Peds - Reflexes
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
imported from quizlet sanaah sonnier
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
20
Weeks of gestation at which ATNR appears?
4-5 mo
When does ATNR integrate after birth?
ATNR - stimulus
Turn the infant's head to one side while the infant is in supine
ATNR - response
Extension (and ABD) of the arm and leg on the side the child is looking at with flexion (and ABD) of the arm and leg on opposite side (i.e., when the infant looks to the L, the L UE + LE extends)
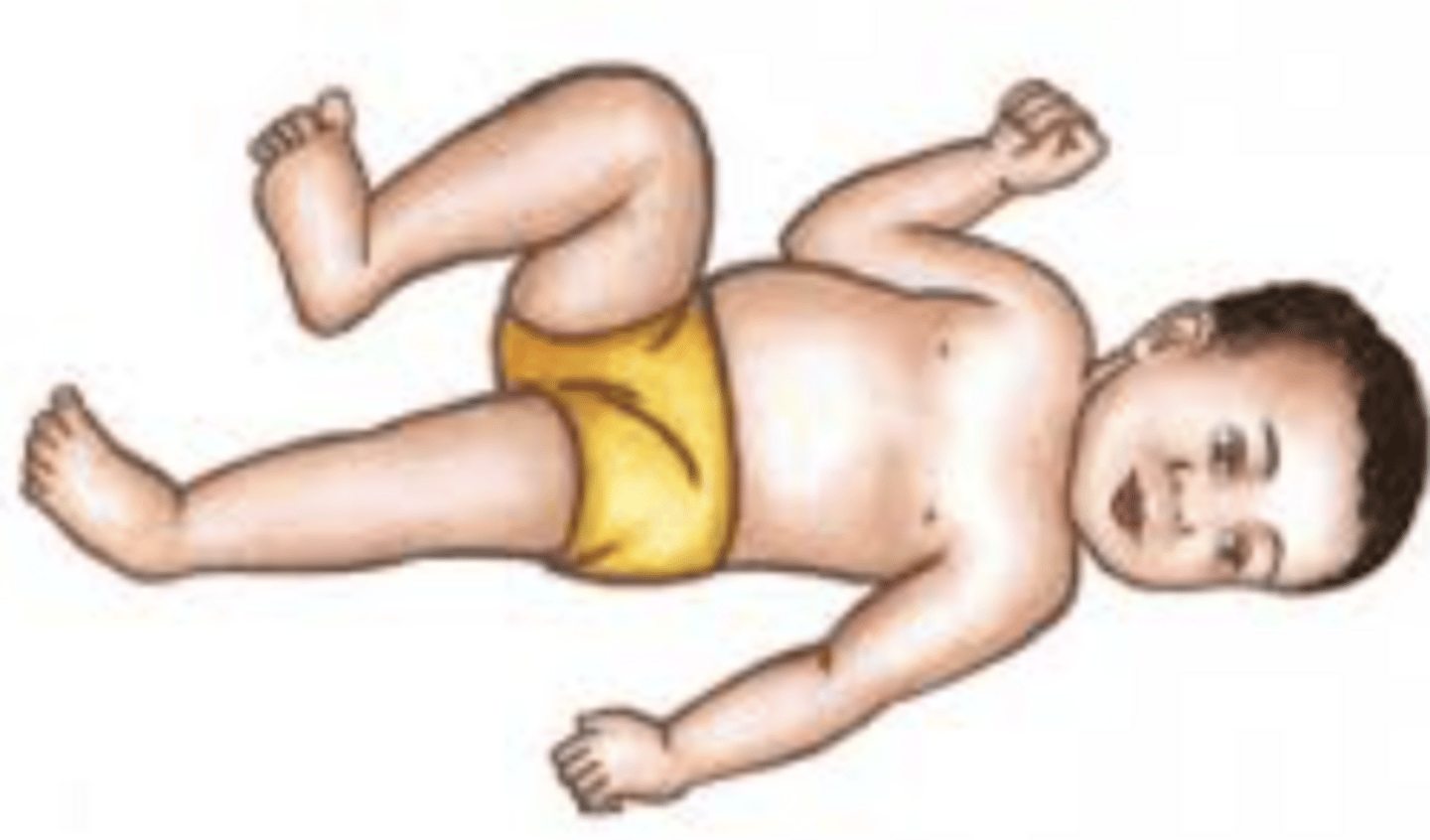

• Asymmetrical posture
• Poor bilateral coordination
• Difficulty with reading and motor milestones
If ATNR persists-
CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
If ATNR is absent-
28
Weeks of gestation at which rooting appears?
3 mo
When does rooting integrate after birth?
Rooting - stimulus
Lightly stroke the cheek or corner of the mouth
Rooting - response
Infant turns head toward the stimulus and opens the mouth
Interferes with normal sucking
If rooting persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• Inability to locate object for sucking
If rooting is absent-
28-34
Weeks of gestation at which suck-swallow appears?
5 mo
When does suck-swallow integrate after birth?
Suck-swallow - stimulus
Touch lips and inside mouth for sucking and liquid for swallowing
Suck-swallow - response
Rhythmic sucking followed by coordinated swallowing (tongue moves up and down, then swallow)
• Inhibits volitional sucking
• Abnormal tongue movement
• Delayed sound production
If suck-swallow persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• Poor nourishment and decreased oral sensory input
If suck-swallow is absent-
28
Weeks of gestation at which palmar grasp appears?
4-7 mo
When does palmar grasp integrate after birth?
Palmar grasp - stimulus
Apply pressure to the palm of the hand (base of the fingers).
Palmar grasp - response
Flexion of fingers (resulting in a strong grasp of the object)
Difficulty releasing objects
If palmar grasp persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• Nerve injury or muscle weakness
If palmar grasp is absent-
28
Weeks of gestation at which plantar grasp appears?
9 mo
When does plantar grasp integrate after birth?
Plantar grasp - stimulus
Infant is held upright & pressure is applied to sole of the foot just distal to metatarsal heads
Plantar grasp - response
Flexion of toes
• Difficulty with standing and walking
• Unstable base of support
If plantar grasp persists-
CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
If plantar grasp is absent-
28
Weeks of gestation at which flexor withdrawal appears?
1-2 mo
When does flexor withdrawal integrate after birth?
Flexor withdrawal - stimulus
Noxious stimulus to sole of foot
Flexor withdrawal - response
Flexion withdrawal of leg
Prevents weight bearing and standing
If flexor withdrawal persists-
• CNS inadequacy
• Peripheral N injury or muscle weakness
If flexor withdrawal is absent-
True
T/F? Flexor withdrawal is a bilateral response, more common at LE than UE
28
Weeks of gestation at which crossed extension appears?
1-2 mo
When does crossed extension integrate after birth?
Crossed extension - stimulus
Noxious stimulus to sole of foot
Crossed extension - response
Flexion of stimulated leg and then extension of opposite leg with abduction
• Homologous creeping ("rabbit hopping")
• Difficulty with sitting, standing, floor transfers
If crossed extension persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• N injury or muscle weakness
If crossed extension is absent-
28
Weeks of gestation at which galant (trunk incurvation) appears?
3 mo
When does galant (trunk incurvation) integrate after birth?
Galant - stimulus
In prone, stroke paravertebral skin
Galant - response
Lateral curvature of trunk on stimulated side
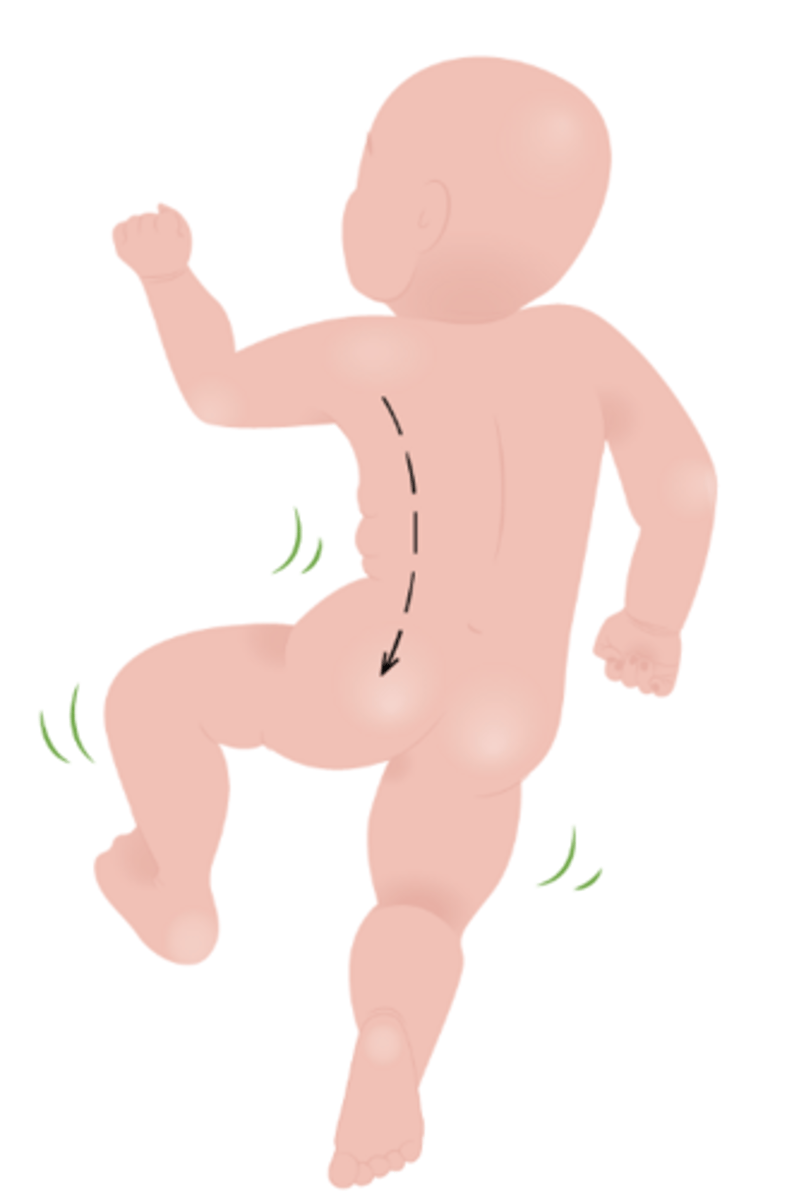
Delayed symmetrical trunk stabilization
If galant persists-
• Brain damage
• Persistent asymmetry (results in scoliosis)
Galant asymmetry indicates-
Crawling, prop sitting
Galant prepares babies for ______ and _________ (to then progress to sitting independently)
28
Weeks of gestation at which moro appears?
3-5 mo
When does moro integrate after birth?
Moro - stimulus
Head drop backward (stimulus for the startle reflex is loud noise with same response)
Moro - response
Adduction and extension of arms, splaying of fingers, may be followed by arm flexion and adduction
• Sensory-motor dysfunction
• Poor head control, sitting, extension patterns
If moro persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• Decreased ability to break flexor patterns
If moro is absent-
35
Weeks of gestation at which positive support appears?
1-2 mo
When does positive support integrate after birth?
Positive support - stimulus
Weight placed through balls of feet while infant is supported upright
Positive support - response
Legs extend to support weight
Delayed development of stepping and pre-walking skills
If positive support persists-
• CNS depression or sensory-motor dysfunction
• Inability to develop stepping reflex
If positive support is absent-
37
Weeks of gestation at which automatic walking/stepping appears?
3-4 mo
When does automatic walking/stepping integrate after birth?
Automatic walking/stepping - stimulus
Supported upright with slight forward lean allowing alternating foot contact
Automatic walking/stepping - response
High stepping movements with regular rhythm
May indicate athetosis
If automatic walking/stepping persists-
May indicate spasticity
If automatic walking/stepping is absent-
4-6 mo after full-term delivery
Weeks of gestation at which STNR appears?
8-12 mo
When does STNR integrate after birth?
STNR - stimulus
Flexion or extension of the neck
STNR - response
With head flexion, UE flexes and LE extends; with head extension, UE extends and LE flexes
True
T/F? STNR prepares infants for crawling + looking at where they are going
UE flexes and LE extends
For STNR reflex, when the head is in flexion, what happens?
UE extends and LE flexes
For STNR reflex, when the head is in extension, what happens?
• Homologous creeping ("rabbit hopping")
• Difficulty with sitting, standing, floor transfers
If STNR persists-
• CNS depression
• N injury or muscle weakness
If STNR is absent-
12
Weeks of gestation at which tonic labyrinthine reflex appears?
3-4 mo
When does tonic labyrinthine reflex integrate after birth?
Tonic labyrinthine reflex - stimulus
Change in head position relative to gravity
Tonic labyrinthine reflex - response
With neck flexion, extremities flex to midline (in prone); with neck extension, extremities extend (in supine)
Flexor
With the tonic labyrinthine reflex, in PRONE (neck flexion) the global (flexor/extensor) tone increases
Extensor
With the tonic labyrinthine reflex, in SUPINE (neck extension) the global (flexor/extensor) tone increases
2-4 mo after full-term delivery
Weeks of gestation at which landau appears?
12-24 mo
When does landau integrate after birth?
Landau - stimulus
Infant is held in horizontal prone suspension
Landau - response
Global extension of the body (head lifts into extension, trunk extends, LE extends)
8-9 mo after full-term delivery
Weeks of gestation at which parachute reflex appears?
~1 year
When does parachute reflex integrate after birth?
Parachute reflex - stimulus
Infant is held upright and rapidly lowered toward a surface (head-first)
Parachute reflex - response
Protective extension of the arms forward
True
T/F? Parachute reflex can elicit with rotation as well
Increased
Infants that suck & DON'T swallow have (increased/decreased) aspiration risk
Babinski - stimulus
Stroke the lateral border of the sole of the foot from heel toward the toes, then medially
Babinski - response
Great toe dorsiflexes (extends) and other toes flare out
UMN lesion
(+) Babinski after infancy suggests-