Biology 288-Lecture 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
What is a neurotransmitter?
A molecule released by a neuron that has an effect on another cell
2
New cards
How is a complex molecule built up?
A precursor molecule takes part in a reaction to produce a secondary molecule which can then remain as it is or continue on into another reaction
3
New cards
Where do cells get their energy and building blocks from?
They breakdown the food we eat into usable materials
4
New cards
The conversion of food to molecules that form a cell produce two products, what are they?
1) Energy in the form of ATP
2)Heat
2)Heat
5
New cards
Explain how the saying “we are what we eat” is essentially true
The food we eat goes through a series of catabolic pathways to be broken down into its simplest forms. These forms are then taken and go through a series of anabolic pathways where they are built into molecules which can then be used to form cells
6
New cards
What are LDL and HDL?
Although often mistaken for forms of cholesterol, they are proteins that carry cholesterol
7
New cards
What do our cells use cholesterol for?
To generate useful cellular material
8
New cards
What makes biological order possible?
The release of heat energy
9
New cards
What is our main source of energy even for organisms that do not make their own energy?
The main source of energy is the sun
10
New cards
How do non-photosynthetic organisms use the sun as an energy form?
The photosynthetic organisms harvest the suns energy to produce their own energy, then they are consumed by other consumers and that energy is passed on
11
New cards
How do cells obtain energy from organic molecules?
They oxidize them
12
New cards
What state does the universe prefer?
The universe prefers a state of disorder
13
New cards
Why does the universe move from order to disorder?
The movement to order is energetically unfavorable and requires a lot of energy
14
New cards
Why can’t mammals properly breakdown plants?
Plants contain a rigid cellulose wall which is hard to breakdown
15
New cards
What is the purpose of carbon dating?
It allows us to examine the different carbon isotopes present and estimate the age of an organism
16
New cards
What is oxidation?
The loss of an electron
17
New cards
What is reduction
The gain of an electron
18
New cards
What kind of molecules are electrons attracted to?
Molecules with high electronegativities
19
New cards
What direction do chemical reactions proceed in?
The direction that causes a loss of free energy
20
New cards
What is the function of an enzyme?
An enzyme lowers the energy needed to initiate a spontaneous reaction while also remaining unchanged
21
New cards
What is determined by the free energy change?
Free energy change determines if a reaction will occur
22
New cards
If the change in free energy is very negative, will the reaction occur?
yes
23
New cards
What happens to a reaction if we change the concentration of its components?
The direction which the reaction proceeds in will change
24
New cards
What do enzyme-catalyzed reactions depend on?
Depends on rapid molecular collisions
25
New cards
What is the function of a catalyst?
It reduces the energy required for a reaction to occur and allows reactions to occur more easily
26
New cards
Draw a diagram representing an uncatalyzed reaction pathway and a catalyzed reaction pathway
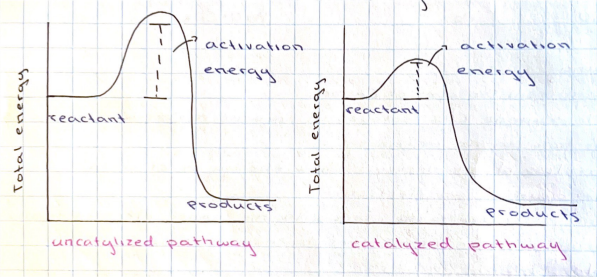
27
New cards
If the change in free energy is positive, will the reaction occur?
The reaction will occur but it requires energy to initiate it
28
New cards
What is the 0th law of thermodynamics?
Two systems in equilibrium with a third system are also in equilibrium with each other
29
New cards
What is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
Energy can change forms but is not created or destroyed
30
New cards
What is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
Entropy of an isolated system always increases
31
New cards
What is the 3rd law of thermodynamics?
Entropy of a system approaches a constant as the temperature approaches absolute 0
32
New cards
What is the purpose of reaction coupling?
Allows and energetically unfavorable reaction to take place
33
New cards
What are two possible ways that a reaction may cause disorder?
1) Changes the bond energy of the reacting molecules that can cause heat to be released
2) Decrease in the amount of order in the cell
2) Decrease in the amount of order in the cell