General Anesthetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the indications for oral pre-anesthetic agents?
prepping pts for surgery
anxiety relief
hypnosedatives: diazepam/phenobarb
decreasing GIT mobility + bronchial secretions
anticholinergics: atropine
subside pain
analgesics: morphine
relax skeletal muscles
NM blockers: succinylcholine chloride
What is one major criteria for induction (IV) anesthetic agents?
must be FULLY water soluble
Thiopental sodium
induction agent
barbiturate derivative
fast acting
lipophilic sulfur → fast entry to CNS
short acting
rapid metabolism by aliphatic hydroxylation
injection as Na salt
Why should IV solutions, like thiopental sodium, not be mixed with acidic pH solutions?
precipitation will occur
Ketamine
induction agent
very powerful central analgesic
MOA: glutamate antagonist
ketone
amine
injected as HCl salt → NO alklaline solution mixtures!
Etomidate
induction agent
MOA: GABA potentiation
ethyl ester
imidazole ring
basic nature
sedative
If etomidate were to be given as a HCl salt injection, why would it need to be solubilized with propylene glycol and ethanol?
to protect ester from acidic pH
Midazolam
induction agent
MOA: GABA potentiation
given as HCl salt (do not mix w/ alkaline solutions)
benzodiazepine
sedation + muscle relaxation
Propofol
induction agent
MOA: GABA potentation
2 isopropyl groups
phenol → low acidity
given as emulsion w/ soya oil and glycerol
produces hypnosis + sedation
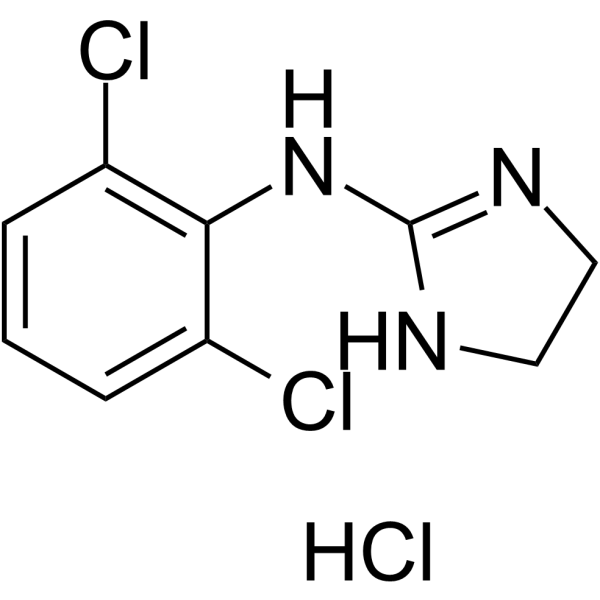
Clonidine
induction agent
central alpha 2 agonist → reduces sympathetic outflow
2-imidazoline group
given as HCl salt injection intrathecally
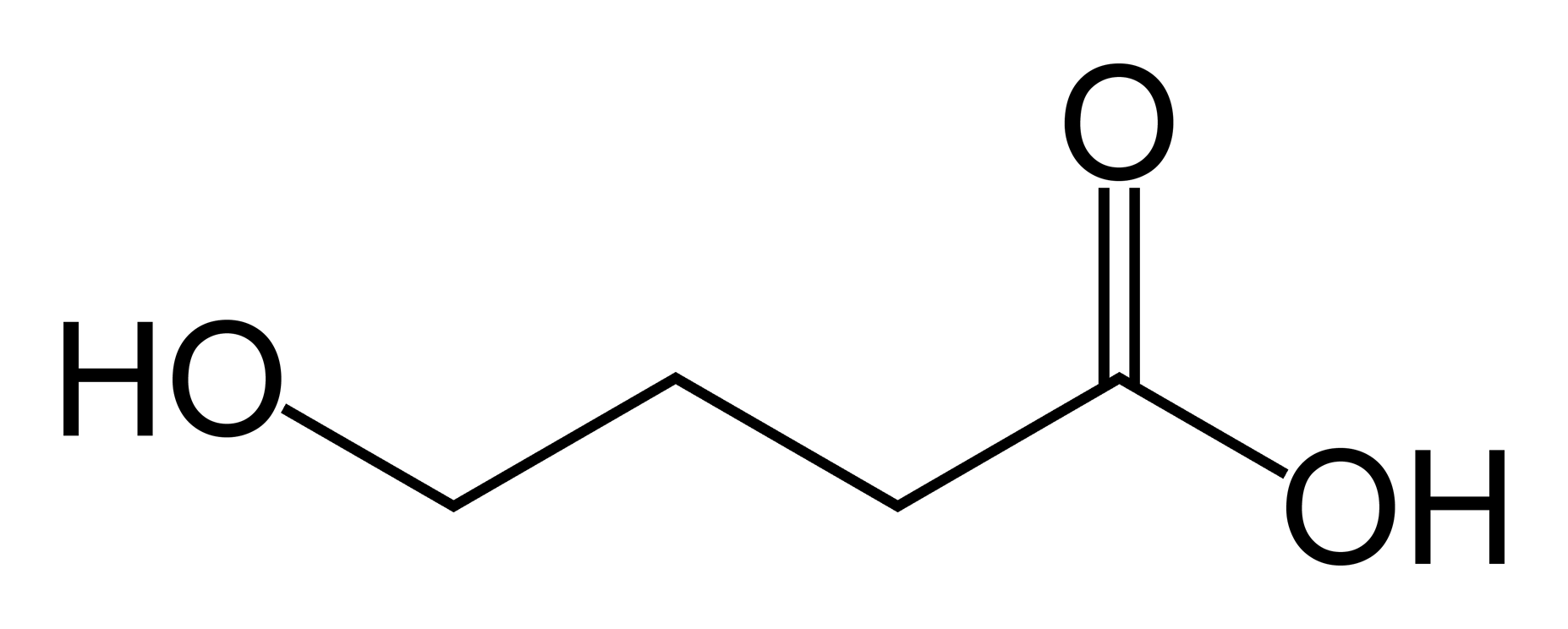
Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid
induction agent
bioisotere of GABA
MOA: direct GABA and DA agonist
given as Na salt injection
produces sleep + sedation (NOT hypnosis)
T/F: Inhalation anesthetic agents lead to total loss of all sensations
TRUE
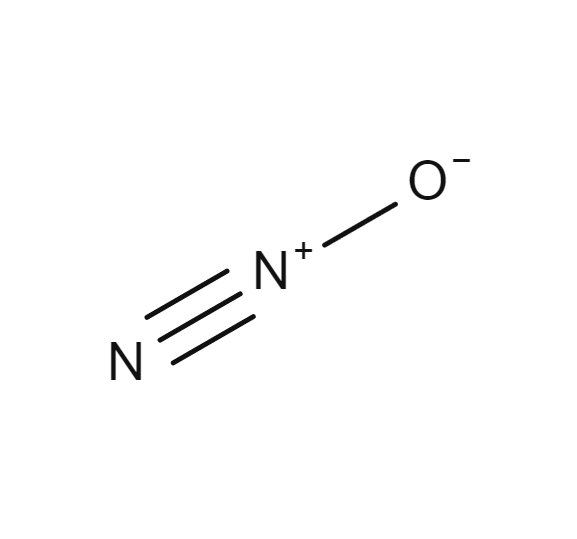
Nitrous oxide
inhalation agent → “laughing gas”
very powerful central analgesic
may cause hypoxia

Diethyl ether
inhalation agent
volatile liquid
2 ethyls
flammable properties → halogenation efforts (hypnosis)
Halothane
inhalation agent
volatile liquid → nonflammable
hepatotoxic (due to halogenated C’s)
produces sleep and sedation
NO muscle relaxation

Methoxyfluorane
inhalation agent
volatile liquid → somewhat flammable (due to ether)
2 Chloros and 2 fluoros (NO bromos like halothane)
ether structure
produces analgesia + muscle relaxation
What is the structural difference between halothane and methoxyflurane?
halothane: 3 fluoros + 1 bromo
methoxyflurane: 2 fluoros, 2 chloros, ether
What is the clinical difference between halothane and methoxyflurane?
halothane: sleep + sedation ONLY
methoxyflurane: analgesia + muscle relaxation ONLY
Sevoflurane
inhalation
volatile liquid
halogenated ether
produces analgesia and muscle relaxation
SATA: Which anesthetic agents have flammable properties?
a. diethyl ether
b. propofol
c. halothane
d. methoxyflurane
e. ketamine
a. diethyl ether
d. methoxyflurane (somewhat flammable)
SATA: Which inhalation agents do NOT cause sedation?
a. halothane
b. methoxyflurane
c. nitrous oxide
d. sevoflurane
e. diethyl ether
b. methoxyflurane → analgesia + muscle relaxation
c. nitrous oxide → analgesia
d. sevoflurane → analgesia + muscle relaxation
What inhalation agents cause muscle relaxation AND analgesia?
sevoflurane
methoxyflurane