HSC 3537 Chapter 2 Body Organization
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
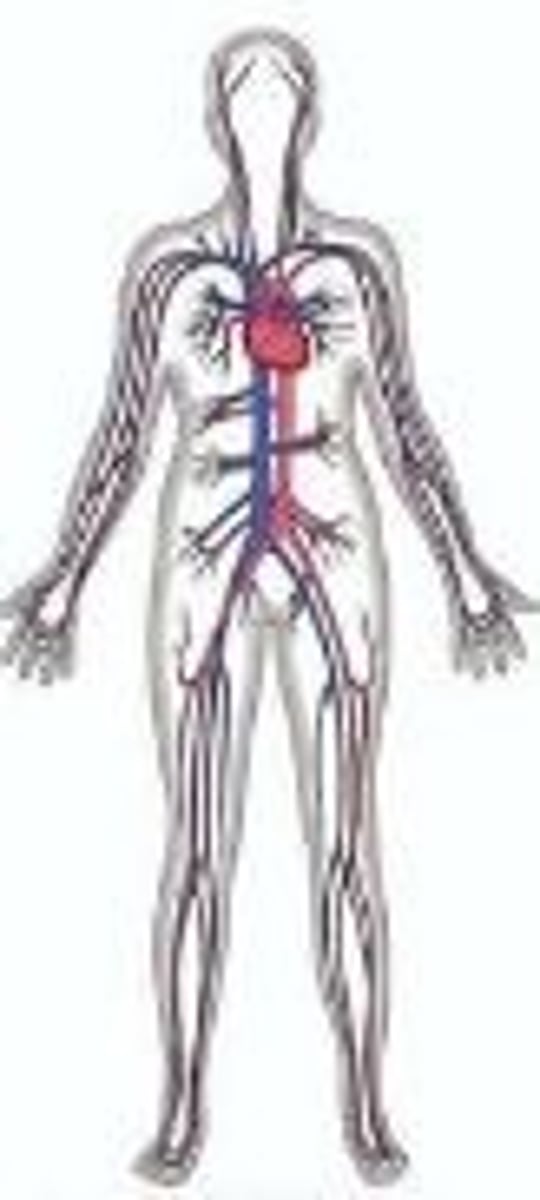
Cardiovascular System (CV)
Pumps blood throughout the entire body to transport nutrients, oxygen, and wastes.
• Heart
• Arteries
• Veins
abdomin/o
abdomen
adip/o
fat
anter/o; ventral
front
brachi/o
arm
cardi/o
heart
caud/o
tail
cephal/o
head
cervic/o
neck
chondr/o
cartilage
crani/o
skull
crin/o
to secrete
crur/o
leg
cyt/o
cell
dermat/o
skin
dist/o
away from
dors/o
back
enter/o
small intestine
epitheli/o
epithelium
gastr/o
stomach
glute/o
buttock
gynec/o
woman, female
hemat/o
blood
hist/o
tissue
immun/o
immune, protection
infer/o; caudal
below
inguin/o
groin
laryng/o
larynx (voice box)
later/o
side
lumb/o
loins (lower back)
lymph/o
lymph
medi/o
middle
muscul/o
muscle
nephr/o
kidney
neur/o
nerve
ophthalm/o
eye
orth/o
straight, upright
ot/o
ear
pariet/o
cavity wall
ped/o
foot
pelv/o
pelvis
peritone/o
peritoneum
pleur/o
pleura
poster/o; dorsal
back
proct/o
anus and rectum
proxim/o
near
pub/o
genital region
pulmon/o
lung
rhin/o
nose
spin/o
spine
super/o; cephal/o
above
thorac/o
chest
ur/o
urine
urin/o
urine
vascul/o
blood vessel
ventr/o
belly
vertebr/o
vertebra
viscer/o
internal organs
levels of organization in the body
cell, tissue, organ, organ system
cells
the smallest structure of a body that has all the properties of being alive: responding to stimuli, engaging in metabolic activities, and reproducing itself.
tissues
cytology
study of cells
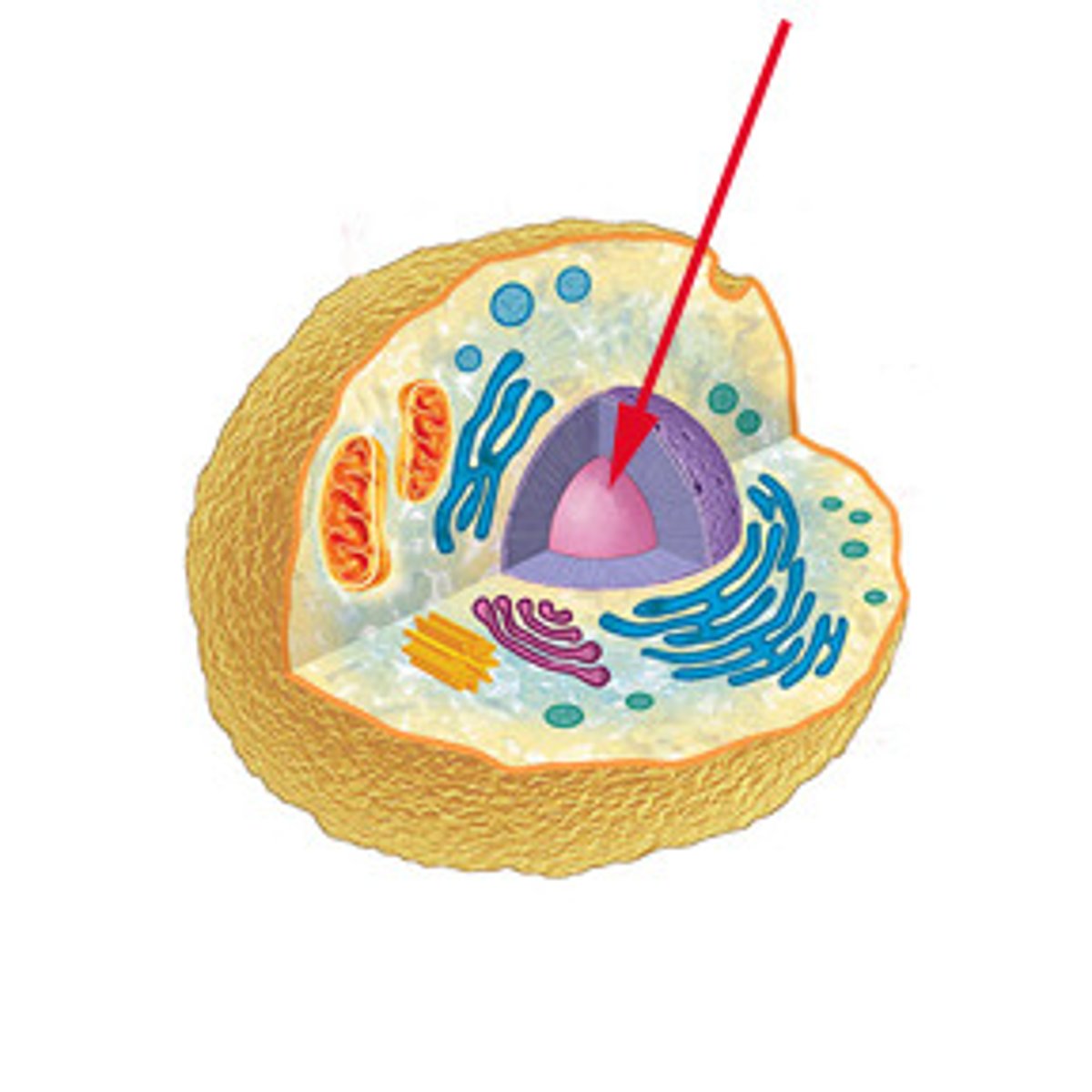
Nucleus
contains the cell's DNA
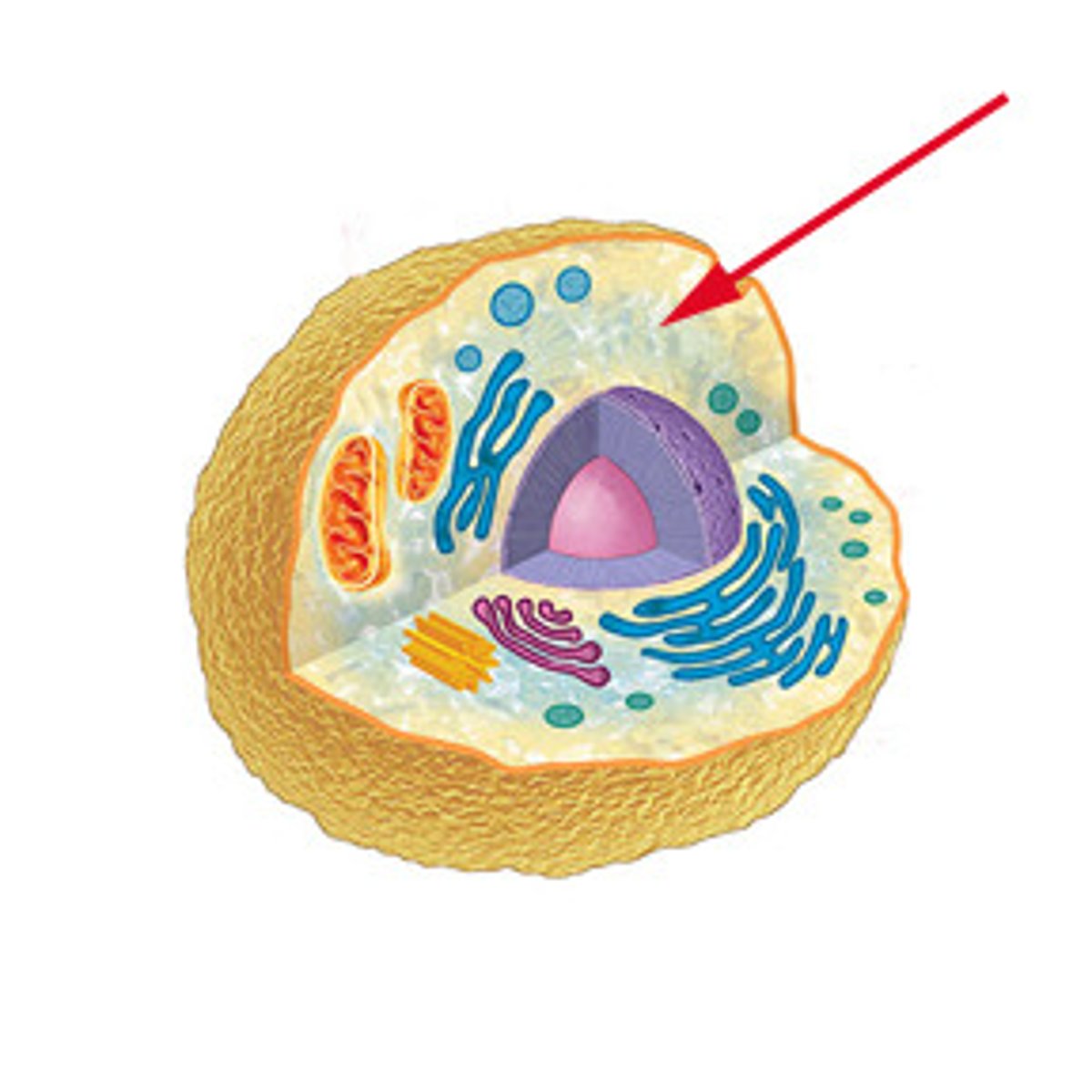
Cytoplasm
the watery internal environment of the cell
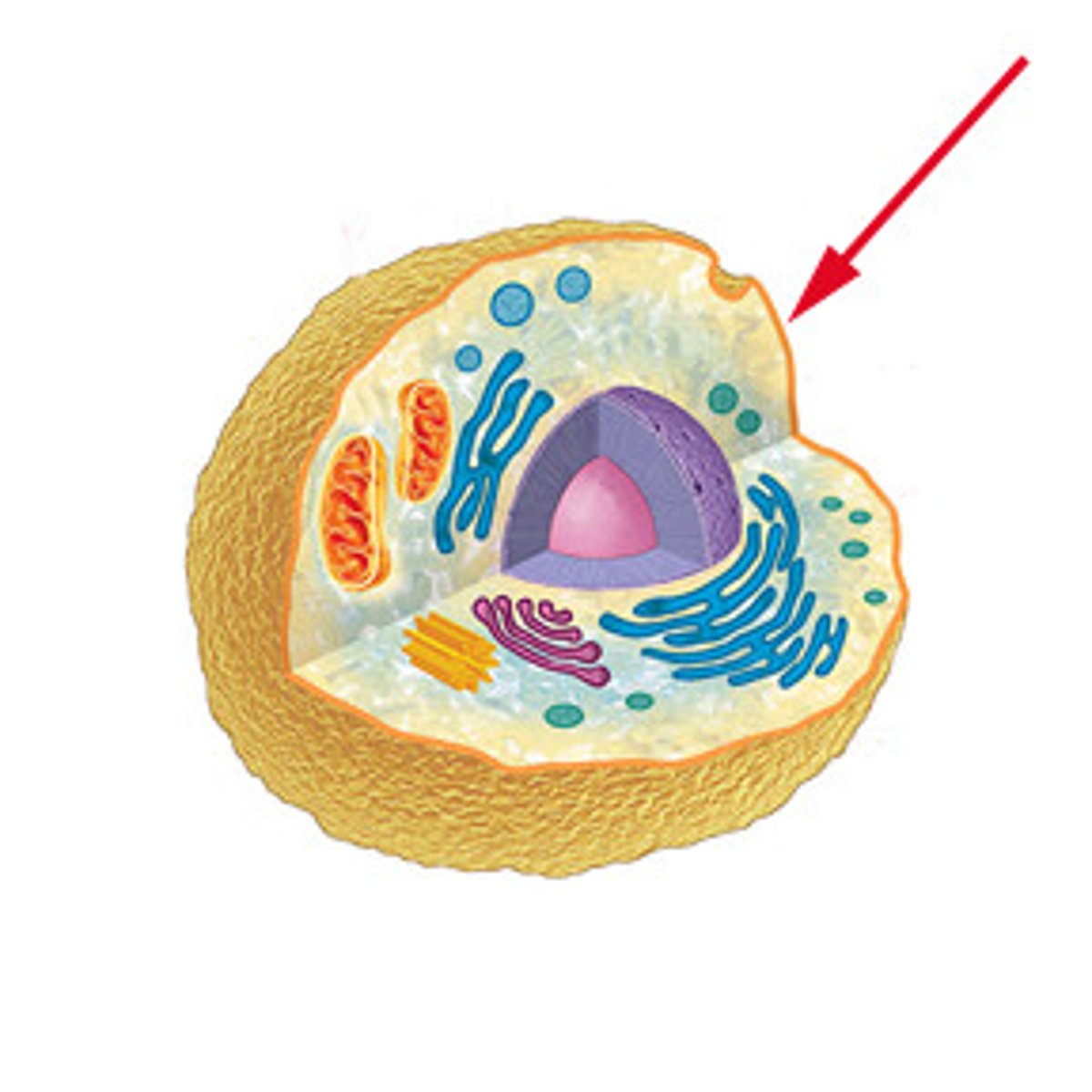
cell membrane
the outermost boundary of a cell. It encloses the cytoplasm and the nucleus
Types of tissues
- epithelial
- connective
- muscle
- nervous
muscular tissue
produces movement in the body through contraction, or shortening in length, and is composed of individual muscle cells called muscle fibers
- 3 types: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, or cardiac muscle.
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
smooth muscle
involuntary muscle found in internal organs
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
epithelial tissue/epithelium
found throughout the body and is composed of close-packed cells that form the covering for and lining of body structures
- ex: top layer of skin & lining of stomach
- can also absorb nutrients
connective tissue
the supporting and protecting tissue in body structures
- bones, cartilage, tendons, adipose
bone
provides structural support for the whole body
Cartilage
shock absorber in joints
tendons
tightly connect skeletal muscles to bones
adipose
fat tissue; provides protective padding around body structures
nervous tissue
- composed of cells called neurons
- forms the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves throughout the entire body, allowing for the conduction of electrical impulses to send information between the brain and the rest of the body.
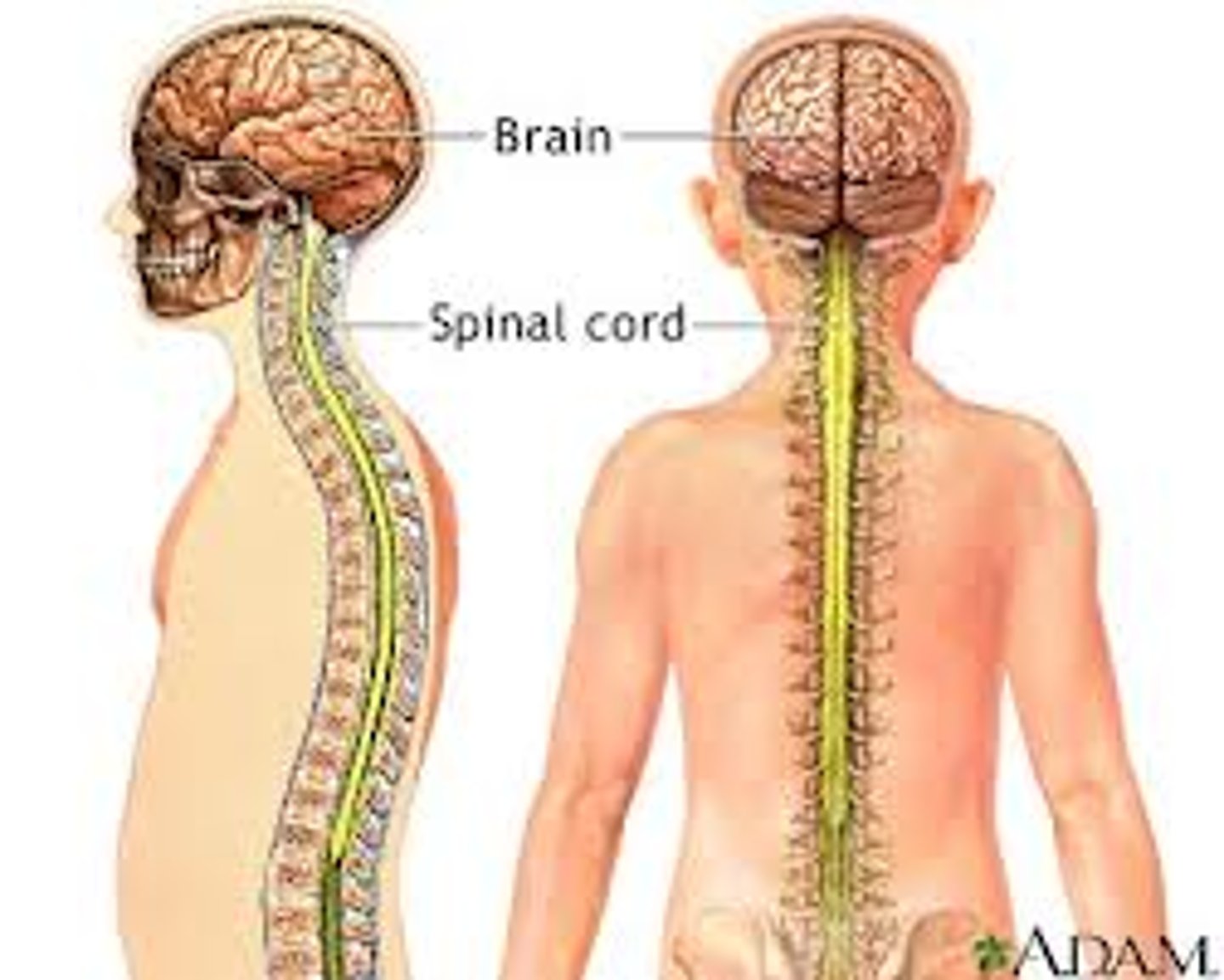
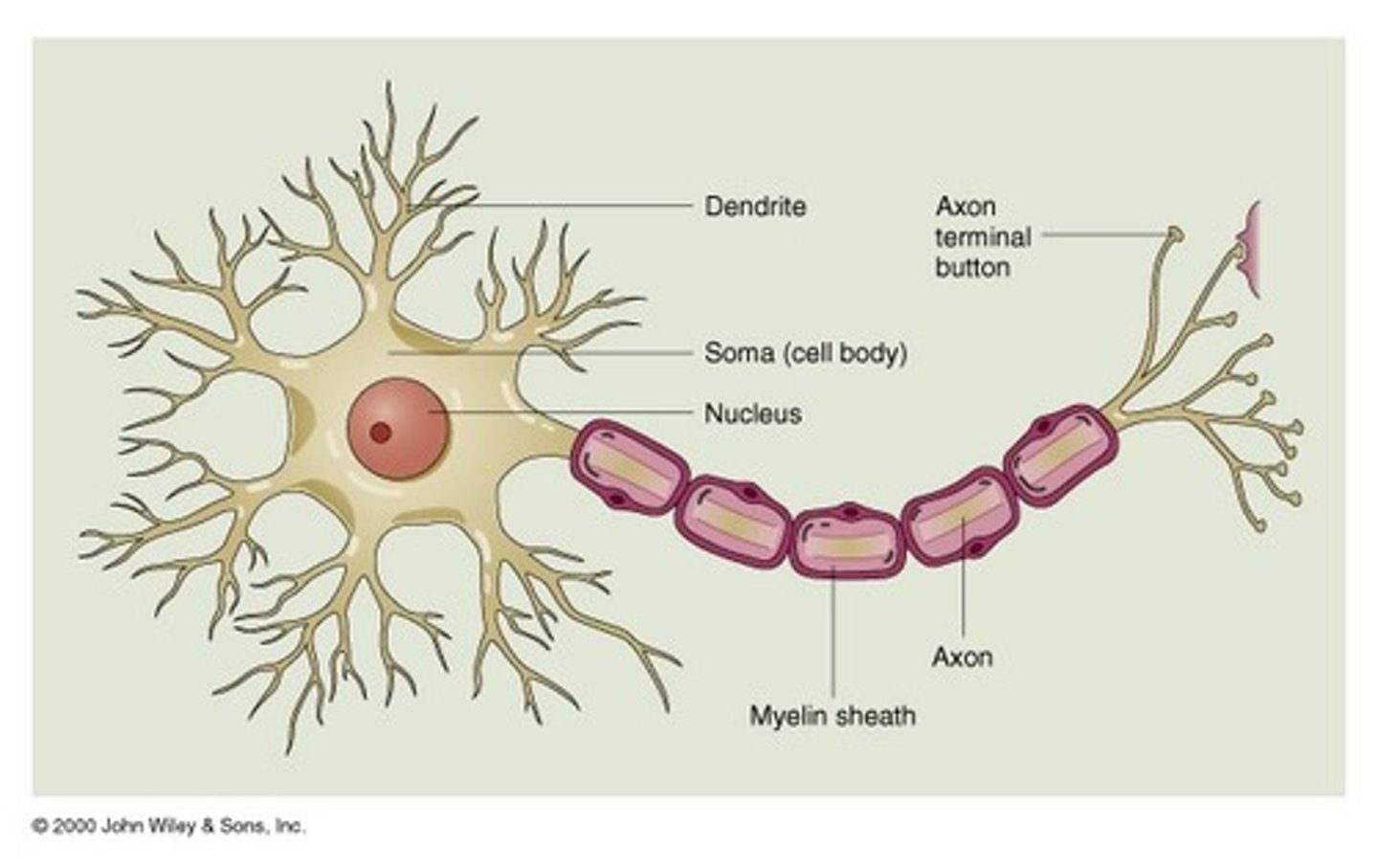
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Integumentary System
Forms protective two-way barrier and aids in temperature regulation.
• Skin
• Hair
• Nails
• Sweat glands
• Sebaceous glands
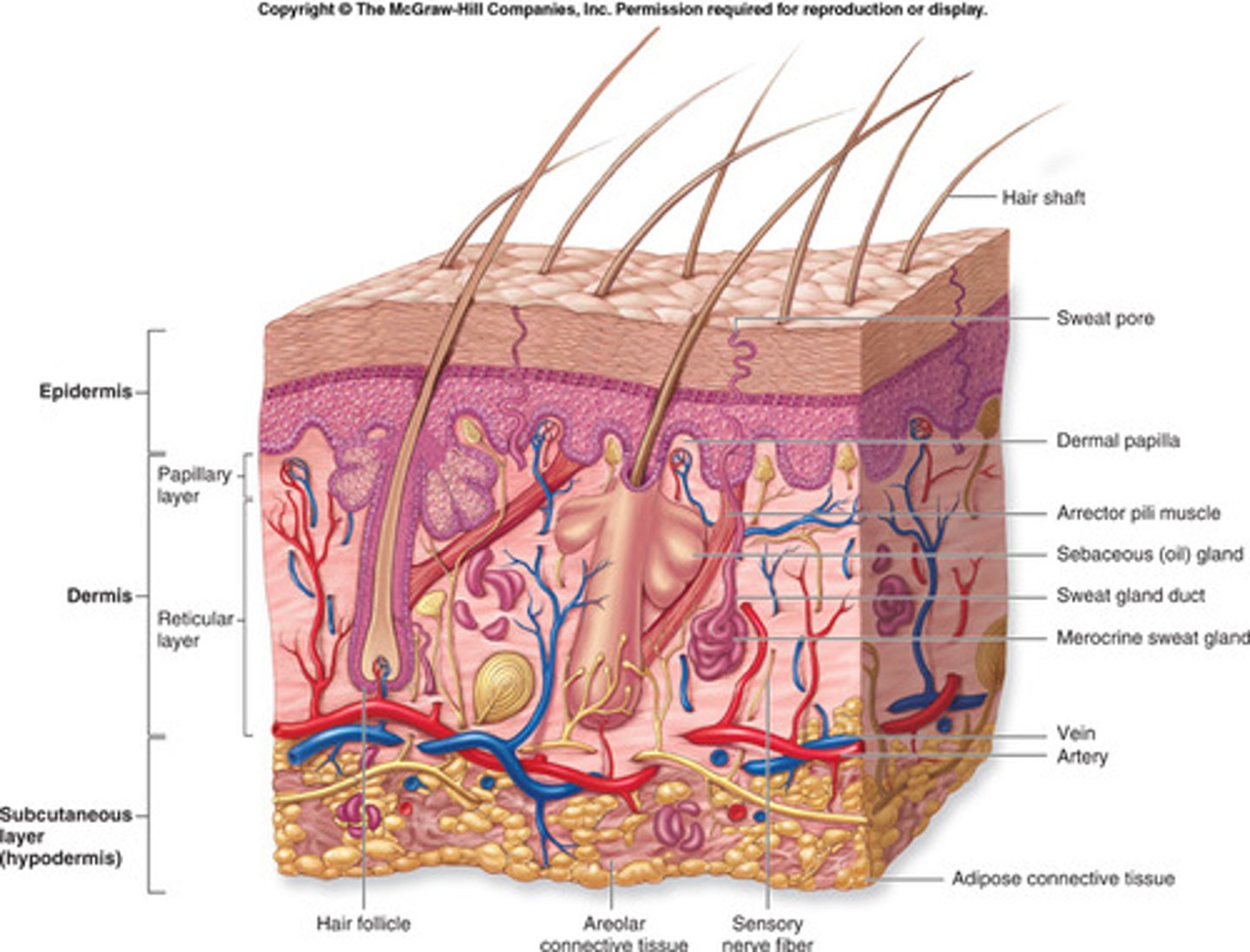
dermatology
study of the skin
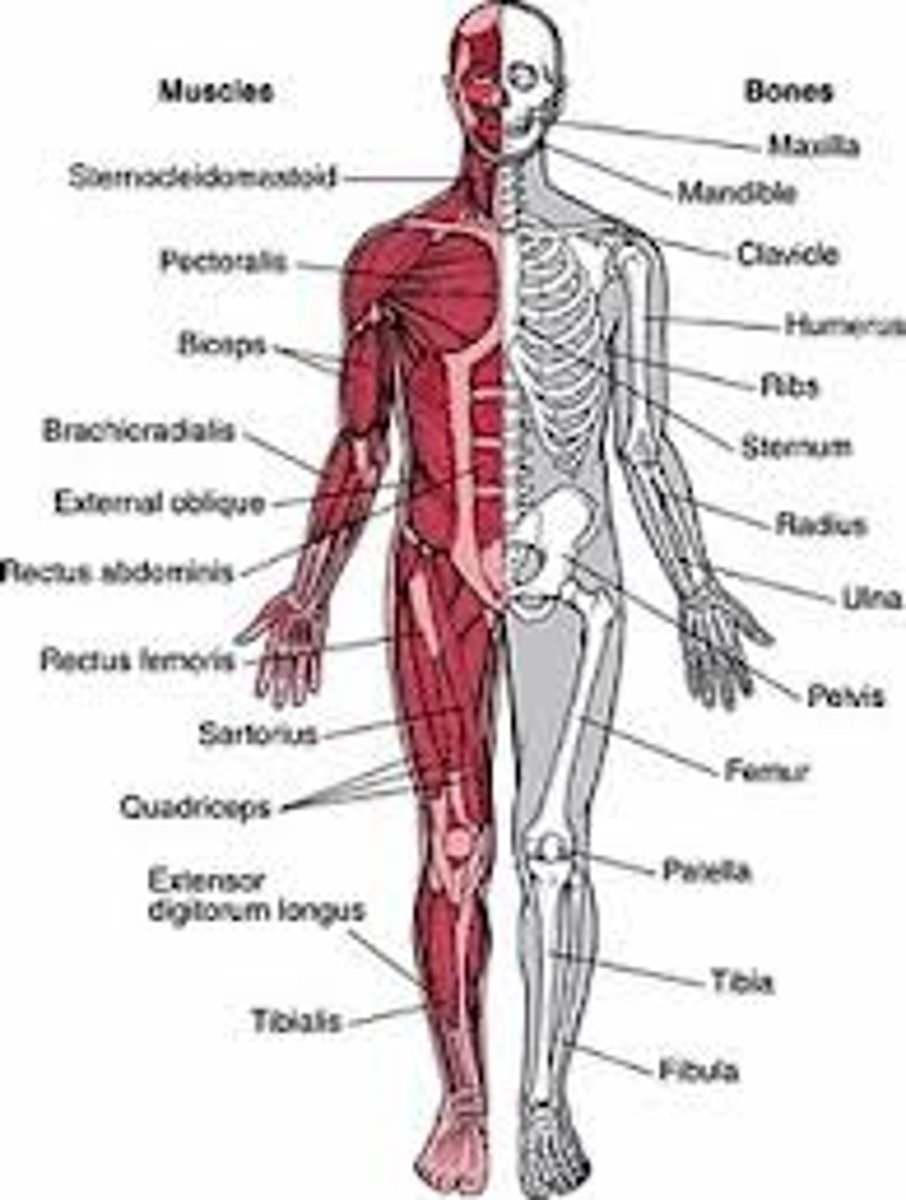
Musculoskeletal System (MS)
Skeleton supports and protects the body, forms blood cells, and stores minerals. Muscles produce movement.
• Bones
• Joints
• Muscles
cardiology
study of the heart
Blood (Hematic System)
Transports oxygen, protects against pathogens, and controls bleeding.
• Plasma
• Erythrocytes
• Leukocytes
• Platelets
hematology
study of blood
Lymphatic System
Protects the body from disease and invasion from pathogens.
• Lymph nodes
• Lymphatic vessels
• Spleen
• Thymus gland
• Tonsils
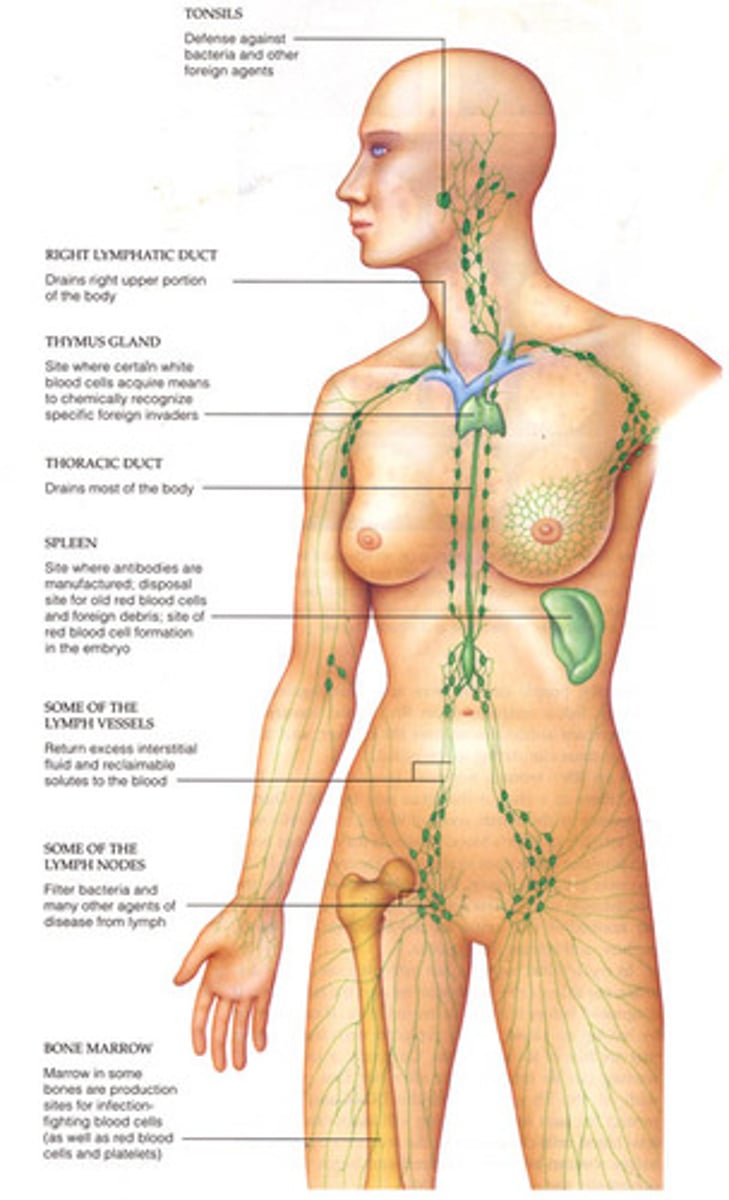
immunology
study of the immune system
Respiratory System
Obtains oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the body
• Nasal cavity
• Pharynx
• Larynx
• Trachea
• Bronchial tubes
• Lungs
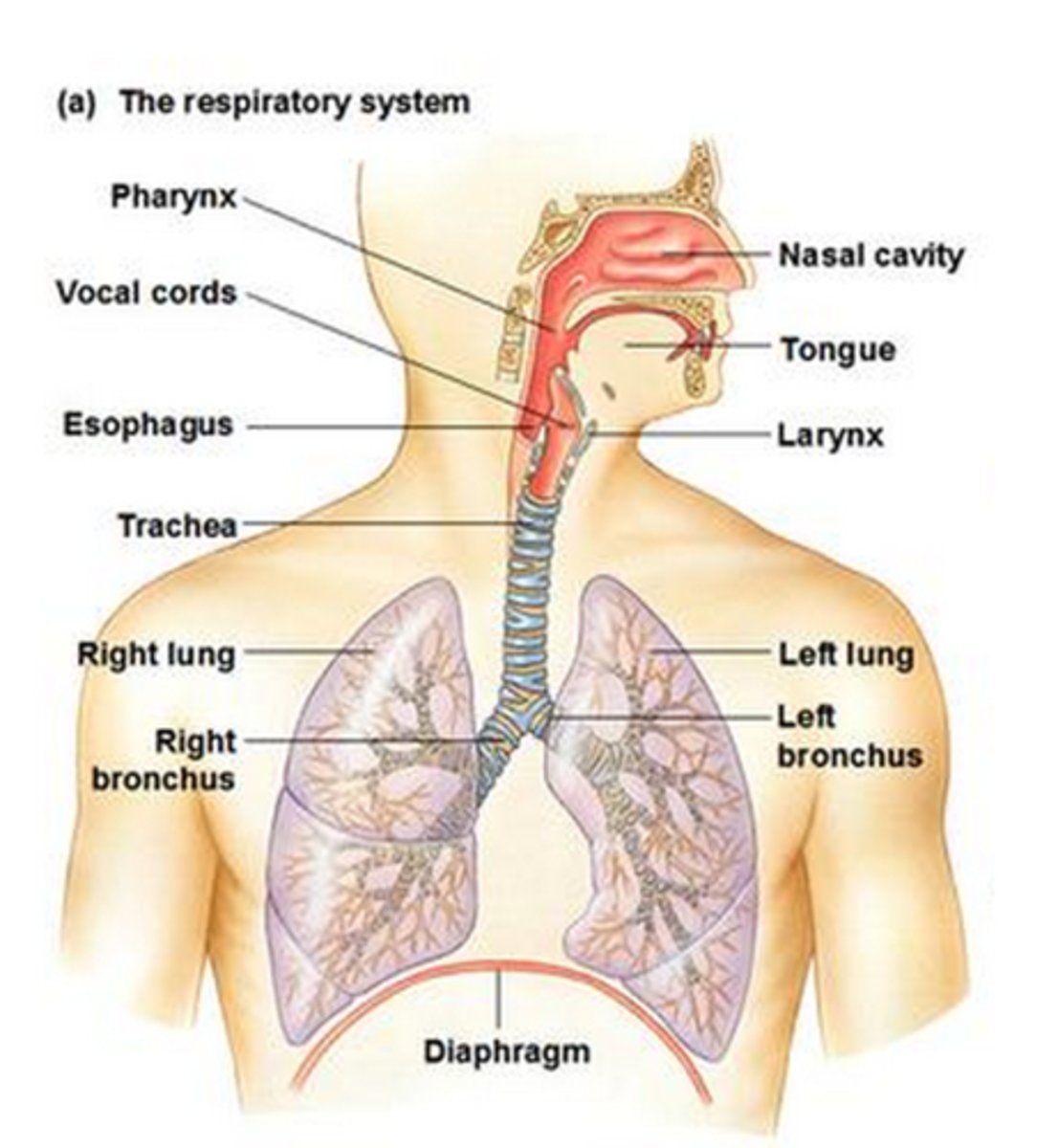
otorhinolaryngology (ENT)
Branch of medicine that treats diseases of the ears, nose, and throat. Also referred to as ENT.
pulmonology
study of the lungs
thoracic surgery
Branch of medicine specializing in surgery on the respiratory system and thoracic cavity.
Digestive or Gastrointestinal System (GI)
Ingests, digests, and absorbs nutrients for the body.
• Oral cavity
• Pharynx
• Esophagus
• Stomach
• Small intestine
• Colon
• Liver
• Gallbladder
• Pancreas
• Salivary glands
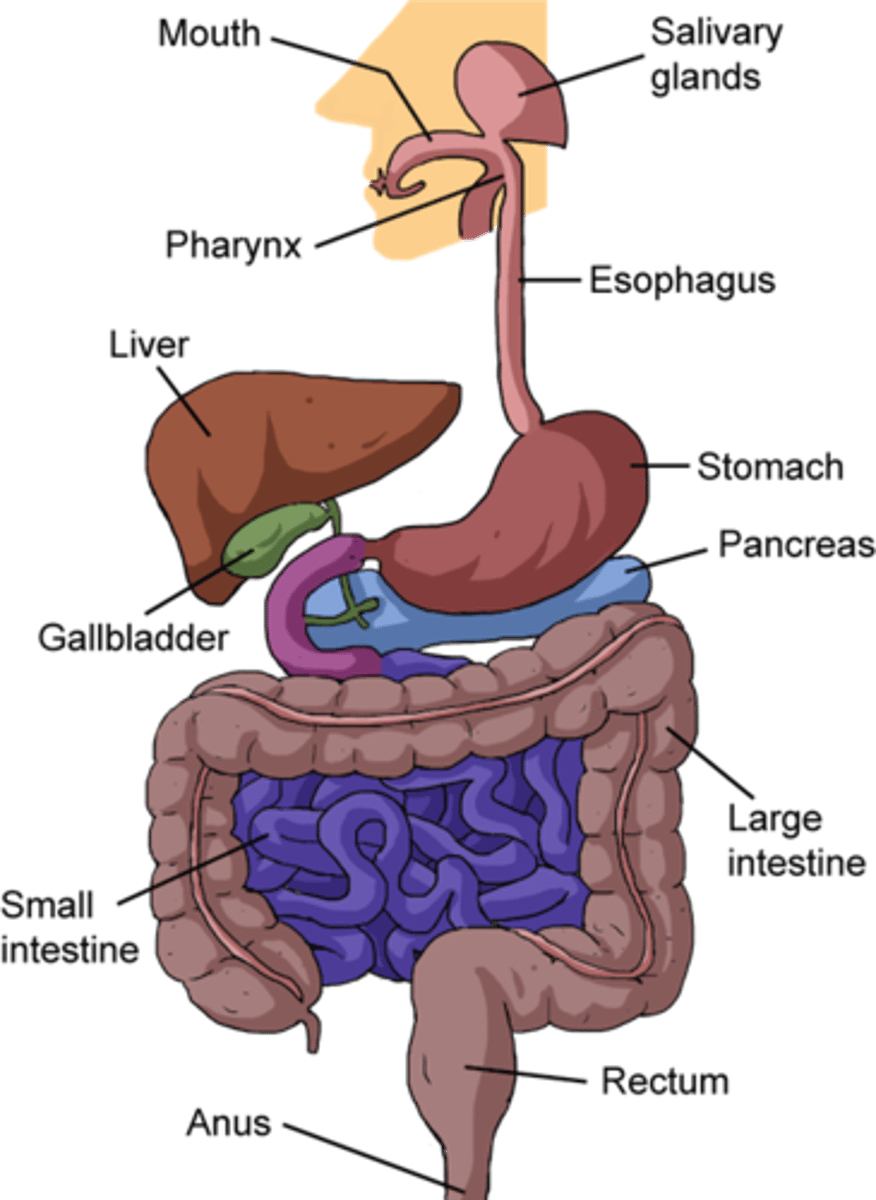
gastroenterology
study of the stomach and intestines
proctology
study of the rectum and anus
Urinary System
Filters waste products out of the blood and removes them from the body.
• Kidneys
• Ureters
• Urinary bladder
• Urethra
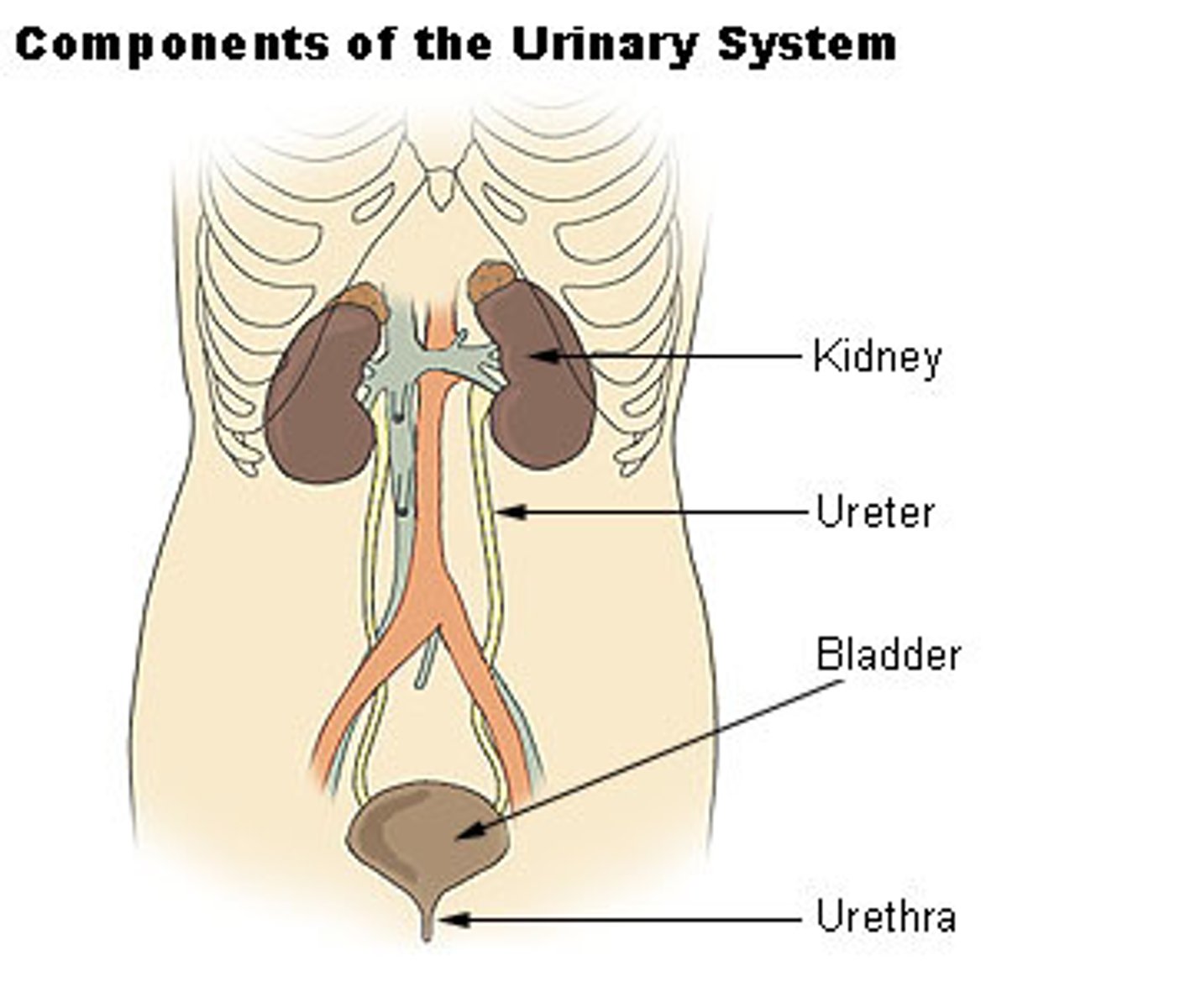
nephrology
study of the kidney
urology
study of the urinary tract
Female Reproductive System
Produces eggs for reproduction and provides place for growing baby.
• Ovary
• Fallopian tubes
• Uterus
• Vagina
• Vulva
• Breasts
gynecology (GYN)
study of women
obstretrics
medical specialty dealing with pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium
Male Reproductive System
Produces sperm for reproduction.
• Testes
• Epididymis
• Vas deferens
• Penis
• Seminal vesicles
• Prostate gland
• Bulbourethral gland