Bootcamp.com - Cellular Energy
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
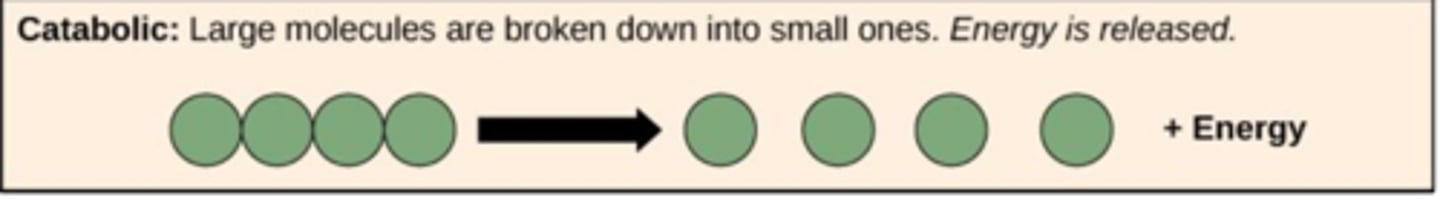
_____ processes break down large macromolecules into smaller pieces, and usually release energy in the form of ATP
Catabolic processes break down large macromolecules into smaller pieces, and usually release energy in the form of ATP
(think catabolic = cannibalism)
_____ processes extract energy from ATP and use it to build larger, more complex macromolecules
anabolic

_____ is a unique type of potential energy, where the chemical bonds serve as a store of internal energy (U) and have the potential to be used to do work
chemical energy
(potential energy has to do with an object's position)
what is the most common form of "non-useful" energy release?
heat
_____ measures a system's useful, work performing energy
Gibbs free energy (G)
_____ describes a system's energy as it progresses from an initial to final state
free energy change (ΔG)
_____ is the energy associated with molecular bond energies
enthalpy (H)
change in enthalpy (ΔH) is the _____ between the initial and final states of a reaction
bond energy difference
a negative ΔH means that heat is _____, while a positive ΔH implies that heat is _____
released; absorbed
catabolic reactions release free energy (_____), so they are an example of an _____ reaction
-ΔG; exergonic
reactants (initial position) contain more internal energy than the products (final state) in _____ reactions
exergonic
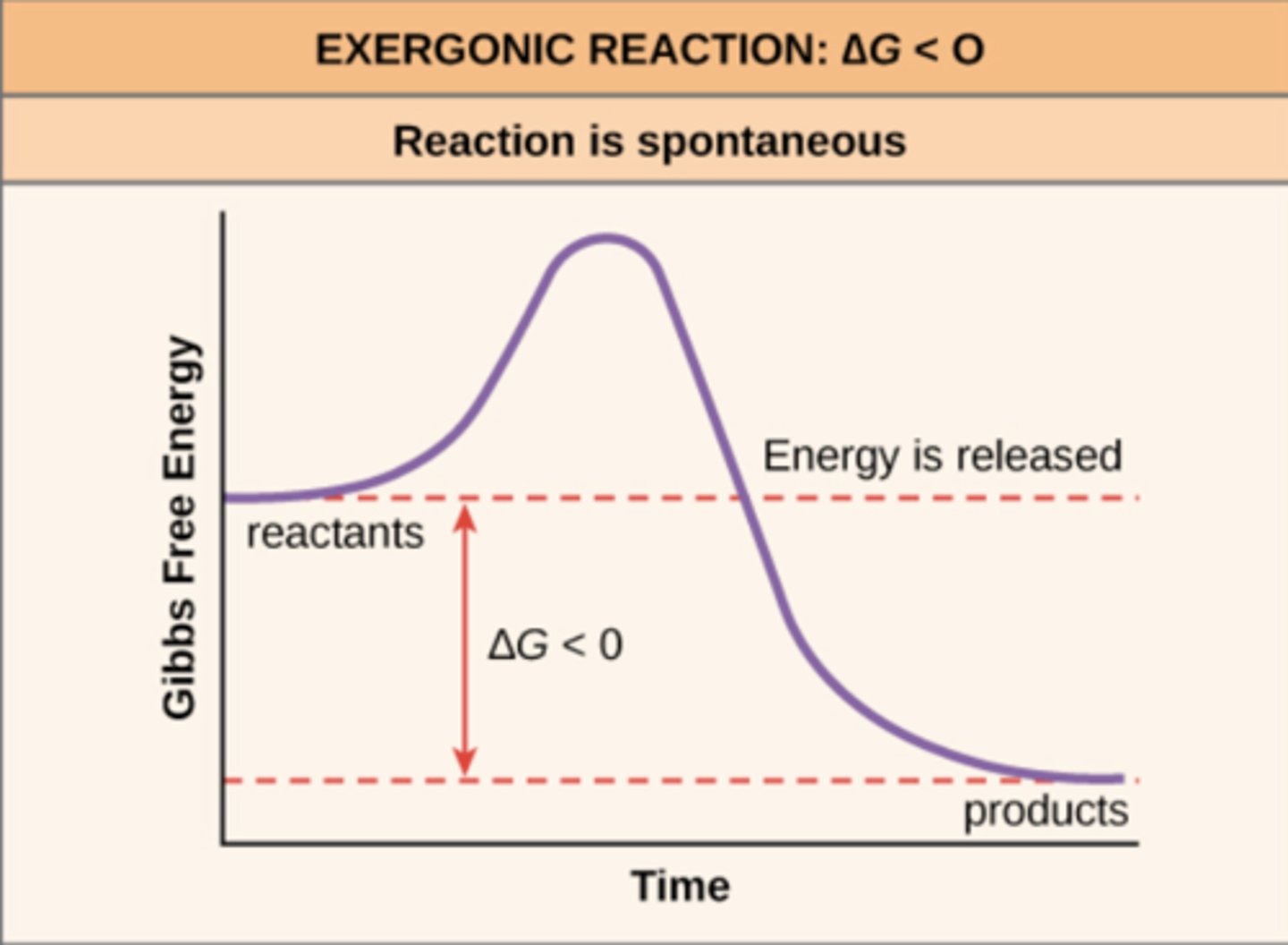
EXergonic reactions mean that free energy is _____ the system
EXiting
exergonic reactions are _____
spontaneous
anabolic reactions absorb free energy (_____), so they are an example of an _____ reaction
+ΔG; endergonic
reactants (initial state) contain less internal energy than the products (final condition) in _____ reactions
endergonic
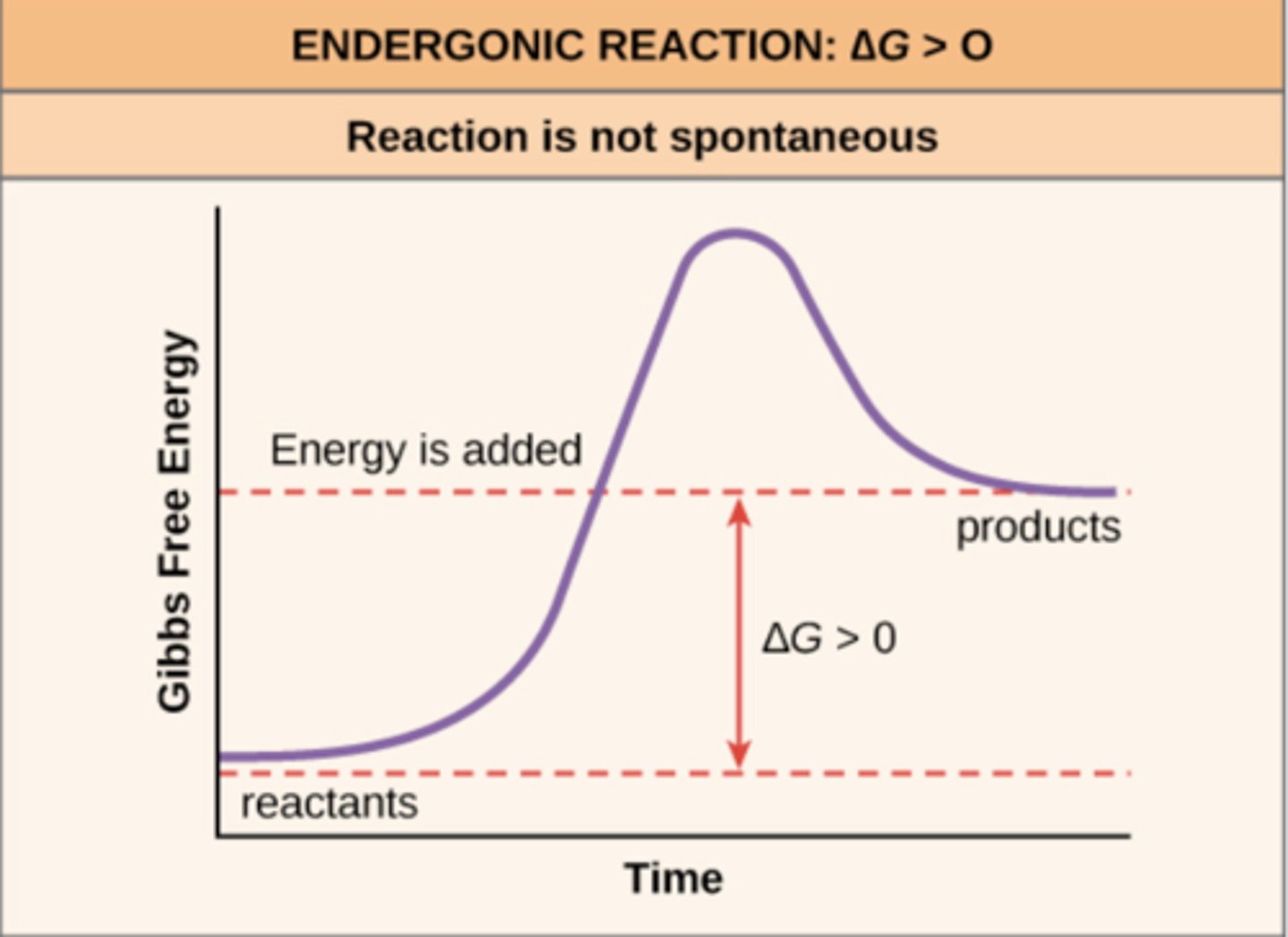
endergonic reactions are _____ reactions
non-spontaneous
if ∆G is _____, the reaction can occur spontaneously
negative
if ∆G is _____, the reaction is non-spontaneous
positive
a system with a higher Gibbs free energy is considered _____ stable
less
a system with a lower Gibbs free energy is considered _____ stable
more
ATP is an _____ nucleoside triphosphate
RNA
write the overall chemical formula for aerobic cellular respiration:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
ATP has 3 phosphates covalently linked to a _____ sugar, which also connects to an _____ nitrogenous base
ribose; adenine

_____ are the bonds found between phosphate groups
phosphoanhydride bonds
ATP molecules are _____ because the three phosphate groups are all negatively charged and repel each other
unstable
_____ is the cellular energy currency
ATP
ATP → ADP +Pi is a _____ reaction
hydrolysis
ATP hydrolysis reactions release free energy, making them _____ and _____
spontaneous; exergonic
ADP + Pi → ATP is a _____ reaction
condensation
condensation reactions absorb free energy, making them _____ and _______
non-spontaneous; endergonic
ATP provides energy for all cells by transferring _____ from ATP to another molecule
phosphate
(reaction coupling)
_____ links unfavorable reactions with favorable ones, as long as the net free energy change (ΔG) for the two reactions is negative (exergonic and spontaneous)
reaction coupling
_____ make many ATP molecules through cellular respiration
mitochondria
where are mitochondria found in a eukaryotic cell?
floating in the cytosol
(as a component of the cytoplasm)
how many membranes do mitochondria have?
2
the inner mitochondrial membrane has many infoldings called _____ that increase the surface area
cristae
the acidic region between the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes is the _____
intermembrane space
the intermembrane space between the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes is the_____ region
acidic
the area deep to the inner mitochondrial membrane is the _____
mitochondrial matrix
Human muscle cells (myocytes) have a high energy requirement, so there are many _____ in them
mitochondria
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) function to carry as much oxygen as possible, therefore, they tend to not contain any _____
mitochondria
the mitochondrial matrix contains its own circular _____ and _____
DNA; ribosomes
the _____ says that the aerobic bacteria became mitochondria, while the photosynthetic bacteria became chloroplasts
endosymbiotic theory
the endosymbiotic theory says that the aerobic bacteria became _____, while the photosynthetic bacteria became _____
mitochondria; chloroplasts
aerobic cellular respiration is a sizable _____ pathway that requires _____
catabolic; oxygen
what are the 4 components of aerobic cellular respiration?
glycolysis; pyruvate manipulations; the Krebs cycle; oxidative phosphorylation
the 4 pathways of aerobic cellular respiration work to break _____ into carbon dioxide and water, with the generation of _____
glucose; ATP
the 4 pathways of aerobic cellular respiration work to break glucose into _____ and _____, with the generation of ATP
carbon dioxide; water
is aerobic cellular respiration overall endergonic or exergonic?
exergonic
is aerobic cellular respiration overall oxidative or reductive?
oxidative
_____ converts a six-carbon glucose molecule into 2 three-carbon compounds called pyruvate
glycolysis
glycolysis converts a six-carbon glucose molecule into _____ three-carbon compounds called _____
2; pyruvate
glycolysis does not depend on _____, which is why it can participate in fermentation as well
oxygen
In what location of the cell does glycolysis occur?
cytosol
NAD+/NADH is a _____ (organic cofactor)
coenzyme
glycolysis extracts high energy e- as glucose is broken down, using them to _____ NAD+ into NADH, which then may travel to the _____ for further ATP creation
reduce; electron transport chain (ETC)
glycolysis has 2 main phases: an _____ phase, and an _____ phase
energy investment; energy payoff
during glycolysis, hexokinase and the free energy released from 1 ATP hydrolysis to "trap" glucose in the cell as _____
glucose-6-phosphate
during glycolysis, isomerase is used to turn glucose-6-phosphate into _________
fructose-6-phosphate
during glycolysis _____ (enzyme) and the free energy released from _____ is used to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
phosphofructokinase; 1 ATP hydrolysis
what molecule breaks down into 2 G3P molecules?
fructose-1,6,bisphosphate
_________ is an essential regulatory enzyme of glycolysis
phosphofructokinase (PFK)
during the energy payoff phase of glycolysis G3P is oxidized and ____ is reduced
NAD+ (is reduced to NADH)
(makes 2 NADH - 1 for each step 6 that is occurring)
_____ uses ADP as a direct substrate for its phosphorylation into ATP
substrate-level phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation occurs directly in the _____ during the energy payoff phase of glycolysis
cytosol
a _____ is an enzyme which phosphorylates a molecule, and it is responsible for the ADP phosphorylations of glycolysis
kinase
the energy payoff phase produces _____ ATP, _____ NADH and _____ pyruvate
4; 2; 2
list the net products of glycolysis from 1 glucose
2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate
if glycolysis makes 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvates, why does glycolysis only produce a net of 2 ATP?
need to account for the 2 ATP used during the energy investment phase
list what molecules go into glycolysis initially:
1 glucose, 2 ATP
which group of 3 reactions link glycolysis to the rest of cellular respiration?
the pyruvate manipulation reactions
where do the pyruvate manipulation reactions occur?
in the mitochondrial matrix
pyruvate manipulations occur in the _____ for prokaryotes because they do not have membrane-bound organelles
cytosol
list the 3 separate reactions of the pyruvate manipulations:
1. decarboxylation; 2. oxidation; 3. add CoA
what enzyme catalyzes the pyruvate manipulation reactions?
the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)
the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is composed of _____ enzymes, with 1 for each pyruvate manipulation
3
during pyruvate decarboxylation, pyruvate releases a carbon atom as _____
carbon dioxide
during pyruvate oxidation, the decarboxylation product is converted to a two-carbon _____
acetyl group
pyruvate oxidation is accompanied by the reduction of _____ to _____
NAD+ to NADH
pyruvate oxidation indirectly depends on _____
oxygen
(regenerates NAD+ in the ETC)
after the decarboxylation and oxidation steps of the pyruvate manipulations, the remaining acetyl group will bind to _________ and this results in the formation of __________
Coenzyme A (CoA), acetyl-CoA
list the net products of pyruvate manipulations from one glucose
2 CO₂, 2 NADH, 2 acetyl-CoA
where does the Krebs cycle take place in eukaryotes?
mitochondrial matrix
in prokaryotes, the Krebs cycle takes place in the _____
cytosol
the Krebs cycle has _____ intermediates and a total of _____ steps.
7; 8
the acetyl-CoA from the pyruvate manipulations merges with _____ to form citrate.
oxaloacetate
the acetyl-CoA from the pyruvate manipulations merges with oxaloacetate to form _____
citrate
_____ molecules are _____ by the Krebs cycle for every 1 glucose
2 acetyl-CoA; oxidized
_____ cycles of the Krebs cycle occur per glucose
2
what is the net production of 1 Krebs cycle
2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP
what is the net production of 2 Krebs cycles (from 1 glucose molecule)?
4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 2 ATP
what is the waste product of the Krebs cycle?
CO₂
_____ encompasses two linked components - the ETC and chemiosmosis
oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation encompasses 2 linked components - the _____ and _____
ETC; chemiosmosis
_____ is the mechanism of ATP generation that occurs when energy is stored in the form of a H+ concentration gradient across a membrane
chemiosmosis
the ETC is in the _____ of eukaryotes
mitochondrial inner membrane/cristae
the ETC is in the _____ of prokaryotes
cell membrane
e- release energy through the ETC, which goes toward _____
H+ pumping
the ETC couples the _____ flow of e- with the _____ pumping of H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane (eukaryotes)
exergonic, endergonic
which ETC proteins act as H+ pumps?
complex-I, III, and IV