ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Conformations and Cis-Trans Stereoisomers
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
conformations
different spatial arrangements of a molecule that are generated by rotation about single bonds
conformational analysis
the study of how conformational factors affect the structure of a molecule and it's properties
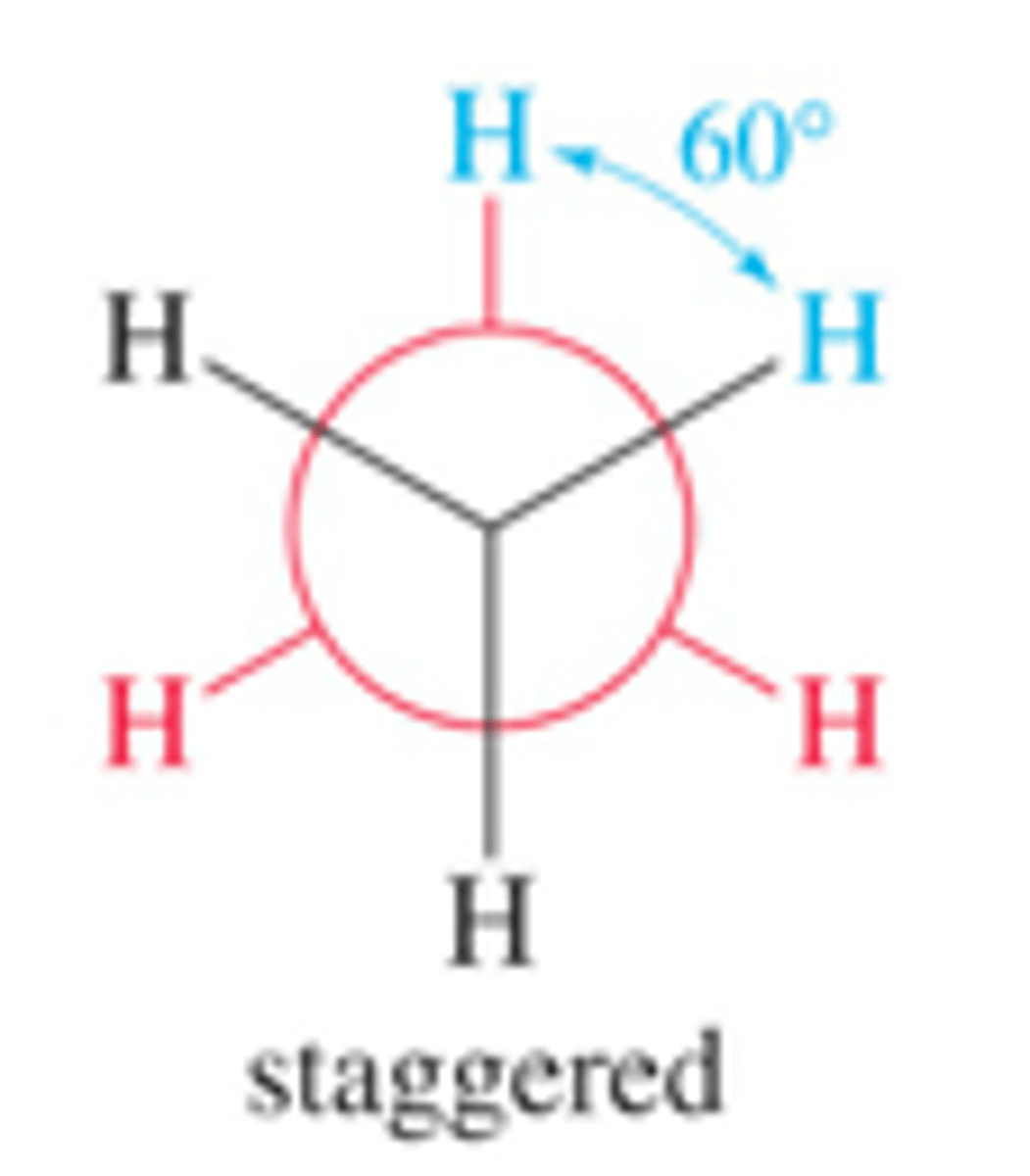
staggered conformation of ethane
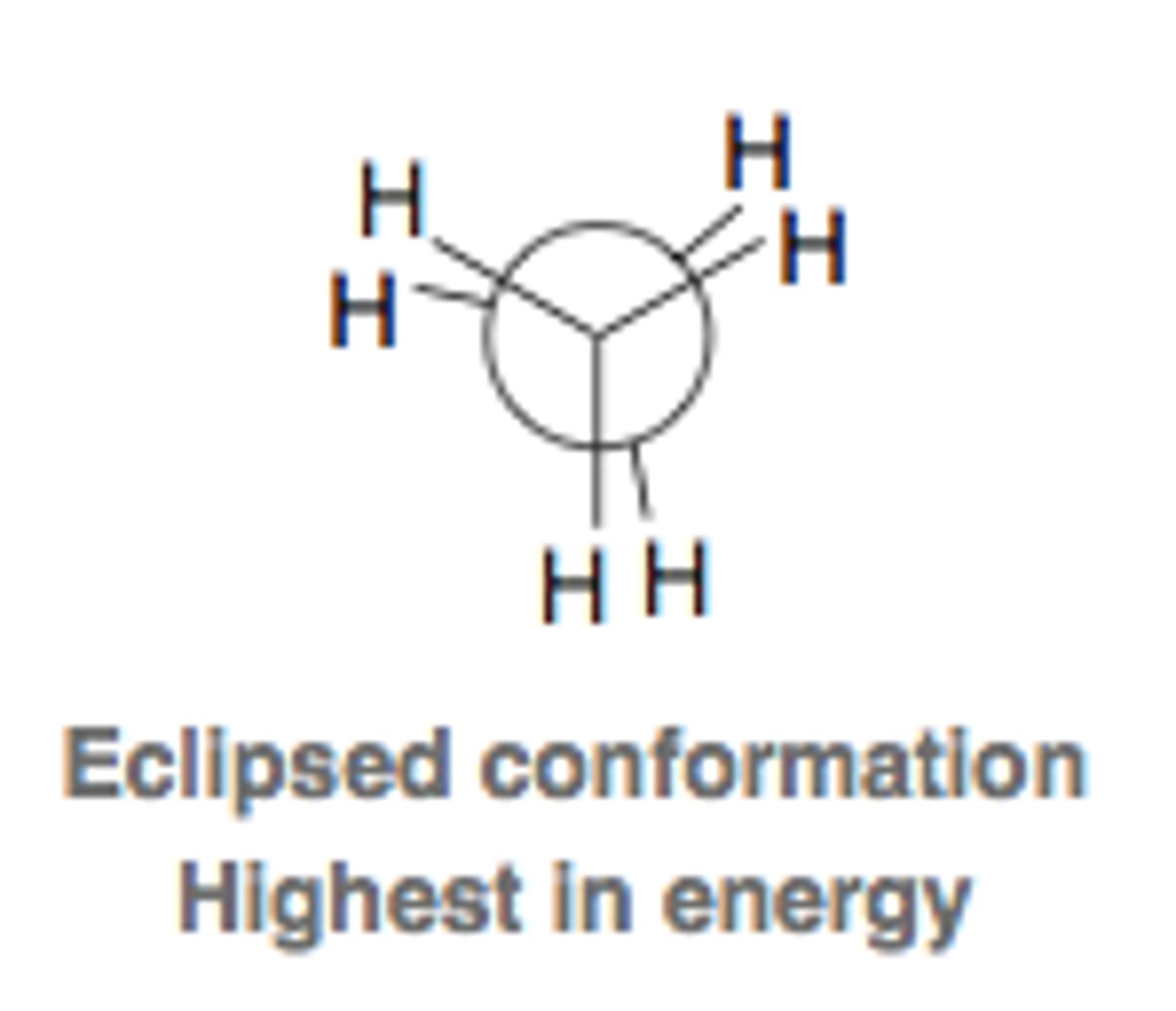
eclipsed conformation of ethane
What is the most stable conformation of ethane?
staggered
What is the least stable conformation of ethane?
eclipsed
types of staggered conformations
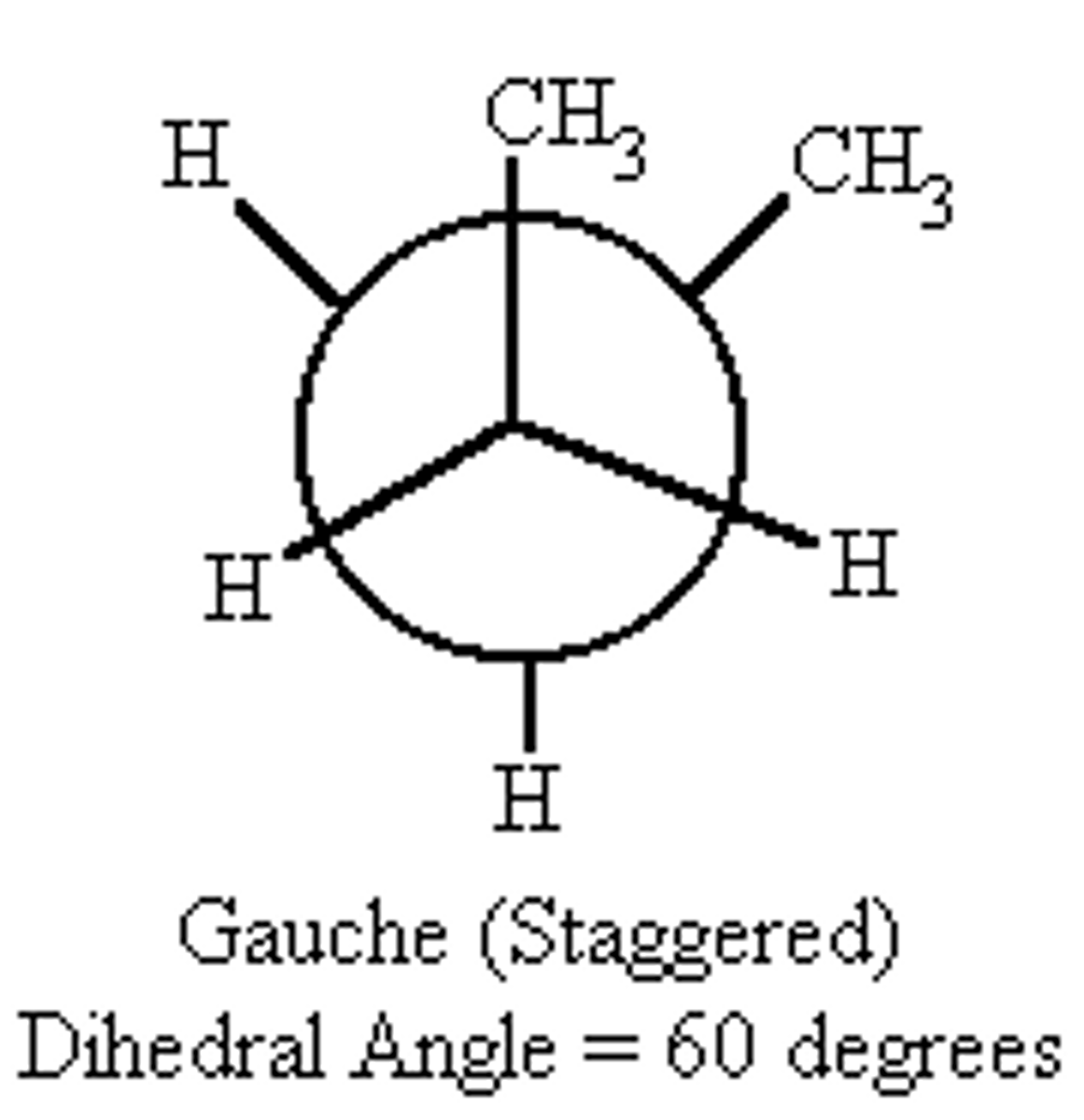
gauche (60 degree torsion angle)
anti (180 degree torsion angle)
torsional strain
ethane conformations in which torsion angles between adjacent bonds are not 60 degrees
Which type of bonds in ethane produce the most torsional strain?
eclipsed bonds
steric strain
comprised of additional sources of strain and torsional strain
potential energy maxima
conformations appearing at the highest points of the curve
eclipsed for ethane
potential energy minima
conformations appearing at the lowest points of the curve
staggered for ethane
conformers
conformations that correspond to potential energy minima
transition state
the point of maximum potential energy encountered by the reactants as they proceed to products
What is the transition state for the conversion of one staggered conformation of ethane to another?
eclipsed conformation
two ways to measure speed of a reaction
half-life
Arrhenius equation
van der waals strain / steric hindrance
the destabilization of a molecule that results when two of its atoms are too close to eachother
Why is the gauche conformation less stable than anti conformation?
van der waals strain / steric hindrance
Higher alkanes with unbranched carbon chains are most stable in WHAT conformation?
all anti-conformations
angle strain
the strain a molecule has because one or more of its bond angles deviate from the ideal value
What is the ideal bond angle for alkanes?
109.5 degrees
Baeyer strain theory
predicts cycloalkanes beyond cyclopentane should become increasingly strained and less stable
Which cycloalkane is planar?
cyclopropane
Which cycloalkane is nonplanar?
ALL except cyclopropane
Does cyclopentane have angle strain?
no
Does cyclopentane have torsional strain?
yes, significant because five bonds eclipsed on both the top and bottom faces of the ring
Where is torsional strain relieved in cyclopentane?
nonplanar conformations
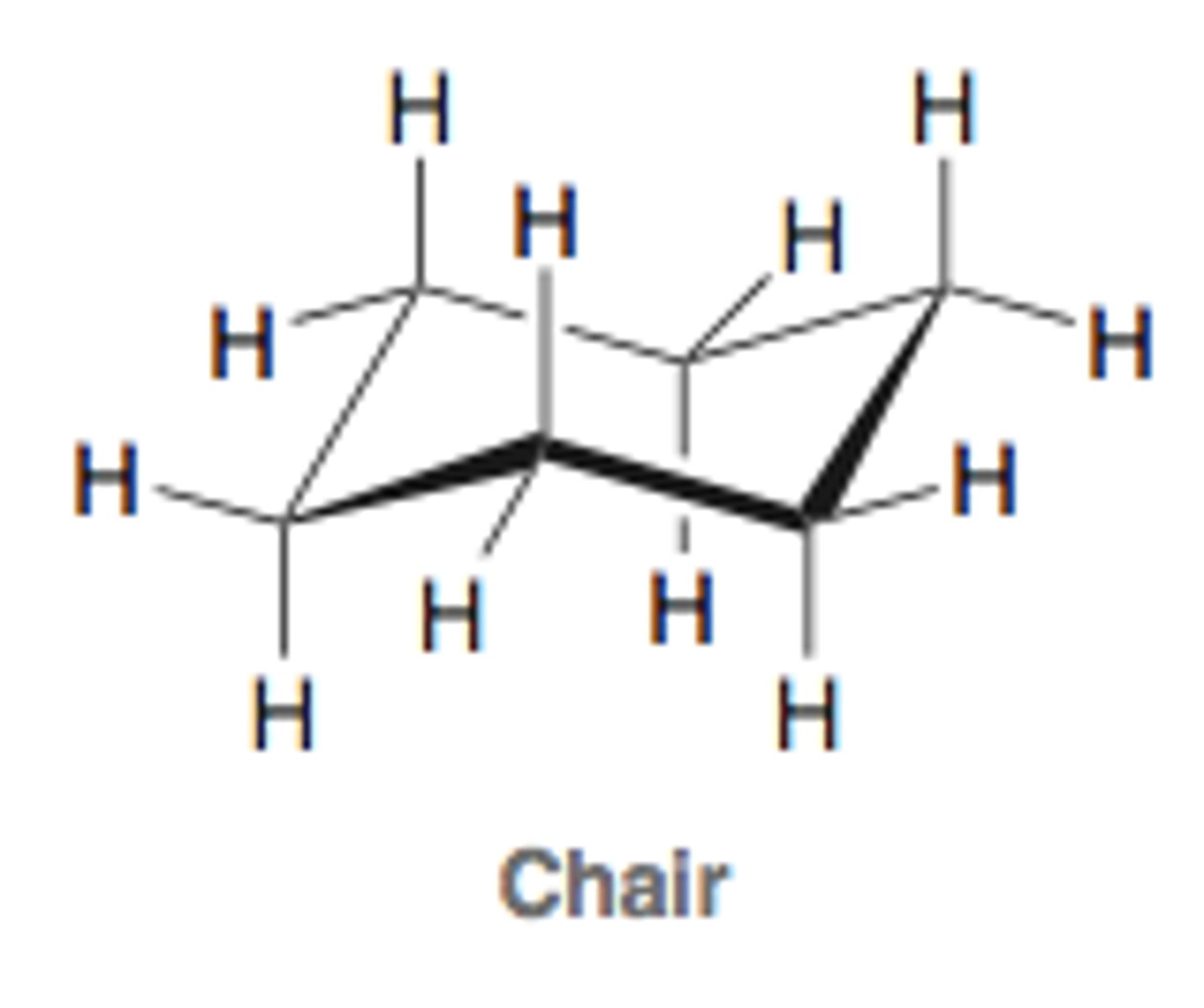
What is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane?
chair conformation
all staggered bonds (no torsional strain)
barely any angle strain (111 degree angles)
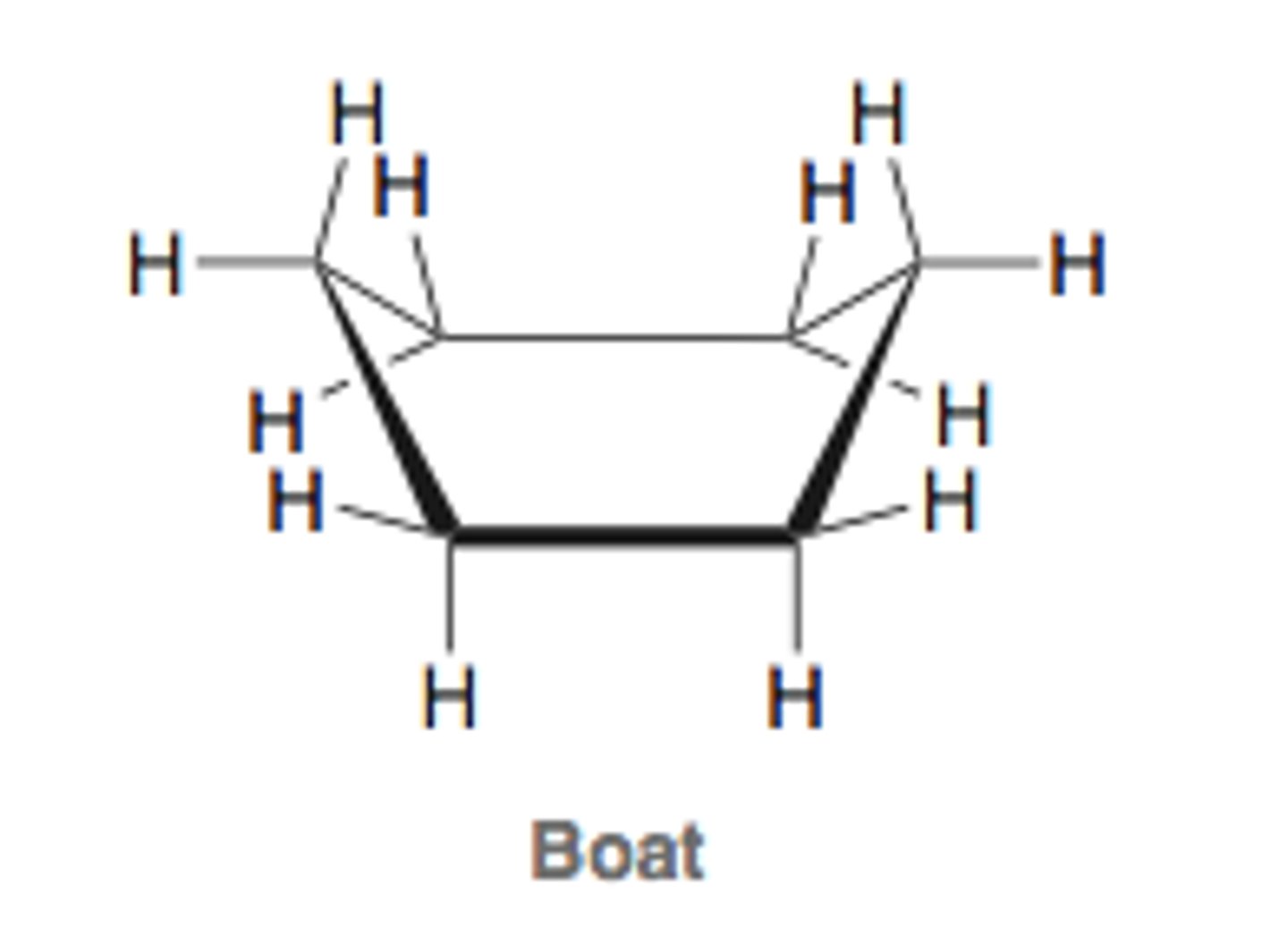
boat conformation
bond angles are approx. tetrahedral (free of angle strain)
destabilized by torsional strain from eclipsed bonds on four carbons
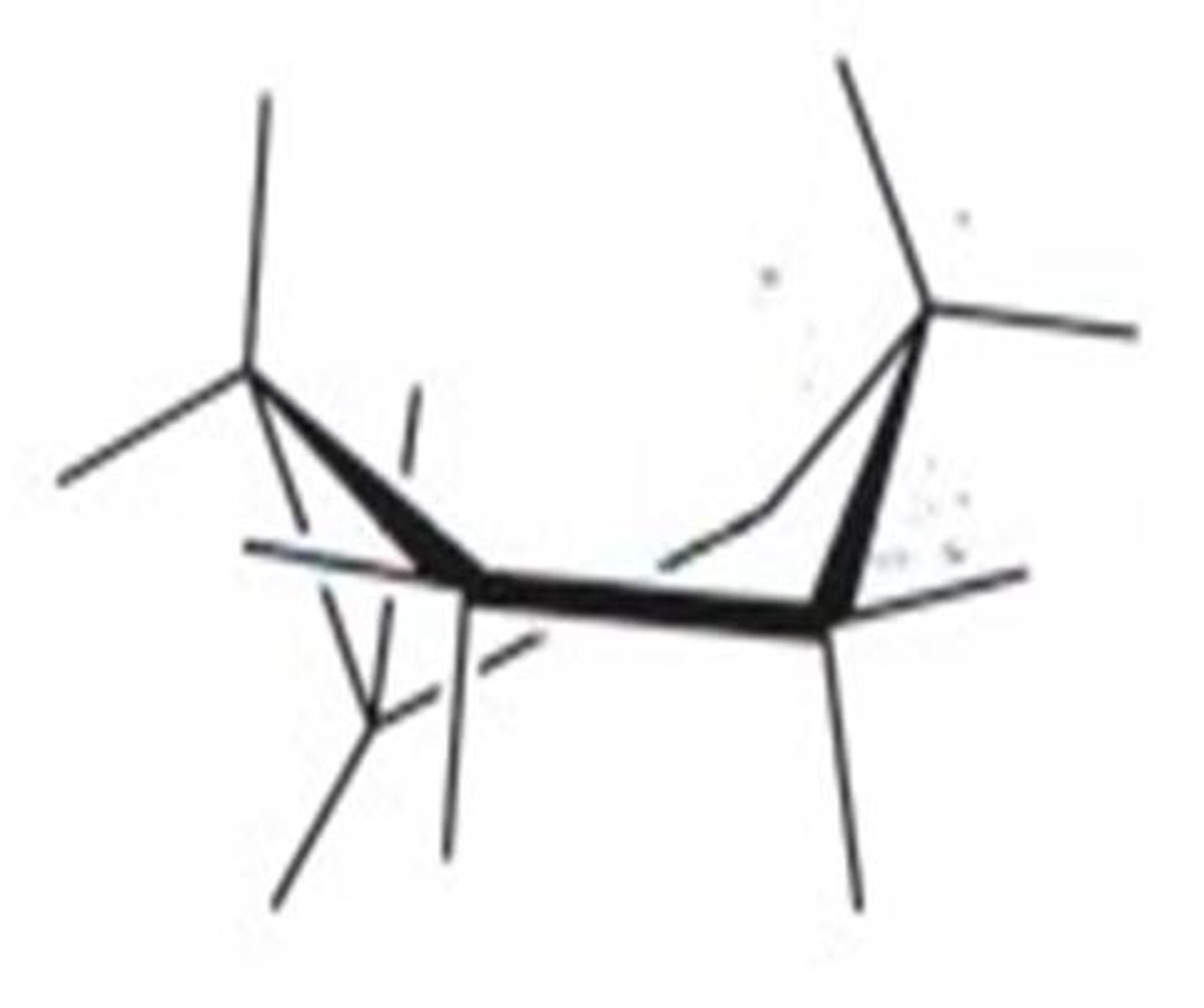
twist/skew boat conformation
more stable than the boat conformation
axial
bonds parallel to a vertical axis that passes through the ring's center
equatorial
located approximately along the equator of the molecule
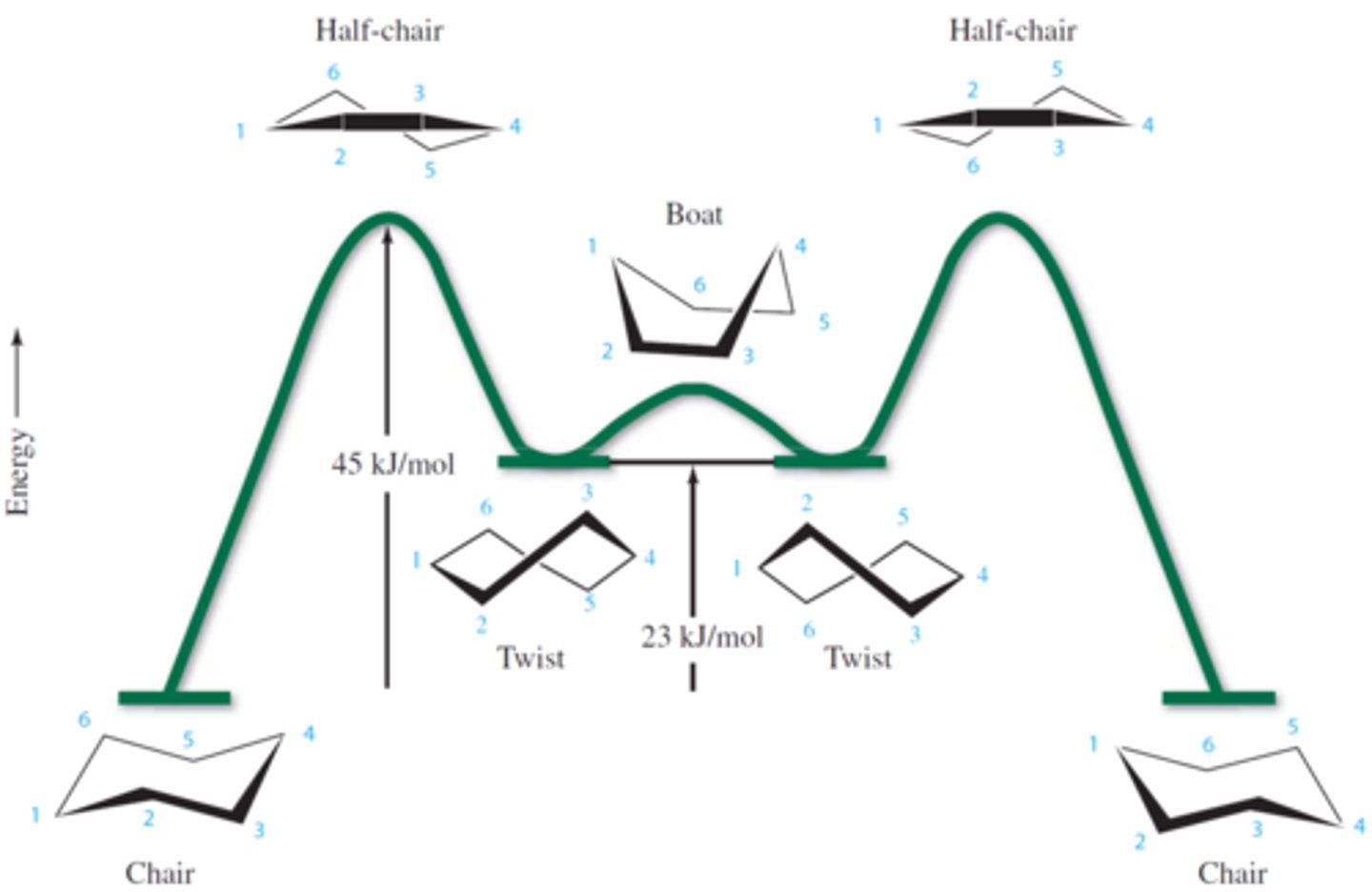
ring inversion / chair-chair interconversion
process in which one chair conformation is converted to another
What are the intermediates of cyclohexane?
twist conformations
intermediate
not a potential energy maximum but a local minimum on the potential energy profile
Which conformation of cyclohexane is highest in energy?
half-chair
because they have the most eclipsing interactions
What is the most important result of ring inversion?
any substituent that is axial in the original chair conformation becomes equatorial in the ring-inverted form and vice versa
energy diagram for ring inversion in cyclohexane
When two conformations of a molecule are in equilibrium with each other, which one dominates?
the one with the lower free energy
What are 1,3 diaxial repulsions in substituted cyclohexane comparable to?
van der waals strain in the gauche conformations of alkanes
The relative amounts of the two conformations depend on ....
effective size of the substituent
What is the size of the substituent, in the context of cyclohexane conformations, related to?
the degree of branching at the atom connected to the ring
cis
substituents on the same side
trans
substituents on the opposite sides
stereoisomers
isomers that have their atoms bonded in the same order but differ in arrangement of atoms in space
T/F: Any substituent is more stable in an axial orientation.
FALSE
Any substituent is more stable in an EQUATORIAL orientation rather than an axial one.
If a disubstituted cyclohexane has two different substituents, which is the most stable conformation?
the chair that has the larger substituent in an equatorial orientation
polycyclic
compounds that contain more than one ring
How are polycyclic compounds classified?
according to minimum number of bond cleavages required to generate a noncyclic structure
spiro compound
one atom is common to two rings
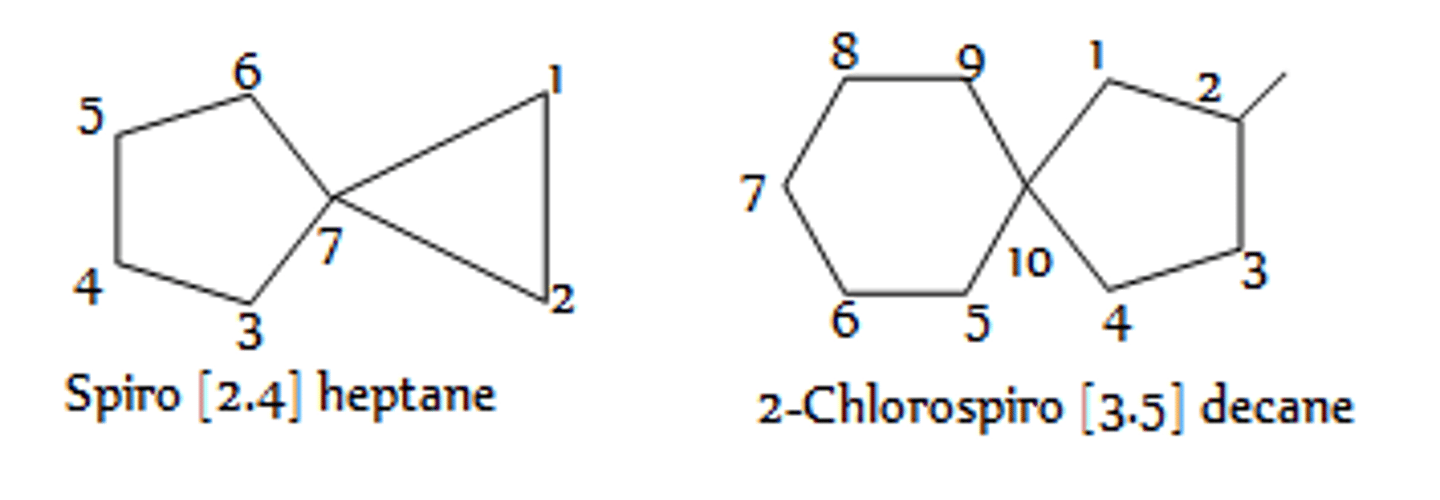
names of spiro alkanes
spiro[number.number]alkane
numbers (in ascending order) are number of carbons unique to each ring
When substituents are present in spiro compounds, where does numbering begin?
in the smaller ring, adjacent to the spiro carbon and proceeds consecutively around the smaller ring away from the spiro carbon, through it, and then around the larger ring
bridged compound
two atoms are common to two or more rings
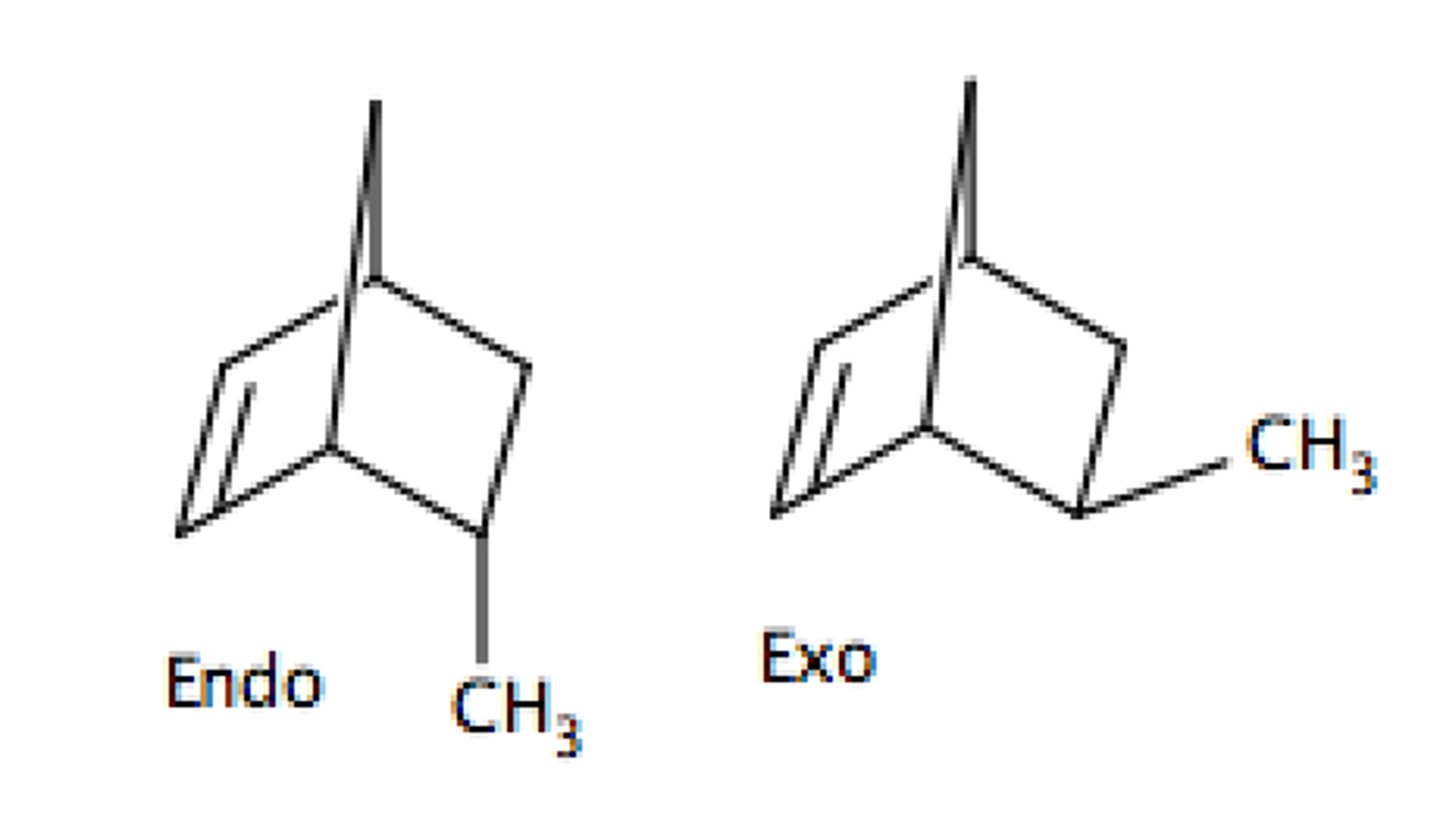
bridged bicyclic alkanes names
bicyclo[number.number.number]alkane
parent alkane = same number of carbons as the total in the bicyclic skeleton
bracketed numbers = number of carbons in the three bridges in descending order
- numbering beings at the bridgehead position and proceeds consecutively in direction of the largest bridge and continues thru next largest, atoms in smallest bridge are numbered last
fused-ring compounds
contain rings that share a common side
(for classification and naming, they are placed in the bridge category)
Are all cyclic compounds hydrocarbons?
NO
heteroatom
substances that include an atom other than carbon
heterocycle
a ring that contains at least one heteroatom
heterocyclic compound
a substance based on a heterocyclic ring
ethylene oxide
tetrahydrofuran
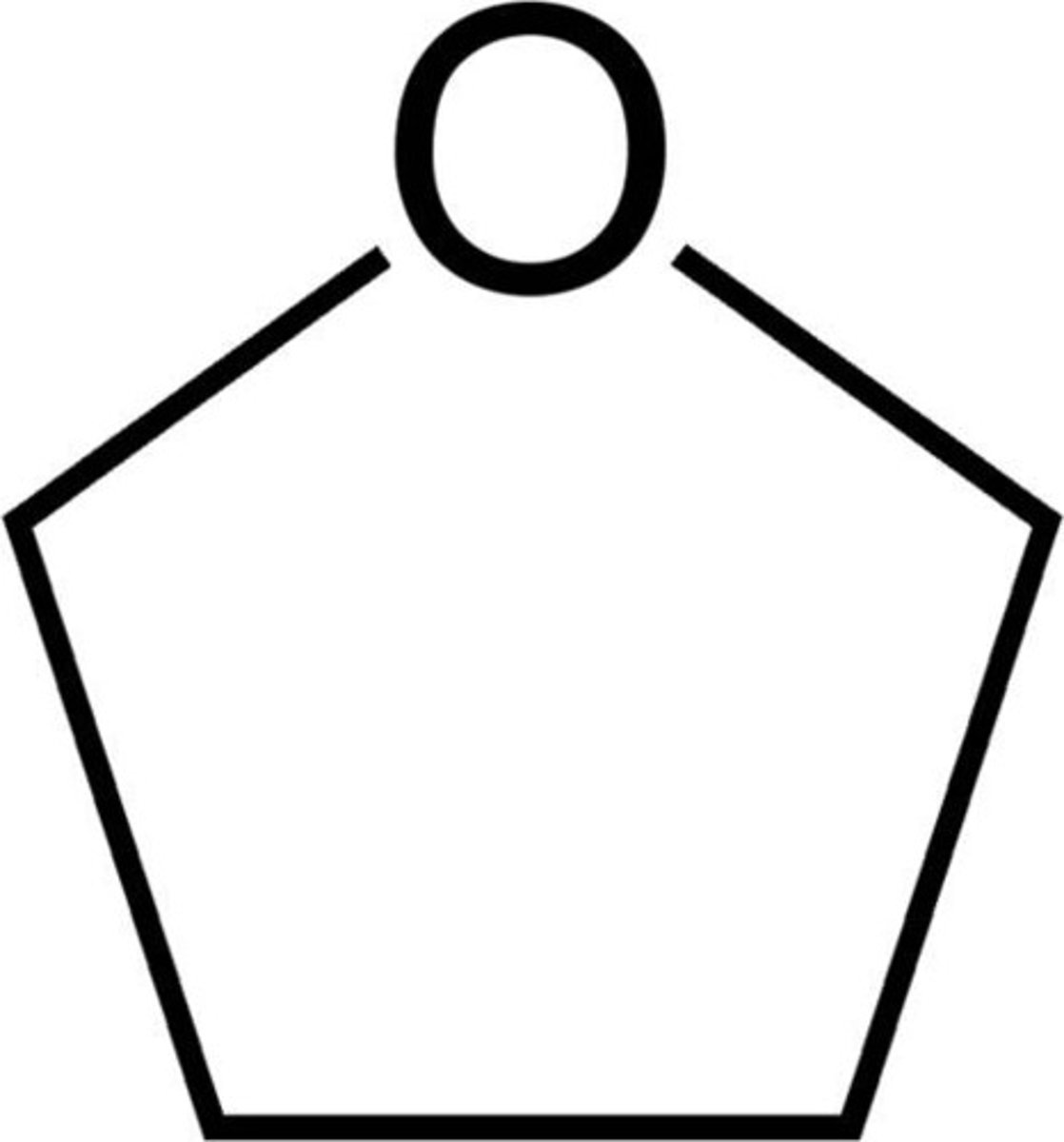
pyrrolidine
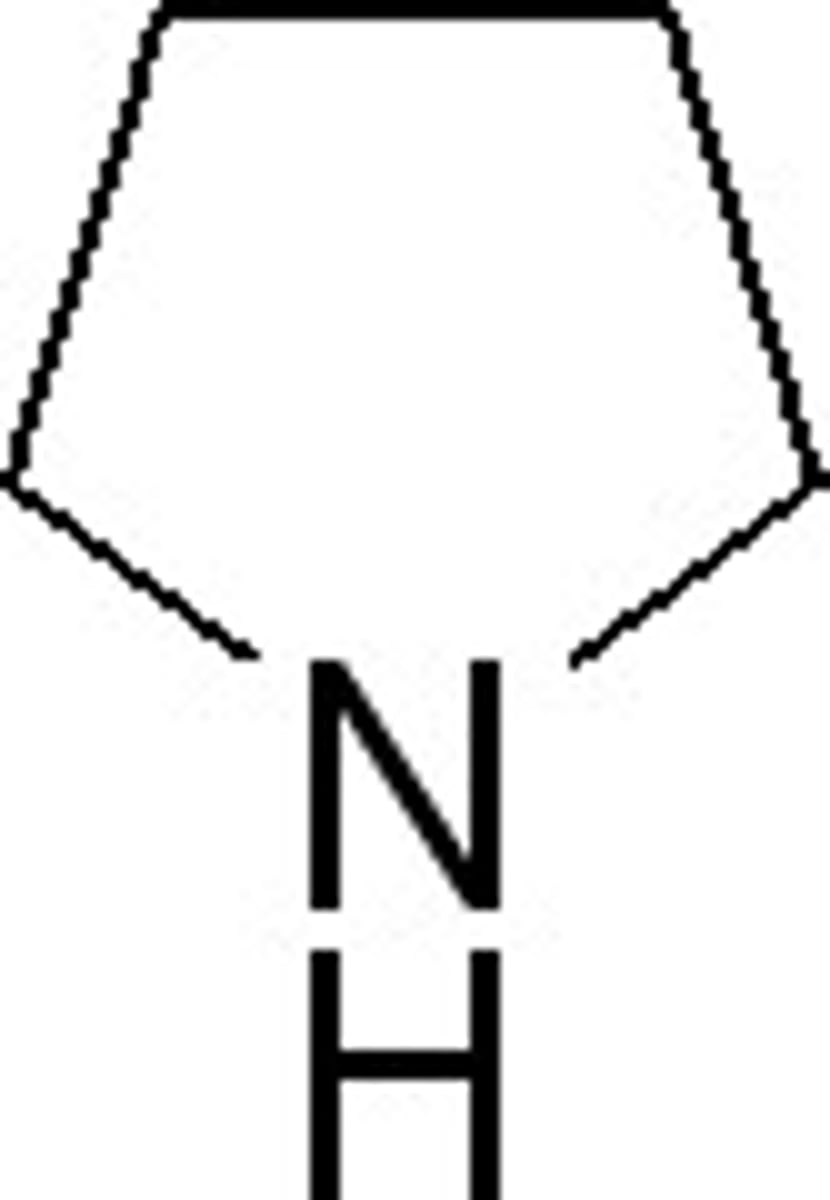
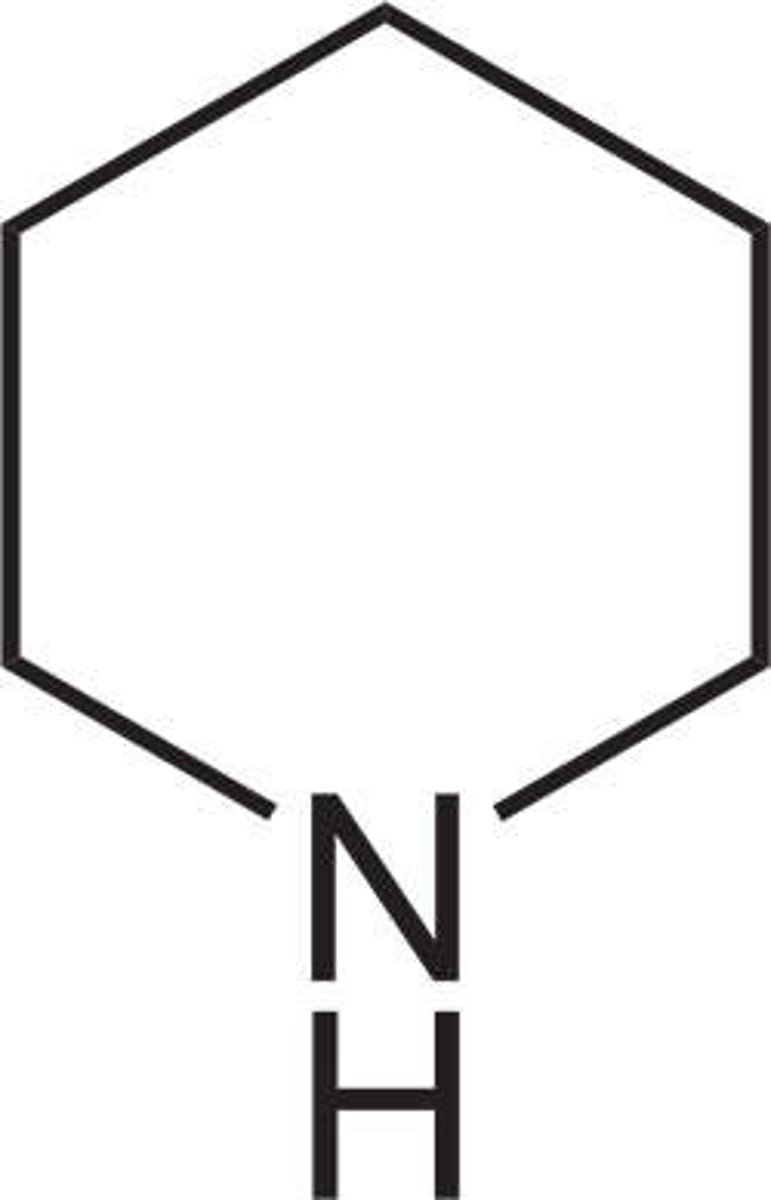
piperidine