histo exam 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Elastic artery (Aorta)
circular lumen w thick walls
Intima: Thick and typically folded
Media: thich w Hella elastic fibers within smooth muscle
Adventitia: Thin
vasa vasorum in media + intima
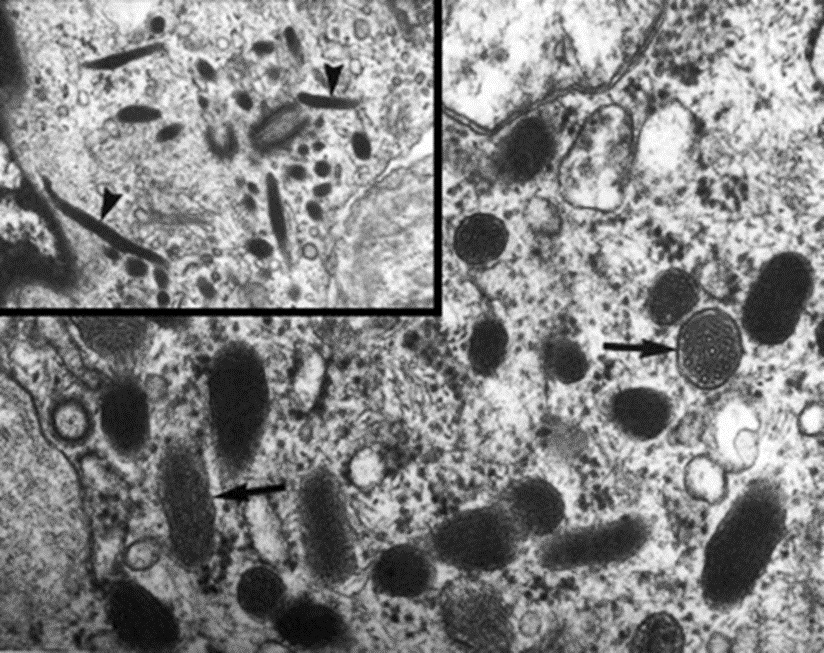
WPBs
in tunica intima of endothelial cells
von Willebrand Factors
P-selectin (recruits circulating leukocytes to site of injury)
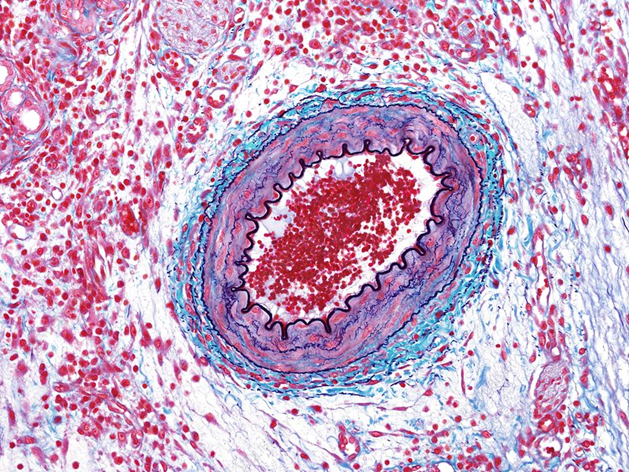
Muscular Artery
Distributing branches to specific body parts (Rad/ ulnar art)
circular lumen w Lots of smooth muscle
Intima: Prominent internal elastic lamina
Media: thick smooth muscle layre
Adventitia: Thick
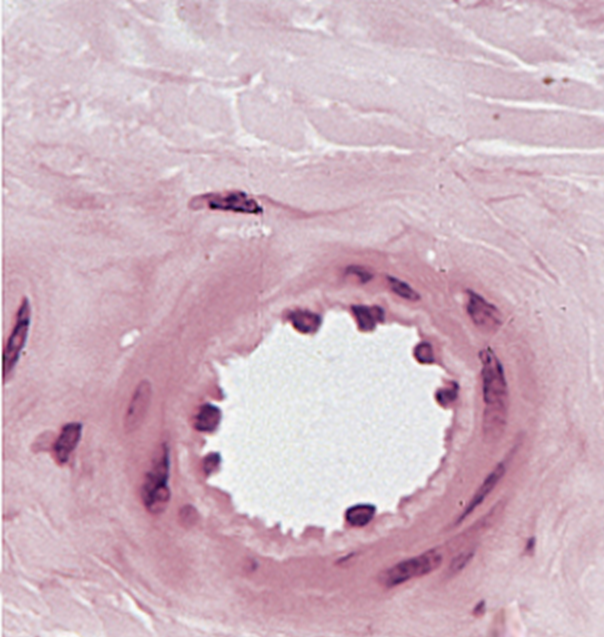
Arteriole
Branches of muscular art
circular lumen w thin wall
Intima: No internal elastic lamina
Media: V thin only 1 or 2 smooth muscle layers
Adventitia: Very thin

Continuous “ Tight” capillaries
Tightly packed endothelial cells
continuous BM
Mol transport via transcytosis or diffusion

Fenestrated capillaries
Small circular fenestrae ( Holes) in endothelial cells
Continuous basal lamina
More extensive molecular exchange
In the kidney, intestine, the choroid plexus, endocrine glands
Sinusoidal “ Discontinuous” capillaries
Bigger than most capillaries
Larger fenestrae
Wide intercellular space and discontinuous basal lamina
Hella exchange of macromolecules and blood cells
In liver, spleen, bone marrow, some endocrine glands
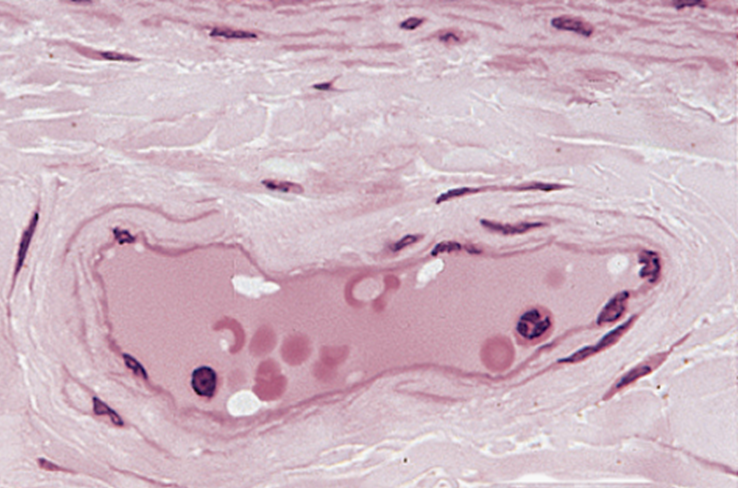
Venules
Irregular shaped and hella large Lumen
V thin wall with 1 - 3 layers of smooth muscle
Material exchange with surrounding tissue
Primary site for white blood cells leaving circulation
Converge into collecting venules, then muscular venule
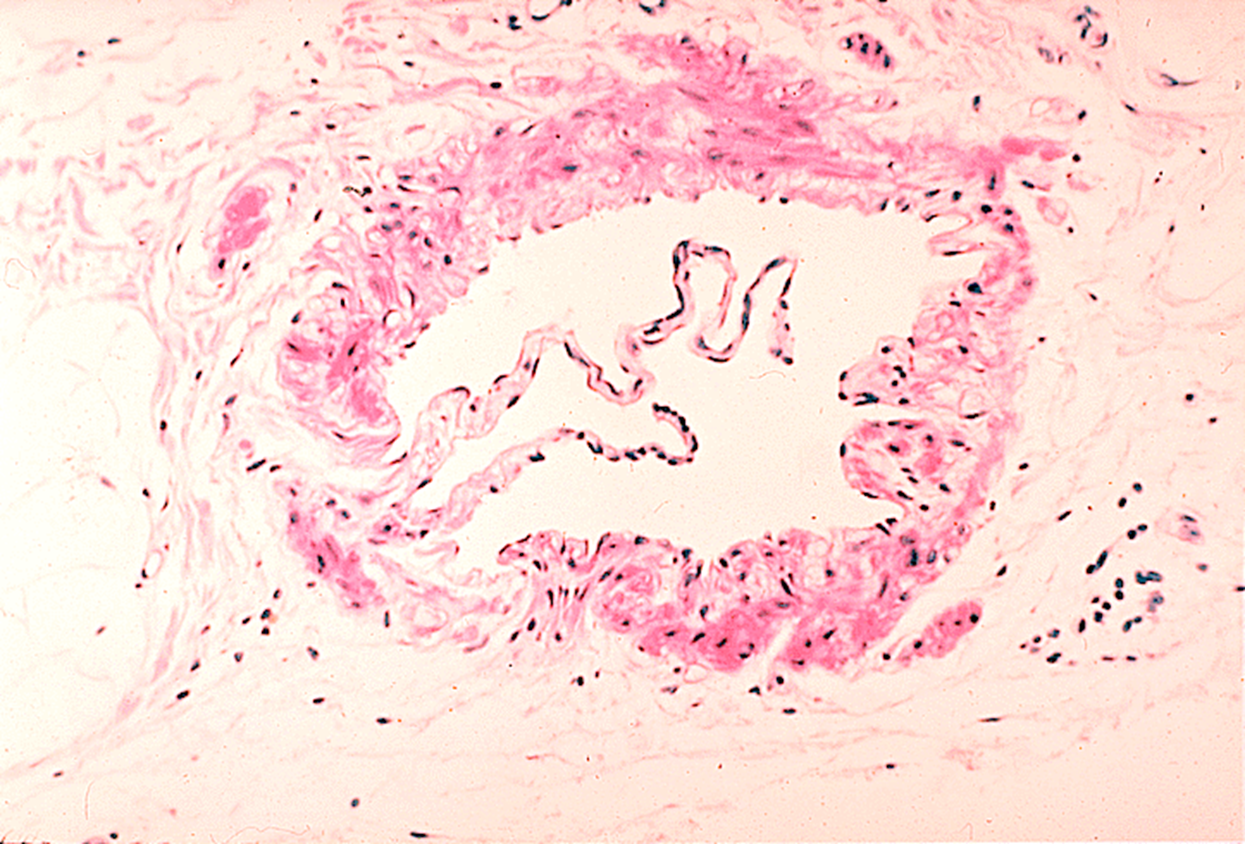
Vein
3 layers of tunics but not well defined,
no elastic lamina
Very low pressure,
large irregular shaped lumen with thin walls
chaotic Valves project from the intima to prevent back-flow of blood
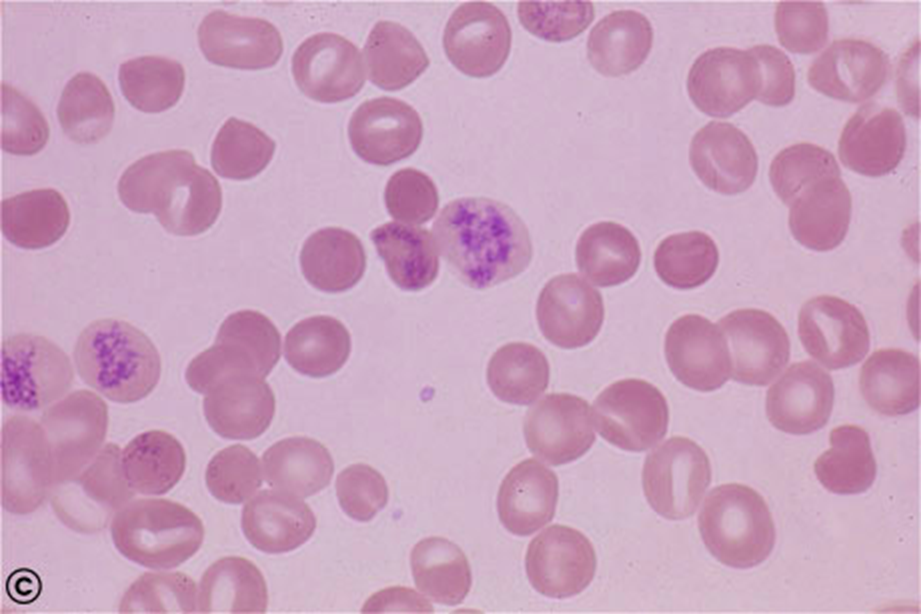
Reticulocytes
rRNA remnants
immature RBC w no nuc
high reticulocytes = low RBC (anemia/ bleeding)
low reticulocytes = bone marrow issue
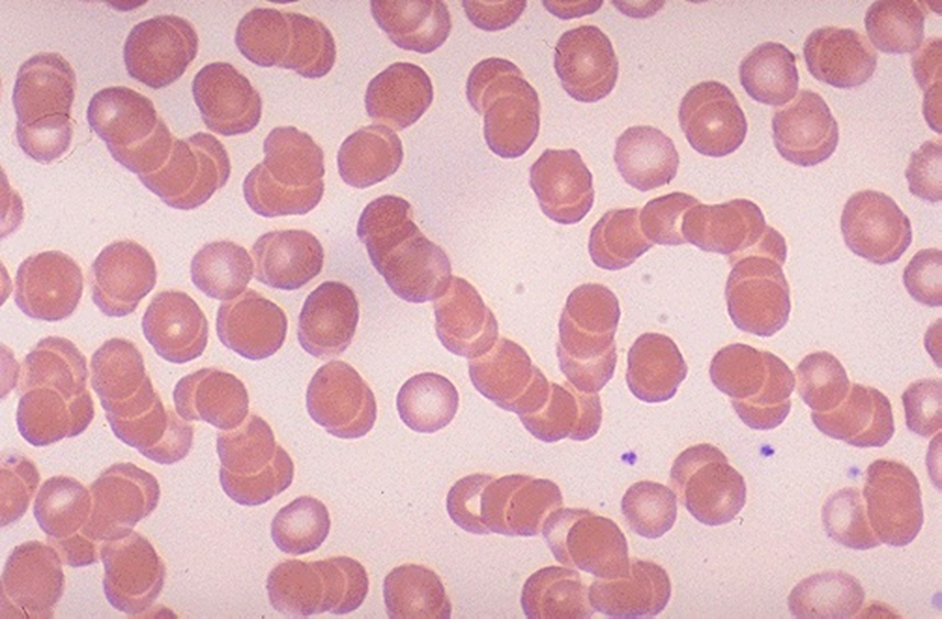
Rouleaux Formation
Occurs with increased plasma proteins, particularly fibrinogen and globulins
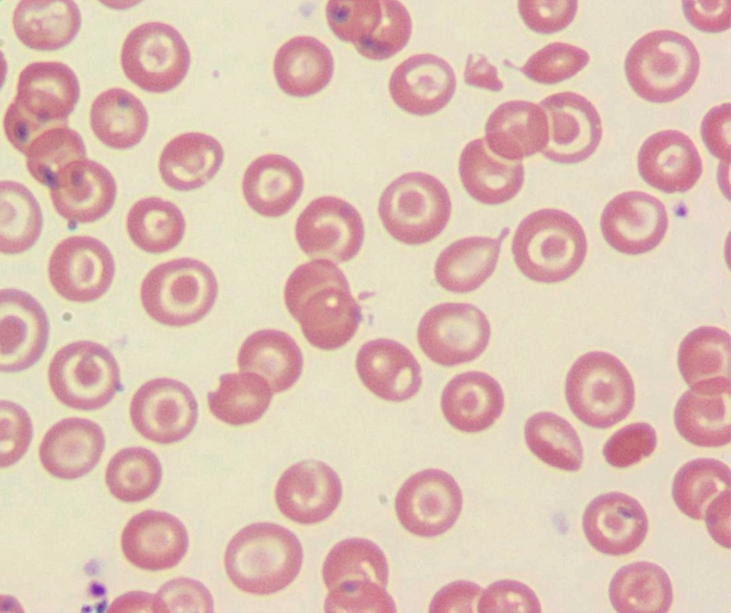
Thalassemia
target cell
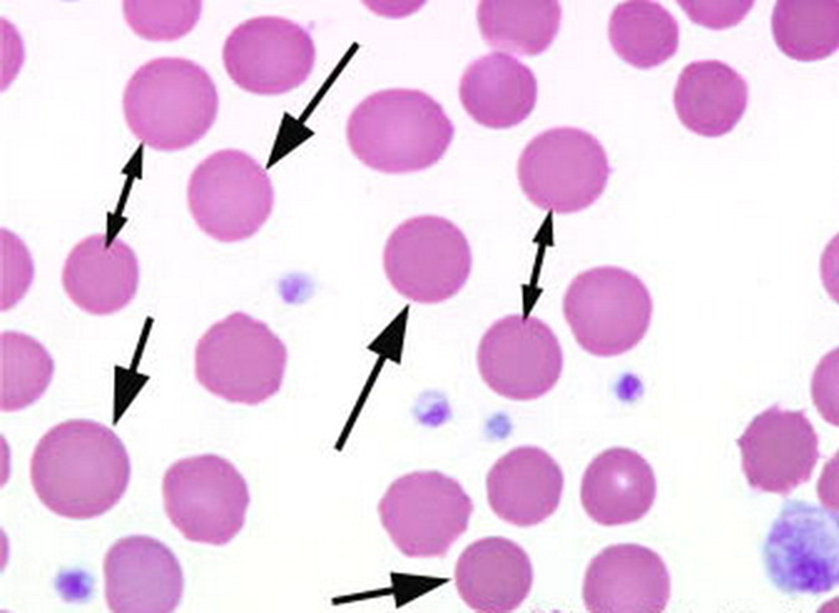
hereditary spherocytosis
deficiencies of band 3, protein 4.2, spectrin (most common), or combined spectrin and ankyrin deficiency
Sphere-shaped RBCs with NO ZONE OF PALLOR
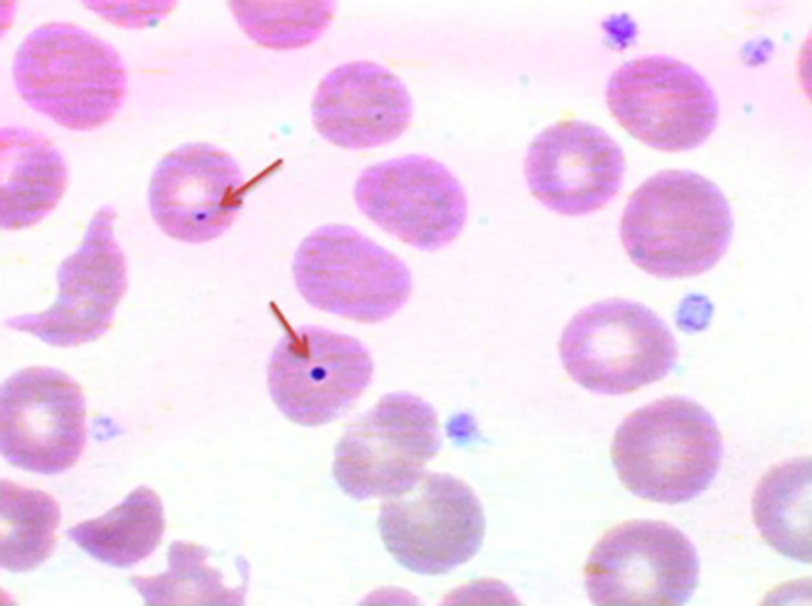
Howell - Jolly Bodies
Inclusions of nuclear chromatin remnants
only a few dots in rbc
happens when spleen isnt working right or not there
megaloblastic anemia, hemolytic anemia
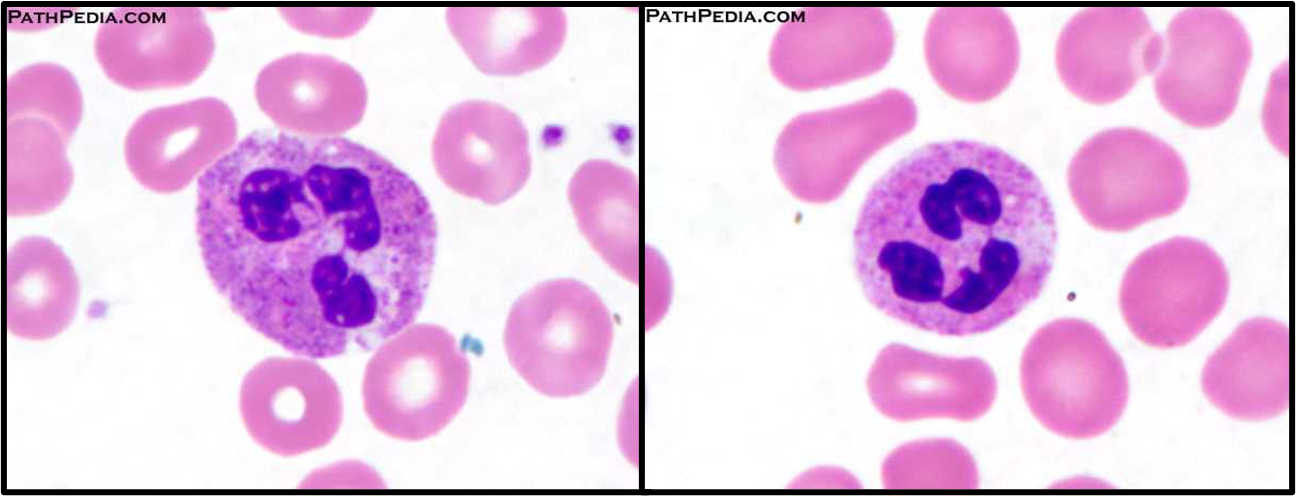
Neutrophil
nuc have 3 - 4 lobes connected by chromatin
60%-70% of total leukocytes
Larger than RBC
Contain only neutrophilic secondary granules
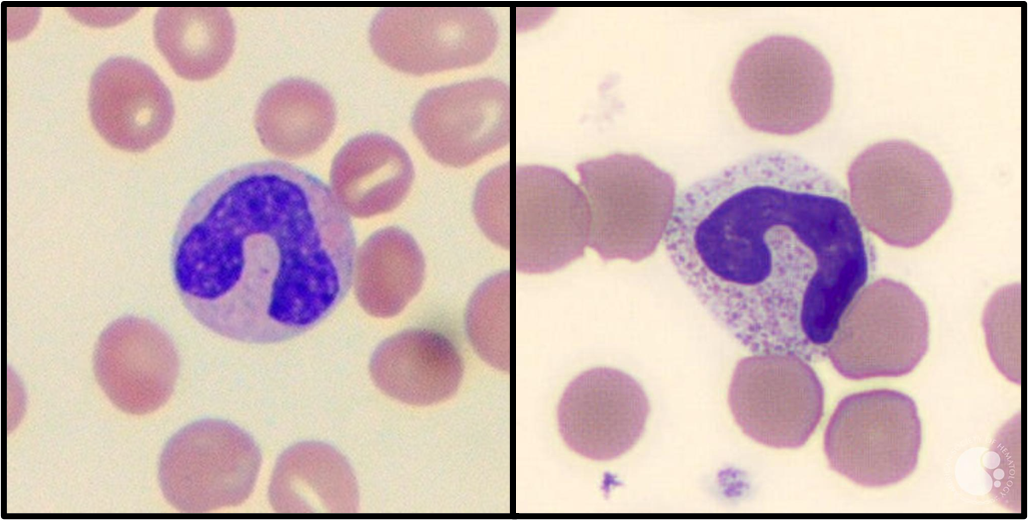
Band neutrophil
immature neutrophils
Increased number commonly seen in infection
hoarse shoe but nondemented nuc
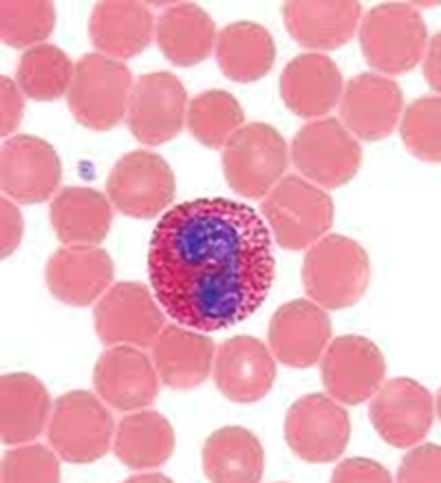
Eosinophil
Bilobed nuclei with eosinophilic red/ pink granules
Granules contain peroxidase, eosinophilic cationic protein, and histaminase
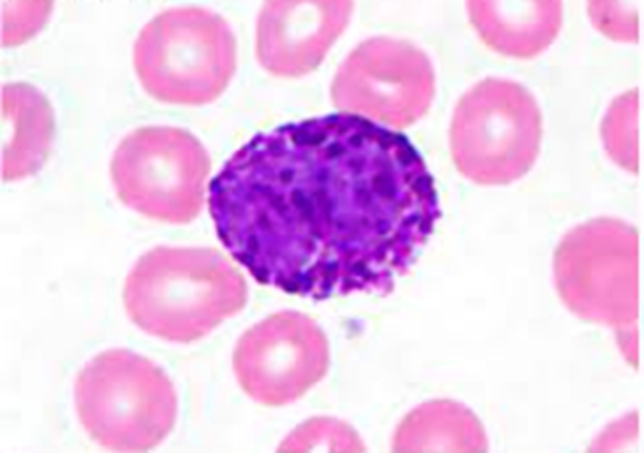
Basophil
Irregular nuclei, hidden by large basophilic specific granules
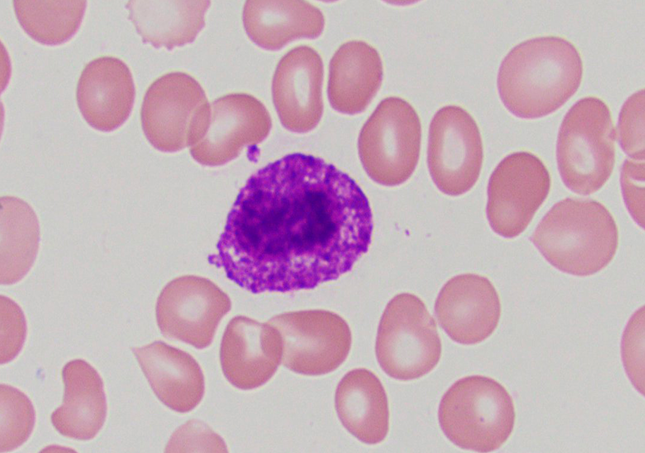
Mast cell
very condensed basophilic (purple) granules that hide nuc
darker in center!
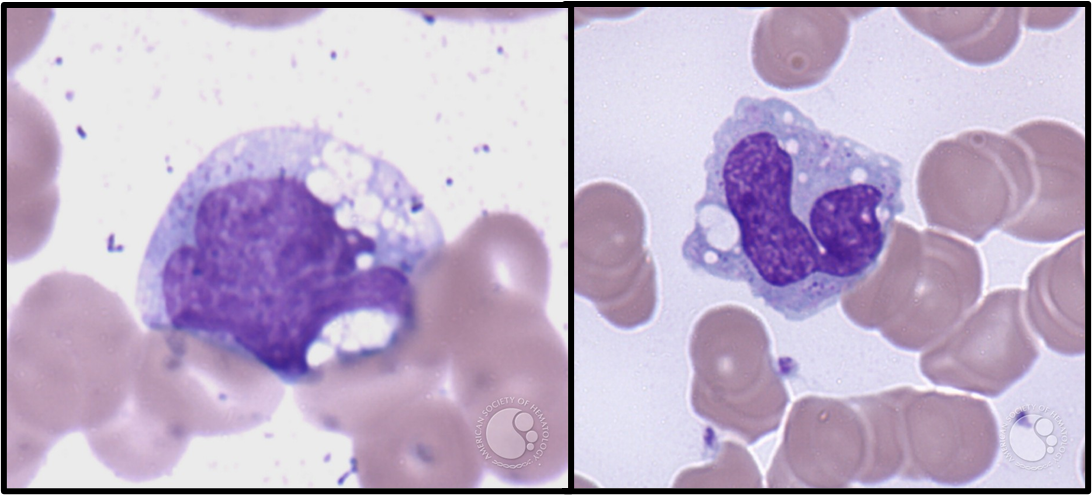
Monocyte
Bigger than RBC
Kidney or C-shaped nuclei
NO specific granules
cytoplasmic vacuoles!
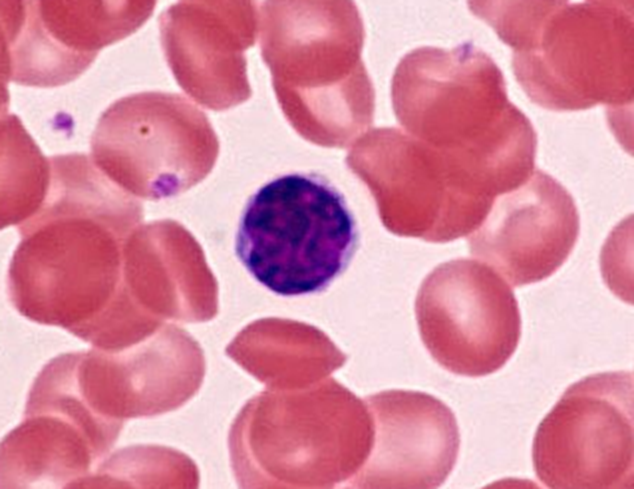
Lymphocyte
(Bcell, Tcell, or NKcell)
Round oval nuc
scant cytoplasm
NO GRANUALES
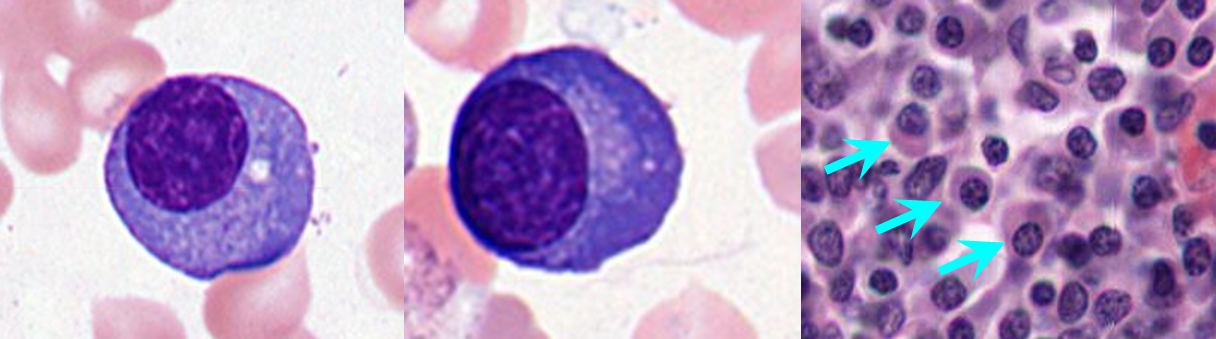
Plasma Cells
Large dense eccentric reound / oval nuc
peripherally dispersed heterochromatin with "clock-face" pattern
Enlarged Golgi apparatus
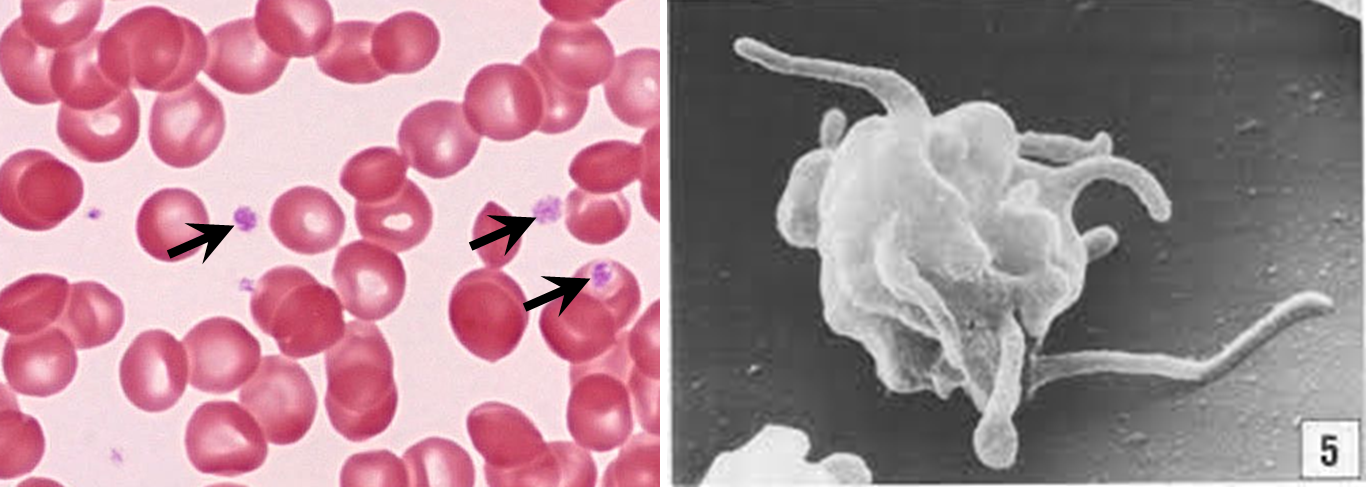
Platelets
not real cell its a cytoplasmic fragment
no nuc
tiny + basophilic
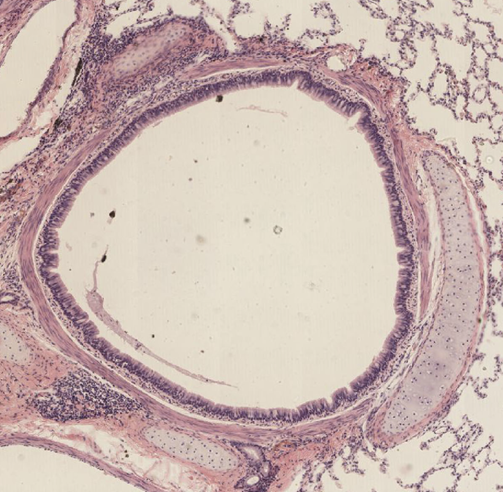
Primary bronchi
C-shape rings of hyaline cartilage
thin layer of smooth muscle
respiratory epithelium
glands
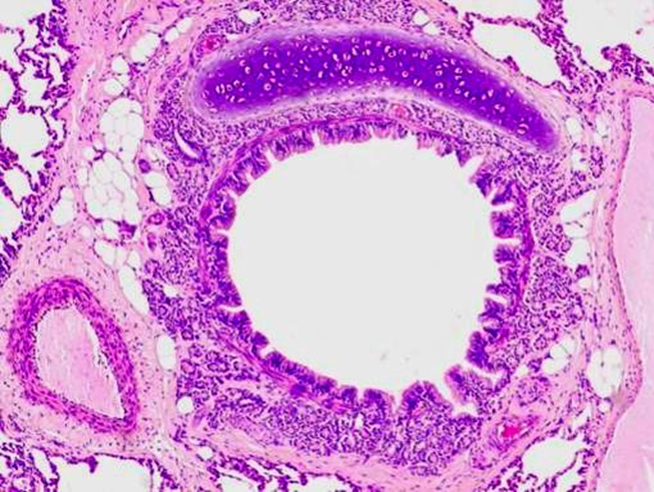
secondary / tertiary bronchi
have plates of hyaline cartilage
folded resp mucosa
glands
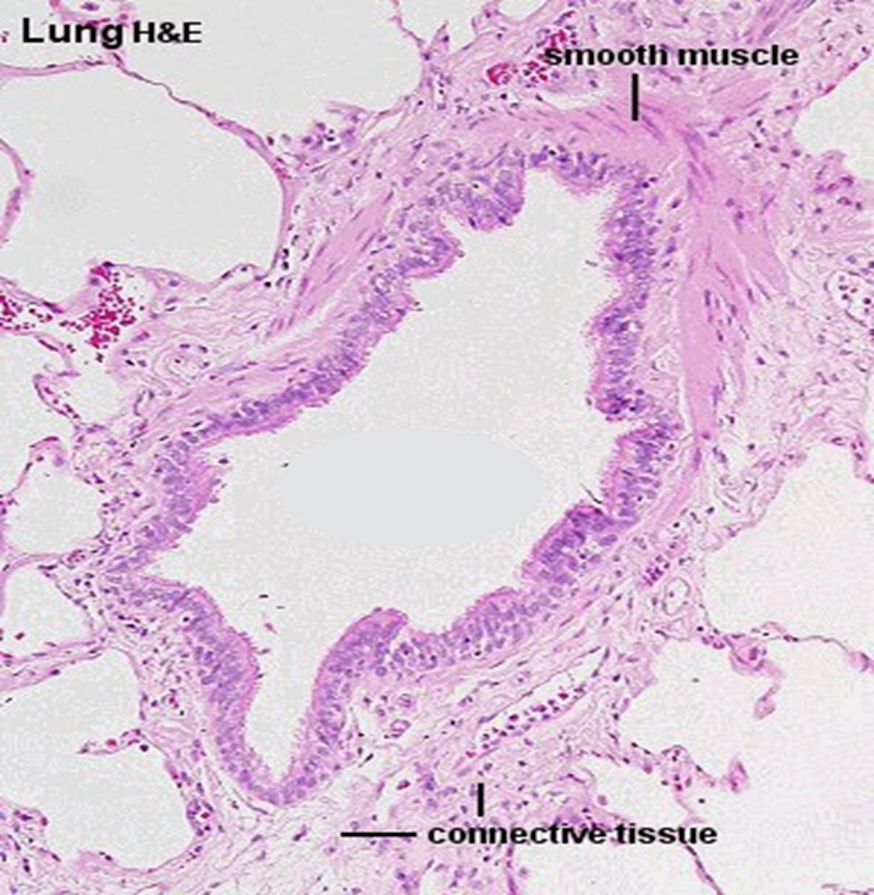
Bronchiole
ciliated pseudostratified columnar transitions to simple cuboidal
hella smooth muscle
No cartilage, glands, or goblet cells
Dense connective tissue
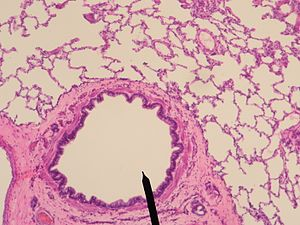
Terminal Bronchiole
end of conducting zone
Ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium
Club/ Clara Cell
NO GOBLET CELLS
less smooth muscle than other bronchioles
Clara / Club Cells
Replace goblet cells and protect the bronchioles
Dome-shaped non-ciliated
apical projection within epithelial cells
Secrete surfactant-like material and antibiotic peptides
Detoxification of inhaled particles by enzymes
stem cells for all bronchiolar epithelium
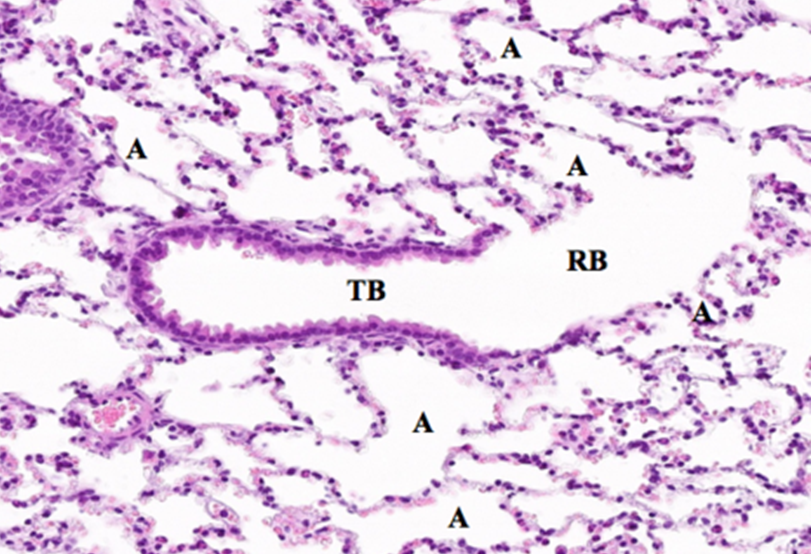
Respiratory Bronchioles
ciliated cuboidal epithelium and club cells
Walls interrupted by openings to alveoli
Smooth muscle underneath
club cells and scattered alveoli
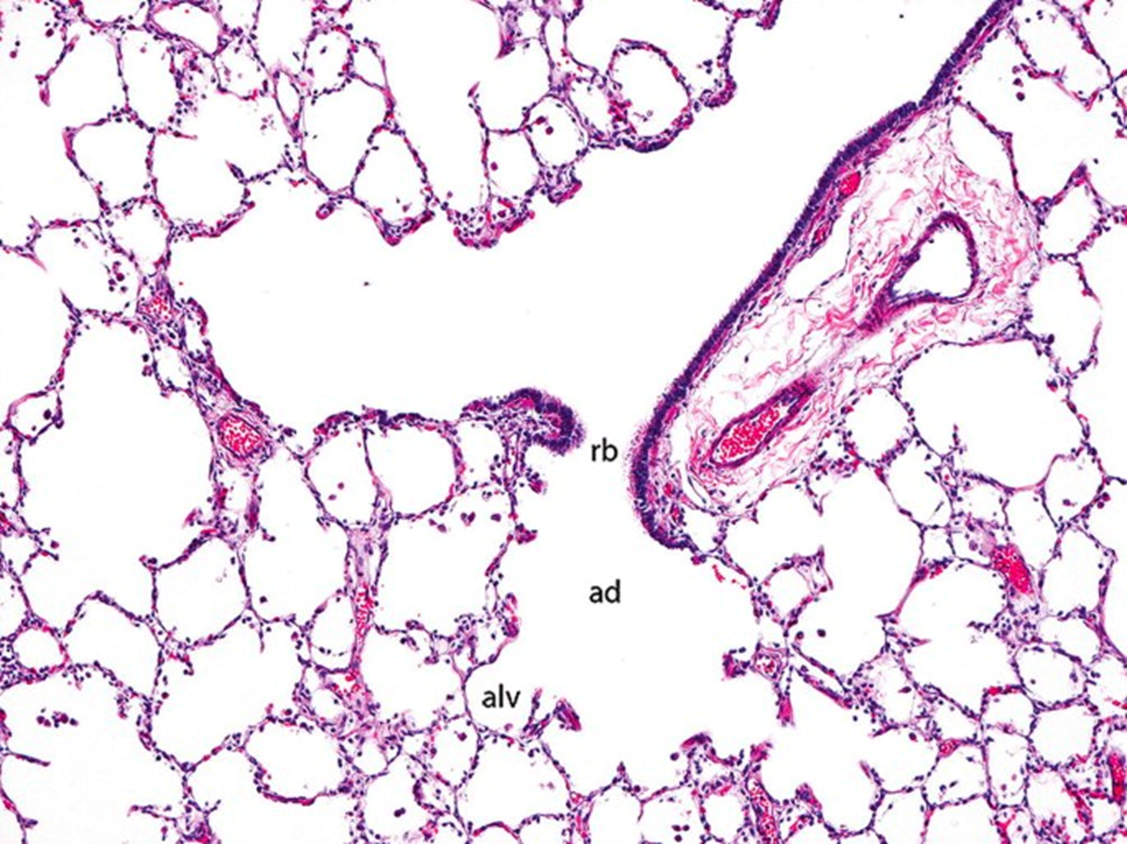
Alveolar Ducts
Distal end of the respiratory bronchioles branch into alveoli ducts that are completely lined by the openings of alveoli
Small knobs of smooth muscle covered by cilia-free simple cuboidal cells that project into lumen
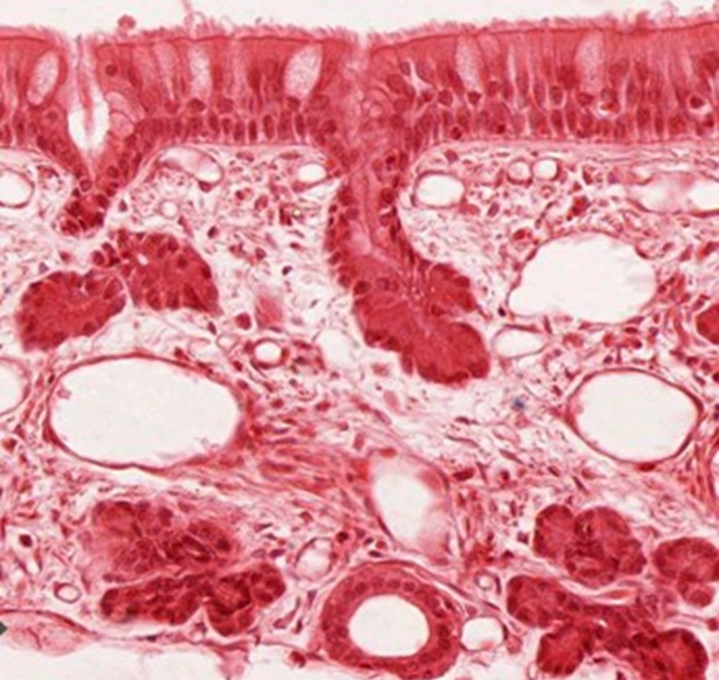
Respiratory epithelium
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar all attached to the basement membrane
goblet and basal cells throughout
Goblet Cells
Found in respiratory epithelium ( nasal cavity, sinuses, trachea)
produce mucus/ pale staining
apical surface between pseudostratified columnar cells
Basal Cells
stem cells for epithelial cells
single layer on basal surface of columnar cells resting on basement membrane
Anterior nasal cavity
vestibule
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium near opening changes to nonkeratinized deeper
contains sebaceous and sweat gland
Paranasal Sinuses
Air filled cavities communicating with nasal passages
Lined with respiratory mucosa continuous with nasal cavities
Venous sinuses warm air, mucus traps junk, cilia sweep it towards nasopharynx
a few small seromucous glands and fewer goblet cells than nasal cavity
Chonchae
Superior conchae : olfactory epithelium
Middle and inferior conchae : Lined with respiratory epithelium
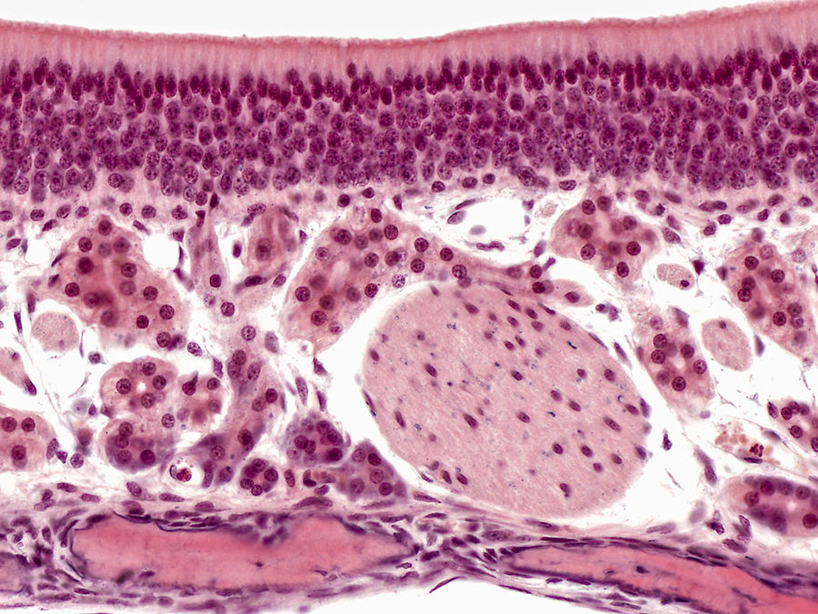
Olfactory epithelium
lines Superior nasal concha and roof of nasal cavity and upper septum
Olfactory cells
Sustentacular cells
Basal cells
Bowman’s glands
NO GOBLET CELLS
loose ct
Olfactory cells
bipolar neurons which initial nerve impulse
Nuc in middle of epithelium
replaced by basal cells
axons in lamina propria
Sustentacular cells
supporting cells for olfactory cells
apical surface
Structural support
Small microvilli
Bowman’s glands
secrete mucus, IgA, and lysozymes
Produce odorant binding molecules that aids in transporting scents to olfactory receptors
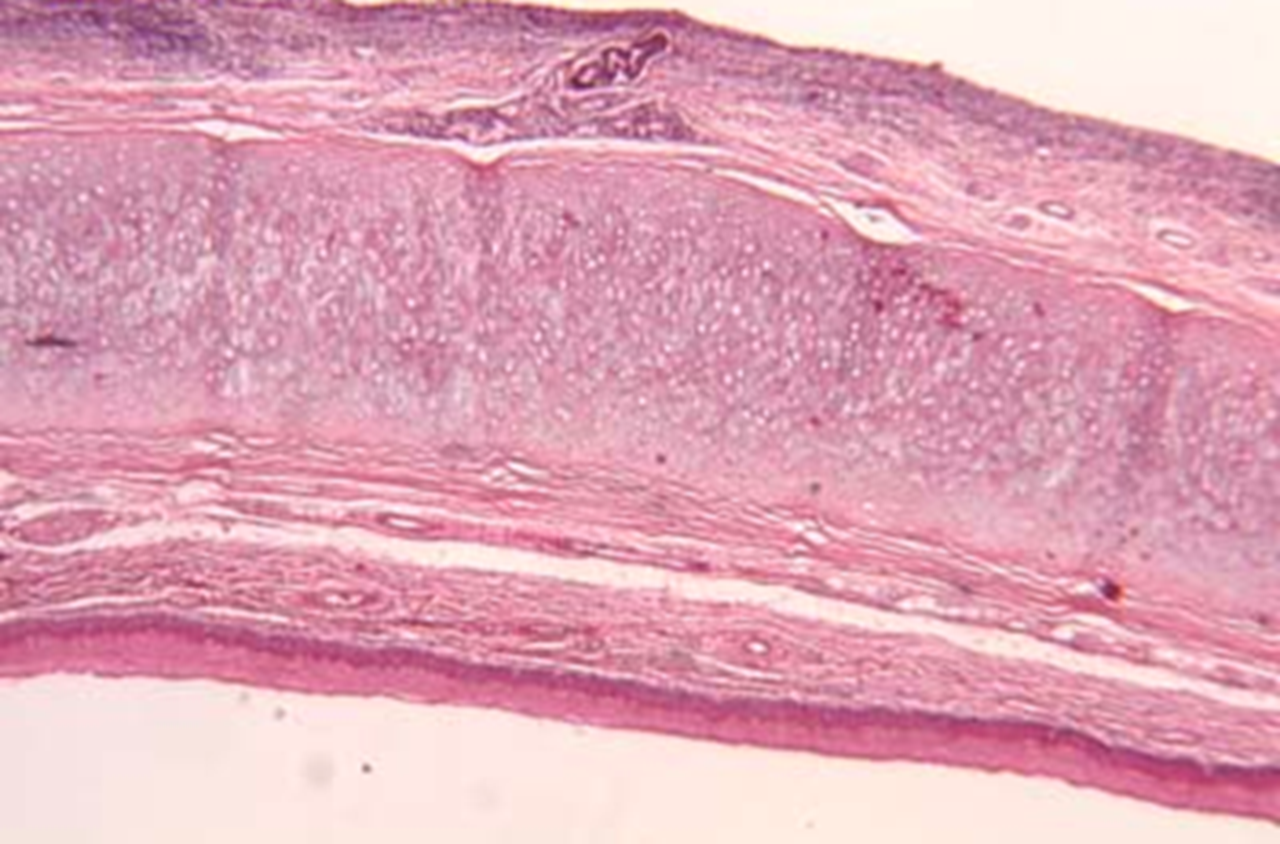
Epiglottis
Elastic Cartilage
Covers entrance to larynx during swallowing and attaches to hyoid bone
Superior/ lingual surface: nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Inferior/ laryngeal surface: respiratory epithelium
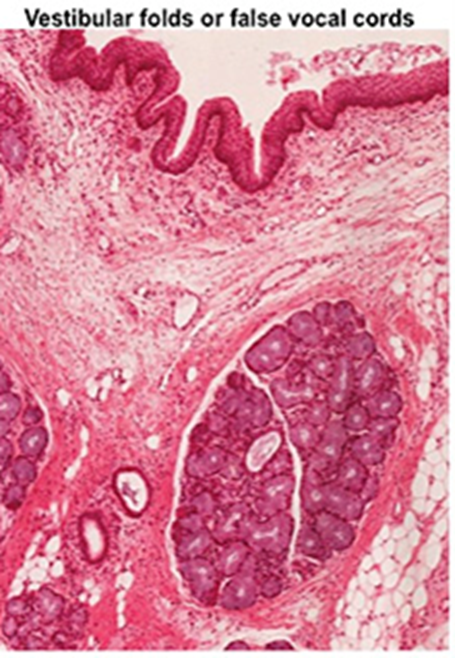
Upper / False vocal folds (vestibular folds)
non-keratinized stratified squamous + respiratory epithelium
bumpy surface w seromucous glands,
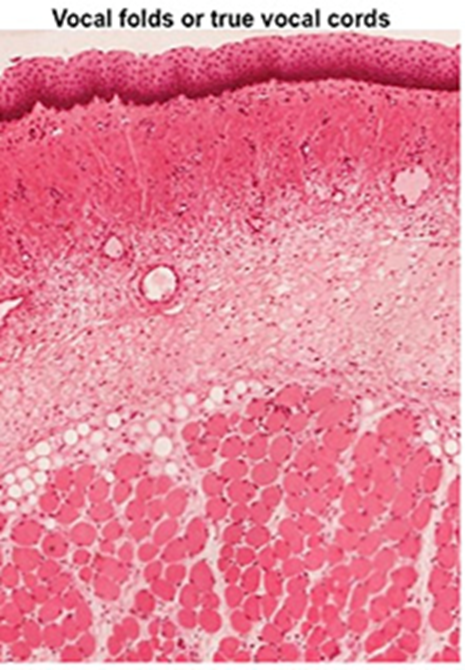
Lower/ true vocal folds
non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
vocalis muscle
No seromucous glands
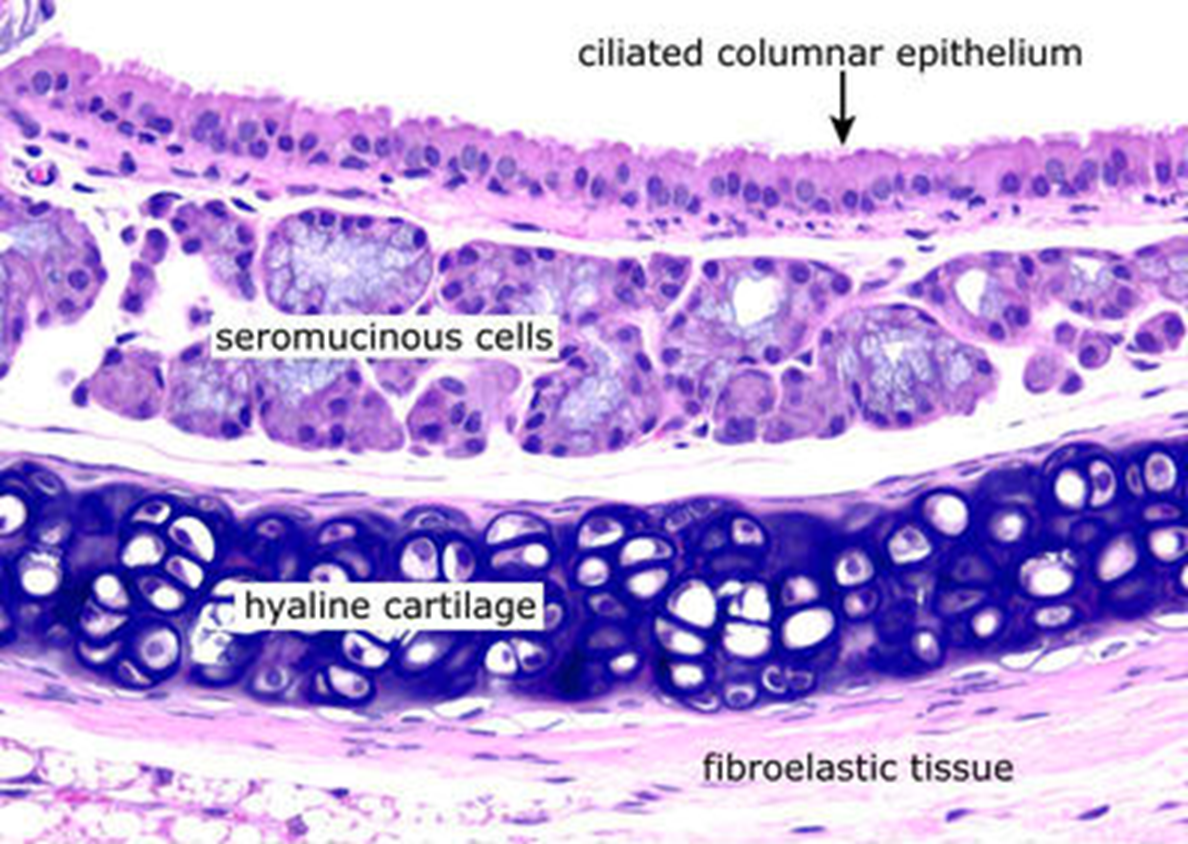
Trachea
Hyaline cartilage
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
hella seromucous glands