A&P Test 3
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
In a muscle contraction, what shortens?
sarcomere
A discrete bundle of muscle fibers is wrapped in ____ connective tissue.
perimysium
In mature muscle fiber, the stem cell that is responsible for maintaining muscle tissue is called __.
myosatillite
To propagate the an electrical impulse to the muscle fiber, __ ions must leave the cell to depolarize the cell and shift the electrical impulse down the axon.
sodium
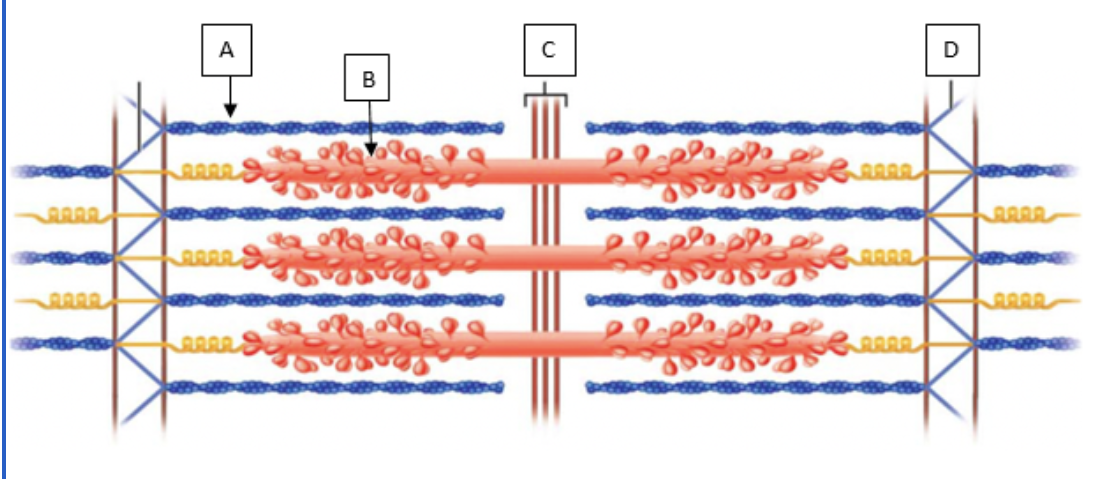
Match the letter in the diagram below to the correct structure in the sarcomere.
myosin, actin, z disc, m-line
B, A, D, C
A tendon is formed via the extension of the connective tissue - endomysium, epimysium, and perimysium that attaches bone to bone.
False
The "triad" in skeletal muscle forms between which structures? (select all that apply)
sarcoplasmic reticulum, t-tubule
Select the choice that correclty ranks muscle organization from least to most organized.
myofilaments, myofibril, fiber, muscle
Contractile unit of the musle is the __.
sacomere
Extensibility
ability of the muscle to stretch
Elasticity
ability of the muscle to recoil to its resting length
Excitability
ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Contractility
ability of cells to shorten
Muscles on the anterior surface of the forearm are flexors.
True
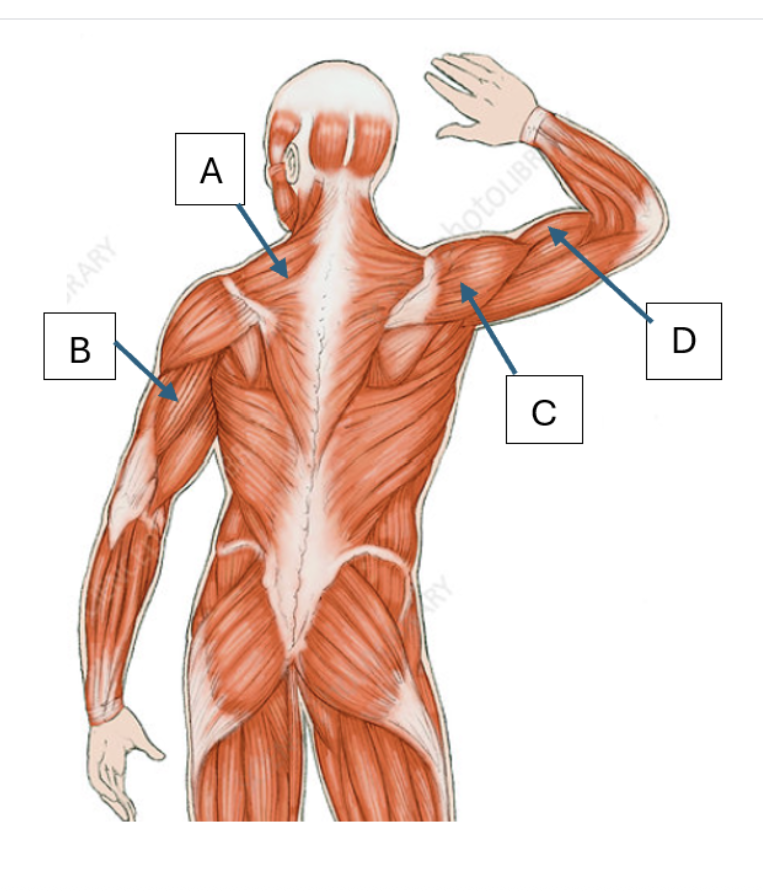
Match the letter to the muscles listed below:
Trapezius, Triceps brachii, Deltoid, Bicep brachii
A, B, C, D
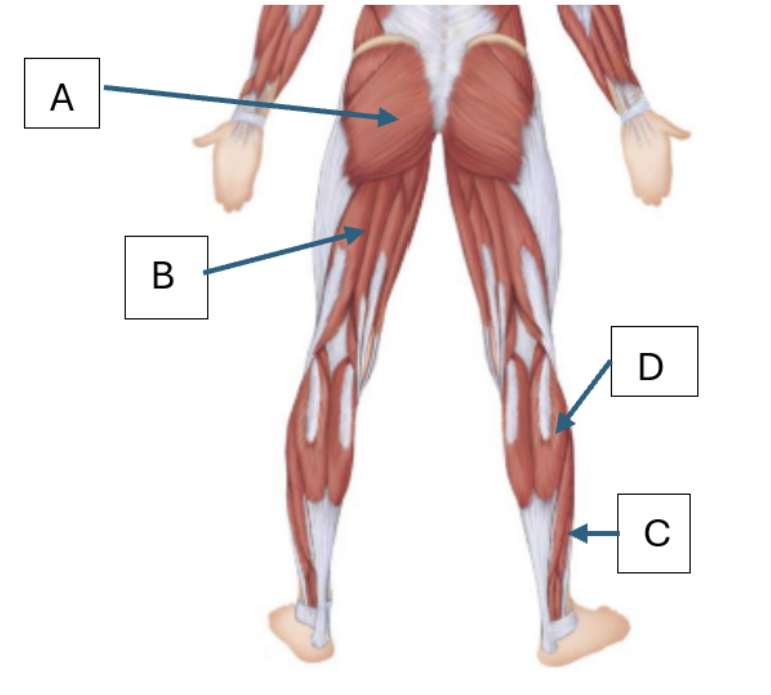
Match the letter to the muscle below:
Gluteus maximus, Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Biceps femoris
A, D, C, B
When the amount of K+ moves out dropping the charge of cell below resting state.
Hyperpolarization
Occurs when Na+ rush into the axon.
Depolarization
As K+ moves out of the axon the cell is ____.
Depolarized
The resting charge of a neuron is -70mv refers to its ___.
Polarity
Arrange the following events of the sliding filament theory and cross-bridge cycle in the correct order.
ATP binds to the myosin head, causing it to detach from actin.
The myosin head hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, returning to the “cocked” position.
Calcium ions bind to troponin, causing tropomyosin to move and expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
The myosin head binds to actin, forming a cross-bridge.
The power stroke occurs as ADP and inorganic phosphateare released, pulling the actin filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
Calcium ions are actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and the muscle fiber relaxes.
3, 4, 5, 1, 2, and 6
Rank the following events in order correct order:
a. Acetylcholine moves across the synapse to trigger the dopolarization of the muscle.
b. Tropymosin is triggered to move when Ca2+ binds to troponin.
c. Ca2+ leaves the sarcoplasmic reticulum via exocytosis into the sarcoplasm.
d. Action potential moves down the t-tubule
a, d, c, and b

Match the letter in the diagram that matches the muscles: External oblique, Transverse abdominis, Rectus Abdominis, Pectoralis major
D, B, C, A

Match the letter in the diagram that represents each muscle: Orbicularis Oculi, Zygomaticus, Masseter, Orbicularis Oris
A, D, B, C
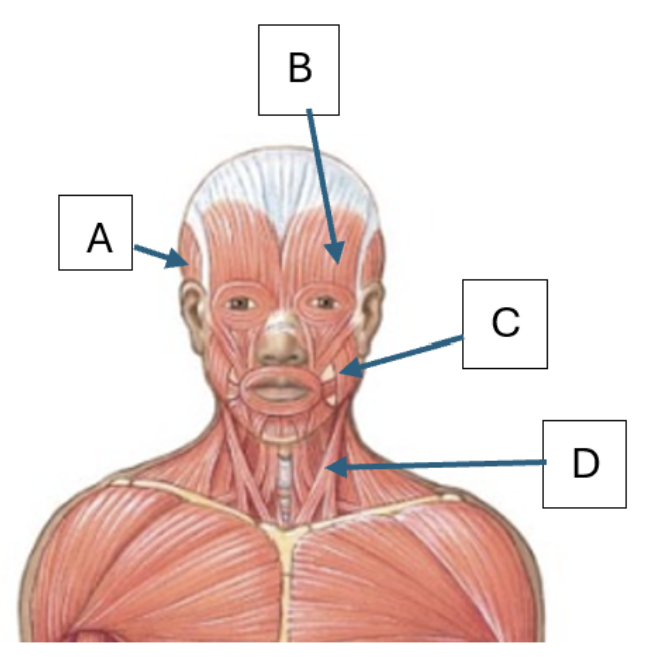
Match the letter in the diagram that represents the muscle: Masseter, Temporalis, Sternocleidomastoid, Frontalis
C, A, D, B
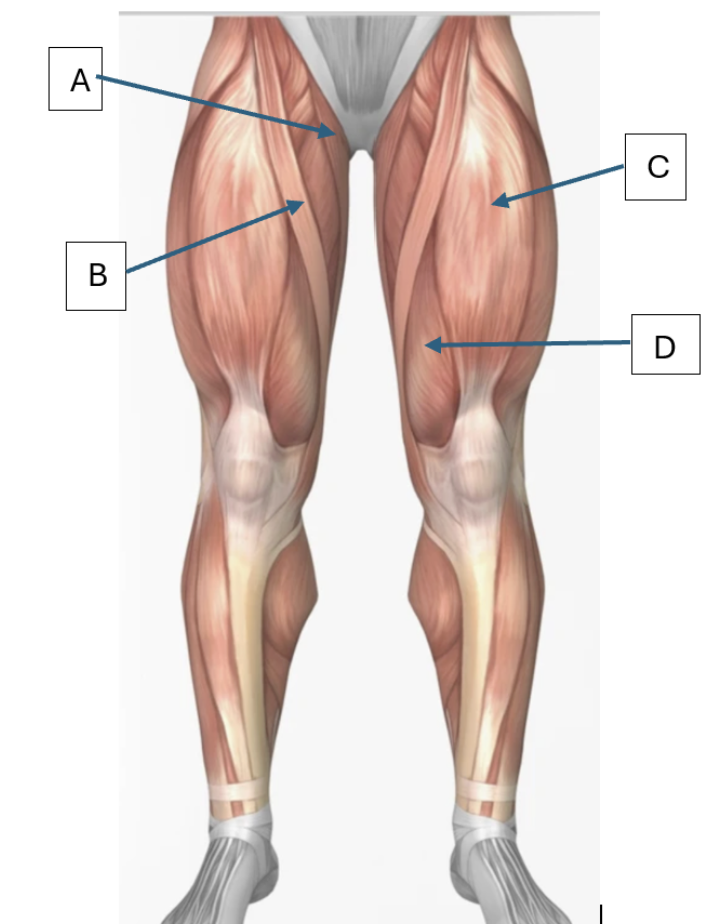
Match the letter to the muscle below: Rectus femoris, Sartorius, Vastus medialis, Gracilis
C, B, D, A
An excitatory neurotransmitter results in ___ ions moving across the post synaptic membrane in a chemical synaptic event.
Na+
Motor neuron is an example of a ____ neruon.
multipolar
Phagocytes that remove debri, waste, and pathogens from CNS
Microgila
Regulates the O2, CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons in ganglia
Satellite cells
Provides myelination for axons of the PNS
Schwann cells
Provides myelination for axons of the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
The central nervous (CN) system includes all the following: (select all that apply)
spinal cord, brain
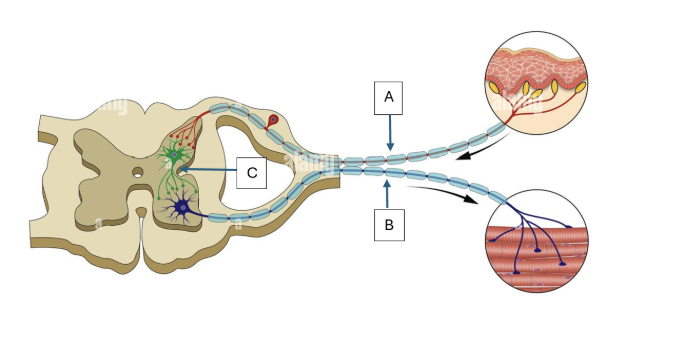
Match the following parts of the reflex arc to the terms below: interneuron, sensory neuron, motor neuron
C, A, B

Match the correct term to each of the parts of the neuron below: Schwann cell, Axon terminal bud, Axon, Dendrites, Cell body, Node of Ranvier
C, E, F, A, B, D
Demyelination of the axon speeds up the propagation of the action potential.
False