OU anatomy 2255 exam 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
axial
trunk and head
appendicular
appendages
brachium
arm
antebrachium
forearm
axilla
armpit
manus
hand
pes
foot
crural
leg
frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
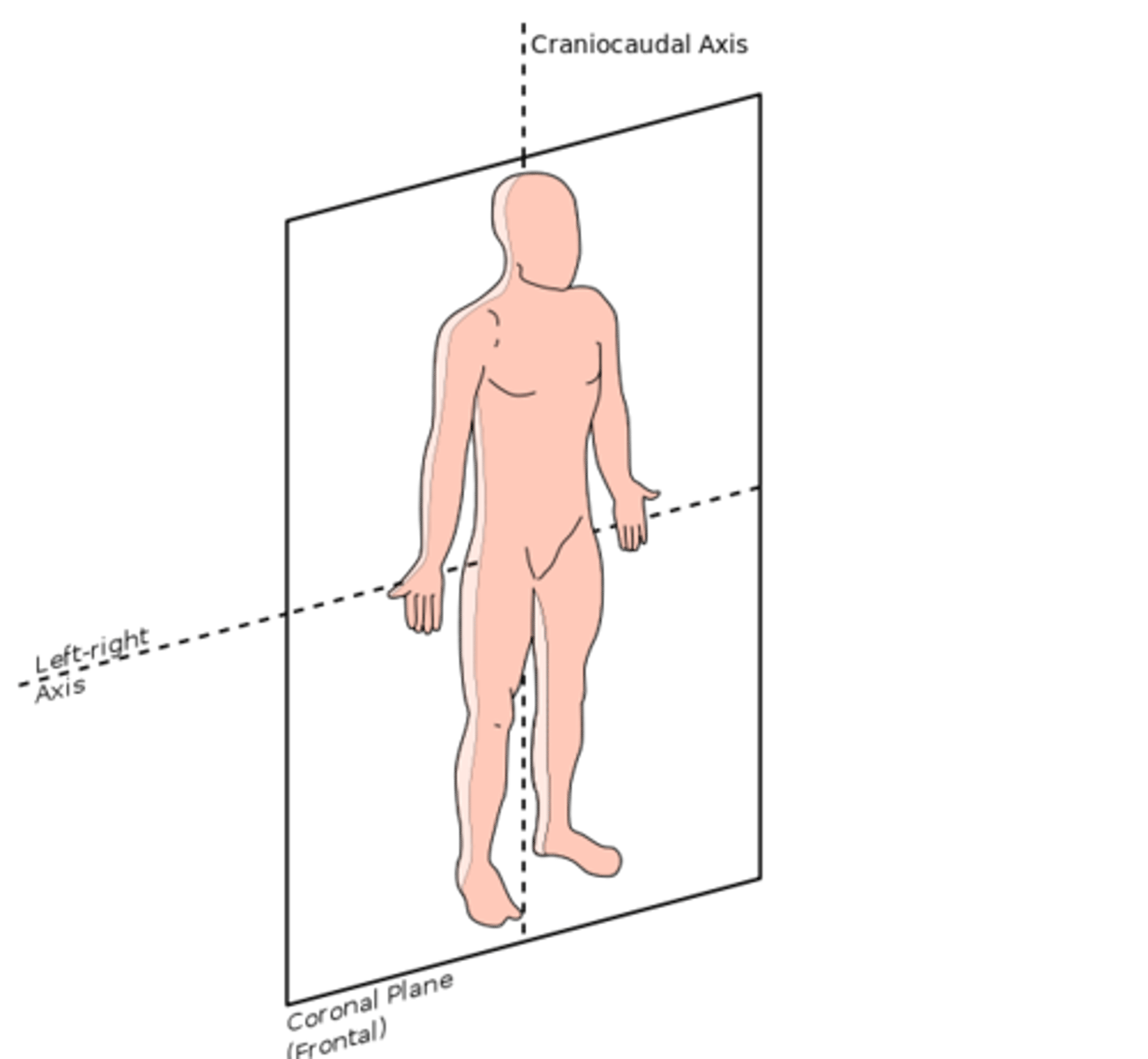
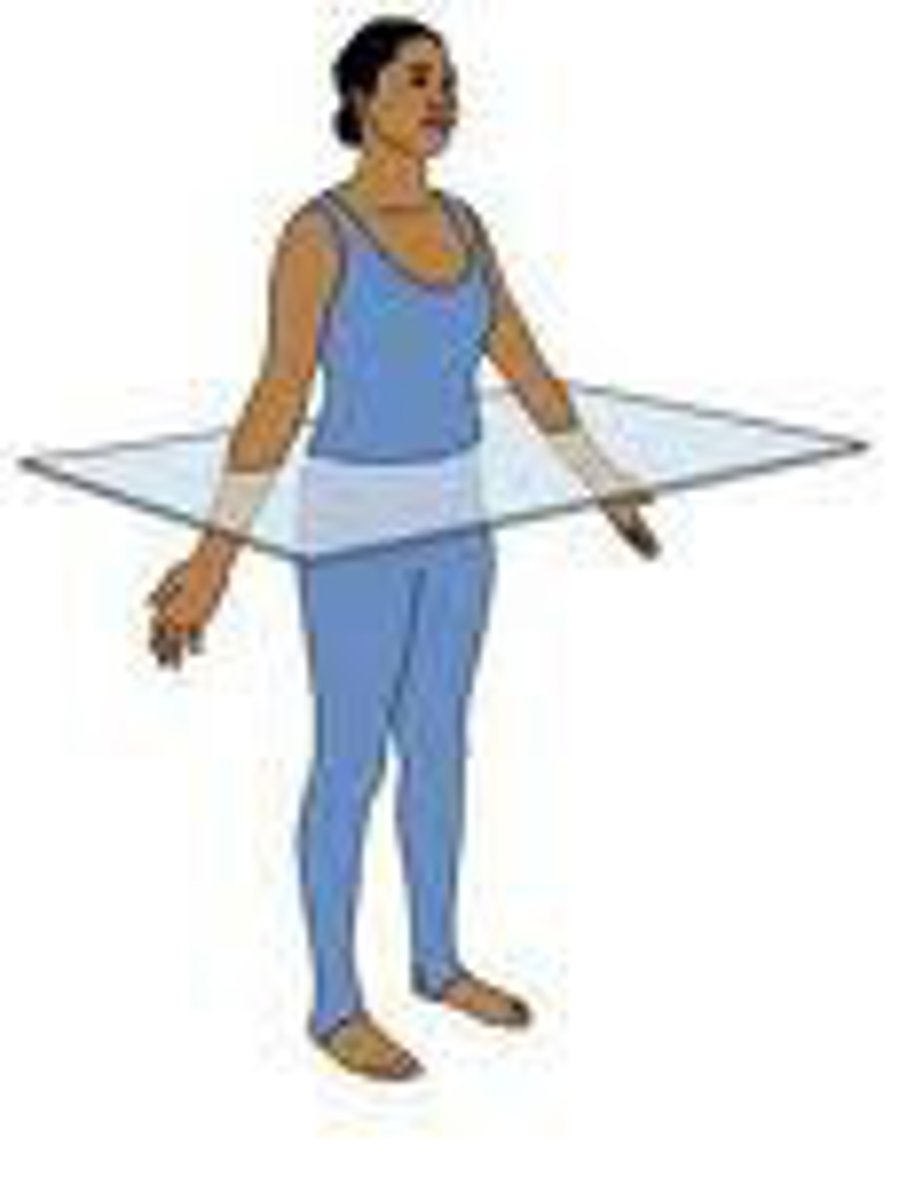
transverse (horizontal) plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
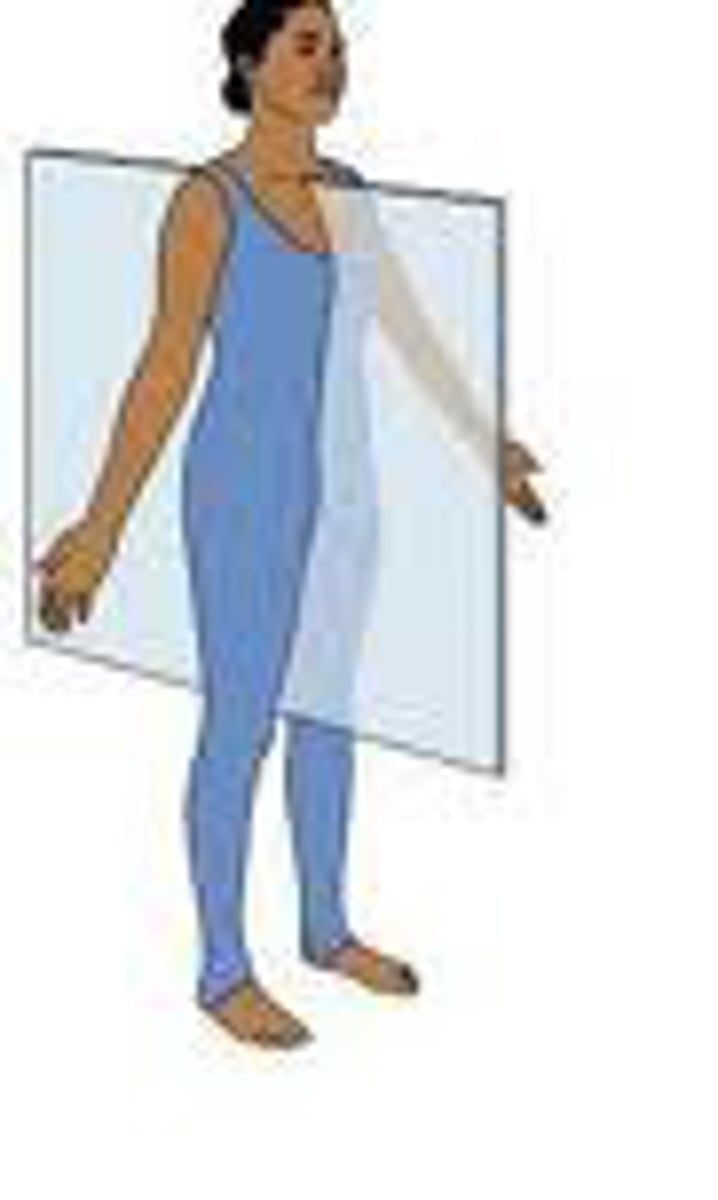
saggital plane
divides the body into medial and lateral parts
cranial
towards the head
caudal
towards the tail
lateral
away from the midline
medial
toward the midline
proximal
toward the point of attachment
distal
further from the point of attachment
superior
above
inferior
below
posterior (dorsal)
back
anterior (ventral)
front
extension
straightening of a body part
flexion
bending at a joint (decreasing the angle between two body parts)
extension and flexion are referred to in what plane?
saggital plane
hyperextension
going past anatomical position
lateral flexion
bending at the waist (left or right)
abduction
moving away from the midline
adduction
moving towards the midline
abduction and adduction are referred to in what plane?
coronal plane
medial rotation
toward the midline
lateral rotation
away from the midline
circumduction
a large circular motion
what type of rotation occurs at the waist?
just rotation because lateral and medial rotation can not occur
elevation
ex. raising of shoulders
depression
ex. pushing down of shoulders
inversion
turning the sole of the foot inward
eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
dorsiflexion
raising the toes toward the shin
plantar flexion
pointing toes toward the floor
protraction
pushing something forward
retraction
pulling something backward
pronation
medially rotating forearms so palms face backwards
supination
laterally rotating forearms so palms face forward (anatomical position)
opposition
involves flexion, abduction, and medial rotation of thumb (putting thumb against any finger)
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
unilateral
only on one side
bilateral
on both sides
extrinsic
a muscle that originates and inserts on different parts of the body (crosses a joint)
intrinsic
a muscle that has both its origin and insertion on the same part of the body (intrinsic back muscles)
pectoral girdle
clavicle and scapula
scoliosis
lateral deviation
kyphosis
posterior curvature (hunch back)
lordosis
increased lumbar curvature (sway back)
how many vertebrae are there in each section
7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar
pelvic girdle
os coax, sacrum, and coccyx
deltoid (action)
anterior fibers- flex, medially rotate arm
middle fibers- abduct arm
posterior fibers- extend and laterally rotate arm
deltoid (innervation)
axillary nerve
infraspinatus (action)
adducts, laterally rotates arm
infraspinatus (innervation)
suprascapular nerve
teres major (action)
extends, adducts, medially rotates scapula
rhomboid minor (action)
elevates, retracts (adducts), inferiorly rotates scapula
Serratus Posterior Superior (action)
elevates ribs during forced inhalation
Serratus Posterior Inferior (action)
depress ribs during forced exhalation
levator scapulae (action)
elevate, inferiorly rotate scapula
levator costarum (action)
elevate ribs
splenius crevices (action)
uni- rotates head toward same side bi- extends vertebral column and neck
iliocostalis group (action)
uni- laterally flexes vertebral column bi- extends vertebral column and maintains posture
longissimus group (action)
uni- laterally flexes vertebral column bi- extends vertebral column and maintains posture
spinals group (action)
uni- laterally flexes vertebral column bi- extends vertebral column and maintains posture
multifidus (action)
uni- rotates vertebral column toward opposite side bi- extends vertebral column
rotatores (action)
uni- rotates vertebral column toward opposite side bi- extends vertebral column
semispinalis group (action)
uni- laterally flexes vertebral column/head bi- extends vertebral column/head
interspinalis (action)
uni- rotates vertebral column toward opposite side bi- extends vertebral column
Intertransversarii (action)
uni- laterally flexes vertebral column bi- stabilizes vertebral column
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major (action)
extends head/neck
Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor (action)
extends head/neck
Oblique Capitis Superior (action)
turns head to same side
Oblique Capitis Inferior (action)
turns head to same side
gluteus minimus (action)
abducts and medially rotates thigh
piriformis (action)
laterally rotates thigh
superior gemellus (action)
laterally rotates thigh
inferior gemellus (action)
laterally rotates thigh
obturator internus (action)
laterally rotates thigh
quadrates femurs (action)
laterally rotates thigh
anterior longitudinal ligament
on the anterior side of the vertebral body; helps stabilize and prevent hyperextension of back
posterior longitudinal ligament
on the posterior side of the vertebral body; helps limit hyper flexion and reinforce disks (weaker and narrower than anterior)
ligamentum flavum
lines underneath of vertebral arch
rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
spinal cord regions
Cervical (8) (C1-C7)
Thoracic (12) (T1-T12)
Lumbar (5) (L1-L5)
Sacral (5) (S1-S4)
Coccygeal (1) (S5)
conus medullaris
tapering of spinal cord around L1 or L2
cauda equina
long spinal nerve roots that go from conus medullaris down to the sacral region
film terminale
an extension of the pia mater that anchors the spinal cord the the coccyx
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs
dura mater
("tough mother") first of the meningeal layer that covers the spinal cord
arachnoid membrane
space if filled with csf (shock absorber and diffusion medium for dissolved gasses, nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste)
pia mater
("gentle mother") where the vasculature of the spinal cord is
denticulate ligaments
provides lateral stability of the spinal cord (extensions of the pia mater)
spinal reflex arc
pathway of sensory impulses from receptors to effectors without first going to brain
axon of sensory neurons
go from the body to the spinal cord