Carotid Duplex Imaging
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Completed brain stroke
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
stroke-like symptoms resolve within 24 hrs
Reversible Ischemic Neurologic Deficit (RIND)
stroke-like symptoms resolve but not within 24 hrs
Balance off/dizzy
What does the "B" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Eyes (sudden blurred vision, double vision, etc)
What does the "E" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Face drooping
What does the "F" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Arm weakness
What does the "A" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Speech difficulty
What does the "S" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Time to call 911
What does the "T" in "BEFAST" stand for?
Aphasia
_________ is the inability to speak or express oneself.
Dysphasia
________ is impairment of speech, lack of coordination and failure to arrange words in proper order.
Dysphagia
_______ is difficulty swallowing.
Dysarthria
_______ is imperfect articulation of speech due to disturbances of muscle control, slurring.
Ataxia
_______ is gross incoordination of muscle movement.
Paresthesia
________ is lateralized tingling and numbness.
Hemiparesis
_______ is lateralized weakness.
Hemiplegia
______ is lateralized paralysis.
thrombus
blood clot that stays in one place
occlusion
complete blockage of a blood vessel or a hollow organ
embolus
when a piece of a thrombus breaks off, travels via blood, and lodges somewhere else
cessation of perfusion
the stopping of blood from reaching the part of the brain it is intended for
syncope
transient state of being unconscious without losing consciousness
diplopia
double vision
vertigo
a feeling of motion or spinning when the patient is stationary
hemorrhagic
Approximately 15% of strokes are _________ in nature.
vasospasm
a spasm of the intracranial arteries that can lead to a stroke
ischemic stroke
when blood flow through the artery that supplies oxygen rich blood to the brain becomes blocked
hemorrhagic stroke
A weakened blood vessel bursts and bleeds into the surrounding brain. Pressure from the leaked blood damages brains cells, and, as a result, the affected or damaged area is unable to function properly.
brachiocephalic artery
The innominate artery is also called the ____________
fistula = manmade
malformation = congenital
What's the difference between a fistula and malformation?
subclavian steal
A ____________ describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery because of a proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion.
External carotid artery
Which normal cerebrovascular vessel demonstrates the highest flow resistance?
It lies more posterior to the ECA
Which of the following best describes the position of the ICA in the neck?
Severe distal ICA stenosis
A high resistance flow pattern in the distal portion of the ICA suggests which of the following conditions?
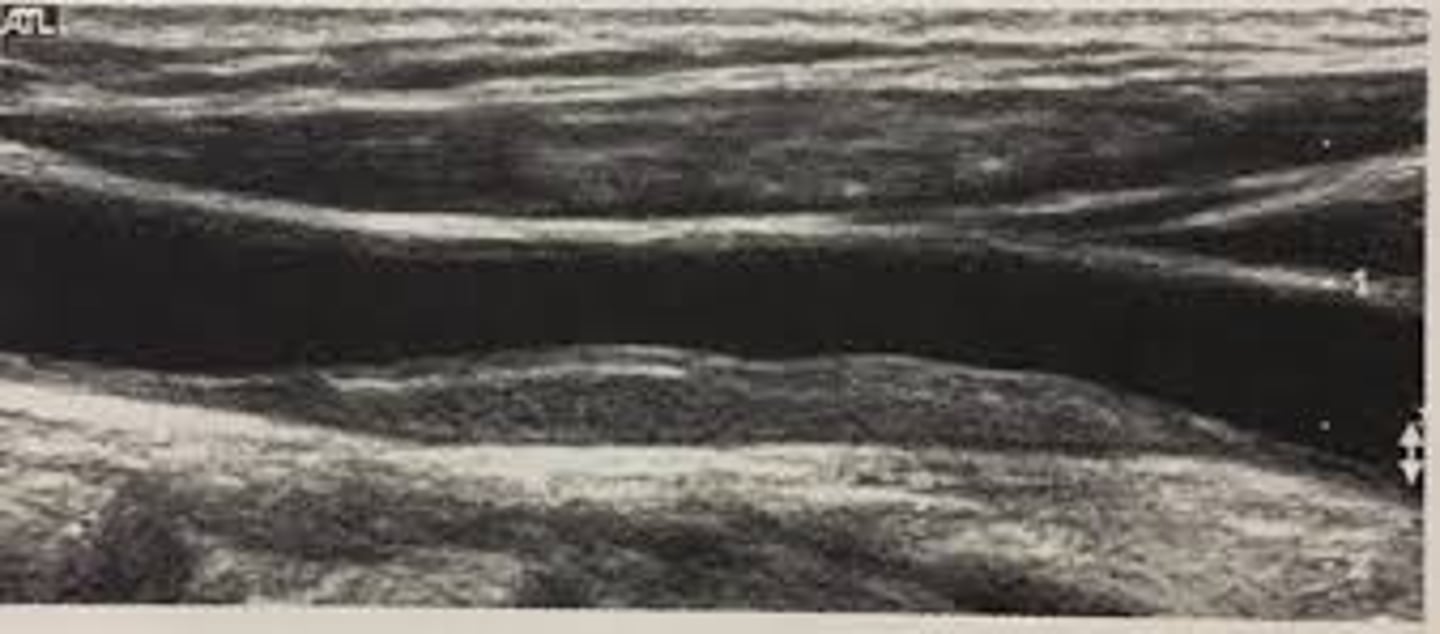
Homogenous plaque with smooth surface characteristics
In the following image, how would you describe the arterial wall?
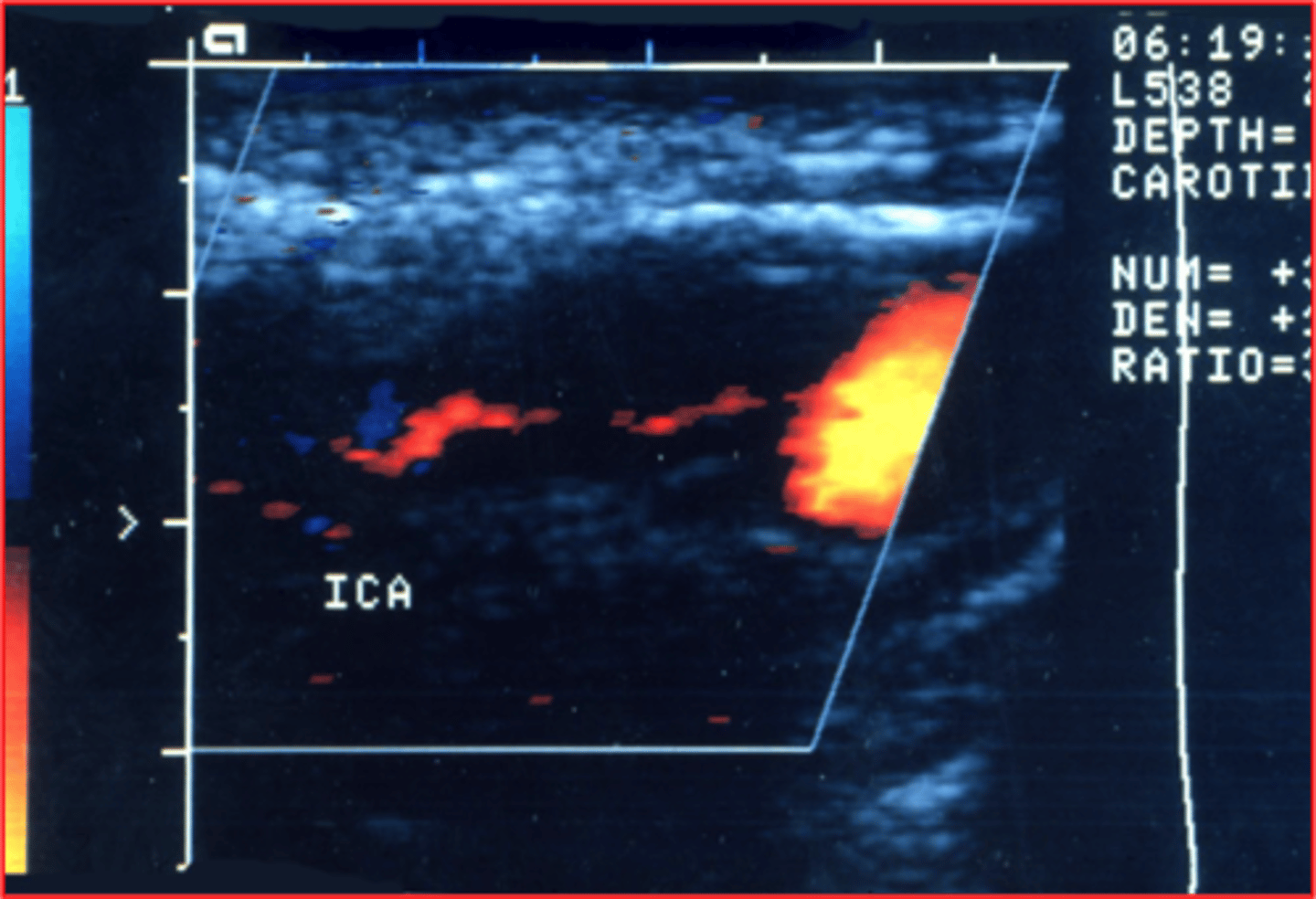
trickle flow
This occurs in nearly occluded vessels and involves very low velocities.
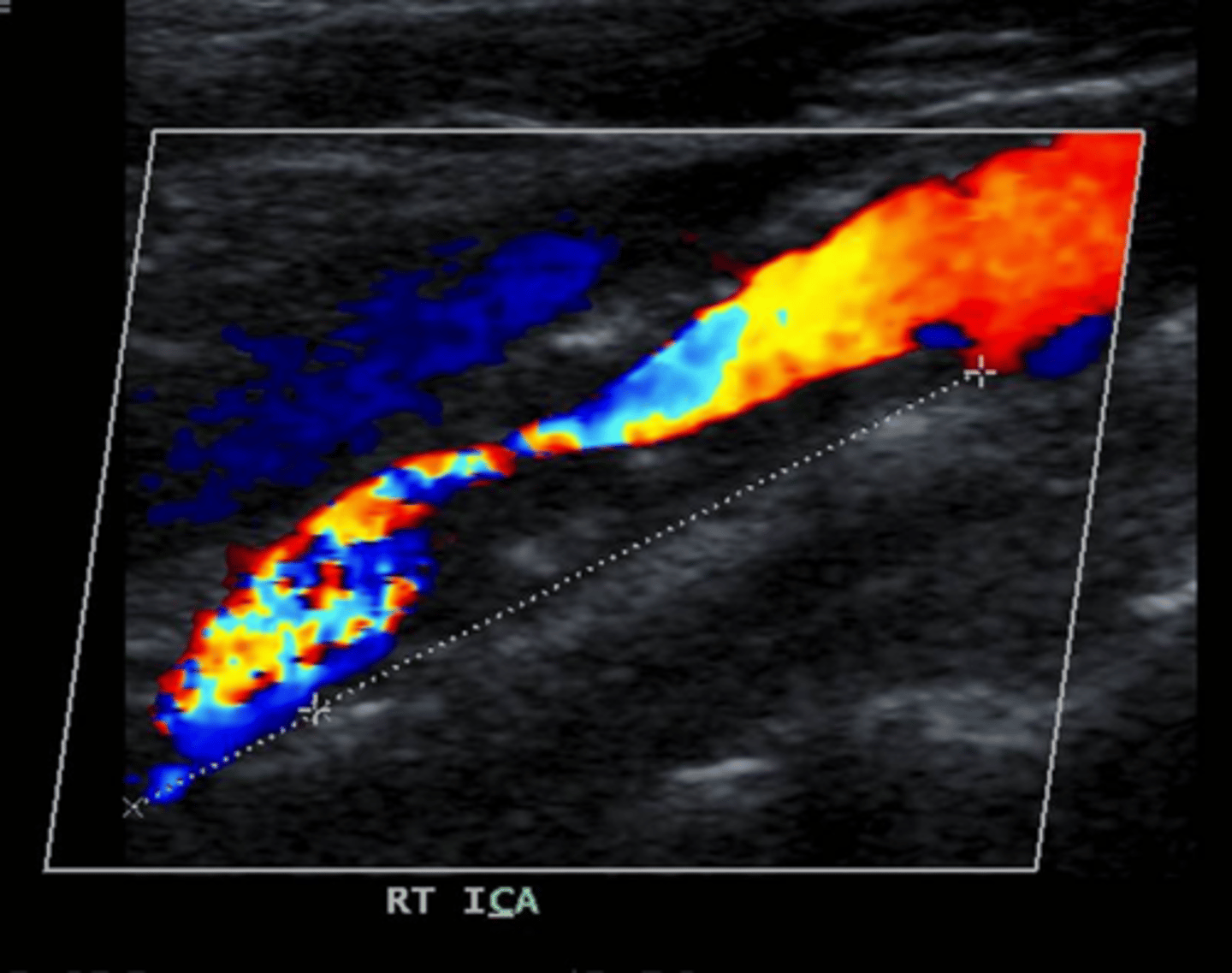
string sign
This is seen just before an occlusion occurs and is considered an emergency
carotid dissection
Tear in the intimal lining of the carotid artery
B. Superior thyroid artery
What is the first branch of the ECA?
Ophthalmic artery
What is the first branch of the ICA?
Atheroemboli from the left ICA.
A patient presents with the classic cerebrovascular symptom of left amaurosis fugax. Of the choices below, what is the most likely cause?
Neointimal hyperplasia
Which of the following is the most common cause of re-stenosis following carotid endarterectomy?
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Which of the following is a non-atherosclerotic disease involving the mid segment of the ICA and found predominately in females?
Slice thickness of the beam
A longitudinal image of carotid plaque can sometimes be misleading as to the diameter reduction due to which of the following?
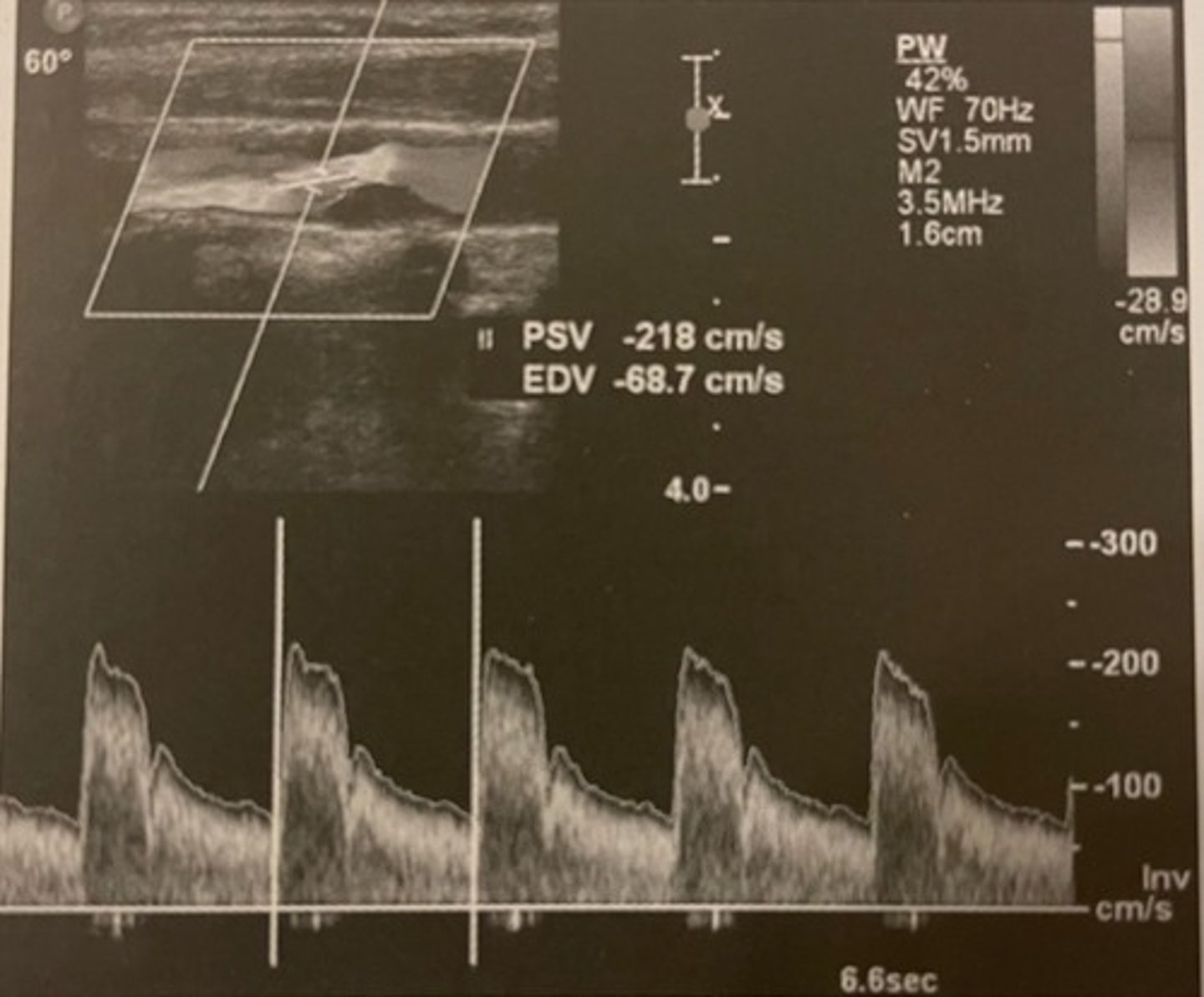
Sample was not obtained at maximum stenosis.
In this example, the ICA velocities may underestimate the category of stenosis. Why?