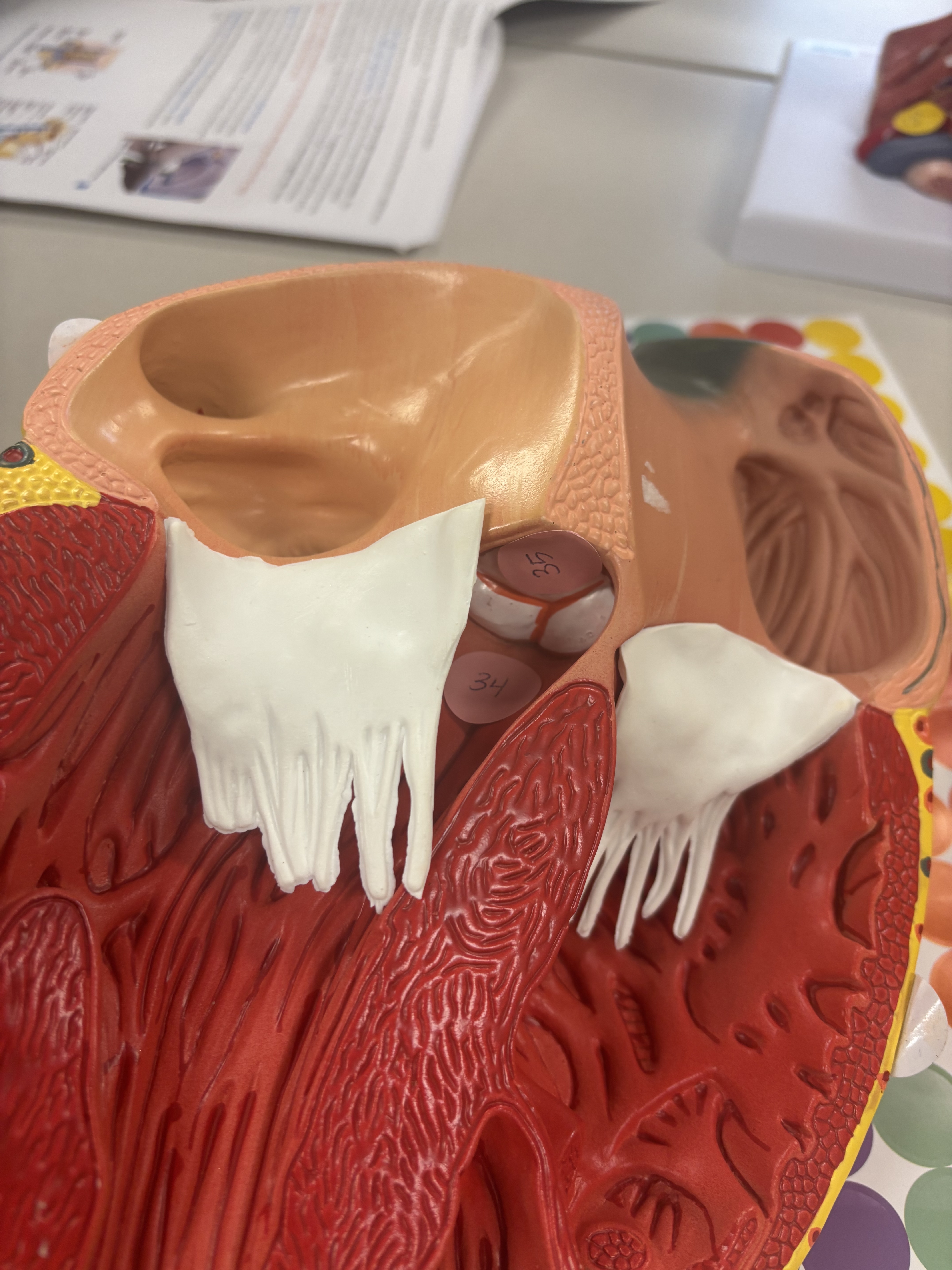
what is number 34
aortic vestibule (smooth muscle wall in left ventricle)
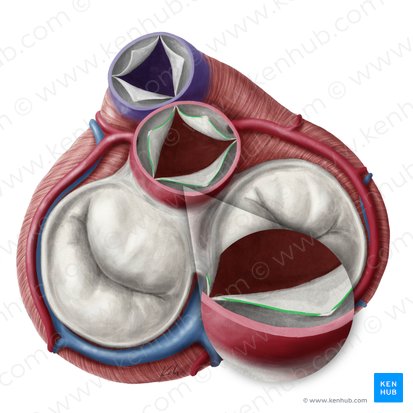
what is the smaller green structure (superior view)
aortic valve
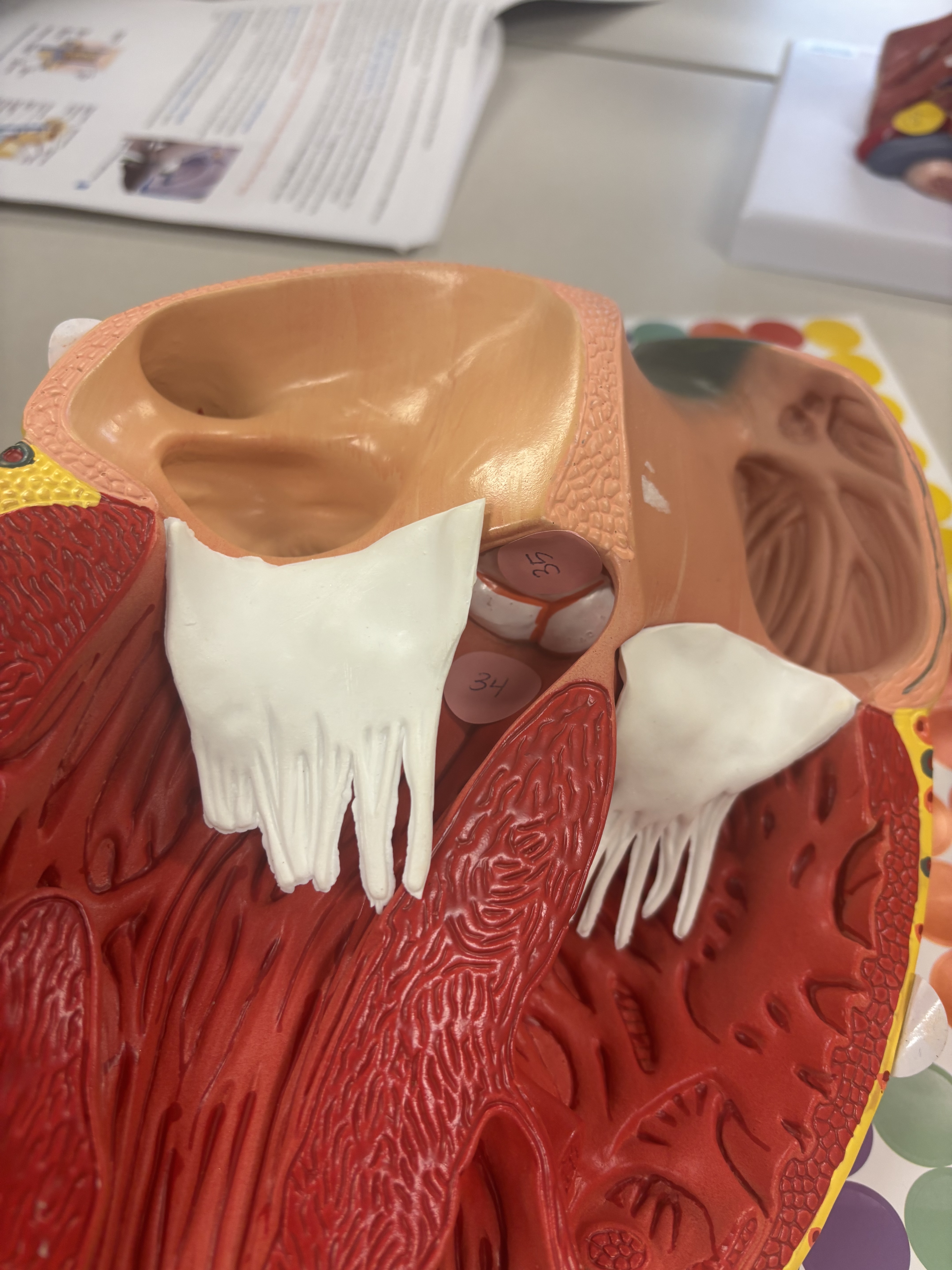
what is number 35 (inferior)
aortic valve (tricupsid valve)
aortic valve function
prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle during diastole.
c
right atrium receives what from what
deoxygenated blood from heart and body
coronary sinus function
The coronary sinus serves as the main venous drainage system of the myocardium, collects most heart’s deoxygenated blood and returns to right atrium
think sinus = drains
where is the opening of the coronary sinus
bottom of right atrium
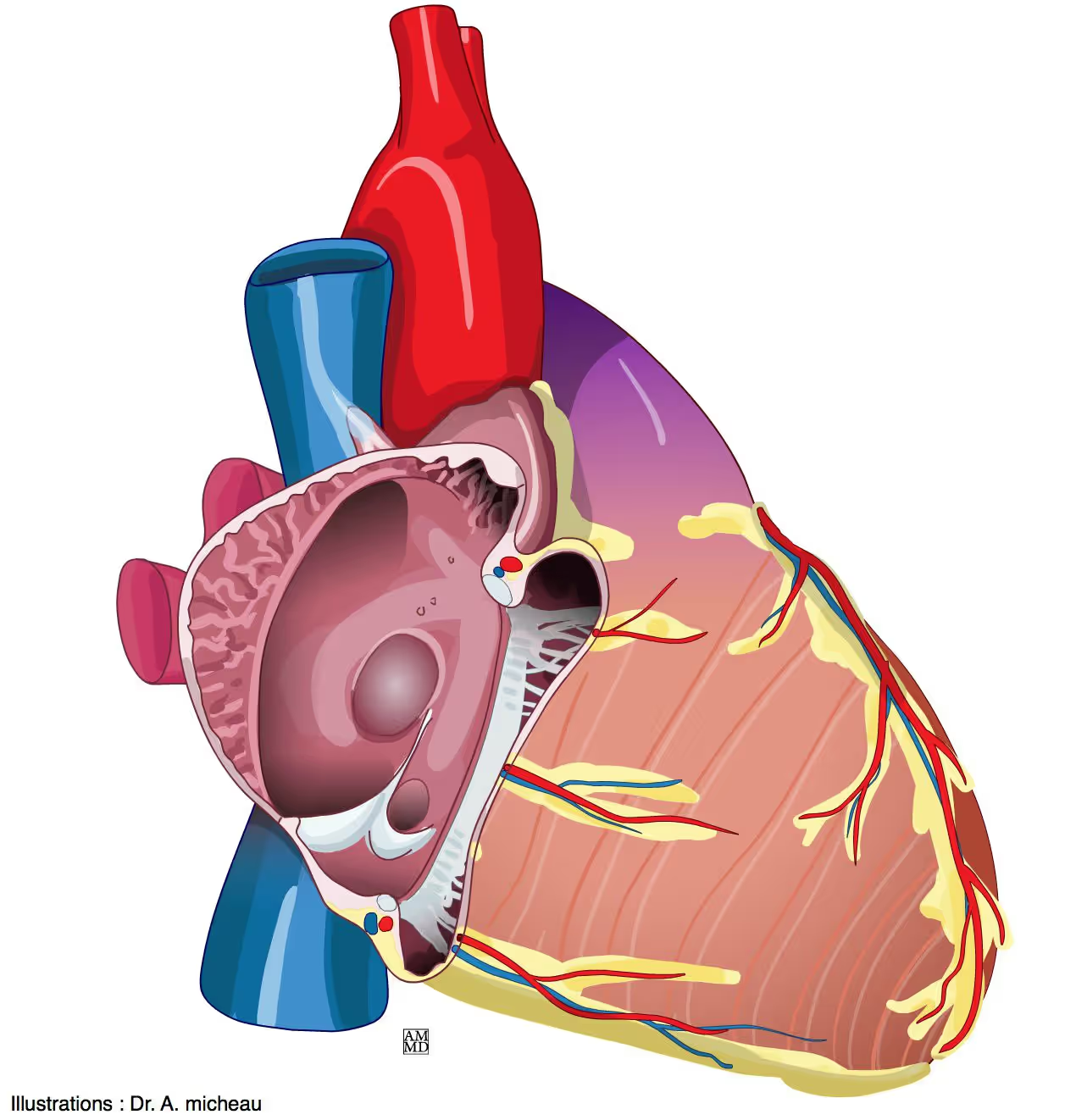
(lateral right view) what is the opening slightly above the right ventricle
opening of the coronary sinus
where is the opening of the inferior vena cava
posterior wall of the right atrium
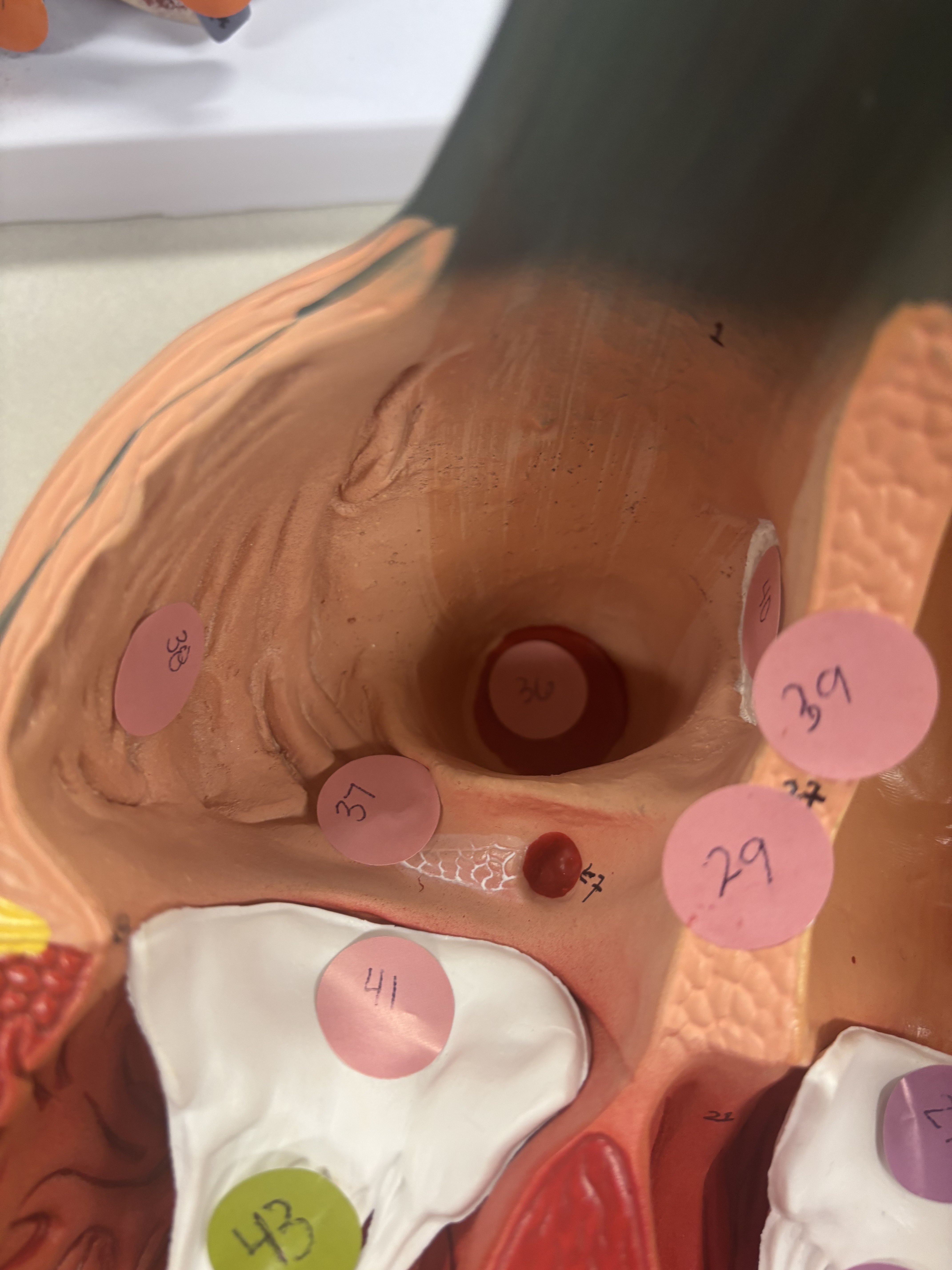
what is number 36 (this is the right atrium)
inferior vena cava opening
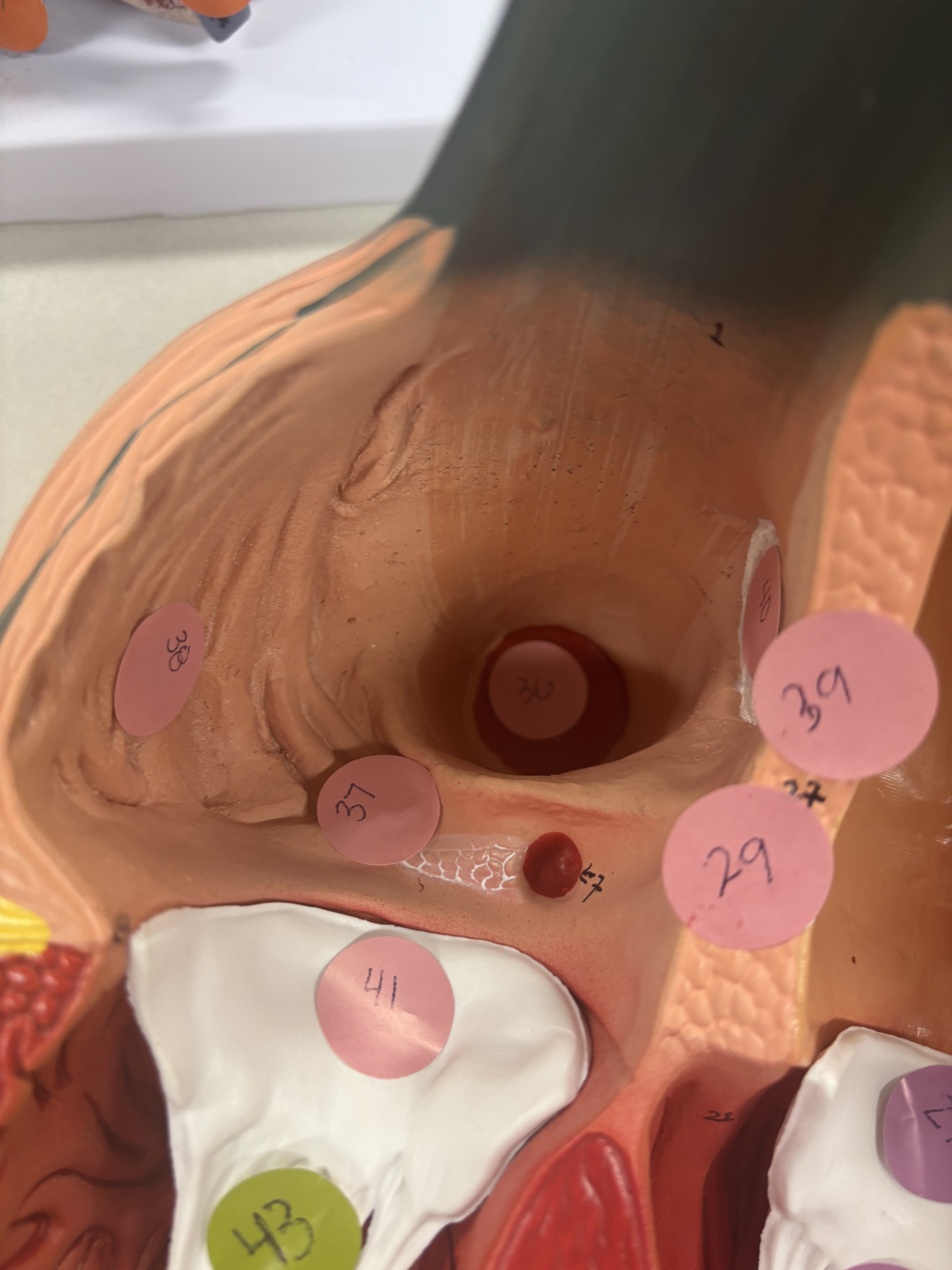
what is number 38 in right atrium
pectinate muscles
pectinate muscles function
ridges that increase the power of contraction without increasing heart mass substantially
where are pectinate muscles?
the outer part of the wall of the right atrium has parallel ridges in it
what does conus arteriosus lead to
pulmonary valve
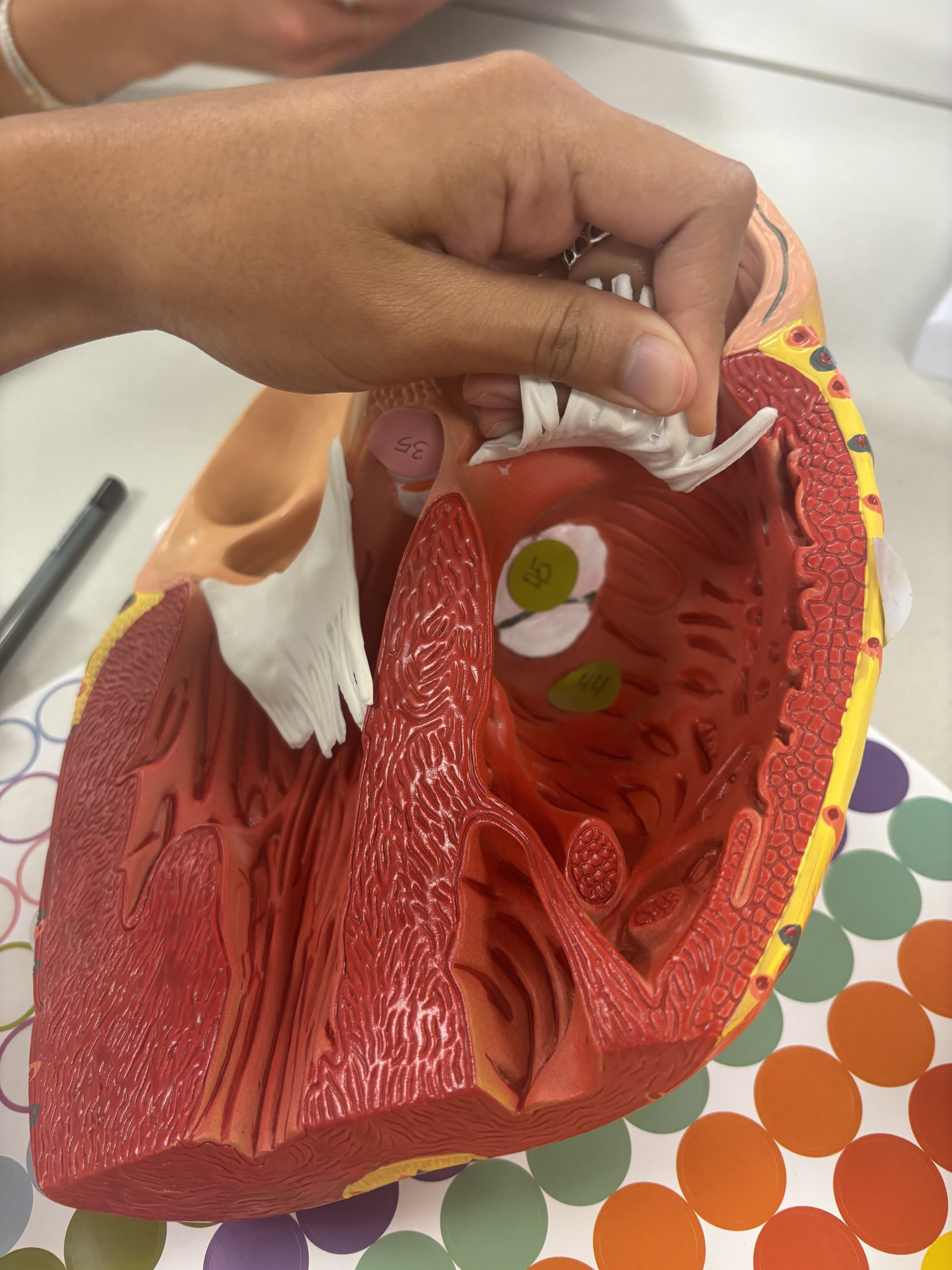
what is number 44
conus arteriosus
conus arteriosus function
directing blood from the right ventricle into pulmonary artery, leading to lungs for oxygenation.