(9) Brain Stem & CN Nuclei
1/286
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
287 Terms
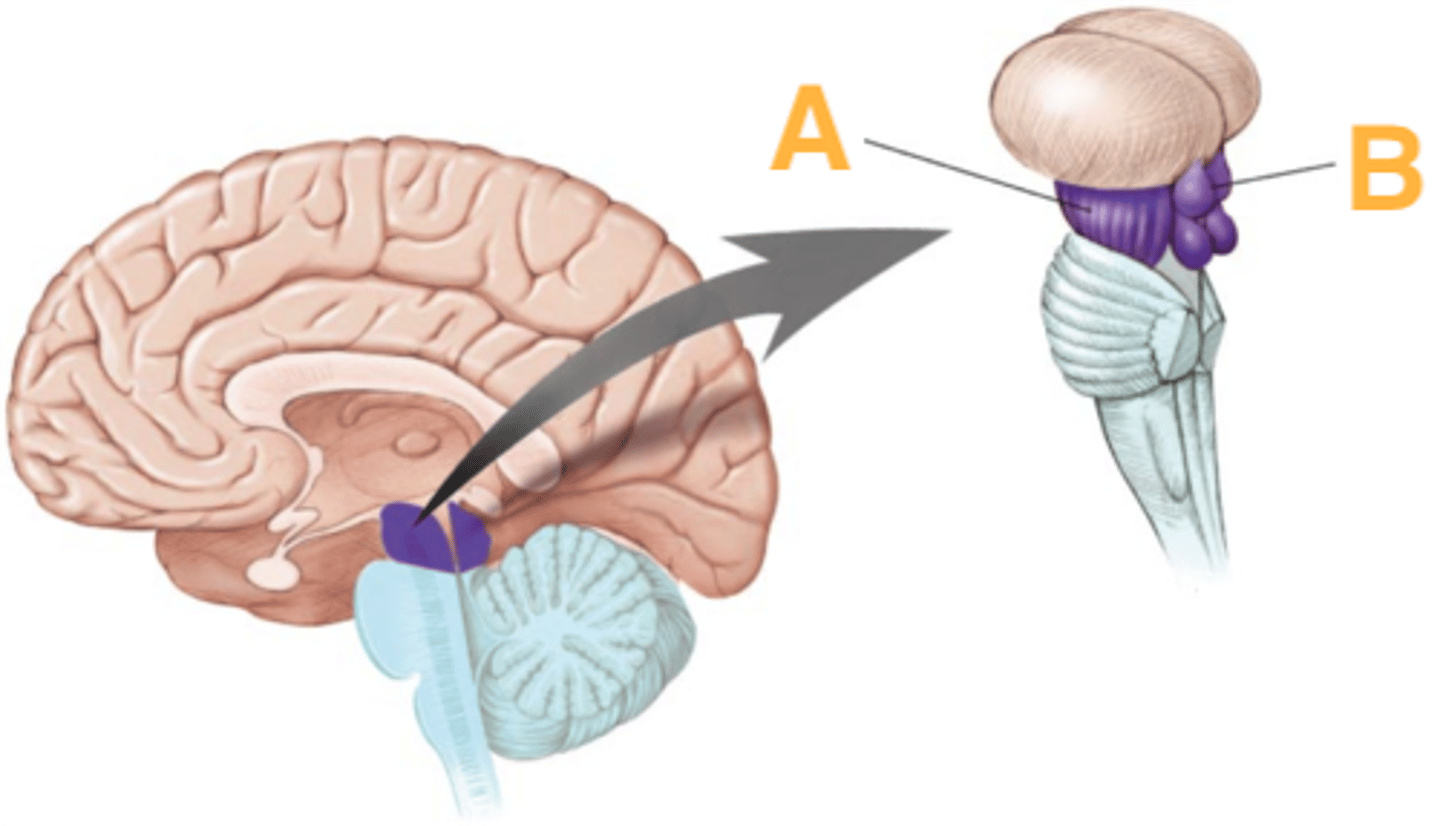
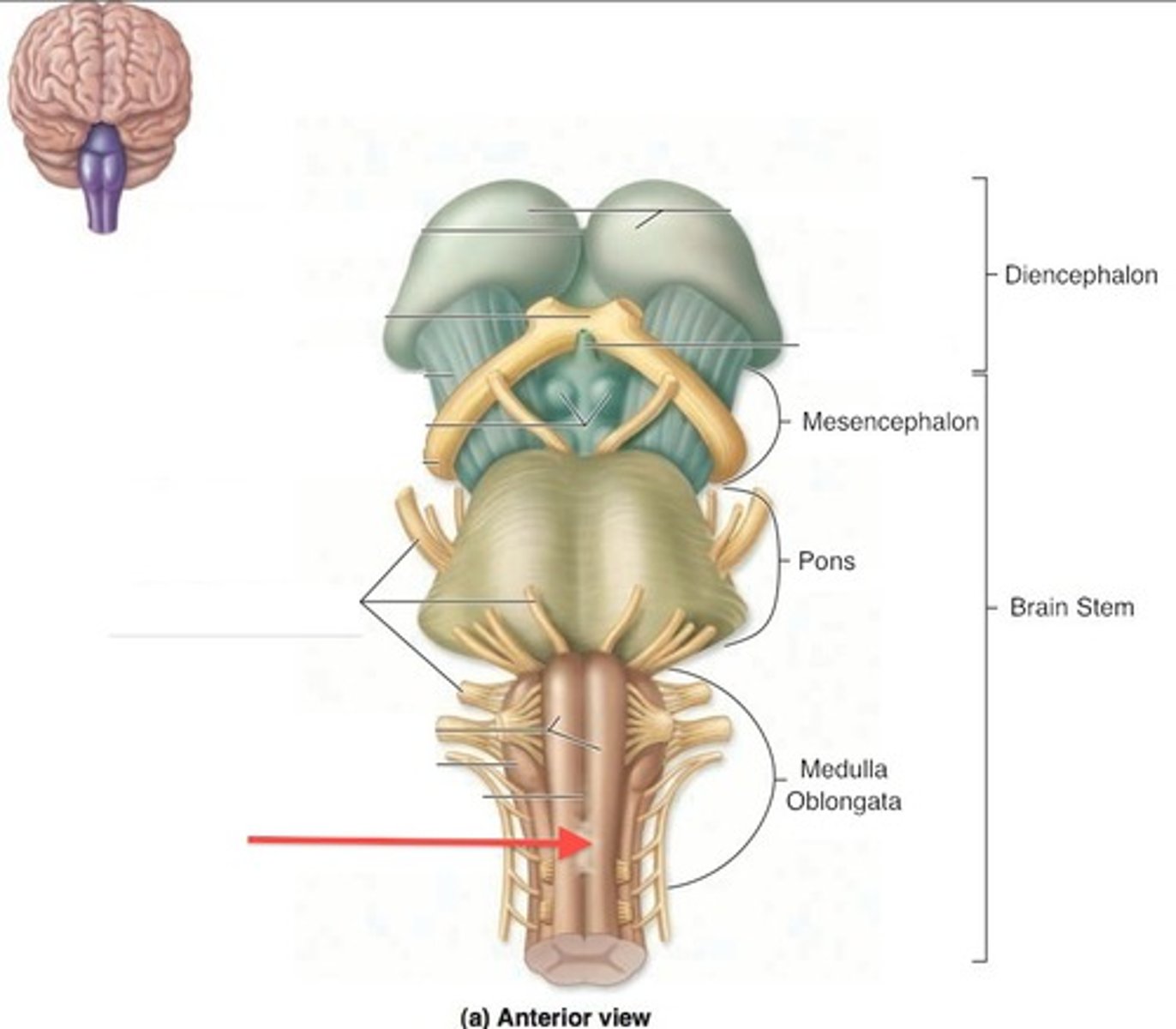
What are the 3 parts of the brain stem?
midbrain, pons, medulla
Which primary brain vesicles is the brain stem derived from?
mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
Which secondary brain vesicles is the brain stem derived from?
mesencephalon, metencephlon, myelencephalon
What is the superior boundary of the medulla?
pontomedullary sulcus
What is the inferior boundary of the medulla?
foramen magnum
What other part of the CNS is the medulla continuous with?
spinal cord
refers to the rostral portion of the medulla since there is no medullary tissue here on the dorsal aspect of the 4th ventricle
open
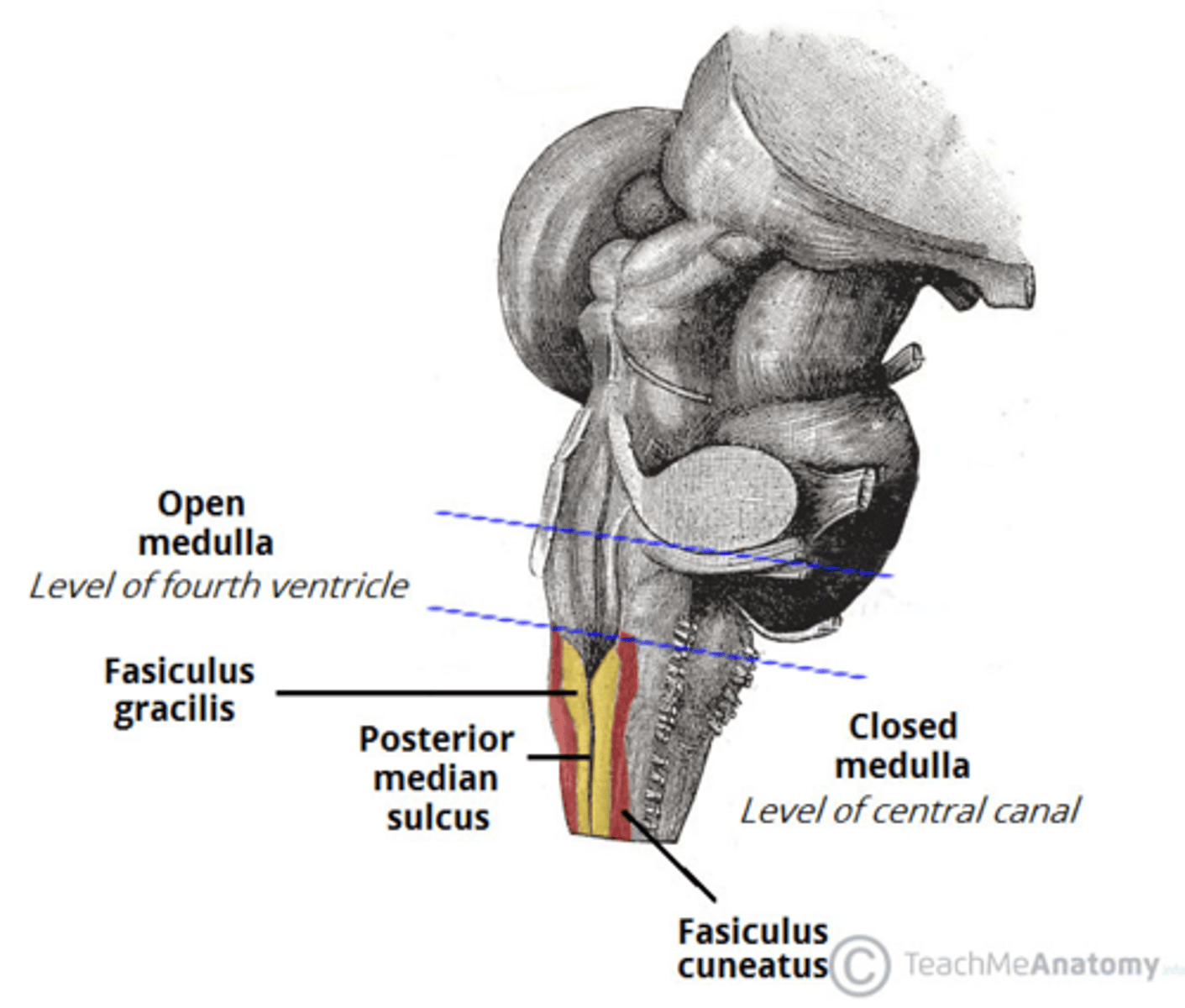
refers to the caudal portion of the medulla since there is medullary tissue here on the dorsal aspect of the 4th ventricle (therefore it is enveloped by the medulla)
closed
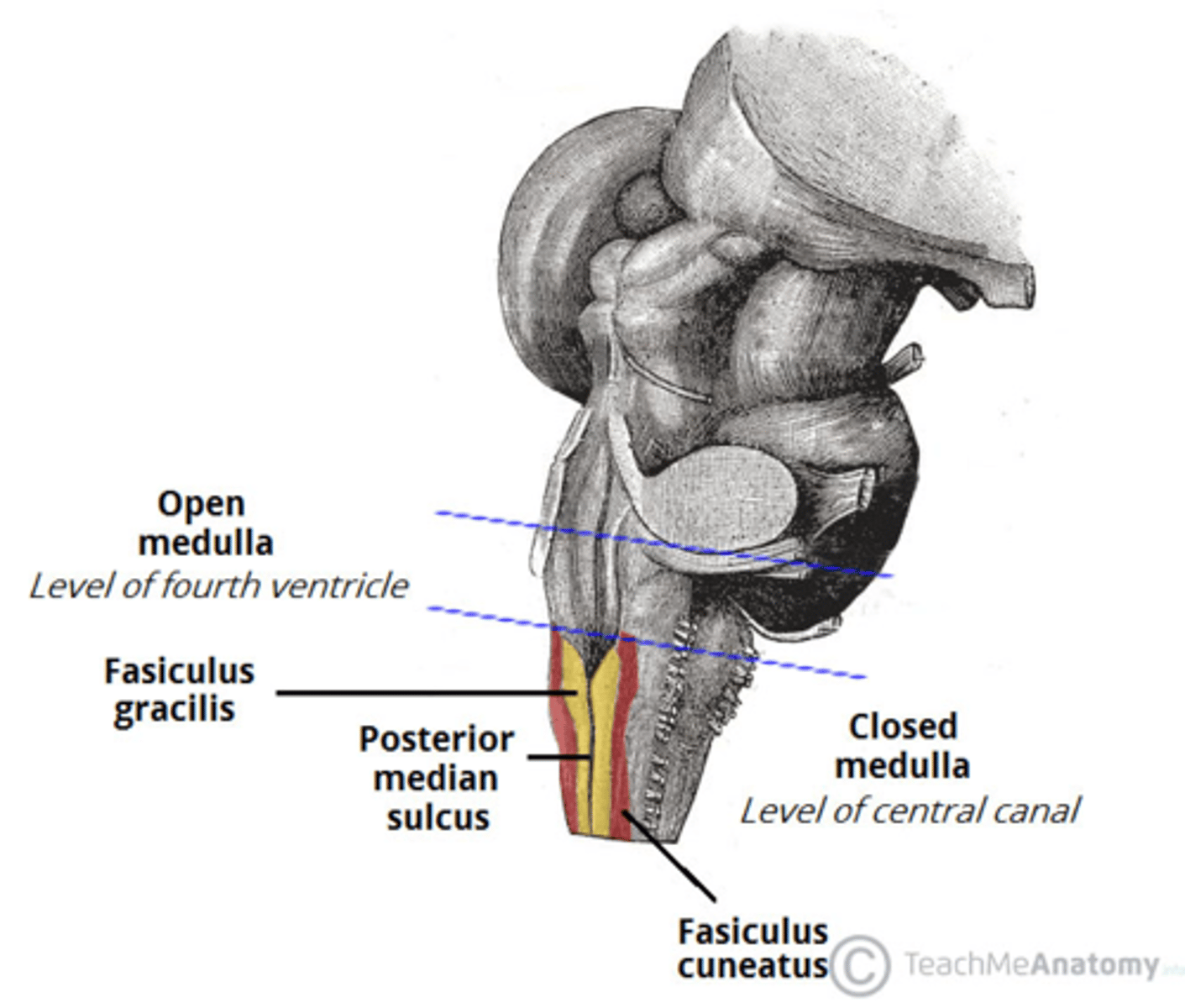
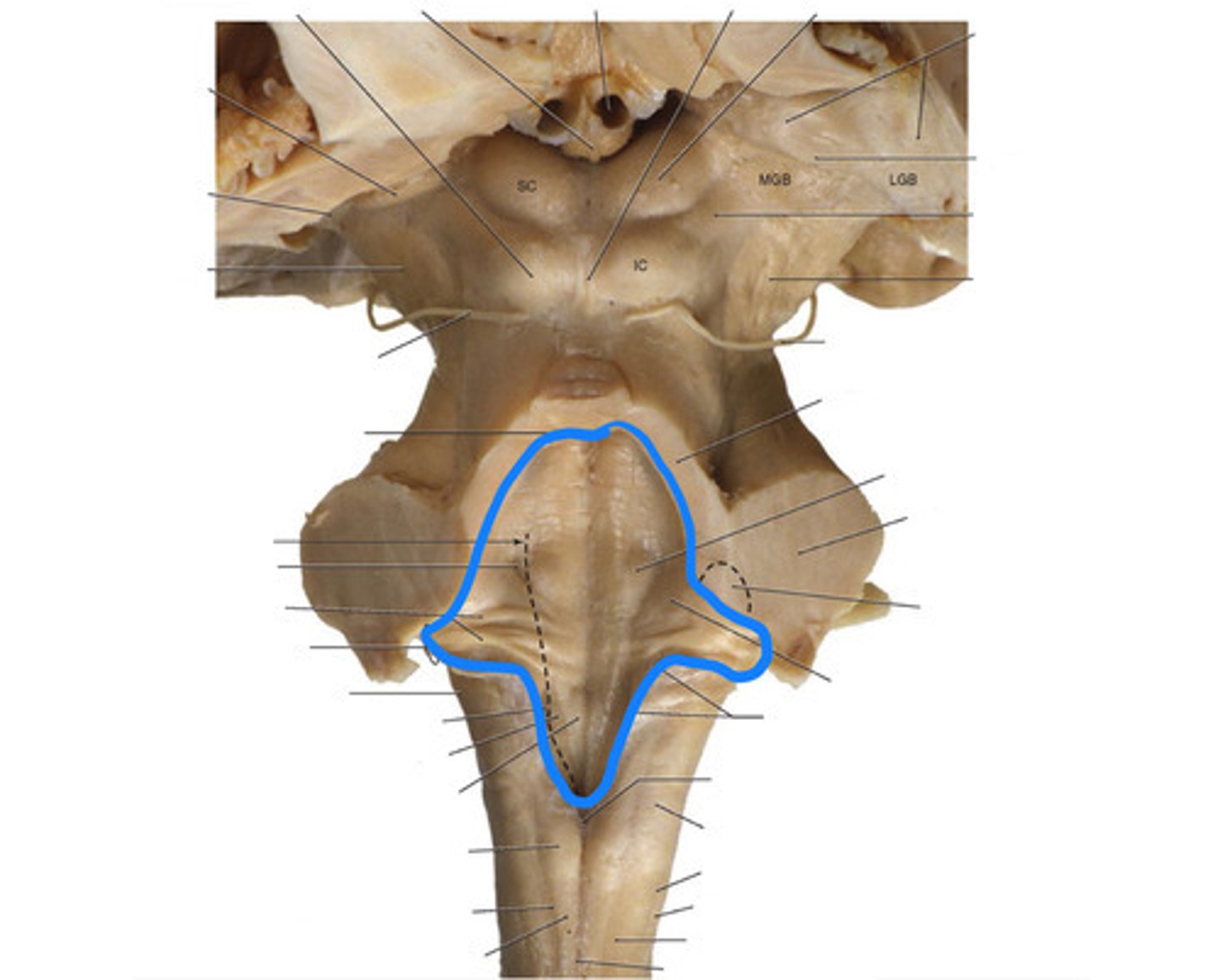
narrowed down portion of the 4th ventricle in the closed portion of the medulla
central canal
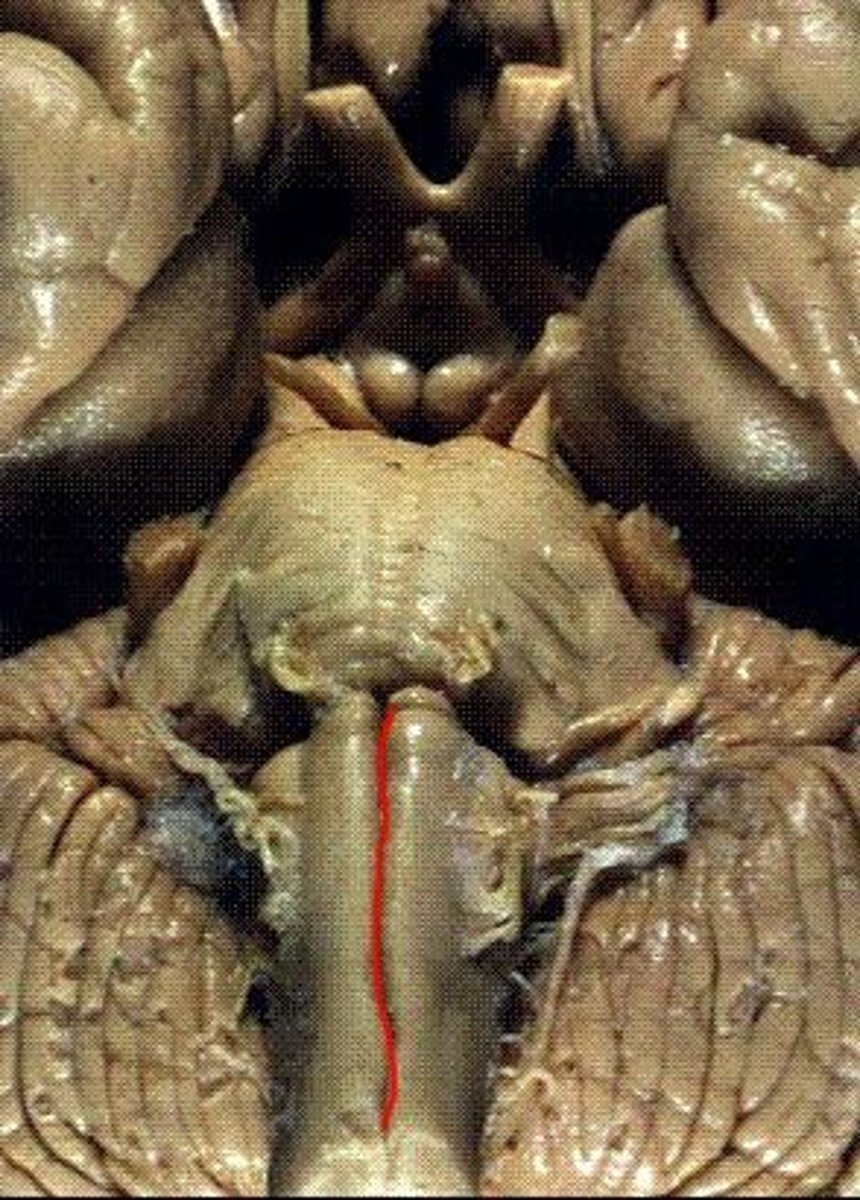
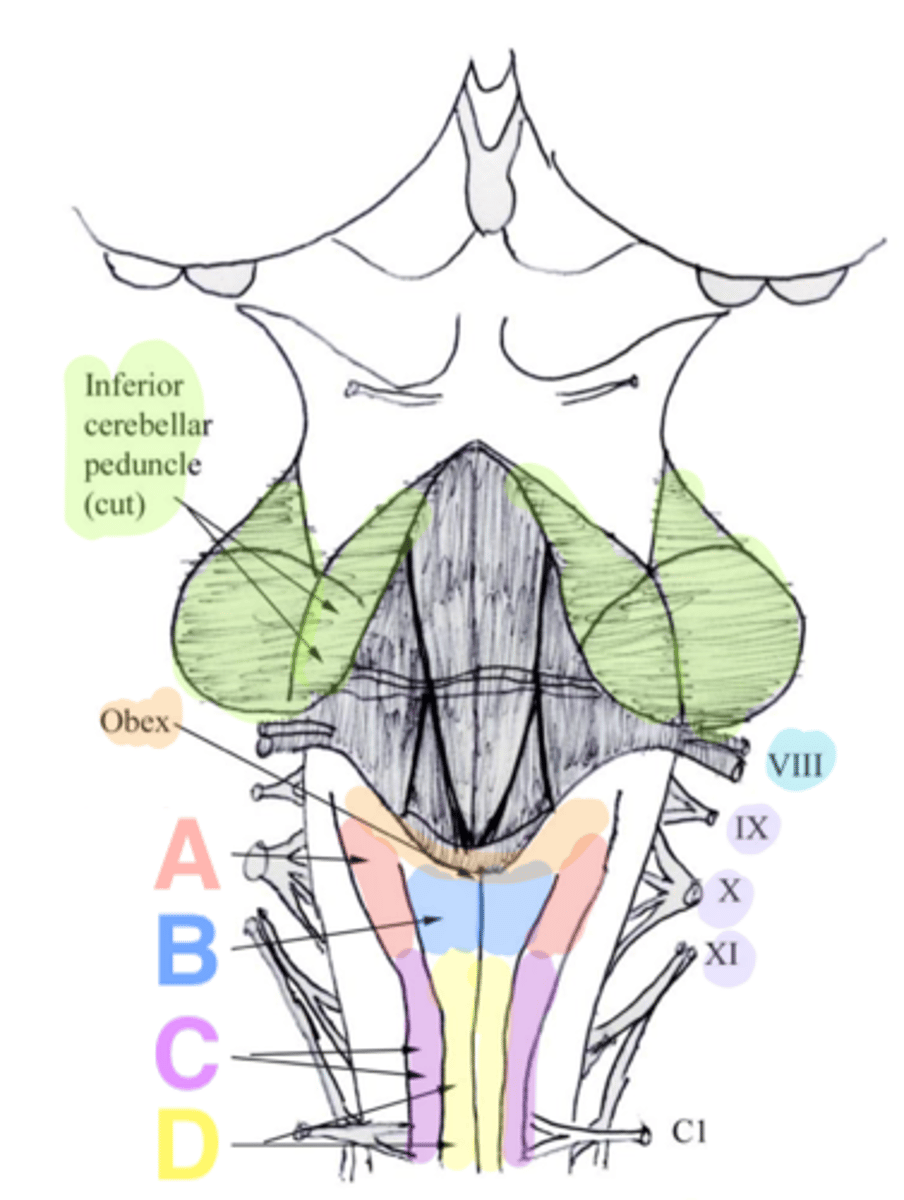
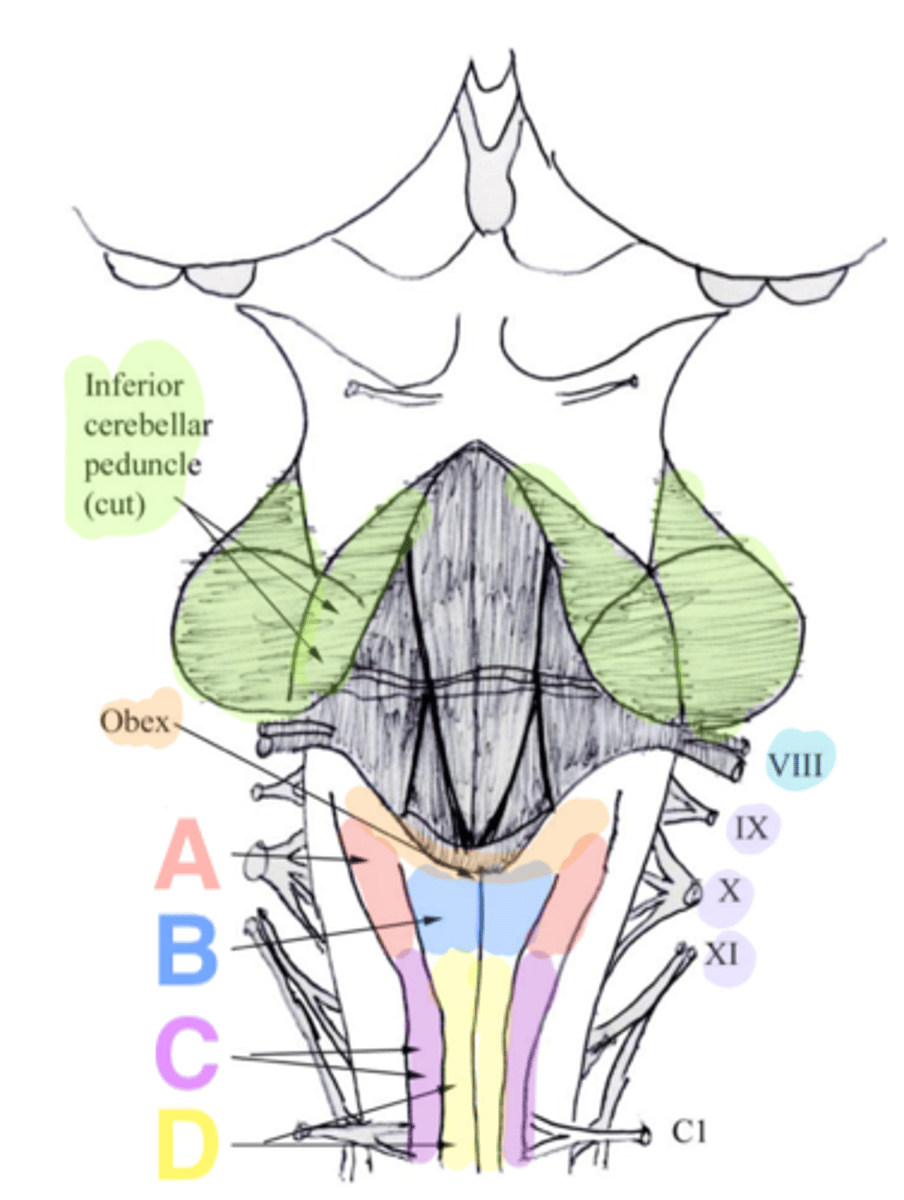
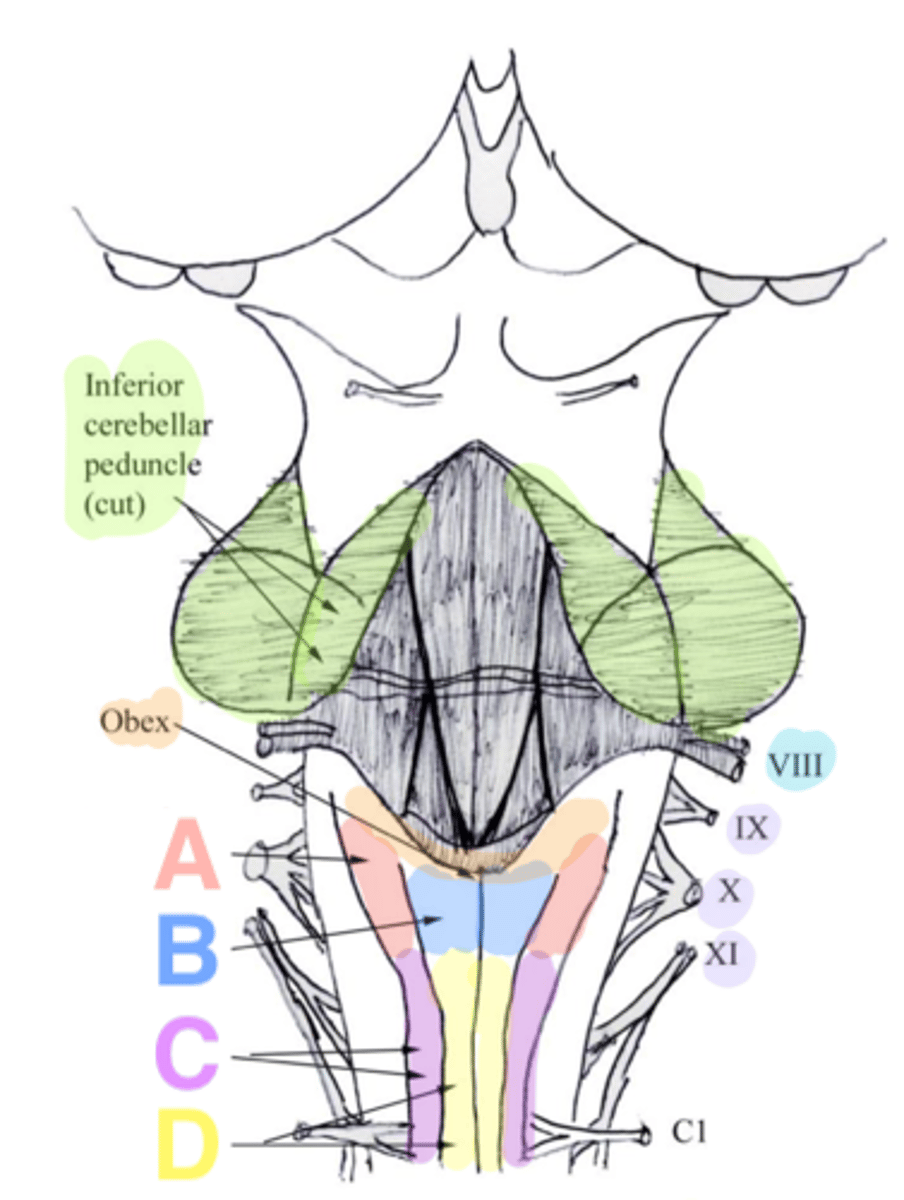
two ridges of tissue on the ventral aspect of the medulla, separated from each other by the ventral median fissure
pyramids

area where most corticospinal fibers decussate over the lower medulla, therefore obscuring the ventral median fissure
pyramidal decussation
elongated mounds of tissue lateral to the medullary pyramids
olives
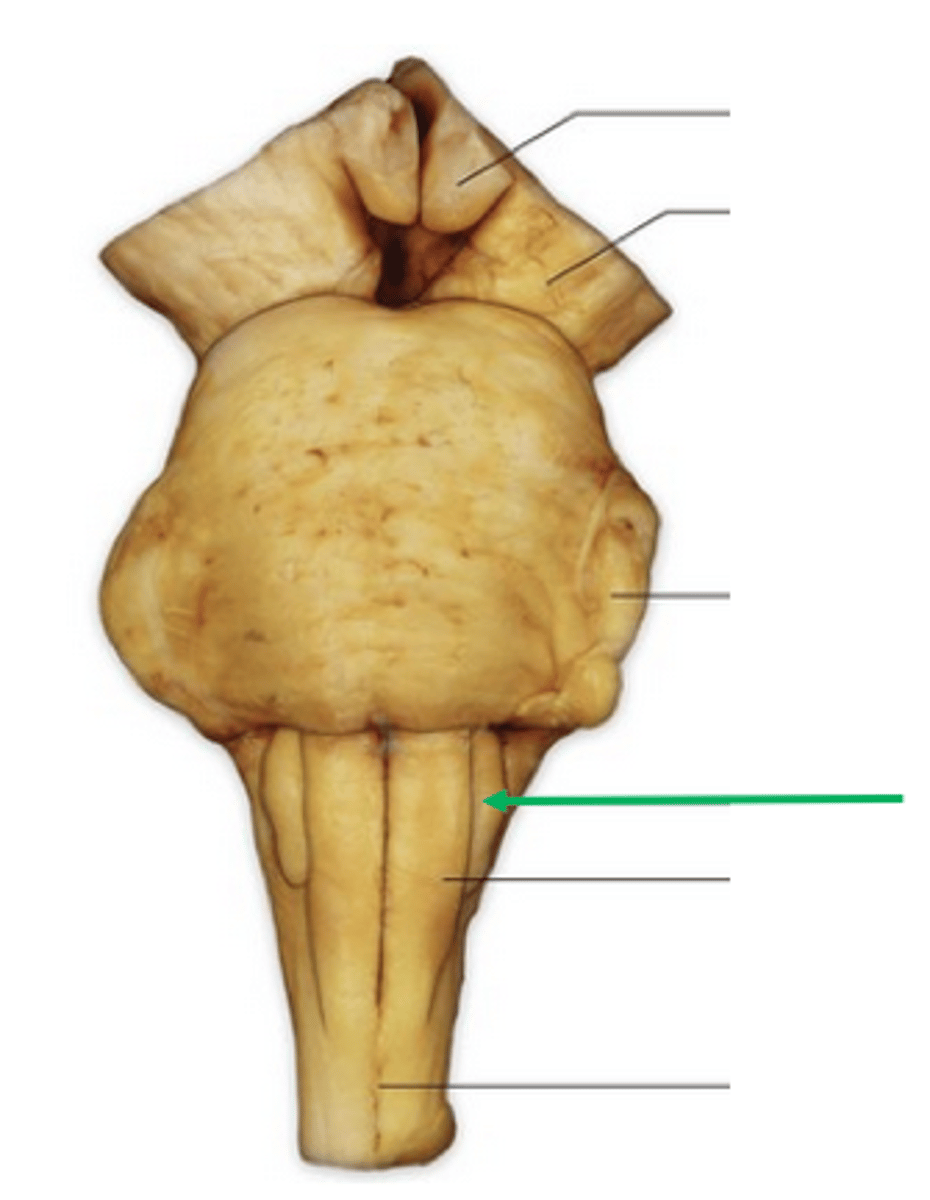
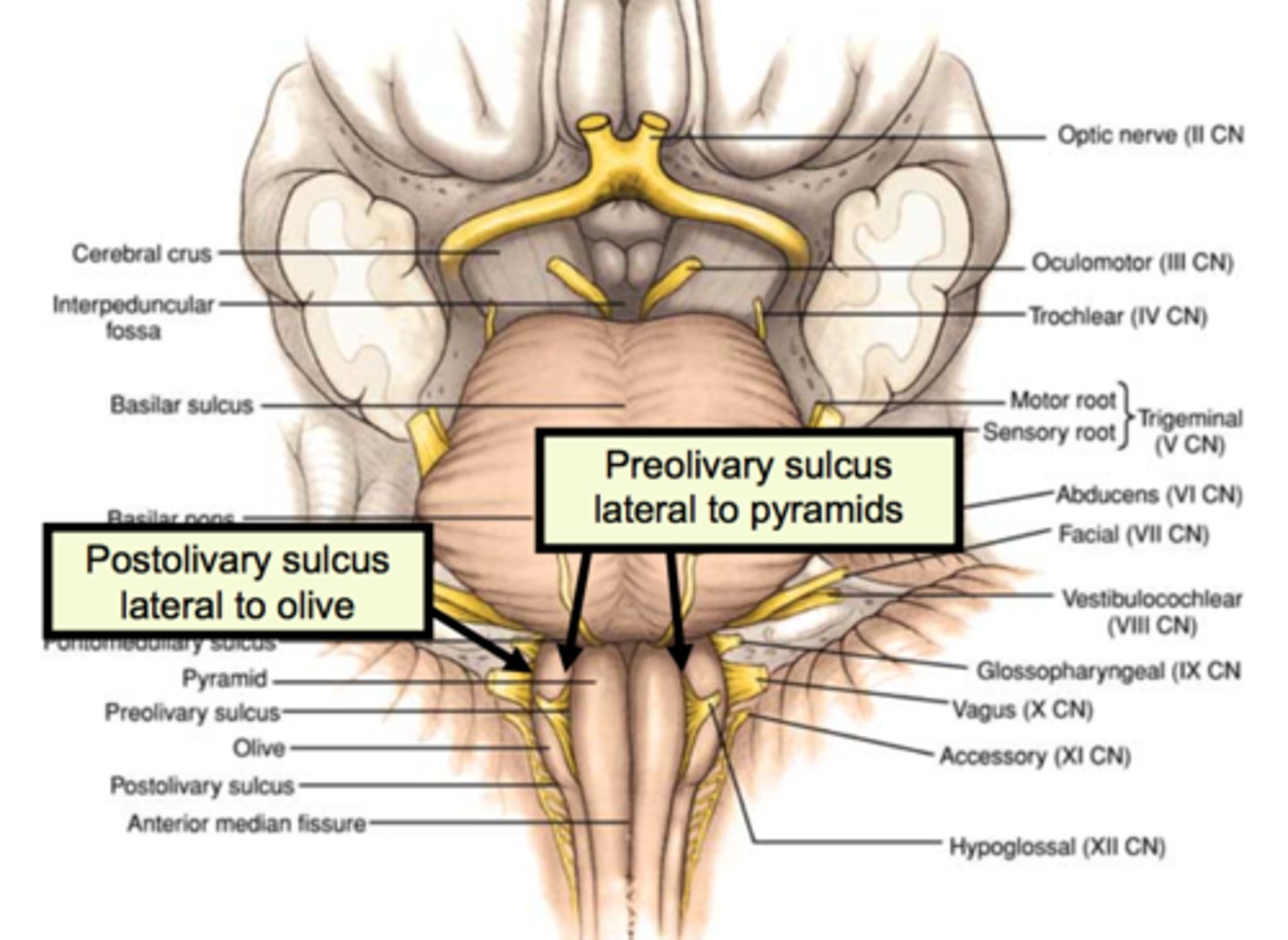
vertical groove dorsolateral to the inferior olive on each side that gives rise to CN IX and X
postolivary sulcus
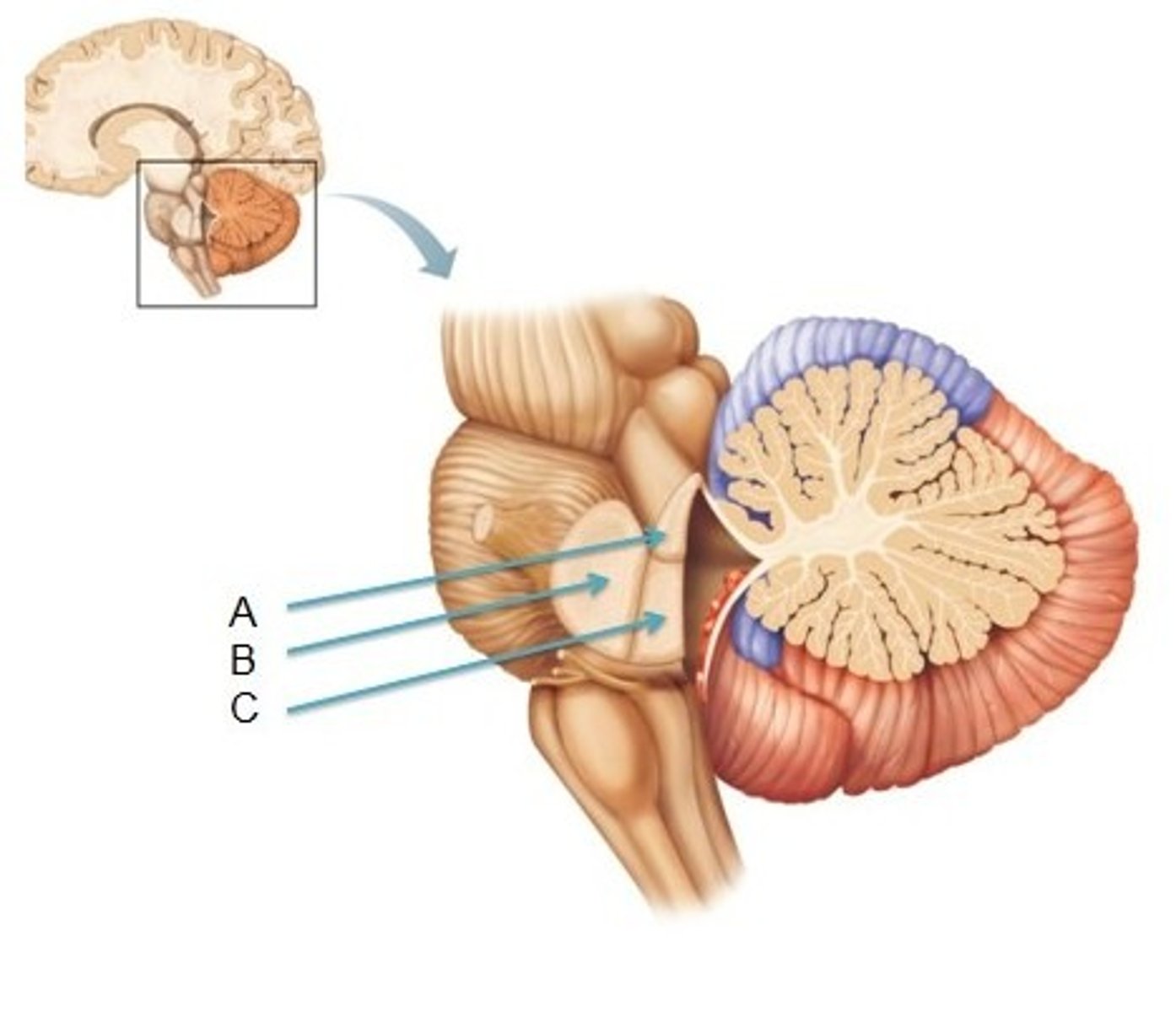
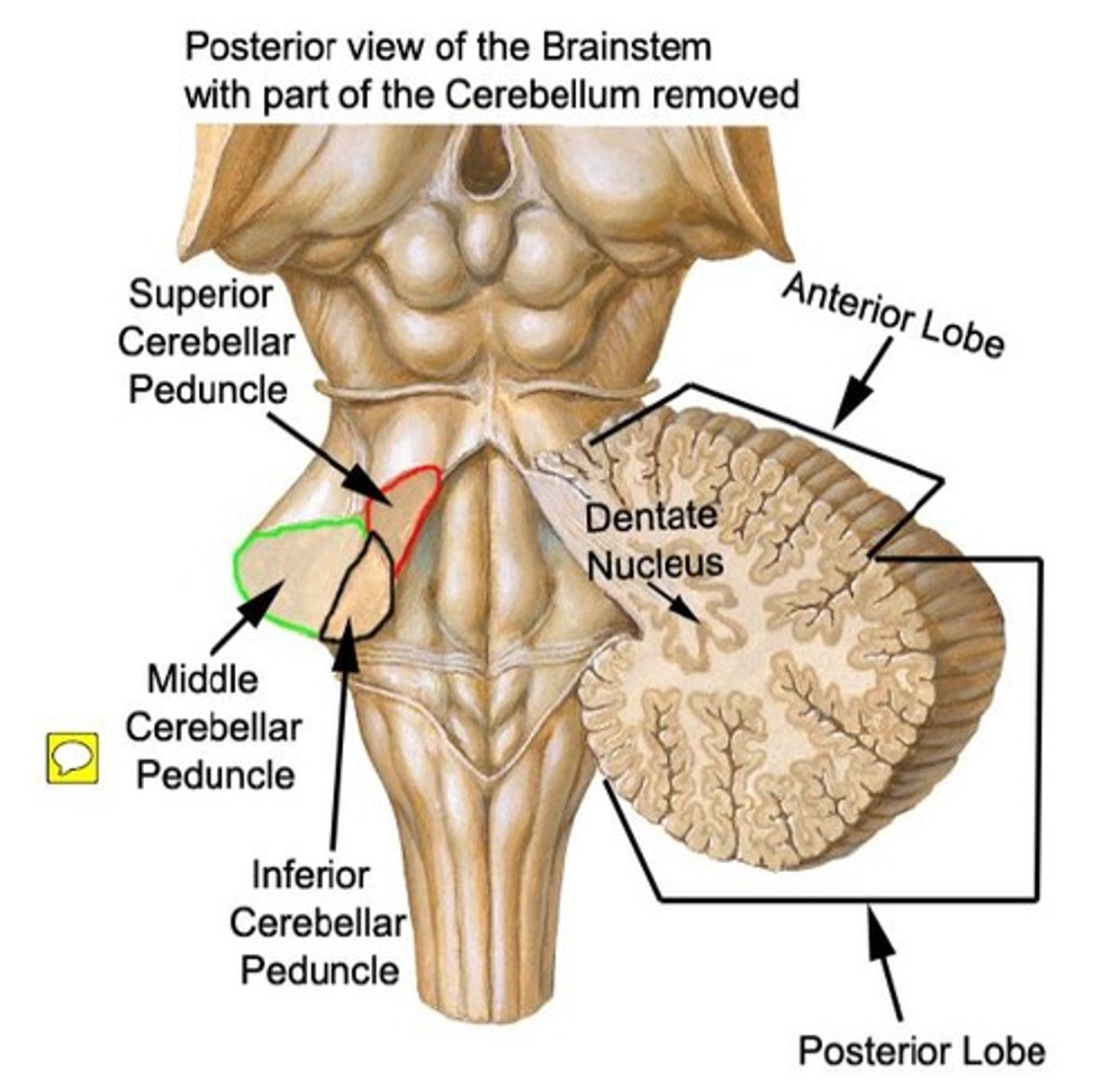
white matter stalks that connect the medulla to the cerebellum
**these help to form the lateral walls of the caudal portion of the 4th ventricle
inferior cerebellar peduncles
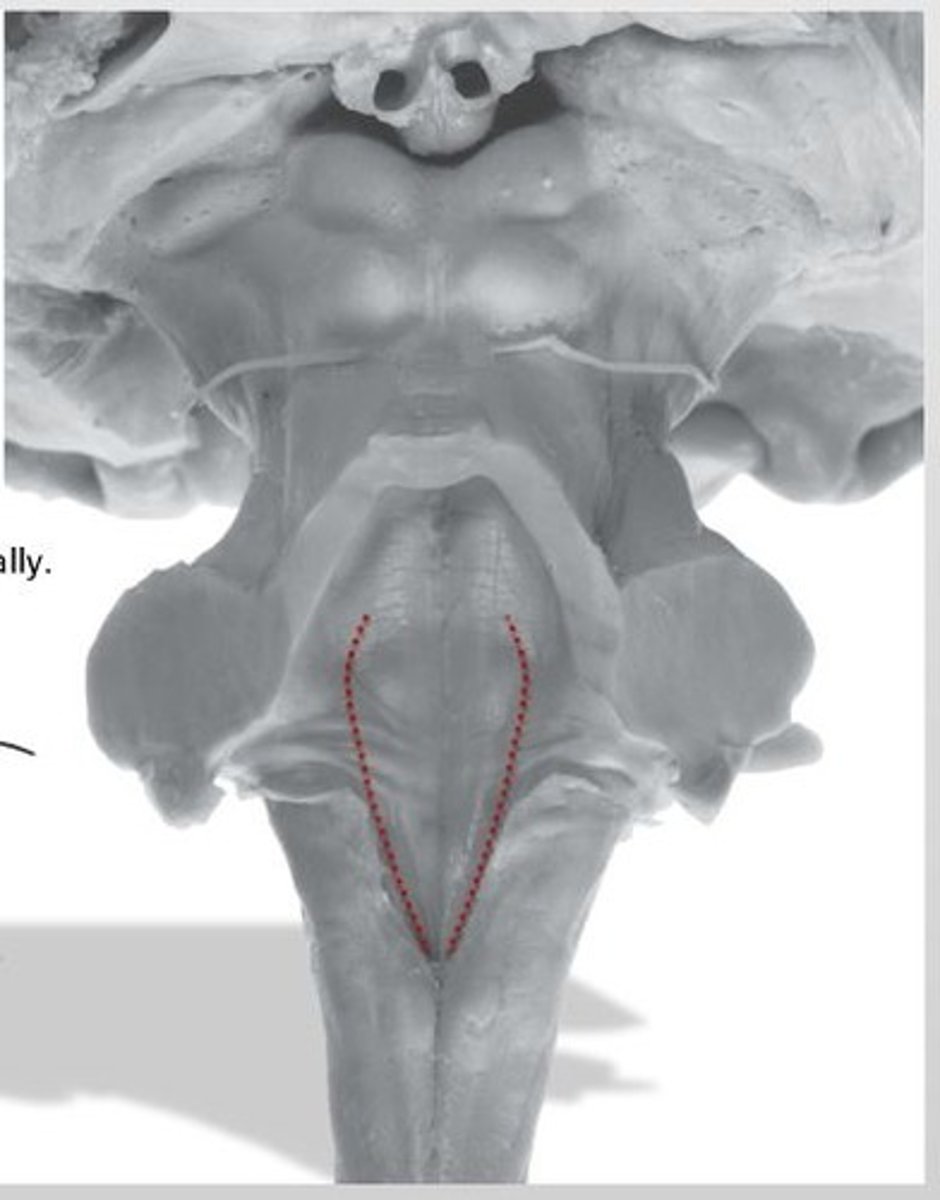
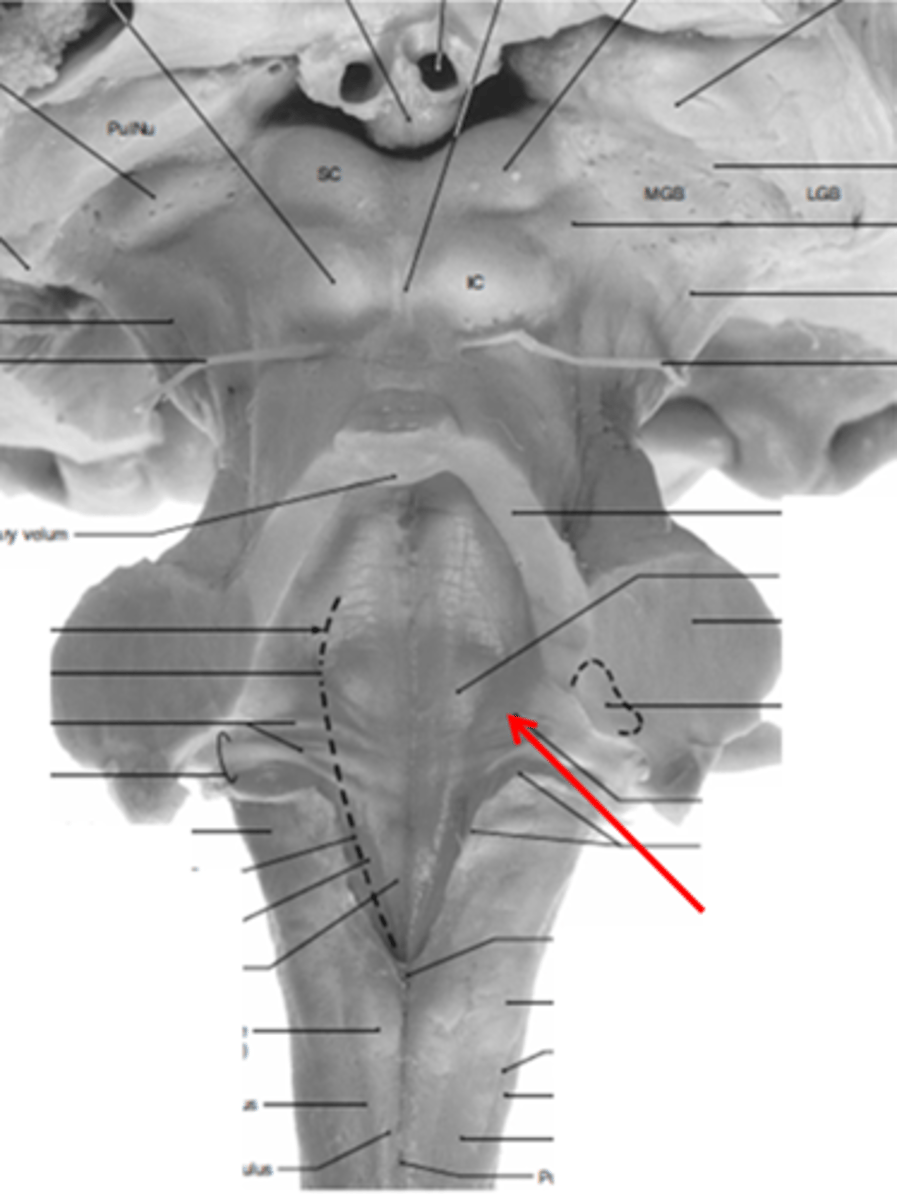
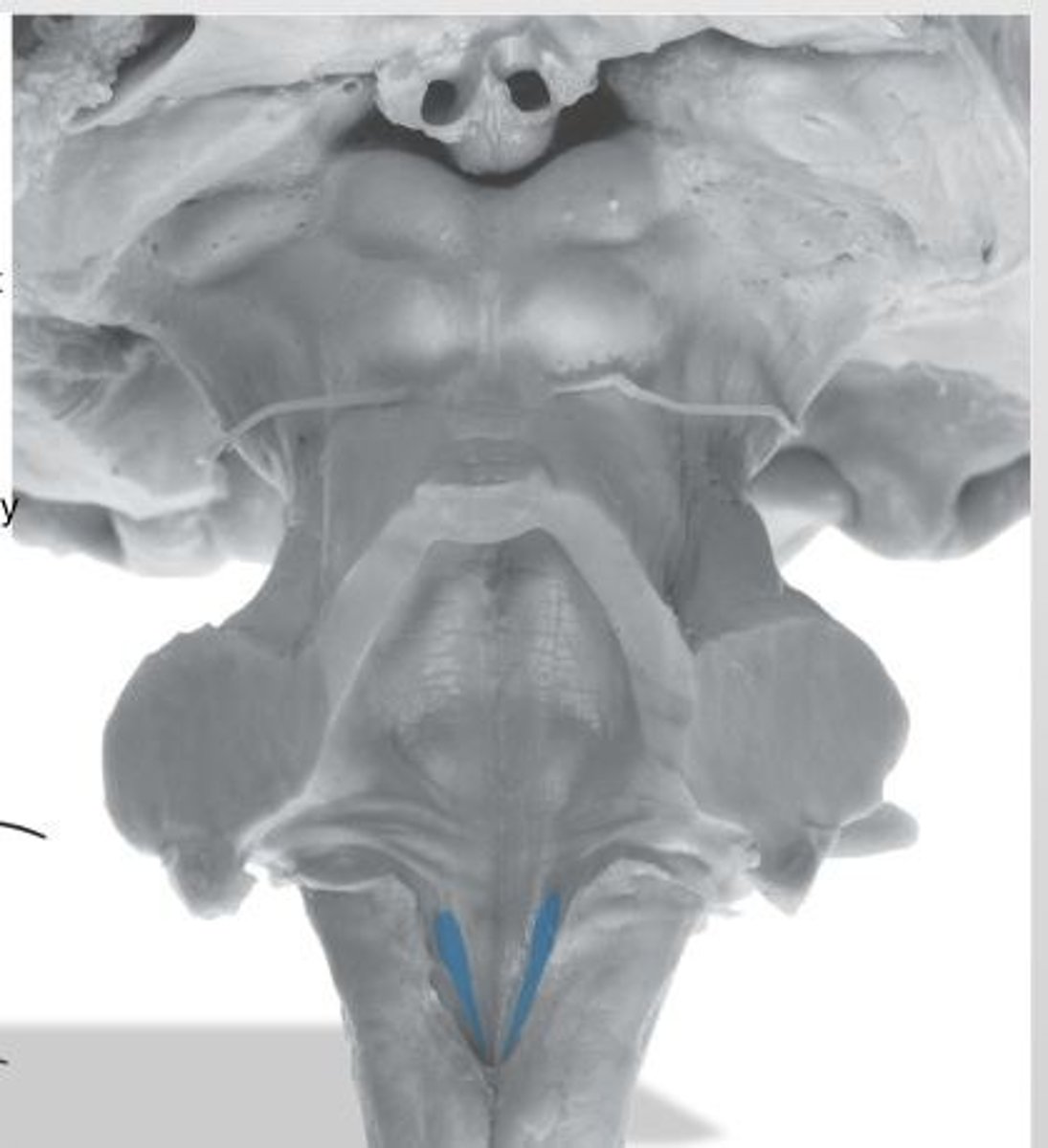
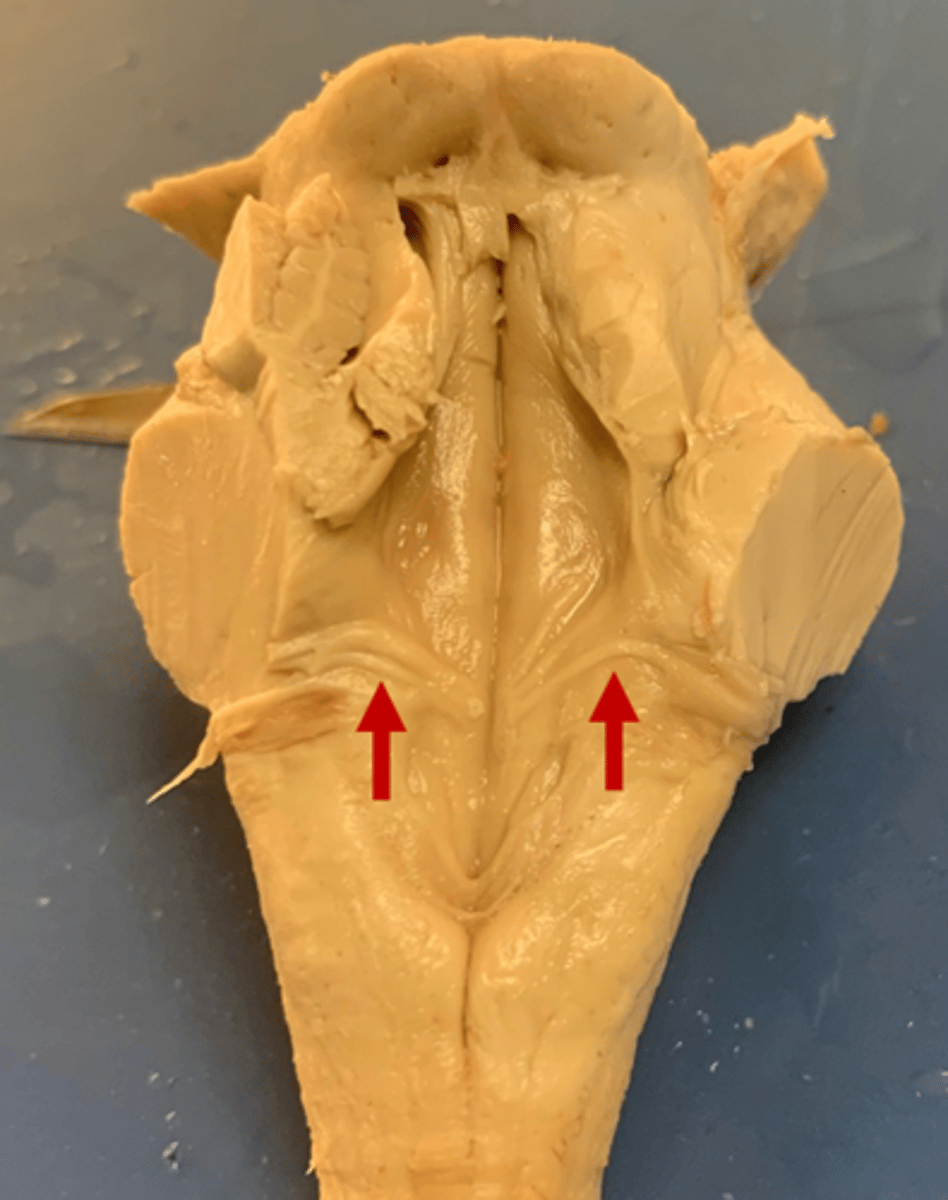
medial paired ridges of tissue on the dorsal aspect of the closed portion of the medulla
tractus gracilis
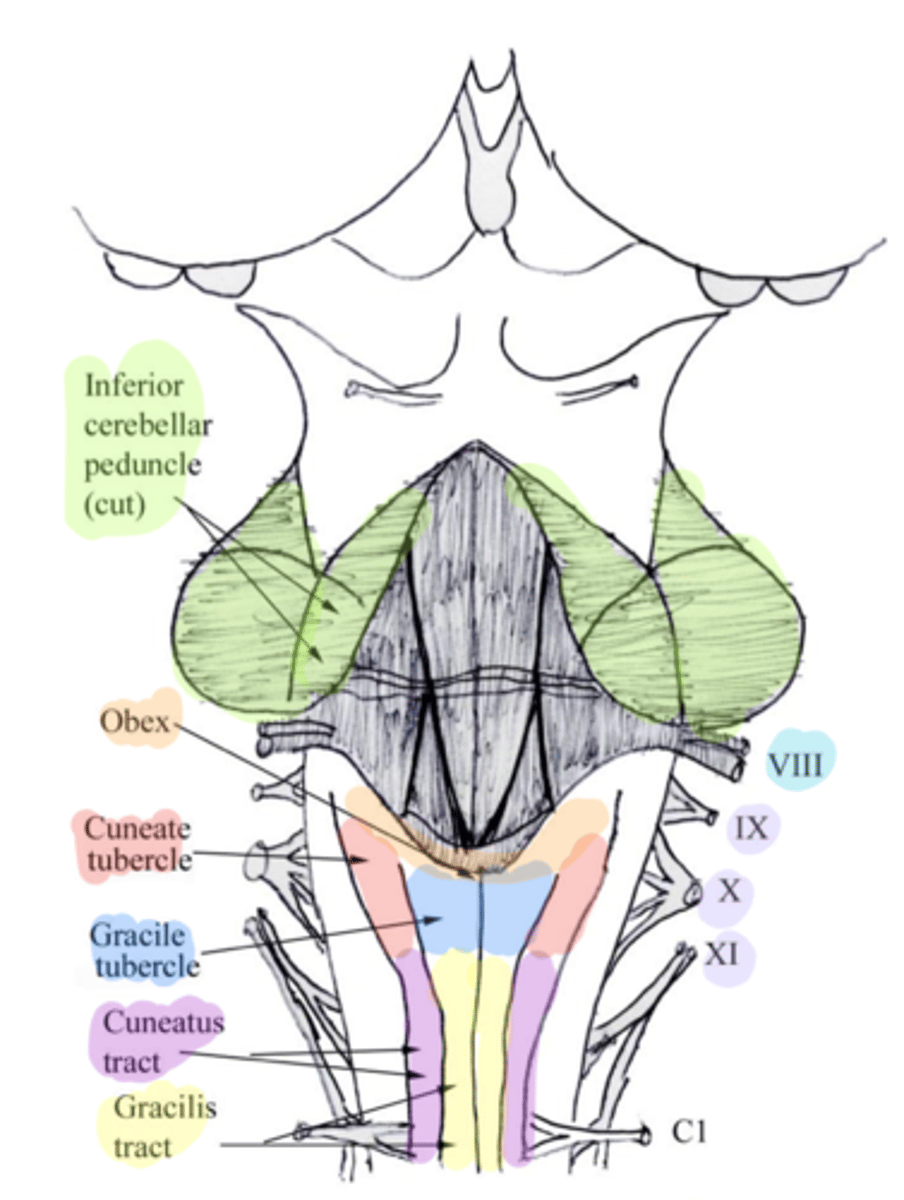
lateral paired ridges of tissue on the dorsal aspect of the closed portion of the medulla
tractus cuneatus
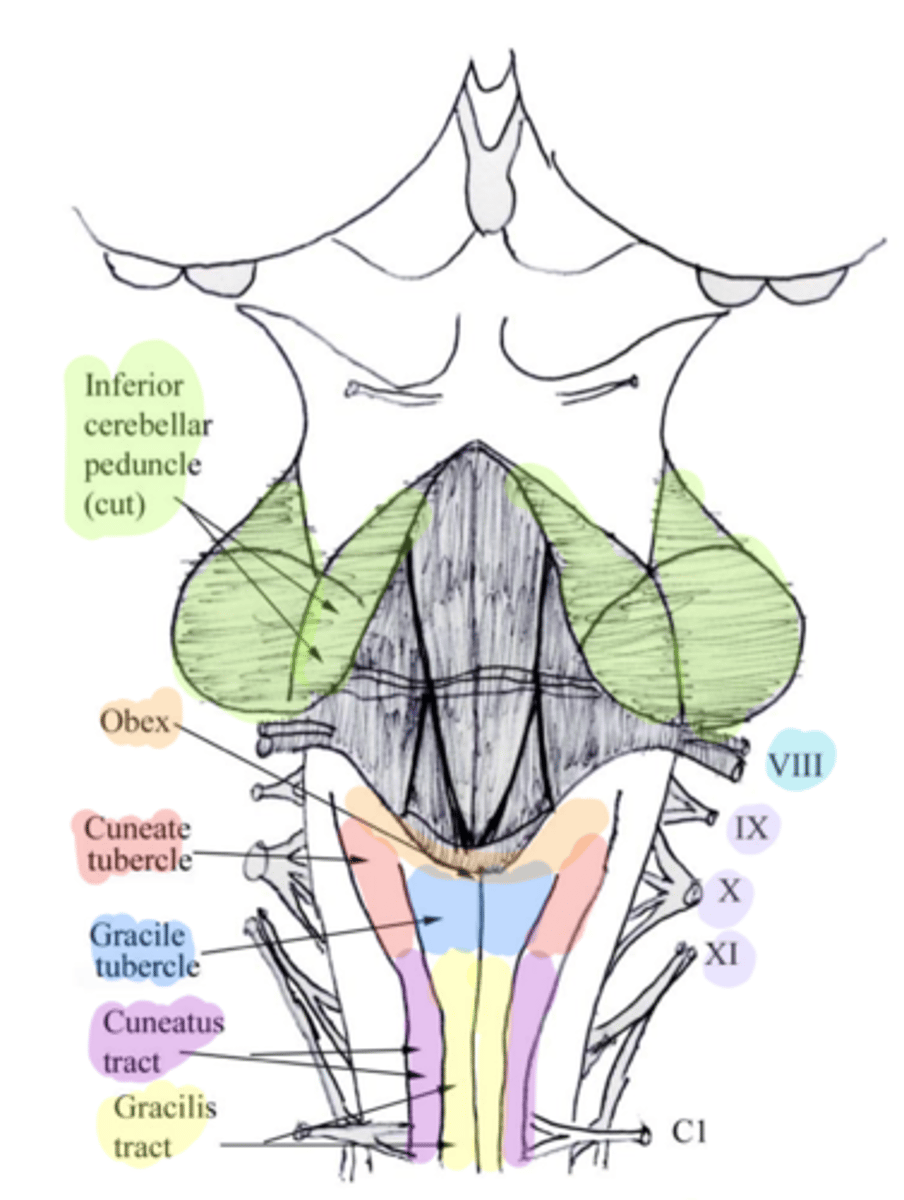
superior ends of the medial paired ridges of tissue on the dorsal aspect of the closed portion of the medulla, formed by namesake nuclei
gracilis tubercles
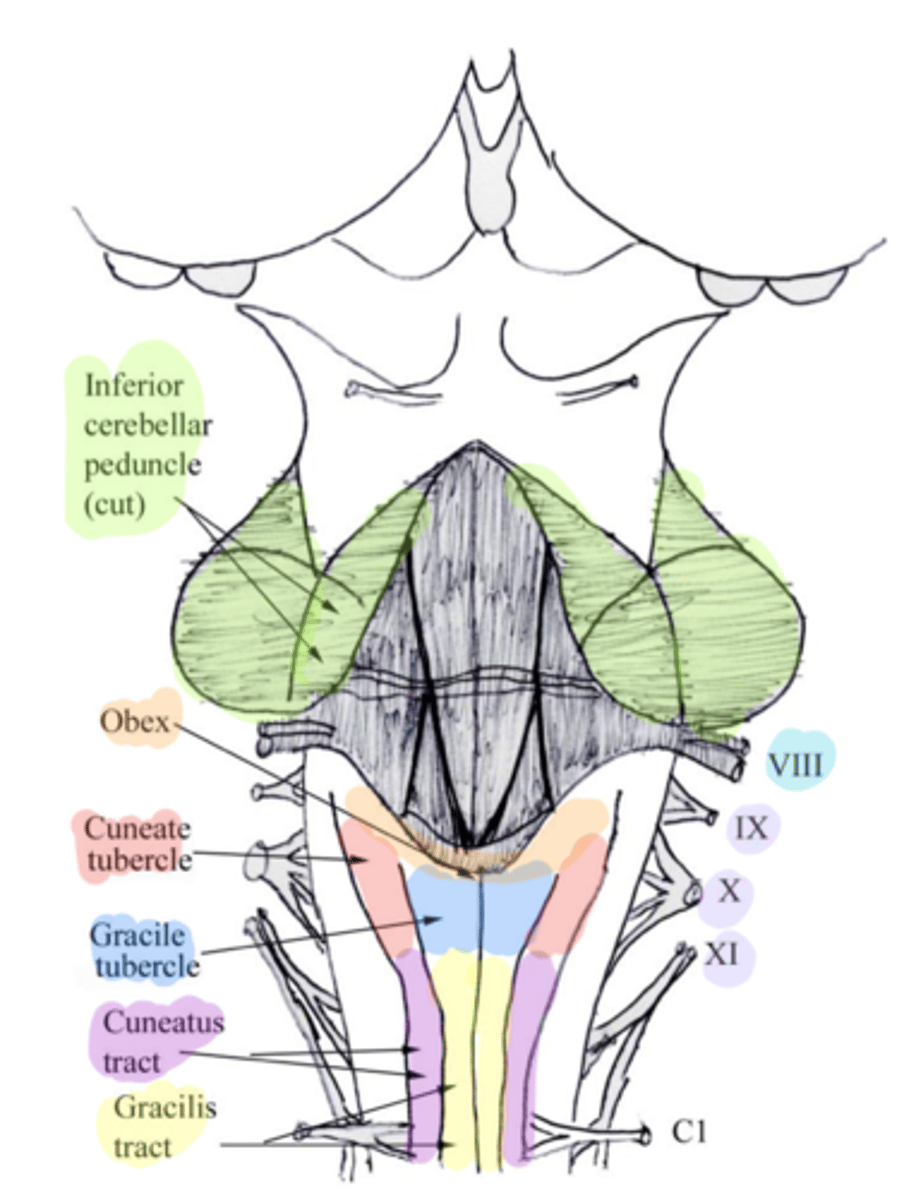
superior ends of the lateral paired ridges of tissue on the dorsal aspect of the closed portion of the medulla, formed by namesake nuclei
cuneatus tubercles

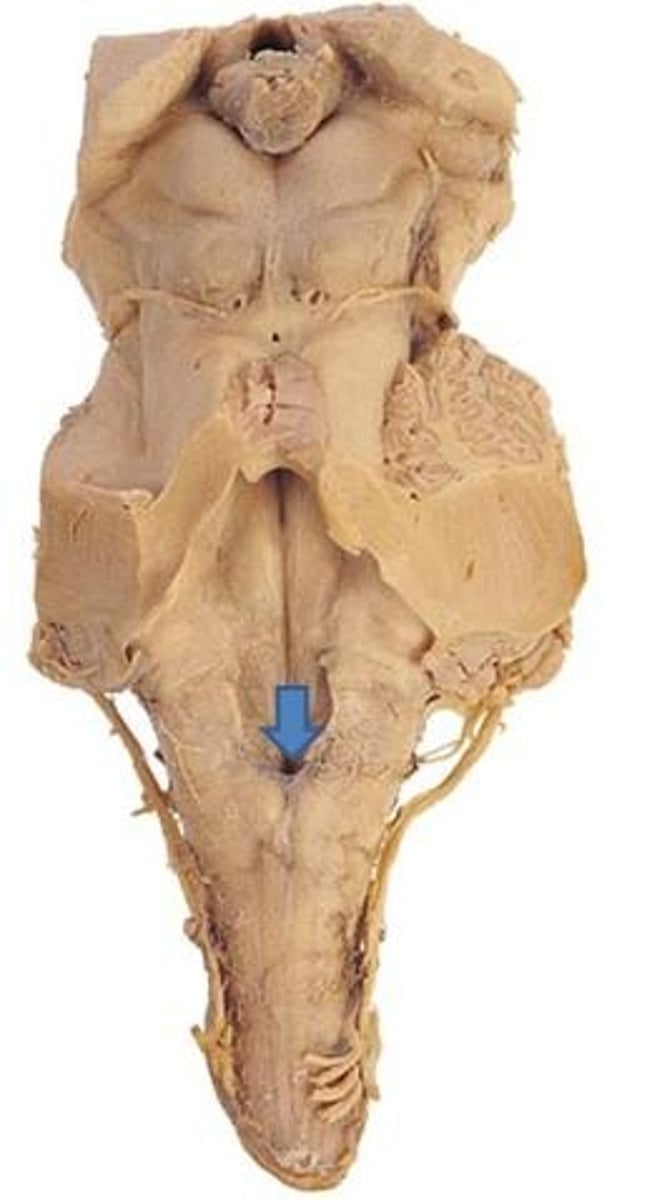
V-shaped boundary of the caudal aspect of the 4th ventricle that marks the boundary between the open and closed portions of the medulla
obex
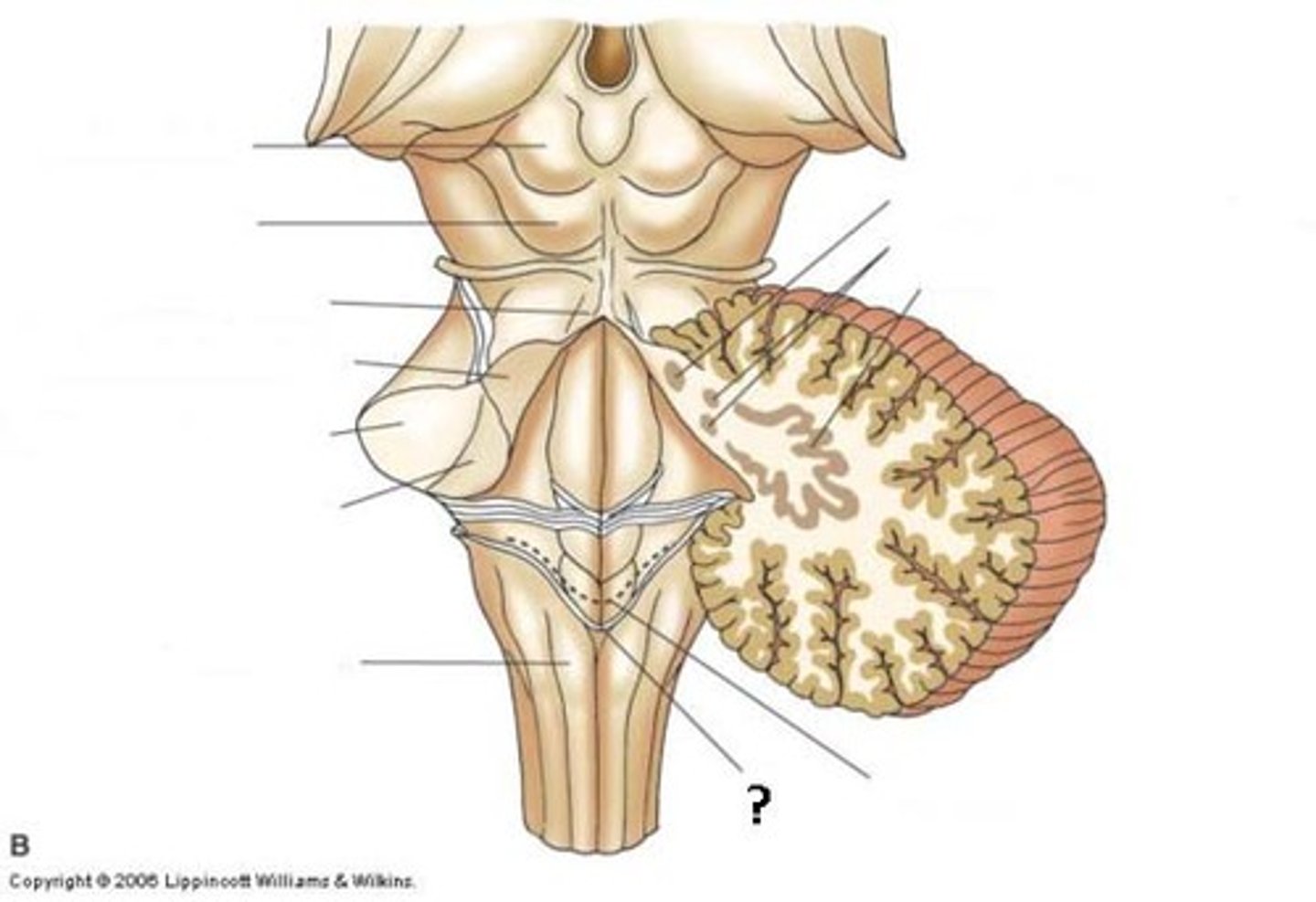
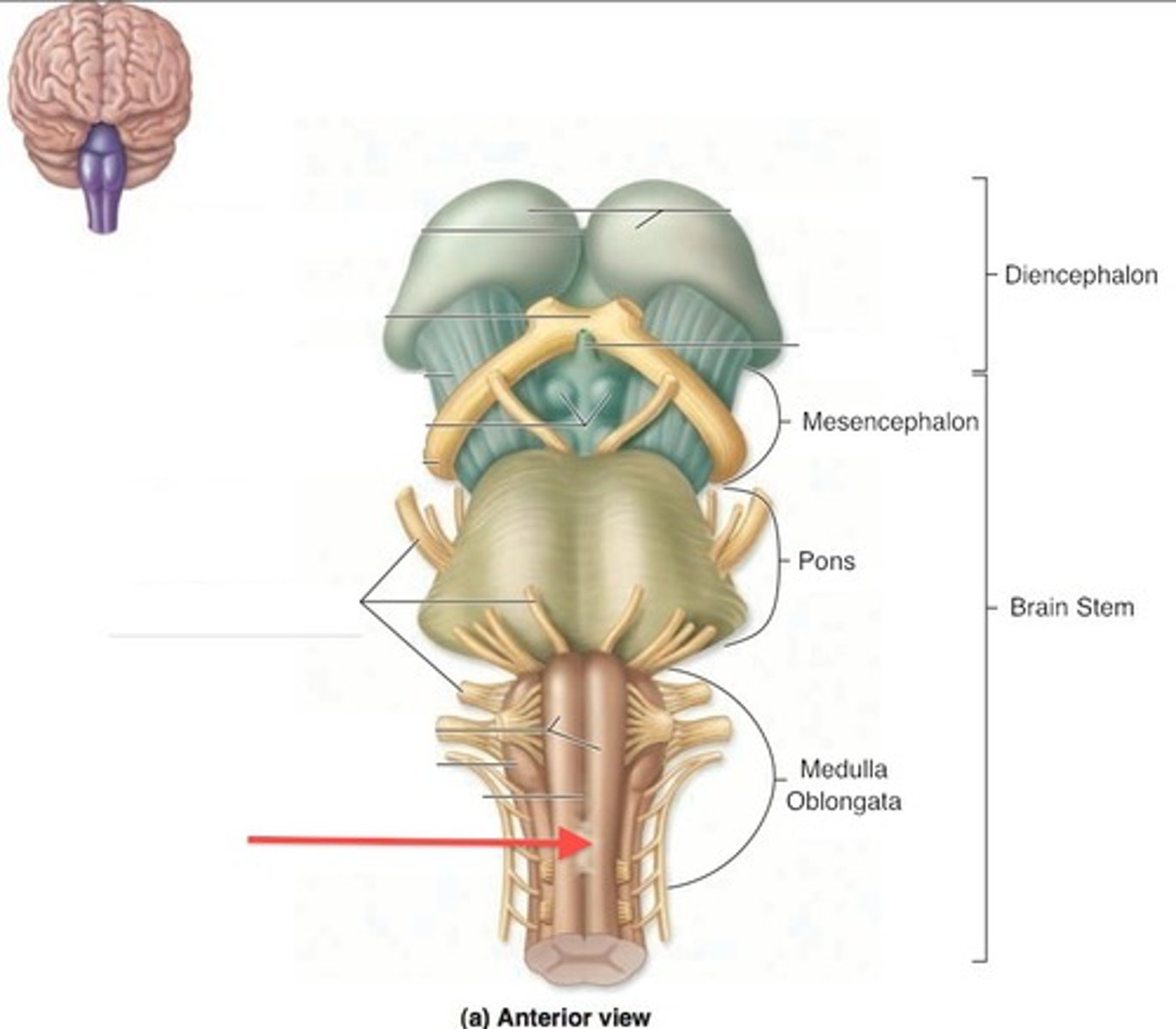
Which cranial nerves arise from the medulla? (and pontomedullary junction)
6-10, 12
name the groove
pontomedullary junction
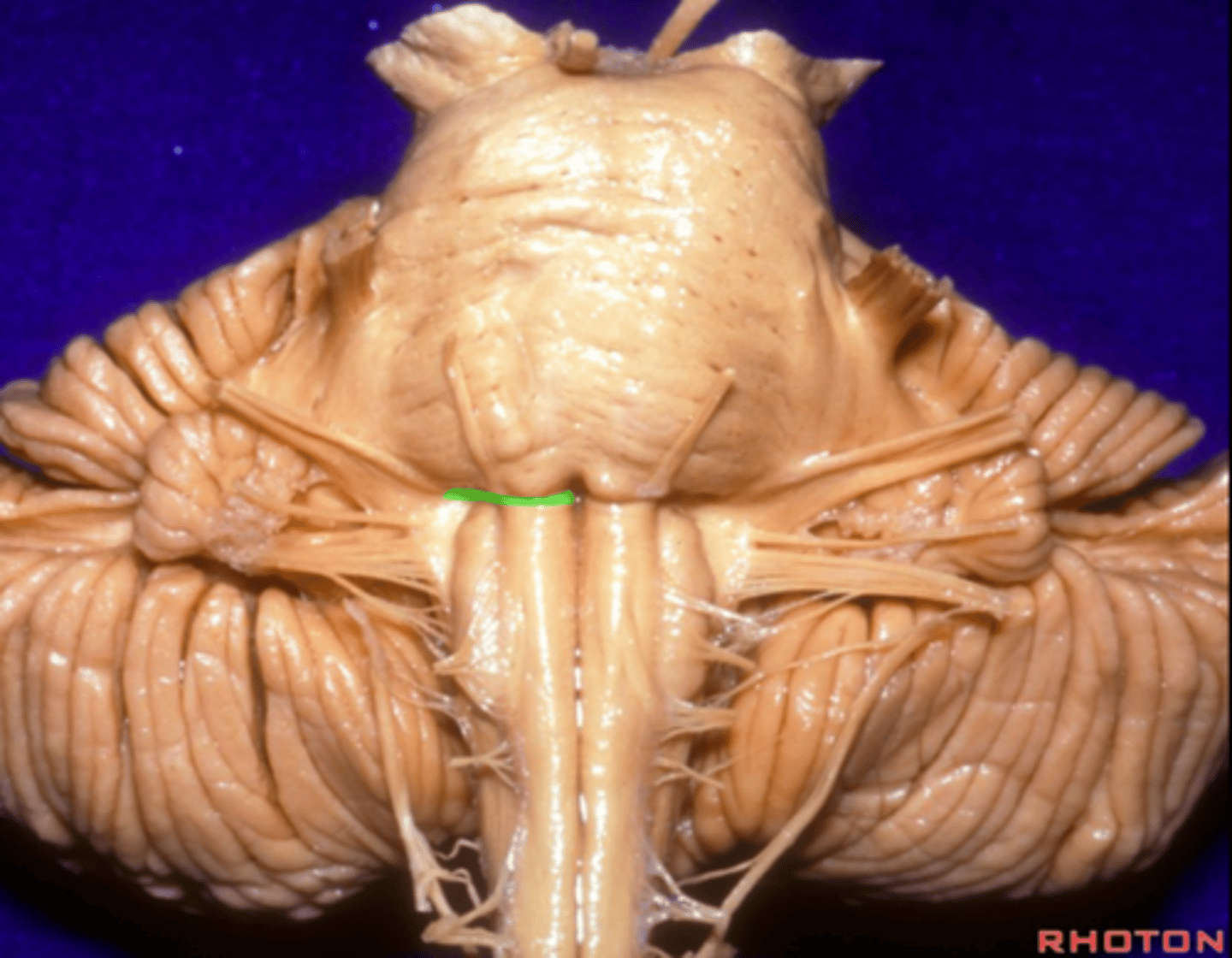
general portion of the medulla
open medulla
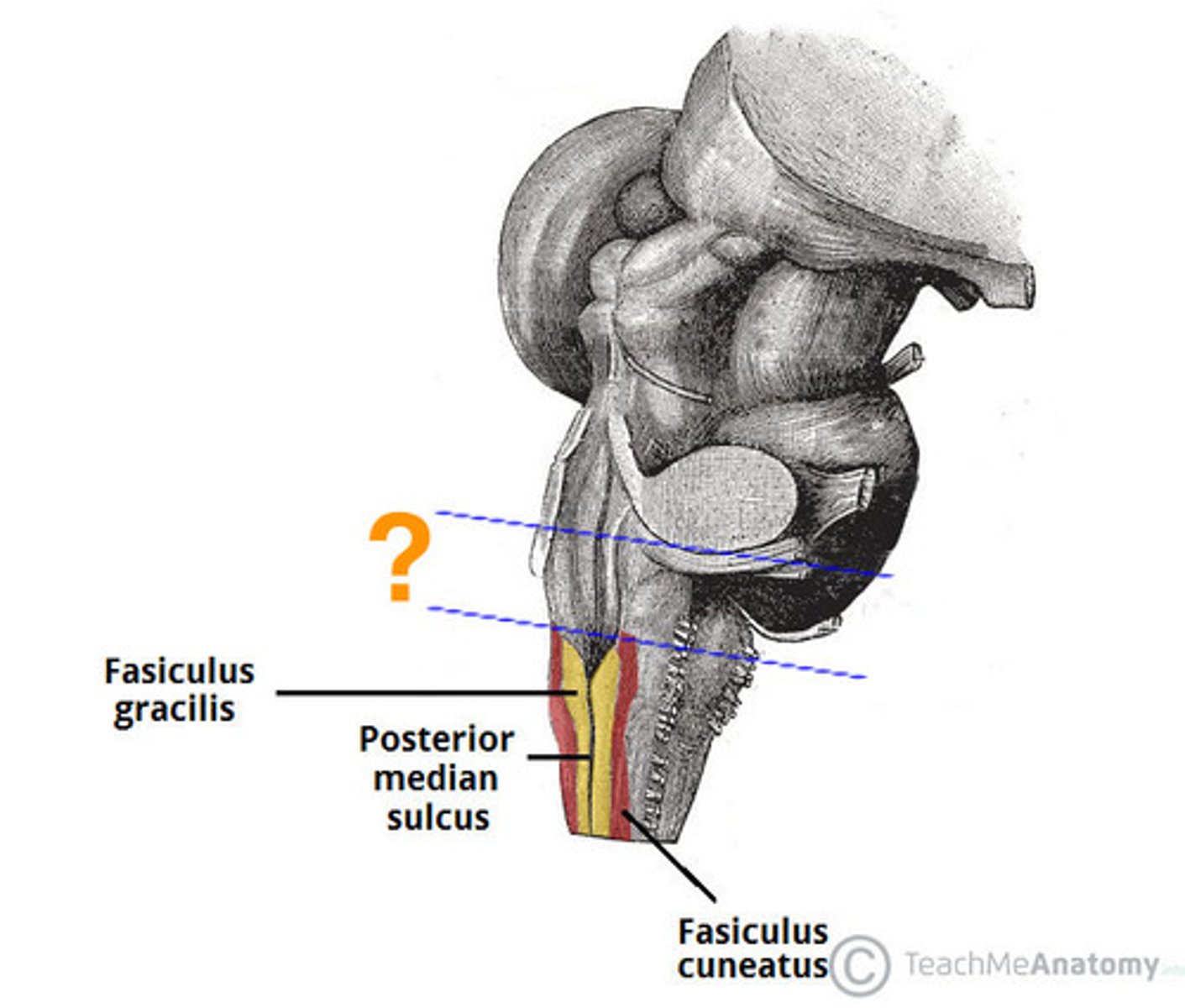
general portion of the medulla
closed medulla
pyramids
ventral median fissure
pyramidal decussation
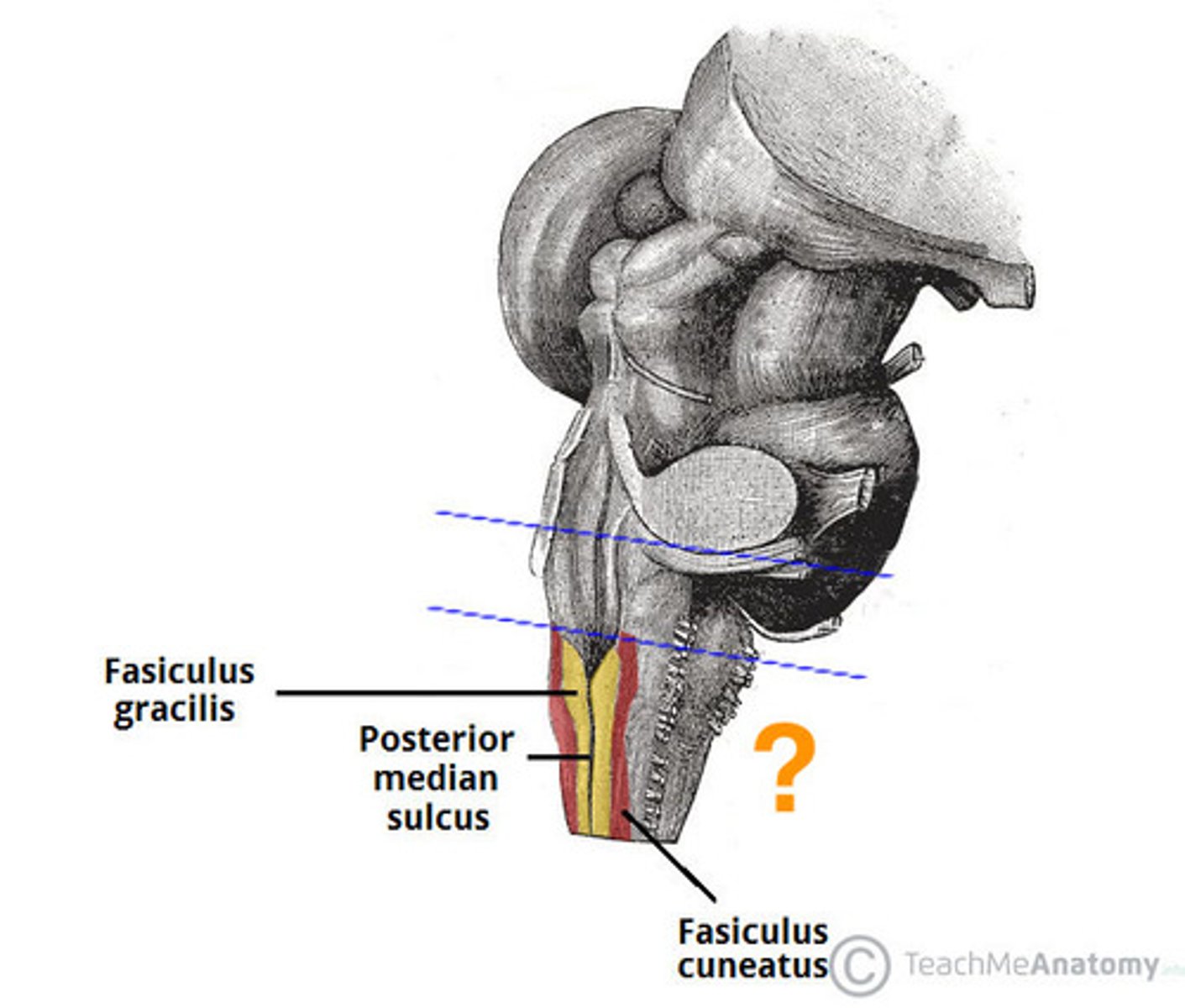
C
inferior cerebellar peduncles
cuneate tubercle
gracilis tubercle
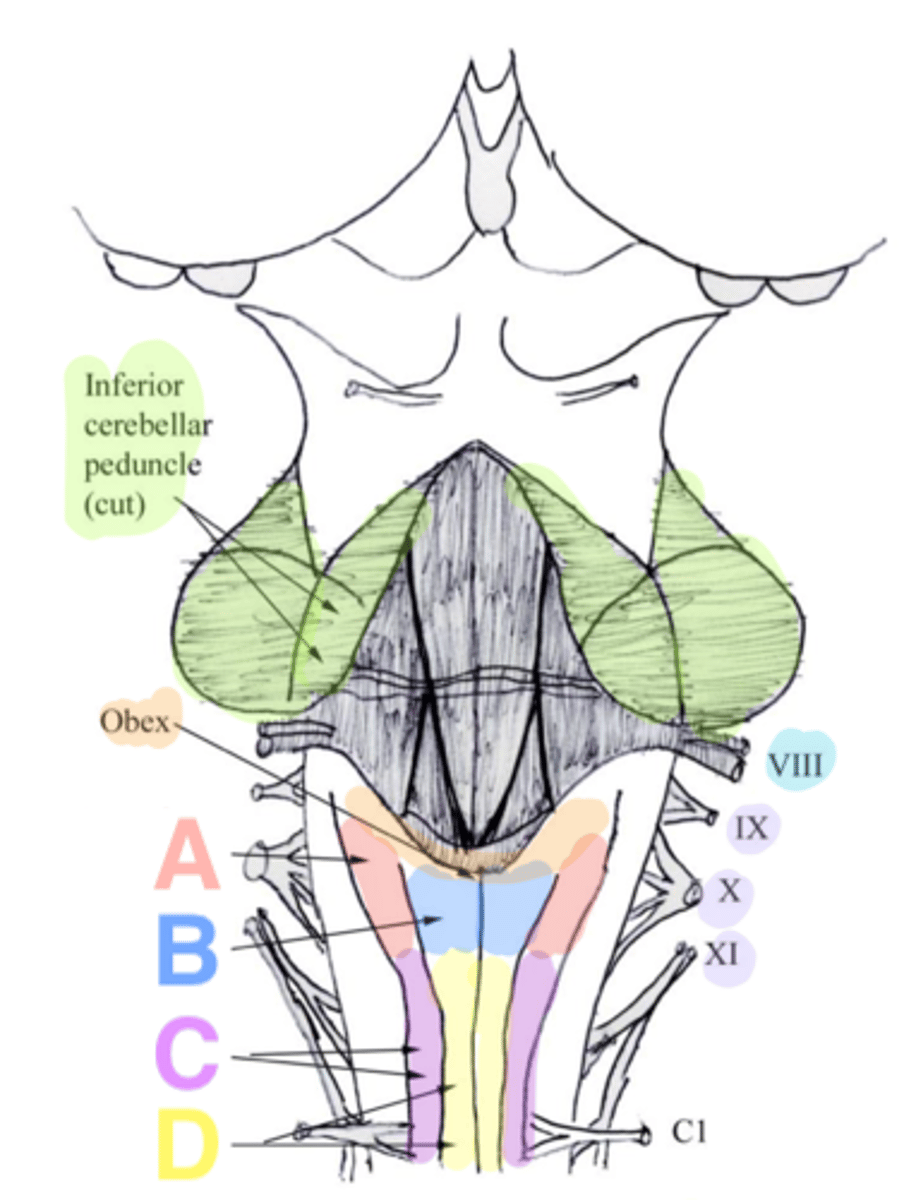
cuneatus tract
gracilis tract
obex
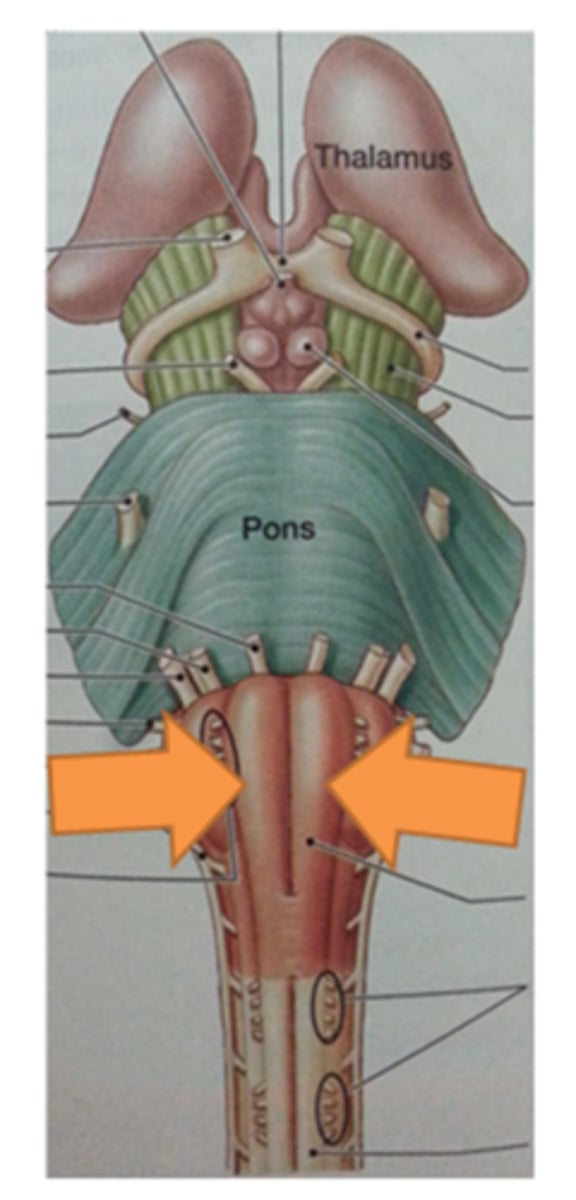
What is the superior boundary of the pons?
isthmus of the brain stem (between pons and cerebral peduncles)
What is the inferior boundary of the pons?
pontomedullary junction
refers to the large round protuberance on the ventral pons that represents a "bridge" of horizontally oriented fibers connecting the right and left sides
basilar portion
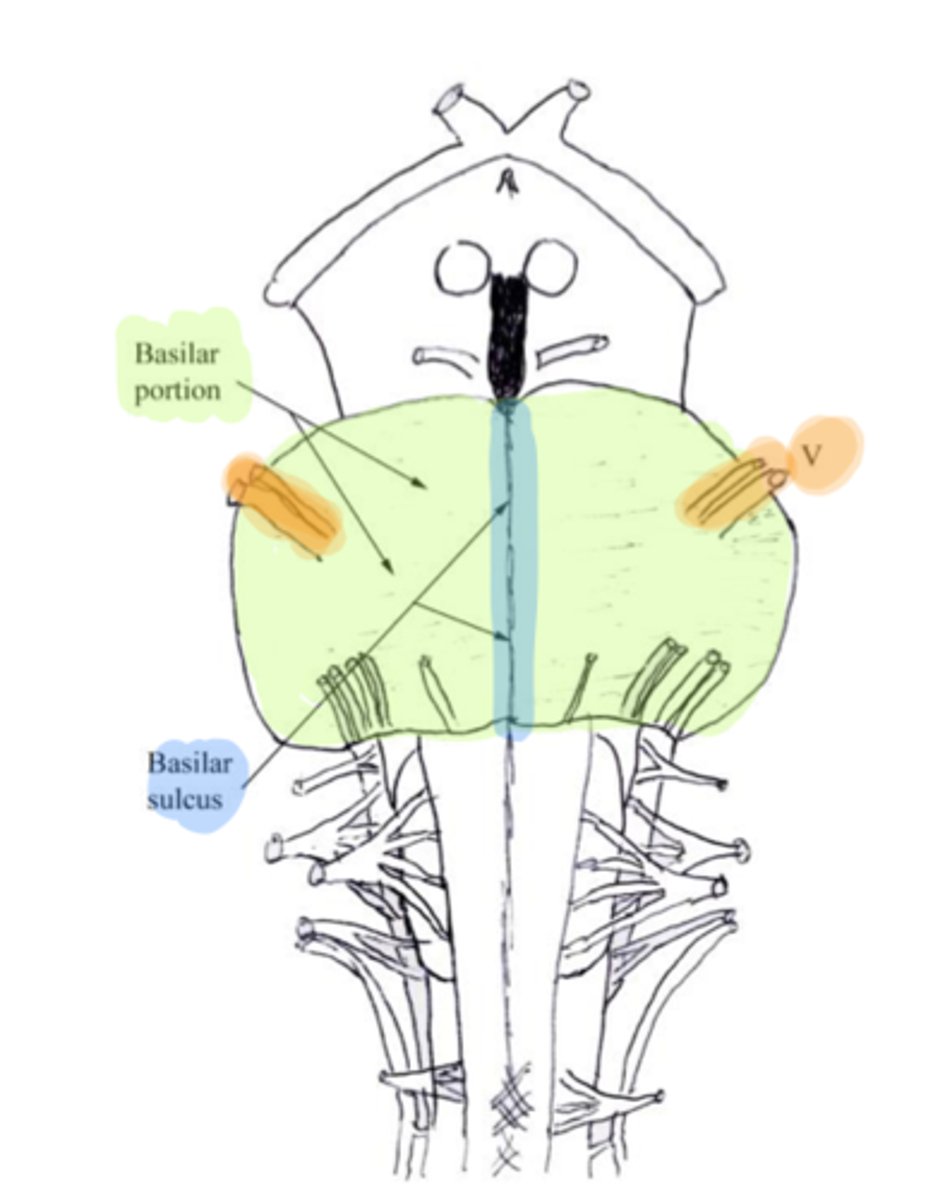
longitudinal midline groove of the pons that is the superior continuation of the ventral median sulcus/fissure, containing a namesake artery
basilar sulcus
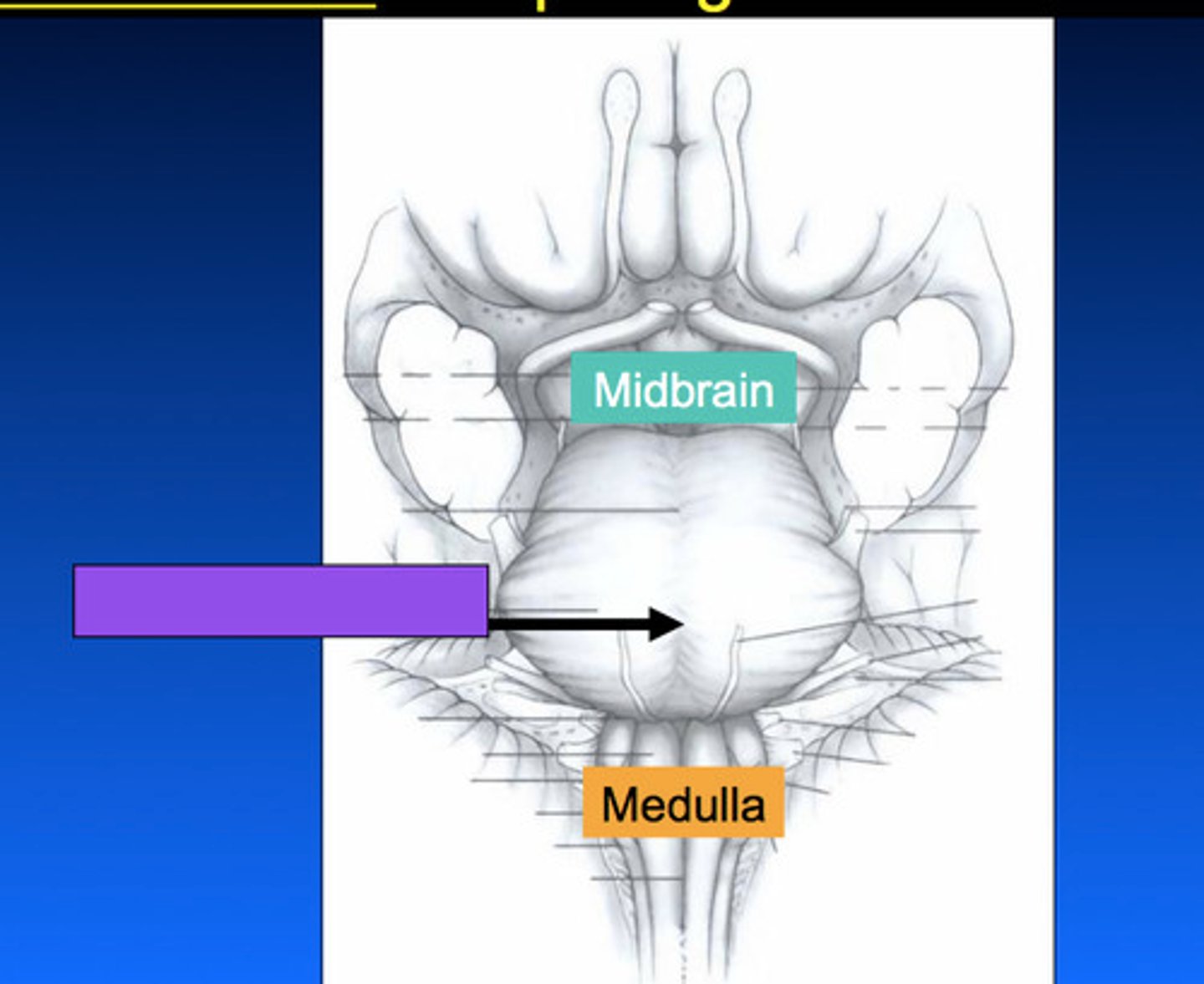
white matter stalks that connect the pons to the cerebellum
middle cerebellar peduncles
What is the only cranial nerve that attaches to the pons?
CN V
portion of the pons that is dorsal to the basilar portion and represents mostly longitudinally oriented fibers and cranial nerve nuclei
**also helps to form the floor of the 4th ventricle
tegmentum
A
basilar portion
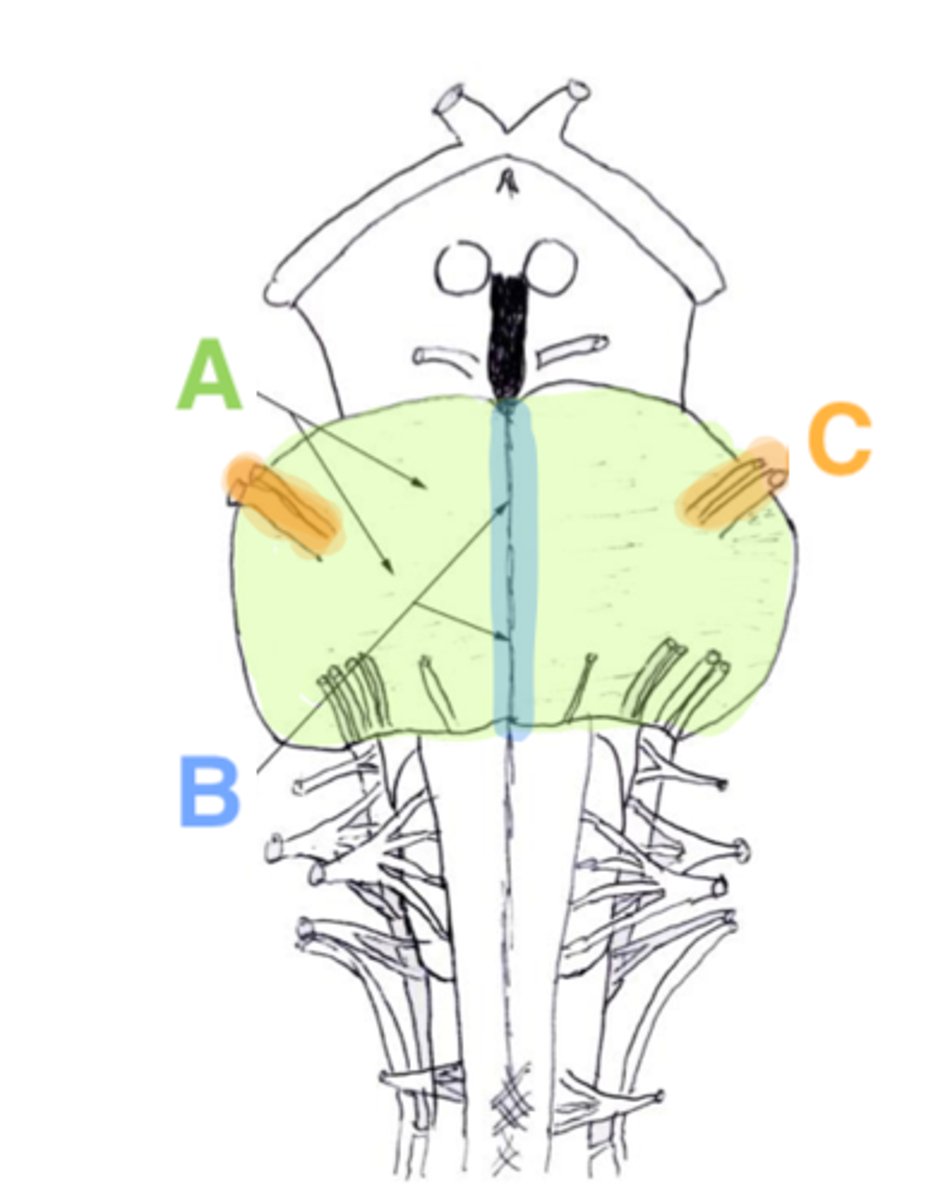
B
basilar sulcus
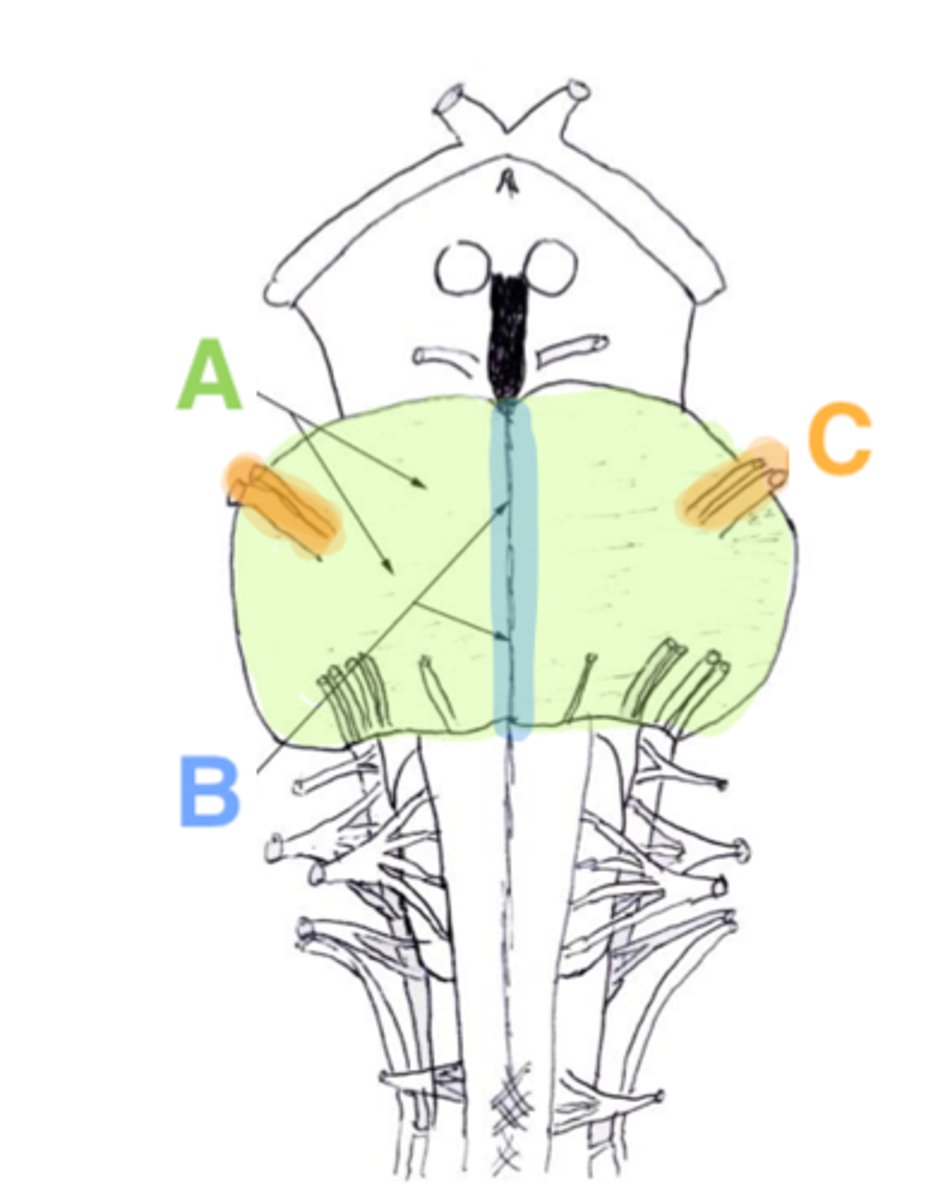
C
CN V
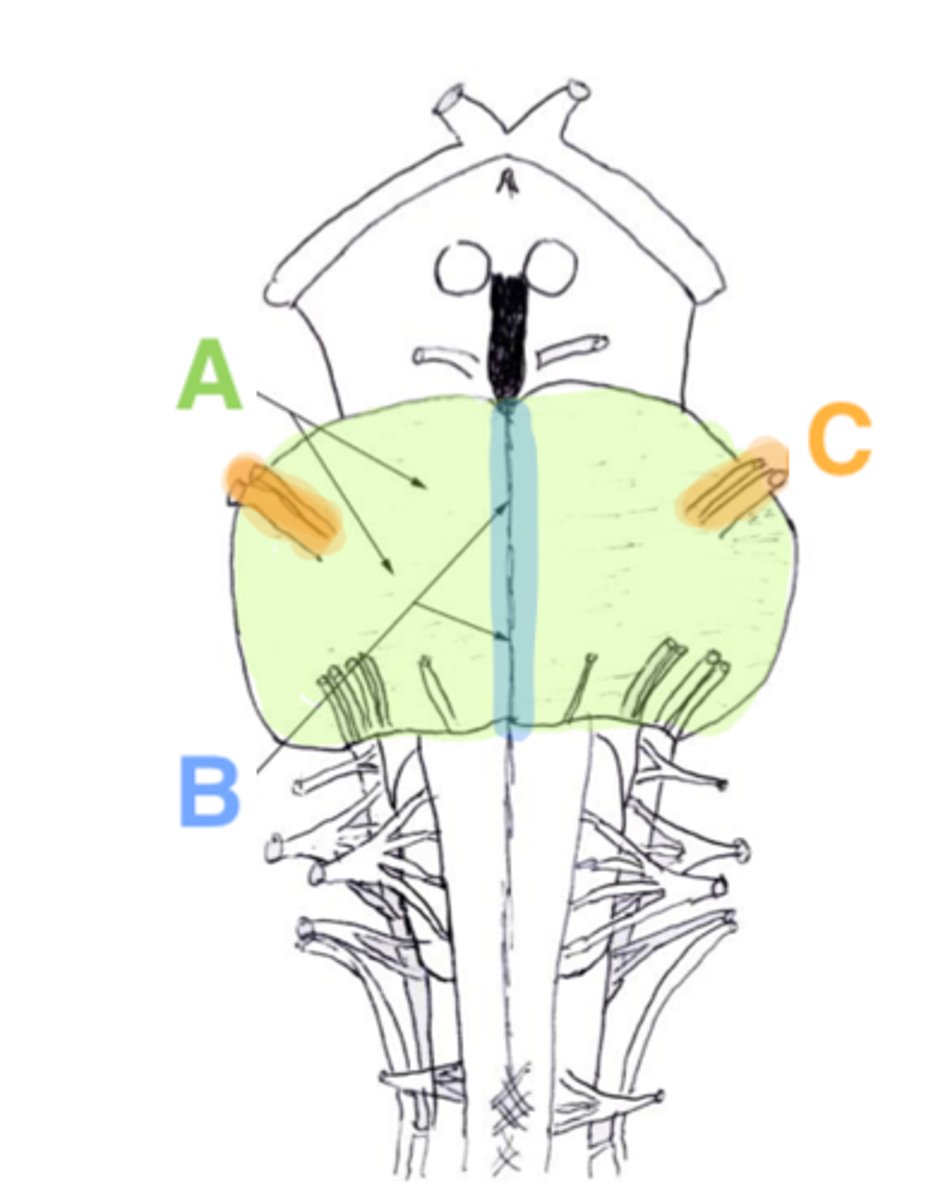
B
middle cerebellar peduncles
tegmentum
What anatomical aspect of the 4th ventricle is considered its floor?
ventral
refers to the floor of the 4th ventricle
rhomboid fossa
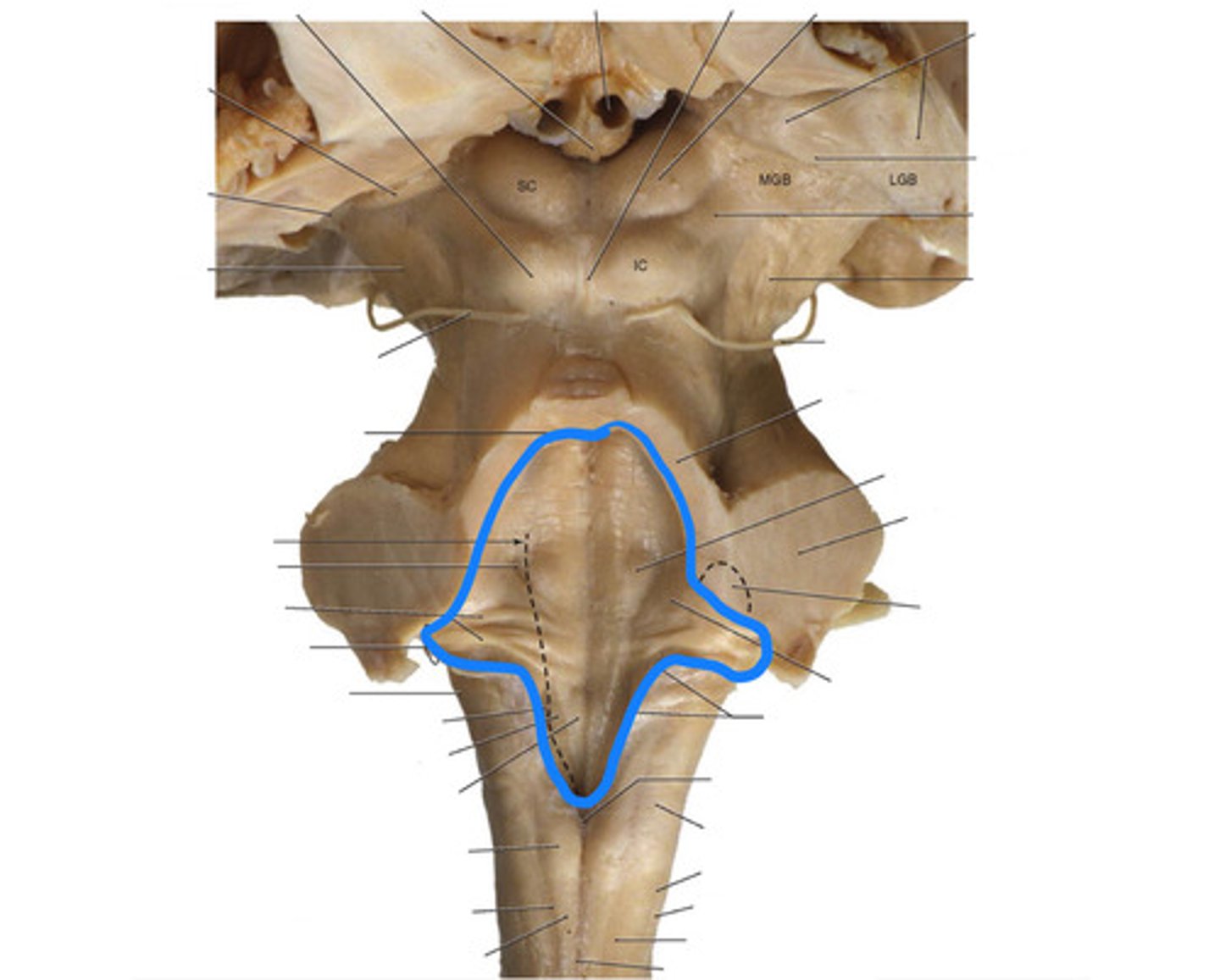
What forms the floor (rhomboid fossa) of the 4th ventricle?
dorsal surfaces of pons tegmentum and open medulla
inferior angle of the floor of the 4th ventricle
obex
vertical groove running in the floor of the 4th ventricle that separates it into right and left halves
dorsal median sulcus
vertical groove lateral to the dorsal median sulcus of the 4th ventricle
**same one that separated the alar and dorsal plates in the neural tube during development
sulcus limitans
refers to most of the floor of the 4th ventricle lateral to the sulcus limitans
**namesake nuclei are here
vestibular area
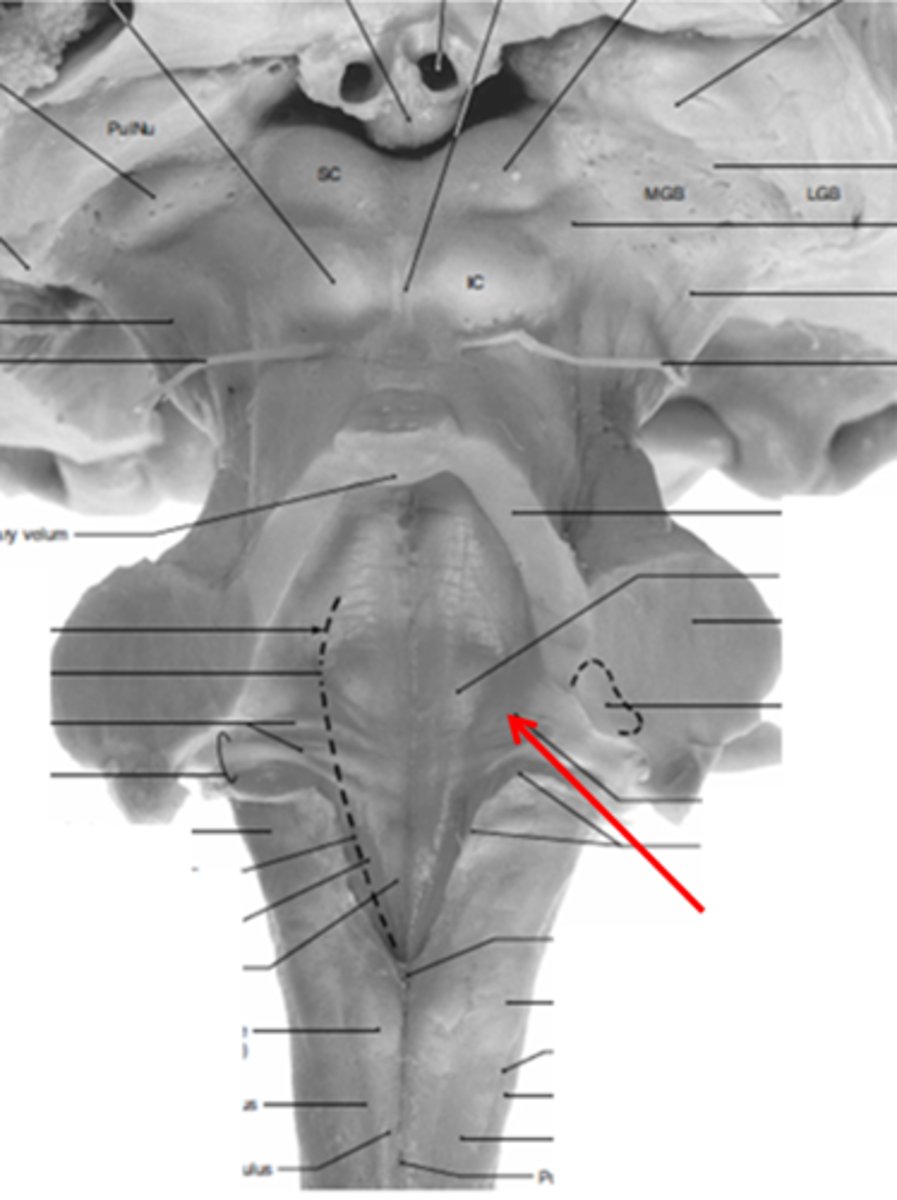
triangular region located in the caudal portion of the rhomboid fossa of the 4th ventricle, where the dorsal motor nucleus of CN X is
vagal trigone

Which parasympathetic nucleus is found in the vagal trigone of the 4th ventricle?
dorsal motor nucleus of X
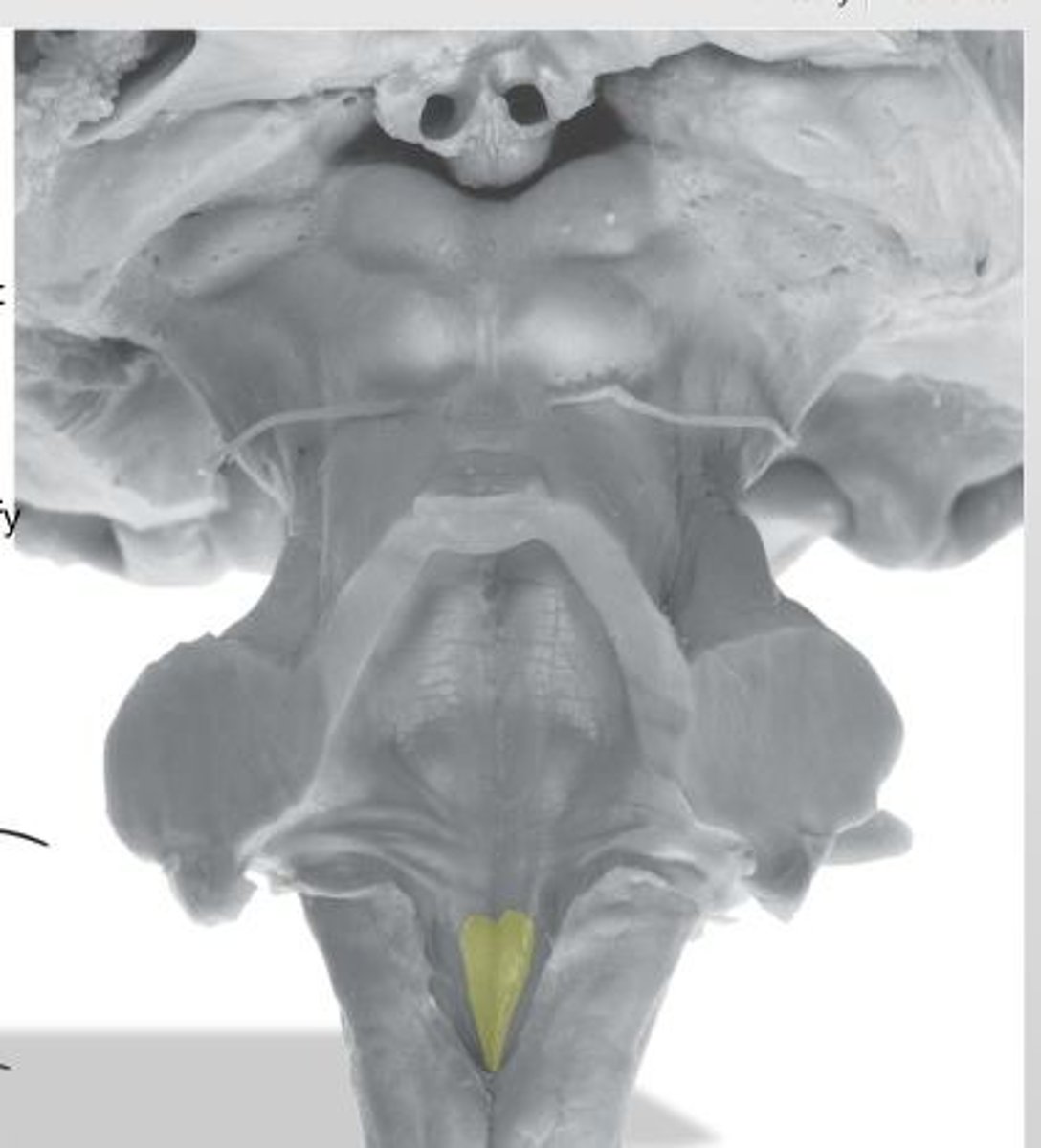
triangular region located most medially in the caudal portion of the rhomboid fossa of the 4th ventricle, where the CN XII nucleus is
hypoglossal trigone
part of the 4th ventricle superior to the vagal and hypoglossal trigones (still medial to the sulcus limitans)
medial eminence
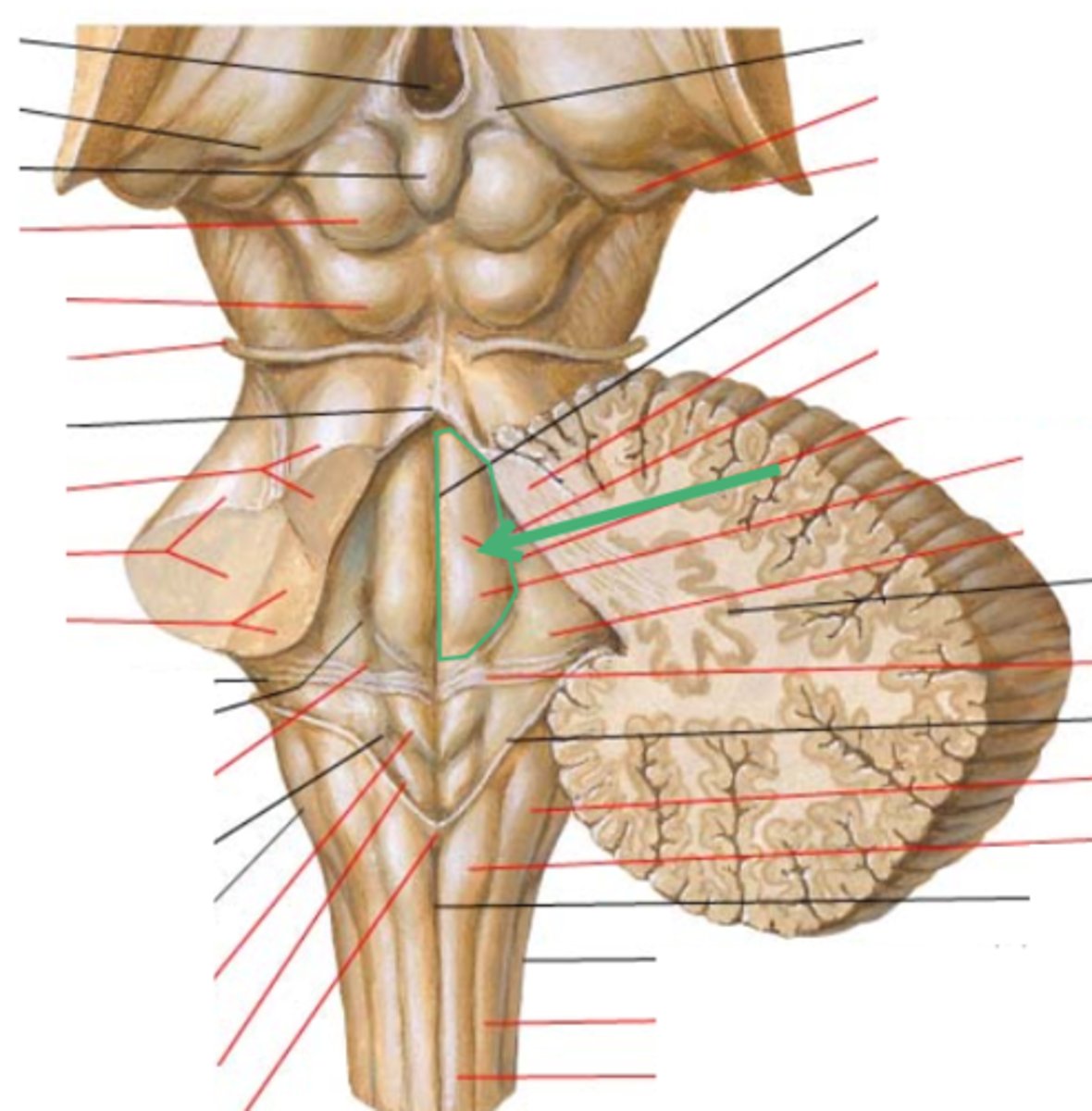
small bump located in the caudal portion of the medial eminence which forms from the motor fibers of CN VII as they wind around the underlying CN VI nucleus
facial colliculus
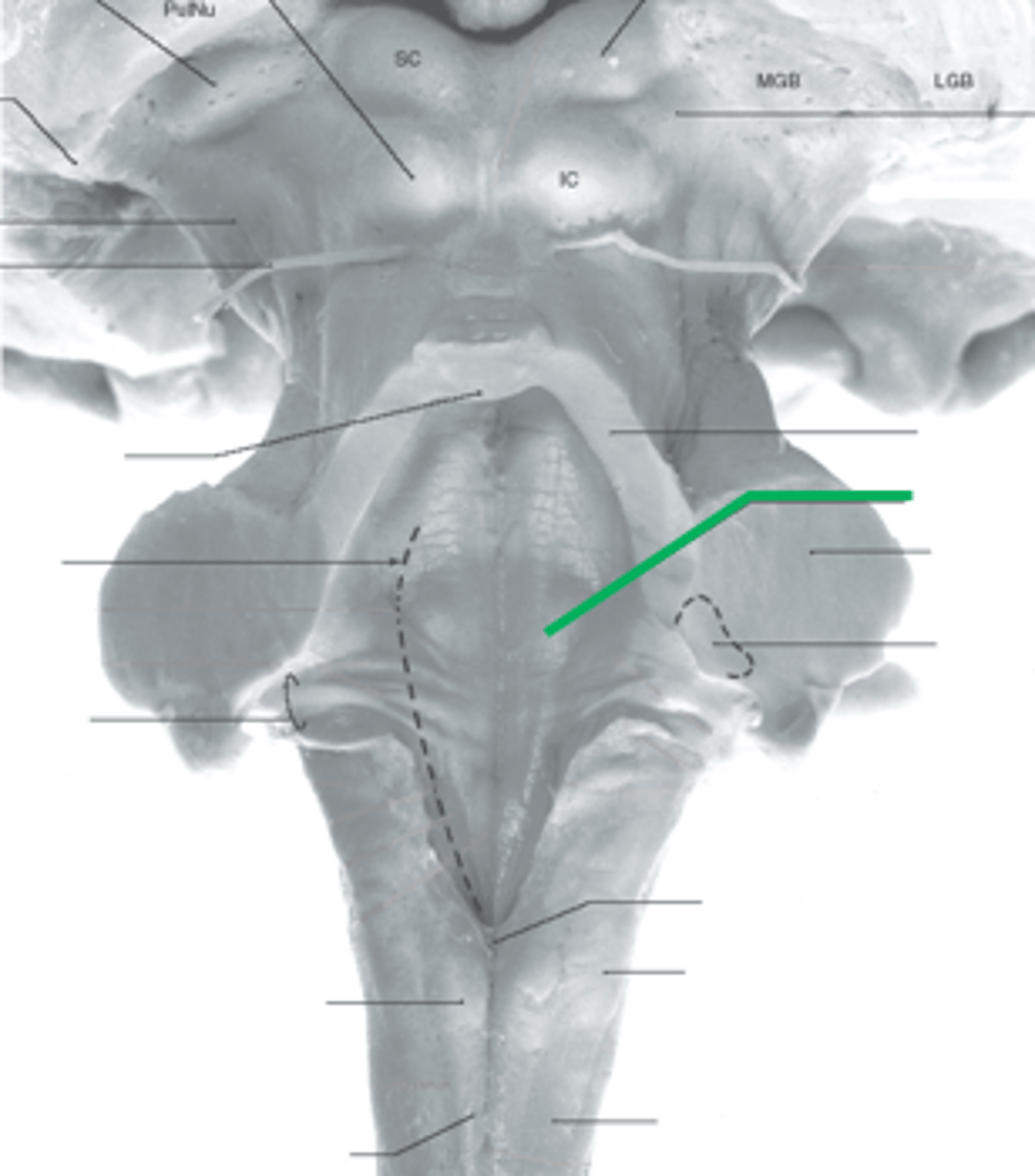
pigmented area that looks blue near the superior aspect of the sulcus limitans; cluster of noradrenergic cells
locus ceruleus
fibers that run horizontally in the central region of the rhomboid fossa of the 4th ventricle
stria medullares
area that helps to make the walls of the obex and is thought to be the "vomit trigger"
area postrema
What anatomical aspect of the 4th ventricle is considered its roof?
dorsal
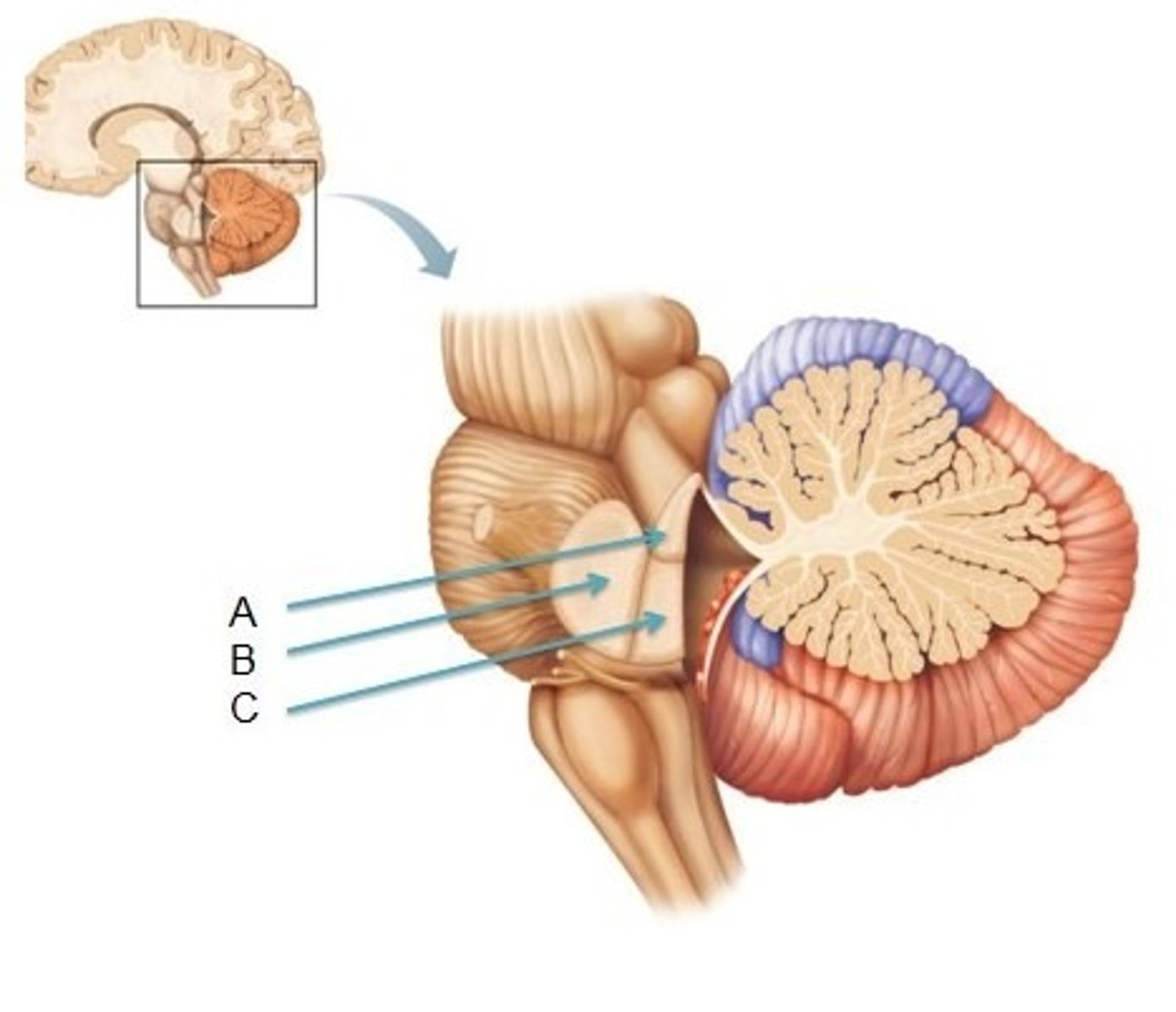
What forms the superior portion of the roof of the 4th ventricle? (A)
superior cerebellar peduncles
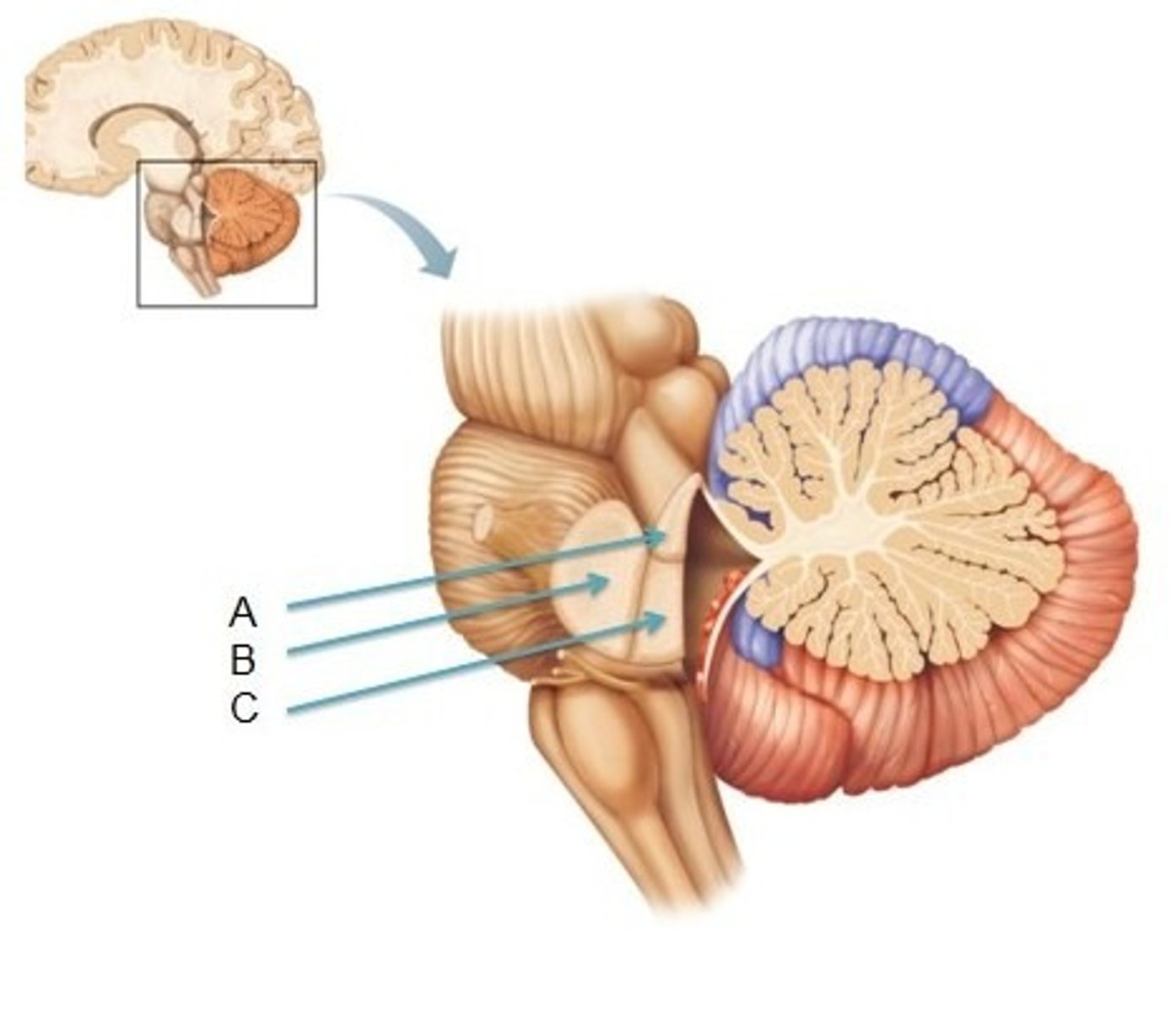
inverted V shaped interval between the superior cerebellar peduncles that is filled by a thin layer of white matter
superior medullary velum
lower portion of the roof of the 4th ventricle formed by a thin layer of pia mater and ependymal cells
inferior medullary velum
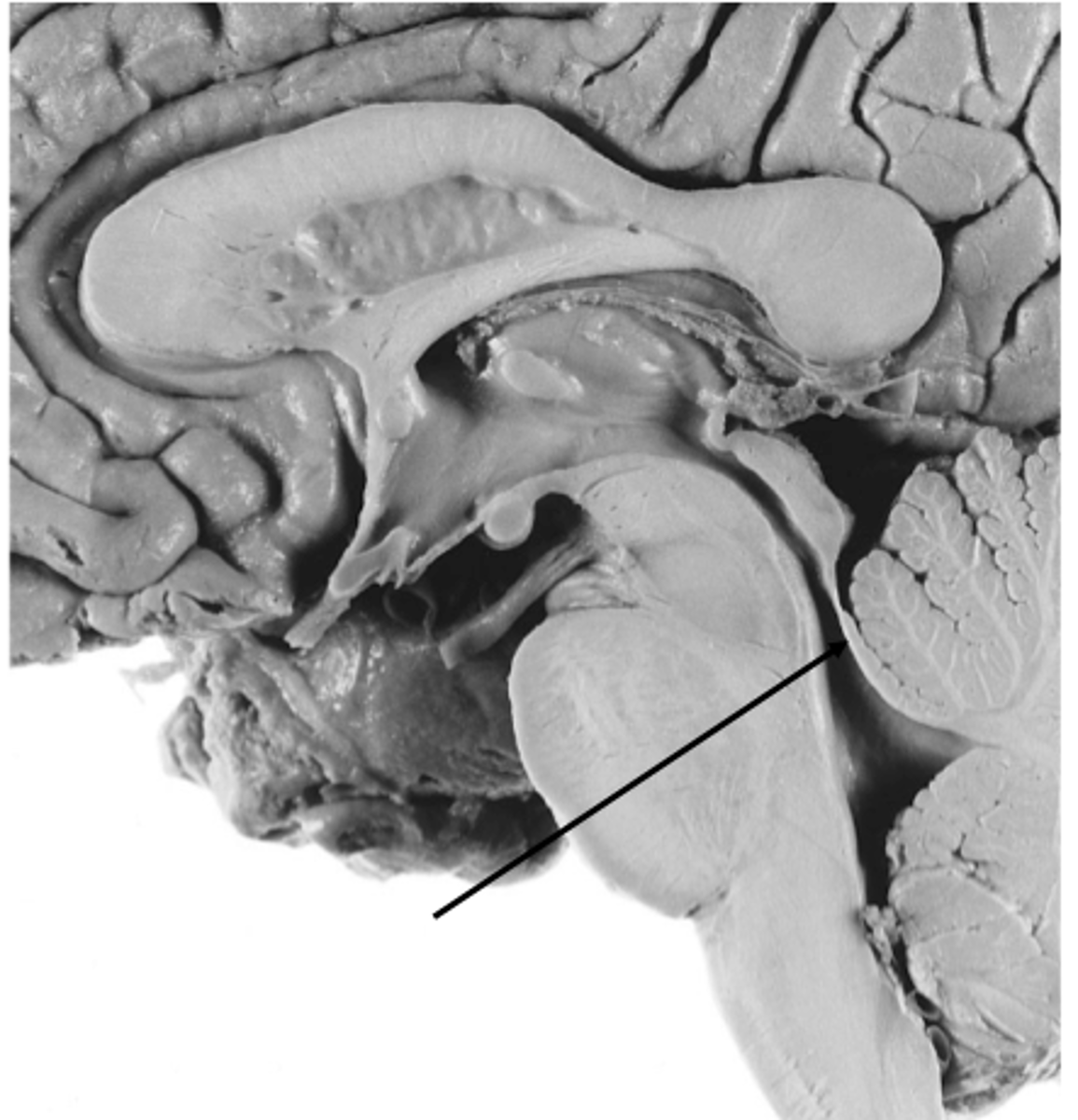
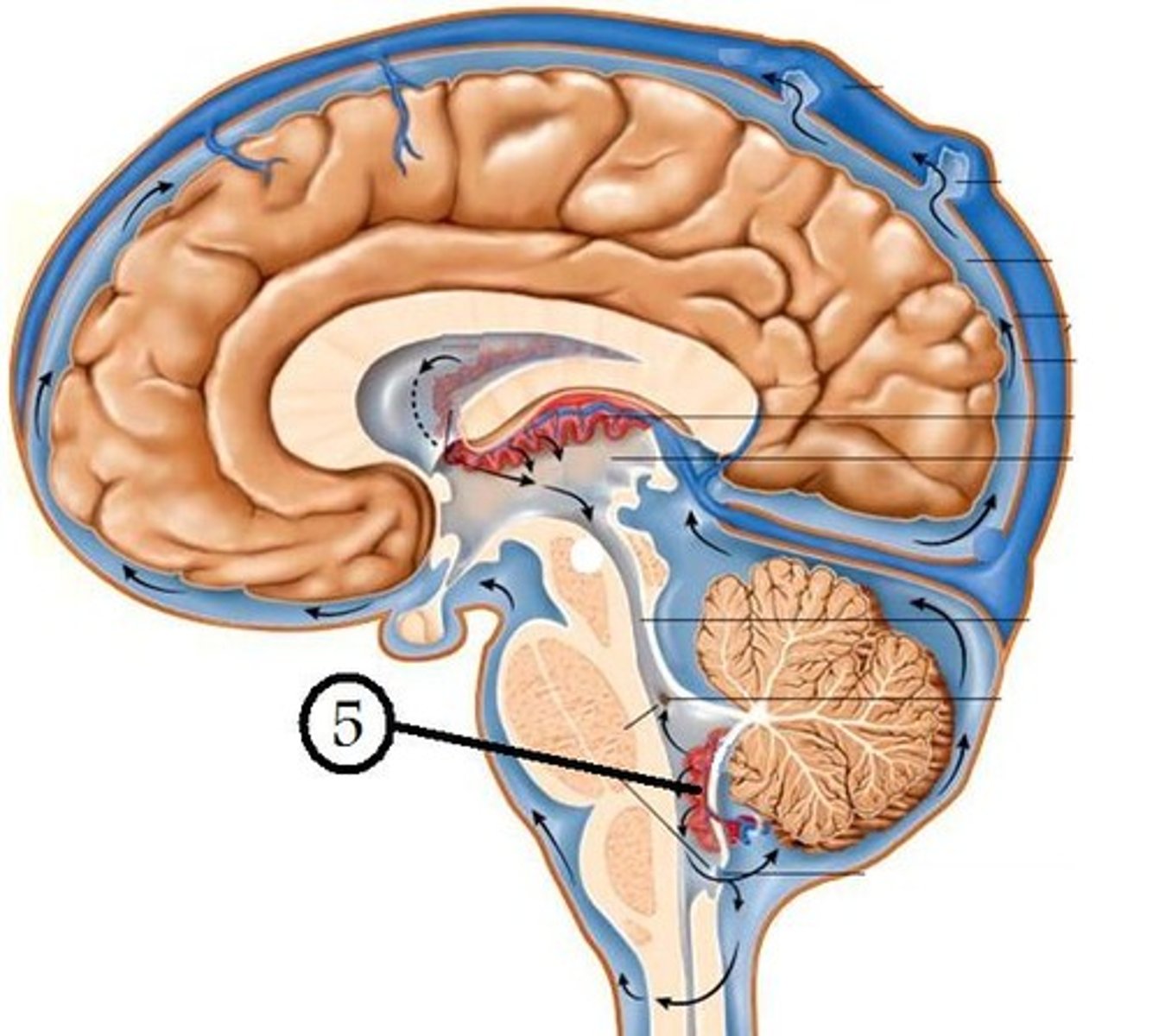
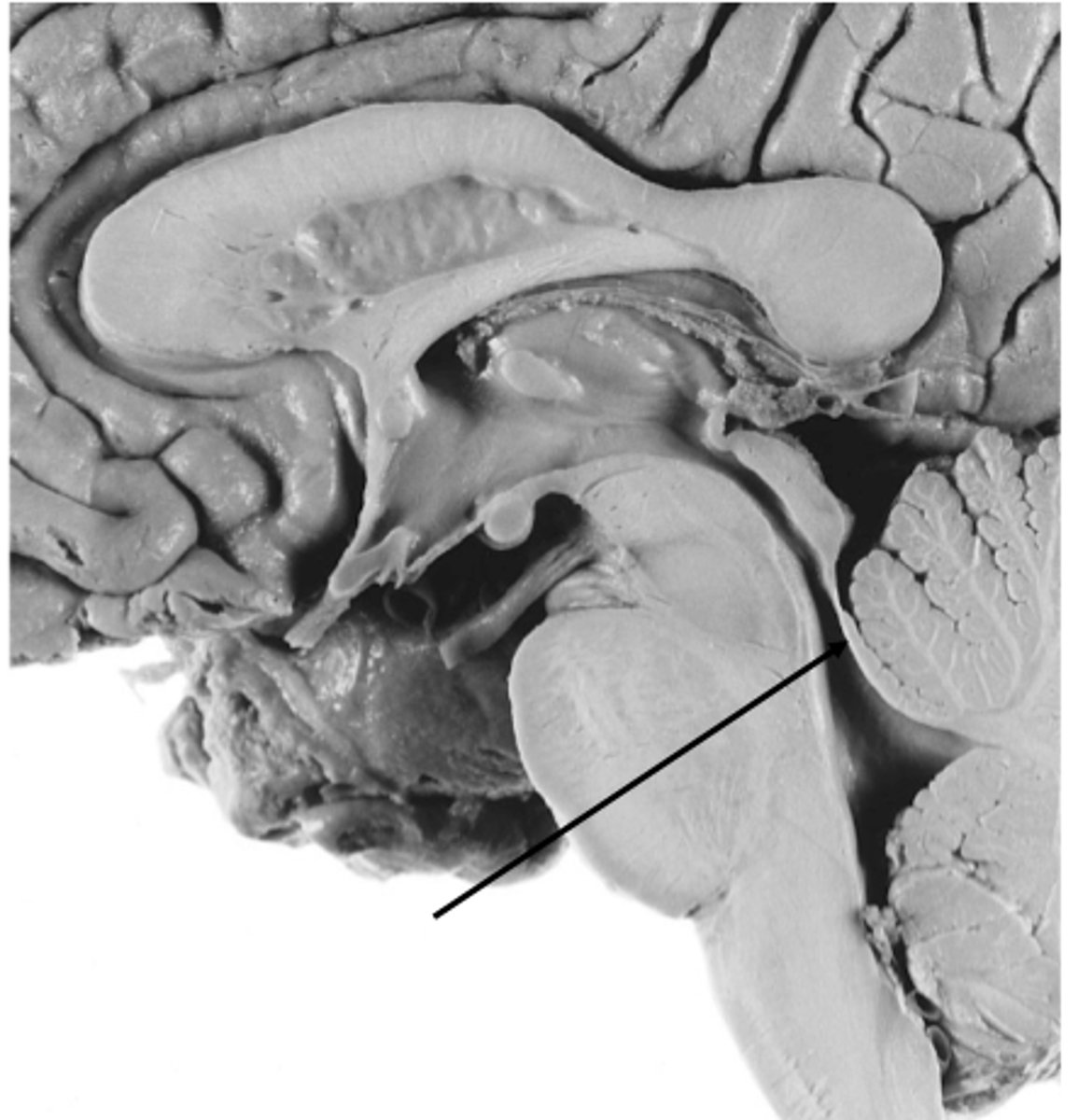
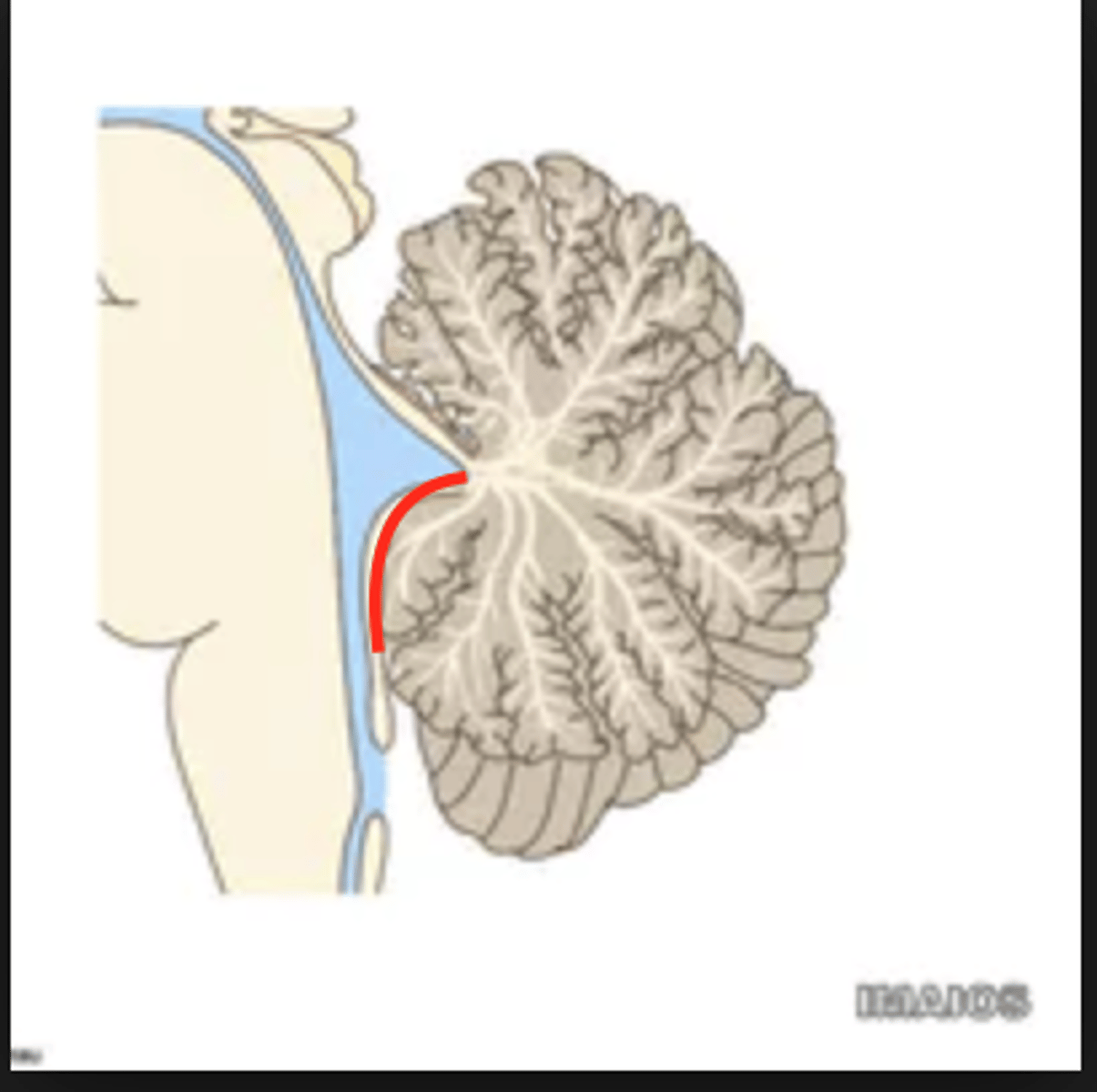
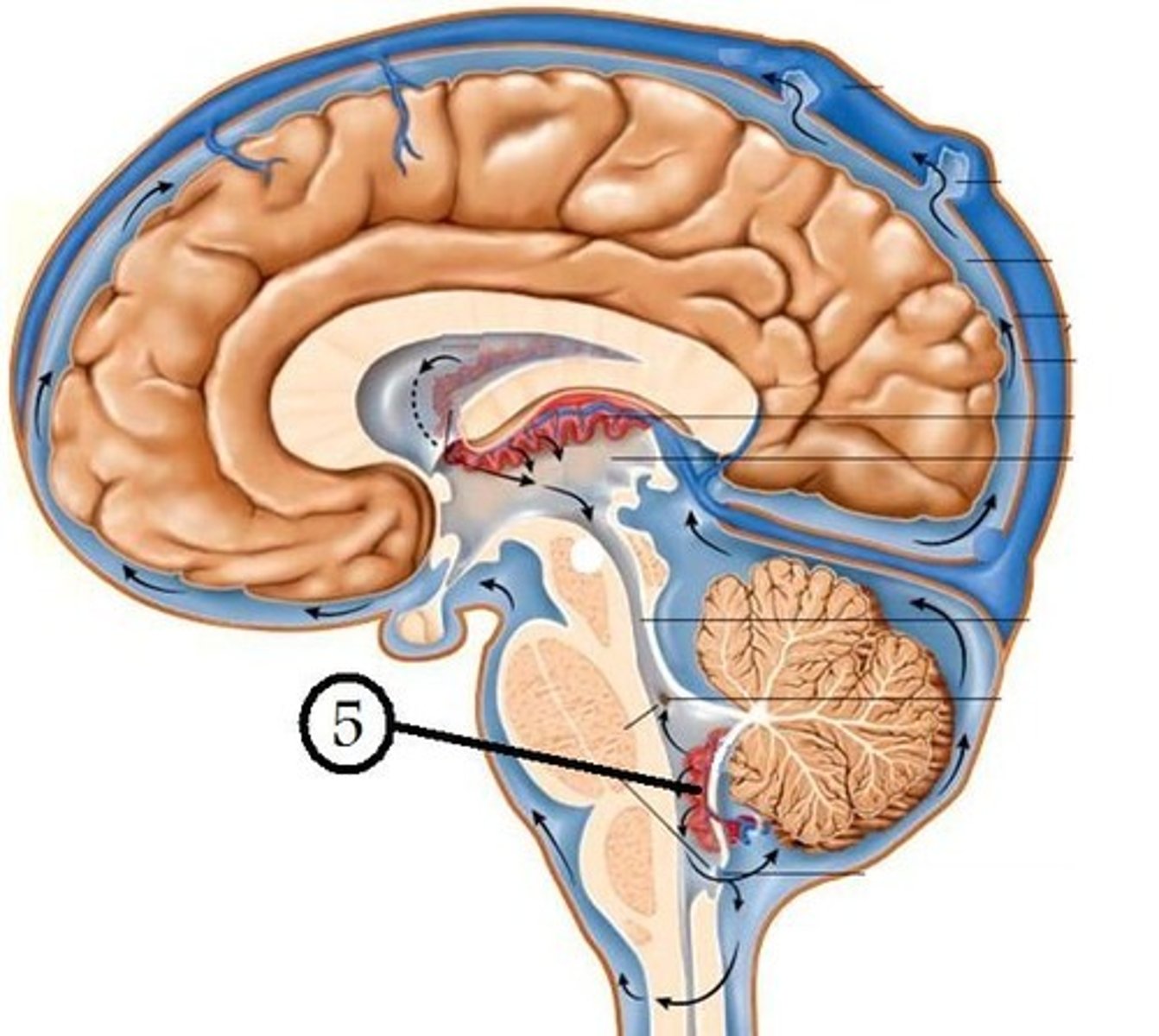
structure attached to the ventral surface of the inferior medullary velum in the 4th ventricle that helps form CSF
choroid plexus
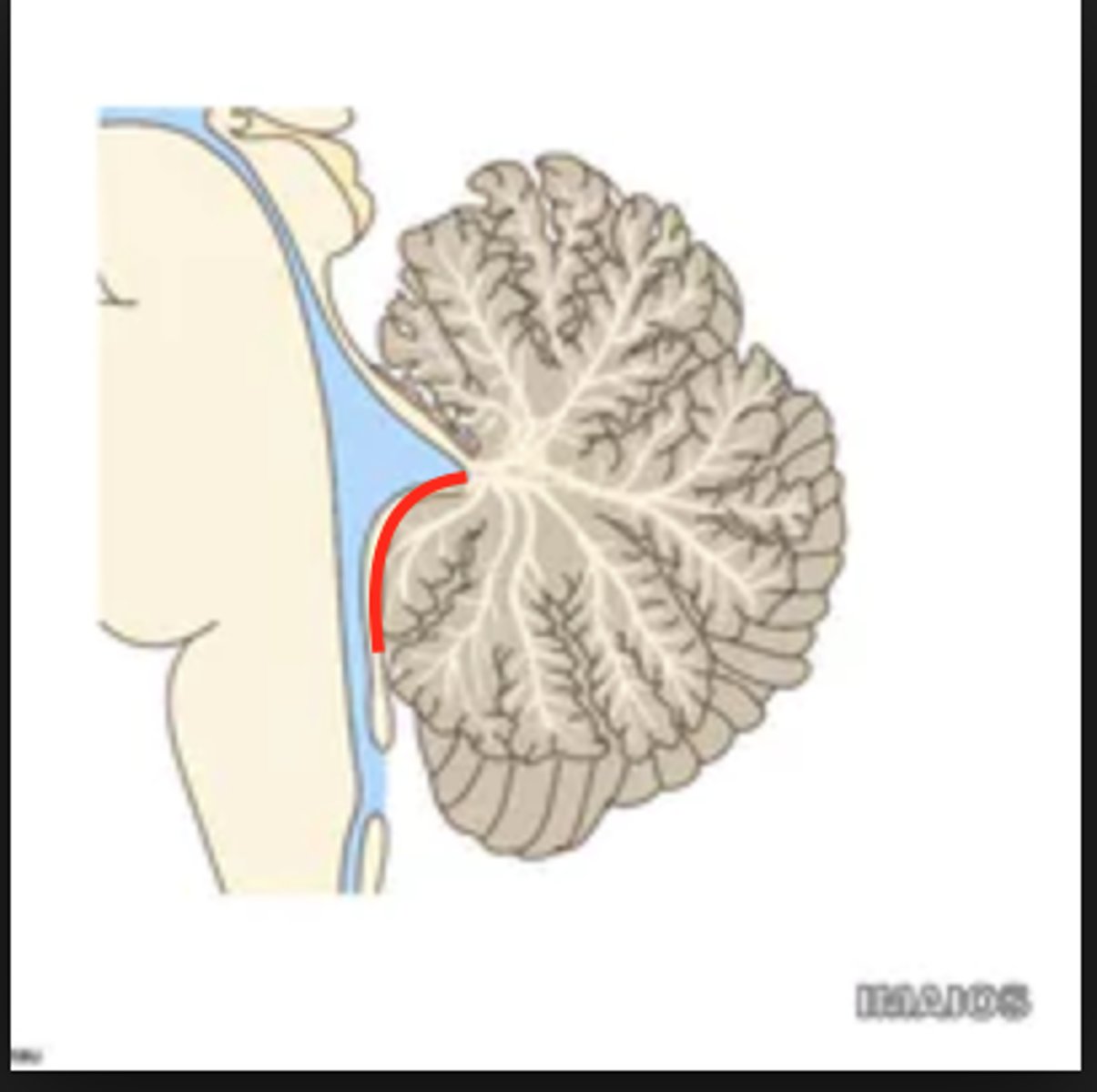
opening in the caudal aspect of the inferior medullary velum that allows CSF from the 4th ventricle to flow into the cisterna magna of the subarachnoid space
foramen of Magendie (or median aperture)
What mostly forms the lateral walls of the 4th ventricle?
inferior cerebellar peduncles and choroid plexus
openings in the 4th ventricle that allows CSF to flow from the 4th ventricle into the pontine cistern of the subarachnoid space
foramen of von Luschka (or lateral apertures)
floor of 4th ventricle
rhomboid fossa
sulcus limitans
floor of 4th ventricle lateral to sulcus limitans
vestibular area
vasal trigone
hypoglossal trigone
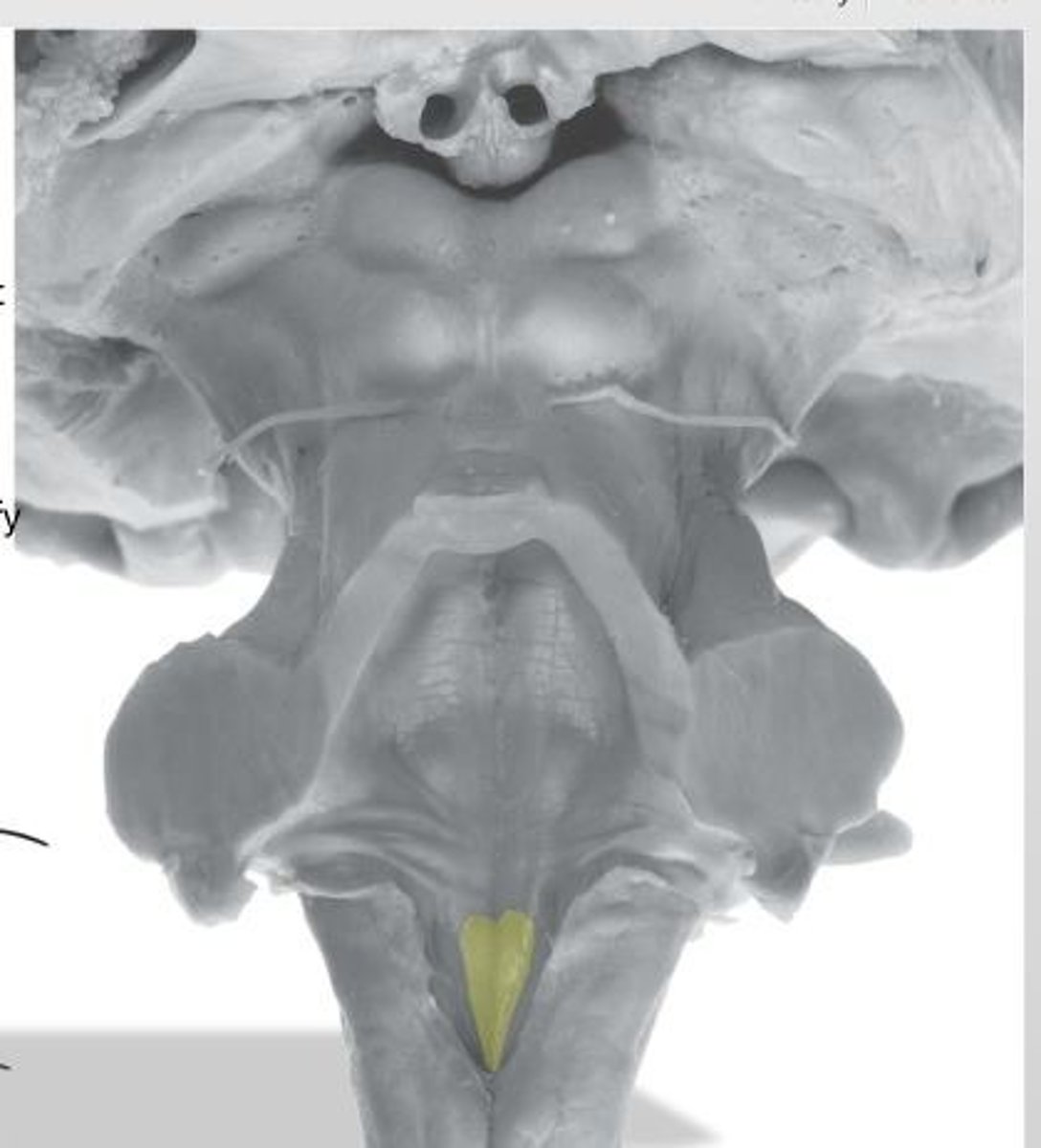
medial eminence
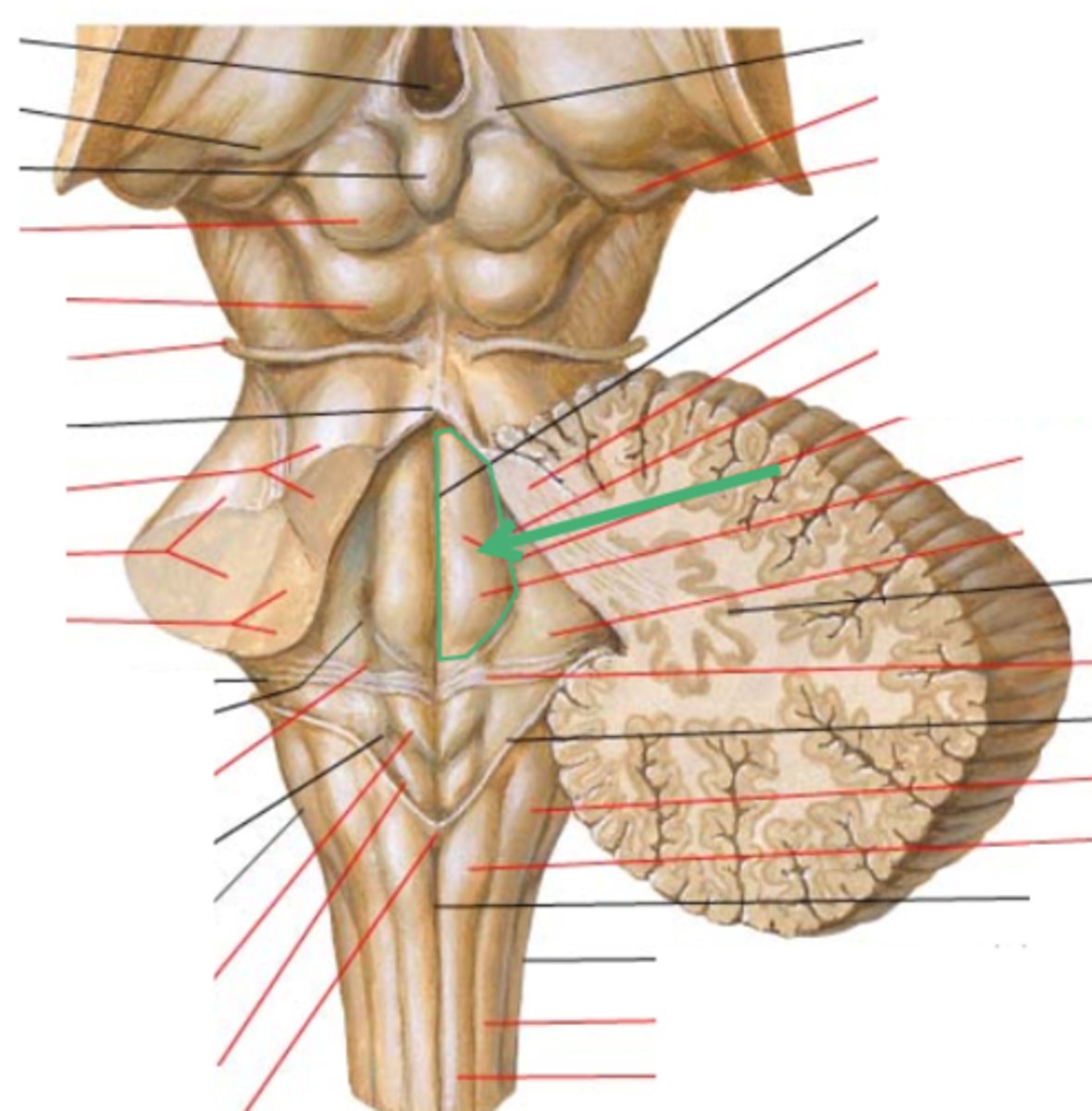
small bump in caudal portion of medial eminence
facial colliculus
stria medullares
A
superior cerebellar peduncles
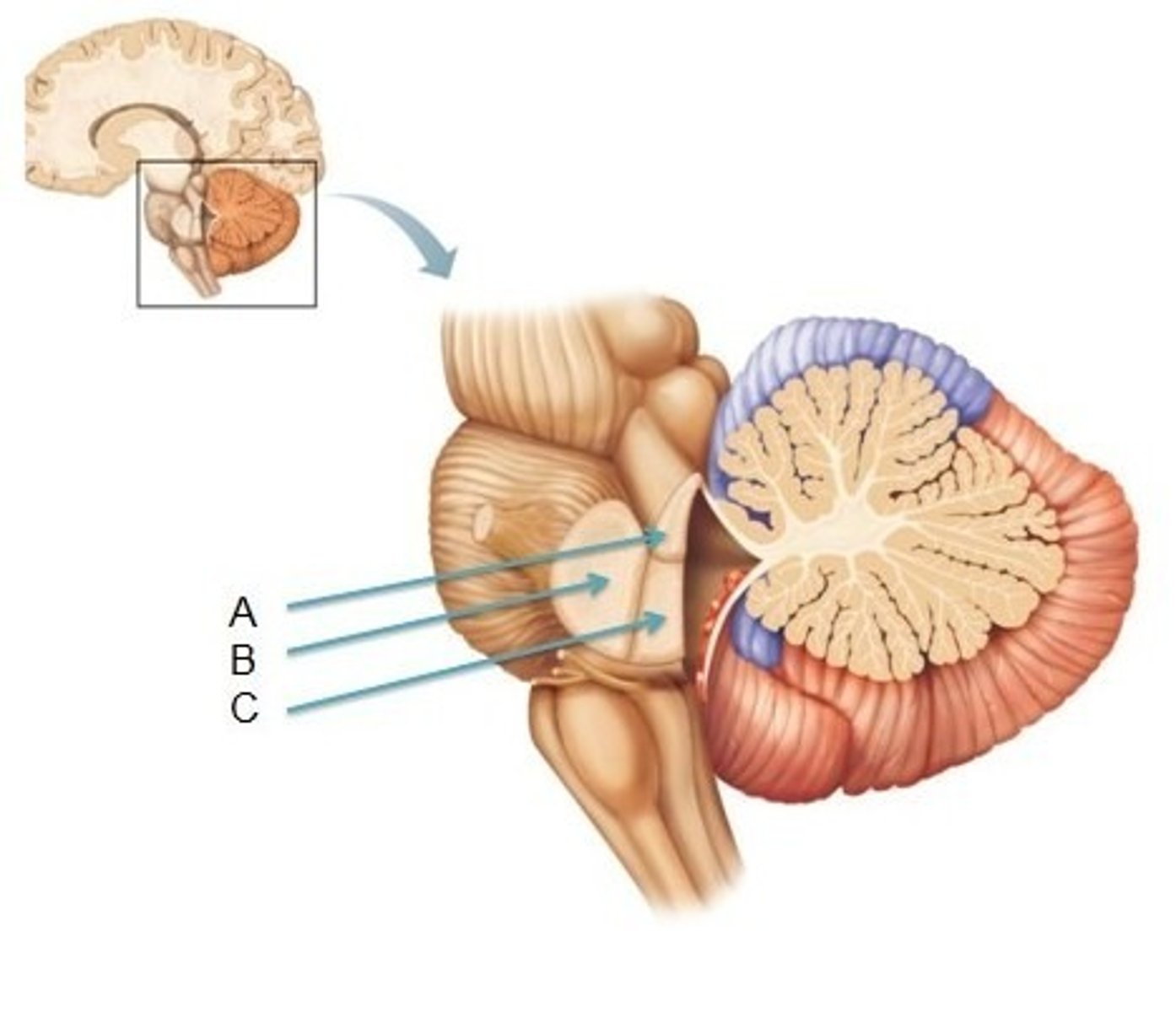
superior medullary velum
inferior medullary velum
What is the superior boundary of the midbrain?
just under the mamillary bodies of the diencephalon
What is the inferior boundary of the midbrain?
isthmus of brain stem
opening running through the midbrain that separates it into the cerebral peduncles and tectum
cerebral aqueduct (iter or aqueduct of Sylvius)
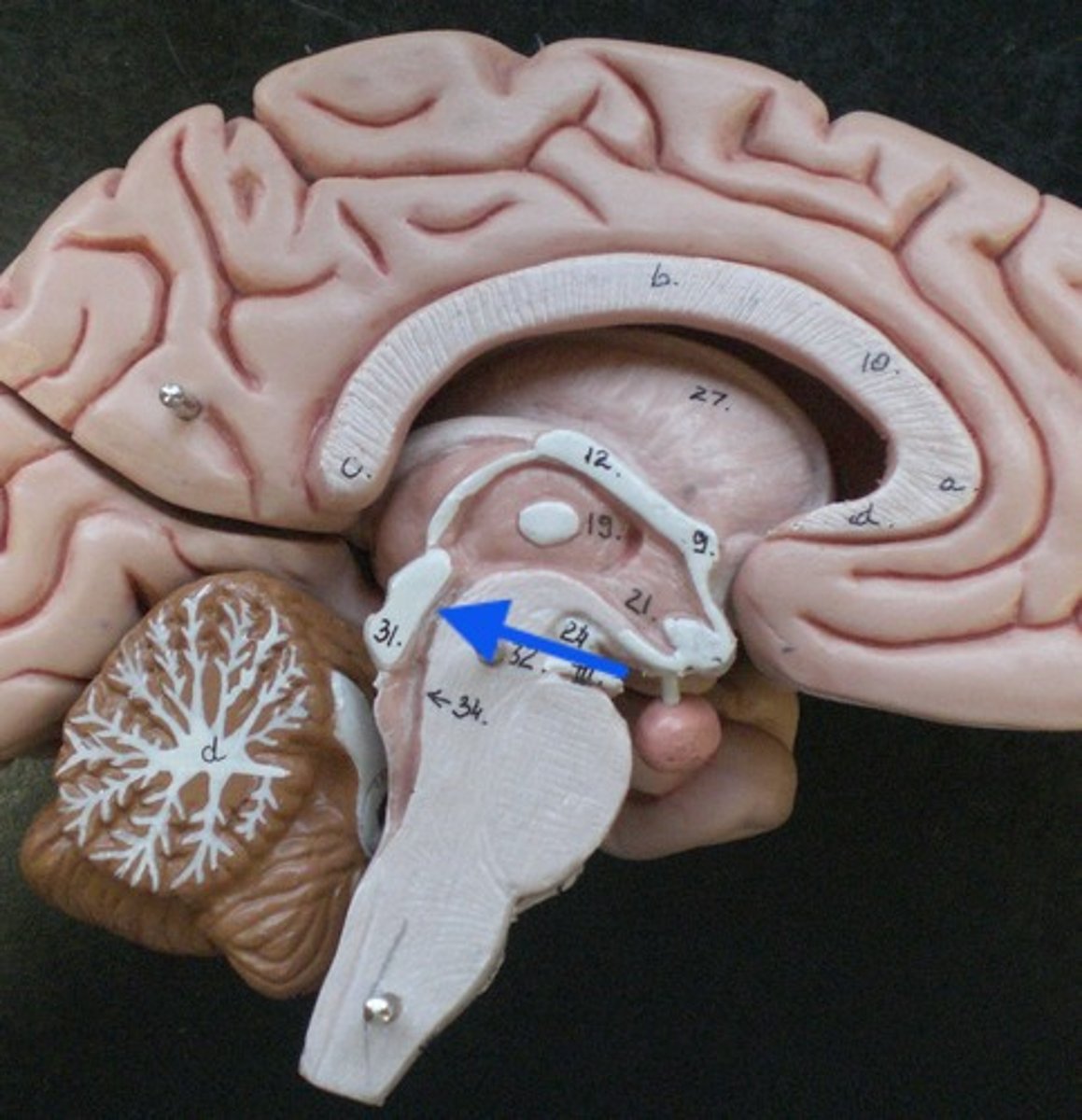
What does the cerebral aqueduct separate the midbrain into?
cerebral peduncles, tectum
area separating the cerebral peduncles
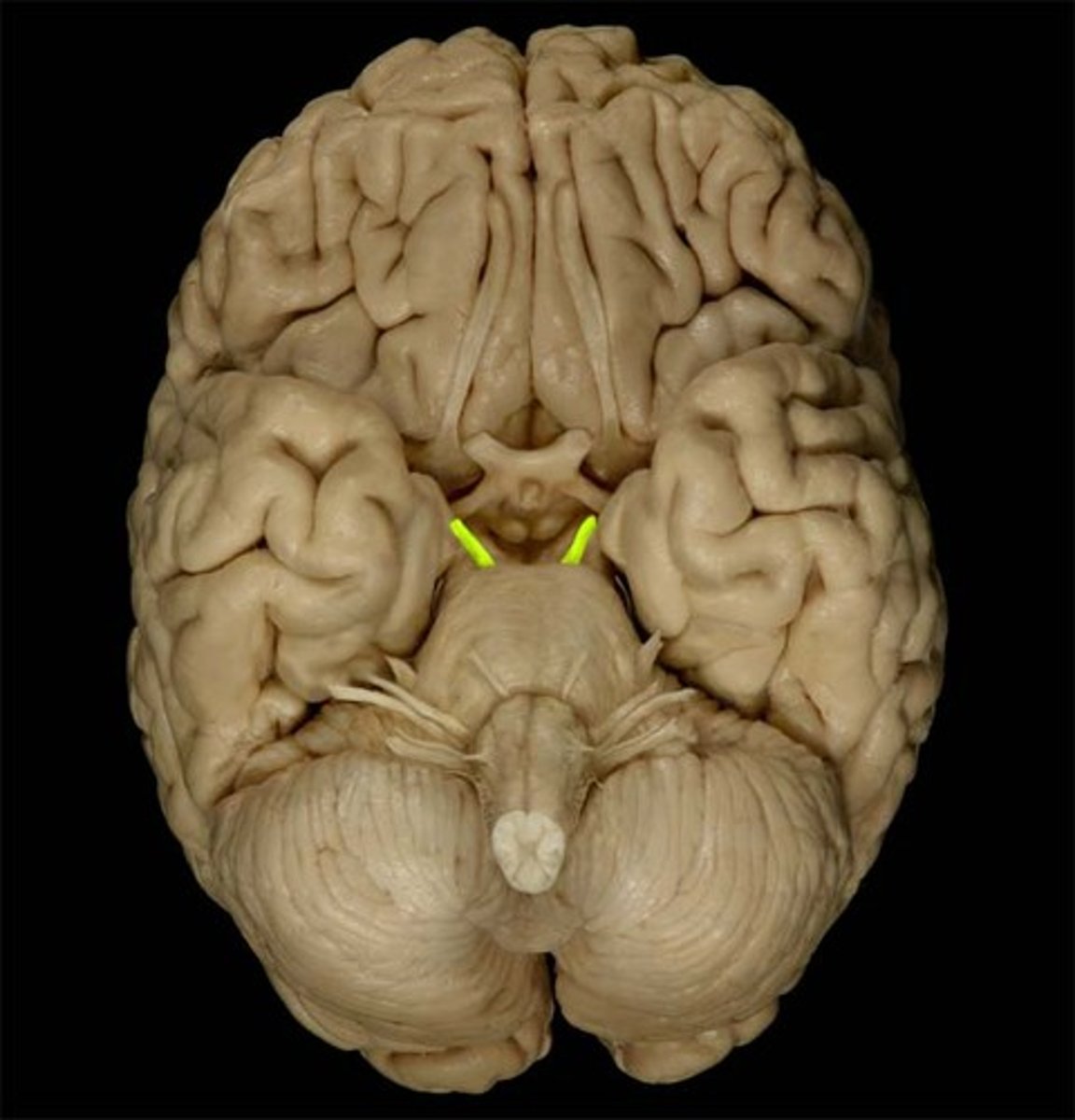
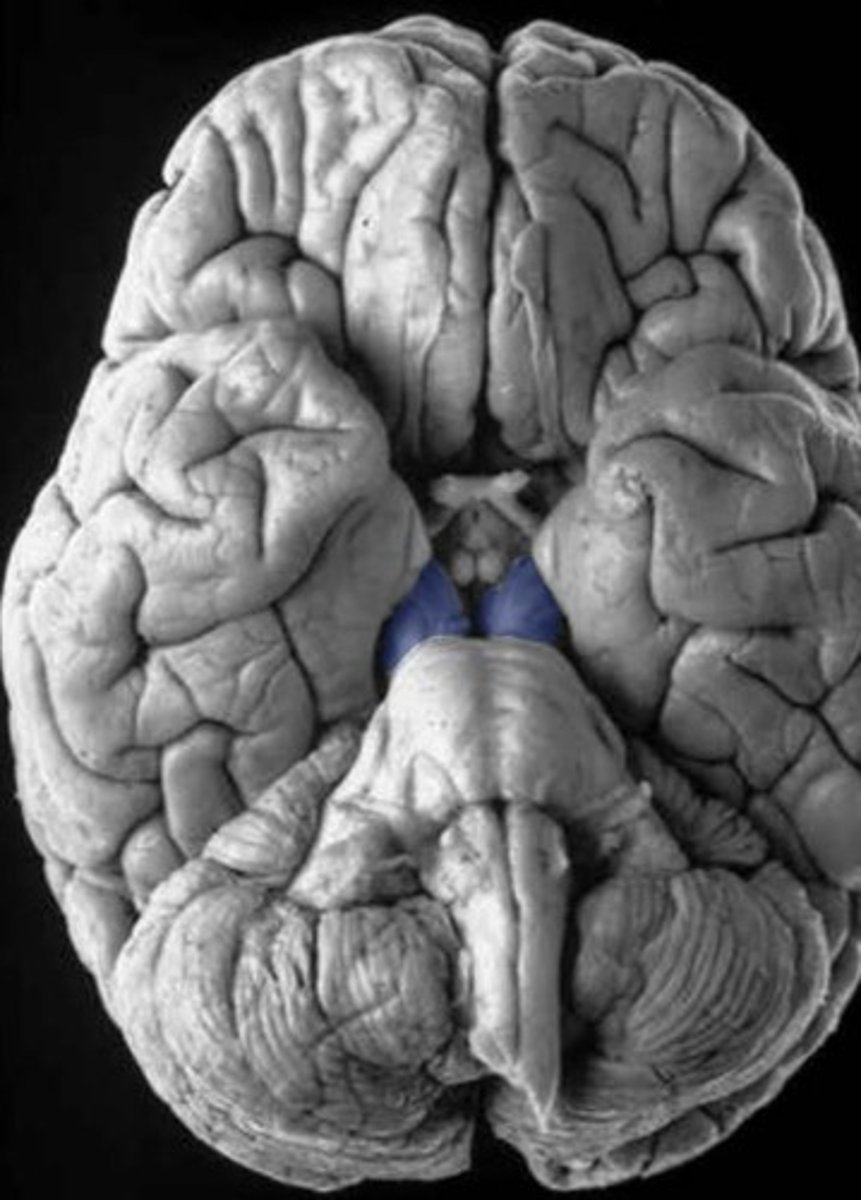
interpeduncular fossa
Which cranial nerve emerges from the floor of the interpeduncular fossa?
CN III
refers to the ventral part of the cerebral peduncles
columns of white matter that are the corticospinal and corticonuclear (upper motor neuron fibers going to cranial nerve nuclei) running through the midbrain
basis pedunculi (or crus cerebri)
refers to the dorsal part of the cerebral peduncles
tegmentum
(continuous with tegmentum of pons)
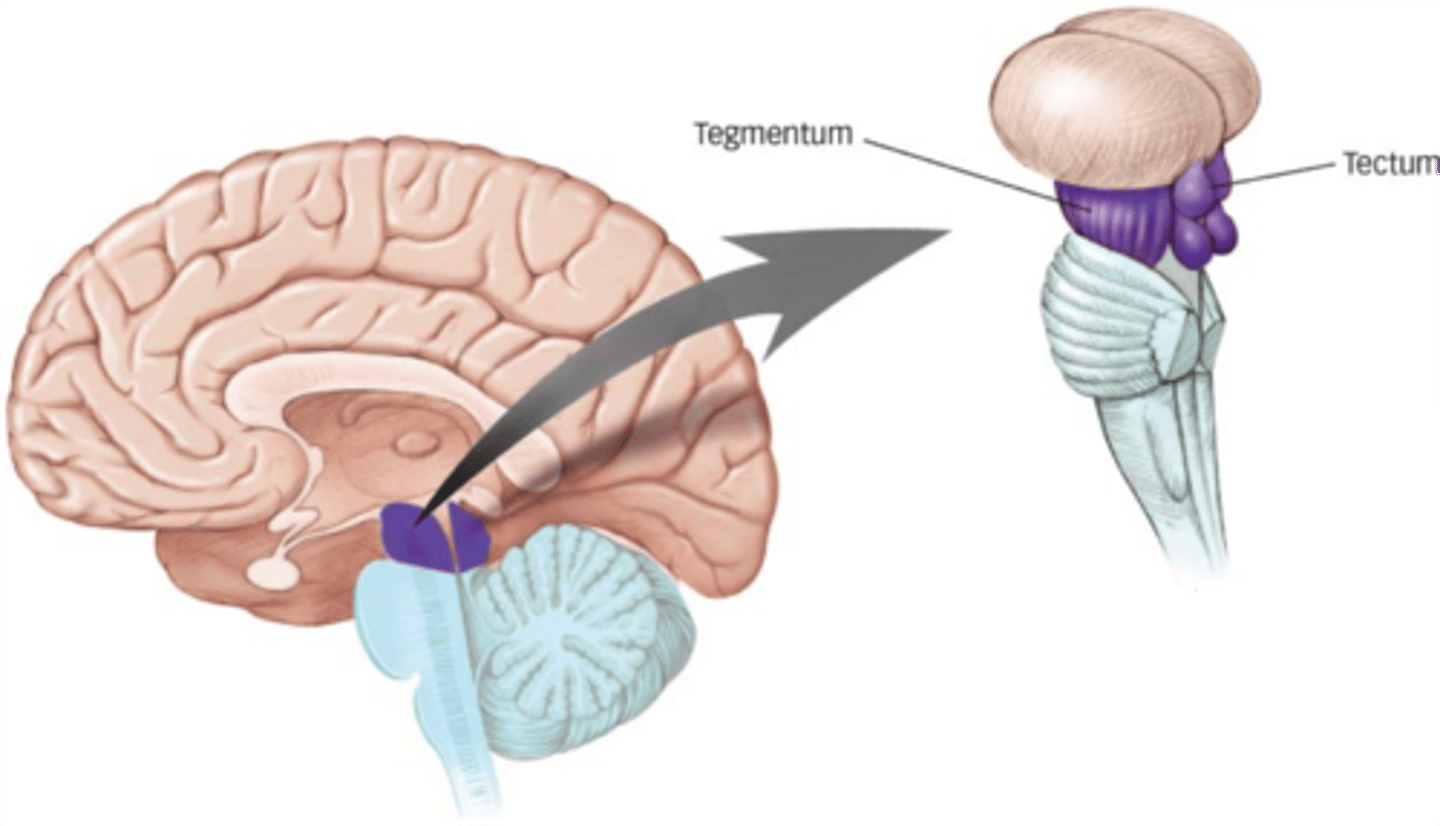
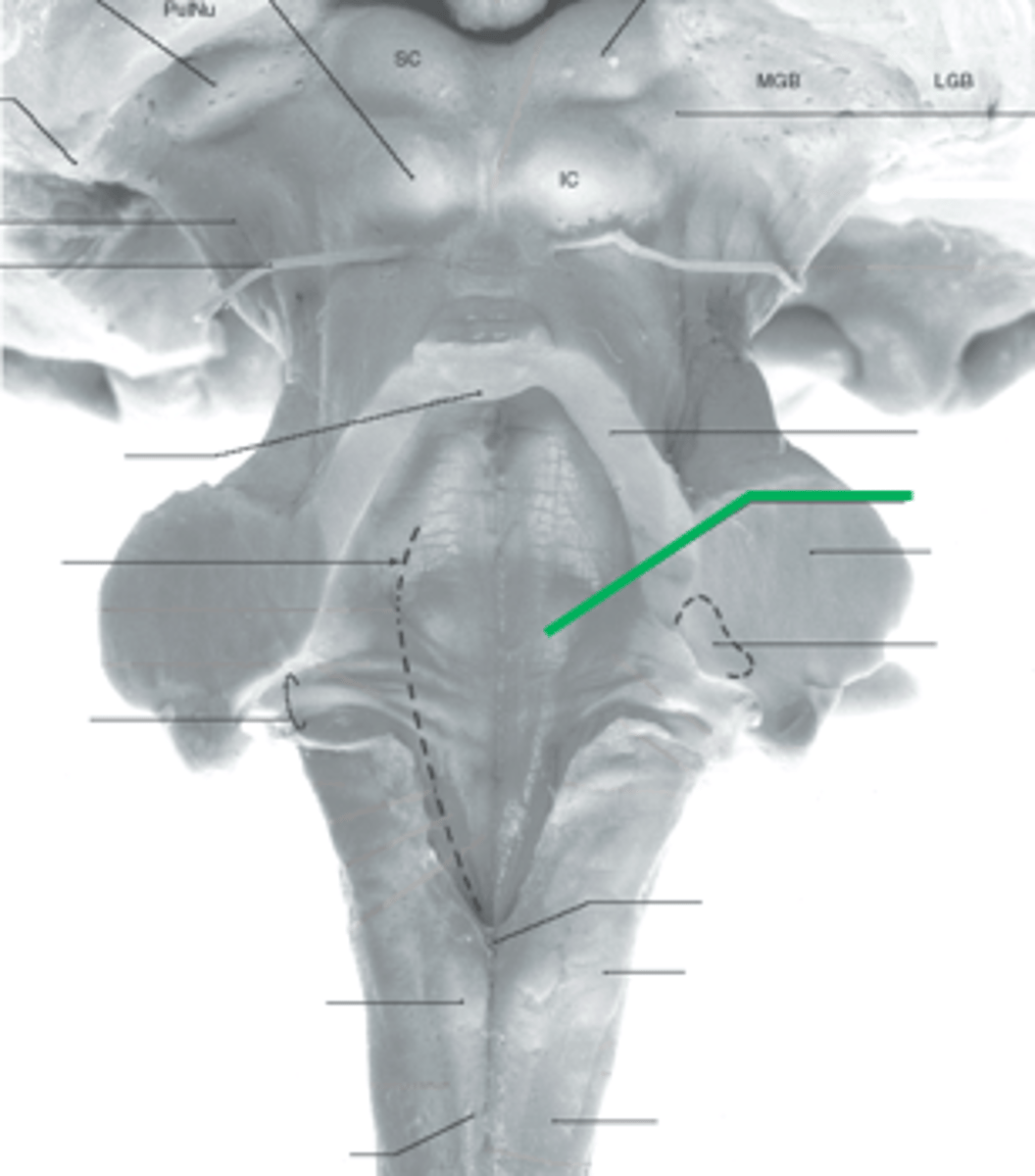
part of the midbrain that consists mainly of two (2) pairs of small mounds known collectively as the corpora quadrigemini
tectum
2 pairs of small mounds on the tectum of the midbrain
corpora quadrigemini
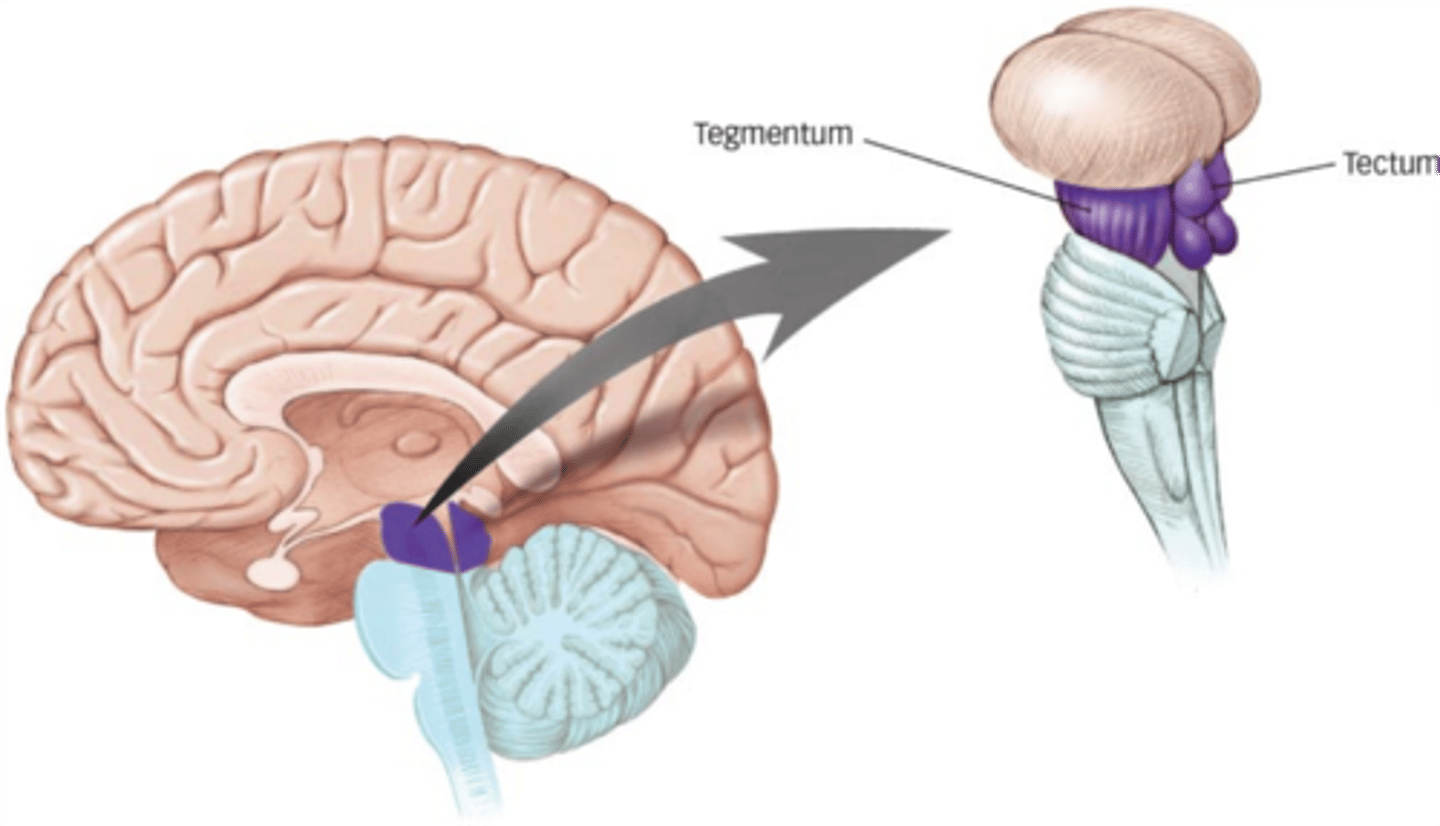
ridge of white matter extending laterally from each SUPERIOR colliculus in the corpora quadrigemini of the tectum of the midbrain
superior brachium
What is included in the lower pair of corpora quadrigemini in the tectum of the midbrain?
inferior colliculi
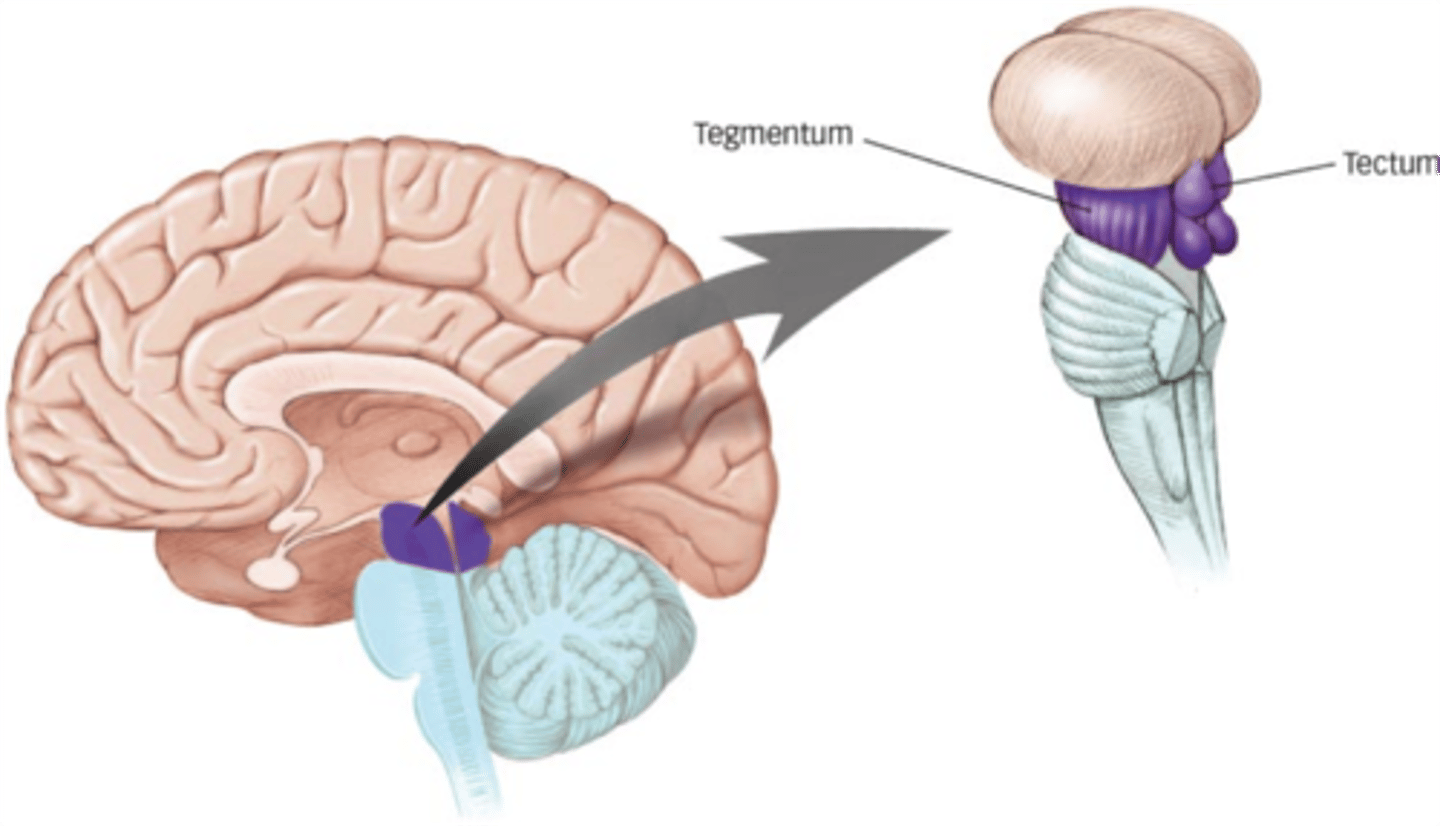
What is included in the upper pair of corpora quadrigemini in the tectum of the midbrain?
superior colliculi
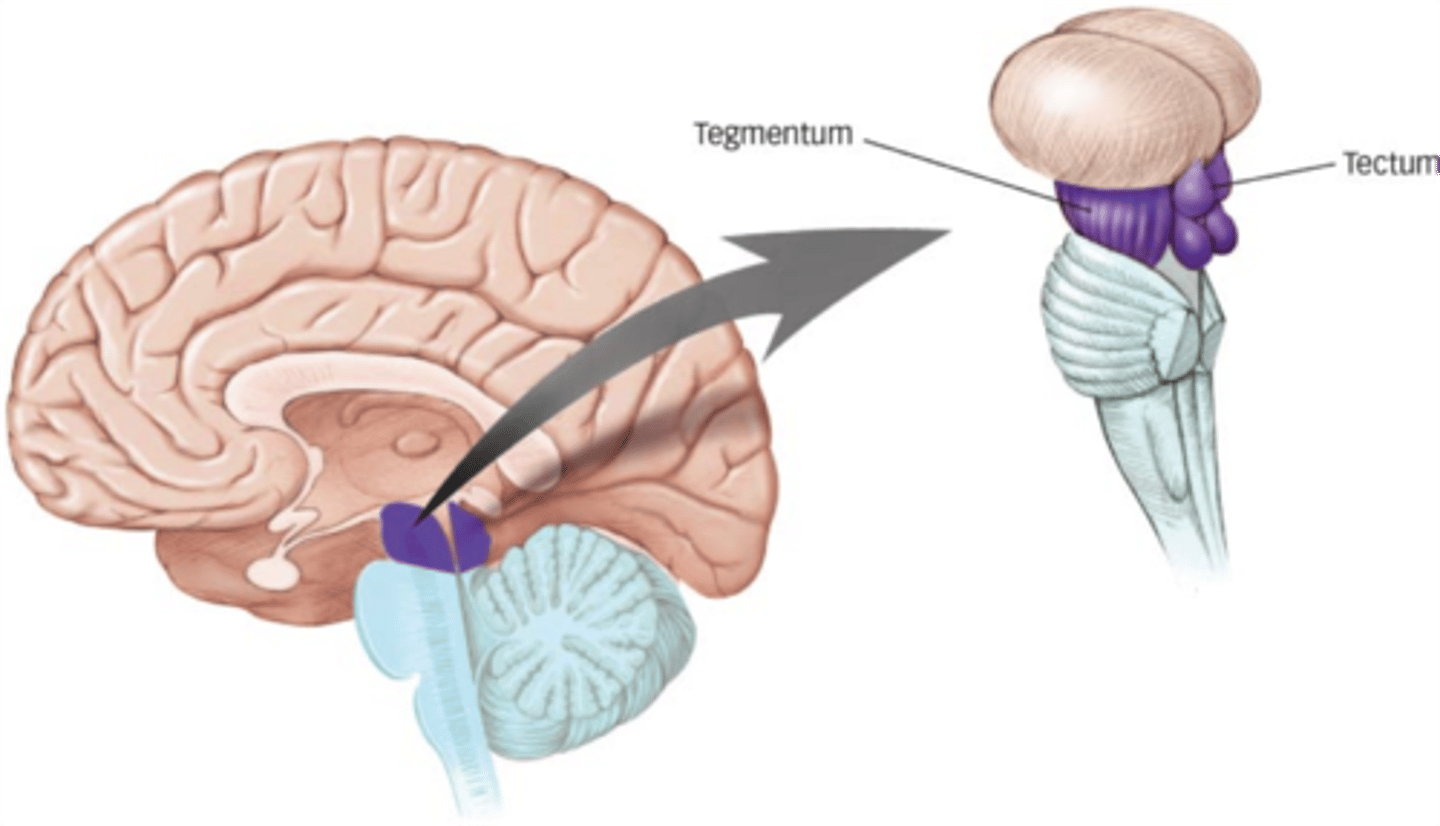
ridge of white matter extending laterally from each INFERIOR colliculus in the corpora quadrigemini of the tectum of the midbrain
inferior brachium
small region located just ventral and rostral to the superior colliculus that is important for the pupillary light reflex
pretectal area
Which cranial nerve emerges just caudal to the inferior colliculus?
CN IV
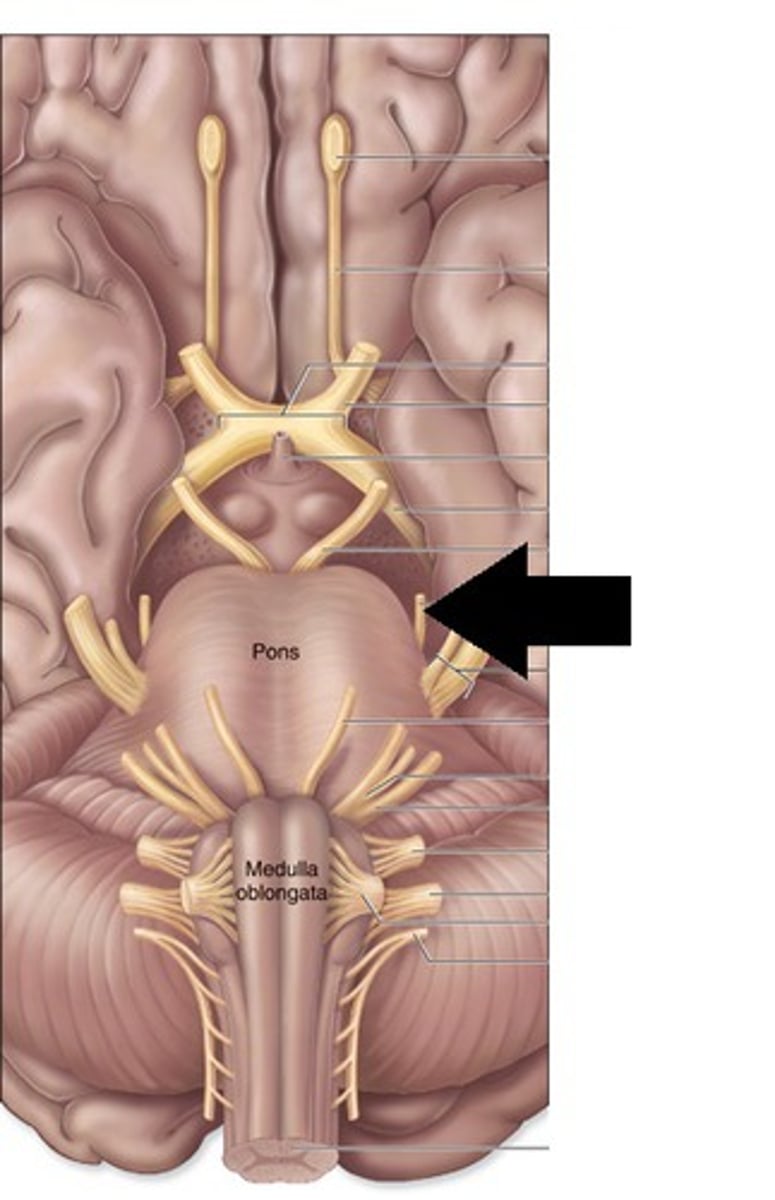
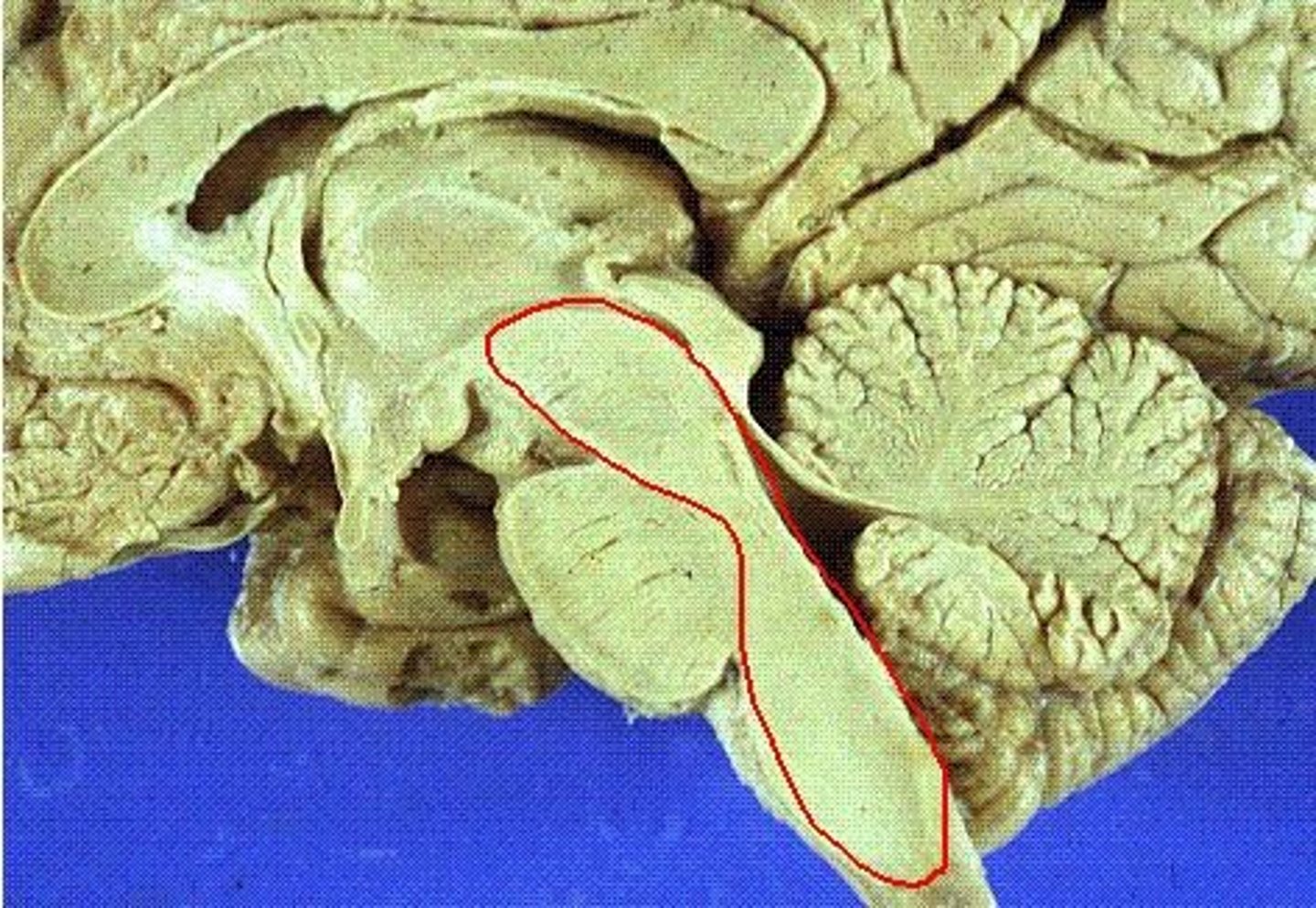
interpeduncular fossa
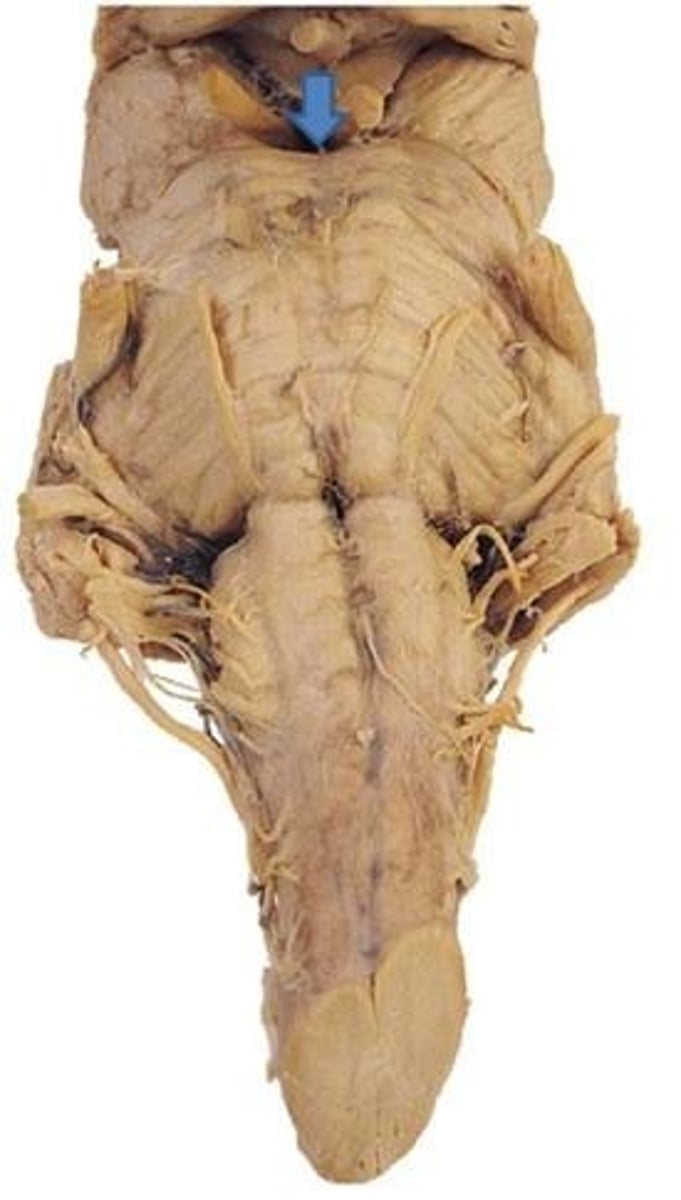
cerebral aqueduct
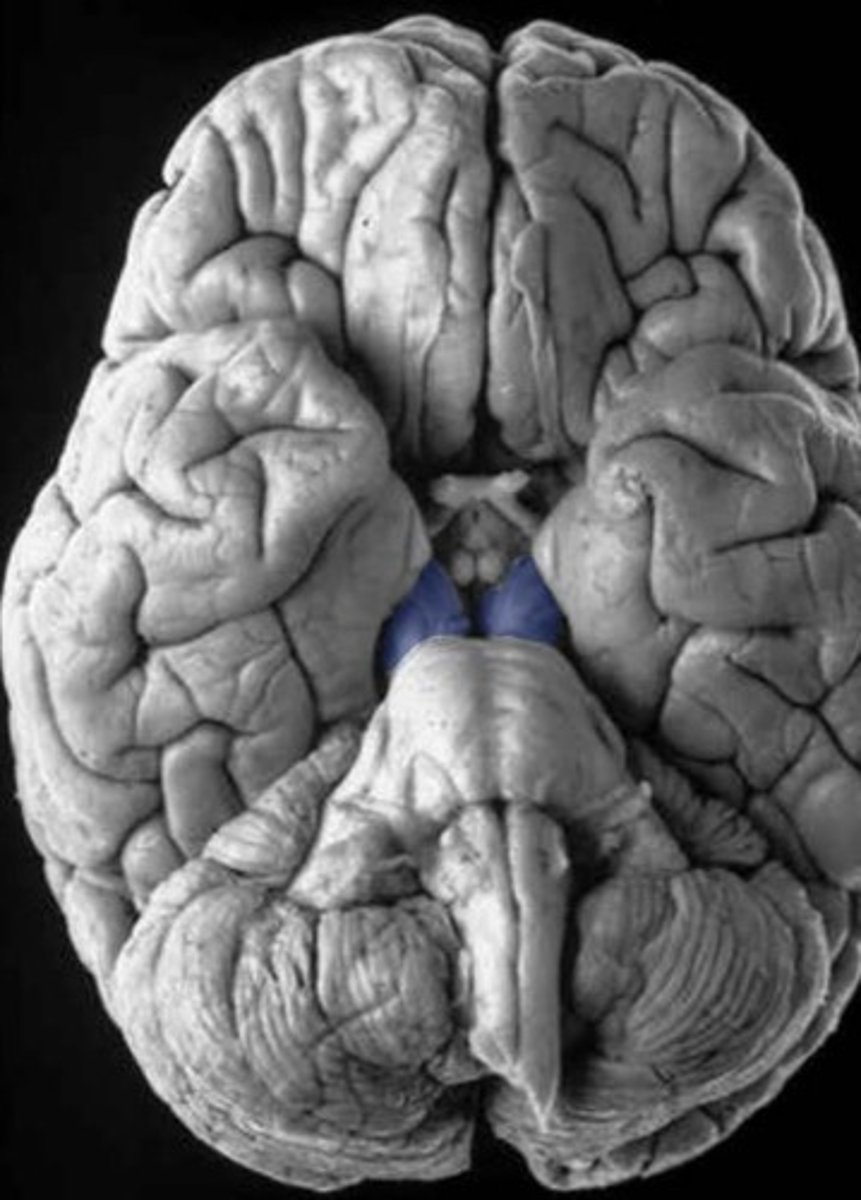
general structure + specific name for this side
cerebral peduncles, basis pedunculi
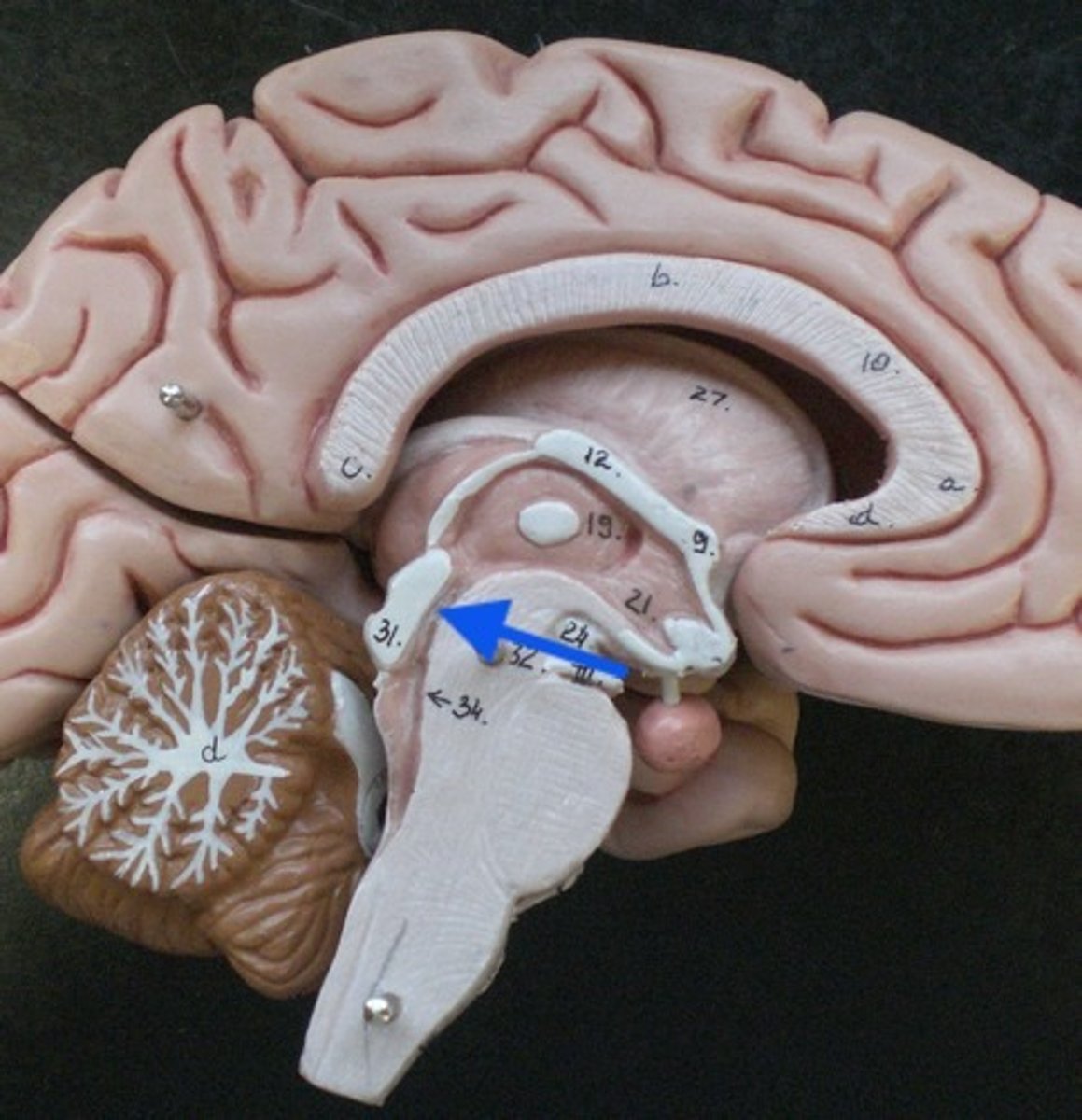
tegmentum
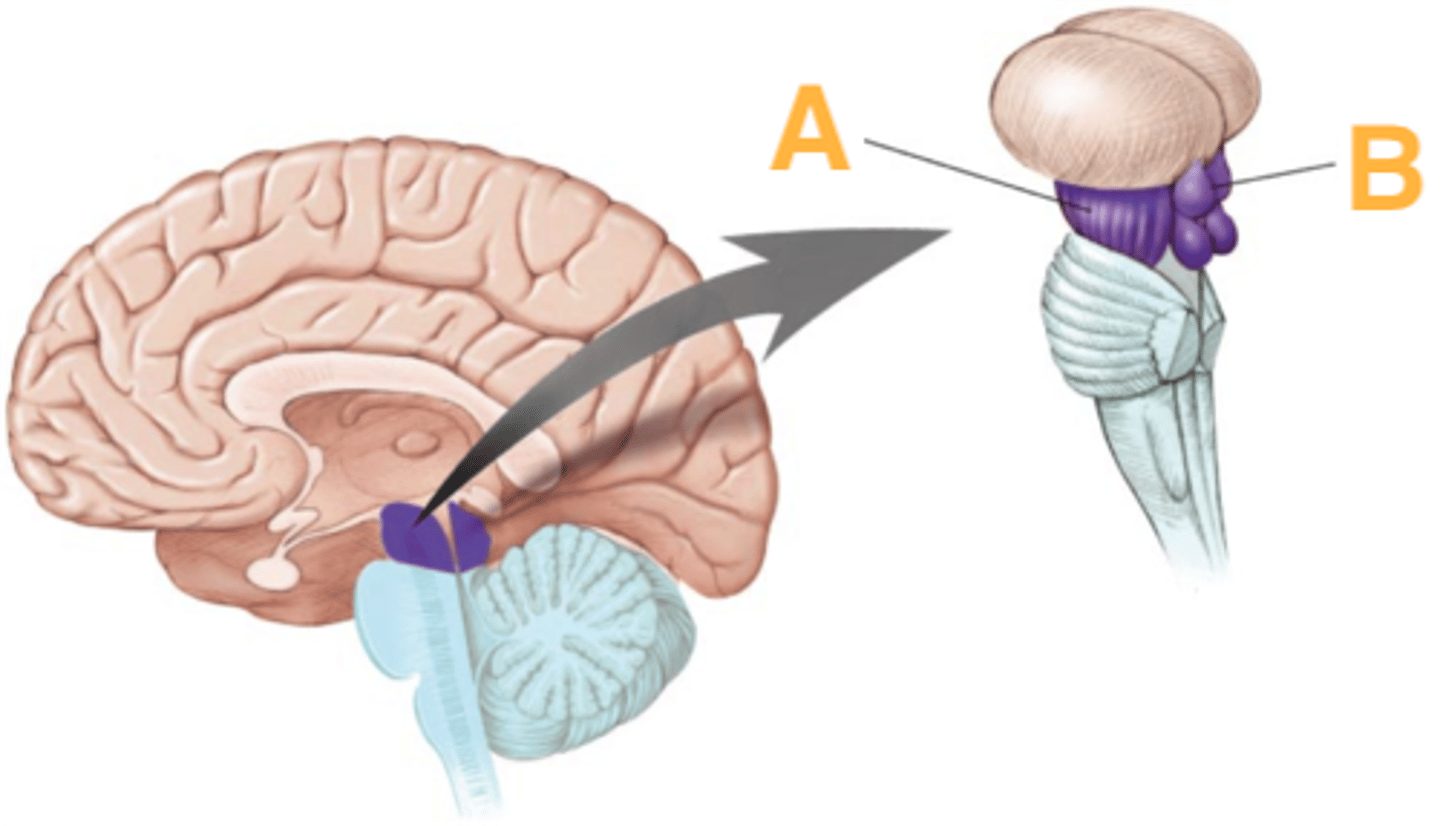
tectum