Lecture 16: Limbic System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
limbic system
set of interconnected forebrain structures which play key role in mediating certain aspects of behavior/drives, memory and emotion
hypothalamus
serves executive role in regulation of emotional responses
James Lange Theory
the theory that a person expresses emotion first and then has an emotional experience that correlates with the expression
Cannon-Bard Theory
the theory that a person has an emotional experience and then expresses that emotion
telencephalon
gray matter structure made up of the limbic cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, and septal nuclei
diencephalon
gray matter structures made up of the thalamus and hypothalamus
limbic connections
connections throughout the limbic system of white matter
cingulate gyrus

parahippocampal gyrus

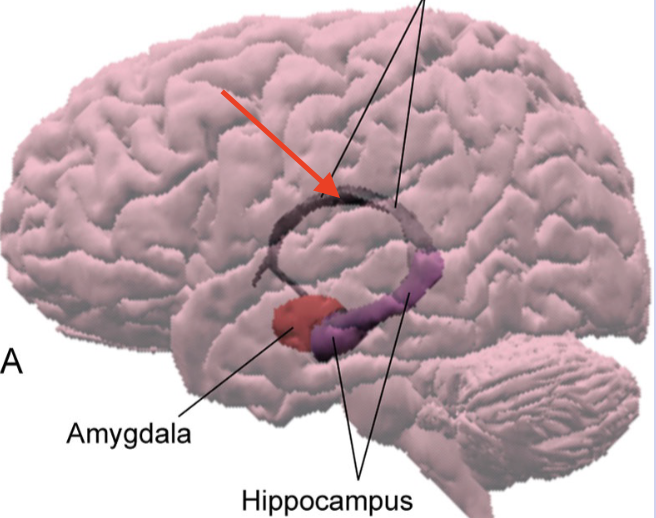
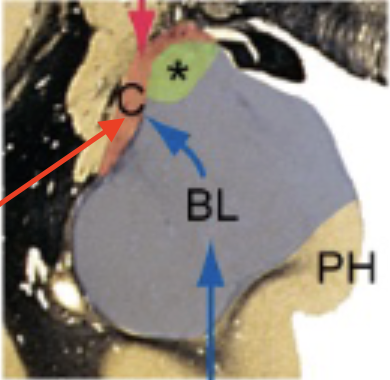
hippocampus
forms floor of interior horn of lateral ventricle and folds into medial surface of temporal lobe; lays down and consolidates new memories
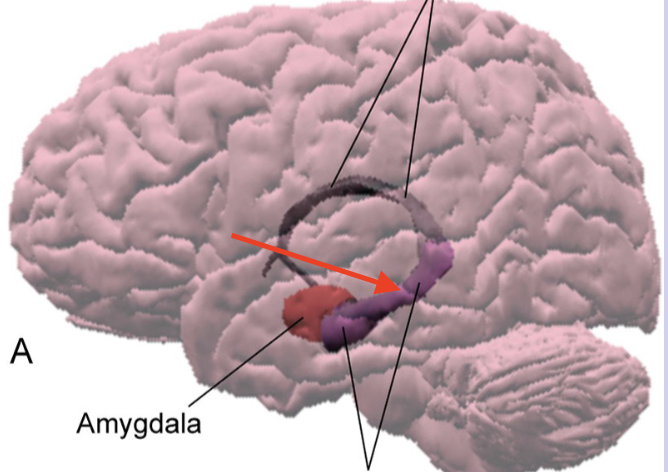
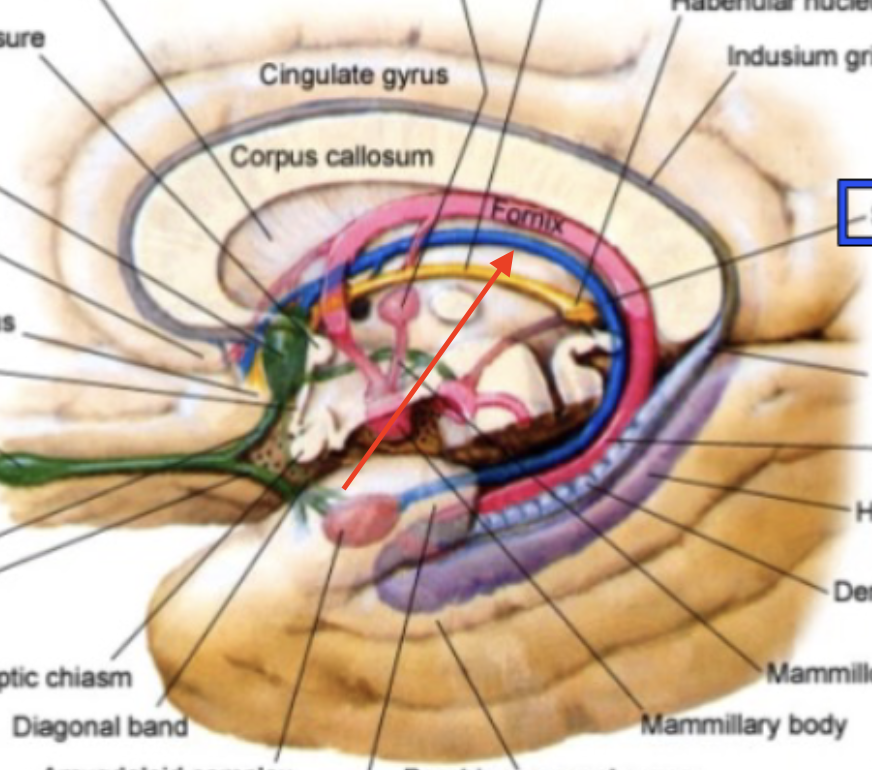
fornix
major efferent pathway of hippocampus which forms a C shape
hippocampus proper
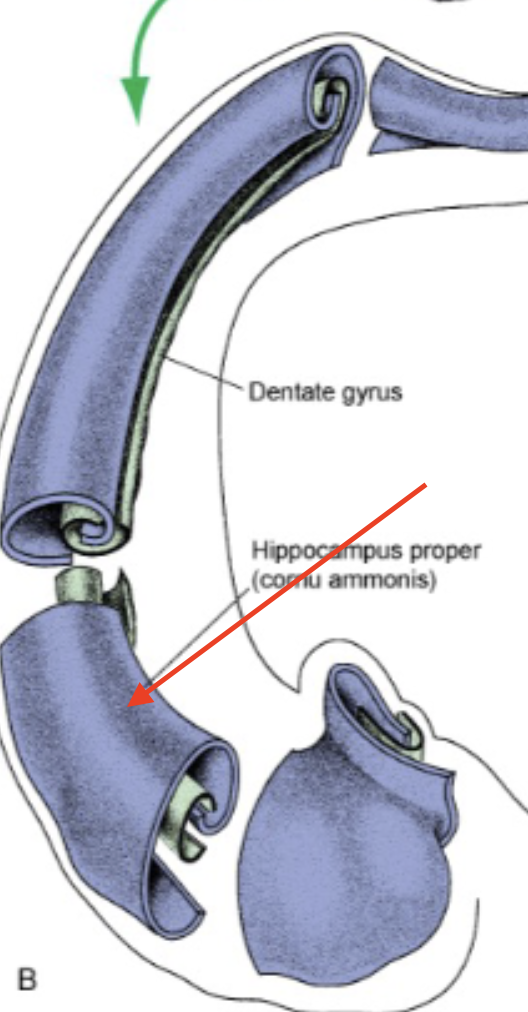
subiculum
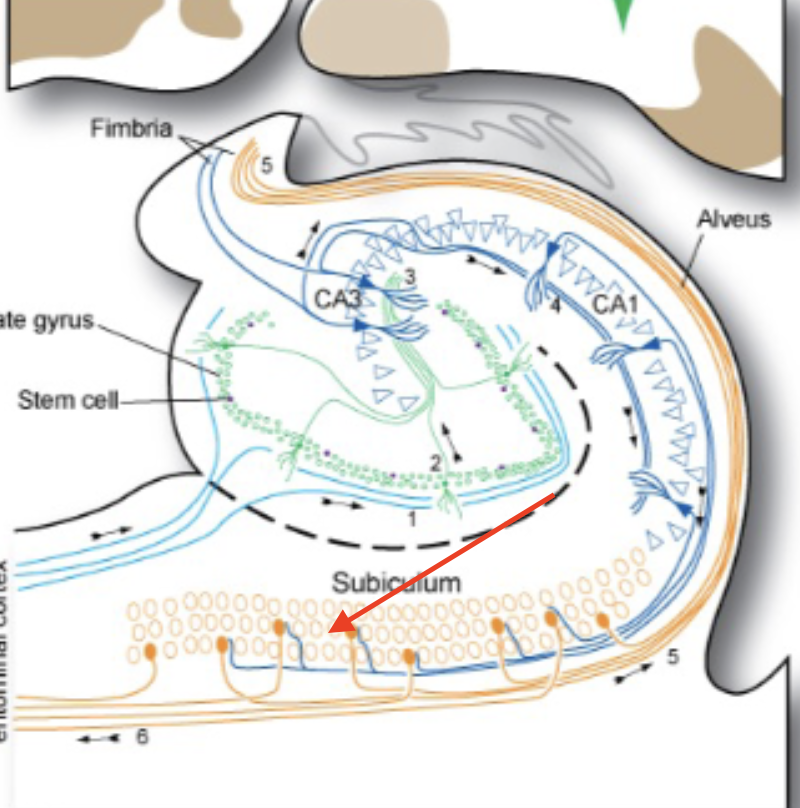
dentate gyrus
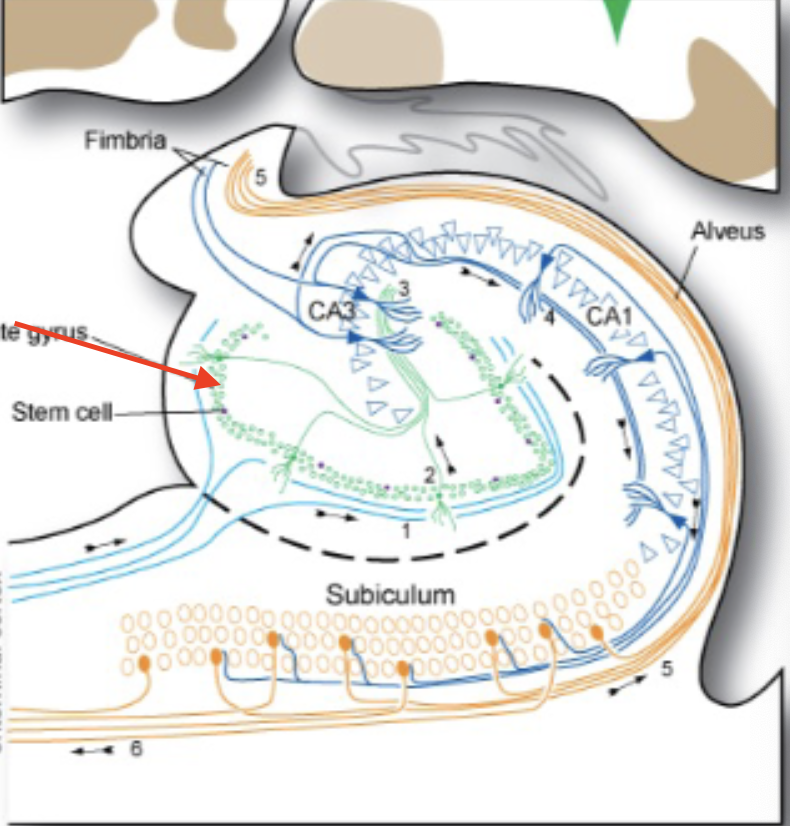
hippocampal afferent connections
parahippocampal (entorhinal) cortex → septal nuclei → fornix → amygdala
hippocampal efferent connections
hypothalamus (especially mammillary bodies) via fornix; parahippocampal cortex → septal nuclei via fornix; amygdala, and anterior thalamus
explicit (declarative) memories
things that are clear cut details (ex: mom’s birthday, periodic table of elements), from medial temporal lobe
implicit (non-declarative) memories
knowledge of skills or how to do things (ex: baking, sewing) from basal ganglia, cerebellum, neocortex, and amygdala
amnesia
loss of memory
anterograde amnesia
lost capacity for consolidating short-term memories into long term memories; cannot form new memories
retrograde amnesia
loss of memory prior to injury/accident
Korsakoff’s psychosis
damage to mammillary bodies or DM thalamus; patients cannot form new memories or recall events; confabulations
confabulations
making up an answer to something they don’t remember
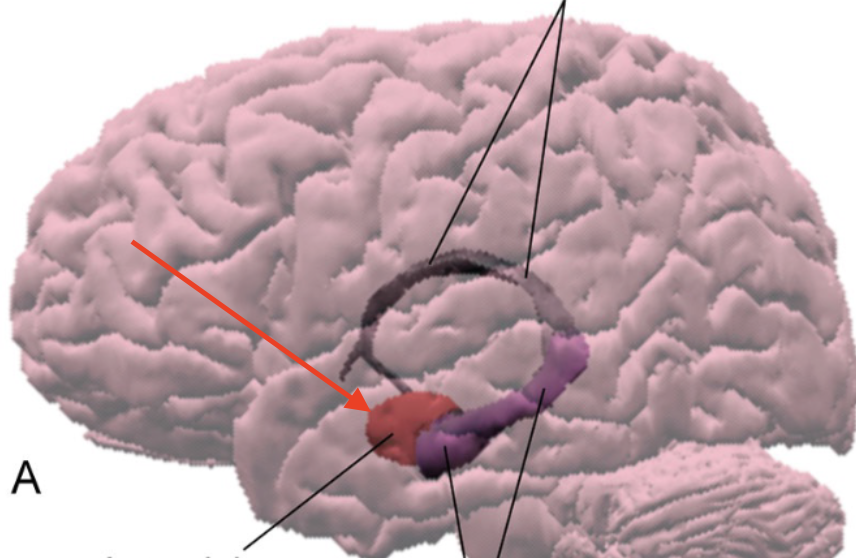
amygdala
almond shaped collection of nuclei within anterior temporal lobe
medial amygdala
used mostly by animals to assess food/mate/danger; in humans, greatest connection to olfactory system
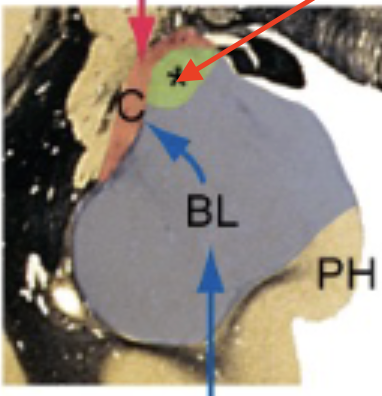
basolateral amygdala
more important for humans, extensive connections with cortex; formulation response to sensations, expression of emotions, and associations with memories
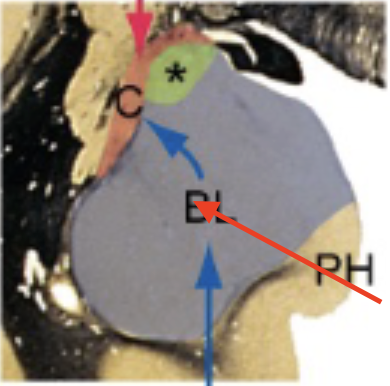
central amygdala
interacts with hypothalamus; important for autonomic and emotional responses
major afferent connections of amygdala
hypothalamus & septal nuclei via stria terminalis; thalamus (DM) & hypothalamus via VAP; olfactory bulb
stria terminalis
big connecting fiber bundle of amygdala
major efferent connections of amygdala
hypothalamus & septal nuclei via stria terminalis; thalamus (DM), hypothalamus, ventral striatum, and brainstem via VAP
amygdala function
determines appropriate emotional responses, helps effect autonomic responses and behavioral reactions, important for attachment of emotional significance to various stimuli (9/11), mediates anxiety and formation of fearful associations
bilateral amygdala destruction
experiences lose emotional significance, inability to response appropriately to social cues, loss of fear, decreased aggression, placid emotions
Kluver-Bucy Syndrome
bilateral damage to temporal lobe, loss of amygdala, some of hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus; general characteristics of increased inappropriate sexual behavior, increase oral behavior, loss of fear/flattened emotions, indiscriminate dietary behavior
septal nuceli
located medial to anterior horns of lateral ventricle; may be a part of pleasure reward circuitry, role in memory, and social behavior and expression of fear

major afferent connections of septal nuclei
hippocampus via fornix; amygdala via stria terminalis
major efferent connections of septal nuclei
hippocampus via fornix, amygdala via stria terminalis, and hypothalamus and midbrain via MFB
septal nuclei lesion
violent aggression provoked by innocuous stimuli “Sham Rage”
Paul Broca
identified limbic system
James Papez
originated ideas about limbic system and hippocampal function; suggested that compex set of interconnections between hippocampus and other limbic structures constituted anatomical circuit for emotion and memory
Papez circuit
hippocampus → fornix → mammillary bodies → mammillothalamic tract → anterior nucleus of thalamus → cingulate gyrus → cingulum → parahippocampal cortex → hippocampus