SPDI WEEK 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms

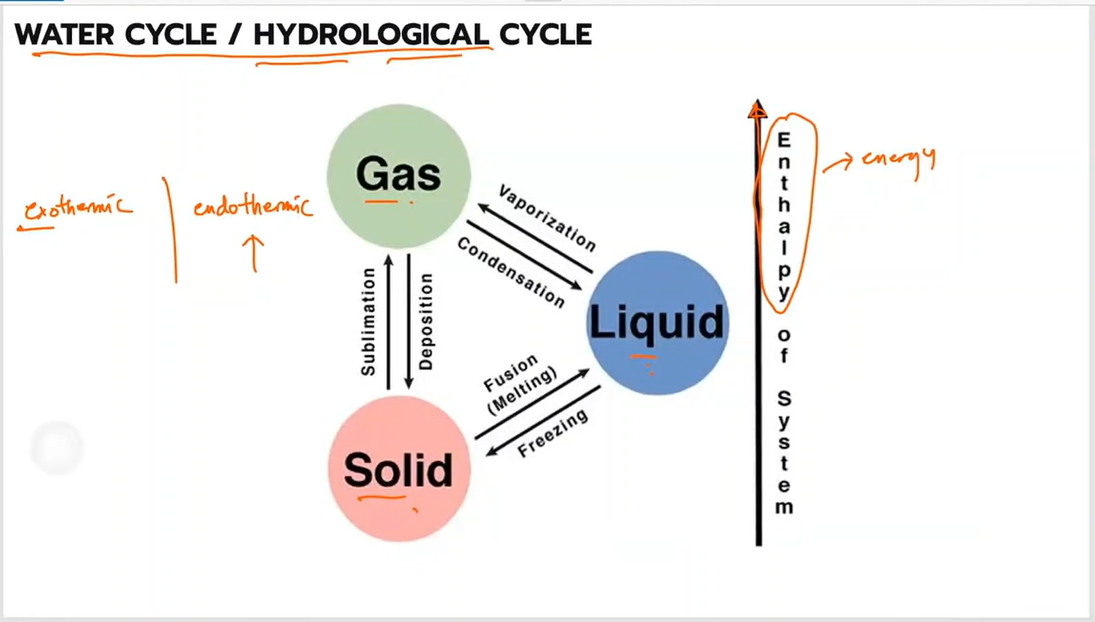
Evaporation

Condensation

Precipitation

Canopy interception

Infiltration

Percolation
The evaporation of water from plants occurring at the leaves
Transpiration
The sum of all processes by which water moves from the land surface to the atmosphere
Evapotranspiration
The transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase
Sublimation
The phase change from gas directly to solid, with no intermediate liquid phase
Desublimation or deposition
Familiarize

Memorize
A container for holding liquids such as water. They are generally used for rainwater catchment and storing rainwater.
Cistern
Computation of volume of Rainwater Harvesting according to the Green Building Code.
Building Footprint/75


Stormwater outlet


Stormwater outfall

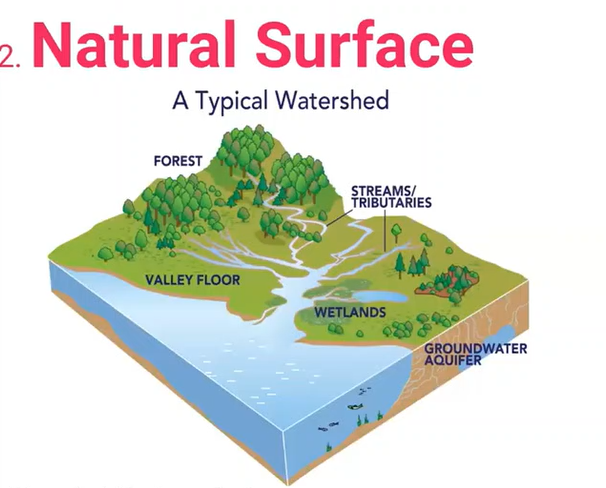
A land area that channels rainfall to creeks, streams, and rivers, and eventually to outflow points such as reservoirs, bays, and the ocean.
Watershed / Drainage Basin
A large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply
Reservoir
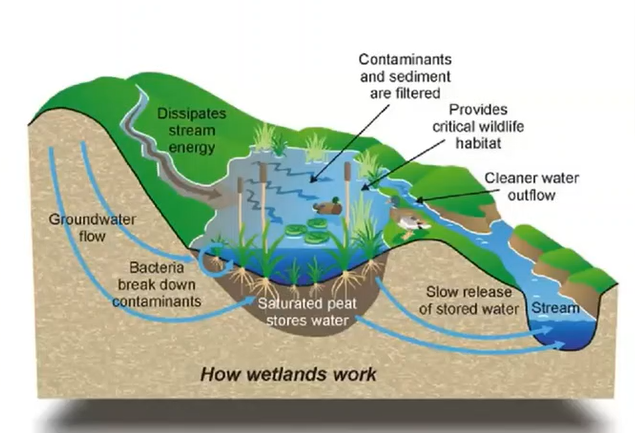
An area of land that is either covered by water or saturated with water.
Benefits:
flood control
water quality improvement
Wildlife habitat
Carbon storage
Groundwater Recharge
Wetland
Types of wetlands
Marsh
Swamp
Bog
Fen
A type of wetland characterized by standing water and emergent vegetation; plant life dominated by grasses
Marsh

A type of wetland characterized by the presence of woody plants, such as trees and shrubs
Swamp

Receive water primarily from precipitation; acidic wetlands filled with slowly decaying vegetation (peat)
Bog

Also peatlands where slow decomposition causes dead vegetation to build up in a thick floating mat
Fen


Underground Water
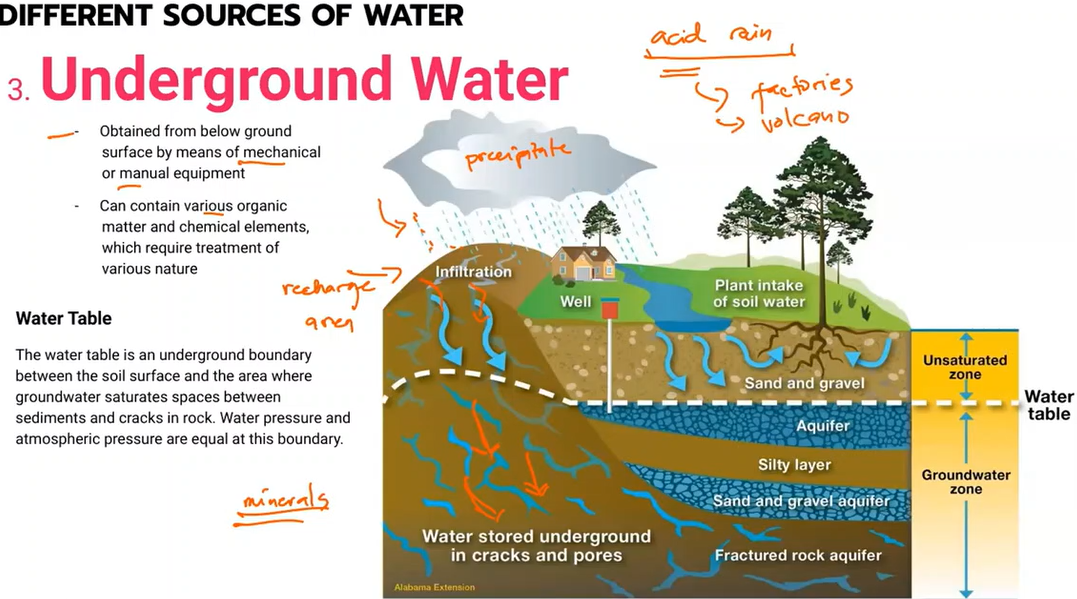

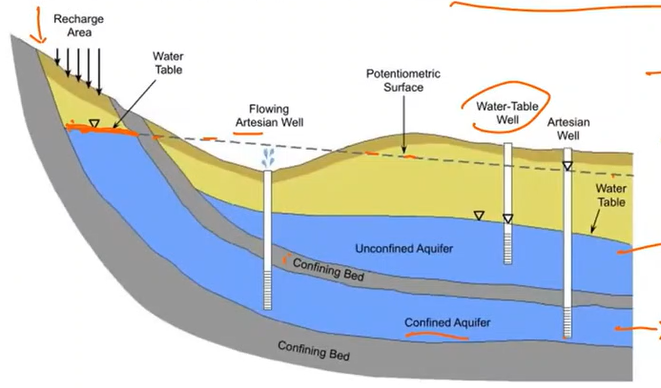
Water table
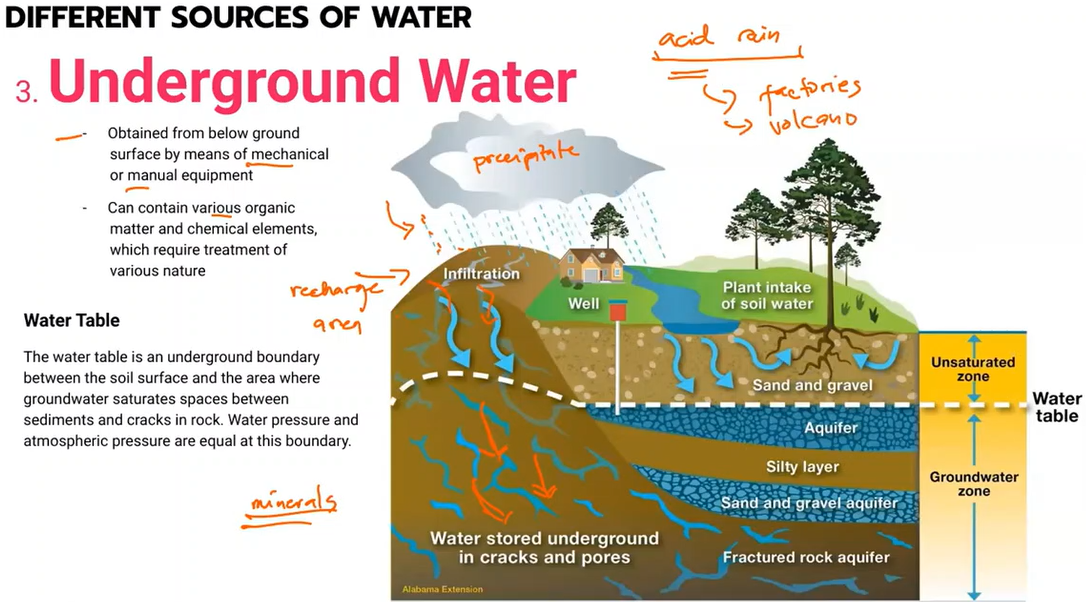
a body of rock and/or sediment that holds groundwater
Aquifer
-Not pressurized
-also called “water table well”
Unconfined Aquifer
A well that taps into a confined aquifer. Under artesian pressure, water in the well rises above the top of the aquifer, but does not necessarily reach the land surface.
Artesian Well
A type of artesian well that has been drilled into an aquifer where the pressure within the aquifer forces the groundwater to rise above the land surface naturally without using a pump.
Flowing artesian well
Code that governs wells
PD 1067 Water code of the Philippines
Once the pumping of the wells starts, the water table is lowered in the vicinity of the well, and the resulting water table surface is known as the ____.
Cone of depression
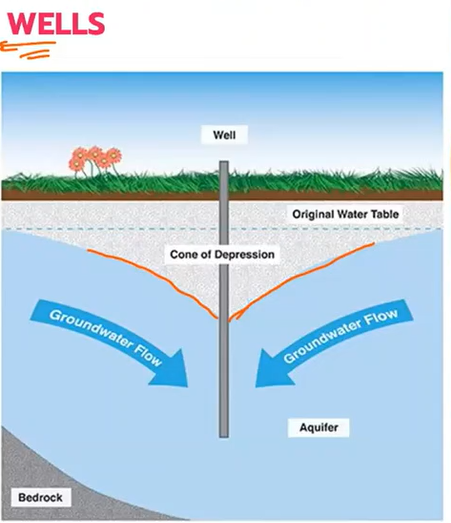
The decrease in the water level at and in the vicinity of the well
Drawdown
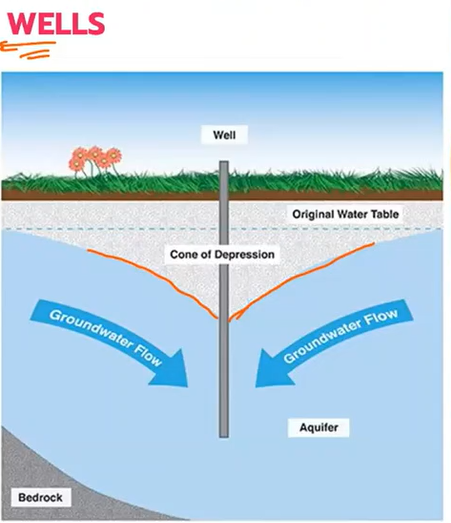
The maximum rate in gpm that a well can be pumped without lowering the water level.
Well yield

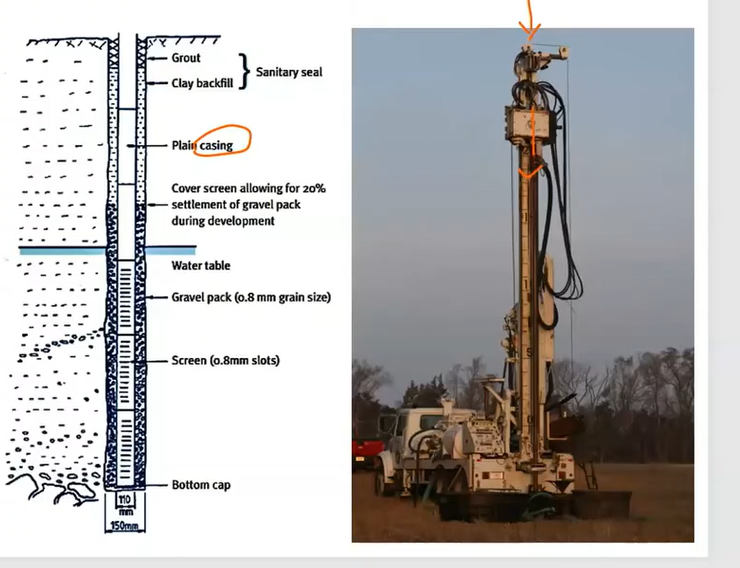
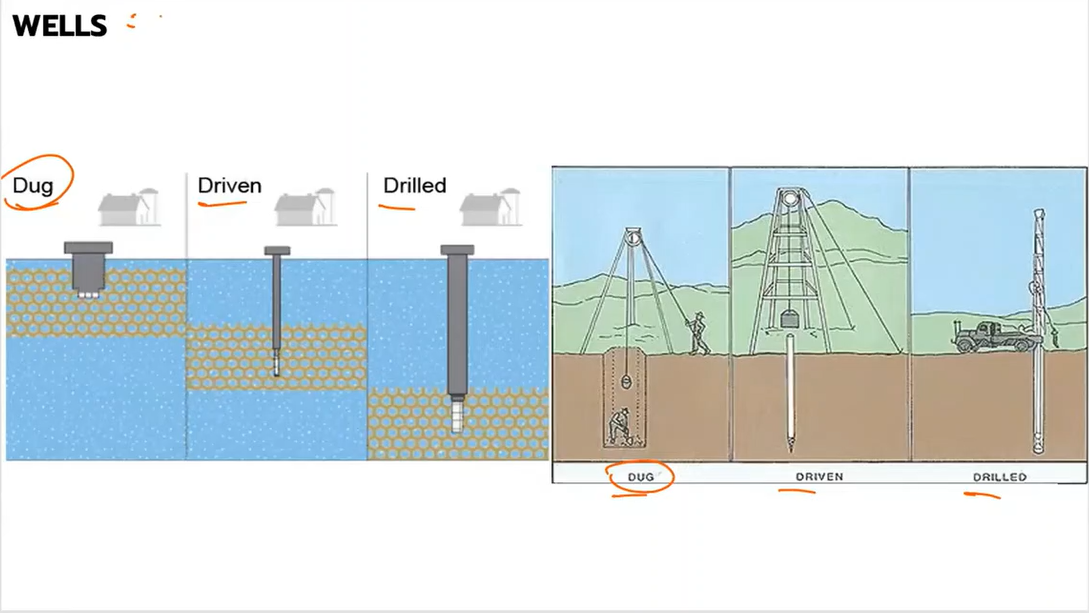
Dug wells
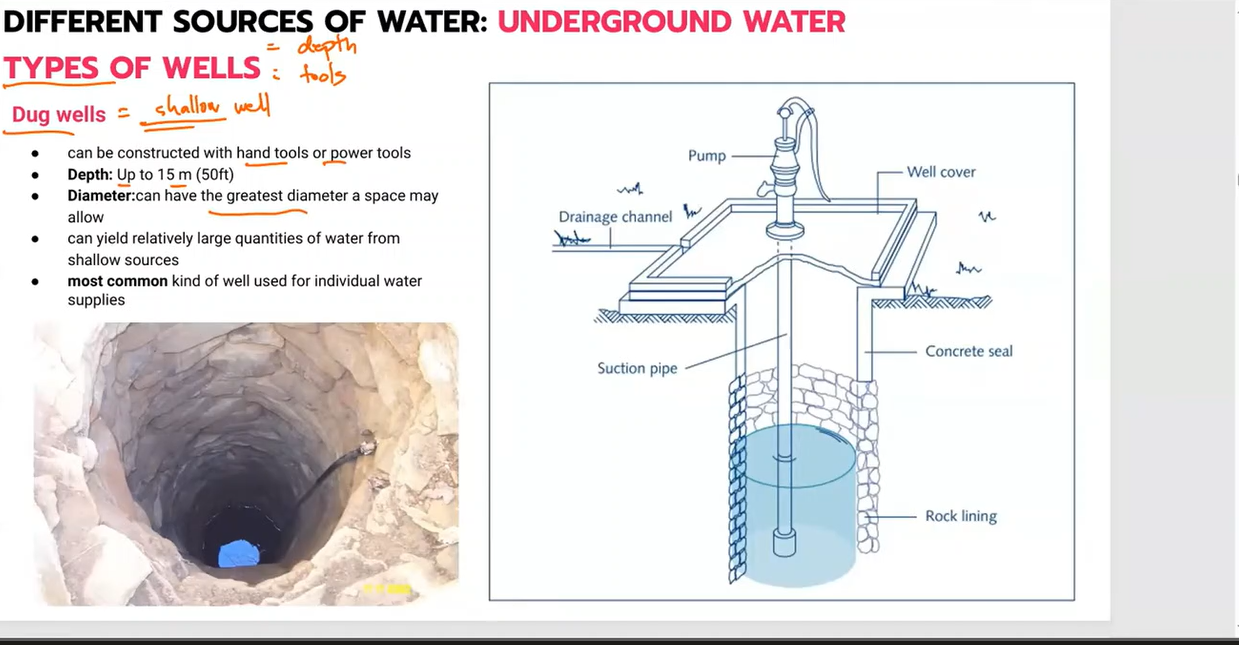

Are shallow in depth and draw water from sections of the earth above the bedrock
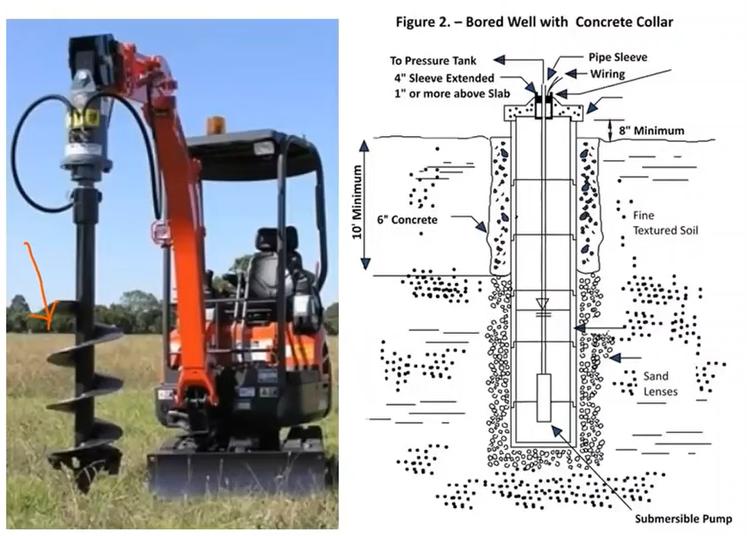
Bored wells

Driven wells
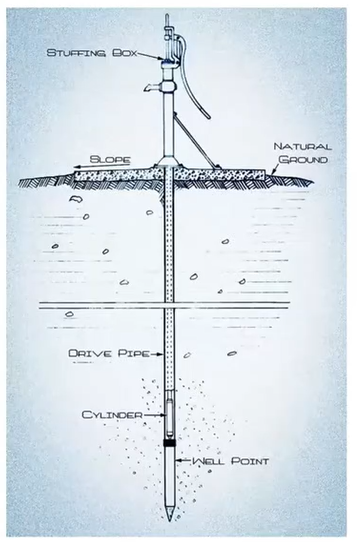
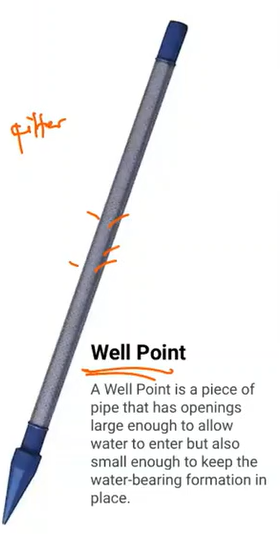
is a piece of pipe that has openings large enough to allow water to enter but also small enough to keep the water-bearing formation in place.
Well point

Drilled well
3 types of wells
Dug well or Bored well
Driven well
Drilled well
3 Levels of water supply as per National Standards of Drinking Water
Level 1 (Point source)
Level 2 (Communal faucet system or standposts)
Level 3 (Waterworks system or Individual house connections)


Level 1 point source

Level 2 (Communal faucet system or standposts)

Level 3 (Waterworks system or Individual house connections)
Occurs when a portion of the water that falls as rain and snow pass through subsurface soil and rock.
a. Sublimation
b. Transpiration
c. Infiltration
d. Percolation
c. Infiltration
The drop in level of water in a well when water is being pumped.
a. Cone of depression
b. Drawdown
c. Well yield
d. Static Level
b. Drawdown
Familiarize
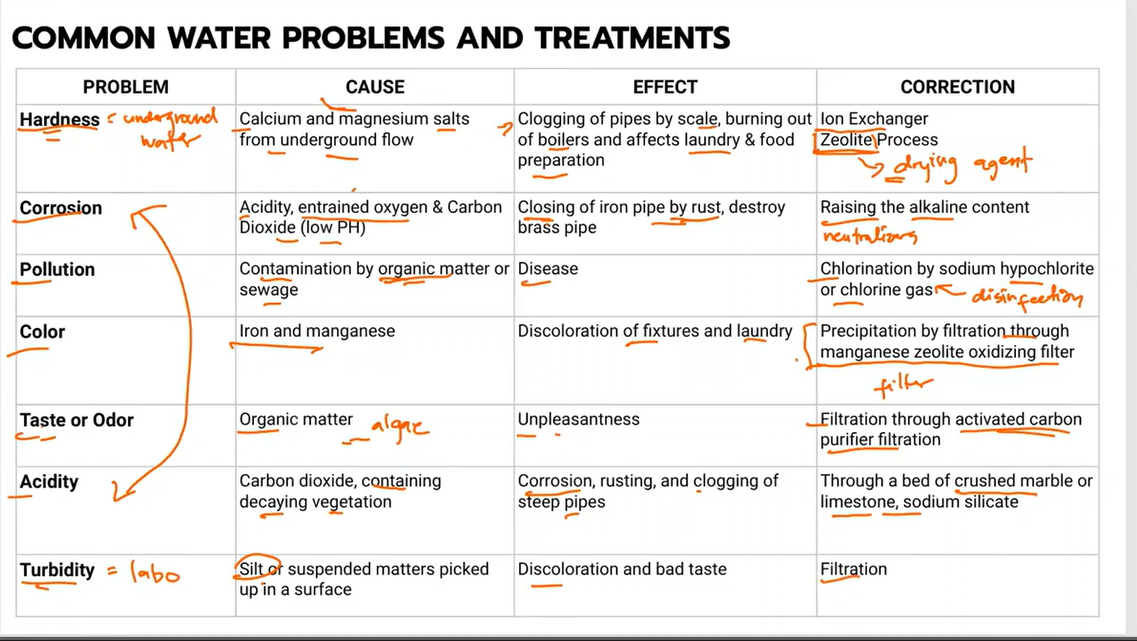
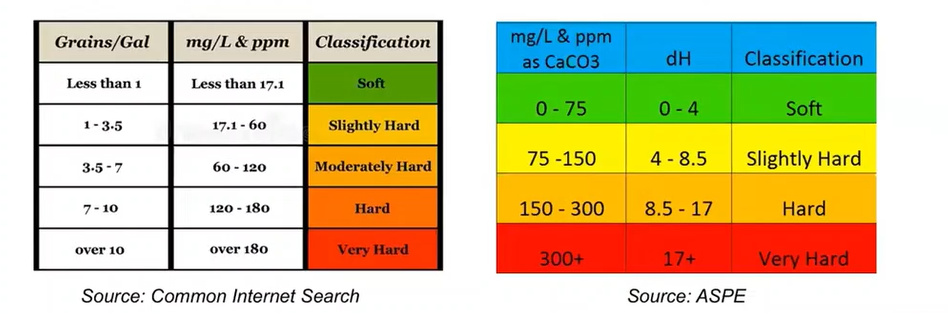
a measure of the total calcium, magnesium, iron, and other metallic elements that contribute to the “hard” feel of the water
Hard water
Temporary Hardness (carbonate hardness) - the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium
Permanent hardness (non-carbonate hardness) - the presence of noncarbonic salts (sulfates, chlorides, and nitrates)
Effects of hard water
Skin and hair
Scale buildup appliances and plumbing
Soap and detergents
Clothing and fabrics
Dishes and glass

is a process that involves the exchange of the hardness minerals in water, chiefly calcium and magnesium, for sodium minerals.
Ion exchange

Most common cause is the presence of carbon dioxide
can be caused by the removal of minerals during evaporation
Highly corrosive that it can damage the plumbing system
Acidity
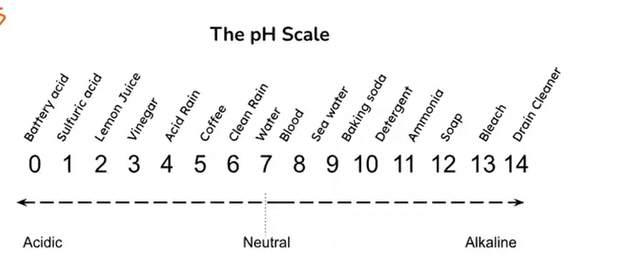
Caused by suspended insoluble matter, including coarse particles that settle rapidly in standing water.
Turbidity

Familiarize
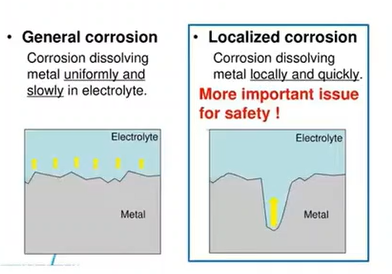
the loss and eventual failure of metals and alloys from the electrochemical reaction between water and the pipe material
Corrosion
A type of corrosion that refers to the breakdown of the pipe material at a uniform rate over its entire surface by direct chemical attack
General Corrosion
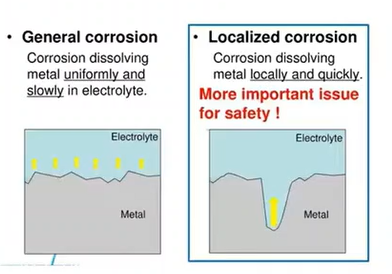
A type of corrosion that takes place on small areas of the surface, usually at high rates, and takes various forms.
Localized Corrosion
6 Basic water types
Raw water (untreated)
Tower water
Potable water
Soft water
Deionized water (Demineralized)
Pure water

A type of water received from a well, surface water, etc.
Raw water
A type of water monitored and controlled for pH, algae, and total dissolved solids
Tower water
A type of water filtered, chlorinated, and/or otherwise treated
Potable water
A type of water that meets additional requirements to reduce hardness.
Soft water
A type of water specified in ranges of conductivity.
Deionized water
Water that is mostly free from particulate matter and dissolved gases that may exist in the potable water supply.
Pure water
A method of producing high-grade water: Conversion of a liquid into vapour that is subsequently condensed back to liquid form
Distillation
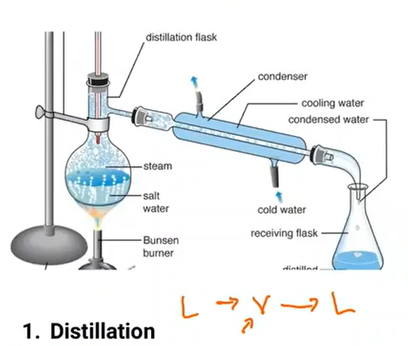
A method of producing high-grade water:
Removal of dissolved mineral solids through an IX (ion exchange) process
Medical uses
Demineralization
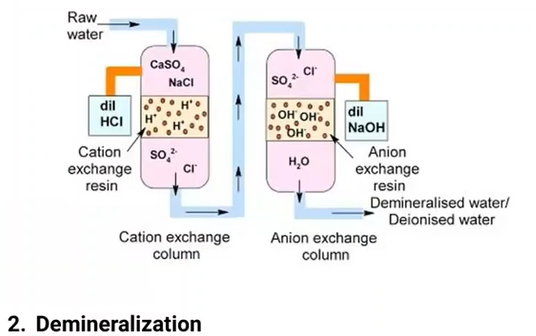
A method of producing high-grade water:
uses a semi-permeable membrane (synthetic lining) to filter out unwanted molecules and large particles such as contaminants and sediments like chlorine, salt, and dirt from drinking water.
Reverse osmosis
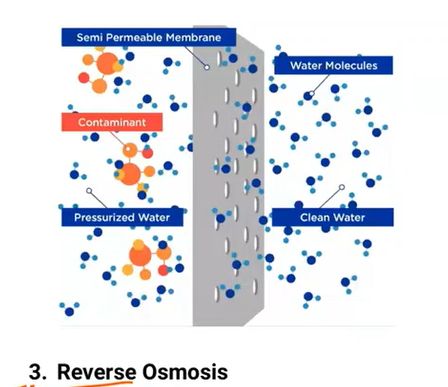
A method of producing high-grade water:
-the process in which solid particles in a liquid or gaseous fluid are removed by the use of a filter medium that permits the fluid to pass through but retains the solid particles
Filtration

Physical characteristics of sewage
color
odor
temperature
Turbidity
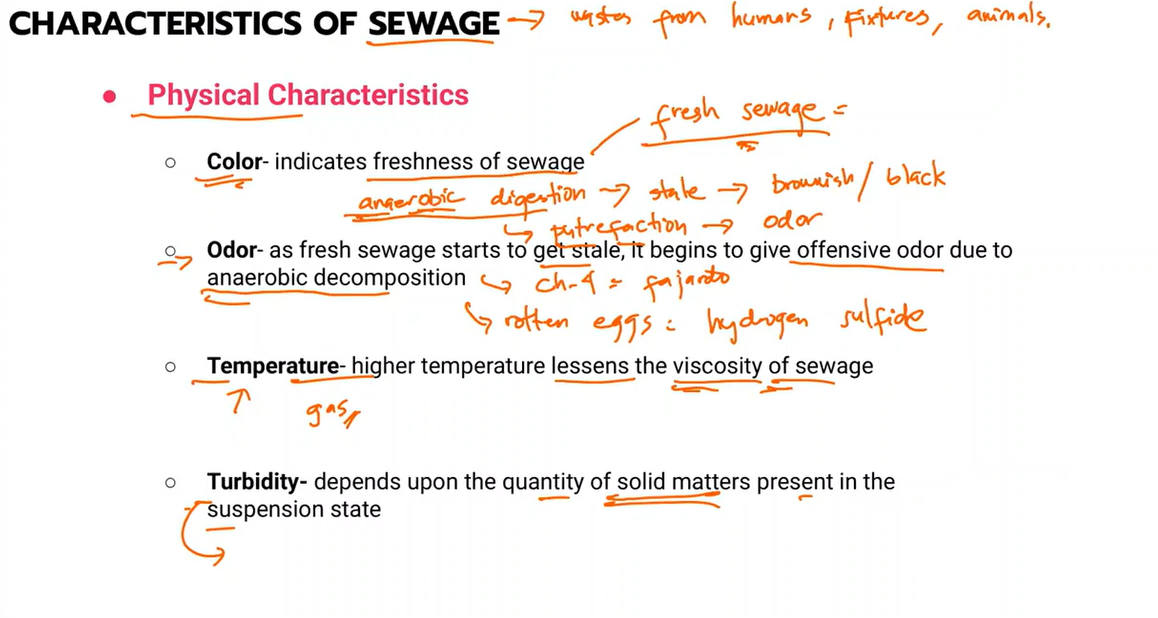
Chemical characteristics of sewage
pH level
Nitrogen compounds
Phosphorus
Solids
Dissolved oxygen
BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand)
COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand)
The sewage contains many microorganisms like bacteria, algae, fungi, protozoa, etc., bacteria being the most predominant.
Biological characteristics of sewage
Sewage water treatments
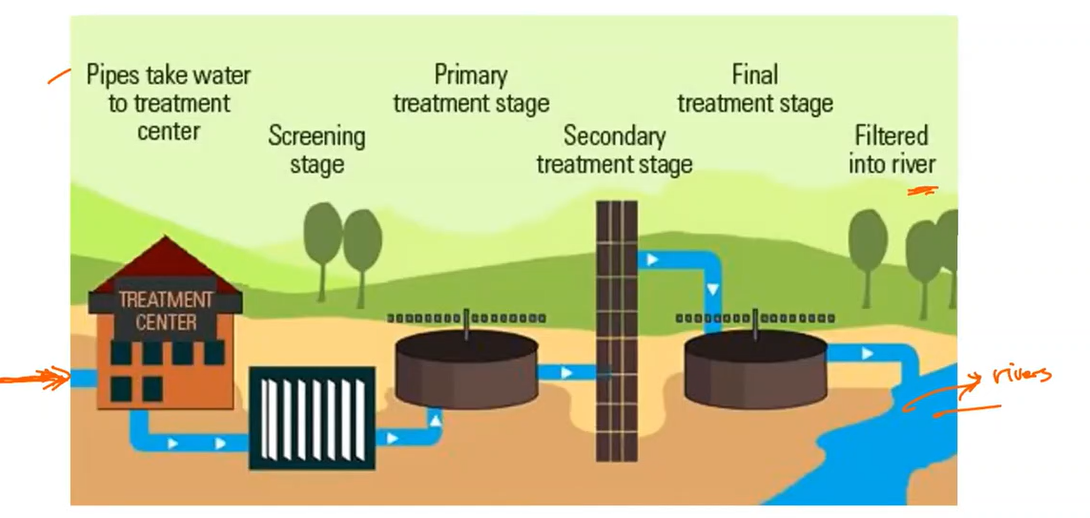
Steps in sewage water treatments
Step 1. Bar screening
Step 2. Screening / Grit removal
Strep 3. Primary Clarifier
Step 4. Aeration
Step 5. Secondary clarifier
Step 6. Filtration
Step 7. Disinfection
Step 8. Oxygen uptake

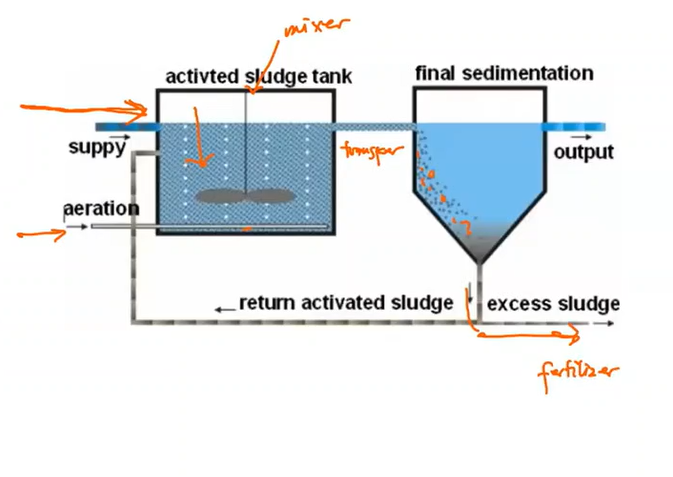
Activated sludge process (ASP)

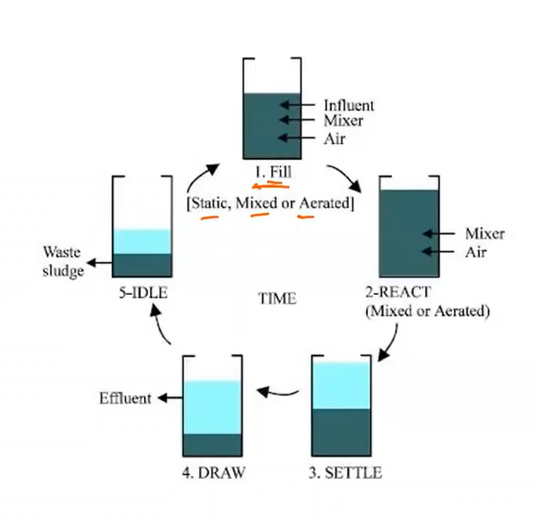
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)

Sequencing Batch Bioreactors
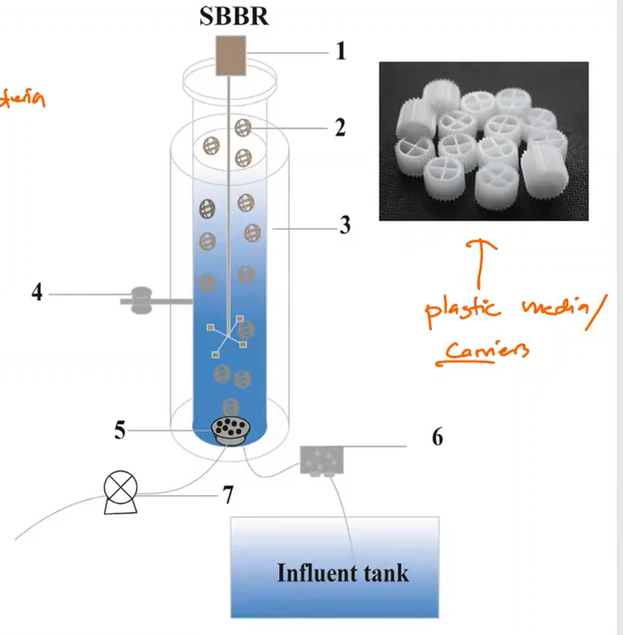

Type of aeration process
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
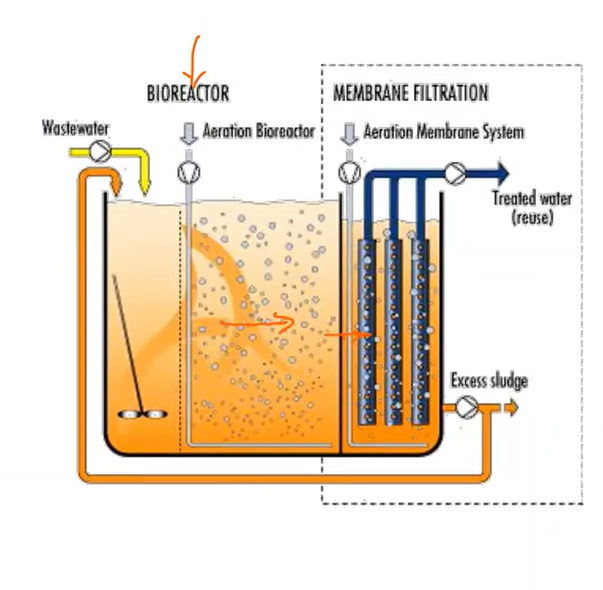

Type of aeration process
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
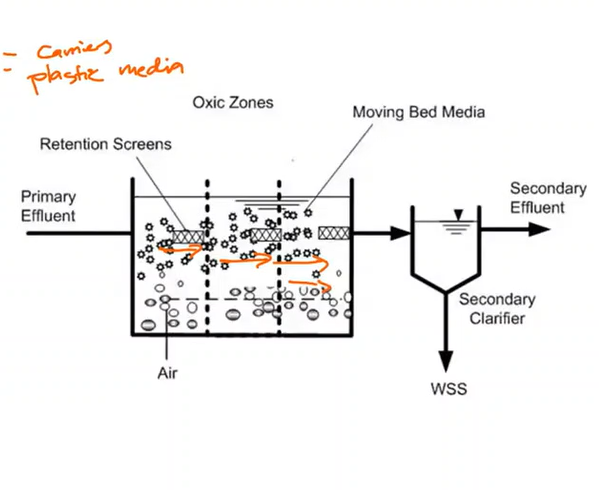
Other materials for filtration
Granular Activated carbon (aka charcoal filter)
Sandstone
Animal charcoal (aka bone charcoal)
Diatomaceous earth
Sponge iron
Types of disinfection
Chlorination
Type of disinfection that is most frequently used method is chlorine that enters the water in liquid form.
Chlorination
A dry solid compound having the highest possible chlorine content (around 90%)
Trichlor
Available as its dihydrate form or the anhydrous form
Dichlor
A type of disinfection exposed to ultraviolet radiation which kills undesirable microorganisms, leaving them unable to reproduce.
Ultraviolet Disinfection
A type of disinfection where ozone is injected into water, and immediately starts oxidizing and eliminating contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, and metals.
Ozone Treatment
Potable water treatments
Coagulation
Flocculation
Sedimentation
Filtration
Disinfection
Fluoridation
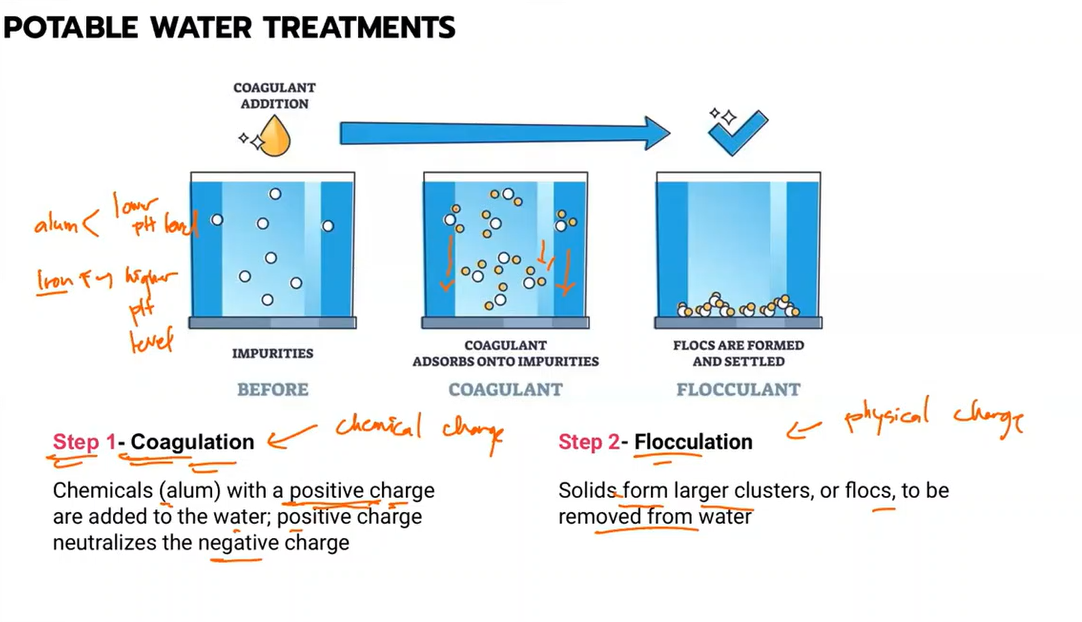
Type of potable water treatment where chemicals (alum) with a positive charge are added to the water; positive charge neutralizes negative charge
Coagulation
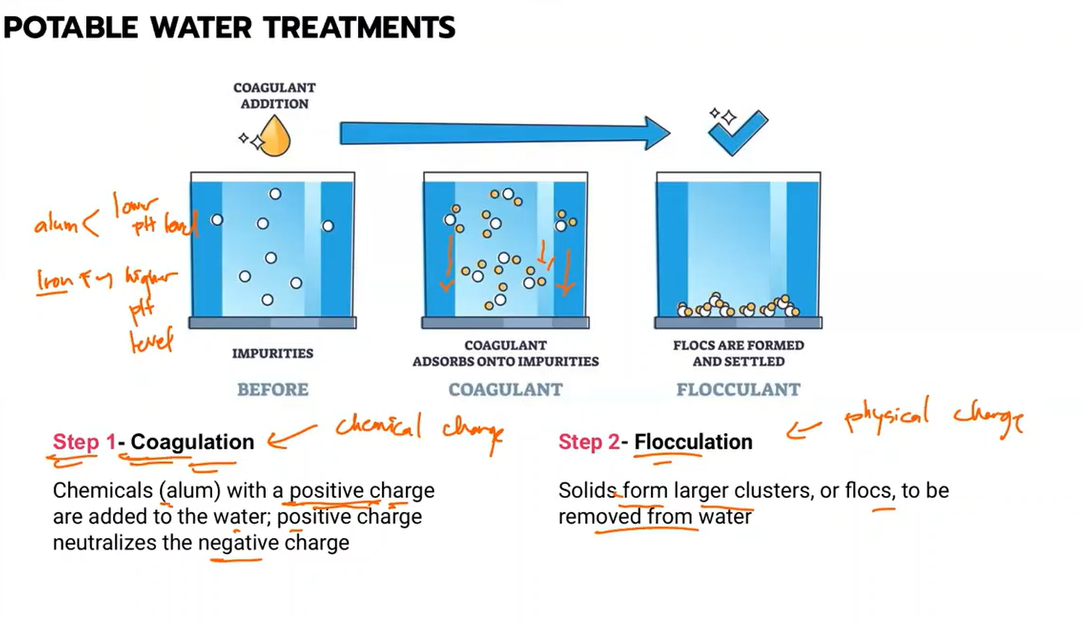
Potable water treatment where solids form larger clusters, or flocs, to be removed from water
Flocculation
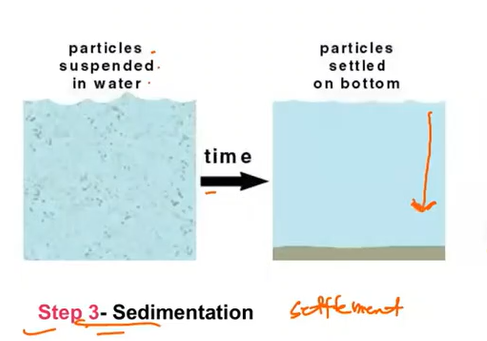
Potable water treatment where suspended solids are removed from the water by gravity settling and deposition
Sedimentation
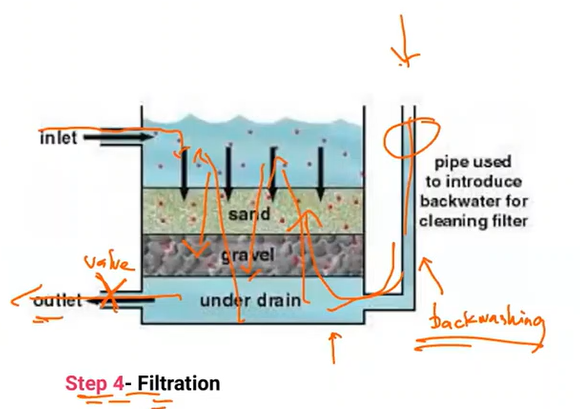
The process in which solid particles in a liquid or gaseous fluid are removed by the use of a filter medium that allows the fluid to pass through while retaining the solid particles.
Filtration
Different types of filtration process
Slow sand filtration
Rapid sand filtration
A type of filtration process where water is passed through a porous bed of filter medium; utilize the effluent either from plain sedimentation or directly from sources
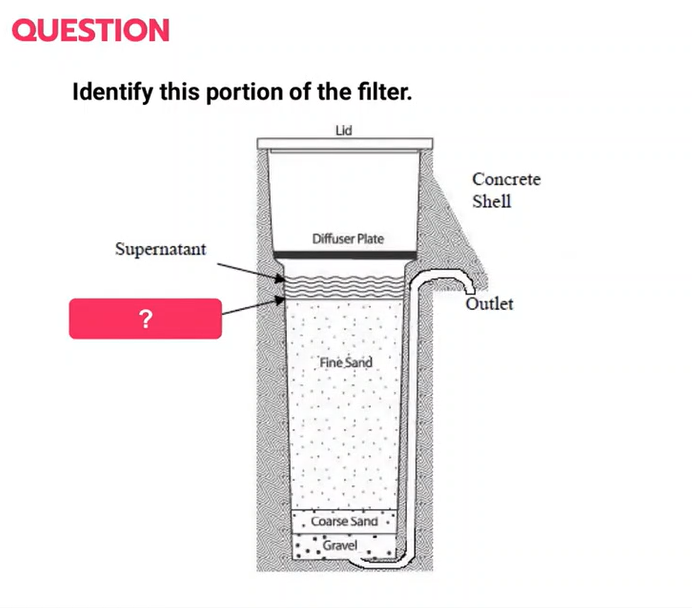
Slow sand filter
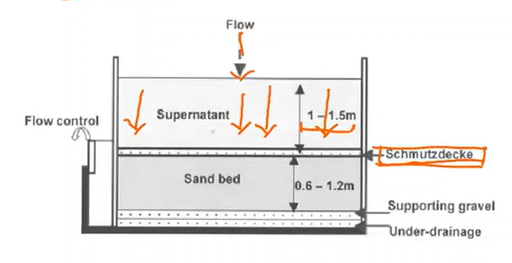
water above the filter sand that provides hydraulic head for the process
Supernatant
A hypogeal biological layer; consists of biologically active microorganisms that break down organic matter. German for “dirt cover”.
Schmutzdecke
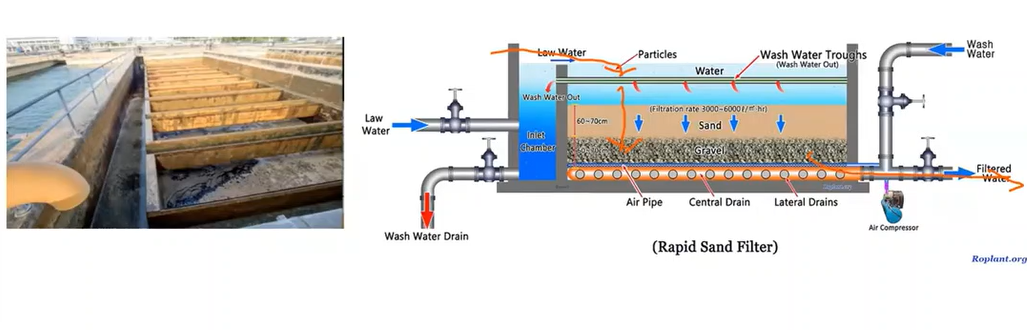
A technique common in developed countries for treating large quantities of drinking water. A relatively sophisticated process usually requiring power-operated pumps, regular backwashing or cleaning, and flow control of the filter outlet.
Rapid Sand Filtration
The addition of one or more chemical disinfectants to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, or viruses.
50 mg/L - Chlorine solution for system allowed to stand for 24 hours
200 mg/L - 3 hours
Disinfection
The controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay
Fluoridation
It is due to presence of sulfates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium in water.
a. Temporary Hardness
b. Permanent Hardness
c. Total Hardness
d. Maximum Hardness
b. Permanent Hardness

What is a treatment for water acidity?
a. Chlorination
b. Passing through water filter
c. Filtration
d. Manganese zeolite
b. Passing through water filter
Schmutzdecke - german for “dirt cover”