VI : Gram – Cocci
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
T
Neisseria is non-motile (t/f)
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria meningitidis
Moraxella catarrhalis
Species of Neisseria
F
Neisseria is AEROBIC (t/f)
Neisseria is ANAEROBIC (t/f)
Neisseria is capnophilic (5-10%)
Neisseria is capnophilic (-%)
F
Neisseria is COLD SENSITIVE
Neisseria is HEAT SENSITIVE (t/f)
T
Neisseria is non-hemolytic (T/F)
T
Neisseria (t/f)
most species are CHO fermenters
- Pathogenic Neisseria are usually fastidious and would usually grow optimally at 35-37 °C
- Pathogenic Neisseria are usually fastidious and would usually grow optimally at -
Neisseria requires enriched media containing IRON, HEMMIN, COENZYME I, which can be found in Chocolate Agar Plate (CAP)
Neisseria requires enriched media containing -, which can be found in Chocolate Agar Plate (CAP)
T
Most commensal Neisseria can grow on Chocolate Agar Plate (CAP) or Blood Agar Plate (BAP) at room temp (t/f)
N. flava
N. flavescens
N. subflava
FFS
Neisseria develops non-pigmented colonies except
N. elongata
Neisseria
all are catalase test (+) except:
N. elongata
Neisseria
all are cytochrome oxidase tests except
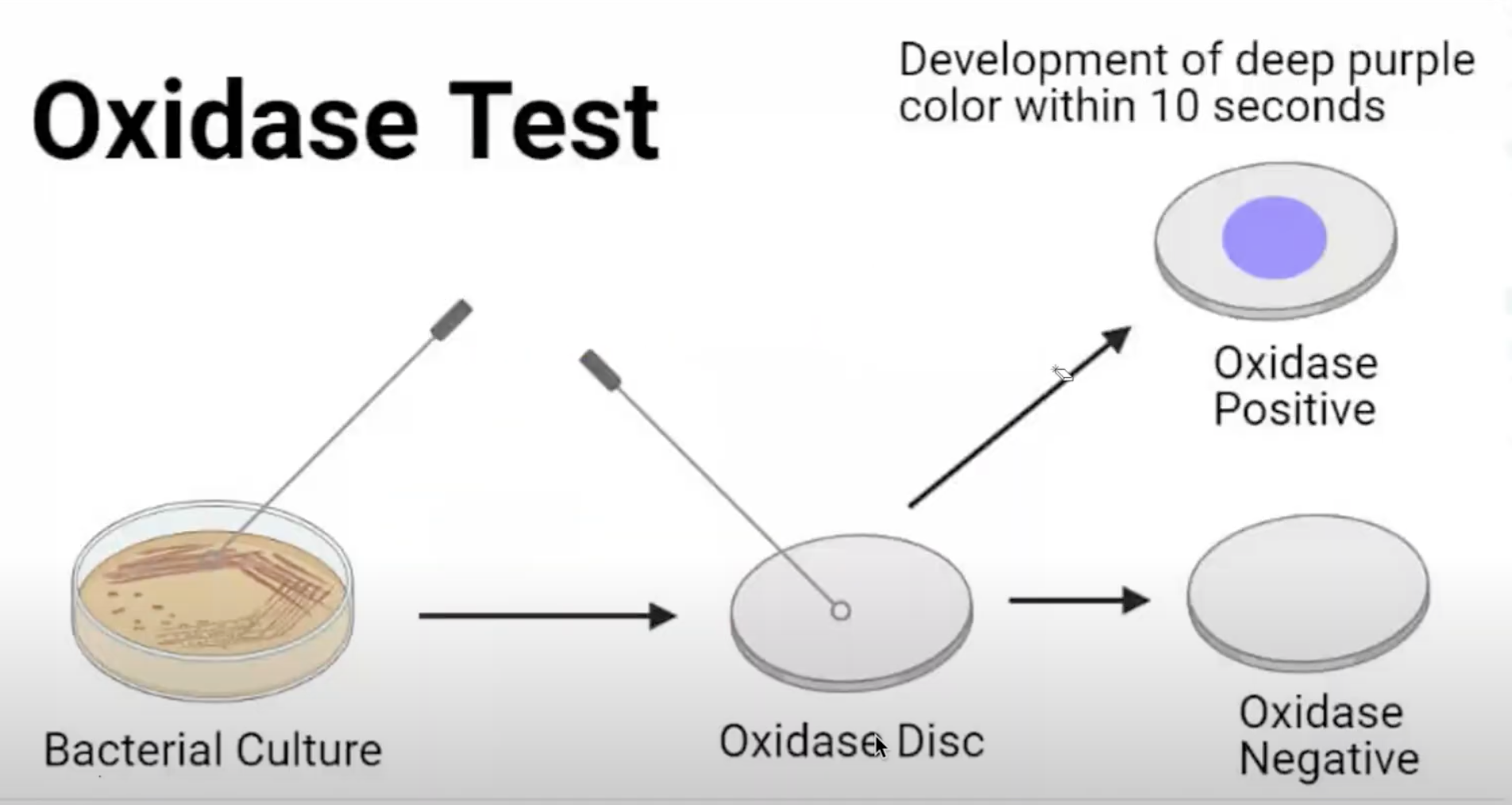
Oxidase / Cytochrome Oxidase Test / Taxo N
Screening test/ Presumptive Test of Neisseria
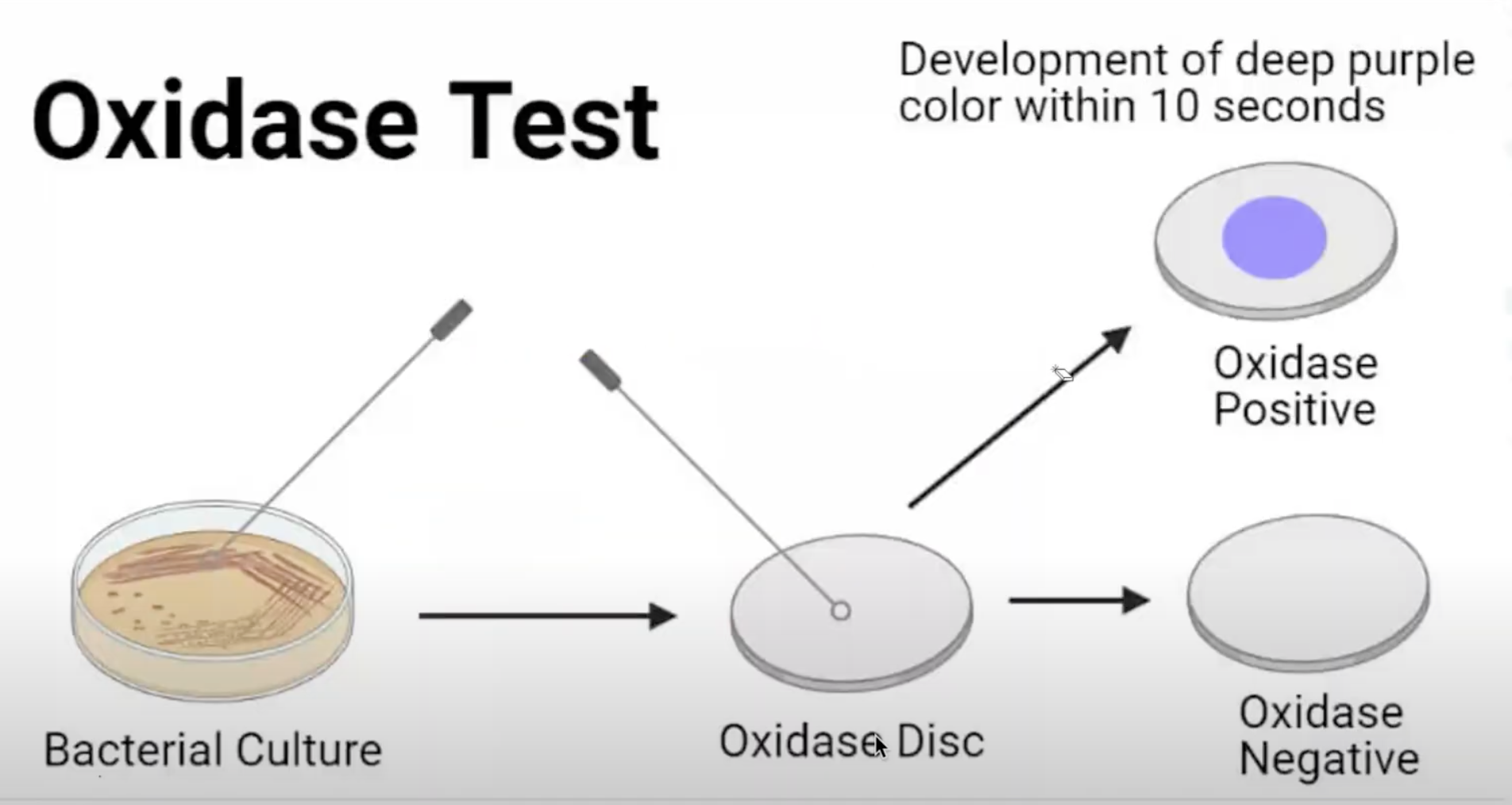
1% tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride
Neisseria
Oxidase / Cytochrome Oxidase Test’s reagent
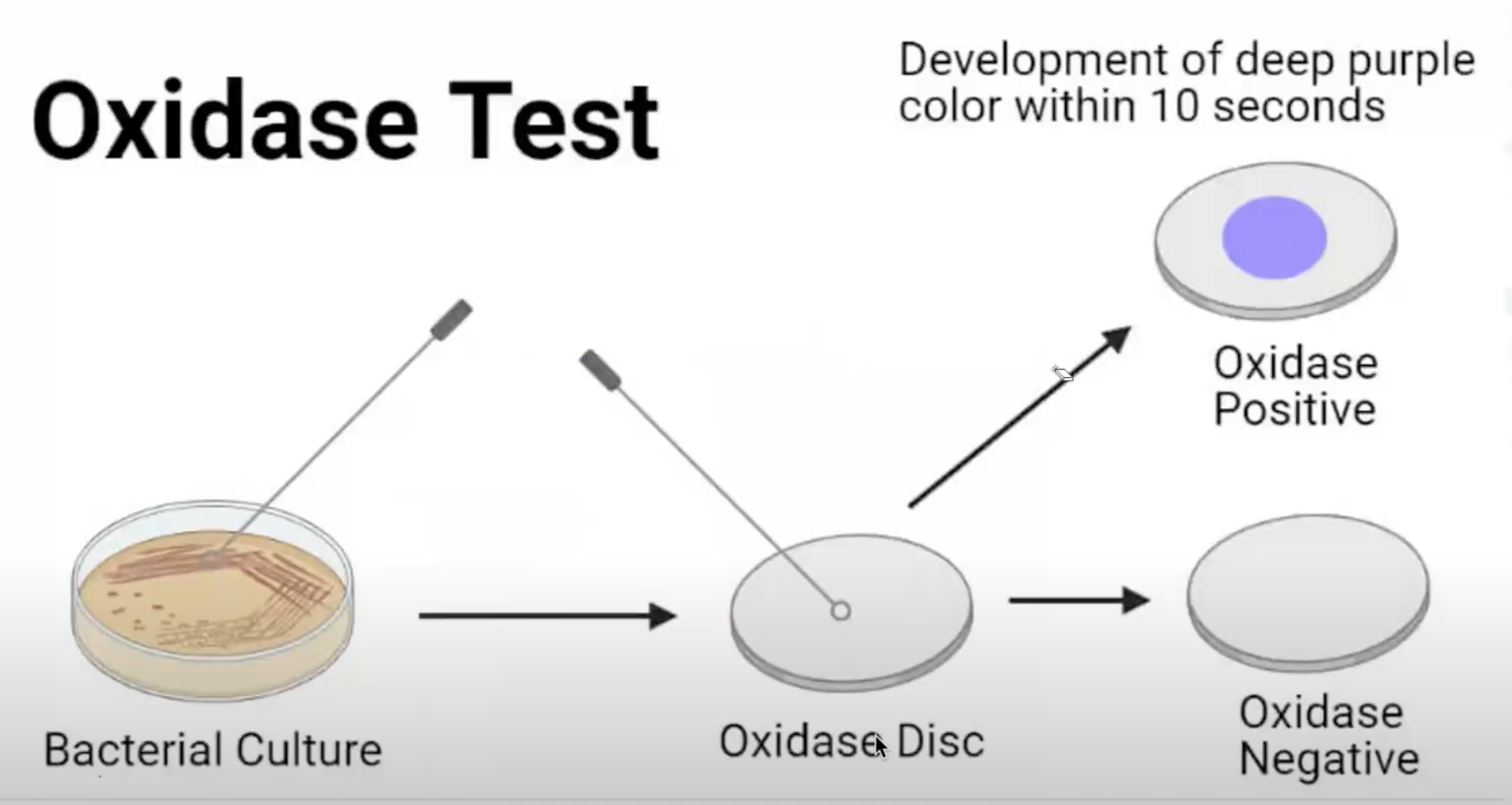
Purple
Neisseria
Oxidase / Cytochrome Oxidase Test’s + result
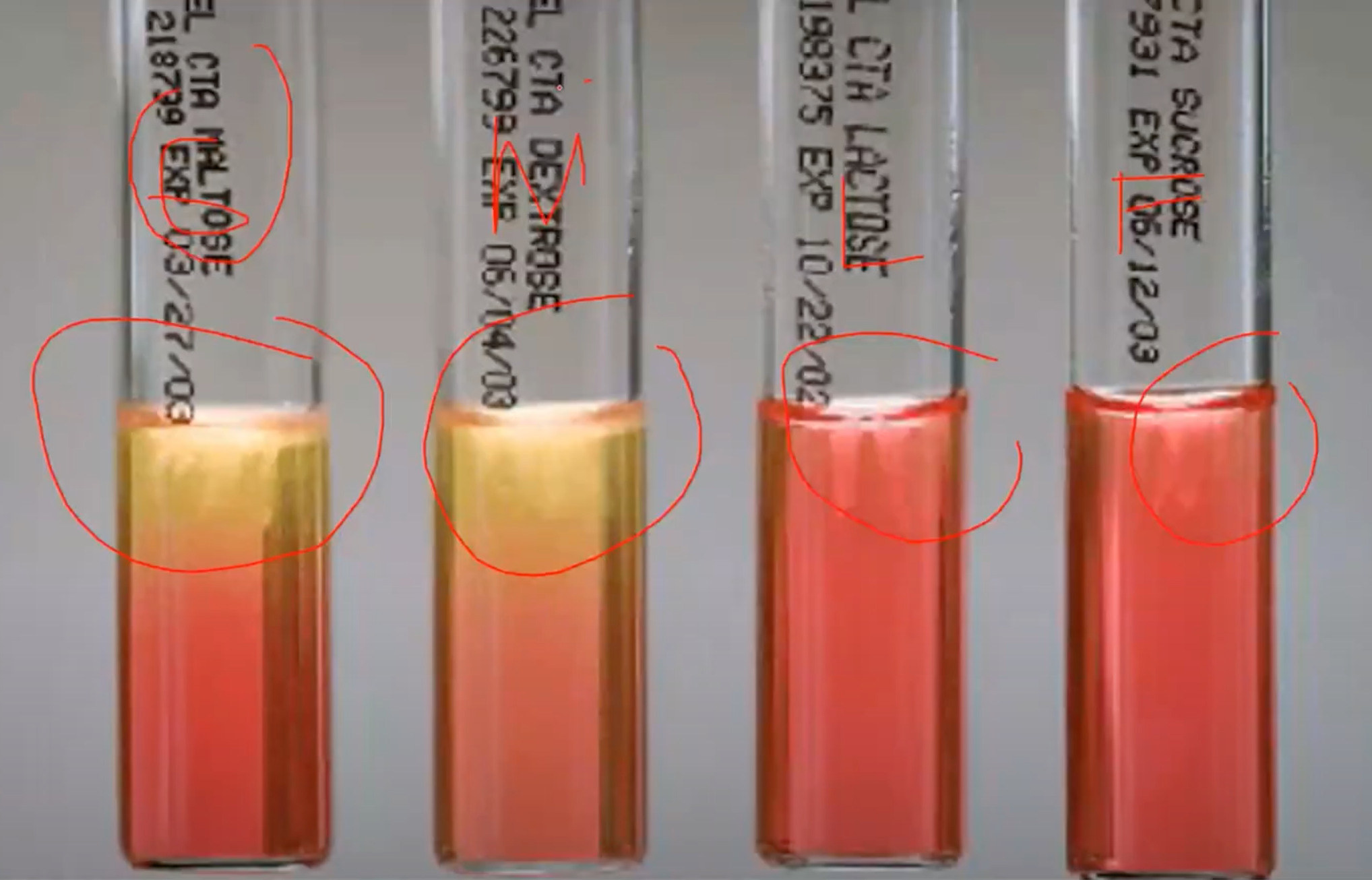

CHO Utilization / Sugar Fermentation Test
Confirmatory test of Neisseria
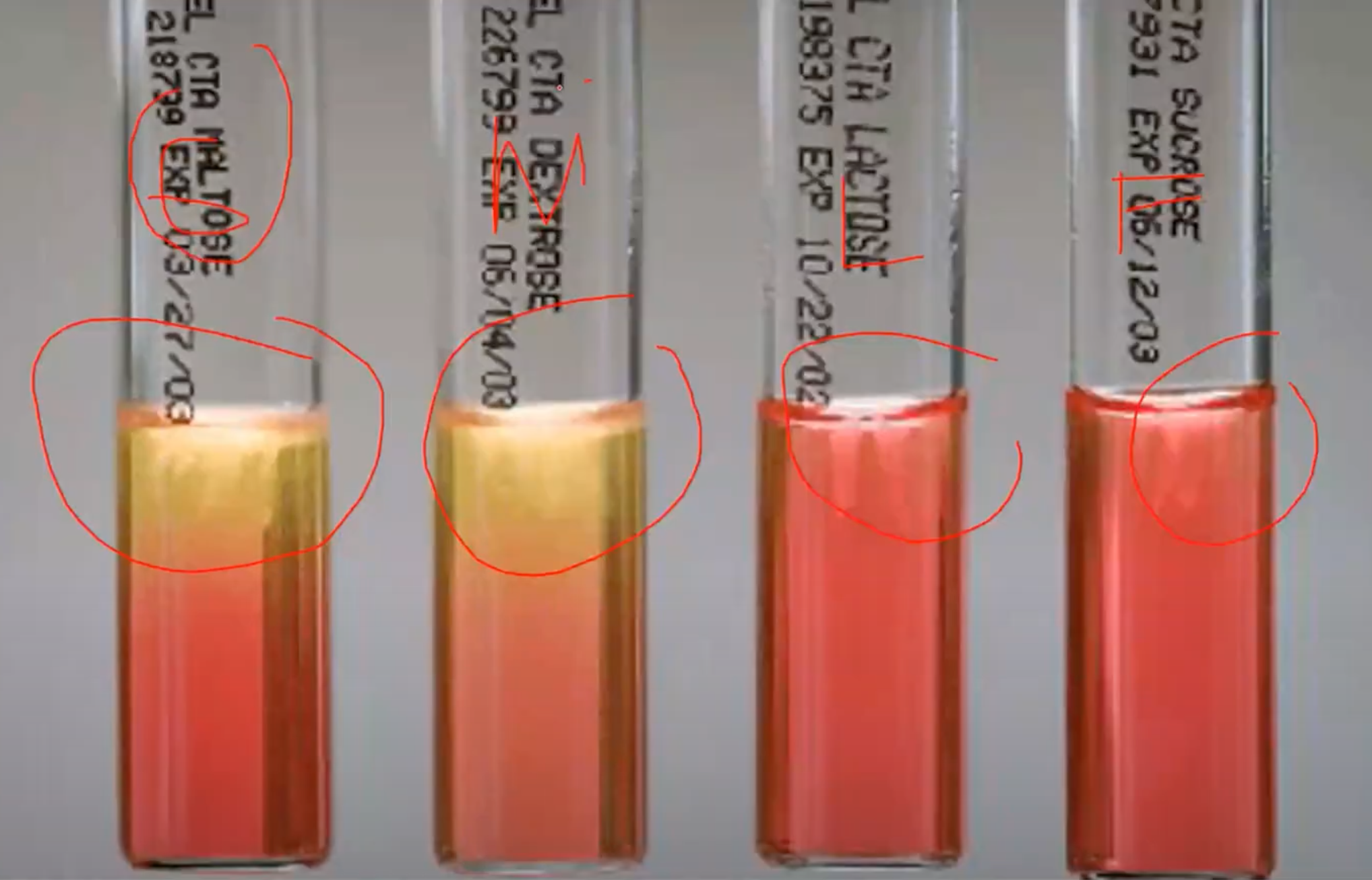

CYSTEINE TRYPTICASE AGAR (CTA) + added 1% sugar (sucrose, lactose, glucose, fructose - SFLG)
Neisseria
Agar used in CHO Utilization / Sugar Fermentation Test
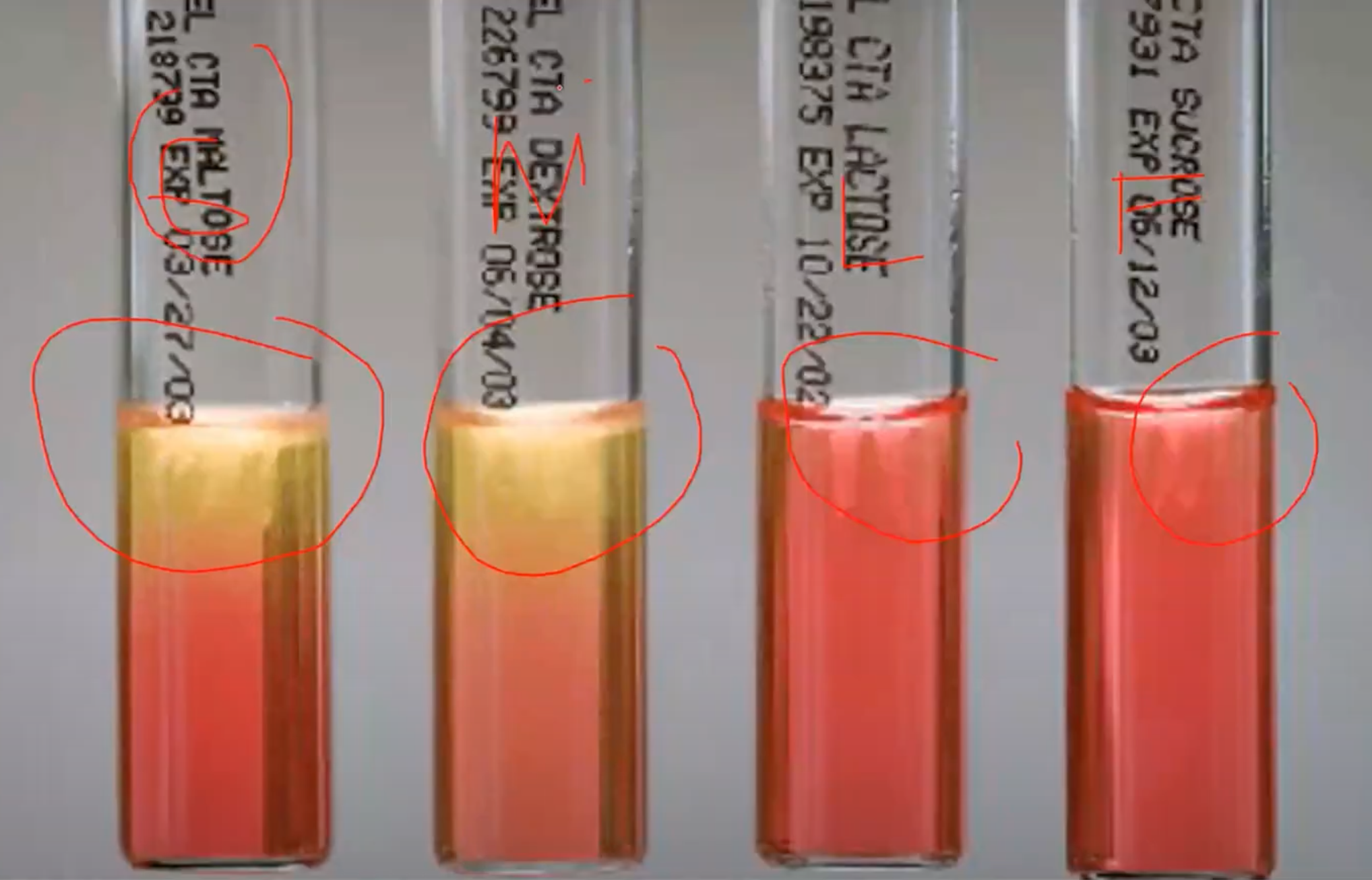

Phenol Red
Neisseria
Indicator in CHO Utilization / Sugar Fermentation Test
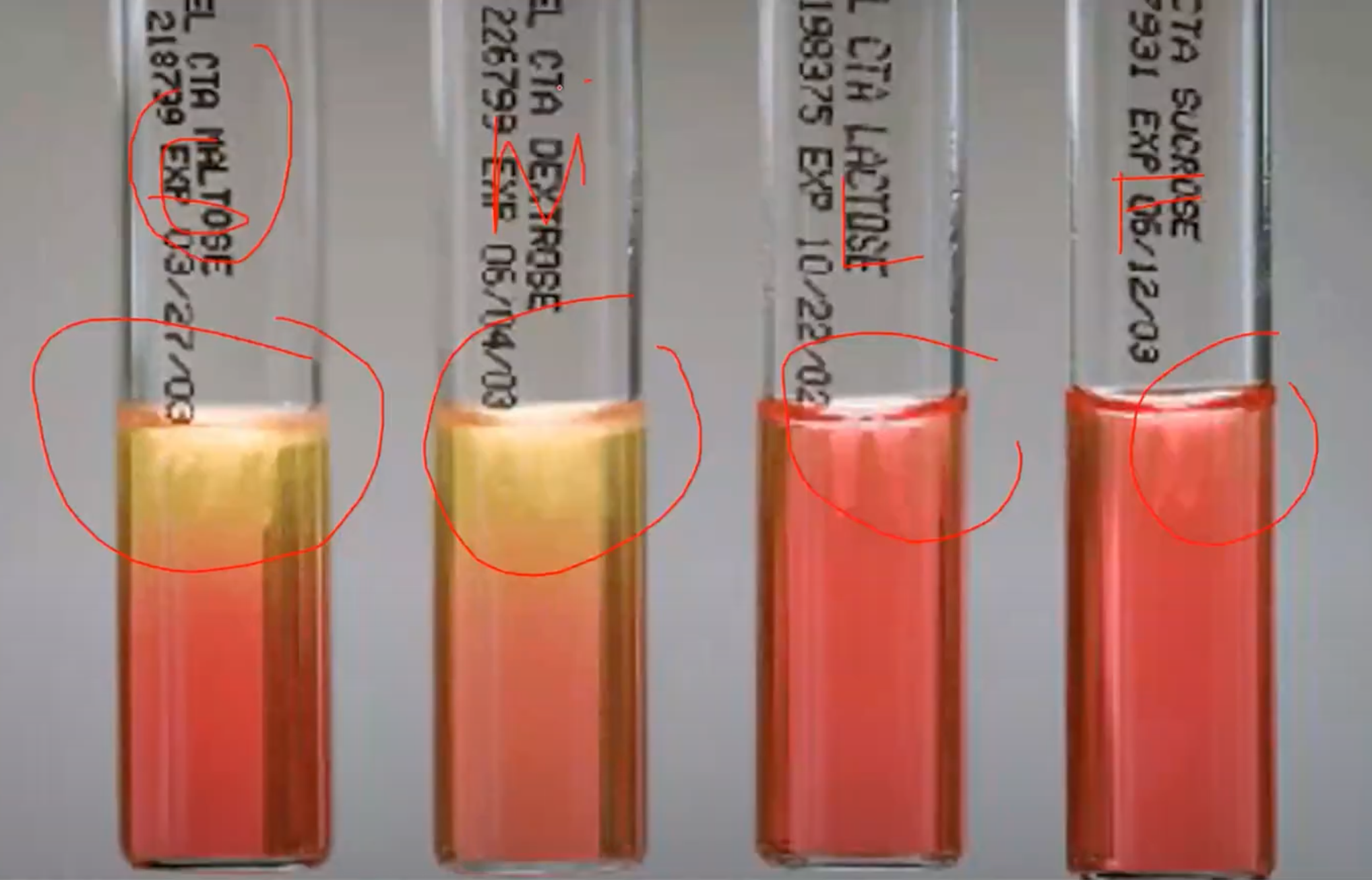

Yellow
Neisseria
Indicator in Acid pH of CHO Utilization / Sugar Fermentation Test will turn media into
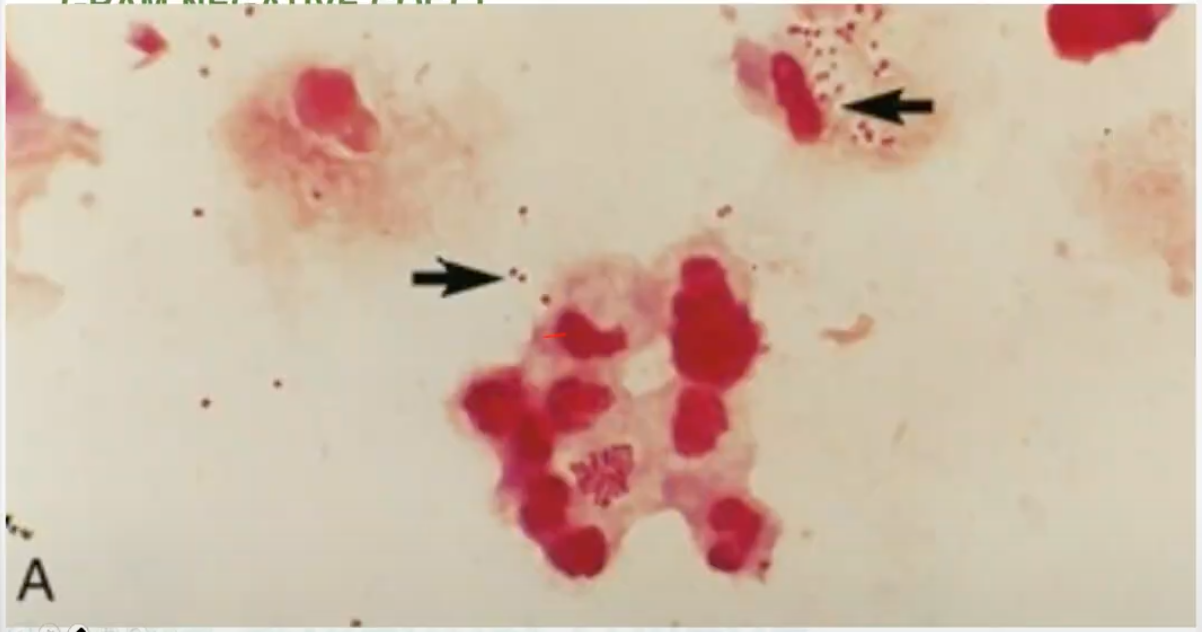
kidney, coffee bean-shaped
shapes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
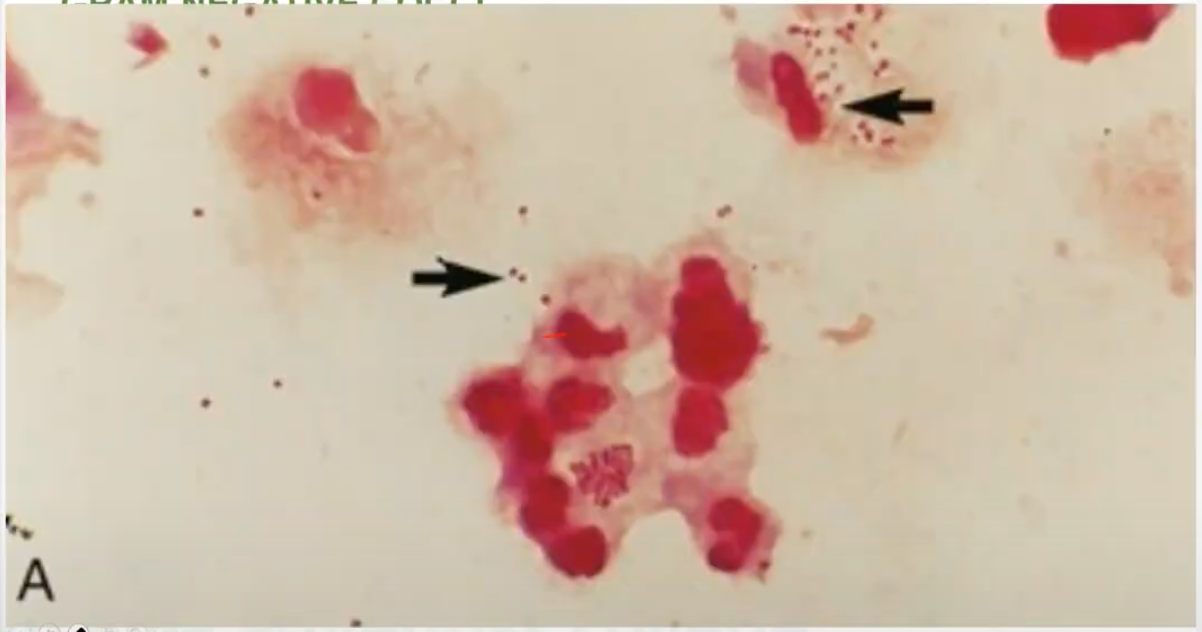
T
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is diplococci (t/f)
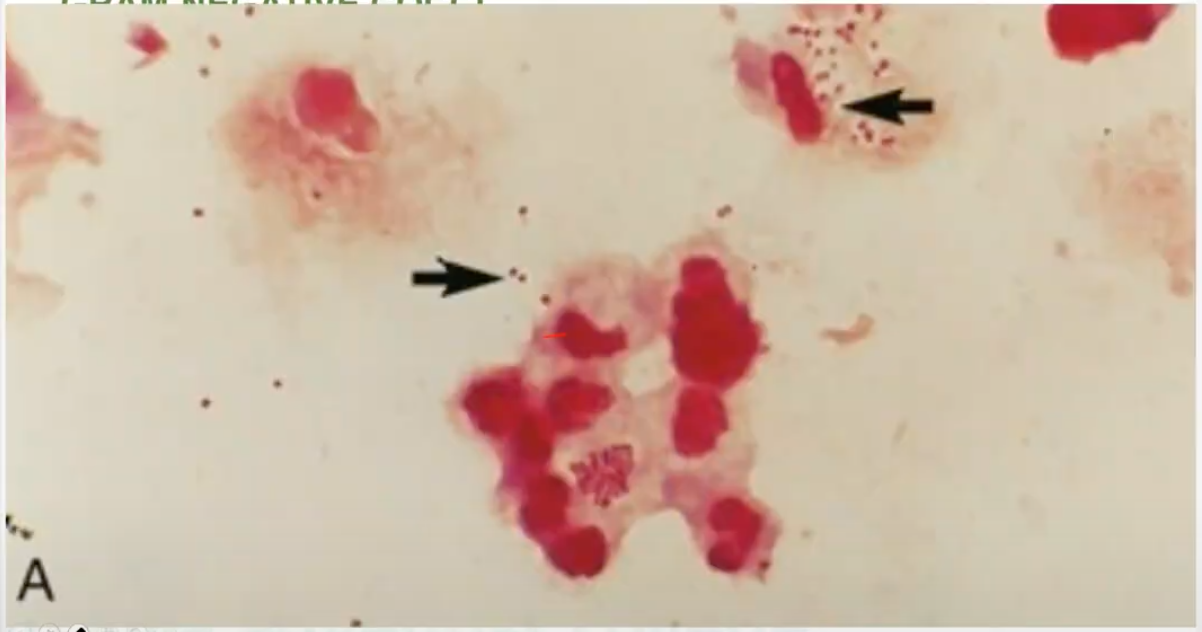
T
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is INTRACELLULAR within PMN (t/f)
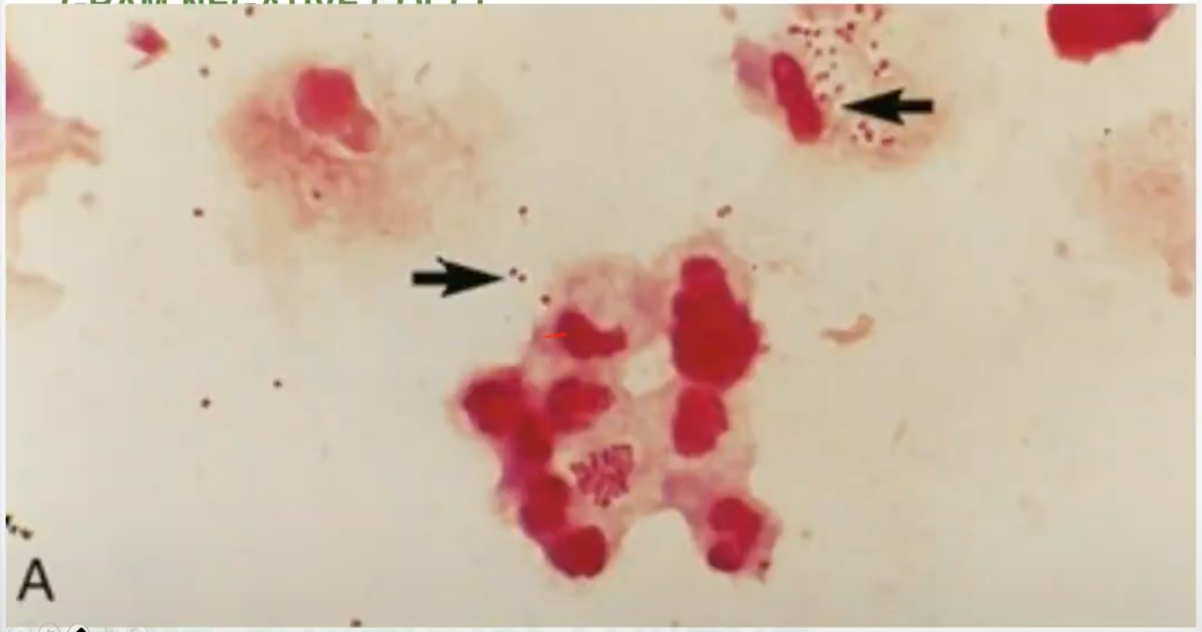
T
Neisseria gonorrhoeae ferments GLUCOSE only (t/f)
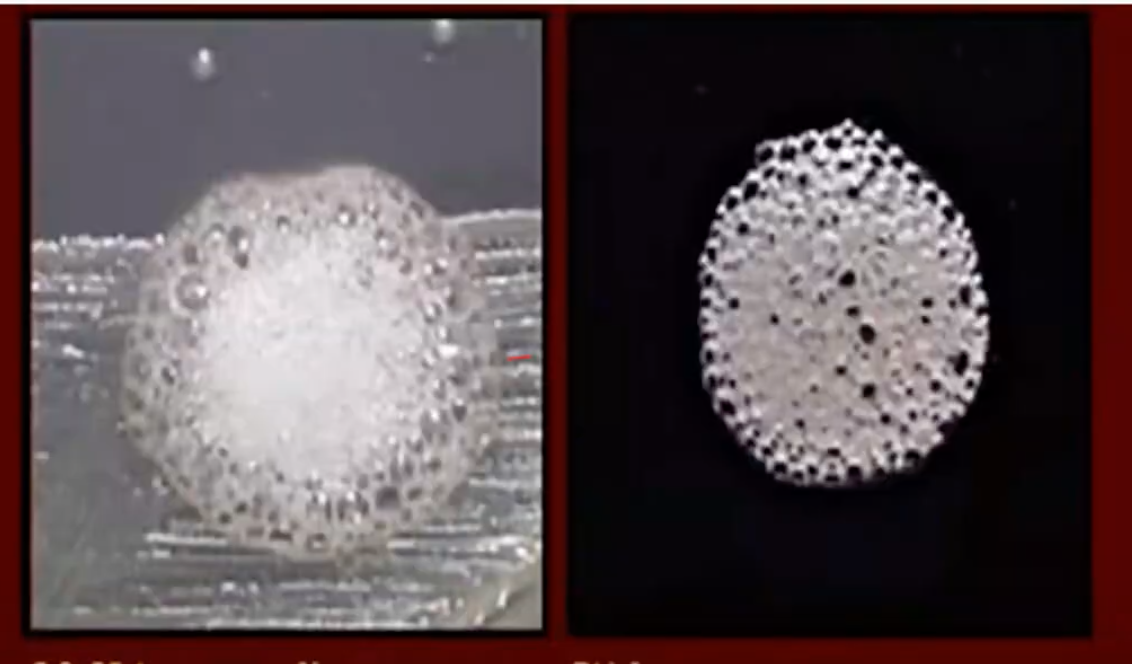

Superoxol / Catalase Test
a rapid test to detect N. gonorrhoeae
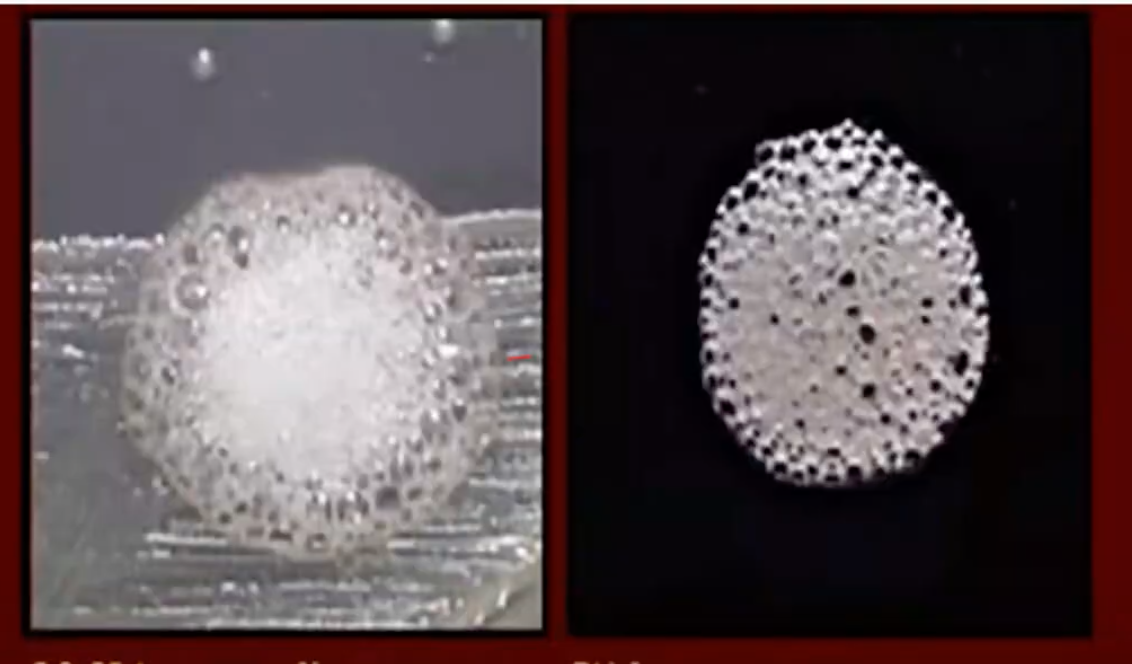

Superoxol / Catalase Test uses 30% H2O2 with a (+) result: vigorous bubbling
Superoxol / Catalase Test uses - H2O2 with a (+) result:
Pili
Lipopolysaccharide
Outer Membrane Protein
Protein I
Protein II
IgA Protease
Cellular Membrane proteins (PorB only)
Lipooligosaccharide (LOS)
Virulence Factor of N. gonorrhoeae
Pili
Virulence Factor of N. gonorrhoeae
promotes attachment to the host cell
Lipopolysaccharide
Virulence Factor of N. gonorrhoeae
source of ENDOTOXIN
Outer Membrane Protein
Protein I
Protein II
Virulence Factor of N. gonorrhoeae
affects antibody formation
Cellular Membrane proteins (PorB only)
Virulence Factor of N. gonorrhoeae
inhibits phagocytosis
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI)
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pharyngitis
Anorectal Infections (Rectal Gonorrhea)
Disseminated infections (bacteremia, arthritis, and metastatic infection)
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI)
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
acute purulent urethritis, prostatitis, and epididymitis (males); acute cervicitis (females)
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) causes acute purulent urethritis, prostatitis, and epididymitis (males); acute cervicitis (females)
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) causes acute purulent urethritis, prostatitis, and - (males); - (females)
Ophthalmia neonatorum
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) that has been transmitted to an infant through mother during pregnancy which can be treated Erythromycin to prevent blindness
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) with untreated gonococcal cervicitis may cause sterility and perihepatitis / Fitz-Hugh Curtis Syndrome
bacteremia
arthritis
metastatic infection
BAM
DX associated with N. gonorrhoeae
Disseminated infections which are
PUS
Secretions from urethra, cervix, prostate, rectal mucosa, throat, and joint fluid (UCRPTJ)
Spx of N. gonorrhoeae
V - ancomycin
C - ystatin
N - ystatin
VCN
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Thayer Martin
Vancomycin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Thayer Martin
inhibits G + bacteria
Nystatin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Thayer Martin
inhibits G – bacteria
Cystatin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Thayer Martin
inhibits growth of fungi
VCN - T
(Trimethoprim lactate )
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Modified Thayer Martin
Trimethoprim lactate
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Modified Thayer Martin
inhibits swarming of proteus
VCAn-T
An - Anisomycin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Martin-Lewis
Anisomycin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Martin-Lewis
inhibits growth of fungi
VCAm-T
Am - Amphitericin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
New York City
VCAm- TL
L - Lincomycin
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
GC LECT
VCAm- TL (Lincomycin)
MEDIA USED FOR CULTURING Neisseria gonorrhoeae
GC LECT
inhibits G + bacteria
F
Neisseria meningitidis is bean-shaped diplococci; sensitive to SPS
Neisseria meningitidis is bean-shaped diplococci; resistant to SPS (t/f)
Neufeld Quellung Test (+)
Neisseria meningitidis
Neufeld Quellung Test
Neisseria meningitidis
Ferments glucose and maltose
Neisseria meningitidis
ferments - and -
Neisseria meningitidis
natural habitat: ORO & NASOPHARYNX
Neisseria meningitidis
natural habitat:
F
—for lactose, sucrose, and fructose
Neisseria meningitidis (t/f)
– or + for lactose, sucrose, and fructose
T
Neisseria meningitidis (t/f)
- serogroups are based on the type of capsular polysaccharide
A
B
C
D
X
Y
Z
29E
W135
L
Neisseria meningitidis
serogroups include
Capsule
Pili
Endotoxin
IgA protease
Cellular membrane proteins (Por A and Por B)
Lipooligosaccharide (LOS) endotoxin
Virulence Factors of Neisseria meningitidis
Capsule
Virulence Factors of Neisseria meningitidis
enables organisms to resist phagocytosis
Pili
Virulence Factors of Neisseria meningitidis
promotes attachment
Endotoxin
Virulence Factors of Neisseria meningitidis
causes petechial formation and DIC
IgA Protease
Virulence Factors of Neisseria meningitidis
important in pathogenesis; antibody found in mucous membrane
BSL 3/4
What BSL is Neisseria meningitidis under
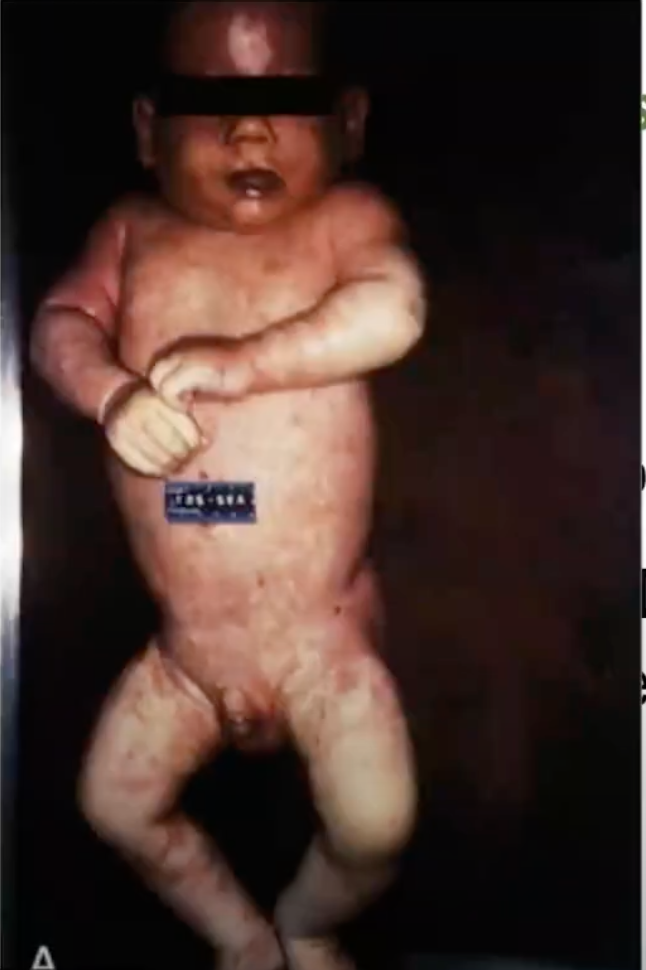
Bacterial Meningitis
Meningococcemia
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
Diseases associated with Neisseria meningitidis
Meningococcemia
Diseases associated with Neisseria meningitidis
organism in the blood; VERY FATAL
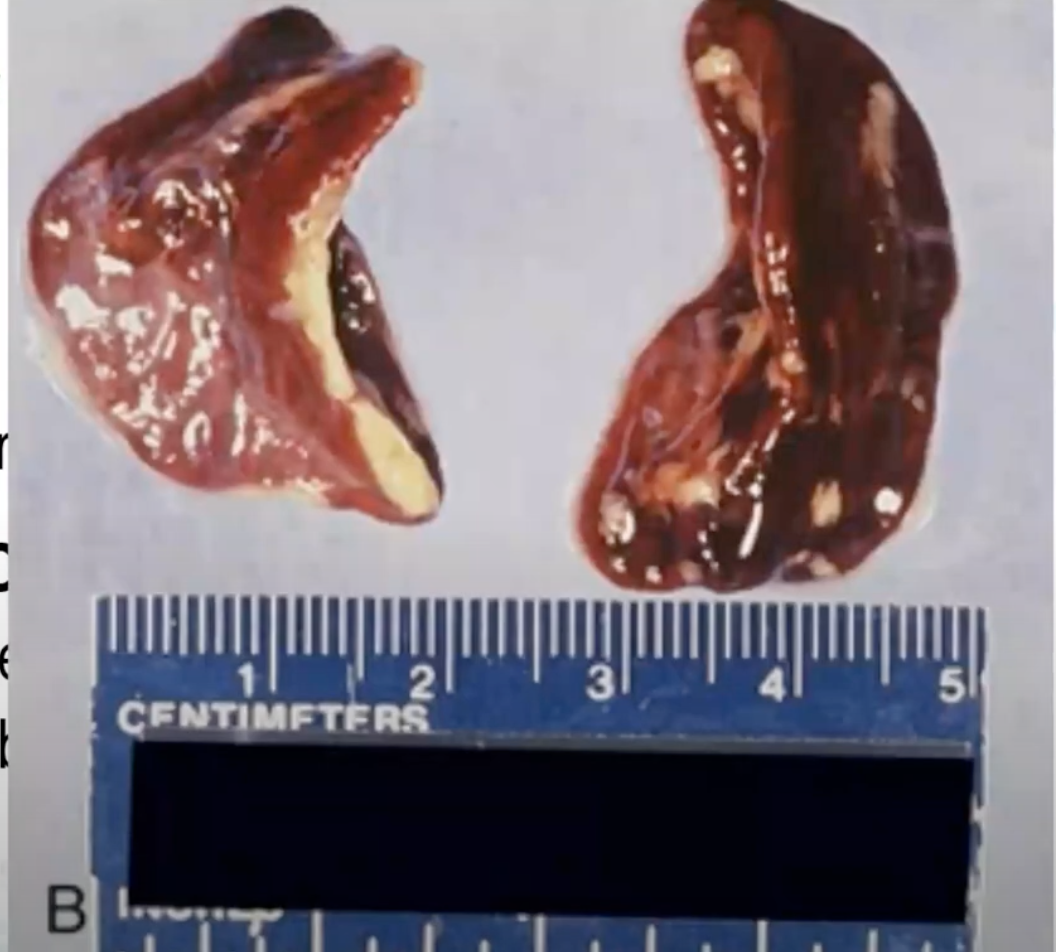
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
Diseases associated with Neisseria meningitidis
a severe form of meningococcemia
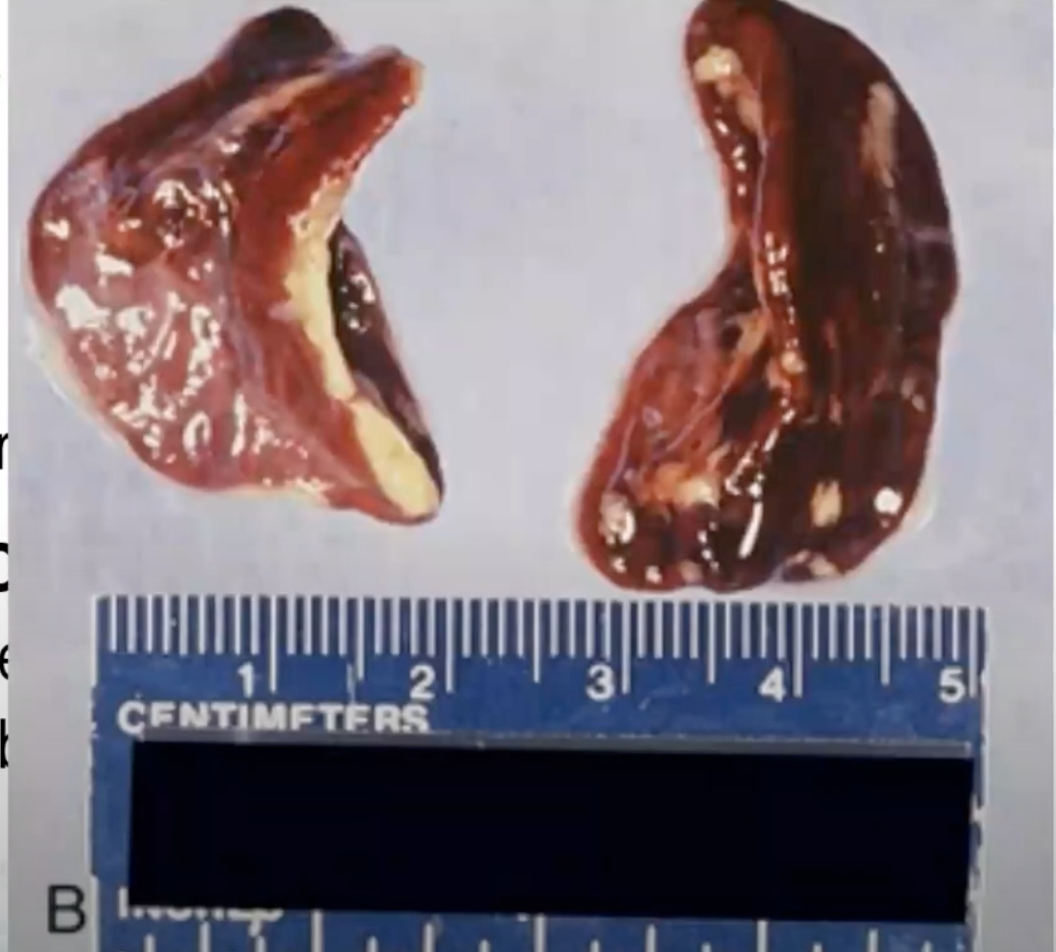
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
Diseases associated with Neisseria meningitidis
bleeding of adrenal glands and uncontrollable clotting of blood
CSF
blood
nasopharyngeal swab
petechial skin lesions
Specimen of Neisseria meningitidis
Moraxella catarrhalis
morphologically and biochemically resembles
Neisseria
T
Moraxella catarrhalis is encapsulated with pili, non-motile (t/f)
Moraxella catarrhalis is catalase and oxidase (+)
Moraxella catarrhalis is catalase and oxidase
nonhemolytic
Moraxella catarrhalis on BAP
Moraxella catarrhalis
a normal flora of ORO and NASOPHARYNX but may cause OTITIS MEDIA
F
Moraxella catarrhalis it does not degrade sugar (assacharolytic)
Moraxella catarrhalis does degrade sugar (assacharolytic) (t/f)
Butyrate Disk Test
Screening Test of Moraxella catarrhalis
blue (after 5 minutes of incubation)
Butyrate Disk Test + result
BROMO- CHLORO- INODNYL BUTYRATE
Butyrate Disk Test reagent
a. N. gonorrhoeae
Which of the following is a leading STI?
a. N. gonorrhoeae
b. N. lactamica
c. N. sicca
d. N. mucosa
c. Blood
Which of the following media is not acceptable for primary growth of N. gonorrhoeae ?
a. Chocolate
b. Thayer-Martin
c. Blood
d. Martin Lewis
b. Maltose fermentation
N. gonorrhoeae can be differentiated from N. meningitidis by:
a. Dextrose fermentation
b. Maltose fermentation
c. Lactose fermentation
d. Nitrate reduction
Hockey Puck
colonies remain intact when pushed across the plate using inoculating loop
DNase Test / Taxo M
best test differentiate M. catarrhalis to another Moraxella
Moraxella catarrhalis
An organisms grows on blood agar at RT & nutrient agar at 37C. The organism has the ability to use CHO & is nitrate +, DNase +, & ONPG –. The organism is:
T
PPNG (Penicillinase producing N. gonorrhoeae) (t/f)
purple
Taxo N ---cytochrome oxidase→Indophenol blue
+result
Neisseria
Moraxella
Pseudomonas
PMN
Taxo N ---cytochrome oxidase→Indophenol blue
+for what species
Nitrocefin
SUMMARY OF LABORATORY TESTS FOR Neisseria
Best substrate of Beta-lactamase test:
color change
SUMMARY OF LABORATORY TESTS FOR Neisseria
▪ (+) result of Beta-lactamase test
Beta-lactamase test
SUMMARY OF LABORATORY TESTS FOR Neisseria
Held on primary culture because plasmid is lost on subculture
Beta-lactamase test
SUMMARY OF LABORATORY TESTS FOR Neisseria
Done on bacteria resistant to penicillin
Chromogenic cephalosporin test
Iodometric test- starch iodine complex + penicillin
Acidimetric test- phenol red +CITRATE- BUFFERED PEN
SUMMARY OF LABORATORY TESTS FOR Neisseria
Beta-lactamase test are
Pink / Red
Chromogenic cephalosporin test + result
Yellow
Chromogenic cephalosporin test – result
Colorless
Iodometric test- starch iodine complex + penicillin + result
Purple
Iodometric test- starch iodine complex + penicillin – result
Yellow
Acidimetric test- phenol red +CITRATE- BUFFERED PEN + result
Red
Acidimetric test- phenol red +CITRATE- BUFFERED PEN – result