Unit 3: Biology & Behavior
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
central nervous system
the brain and the spinal cord; coordinates body functions, connects body with brain, and simple reflexes
peripheral nervous system
all nerve cells in the body that are not part of the central nervous system; includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems
neurons
basic units of the nervous system; cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information; operate through electrical impulses, communicate with each other through chemical signals, and form neural networks
dendrites
branchlike extensions of the neuron that detect information from each other
cell body/soma
the site in the neuron where information from thousands of other neurons is collected and integrated; the contains the nucleus and other parts that keep the cell healthy
axon
a long, narrow outgrowth of a neuron by which information is conducted from the cell body to the terminal buttons; sends neural impulse
terminal buttons/terminals/axon terminals
at the ends of axons, small nodules that release chemical signals from the neuron into the synapse, hold neurotransmitters
synapse
the tiny, fluid-filled gap between the terminal buttons of a “sending” neuron and the dendrites of a “receiving” neuron; where chemical communication occurs between the neurons
action potential
the electrical signal that passes along the axon and subsequently causes the release of chemicals from the terminal buttons; “on” condition of the neuron; generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane
resting potential
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active; “off” state; positively charged ions waiting to flow into the axon and be stimulated by another neuron
refractory period/hyperpolarization
the brief period of time following action potential when a neuron’s membrane potential is more negative, or hyper-polarized, making it harder to fire again; reloading
all-or-none principle
the principle that when a neuron fires, it fires with the same potency each time; a neuron either fires or not, although the frequency of firing can vary (ex. gunshots)
split brain
a condition that occurs when the corpus callosum is surgically cut and the two hemispheres of the brain do not receive information directly from each other, two separate brains
myelin sheath
a fatty material; made up of glial cells; insulates some axons to allow for faster movement of electrical impulses along the axon; degeneration of this causes multiple sclerosis
nodes of ranvier
small gaps of exposed axon between the segments of myelin sheath, where action potentials take place; gaps in the myelin sheath where there is no myelin among an axon
neurotransmitters
chemical substances that transmit signals from one neuron to another; SNAGGED
receptors
in neurons, specialized protein molecules on the postsynaptic membrane; neurotransmitters bind to these molecules after passing across the synapse
reuptake
the process whereby a neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic terminal buttons, thereby stopping its activity; reabsorption
amygdala
the part of the brain that controls emotional responses such as fear or anger
brainstem
the part of the brain that contains the pons, the medulla, and the reticular formation; responsible for automatic and survival functions like breathing
cerebellum
the part of the brain that helps coordinate voluntary movements, balance, and fine movement
cerebrum
the part of the brain that is the body’s ultimate control and information processing center
corpus callosum
the part of the brain that connects the two brain hemispheres and allows them to communicate with each other
hippocampus
the part of the brain that helps process new memories for permanent storage
hypothalamus
the part of the brain that regulates body maintenance, activities such as eating, drinking, body temperature; linked to emotion; feeding, fighting, fleeing, fOrNiCaTiNg
medulla
the part of the brain that controls life-supporting functions like heartbeat and breathing
pituitary gland
the part of the brain that controls the other endocrine glands
pons
the part of the brain that is involved with movement, sleep, and arousal
reticular formation
the part of the brain that that plays an important role in controlling alertness and arousal; nerve network
thalamus
the part of the brain that acts as the sensory switchboard relay system; directs messages to the sensory receiving areas for all senses except smell
left hemisphere
the hemisphere of the brain that controls verbal processing, logical ability, the right side of the body, language functions, computation, speech, reading, and writing
right hemisphere
the hemisphere of the brain that controls the left side of the body, non-verbal communication, visual spatial tasks, making connections between words, musical ability, and emotions
plasticity
the brain’s capacity for modification and reorganization following damage, especially in children
split brain
a condition in which the two hemispheres are separated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them
frontal lobes
lobes of the brain that are involved in speaking, muscle movement, making plans and judgments, language, and higher-level thinking skills; contains Broca’s area
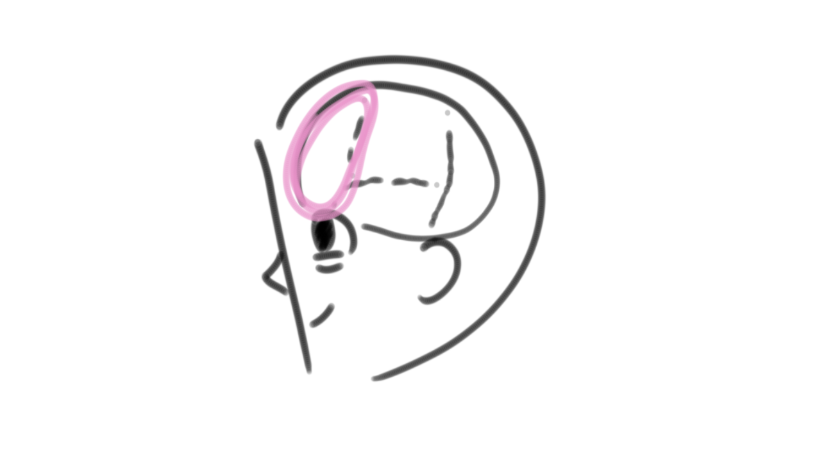
parietal lobes
lobes of the brain that register our sense of touch; include the somatosensory cortex; behind the frontal lobes
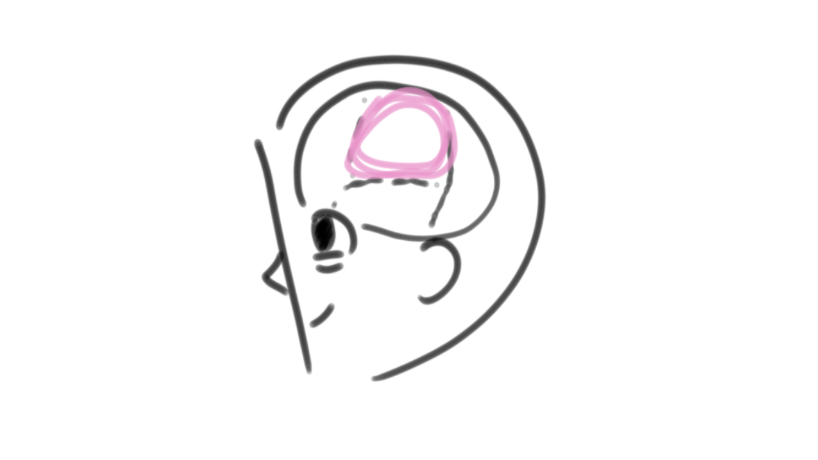
occipital lobes
lobes of the brain that include the visual areas and receive information from the opposite visual field
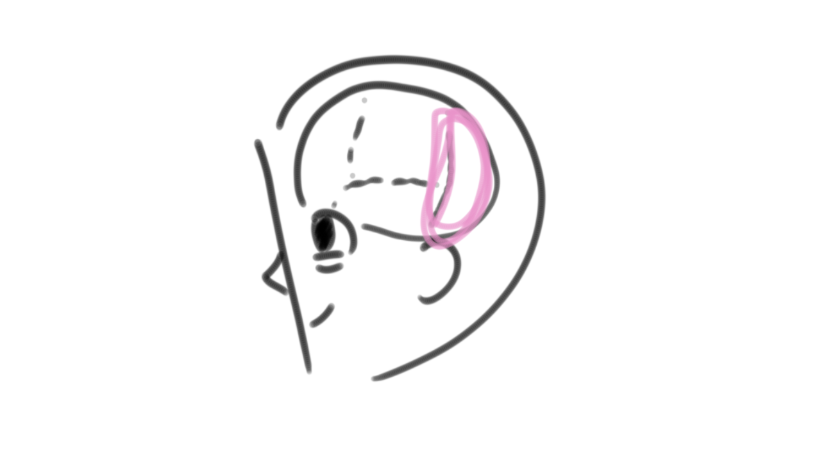
temporal lobes
lobes of the brain that process sound and smell information, and recognition of faces; contains Wernicke’s area
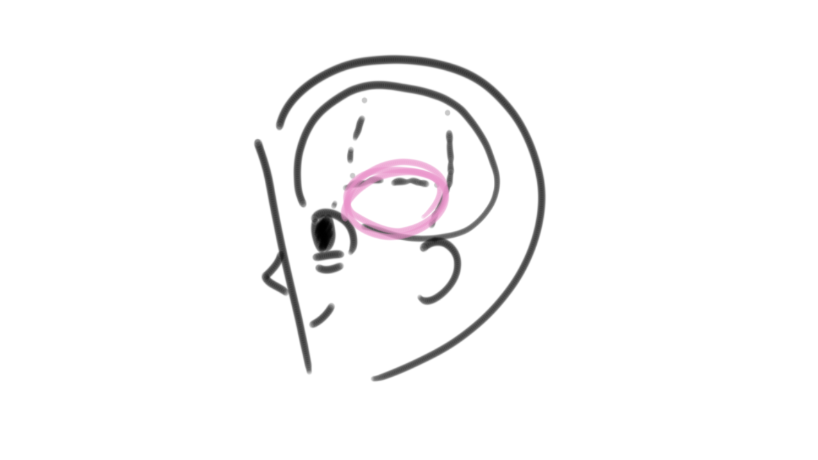
Wernicke’s area
the area in our brain in charge of our ability to understand anything said to us
limbic system
the brain’s emotional center; helps regulate memory, aggression, fear, hunger, and thirst; includes the hypothalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala
lesion
destruction of brain tissue that can be either naturally or experimentally caused
EEG (electroencephalogram)
records electrical activity in brain; electrodes placed on scalp; can show brain wave patterns of electrical activity during sleep stages and seizures; shows function of brain; noninvasive but difficult to determine which specific brain structures are producing electric activity
CT scan (computed tomography)
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles; composite representation of a slice through the brain; looks at brain structure; views large brain abnormalities
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
displays brain activity; detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes; looks at brain function; allows investigation of mental illness, neurological problems, and drugs
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer generated images distinguishing different types of soft tissue; provides an in detail look at brain structure; cannot be used by patients with metal structures
nervous system
the electrochemical communication system of the body
glial cells
provide structural support and insulation for neurons
synaptic vesicles
small sacs within the terminal buttons that contain neurotransmitters
serotonin, norepinephrine/noradrenaline, acetylcholine, glutamate, GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid), endorphins, dopamine
what does SNAGGED stand for? (neurotransmitter acronym)
serotonin
neurotransmitter involved in mood control, appetite, and sleep; linked to depression, increased anxiety, OCD, impulsive behavior, aggression
norepinephrine/noradrenaline
neurotransmitter involved in arousal, reward, fight/flight response; linked to anxiety and mood conditions like depression and bipolar disorder
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter involved in motor movement, short term memory, anger, and agression; lack → Alzheimer’s disease, paralysis; excess → muscle spasms
glutamate
neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning; an excitatory neurotransmitter that encourages neurons to fire
GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid)
neurotransmitter involved in inhibition of the central nervous system; an inhibitory neurotransmitter that reduces neurons’ likelihood of firing an action potential; involved in floods of brain signals epileptic seizures
endorphins
neurotransmitter involved in pain control and positive emotions; natural opiate; released during aerobic exercise
dopamine
neurotransmitter involved in feelings of pleasure, motor movement, reward and motivation, alertness, and mood; lack → Parkinson’s disease; excess → schizophrenia
inhibitory PSP (postsynaptic potential) effect
makes it less likely for the 2nd neuron to fire
excitatory PSP (postsynaptic potential) effect
makes it more likely for the 2nd neuron to fire
agonist
mimics/strengthens the effects of neurotransmitters; ex. heroin, oxycodone, methadone, morphine (mimics endorphins)
interneurons
neurons that act as the middleman between other neurons
somatic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles; contains motor nerves (afferent and efferent) needed for the voluntary muscles
afferent nerves
sensory nerves; connects the sense organs to the brain and spinal cord
efferent nerves
motor nerves; carry messages from the brain and spinal cord to move other parts of your body
autonomic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls glands and muscles that work on their own; controls processes like breathing, blood pressure, digestive processes; contains sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats; freeze/fight/flight response, stimulates the body
parasympathetic nervous system
part of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body and brings it back to its relaxed state; in control most of the time; rest and digest
hormones
slower chemical messenger than neurotransmitters; released from the endocrine glands that travel through the bloodstream to targeted tissues which become influenced; lower communication system with longer lasting effects than neurotransmitters
pineal gland
gland that secretes melatonin and regulates the sleep cycle
adrenal gland
gland that releases norepinephrine; arouses the body in times of stress; located above kidneys
thyroid gland
gland that regulates energy level and metabolism; located in neck
gonads
the organs that secrete either testosterone or estrogen; also glands that influence emotion and physical development
behavior genetics
studies effects of genes vs environmental influence on behavior
depolarization
the process in neural communication in which positively charged ions flood through the axon’s membrane; toilet flushing
direction of impulse
the neural impulse travels in a direction toward the axon terminals
threshold
the level of stimulation required inside the axon to trigger a neural impulse
heritability
a statistical estimate of the extent to which variation in a trait within a population is due to genetics
endocrine system
a communication system that uses hormones to influence thoughts, behaviors, and actions
Broca’s area
part of the brain involved in the physical production of speach
ion channels
these gates are closed when the neuron is at rest and allows ions to flow in and out when the neuron receives a signal
postsynaptic neurons
the type of neuron that receives neurotransmitters and their message
presynaptic neurons
the type of neuron that sends its neurotransmitters across the synapse
fMRI
uses magnetic fields to produce images of the brain and tracks real-time brain activity by measuring blood flow carrying oxygen to active brain tissue; provides a look at both brain function and structure