chm 116 intermolecular forces
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Dispersed phase
Molecules are far apart (gases)
Condensed phase
Molecules are closer together (liquids and solids)
Intramolecular bonds
Bonds within a molecule
Intermolecular bonds
Bonds between molecules
List weakest to strongest intermolecular forces
London disperson, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bond, ion-dipole, ionic bond
Polarizability
The ability of an electron cloud to distort from changes in charge, affecting intermolecular forces
Higher molecular weight —> ? boiling point
Higher
Larger atoms —> ? electron clouds
Larger
Larger atoms —> ? polarizable
More
More polar —> ? boiling point
Higher
What elements can H bond to in hydrogen bonds?
F, O, and N
What does ion-dipole interactions allow ions to do in polar solvents?
Ions can dissolve in polar solvents
Viscosity
Resistance of the flow of a liquid (thickness)
Surface tension
Difference in surface energies between 2 substances
What is surface tension a result of on a molecular scale?
Net inward force experienced by molecules on the surface of a liquid
Capillary action
A liquid’s ability to “crawl” up surfaces
What 2 forces affect capillary action?
Adhesive and cohesive forces
What phases does sublimation change?
Solid —> Gas
What phases does deposition change?
Gas —> Solid
Heat/Enthalpy of Fusion
The energy required to change a solid to a liquid
Heat/Enthalpy of Vaporization
The energy required to change a liquid to a gas
Heat/Enthalpy of Sublimation
The energy required to change a solid to a gas
What is the equation for heat/enthalpy of sublimation?
Heat of fusion + heat of vaporization
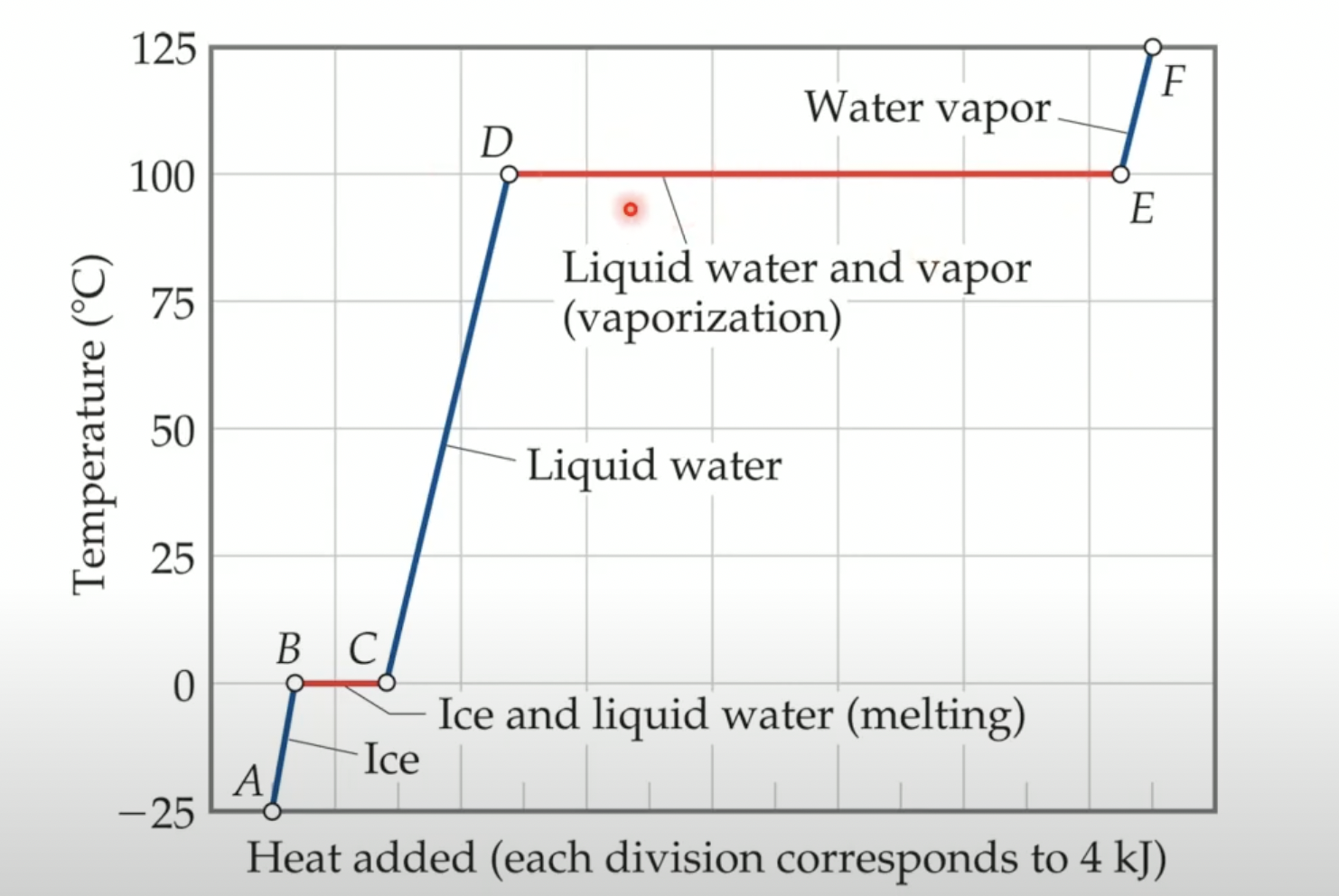
Heating curves
Graphs that show the required amount of energy to raise the temperature and change the phase of a substance
What is the equation for non-phase changes?
q = mCAT
What is the equation for phase changes?
q = (n)(delta H…)
How do you find the total amount of energy needed to change a substance from a solid to a gas?
Add all the sections’ energies together
Vapor pressure
The pressure that gas molecules exert around a liquid/solid when in equilibrium
Higher temperature —> ? vapor pressure
Higher
Higher vapor pressure —> More liquid molecules “?”
Escape
Vapor pressure shows the relationship between vapor pressure and ____?
Temperature
Volatile
A substance that easily vaporizes
Triple point on phase diagrams
An equilibrium point when a substance can have solid, liquid, and gas equally
Increase temperature on liquid —> ? density
Lower
Increase pressure on gas —> ? density
Higher
Critical point on phase diagram
The point when the density of a liquid equals the density of a gas (cannot distinguish liquid and gas)
Supercritical fluid
Anywhere beyond the pressure and temperature of the critical point
What can supercritical CO2 be used to extract?
Caffeine