Luke Anatomy 1 - Exam 1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Hierarchy of Complexity
Organism, Organ System, Organ, Tissue, Cell, Organelle, Molecules, Atoms
3 Components of Feedback Loops
Receptors, Integrating (Control) Center, Effector
Receptors
Something that senses a change in the body
Integrating (Control) Center
Processes info and makes a decision
Effectors
Carries out the final corrective action
Negative Feedback Loop
Body responds with an action in the opposite direction to try to reverse what is happening (ex. sweating when body temp rises)
Positive Feedback Loop
Body responds with an action to continue what is happening (ex. fever above 104, body increases metabolic rate and produces more heat)
Peri-
Around
Ecto-
Outside
Endo-
Inside
Inter-
Between
Sub-
Below
Infra-
Below
Supra-
Above
My-
refers to muscles
Ante-
In front/before
Ceph-
Head
Brach-
Arm
Post-
After/Behind
Supine
Laying on back
Prone
Laying on stomach
Iso-
Equal
Hyper-
Higher than/greater
Hypo-
Lower than/lesser
Epi-
on outside of
Sagittal Plane
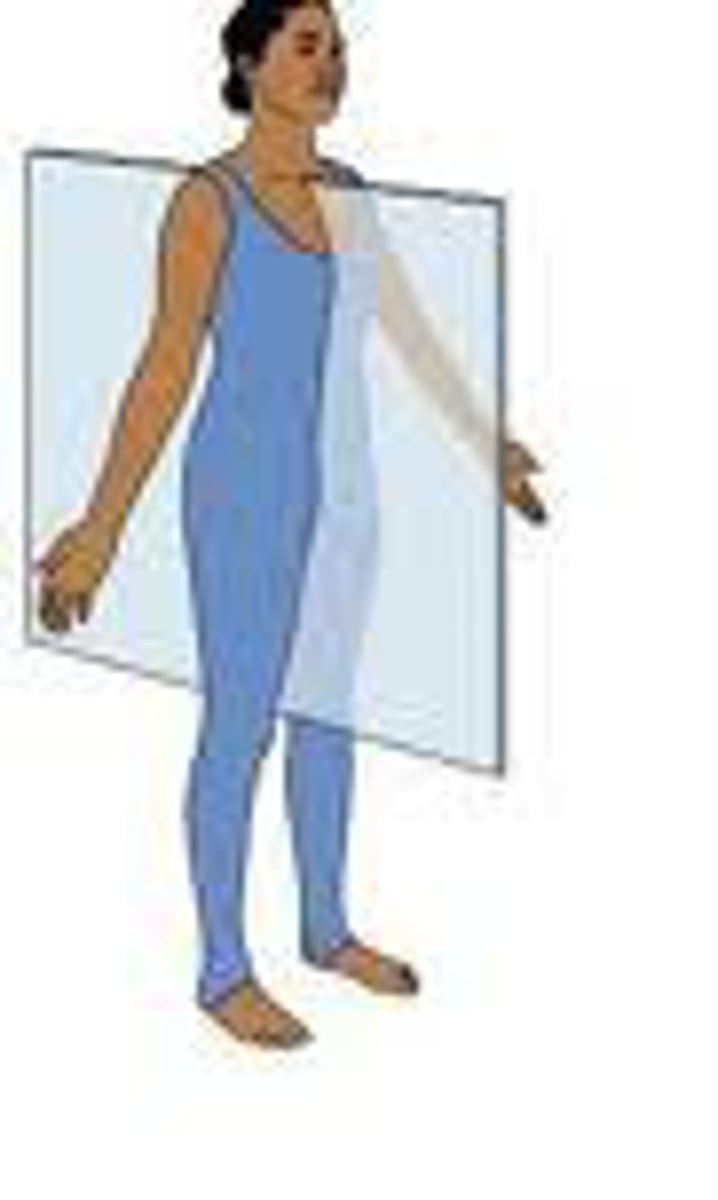
Transverse Plane
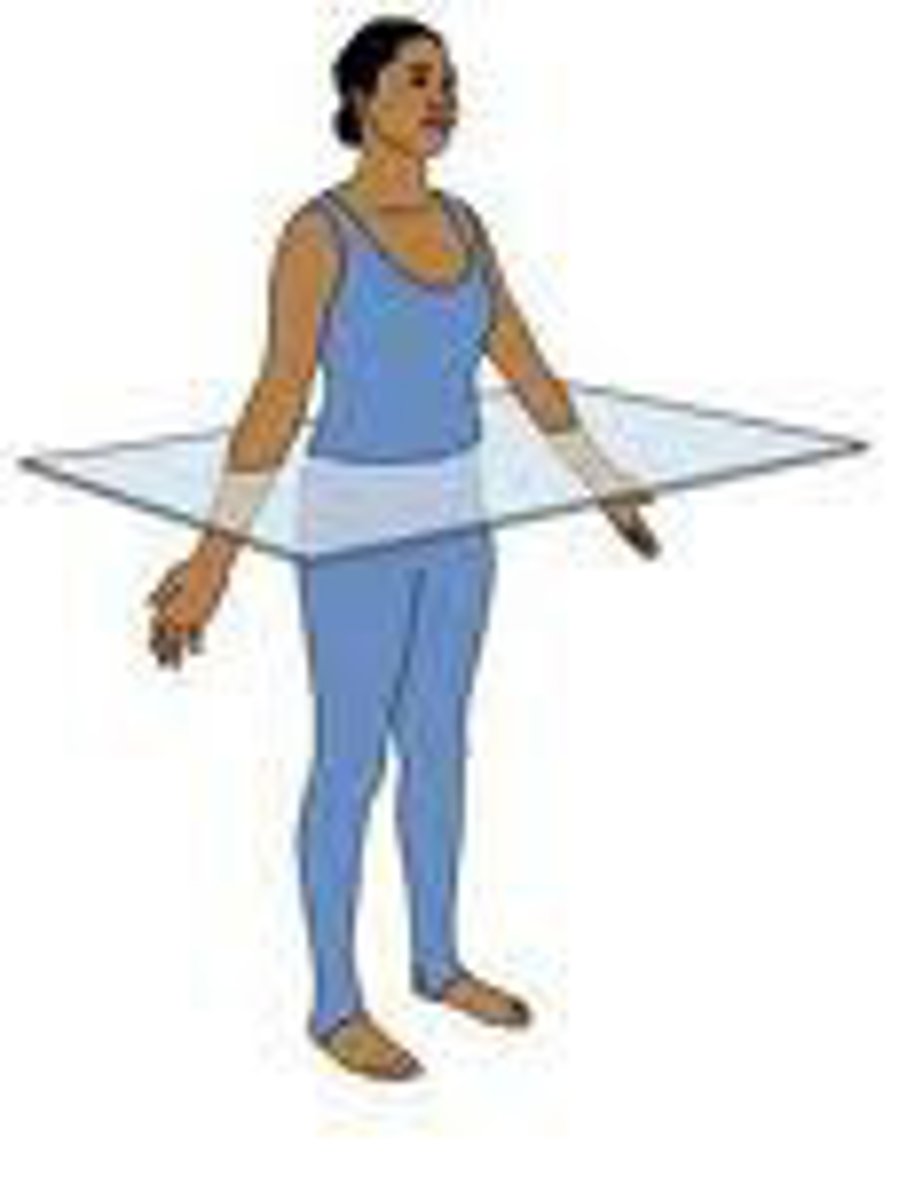
Frontal Plane
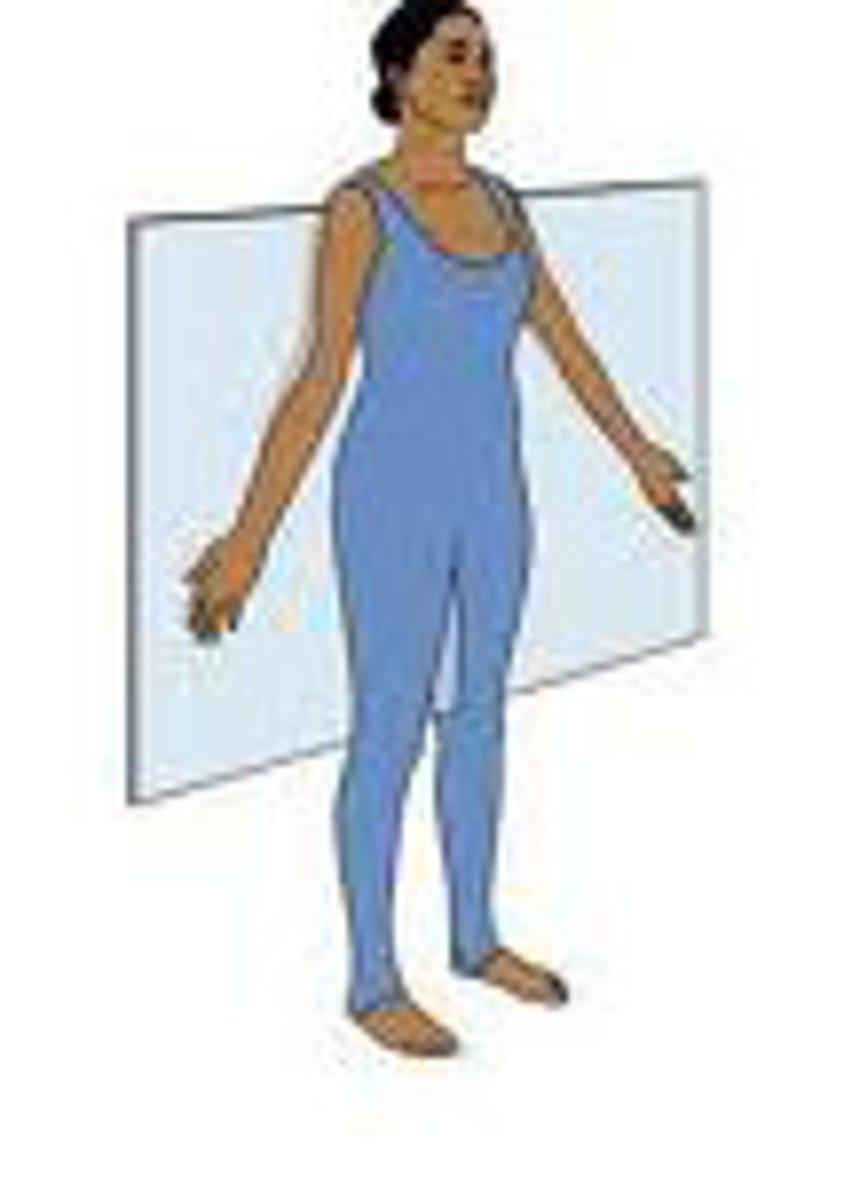

Ventral/Anterior
Front of body
Superior/Inferior
Above/Below
Medial/Lateral
Closer to midline/Away from midline
Cephallic
Head
Dorsal/Posterier
Back of body
Proximal/Distal
Close to/Away from
Superficial/Deep
On top/Underneath
Caudal
Tailbone
Cranial Cavity
Contains Brain
Thoracic Cavity
Contains heart and lungs
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Contains abdomen and pelvis
Mediastinum
Region between lungs, contains heart, esophagus, trachea
Pericardium
Membrane around the heart
Visceral Pericardium
Membrane that touches and surrounds the organ, the heart
Parietal Pericardium
Membrane that lines the Pericardial Cavity
Pericardial Cavity
Cavity surrounding the heart
Right and Left Pleural Cavity
Cavity around the lungs
Visceral Pleura
Membrane that covers the organ, the lungs
Parietal Pleura
Membrane the lines the Pleural Cavity
Peritoneum
Serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity
Visceral Peritoneum
Membrane that covers the organs in abdominopelvic cavity
Parietal Peritoneum
Membrane the lines the abdominopelvic cavity
Decomposition Reactions
Large molecule breaks into 2 or more smaller ones: AB -> A+B (ex. digestion)
Synthesis Reactions
Small molecules combine to form a larger one: A+B -> AB (ex. muscle building)
Reversible Reactions
Reaction can go in either direction under different circumstances: AB <-> A+B (ex. binding and release of oxygen to and from hemoglobin in red blood cells)
Basis for Reaction
Molecular motion and collisions
Reactions are Affected by
Concentration, Temperature, Catalysts (enzymes)
2 Types of Metabolic Reactions
Anabolism and Catabolism
Anabolism
Energy storing synthesis reactions
Catabolism
Energy releasing decomposition reactions